Spatiotemporal Variability of Cloud Parameters and Their Climatic Impacts over Central Asia Based on Multi-Source Satellite and ERA5 Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
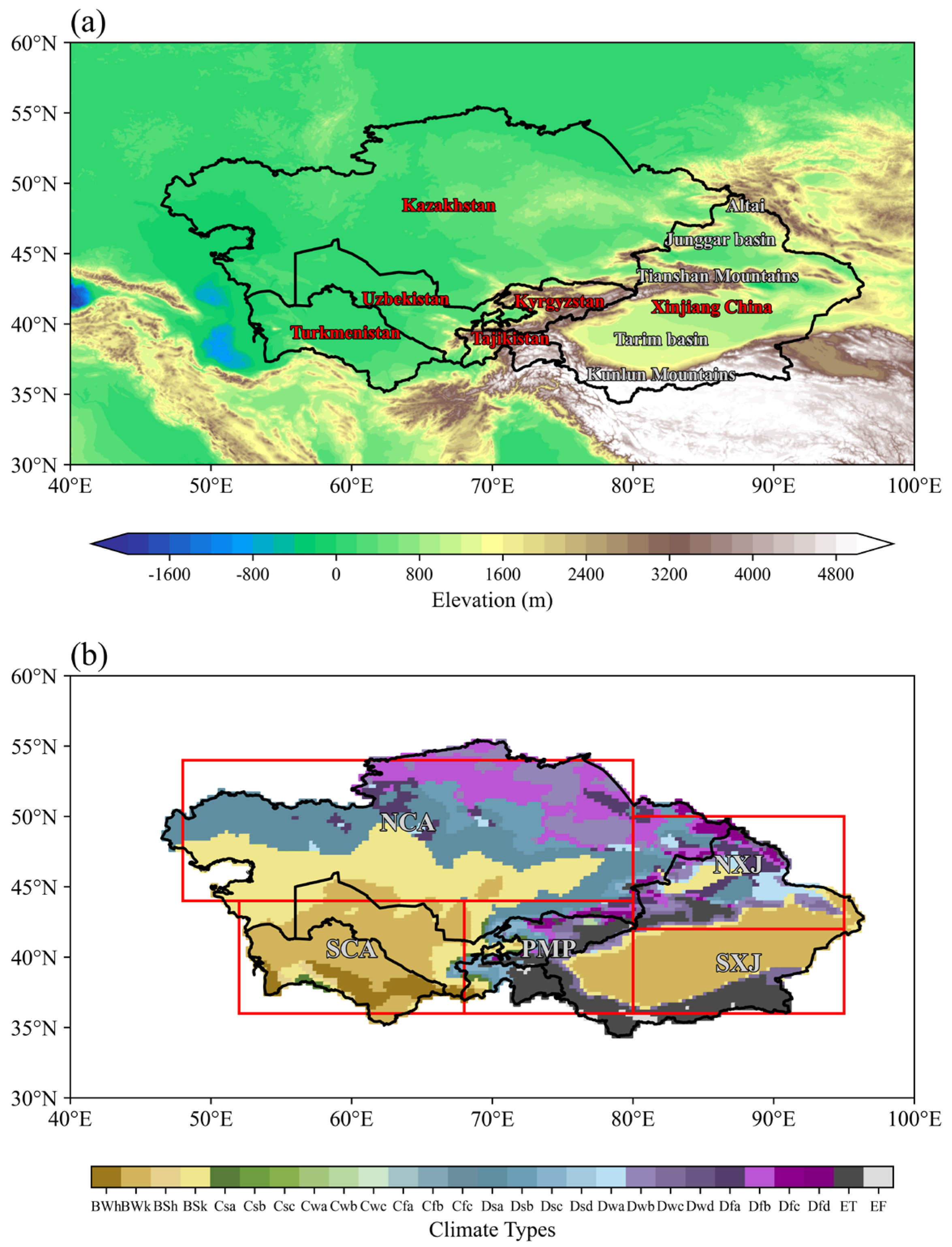
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Methods
3. Results
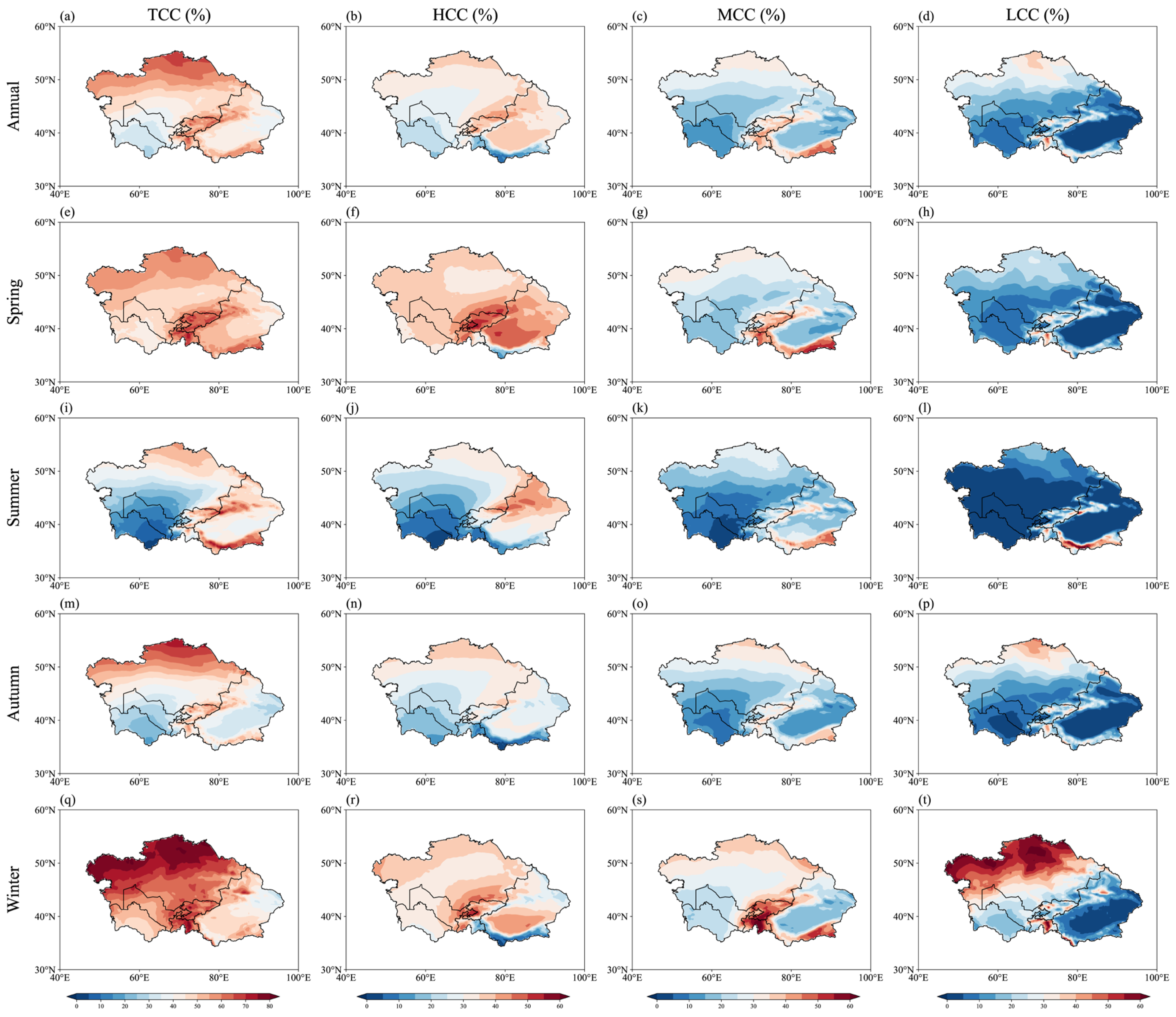
3.1. Seasonal Variation in Cloud Properties over Central Asia
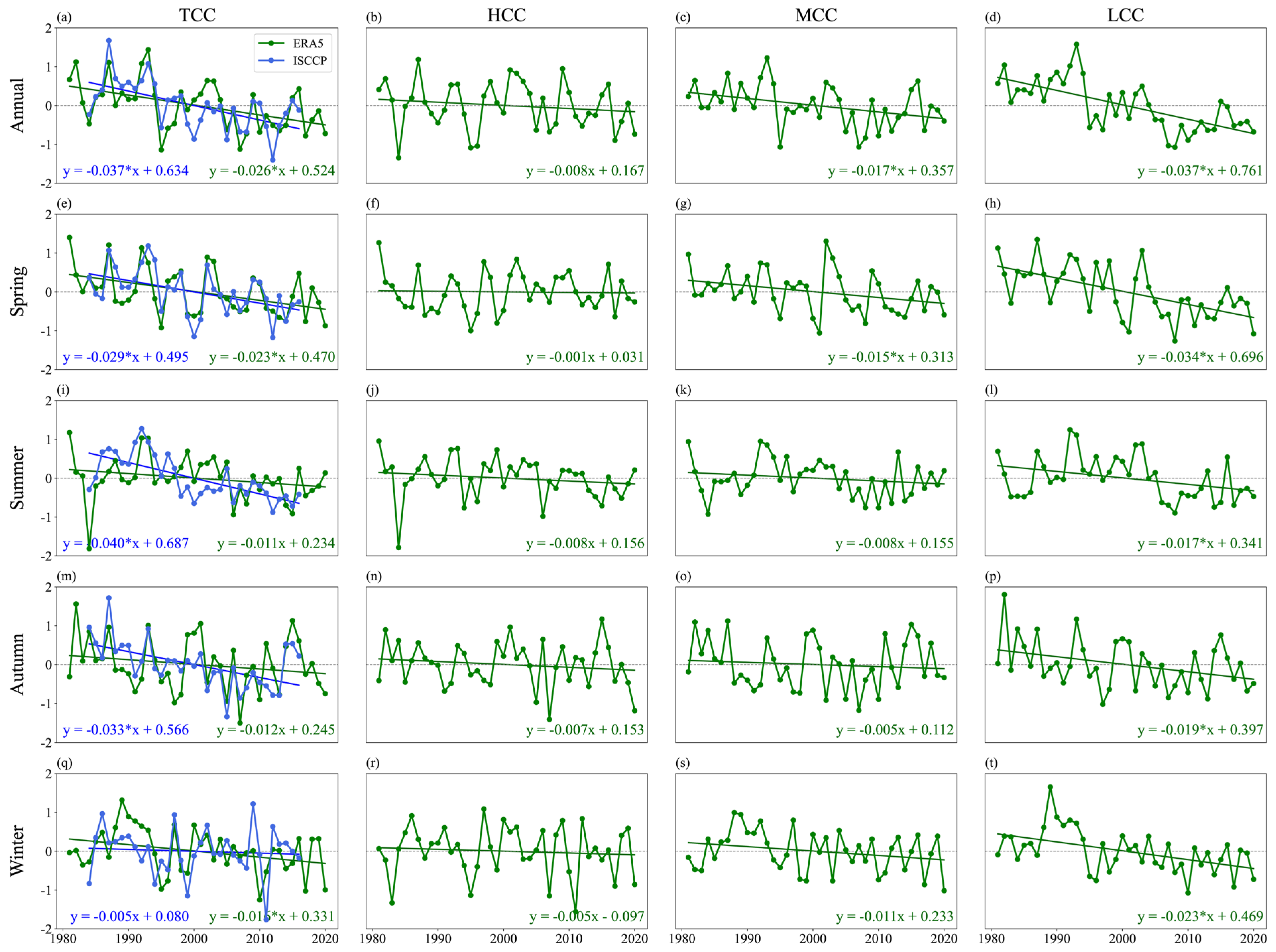
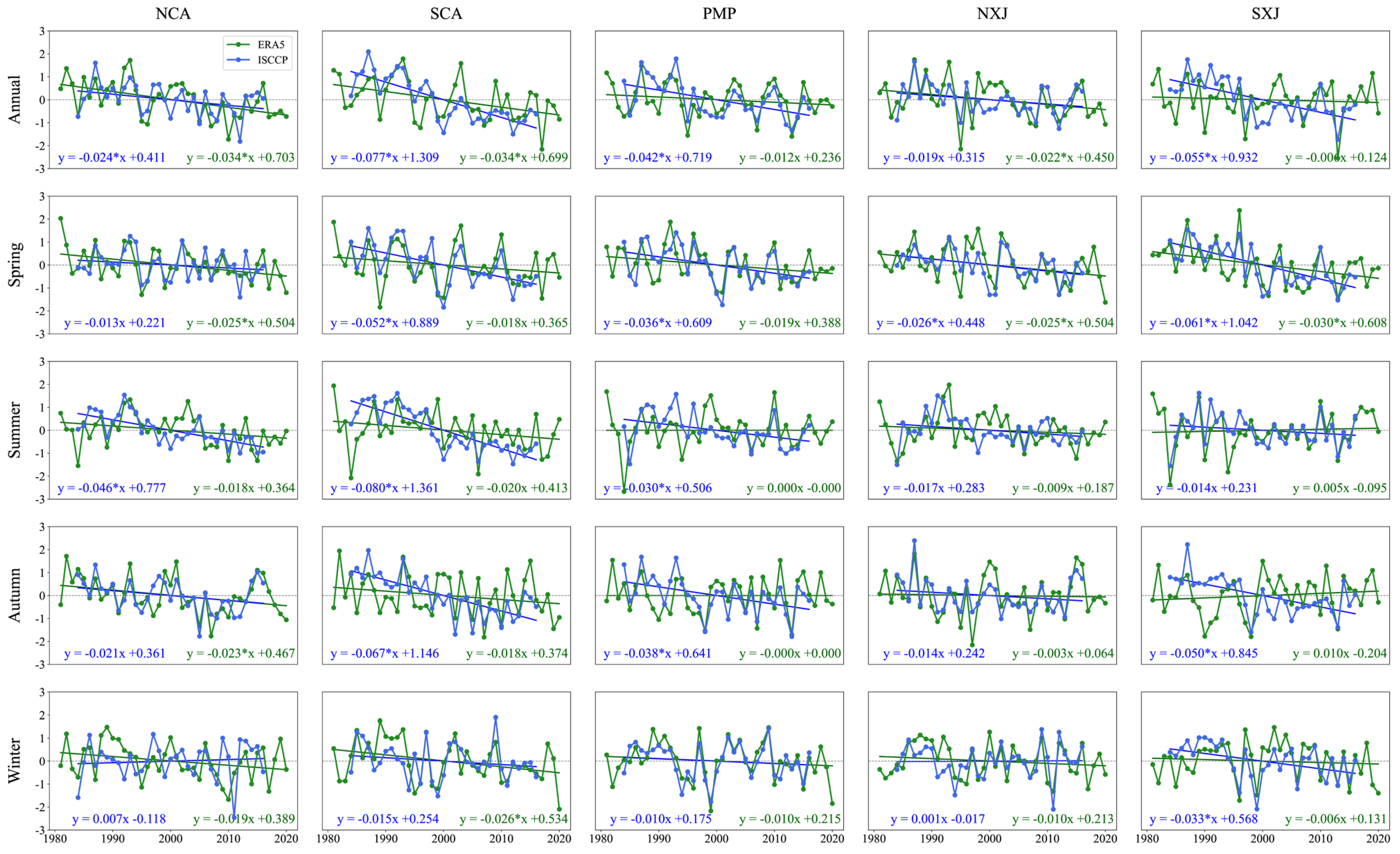
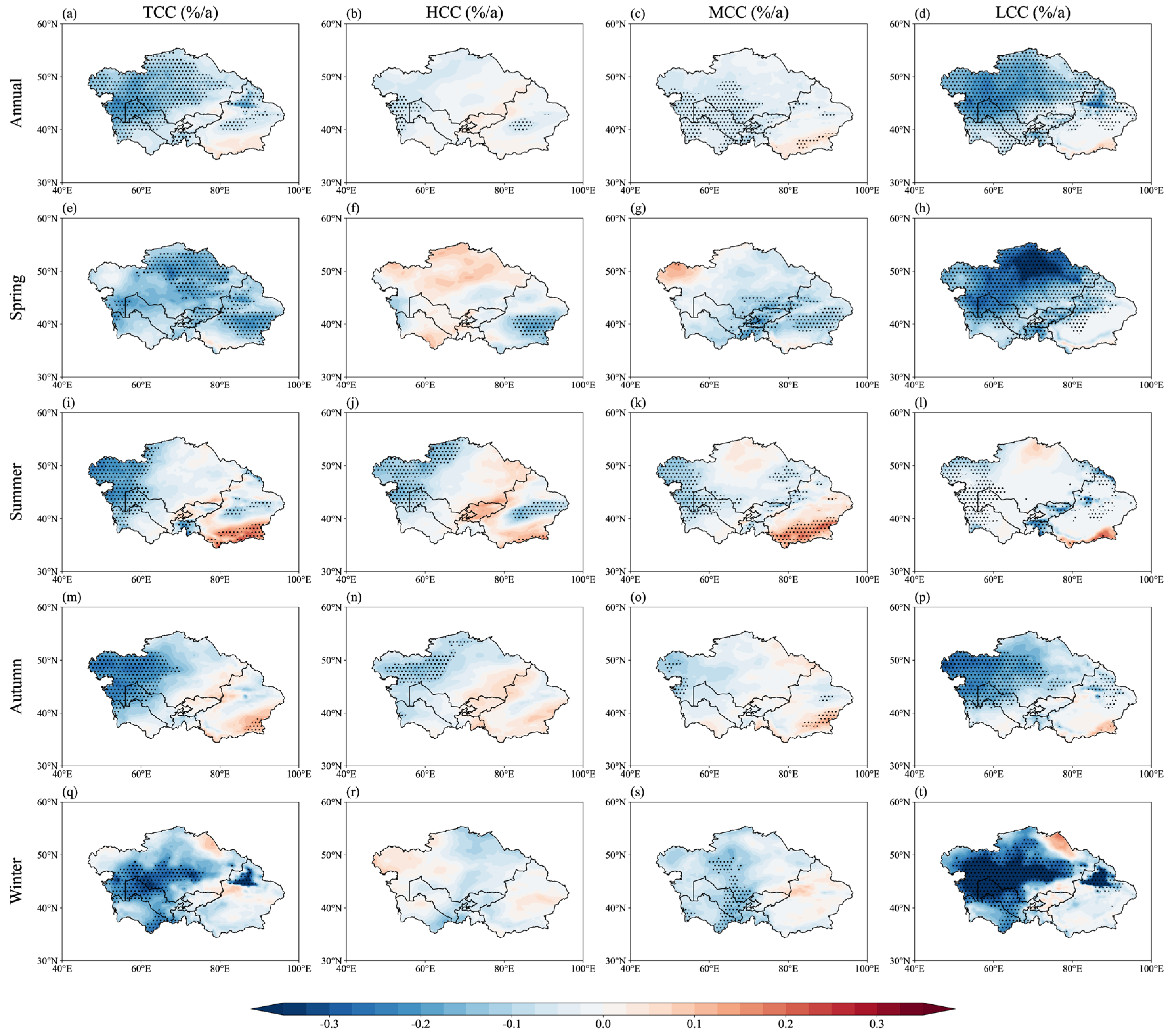
3.2. Trends in Different Cloud Covers over Central Asia
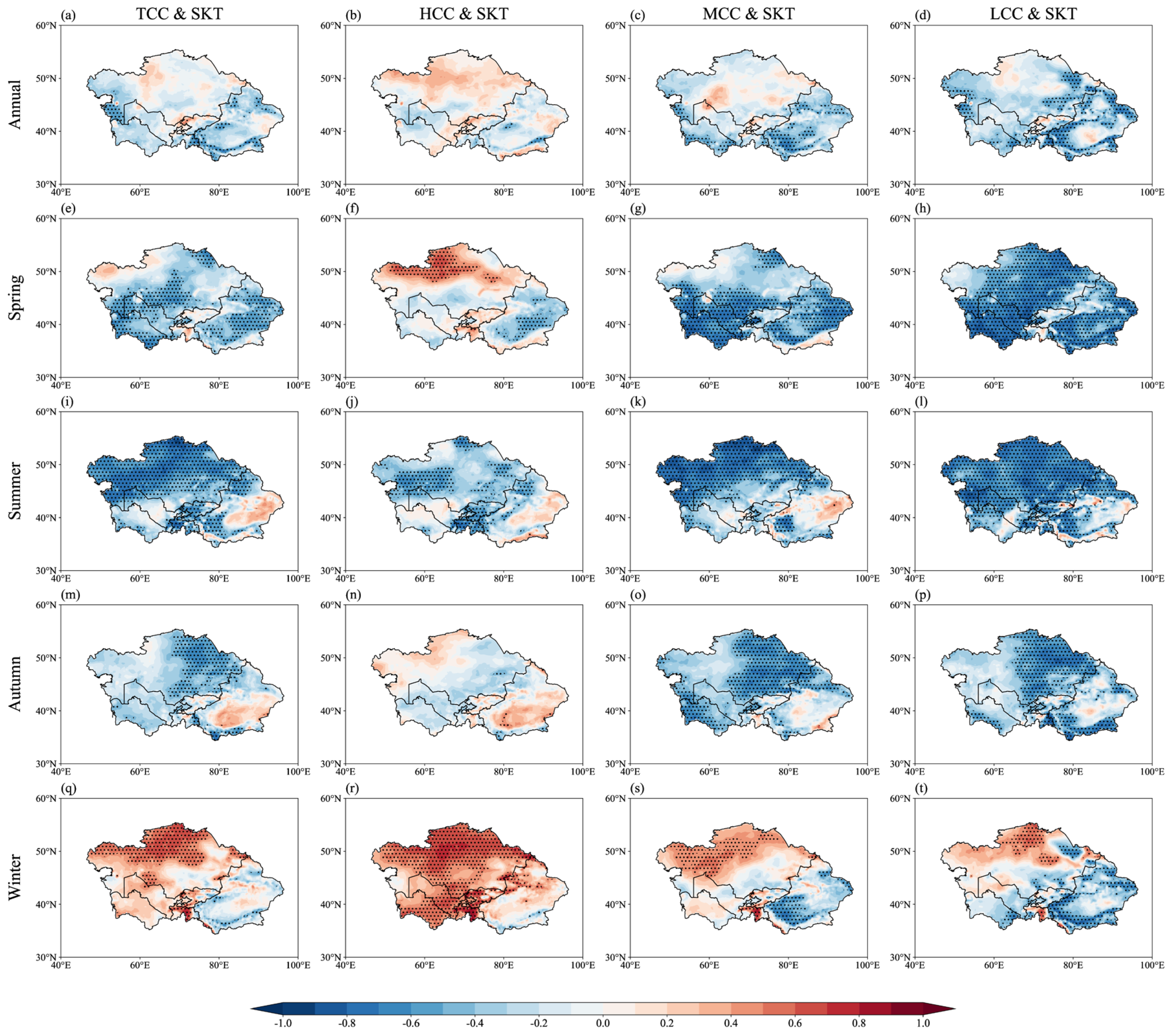
3.3. Influence of Cloud Cover on Skin Temperature over Central Asia
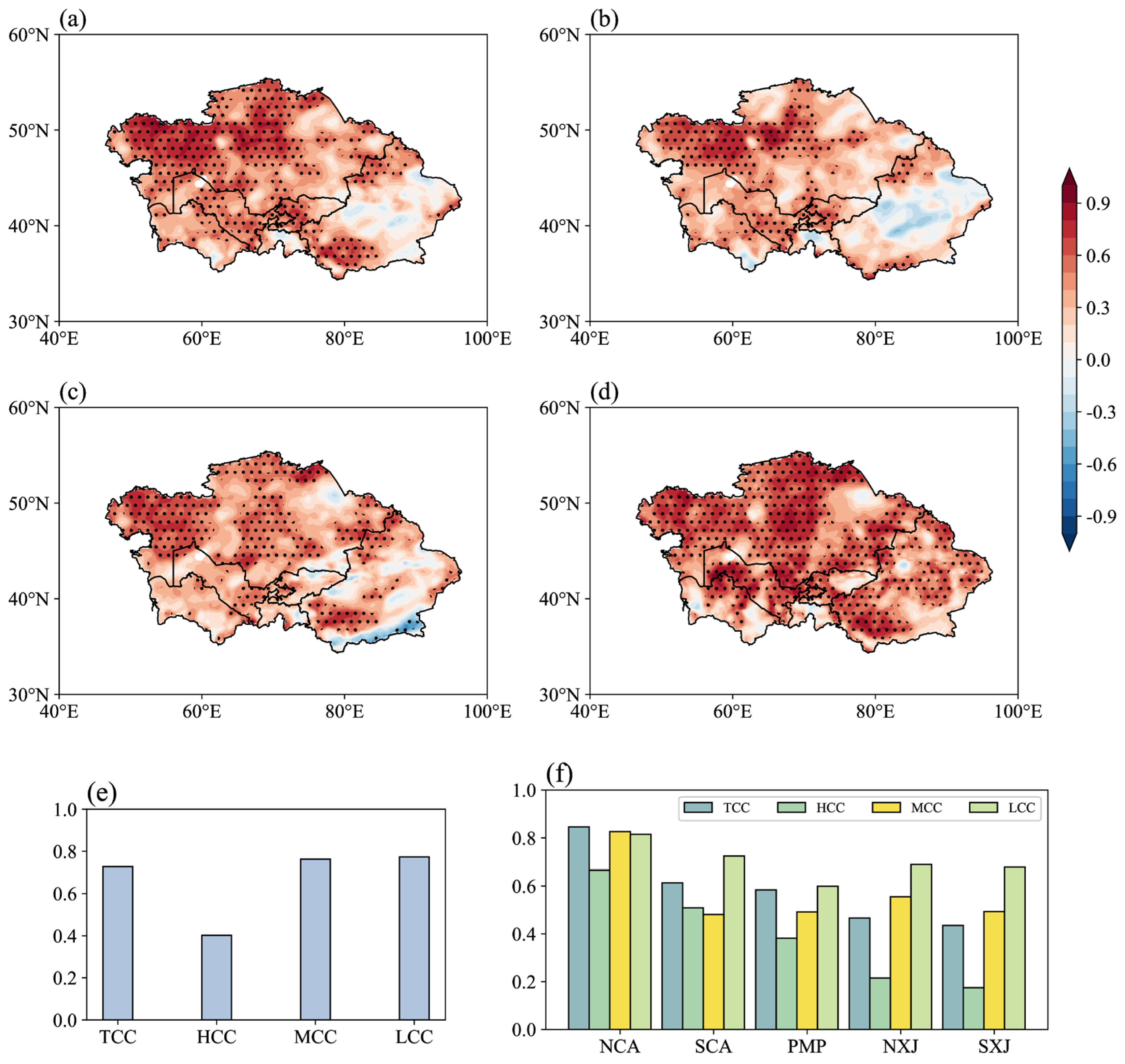
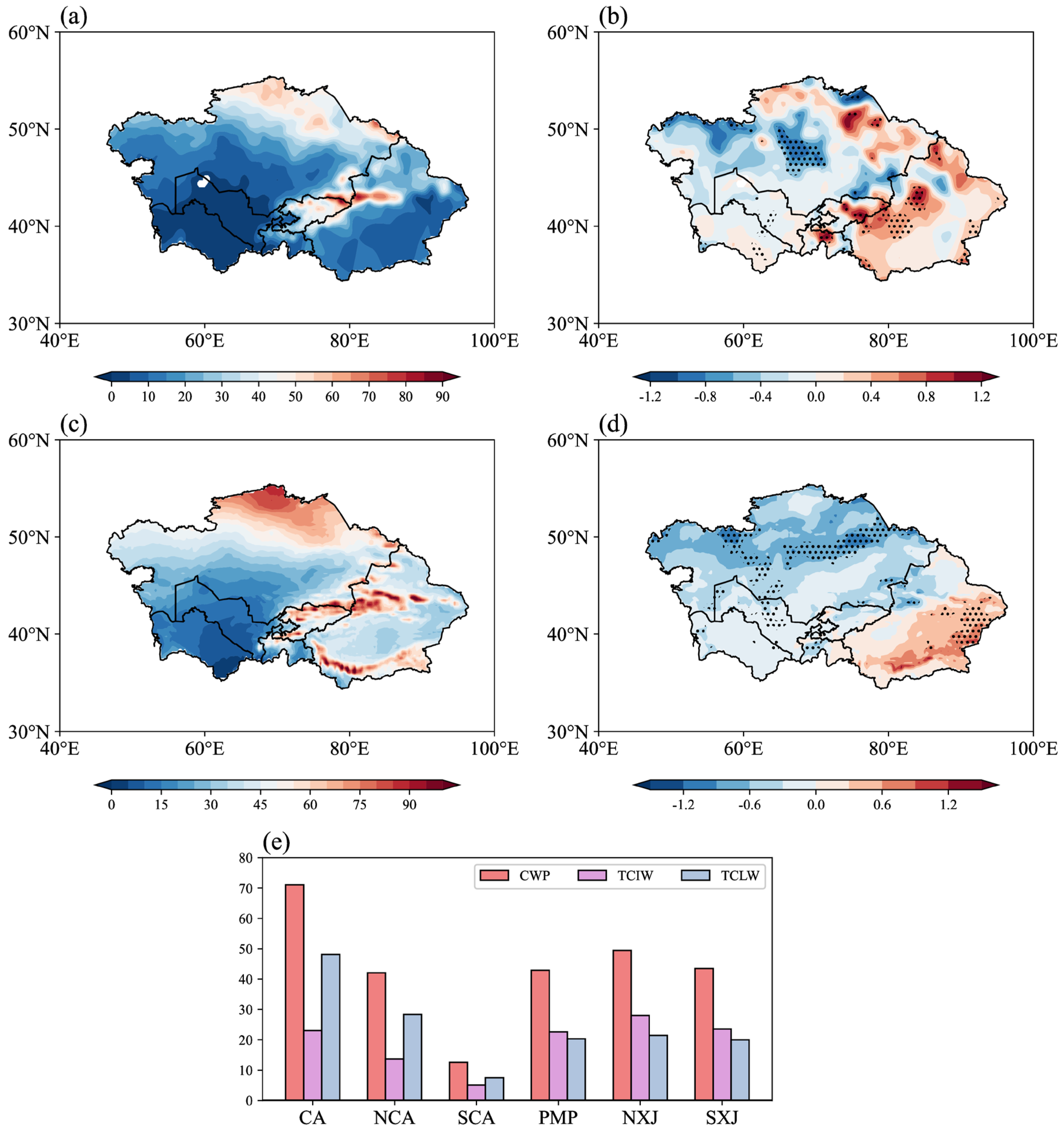
3.4. Influence of Cloud Propertites on Precipitation over Central Asia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bender, F.A.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Tselioudis, G. Changes in extratropical storm track cloudiness 1983–2008: Observational support for a poleward shift. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 2037–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L. Cloud Feedbacks in the Climate System: A Critical Review. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 237–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Folini, D.; Hakuba, M.Z.; Schär, C.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Kato, S.; Rutan, D.; Ammann, C.; Wood, E.F.; König-Langlo, G. The energy balance over land and oceans: An assessment based on direct observations and CMIP5 climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 3393–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zelinka, M.D.; Klein, S.A. Impact of decadal cloud variations on the Earth’s energy budget. