Abstract
The Beidou Global System (BDS-3) innovatively achieves autonomous navigation using inter-satellite links (ISL) across the entire constellation, but it still faces challenges such as the limitations of the prior constraint orbital accuracy and the overall constellation rotation. The gradual availability of satellite laser ranging (SLR) data, with advantages of high precision and no ambiguous parameters, can provide new ideas for solving the current problem. This work firstly deduces the mathematical model for orbit determination by combining inter-satellite links and the introduced satellite laser ranging observations, then designs orbit determination experiments with different prior orbit constraints and different observation data, and finally evaluates the impacts of the prior orbits and the introduction of SLR observations from two dimensions: orbit accuracy and constellation rotation. The experimental results using one month of measured data show the following: (1) There is good consistency among different days, and the accuracy of the prior orbits affects the performance of the orbit determination and the consistency. Compared with broadcast ephemerides, using precise ephemerides as prior constraints significantly improves the consistency, and the orbit accuracy can be increased by about 75%. (2) The type of observation data affects the performance of the orbit determination. Introducing SLR observations can improve the orbit accuracy by approximately 13% to 26%. (3) Regardless of whether broadcast ephemerides or precise ephemerides are used as prior constraints, the constellation translation and rotation still exist after introducing SLR observations. Among the translation parameters, TX is the largest, followed by TY, and TZ is the smallest; all three rotation parameters (RX, RY, and RZ) show relatively large values, which may be related to the limited number of available satellite laser ranging stations during this period. (4) After considering the constellation translation and rotation, the orbit accuracy under different prior constraints remains at the same level. The statistical root mean square error (RMSE) indicates that the orbit accuracy of inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellites in three directions is better than 20 cm, while the accuracy of medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites in along-track, cross-track, and radial directions is better than 10 cm, 8 cm, and 5 cm, respectively.
1. Introduction
Among the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that have been built in the world, the Chinese BDS-3 is the first to realize the whole constellation inter-satellite links (ISL) function [1]. ISL not only ensure the precise orbit determination (POD) performance under the condition of limited regional ground stations but also supports the autonomous navigation of the constellation, which greatly enhances the overall operational capability of the BDS-3 [2,3].
The existing research about the ISL measurement used for POD can be mainly divided into two categories: One is to combine ISL measurements and carrier phase observations of GNSS receivers at ground stations to realize the precise orbit determination, namely joint POD. The other focuses on the autonomous orbit determination only using ISL measurement, namely AOD. For the first type, Yang et al. [4] conducted a POD experiment by combining ISL measurements with carrier phase observations from six GNSS receivers distributed in regional stations. The results show that the orbit-related spatial ranging accuracy was improved by 37–76%, compared to using only pseudorange and phase observations from ground stations, which indicates that introducing ISL measurement can improve the orbit accuracy determined with regional stations. Xie et al. [5] added ISL measurements to GNSS observations from 16 global ground stations for orbit determination. The results show that the 3D overlap accuracy of the orbit is improved by 42%, and the orbit accuracy is up to 9.2 cm, which indicates that ISL can improve the orbit accuracy based on a small number of global ground stations. Lv et al. [6] discussed the contribution of ISL measurements to the phase observations from various quantities and distributions of ground stations, pointing out that almost equivalent POD performance can be achieved when ISL measurements combine 10 regional and 10 global ground stations, respectively. All of the above have shown that, by introducing ISL measurements, the POD can reduce the dependence on ground stations. What is more, centimeter-level orbit can be achieved with regional ground stations. For the second type, POD with only ISL measurements, there are obvious systematic biases, as is known. Chang et al. [7] analyzed its characteristics and proposed an improved method, while the user’s ranging error still reached 3 m in 9 days. Moreover, Xia et al. [8] analyzed the effect of the a priori orbit on the autonomous orbit determination, such as the predicted orbit of the telemetry tracking control system and of the international GNSS Monitoring And evaluation System (iGMAS). They concluded that, under the a priori orbit of 45 m, the orbit accuracy with four ISL measurements can reach about 2 m. Tang et al. [9,10] further explored the performance of autonomous POD and time synchronization with ISL measurements from all BDS-3 satellites. They verified that, on one hand, the radial overlap error of the satellite orbit is better than 15 cm. On the other hand, the clock error accuracy of the satellite is better than the ones solved with only GNSS observations from ground stations.
Moreover, Zhao et al. [11] recently provided a comprehensive review of the existing research on POD, confirming the two conclusions above. Nevertheless, there are still some overlooked issues that need to be taken seriously and addressed, namely the influencing factors on and corresponding effectiveness of the performance of AOD. For example, the a priori orbit may greatly affect the orbital accuracy in AOD. What is more, although introducing the ISL measurement into GNSS observations from ground stations can improve the orbital accuracy in a certain extent, it needs a complex and rigorous algorithm. That is to say, the algorithm to detect the cycle slip and to realize the ambiguity resolution for the GNSS carrier observations must be implemented correctly, otherwise the orbital accuracy will deteriorate sharply in joint POD [12,13]. It is worth noting that all BDS-3 satellites are equipped with laser retro-reflector arrays (LRAs), which support ground-to-satellite laser ranging with high accuracy. Unlike GNSS carrier observation, they are not affected by the ambiguities. Thus, combining the SLR and ISL measurements can be regarded as a good choice for POD.
