Geometry and Kinematics of the North Karlik Tagh Fault: Implications for the Transpressional Tectonics of Easternmost Tian Shan
Abstract
1. Introduction
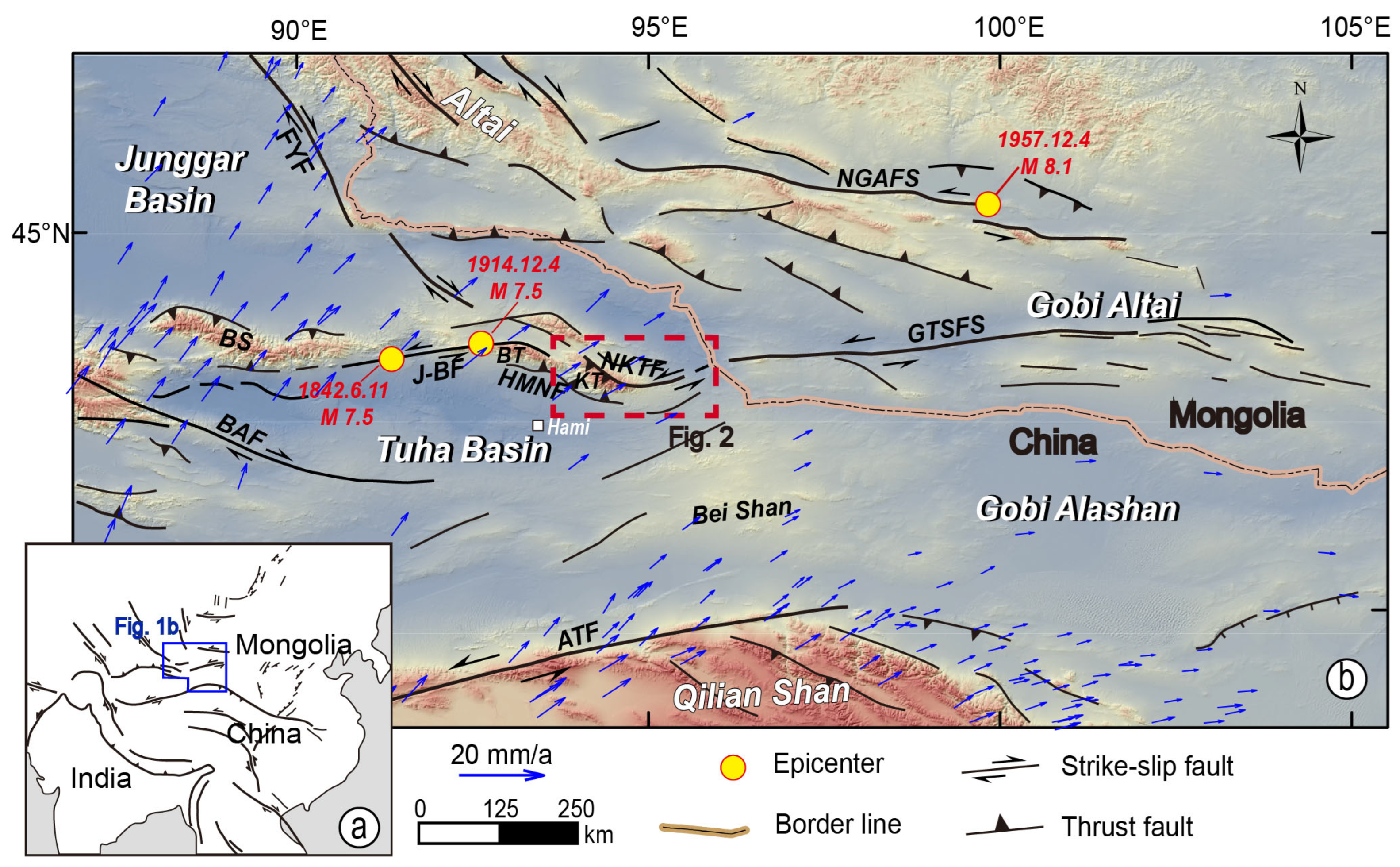
2. Background
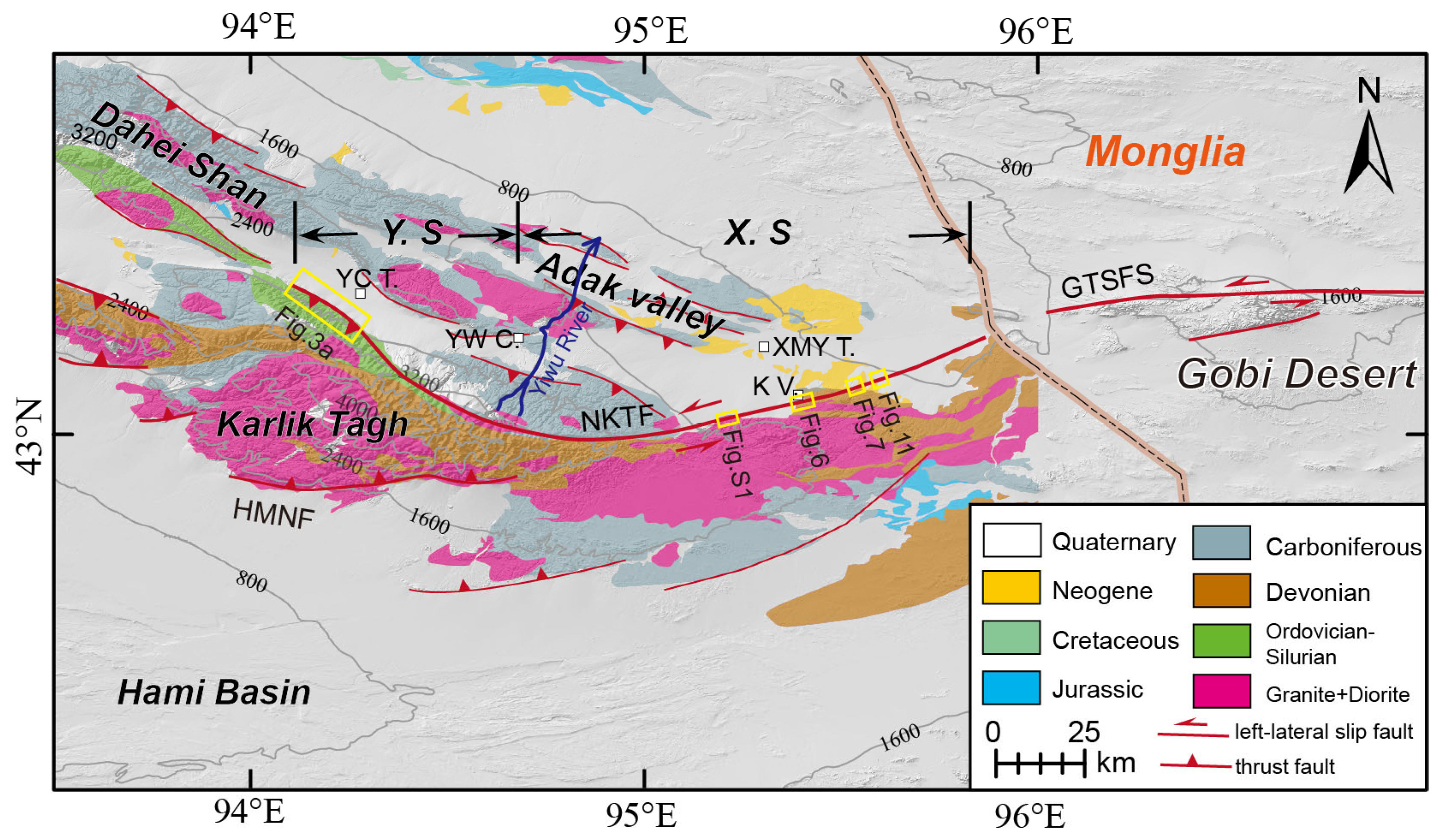
2.1. Geological Setting Easternmost Tian Shan
2.2. Active Tectonics
3. Methods
3.1. Geomorphological Mapping and Offset Measurements
3.2. Cosmogenic Nuclide (10Be) Dating of Quaternary Surfaces
4. Results
4.1. Overview of the North Karlik Tagh Fault
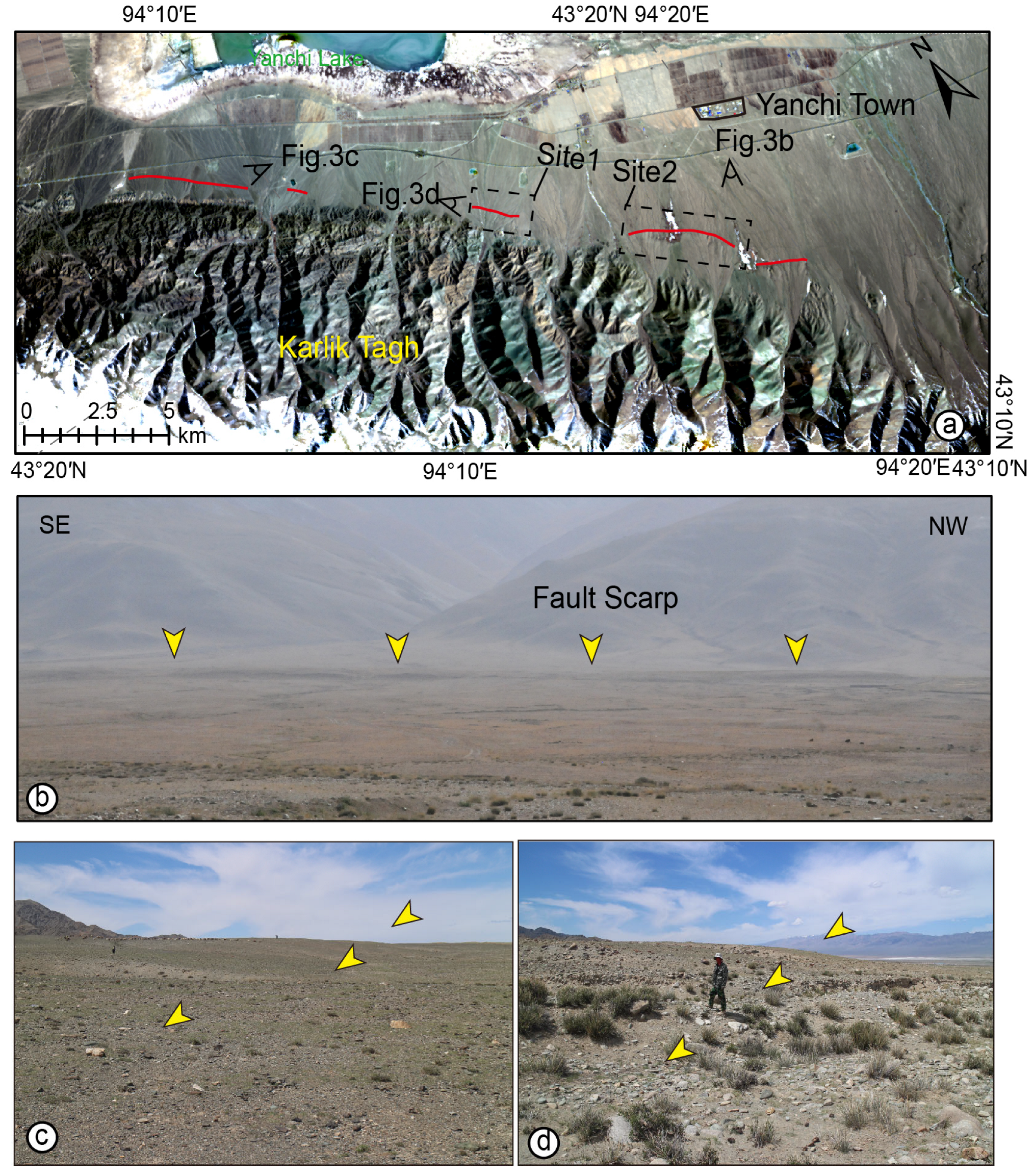
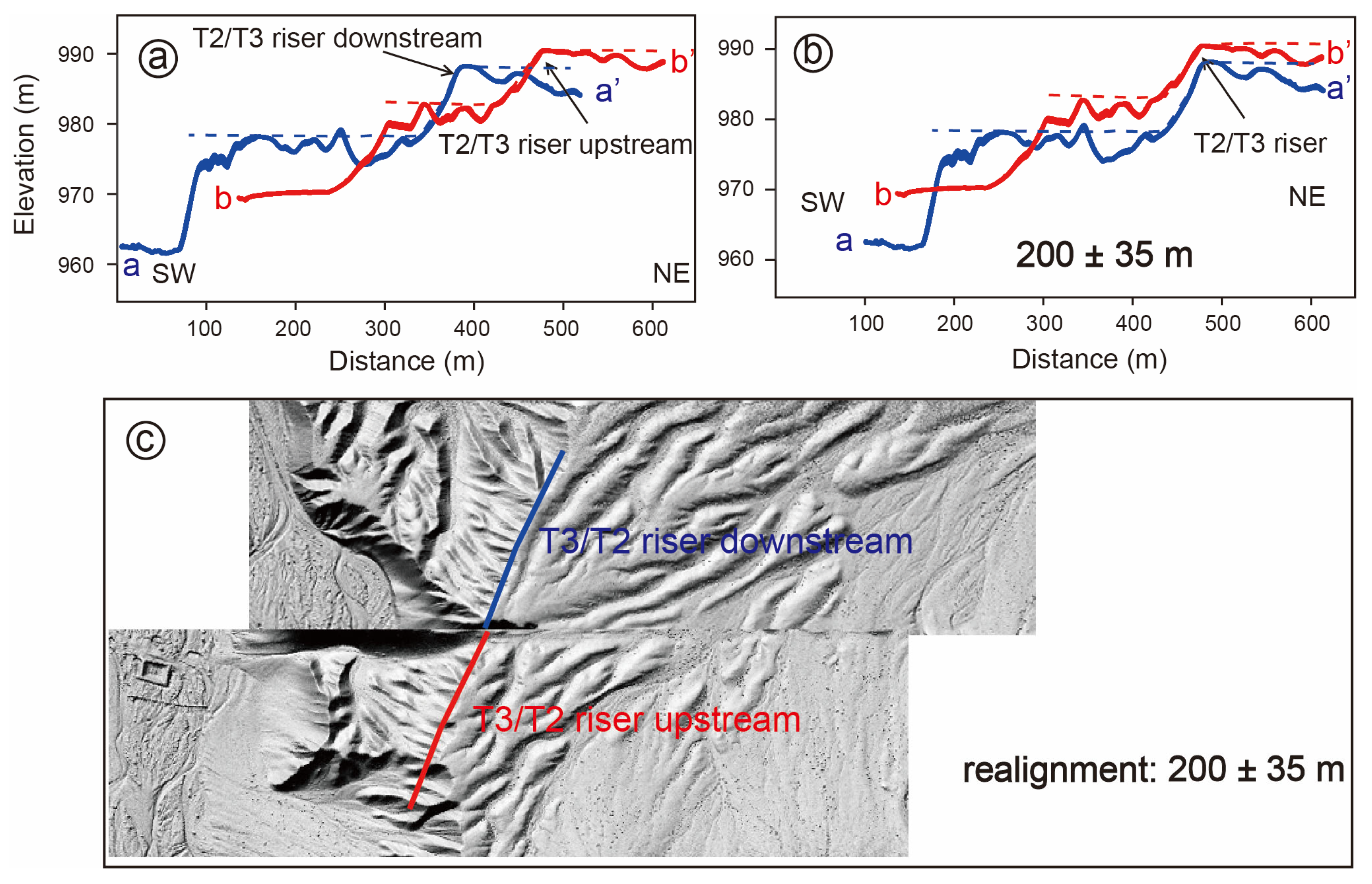
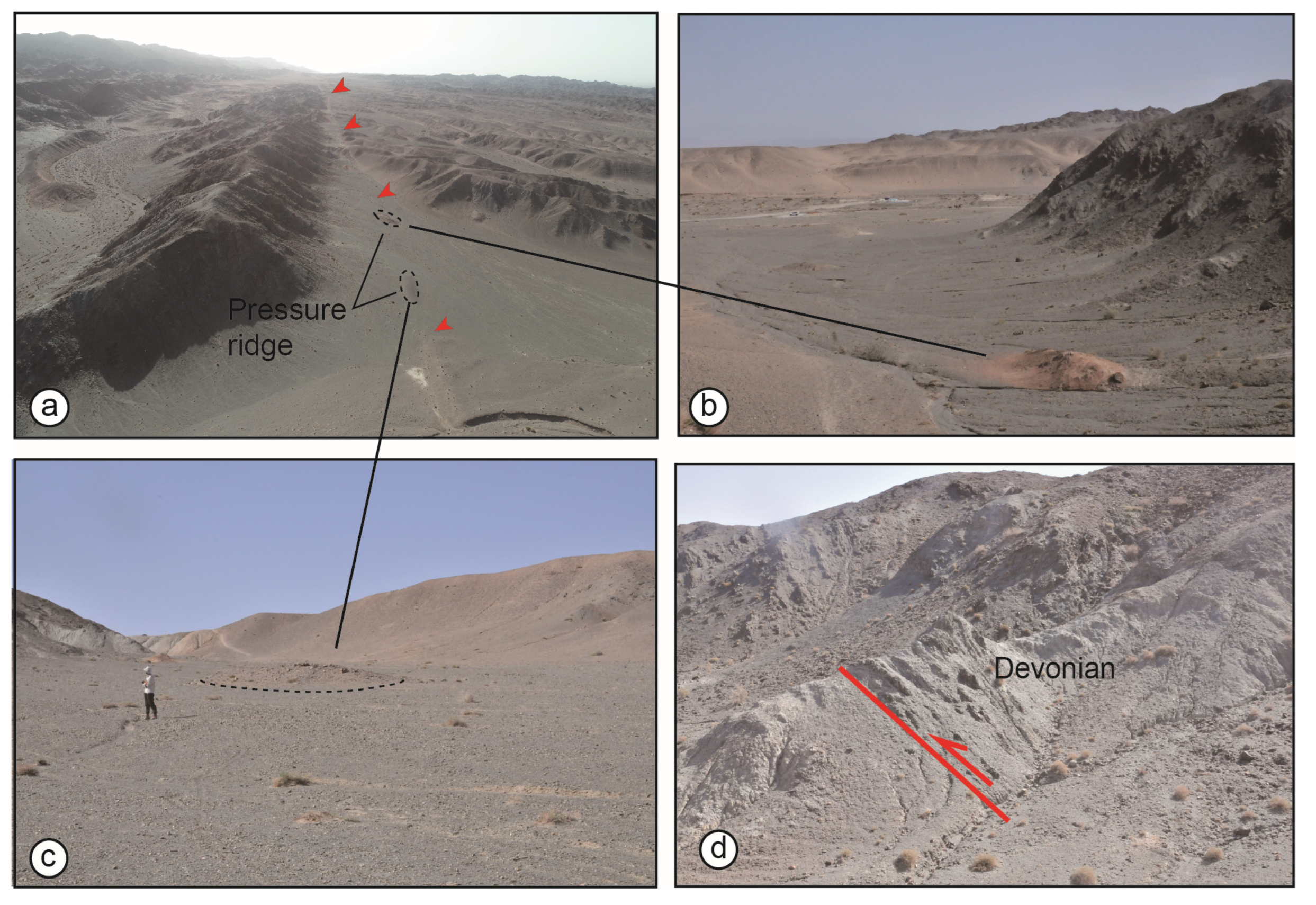
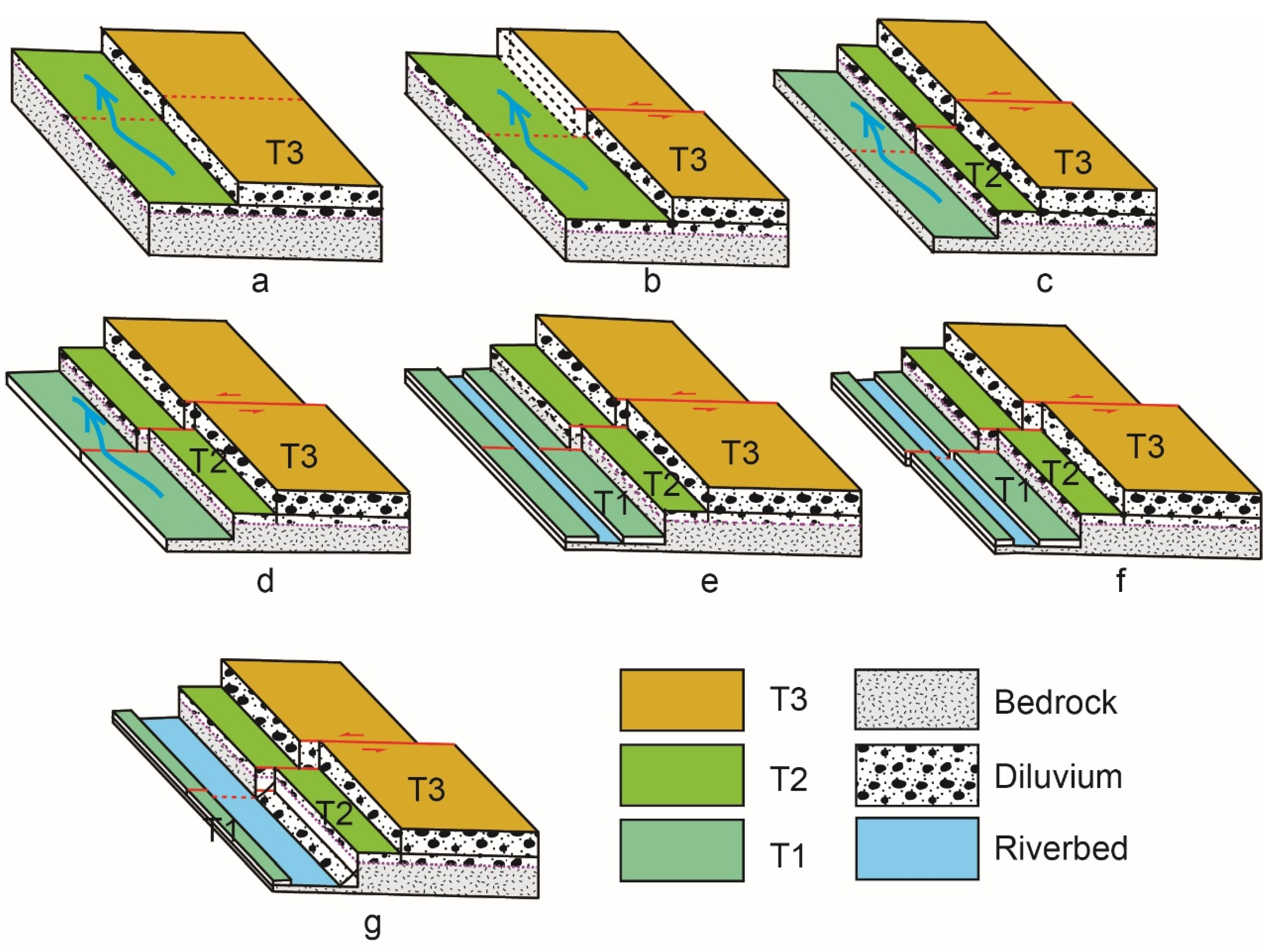
4.2. Deformation Geomorphic Characteristics
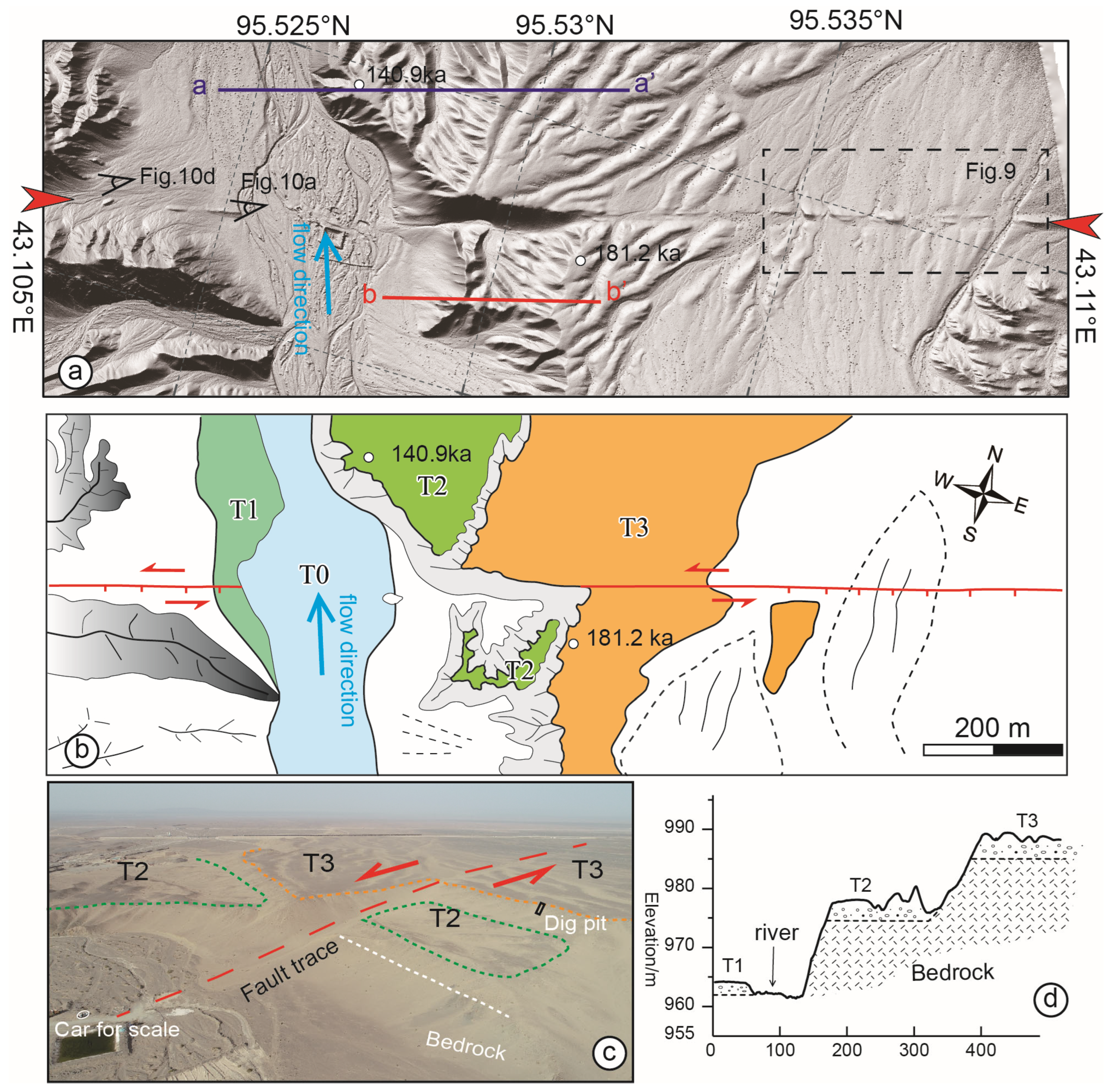
4.2.1. Yanchi Segment
4.2.2. Xiamaya Segment
4.3. Surface Exposure Ages
4.3.1. Geochronology of Yanchi Segment
4.3.2. Geochronology of Xiamaya Segment
5. Discussion
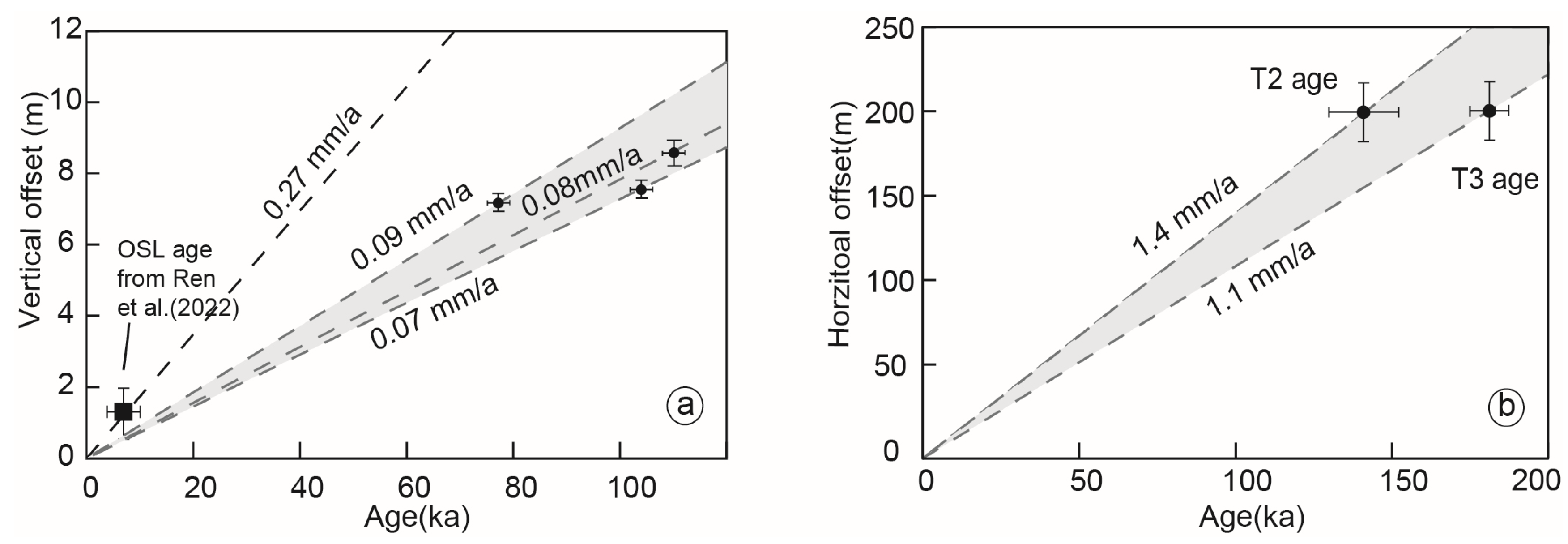
5.1. Slip Rates of the North Karlik Tagh Fault
5.1.1. Vertical Slip Rate Along the Yanchi Segment
5.1.2. Left-Lateral Slip Rate Along the Xiamaya Segment
5.2. Fault Geometry and Kinematics in Easternmost Tian Shan
5.3. Slip Partitioning and Tectonic Implications for Easternmost Tian Shan
5.4. Seismic Hazard of the North Karlik Tagh Fault
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodcock, N.H.; Fischer, M. Strike-slip duplexes. J. Struct. Geol. 1986, 8, 725–735. [Google Scholar]
- Marshak, S.; Nelson, W.; McBride, J. Phanerozoic strike-slip faulting in the continental interior platform of the United States: Examples from the Laramide orogen, mid-continent, and Ancestral Rocky Mountains. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 210, 159–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rizza, M.; Abdrakhmatov, K.; Walker, R.; Braucher, R.; Guillou, V.; Carr, A.S.; Campbell, G.; McKenzie, D.; Jackson, J.; Aumaître, G.; et al. Rate of slip from multiple Quaternary dating methods and paleoseismic investigations along the Talas-Fergana Fault: Tectonic implications for the Tien Shan Range. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2477–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P.; Pollard, D. Mechanics of discontinuous faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1980, 85, 4337–4350. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, R.A.; Friedrich, A.M.; Furlong, K.P. Codependent histories of the San Andreas and San Jacinto fault zones from inversion of fault displacement rates. Geology 2004, 32, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: Effects of a continental collision. Science 1975, 189, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, D. Structural and topographic characteristics of restraining bend mountain ranges of the Altai, Gobi Altai and easternmost Tien Shan. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2007, 290, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrakhmatov, K.E.; Walker, R.T.; Campbell, G.E.; Carr, A.S.; Elliott, A.; Hillemann, C.; Hollingsworth, J.; Landgraf, A.; Mackenzie, D.; Mukambayev, A.; et al. Multisegment rupture in the 11 July 1889 Chilik earthquake (Mw 8.0–8.3), Kazakh Tien Shan, interpreted from remote sensing, field survey, and paleoseismic trenching. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 4615–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayasgalan, A.; Jackson, J.; McKenzie, D. Lithosphere rheology and active tectonics in Mongolia: Relations between earthquake source parameters, gravity and GPS measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 163, 1151–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Blisniuk, K.; Rockwell, T.; Owen, L.A.; Oskin, M.; Lippincott, C.; Caffee, M.W.; Dortch, J. Late quaternary slip rate gradient defined using high-resolution topography and 10Be dating of offset landforms on the southern San Jacinto fault zone, California. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B08401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, W.D.; Mann, P. Tectonics of strike-slip restraining and releasing bends. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2007, 290, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Nur, A. The types and role of stepovers in strike-slip tectonics. In Strike-Slip Deformation, Basin Formation, and Sedimentation; Biddle, K.T., Christie-Blick, N., Eds.; SEPM Special Publications: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1985; Volume 37, pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, P.; Gordon, M. Tectonic uplift and exhumation of blueschist belts along transpressional strike-slip fault zones. In Dynamics of Subduction Zones; Bebout, G., Scholl, D., Kirby, S., Platt, J., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; Volume 96, pp. 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- McClay, K.; Bonora, M. Analog models of restraining stepovers in strike-slip fault systems. AAPG Bull. 2001, 85, 233–260. [Google Scholar]
- Crowell, J.C. Sedimentation along the San Andreas fault, California. In Modern and Ancient Geosynclinal Sedimentation; Dott, R.H., Jr., Shaver, R.H., Eds.; SEPM Special Publications: Claremore, OK, USA, 1974; Volume 19, pp. 292–303. [Google Scholar]
- Biddle, K.T.; Christie-Blick, N. Glossary–strike-slip deformation, basin formation and sedimentation. SEPM Spec. Publ. 1985, 37, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Lowell, J.D. Spitsbergen Tertiary orogenic belt and the Spitsbergen Fracture Zone. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1972, 83, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.; King, G.; Tapponnier, P. Slip partitioning by elastoplastic propagation of oblique slip at depth. Science 2003, 300, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, T.; McClay, K.; Bonora, M. 4D evolution of segmented strike-slip fault systems: Applications to NW Europe. Geol. Soc. Lond. Pet. Geol. Conf. Ser. 1999, 5, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.R.; Tanner, P.W.G. Strain partitioning in transpression zones. J. Struct. Geol. 1995, 17, 793–802. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, L.A.; Cunningham, W.D.; Windley, B.F.; Badamgarov, J.; Dorjnamjaa, D. The landscape evolution of Nemegt Uul: A late Cenozoic transpressional uplift in the Gobi Altai, southern Mongolia. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 1999, 162, 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, D.; Owen, L.A.; Snee, L.W.; Li, J.L. Structural framework of a major intracontinental orogenic termination zone: The easternmost Tien Shan, China. J. Geol. Soc. 2003, 160, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Molnar, P. Active faulting and Cenozoic tectonics of the Tien Shan, Mongolia, and Baykal Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1979, 84, 3425–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayasgalan, A.; Jackson, J.; Ritz, J.-F.; Carretier, S. Field examples of strike-slip fault terminations in Mongolia and their tectonic significance. Tectonics 1999, 18, 394–411. [Google Scholar]
- Seismological Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Collection of Earthquake Information of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1985. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kurushin, R.A.; Bayasgalan, A.; Olziybat, M.; Enkhtuvshin, B.; Molnar, P.; Bayasgalan, C.; Hudnut, K.W. The surface rupture of the 1957 Gobi-Altai, Mongolia, earthquake. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 1997, 320, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.-K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, W.D.; Windley, B.F.; Dorjnamjaa, D.; Badamgarov, J.; Saandar, M. Late Cenozoic transpression in southwestern Mongolia and the Gobi Altai-Tien Shan connection. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 140, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.B.; Windley, B.F.; Zhang, C. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tianshan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics 1993, 220, 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.C.; Weldon, R.J.; Rubin, C.M.; Abdrakhmatov, K.; Molnar, P.; Berger, G.W. Late Quaternary slip rates across the central Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan, central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, ETG 7-1–ETG 7-32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Deng, Q.D.; Yang, X.P.; Peng, S.