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.; Wang, Z. Classifying clouds around the globe with the CloudSat radar: 1-year of results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, A. Cloud properties and dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau—A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 248, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J. Cloud vertical structure, precipitation, and cloud radiative effects over Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5864–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Abulikemu, A.; Li, J. Seasonal Variation in Total Cloud Cover and Cloud Type Characteristics in Xinjiang, China Based on FY-4A. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, N.A.; Tucker, D.F. Flow over Heated Terrain. Part I: Linear Theory and Idealized Numerical Simulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jianjun, L.I.U.; Baode, C. Cloud Occurrence Frequency and Structure over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from CloudSat Observation. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, D.F.; Crook, N.A. The Generation of a Mesoscale Convective System from Mountain Convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Letu, H.; Shang, H.; Shi, J. Cloud cover over the Tibetan Plateau and eastern China: A comparison of ERA5 and ERA-Interim with satellite observations. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2941–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, H.; Yasunari, T. The Seasonal and Intraseasonal Variability of Diurnal Cloud Activity over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 79, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Gong, W.; Kau, W.-S.; Chen, C.-T.; Hsu, H.-H.; Tu, C.-H. Characteristics of Cloud Radiation Forcing over East China. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucong, Y.; Yongqiang, Y.; Minghua, Z. Comparing cloud radiative properties between the Eastern China and the Indian monsoon region. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilinuer, T.; Yao, J.-Q.; Chen, J.; Mao, W.-Y.; Yang, L.-M.; Yeernaer, H.; Chen, Y.-H. Regional drying and wetting trends over Central Asia based on Köppen climate classification in 1961–2015. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, B.; Didovets, I.; Rostami, M.; Hamidi, M. Climate change impacts on Central Asia: Trends, extremes and future projections. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 3191–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tuoliewubieke, D.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Mao, W. Intensification of extreme precipitation in arid Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 125760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Rapid warming in mid-latitude central Asia for the past 100 years. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Sun, P.; Chen, X.; Kong, D. Magnitude, frequency and timing of floods in the Tarim River basin, China: Changes, causes and implications. Glob. Planet. Change 2016, 139, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, A.; Pilz, M.; Wieland, M.; Bindi, D.; Moldobekov, B.; Parolai, S. Landslide susceptibility analysis in data-scarce regions: The case of Kyrgyzstan. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 1117–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. Current problems of water supply and usage in central Asia, Tian Shan basin. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2013, 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. Advances in Understanding Clouds from ISCCP. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2261–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelling, D.R.; Sun, M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nordeen, M.L.; Haney, C.O.; Keyes, D.F.; Mlynczak, P.E. Advances in Geostationary-Derived Longwave Fluxes for the CERES Synoptic (SYN1deg) Product. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, C.; Li, Y.; Jian, B.; Huang, J. Diurnal cycles of cloud cover and its vertical distribution over the Tibetan Plateau revealed by satellite observations, reanalysis datasets, and CMIP6 outputs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 743–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; You, Q.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Niu, M.; Zhang, Y. Changes in cloud amount over the Tibetan Plateau and impacts of large-scale circulation. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernecki, B.; Taszarek, M.; Marosz, M.; Półrolniczak, M.; Kolendowicz, L.; Wyszogrodzki, A.; Szturc, J. Application of machine learning to large hail prediction—The importance of radar reflectivity, lightning occurrence and convective parameters derived from ERA5. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Letu, H.; Zhao, J.; Shang, H.; Lei, Y.; Duan, A.; Chen, B.; Bao, Y.; He, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Spatiotemporal distributions of cloud parameters and their response to meteorological factors over the Tibetan Plateau during 2003–2015 based on MODIS data. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y. Diurnal Variation in Clouds and Radiative Budgets Over the Tibetan Plateau During Summer Using CERES Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinar, E.K.; Dong, X.; Xi, B. Evaluation and intercomparison of clouds, precipitation, and radiation budgets in recent reanalyses using satellite-surface observations. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2123–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.H.; Knapp, K.R.; Inamdar, A.; Hankins, W.; Rossow, W.B. The International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project H-Series climate data record product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, N.G.; Doelling, D.R.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Nguyen, C.; Corbett, J.G.; Liang, L.; Mitrescu, C.; Rose, F.G.; Kato, S. Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) Top-of-Atmosphere (TOA) Edition-4.0 Data Product. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 895–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, W.; Yin, G. Evaluation of three global gridded precipitation data sets in central Asia based on rain gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 3475–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.W. Using the Köppen classification to quantify climate variation and change: An example for 1901–2010. Environ. Dev. 2013, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.P. Combining satellite data and models to estimate cloud radiative effect at the surface and in the atmosphere. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouguo, D.; Guangyu, S.; Chunsheng, Z. Analyzing global trends of different cloud types and their potential impacts on climate by using the ISCCP D2 dataset. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Guo, X.; Tang, J.; Lu, G. Aircraft measurement campaign on summer cloud microphysical properties over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jian, B.; Wang, G.; Yuxin, Z.; Li, Y.; Letu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Climatology of Cloud Phase, Cloud Radiative Effects and Precipitation Properties over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, L. Moisture Sources Associated with Precipitation during Dry and Wet Seasons over Central Asia. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10755–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. 100 Years of Progress on Mountain Meteorology Research. Meteorol. Monogr. 2019, 59, 20.1–20.73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.; Senior, C.; Bony, S.; Morcrette, J.J. Combining ERBE and ISCCP data to assess clouds in the Hadley Centre, ECMWF and LMD atmospheric climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2001, 17, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, W.; Tanikawa, T.; Hori, M.; Aoki, T.; Stamnes, K. Cloud mask over snow-/ice-covered areas for the GCOM-C1/SGLI cryosphere mission: Validations over Greenland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12287–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillinger, T.; Roberts, D.A.; Collar, N.M.; Dozier, J. Cloud Masking for Landsat 8 and MODIS Terra Over Snow-Covered Terrain: Error Analysis and Spectral Similarity Between Snow and Cloud. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6169–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, V.; Pazos, M.; Garduño, R.; Mendoza, B. Thermodynamics of climate change between cloud cover, atmospheric temperature and humidity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Leng, G. Damped summer warming accompanied with cloud cover increase over Eurasia from 1982 to 2009. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudisill, W.; Feldman, D.; Cox, C.J.; Riihimaki, L.; Sedlar, J. Seasonality and Albedo Dependence of Cloud Radiative Forcing in the Upper Colorado River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2025, 130, e2024JD042366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, A.; Prabha, T.V.; Benmoshe, N.; Pandithurai, G.; Ovchinnikov, M. The mechanism of first raindrops formation in deep convective clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9123–9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Rose, F.G.; Rutan, D.A.; Thorsen, T.J.; Loeb, N.G.; Doelling, D.R.; Huang, X.; Smith, W.L.; Su, W.; Ham, S.-H. Surface Irradiances of Edition 4.0 Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) Data Product. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4501–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data | Temporal Coverage | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5 | 1981–2020 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly |
| ISCCP | 1984–2016 | 1° × 1° | Monthly |
| CERES | 2001–2020 | 1° × 1° | Monthly |
| GPCC | 2001–2020 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly |
| Abbreviation | Subregion Distribution | Köppen–Geiger Climate Classification |
|---|---|---|
| NCA: Northern Central Aisa | 44–54°N; 48–80°E | Dry–desert–cold (BWk) Snow–steppe–hot (Dsa) |
| SCA: Southern Central Aisa | 36–44°N; 52–68°E | Dry–desert–cold (BWk) Dry–steppe–cold (BSk) |
| PMP: Pamir Plateau | 36–44°N; 68–80°E | Polar–tundra (ET) Dry–desert–cold (BWk) |
| NXJ: Northern Xinjiang | 42–50°N; 80–95°E | Dry–desert–cold (BWk) Snow–humid–hot (Dfa) |
| SXJ: Southern Xinjiang | 36–42°N; 80–95°E | Dry–desert–cold (BWk) Polar–tundra (ET) |
| Correlation 99% Grid Points 95% Grid Points | TCC | HCC | MCC | LCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | −0.223 0.026 0.084 | −0.148 0.002 0.014 | −0.126 0.033 0.124 | −0.178 0.105 0.223 |