Limited to only a small amount of publicly available SLR measurements in BDS-3, previous studies in China on SLR measurements mainly focused on verifying the determined orbit for BDS and low earth orbit (LEO) satellites [14,15,16,17]. As a matter of fact, the SLR measurements have been fully applied to the POD, clock offset estimation and prediction, and orbit accuracy verification in other global satellite navigation systems, including GLONASS, Galileo, and GPS [18,19,20]. In recent years, benefiting from the development of the hardware devices and LEO satellites, SLR measurements in BDS-3 have gradually become public. Compared with GNSS observations, SLR observations have the advantages of high accuracy and are not affected by ambiguity parameters. Thus, integrating ISL and SLR for orbit determination is an effective means to avoid complex ambiguity parameters and overcome the lack of ground reference in AOD. Numerous studies based on SLR observations have subsequently emerged, typically represented by verifications of the orbit accuracy of LEO satellites [21] and POD of GNSS satellites by combining other observations [22]. Among them, some scholars explored the performance of orbit determination by processing the SLR and ISL measurements of several BDS-3 satellites together, called combined ISL/SLR POD in this paper, and analyzed the influence on the orbit accuracy and earth rotation parameters [23,24,25,26]. The results showed that a 3D orbital precision of about 30 cm was achieved. This indicates that the addition of SLR measurements can not only improve the orbit accuracy but also benefit the autonomous and controllable spatial reference parameters. However, there is currently no relevant research on the impact of the a priori orbit with various accuracies on the combined ISL/SLR POD for all BDS-3 satellites, as well as the on the translation and rotation of the constellation.
In response to the limitations of the current research, to explore the impact of the a priori orbit with various accuracies on orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites using ISL and SLR osbervations, this study uses the method of combined ISL/SLR POD for all BDS-3 satellites, with a focus on analyzing the influence of the a priori orbit on the orbit accuracy and the overall rotation and translation of the constellation. The paper is organized as follows: after an overview of existing studies, the basic combined ISL/SLR POD functional models and methods are derived. The experimental data, processing strategies, and experimental design are then explained. Subsequently, the orbital accuracy with various a priori orbit and observations is analyzed, and the performance of the overall rotation and translation of the constellation is further explored. Some conclusions and disscussion are given at the end of the article.
2. Materials and Methods
For the ISL measurements, a wireless link for communication and ranging between satellites, is descirbed by a dual one-way ranging model that follows a time division multiple access (TDMA) scheme. The SLR measurements refer to the ranging between the SLR station on the ground and the satellites of BDS-3. The orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites can be achieved by integrating the SLR measurement with the ISL measurement. Taking three BDS-3 satellites and two SLR ground stations as an example, Figure 1 illustrates the schematic diagram of the orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites based on SLR and ISL observations.
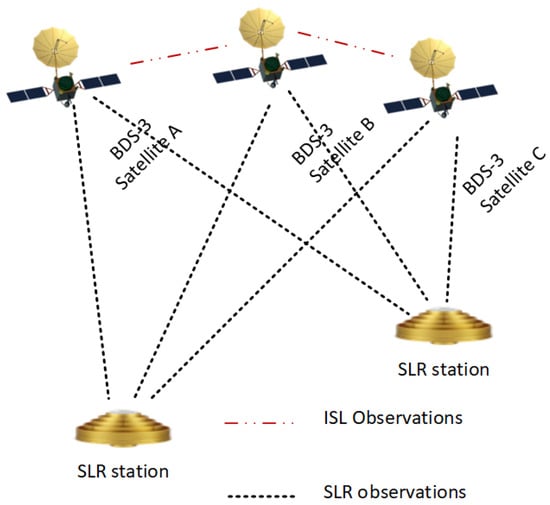
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of POD based on ISL and SLR observation.