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Feng, X.Y. Late Cenozoic tectonic deformation and mechanism along the Tianshan Mountain, Northwestern China. Earthq. Res. China 1996, 12, 127–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.D.; Feng, X.Y.; Zhang, P.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Peng, S.Z.; Li, J. Active Tectonics of Tianshan; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 2000; p. 260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Abdrakhmatov, K.Y.; Aldazhanov, S.A.; Hager, B.H.; Hamburger, M.W.; Herring, T.A.; Kalabaev, K.B.; Makarov, V.I.; Molnar, P.; Panasyuk, S.V.; Prilepin, M.T.; et al. Relatively recent construction of the Tien Shan inferred from GPS measurements of present-day crustal deformation rates. Nature 1996, 384, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Freymueller, J.T.; Bilham, R.; Larson, K.M.; Lai, X.; You, X.; Niu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Present-day crustal deformation in China constrained by global positioning system measurements. Science 2001, 294, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubovich, A.V.; Wang, X.; Scherba, Y.G.; Schelochkov, G.G.; Reilinger, R.; Reigber, C.; Mosienko, O.I.; Molnar, P.; Michajljow, W.; Makarov, V.I.; et al. GPS velocity field for the Tien Shan and surrounding regions. Tectonics 2010, 29, TC6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. The deformation pattern and fault rate in the Tianshan Mountains inferred from GPS observations. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.; Glorie, S.; Jepson, G.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiao, W.J.; Danišík, M.; Collins, A.S. Differential exhumation and crustal tilting in the easternmost Tianshan (Xinjiang, China), revealed by low-temperature thermochronology. Tectonics 2017, 36, 2142–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Ji, J.Q.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wang, L.N.; Sun, D.X.; Gong, J.F.; Zhao, L. The Late Cenozoic transpressional deformation and uplift of Bogda-Harlic Mountains. Chin. J. Geol. 2010, 45, 653–665. [Google Scholar]
- Bande, A.; Sobel, E.R.; Mikolaichuk, A.; Acosta, V.T. Talas–Fergana Fault Cenozoic timing of deformation and its relation to Pamir indentation. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2015, 427, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosboom, R.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Huang, W.; Yang, W.; Guo, Z. Oligocene clockwise rotations along the eastern Pamir: Tectonic and paleogeographic implications. Tectonics 2014, 33, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devyatkin, E.V. Structures and Formational Complexes of the Cenozoic Activated Stage; Tectonics of the Mongolian People’s Republic; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1974; pp. 182–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.X.; Li, C.Y.; Sun, K. Late Quaternary activity and transpressinal deformation of the Karlik Tagh North Fault, easternmost Tianshan. Seismol. Geol. 2022, 44, 46–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Qin, K.; Sun, S.; Li, J. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of central Asia. Am. J. Sci. 2004, 304, 370–395. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Ran, Y.K.; Xu, L.X.; Cao, J.; Li, A. Paleoseismological Study of the Late Quaternary Slip-rate along the South Barkol Basin Fault and Its Tectonic Implications, Eastern Tian Shan, Xinjiang. ACTA Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 91, 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Ding, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z. Quaternary deformation along the Gobi-Tian Shan Fault in the Easternmost Tian Shan (Harlik Mountain), Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calais, E.; Vergnolle, M.; San’Kov, V.; Lukhnev, A.; Miroshnitchenko, A.; Amarjargal, S. GPS measurements of crustal deformation in the Baikal-Mongolia area (1994–2002): Implications for current kinematics of Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 148–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, J.B.; Zhao, C.Q.; Liu, Z.J. Late Quaternary activity characteristics of YiWu fault in east Tianshan. Inland Earthq. 2021, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.; Nissen, E.; Saripalli, S.; Arrowsmith, J.R.; McGarey, P.; Scharer, K.; Williams, P.; Blisniuk, K. Rapid mapping of ultrafine fault zone topography with structure from motion. Geosphere 2014, 10, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, T.C. The age of scarplike landforms from diffusion-equation analysis. In Quaternary Geochronology: Methods and Applications; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 4, pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielke, O.; Arrowsmith, J.R. LaDiCaoz and LiDARimager-MATLAB GUIs for LiDAR data handling and lateral displacement measurement. Geosphere 2012, 8, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, R.; Hampel, A.; Gebbeken, P.; Xu, Q.; Gold, R.D. A constant slip rate for the western Qilian Shan frontal thrust during the last 200 ka consistent with GPS-derived and geological shortening rates. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 509, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, W.; Wu, G.; Miao, S.; Zhang, L. Slip rate and paleoseismology of the Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk (Dzhungarian) right-lateral strike-slip fault in the northern Tian Shan, NW China. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2020TC006604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, E.; Walker, R.T.; Bayasgalan, A.; Carter, A.; Fattahi, M.; Molor, E.; Schnabel, C.; West, A.J.; Xu, S. The late Quaternary slip-rate of the Har-Us-Nuur fault (Mongolian Altai) from cosmogenic 10Be and luminescence dating. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 286, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, R.; Ritz, J.-F.; Braucher, R.; Carretier, S. Dating faulted alluvial fans with cosmogenic 10Be in the Gurvan Bogd mountain range (Gobi-Altay, Mongolia): Climatic and tectonic implications. Terra Nova 2005, 17, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, R.; Ritz, J.-F.; Carretier, S. Control of geomorphic processes on 10Be concentrations in individual clasts: Complexity of the exposure history in Gobi-Altay range (Mongolia). Geomorphology. 2011, 135, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehfuss, P.H.; Bierman, P.R.; Gillespie, A.R.; Burke, R.M.; Caffee, M.W. Slip rates on the Fish Springs fault, Owens Valley, California, deduced from cosmogenic 10Be and 26Al and soil development on fan surfaces. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2001, 113, 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiizumi, K. Preparation of 26Al AMS standards. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2004, 223, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, X.; Jobe, J.A.T.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L. Alluvial plains formation in response to 100-ka glacial-interglacial cycles since the Middle Pleistocene in the southern Tian Shan, NW China. Geomorphology 2019, 341, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, B.; Marrero, S.; Balco, G.; Caffee, M.; Goehring, B.; Lifton, N.; Nishiizumi, K.; Phillips, F.; Schaefer, J.; Stone, J. Geological calibration of spallation production rates in the CRONUS-Earth project. Quat. Geochronol. 2016, 31, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D. Cosmic ray labeling of erosion surfaces: In situ nuclide production rates and erosion models. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 104, 424–439. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, J.O. Air pressure and cosmogenic isotope production. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 23753–23759. [Google Scholar]
- Hidy, A.J.; Gosse, J.C.; Pederson, J.L.; Mattern, J.P.; Finkel, R.C. A geologically constrained Monte Carlo approach to modeling exposure ages from profiles of cosmogenic nuclides: An example from Lees Ferry, Arizona. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.G. Estimating the seismicity from geological structure for seismic risk studies. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1979, 69, 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Field, E. A summary of previous working groups on California earthquake probabilities. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 1033–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Molnar, P.; Xu, X. Late Quaternary and present-day rates of slip along the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 2007, 26, TC5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieh, K.E.; Jahns, R.H. Holocene activity of the San Andreas Fault at Wallace Creek, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1984, 95, 883–896. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, G.S.; Anderson, R.S. Numerical modeling of fluvial strath-terrace formation in response to oscillating climate. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2002, 114, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Lague, D.; Hovius, N.; Davy, P. Discharge, discharge variability, and the bedrock channel profile. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F04006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.Q.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Klinger, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Shao, Y.X.; Han, L.F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Late Quaternary slip rate of the Zihong Shan Branch and its implications for strain partitioning along the Haiyuan Fault, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.; Harkins, N.; Wang, E.; Shi, X.; Fan, C.; Burbank, D. Slip rate gradients along the eastern Kunlun fault. Tectonics 2007, 26, TC2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Tapponnier, P.; Bourjot, L.; Metivier, F.; Gaudemer, Y.; Peltzer, G.; Shunmin, G.; Zhitai, C. Crustal thickening in Gansu-Qinghai, lithospheric mantle subduction, and oblique strike-slip controlled growth of the Tibet plateau, Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 135, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.X.; Li, C.Y.; Sun, K.; Zhou, C.; Luo, Q.X. Late Quaternary tectonic deformation characteristics of the Hami Basin North Fault, Eastern Tian Shan. Chin. J. Geophys. 2025, 68, 1315–1328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Davis, P.M.; Liu, H.; Slack, P.D.; Zorin, Y.A.; Mordvinova, V.V.; Kozhavnikov, V.M.; Meyer, R.P. Seismic anisotropy and mantle flow beneath the Baikal rift zone. Nature 1994, 371, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold, P.R.; Davy, P.H. Indentation tectonics in nature and experiment II: Central Asia. Bull. Geol. Inst. Univ. Upps. 1988, 14, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Ding, D.X. The Balikun earthquake (M = 7.5) on June 11, 1842 in XinJiang. Northwest. Seismol. J. 1987, 9, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.X.; Ran, Y.K.; Liang, M.J.; Wu, F.Y.; Gao, S.P.; Wang, H. Geometric distribution and characteristics of the surface rupture of two historical earthquakes in the Barkol Basin, XinJiang. Seismol. Geol. 2020, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Grützner, C.; Carson, E.; Walker, R.T.; Rhodes, E.J.; Mukambayev, A.; Mackenzie, D.; Elliott, J.R.; Campbell, G.; Abdrakhmatov, K. Assessing the activity of faults in continental interiors: Palaeoseismic insights from SE Kazakhstan. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 459, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, L.; Hetzel, R.; Tao, M.; Li, X.; Guo, J. Deciphering the rate of mountain growth during topographic presteady state: An example from the NE margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 2009, 28, TC4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L.; Coppersmith, K.J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 974–1002. [Google Scholar]








| Sample ID a | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Altitude (m) | Depth (m) | Thickness (cm) | Quartz (g) | 10Be Carrier (mg) | 10Be Concentration (atoms/g) | Exposure Age b (ka) | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KAR-P02 | 95.532764 | 43.109787 | 1049 | 150 | 10 | 30.3571 | 0.2281 | 812,768 | 181.2 | |
| KAR-P03 | 95.532764 | 43.109787 | 1049 | 90 | 10 | 30.2736 | 0.2321 | 1,110,797 | ||
| KAR-P04 | 95.532764 | 43.109787 | 1049 | 60 | 10 | 30.828 | 0.2535 | 1,347,753 | +8.8/−11.2 | |
| KAR-P05 | 95.532764 | 43.109787 | 1049 | 30 | 10 | 30.635 | 0.2468 | 1,673,081 | ||
| KAR-02 | 95.532764 | 43.109787 | 1049 | 0 | 2 | 30.2559 | 0.2393 | 2,607,605 | ||
| KAR-04 | 95.52796 | 43.111134 | 1029 | 0 | 2 | 30.2281 | 0.2535 | 2,125,579 | 140.9 | ±6.2 |
| KAR-Y01 | 94.281073 | 43.282189 | 2174 | 0 | 2 | 30.573 | 0.2268 | 2,580,603 | 103.9 | ±6.5 |
| KAR-Y02 | 94.280307 | 43.282473 | 2172 | 0 | 2 | 30.4725 | 0.2305 | 1,900,598 | 77.3 | ±4.8 |
| KAR-Y03 | 94.302027 | 43.271909 | 2197 | 0 | 2 | 30.7335 | 0.2253 | 2,735,180 | 109.9 | ±6.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, G.; Li, C.; Wu, C.; Sun, K.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zou, B. Geometry and Kinematics of the North Karlik Tagh Fault: Implications for the Transpressional Tectonics of Easternmost Tian Shan. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142498
Ren G, Li C, Wu C, Sun K, Luo Q, Zhang X, Zou B. Geometry and Kinematics of the North Karlik Tagh Fault: Implications for the Transpressional Tectonics of Easternmost Tian Shan. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142498
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Guangxue, Chuanyou Li, Chuanyong Wu, Kai Sun, Quanxing Luo, Xuanyu Zhang, and Bowen Zou. 2025. "Geometry and Kinematics of the North Karlik Tagh Fault: Implications for the Transpressional Tectonics of Easternmost Tian Shan" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142498
APA StyleRen, G., Li, C., Wu, C., Sun, K., Luo, Q., Zhang, X., & Zou, B. (2025). Geometry and Kinematics of the North Karlik Tagh Fault: Implications for the Transpressional Tectonics of Easternmost Tian Shan. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142498