| Spring | −0.553 0.109 0.329 | −0.092 0.050 0.163 | −0.608 0.338 0.493 | −0.676 0.583 0.742 |
| Summer | −0.682 0.406 0.577 | −0.457 0.100 0.259 | −0.720 0.395 0.512 | −0.616 0.600 0.742 |
| Autumn | −0.473 0.070 0.212 | −0.265 0.002 0.017 | −0.644 0.255 0.423 | −0.560 0.238 0.403 |
| Winter | 0.325 0.127 0.268 | 0.534 0.294 0.523 | 0.126 0.055 0.228 | 0.060 0.115 0.252 |
| Subregions | TCC | HCC | MCC | LCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCA | −0.083 | −0.550 | −0.868 | −0.789 |
| SCA | −0.388 | −0.189 | −0.448 | −0.710 |
| PMP | −0.510 | −0.559 | −0.075 | −0.471 |
| NXJ | −0.430 | −0.271 | −0.355 | −0.617 |
| SXJ | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Ma, L.; Yao, J.; Mao, W. Spatiotemporal Variability of Cloud Parameters and Their Climatic Impacts over Central Asia Based on Multi-Source Satellite and ERA5 Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152724
Xie X, Ma L, Yao J, Mao W. Spatiotemporal Variability of Cloud Parameters and Their Climatic Impacts over Central Asia Based on Multi-Source Satellite and ERA5 Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152724
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xinrui, Liyun Ma, Junqiang Yao, and Weiyi Mao. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variability of Cloud Parameters and Their Climatic Impacts over Central Asia Based on Multi-Source Satellite and ERA5 Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152724
APA StyleXie, X., Ma, L., Yao, J., & Mao, W. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variability of Cloud Parameters and Their Climatic Impacts over Central Asia Based on Multi-Source Satellite and ERA5 Data. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152724