As mentioned above, the ISL measurements employ a dual one-way ranging measurement approach based on a time division multiple access scheme. The time difference between the forward and backward observations is less than 3 s. As a consequence, it is essential to convert the dual one-way measurements taken at different times to a common epoch. By synchronizing the dual one-way measurements to a common epoch, clock-free and geometry-free measurements can be derived through subtraction and addition of the synchronized dual one-way measurement, respectively. The former, known as the clcok-free measurement, is usually used in the AOD due to its properties of being unaffected by clock error and only including the geometric distance [27]. Herein, we present the ISL observation equation between satellite A and B after transformation to the common time without derivation as Equation (1) [9]:
where and denote the transformed measurements from satellite A to satellite B and from satellite B to satellite A at time , respectively. and are the forward and backward ISL measurements at the receiver time. and represent the correction values of the satellite distance and clock biases between the observed epoch and the target epoch . is the instantaneous distance between the two satellites. c is the speed of light. Moreover, and are the clock biases of satellite A and B at the same time . and are the hardware delay at the receiver and transmitter of satellite A, respectively. Analogously, and are the hardware delay at the receiver and transmitter of satellite B, respectively. It should be noted that the hardware delay mentioned here refers to the time-lag phenomenon caused by factors such as the characteristics of physical components or signal processing procedures during the transmission and processing of signals in hardware devices. and are the phase center offsets (PCO) of the receiving and transmitting antennas of satellite A and B, respectively. and represent the corresponding measurement errors. Subtracting two original expressions in the above equation yields a combined observation that only includes the geometric distance and is independent of clock offsets, usually used for orbit determination. Referring to the existing research [9], we express the transformed clock-free ISL observation equation at time as
where expresses the transformed clock-free ISL observation, and denotes the functional relationship between the observation and the parameters to be estimated. is the state parameter related to the orbit of satellite, while represents the perturbation parameter. and are the PCO and hardware delay of the ISL. denotes the noise of the transformed clock-free ISL observations.
The principle of SLR technology involves using the ground-based satellite laser ranging system to transmit laser pulses to a target observation satellite. After reflection by the target satellite, these pulses are received by the ground system. According to the round-trip time interval of the measured laser pulse between the ground station and the target satellite, combined with the speed of light c in vacuum, the distance between the station and the satellite can be calculated as
In fact, in SLR observation, there are various error terms in addition to the geometric distance between the satellite and the ground station. Taking into account various errors, the observation equation for SLR can be expressed in detail as follows [26]:
where signifies the actual geometric distance between the ground station and the satellite. is the eccentricity correction term of the station, adjusting for the ground station’s non-central position within the earth’s gravitational feild. The is the tidal displacement correction, which corrects for the deformation of the earth’s shape due to tidal forces exerted by other celestial bodies. In addition, and are the corrections addressing systematic biases in distance measurements and the synchronization errors related to the timing at the ground station, respectively. accounts for delays in the ground system’s signal transmission time, crucial for calibrating the time delay in sending and receiving laser pulses. and express the atmospheric refraction correction and the general relativity correction, respectively. is the satellite eccentricity correction, compensating for the satellite orbital deviations from a perfect circle. Finally, represents the systematic error and random noise of the ground station. Most of the errors can be corrected with the current model, which will be introduced in the following sections. Then, briefly, the SLR observation equation can be expressed as
where expresses the SLR observation, and expresses the functional relationship between the SLR observation and the parameters to be estimated. is the parameter related to the SLR station. denotes the noise of the SLR observations. The other parameters have the same meaning as those in Equation (2).
The precise orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites can be conducted by combining the ISL and SLR observation equations above. It should be noted that the parameters to be estimated in the combined ISL/SLR POD contain the state parameters and perturbation force parameters of the satellite, the state parameter of the SLR station, and some biases. To be specific, taking a satellite as an example, the state parameters of the satellite mean the initial 3D position and velocity parameters . The perturbation forces parameters of the satellite usually include nine parameters of the light pressure model. The biases mainly comprise the antenna phase center offsets and the hardware delay deviation of the ISL observations. It should be noted that there may be some biases with unclear characteristic in the SLR observation, which be ignored in this study and will explored in the future. All parameters to be estimated are written in the following form:
When expanding from a single satellite to multiple ones, observation equations can be formulated according to Equations (2) and (5), in conjunction with the parameters to be estimated listed in Equation (6). The observation equations in combined ISL/SLR POD can be expressed as
By linearizing the observation equations, the error equations can be obtained as
where and are the posteriori residual for the ISL and SLR observations, respectively. Correspondingly, and denote the a priori residual. is the symbol of partial derivation. The remaining parameters have the same meaning as before. Subsequently, by employing the least squares method to solve these error equations, the combined ISL/SLR POD for BDS-3 can be realized.
3. Data and Strategies
3.1. Data Collection
In this study, the ISL observations and publicly available SLR observation of the BDS-3 were collected. To validate the effectiveness and stability of the method proposed, we selected and processed one month’s data, within the day of year (DOY) from 036 to 064 in 2021. The details are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Explanation of the collected data.
For the ISL observations, there are four types of links for BDS-3 satellites: MEO-MEO, MEO-IGSO, IGSO-IGSO, and MEO-GEO. Specifically, for MEO satellites, due to the symmetrical nature of their walker constellation, the chain building relationship of each satellite within the constellation is the same. Each MEO satellite can continuously build a chain with four MEO satellites in the same orbit, four MEO satellites in different orbits, and intermittently build a chain with twelve MEO satellites in different orbits. Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of MEO satellite chain building.
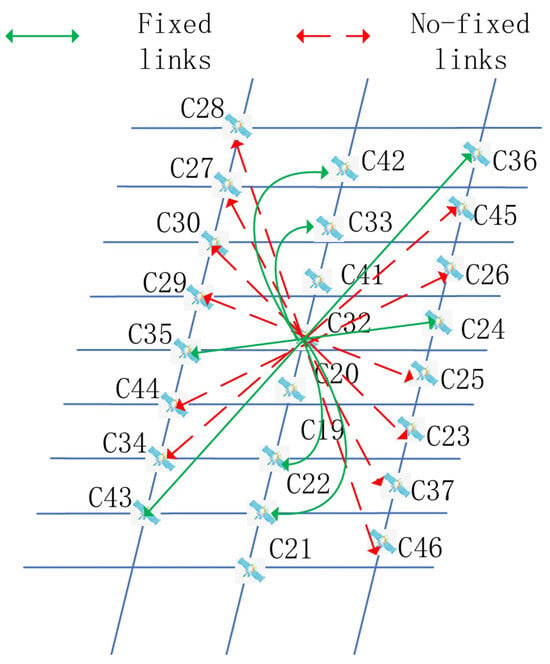
Figure 2.
Diagram of the chain building for MEO satellies.
For the SLR observations, throughout the experiment period, there were nine SLR ground stations in total capable of tracking BDS-3 satellites. The distribution of these nine SLR stations is shown in Figure 3.
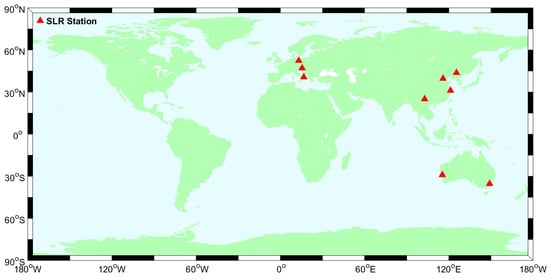
Figure 3.
Distribution of available SLR stations during the experimental period.
Furthermore, the SLR observations cannot be maintained continously at all times. As a result, the actual SLR stations involved in data processing vary from day to day, and the number of the SLR observations also differs accordingly. In order to better support the subsequent analysis, we present the tracking profile of BDS-3 satellites by each SLR station, taking three days as an example, as illustrated in Figure 4. In each subgraph, the horizontal axis indicates the identifier of the available SLR stations, whereas the vertical axis signifies the number of actual SLR observations within a specific DOY.
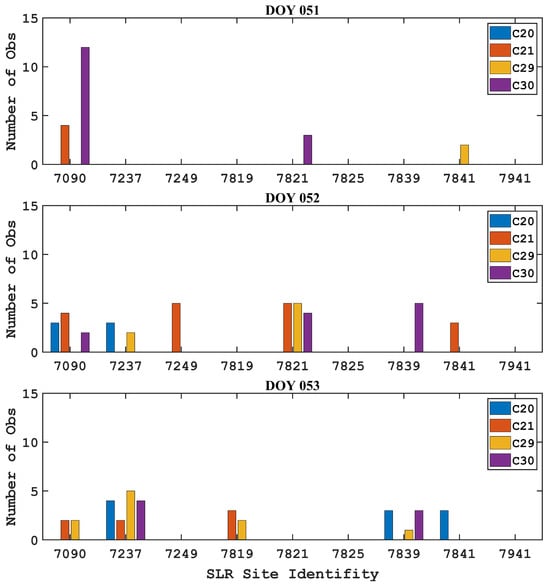
Figure 4.
Tracking of the BDS-3 satellite by SLR stations (DOY 051-053).
To be clear, Table 2 presents the detailed statistical results of the number of effective SLR stations per satellite and the total number of effective observations per station.

Table 2.
Status of valid SLR data.
It can be seen from Figure 4 and Table 2 that, on one hand, there is a limited quantity of SLR observations overall, and on the other hand, there is significant variation in the number of satellites tracked by different stations at different times, both from station to station and from one observation period to another. For instance, during DOY 052, there are six SLR stations available for tracking the BDS-3 satellites, with a total of 41 observations. Yet, there are merely three valid stations tracking BDS-3 satellites during DOY 53, with the total SLR observations reduced to nearly half, at 21. In addition, some stations did not track any satellites during a period, meaning there are no effective observations, such as stations 7237, 7249, and 7819 on DOY 051. This is likely to affect the accuracy of the determinated orbit. What is more, it should also be noted that the sparse SLR data may limit the scalability and robustness of the ISL and SLR combined approach. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the errors and their characteristics that may exist in SLR observations and adoption of reasonable models for processing are key factors affecting this method. The specific processing strategies are described in detail in the next section.
3.2. Processing Strategy
In our study, the Geodetic Spatio-Temporal data Analysis and Research (GSTAR) software independently developed by Beihang University was used for data processing [28]. More specifically, we opted for the post-processing mode when determining satellite orbits, with the arc length specified as 24 h. The a priori accuracy of ISL measurement was set to 0.3 m, whereas that of the SLR observations was set to 0.003 m. In addition, the errors of the observation and perturbing force were corrected with the universal models. It is crucial to note that, due to the influence of the hardware in the transmitting and receiving devices, both the ISL and SLR observations are subject to hardware delays. Consequently, it is imperative to solve these hardware delay together with the satellite orbits and dynamics parameters simultaneously [29,30]. For the hardware delay of the ISL, we estimate it as a constant in one arc. However, owing to the sparse SLR observation and the ambiguous characteristic of its hardware delay, we initially disregarded this aspect and plan to conduct an in-depth investigation in subsequent studies. The data and configuration, SLR error model, dynamic model, and strategies to estimate parameters are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
ISL/SLR POD data processing strategy.
3.3. Experimental Design
After introducing the data processing strategy, this section elaborates on the experimental design. In order to investigate the influence of the a priori orbit on the ISL/SLR combined orbit determination, as well as the impact of introducing the SLR into the ISL orbit determination, we designed four sets of experiments, as shown in Table 4. Specifically, the BDS-3 broadcast ephemeris and precise ephemeris generated by the Wuhan University Analysis Center, one of the International GNSS Service (IGS) analysis centers, are utilized as the prior orbits.

Table 4.
Description of the designed experiment.
4. Experiments and Analysis
Based on the data collection, processing strategy, and experimental design mentioned above, in this section, we describe the experiments and the series of analyses on the residual of the observations, orbital accuracy, and the constellation transform and rotation, in sequence.
4.1. Residual Analysis
The posteriori residuals of the observations refer to the discrepancies between the actual observations and the theoretical predictions, which is an effective means to assess the level of the data processing in orbit determination. Therefore, before analyzing the performation of the combined ISL/SLR orbit determination, it is essential to firstly analyze the observation residuals. Taking the results of DOY 053 with broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit as an example, Figure 5 and Figure 6 present the residual of the ISL and SLR observations, respectively. In Figure 5, the different colors express the residuals of different inter-satellite links, whereas Figure 6 denotes the ground station–satellite SLR observations.
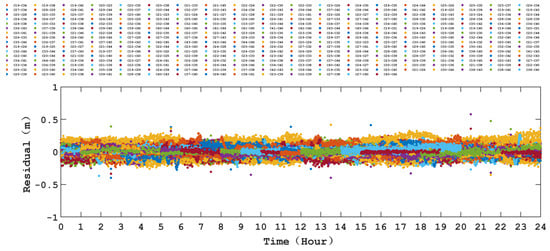
Figure 5.
Residuals of ISL observations.
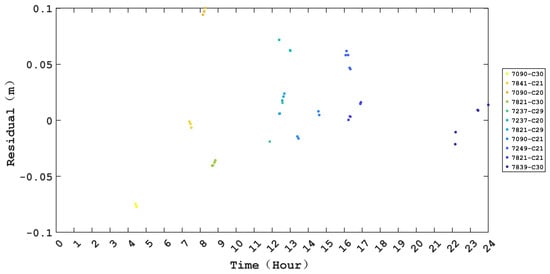
Figure 6.
Residuals of SLR observations.
From Figure 5, it is evident that the residuals of the ISL observations are almost distributed within ±0.20 m. Overall, the comprehensive statistical analysis reveals that the root mean square (RMS) of the residuals of ISL observations for all satellites is around 0.05 m, which aligns with the findings from existing studies [37]. Meanwhile, as depicted in Figure 6, the residuals of the SLR observations are generally within ±0.05 m, with very few outliers reaching 0.08 m. Overall, its RMS value is better than 0.03 m. Considering the insufficient number of SLR observations during the processing period, the statistical results are easily affected by the large residuals. Therefore, it is expected that an increase in the number of SLRs in the future may lower the RMS value. In addition, as mentioned above, the biases in the SLR observation ignored in this study may also affect the RMS of the residual. Despite all this, the current results of the residual statistics fully demonstrate that the data processing strategy used in this study is correct and effective.
4.2. Impact on the Orbital Accuracy
In this section, we analyze the impact of different experimental strategies on the orbit accuracy, including using different prior orbits and adopting different types of observations, as mentioned in Table 4. Specifically, the consistency among various days, the averaged RMS in each direction for every satellite, and the orbital accuracy for different types of satellites were analyzed in sequence. It should be noted that the precise ephemeris provided by the Wuhan University Analysis Center was chosen as the reference to assess the orbital accuracy for all experiments.
Firstly, from the perspective of the consistency among various days, we analyzed the performance of the determined orbit in all the experiments. Using a three-dimensional (3D) example, Figure 7 illustrates the orbital RMS among the various days for each satellite in each experiment. In each subgraph, the horizontal axis represents the satellite, and the vertical axis denotes the statistical value of the RMS in the 3D direction. Different colored dots represent different days.
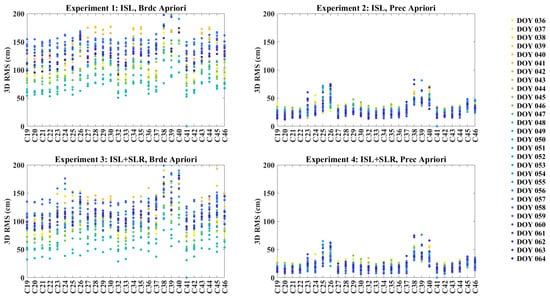
Figure 7.
Orbital 3D RMS of every satellite on multiple days.
Specifically, the top panel shows the results of using only ISL observations, while the bottom panel shows the results of introducing the SLR observation for orbit determination. The left column is based on the broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit, while the right details the precise ephemeris as the a priori orbit.
It can be observed from Figure 7 that, overall, there is good consistency among multiple days. In addition, on the one hand, by observing the left and the right columns of the graph, it can be seen that, compared to the results using broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit, the consistency among various days is more obvious when using the precise ephemeris as the a priori orbit. The 3D RMS of the orbit is approximately 100 cm and below 50 cm, respectively, signifying an enhancement in precision by nearly three times. This phenomenon may be related to the orbit accuracy and reference frames of the broadcast ephemeris and the precise ephemeris [38]. On the other hand, by comparing the upper and lower subgraphs, it can be seen that the introduction of SLR observation to ISL for combined orbit determination improved the overall orbit accuracy. In addition, it is interesting that in Experiments 2 and 4, shown in Figure 7, that, except for the IGSO satellite, the orbital accuracies of the satellite C25 and C26 are slightly lower than those of other satellites. We preliminarily think that this phenomenon is related to the on-orbit characteristics of the antenna phase center deviation of the ISL, which was described in our previous study [29].
Then, to further explore the impact of the a priori orbit and the involved observations on the orbital accuracy in various directions, we counted the RMS value of each satellite in three directions by averaging the values from multiple days. Figure 8 illustrates the statistical RMS for each satellite in along, cross, radial, and 3D directions, respectively.
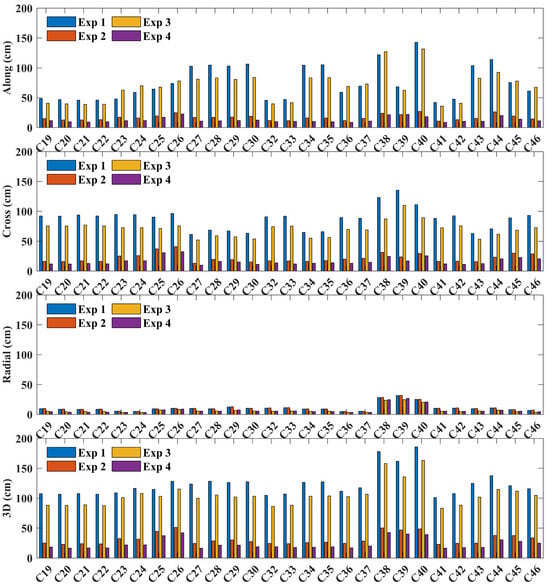
Figure 8.
Average orbital accuracy for all satellites in four experiments.
Similarly, the horizontal axis represents the satellite, while the vertical axis denotes the RMS of the orbit in each direction. The subfigures from top to bottom depict the RMS of the orbit in the along, cross, radial, and 3D directions, respectively. Different colored bars represent different experiments. The blue bars indicates Experiment 1, which only utilizes ISL observations with broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit. The red ones represents Experiment 2, which also only utilizes ISL observations but with precise ephemeris as the a priori orbit. The yellow and purple bars express the results of Experiment 3 and Experiment 4, respectively. Both of these two experiments introduced the SLR observation for ISL/SLR combined orbit determination, but with different a priori orbits.
It can be seen from Figure 8 that, in terms of the orbital accuracy, for almost all satellites and all directions, the orbit accuracy is highest in Experiment 4, followed by Experiment 3, then Experiment 2, and lowest in Experiment 1. For different directions, on the one hand, the orbit accuracy in the radial is the highest for all experiments, followed by the cross, and the ones in along are the lowest. On the other hand, in the radial direction, the difference in orbit accuracy among the four experiments is small. While, in the cross and along directions, the orbit accuracy of experiments 1 and 3 is close, the orbit accuracy of experiments 2 and 4 is also close, but there is a large discrepancy between these two sets. Overall, from the 3D RMS, it can be seen that the orbital accuracy of experiments 1 and 3 is close to 100 cm, with the latter being better than the former, while experiments 2 and 4 have better than 50 cm, with the latter better than the former similarly. That is to say, using the precise ephemeris as the a priori constraint can significantly improve the accuracy of the orbit determination. In addition, for the ISL-only-based autonomous orbit determination, introducing SLR observations can also enhance the accuracy of the orbit, and there are no complex parameters like ambiguities in GNSS to deal with. Thus, this is a very meaningful conclusion for some geoscience research, such as inversion of geocenter motion with post-processing [39,40,41].
Finally, noting the significant differences in accuracy among different types of satellites, we compiled the orbital accuracy of different types of satellites, as well as the improvement situation between different experiments. The averaged RMS for the MEO and IGSO satellites are displayed in Figure 9. In each subgraph, the horizontal axis represents the orbital directions, e.g., along, cross, radial, and 3D, and the vertial axis denotes the RMS values. As before, different colored bars correspond to different experiments. The left subgraph is for the MEO satellites, while the right one is for the IGSO satellites.
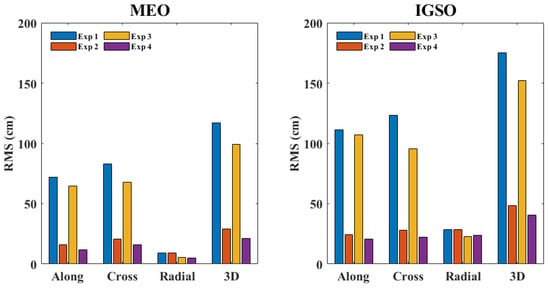
Figure 9.
Average orbital accuracy for MEO and IGSO satellites.
We can see from Figure 9 that the MEO satellite has better accuracy than the IGSO satellite in all directions, which is consistent with the previous Figure 7 and Figure 8. Meanwhile, for the sake of intuition, we display the detailed orbital accuracy values in Table 5. Additionally, we also notice that, for the MEO satellite, the orbital accuracy in the radial direction is significantly better than that in the along and cross directions, while for the IGSO satellite, similar phenomena are observed in Experiments 1 and 3, whereas in Experiments 2 and 4, the orbital accuracy in all three directions is relatively close. This may be related to the dynamics model of IGSO satellites and the number of ISL/SLR observations.

Table 5.
Orbital accuracy for two types of satellites (cm).
Moreover, the improvement proportions of the orbital accuracy between typical experiments were also calculated, as shown in Table 6. In other words, to evaluate the influence of the a priori values and the observations adopted on the orbital accuracy, we calculated the improvement proportion for four typical combinations: Experiments 1 and 2 (namely Exp1-Exp2), Experiments 3 and 4 (namely Exp3-Exp4), as well as Experiments 1 and 3 (namely Exp1-Exp3) and Experiments 2 and 4 (namely Exp2-Exp4).

Table 6.
Improvement proportion of the 3D orbital accuracy.
As shown in Table 6, the improvement ratios of the first two sets (Exp1-Exp2, Exp3-Exp4) indicate that the orbital accuracy can be improved by approximately 75% when using precise ephemeris compared to using broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit. The results of the last two sets show that when SLR observations are incorporated into the ISL for combined orbit determination, the orbital accuracy can be enhanced by between 13% and 26%, with the MEO satellites showing a higher improvement ratio than the IGSO satellites. It should be noted that this conclusion is drawn under the condition of ignoring the influence of hardware delay errors in SLR observations. Some scholars have recently pointed out that when the hardware delay errors in SLR observations are estimated as constants or satellite–station pair-related errors, the accuracy of the satellite orbits and Earth parameters can be further improved by about 30% [42]. Similarly, if the hardware delay errors in SLR observations can be accurately processed in the future, the accuracy improvement of the SLR-aided autonomous orbit determination will be better than the existing conclusions.
4.3. Impact on the Constellation Rotation and Translations
It is well-known that, when using ISL observations for autonomous orbit determination, there are overall constellation rotation and translation. Existing research has shown that the overall rotation and translation of the constellation can be controlled and improved by using ground anchor stations and rotation parameters [43,44,45]. Usually, Helmert transformation parameters can be employed to explain any systematic discrepancies between two sets of positions in separate terrestrial reference frames. In other words, by performing a Helmert transformation on two sets of ephemeris products, seven parameters can be estimated, including three translations (TX, TY, TZ), three rotations (RX, RY, RZ), and one scale parameter (Sc). These seven parameters effectively reveal the overall translation and rotation between two ephemeris products. In this section, we focus on analyzing the impact of a priori values on the constellation rotation and translation in combined ISL/SLR orbit determination.
Since the impact of adding SLR on the translation and rotation in ISL-only-based orbit determination has already been well-established [44,45], in this section, we estimated the seven parameters for Experiments 3 and 4, to examine the impact of the a priori orbit on the constellation’s translation and rotation during the combined ISL/SLR orbit determination. Taking the DOY 053 as an example, we analyzed the magnitude of these seven parameters, along with an evaluation of the orbital accuracy before and after the Helmert transformation. The two sets of the seven parameters achieved are listed in Table 7. The precision ephemeris and the broadcast ephemeris have been abbreviated to prec and brdc, respectively.

Table 7.
Helmert transformation parameters.
Upon comparison, it becomes evident that the magnitudes of the estimated seven parameters are larger when the broadcast ephemeris is used as the a priori orbit, compared to the ones where the precise ehpemeris is employed. Moreover, the discrepancies between the two experiments indicate that, for the translation parameters, the difference in the TX direction is most pronounced, at about 20 mm, followed by approximately 10 mm in the TY direction, while the smallest difference occurs in the TZ direction, not exceeding 5 mm. For the rotation parameters, the differences between the two experiments are considerable in all three directions. In detail, there is a nearly ninefold difference in the RX direction, with values of 0.31 mas and 2.74 mas, respectively, and about four times in both the RY and RZ directions. These results may suggest that there are still translation and rotations for the BDS-3 in the combined ISL/SLR orbit determination with the broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit. Then, we conducted a detailed analysis of the orbital accuracy before and after the Helmert transformation. Figure 10 illustrates the results for DOY 053.
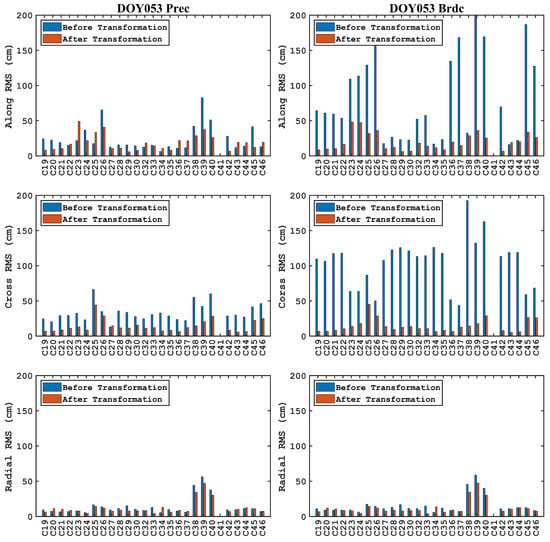
Figure 10.
RMS before and after Helmert transformation of ISL/SLR orbit determination using broadcast ephemeris (right) and precision ephemeris (left) as a priori orbits.
In Figure 10, the left and right columns represent the outcomes using the precise ephemeris and broadcast ephemeris, respectively. The blue bars represent the orbital accuracy before Helmert transformation, while the red bars represent the accuracy after Helmert transformation. The subplots from top to the bottom correspond to the RMS in the along, cross, and radial directions, respectively. It can be seen that, after the Helmert transformation, the orbital accuracy using the broadcast ephemeris as the a priori orbit has improved in all three directions, almost the same as the ones with precision ephemeris. However, the degree of the improvement varies among different directions. To provide a more intuitive demonstration, Table 8 shows the average RMS of the MEO and IGSO satellites in the three directions.

Table 8.
Average RMS in all directions of the orbit of the BDS-3 satellite (cm).
From Table 8, we can see that after Helmert transformation, the RMS of the IGSO satellites is better than 20 cm in three directions. For the MEO satellites, the RMS is better than 15 cm, 10 cm, and 5 cm in the along, cross, and radial directions, respectively. In addition, the difference of the orbit accuracy between different a priori orbits is significantly reduced after the Helmert transformations.
5. Conclusions
Beidou-3 innovatively achieves autonomous navigation through inter-satellite links. However, current issues still exist, such as the overall constellation rotation and the limitation of orbital accuracy by prior constraints. In recent years, SLR observations have been gradually made public. Thanks to their significant advantages of high precision and no ambiguous parameters, they can be introduced into autonomous navigation for joint orbit determination, providing new ideas for solving existing problems. This paper focuses on analyzing the impacts of different prior orbital constraints and different observation data on the orbit determination accuracy and the constellation translation. Firstly, a mathematical model for orbit determination by combining ISL after introducing SLR is derived. Subsequently, experiments are carried out and evaluated using one month of actual ISL and SLR observation data. The results show the following:
- (1)
- There is good consistency across different days. Compared with using broadcast ephemeris as prior constraints, using precise ephemeris as prior constraints shows better consistency;
- (2)
- The accuracy of prior orbits affects the performance of the orbit determination. Compared with using broadcast ephemeris as prior constraints, using precise ephemeris as prior constraints can improve the orbital accuracy by approximately 75%;
- (3)
- The type of observation data affects the performance of orbit determination. Introducing SLR observations for joint orbit determination with ISL can improve the orbital accuracy by 13% to 26%. In addition, the improvement range for MEO satellites is larger than that for IGSO satellites;
- (4)
- Regardless of whether broadcast ephemeris or precise ephemeris is used as prior constraints, constellation translation and rotation still exist, and the results of the former are more obvious. Among the seven estimated parameters, for translation parameters, TX is the largest, followed by TY, and TZ is the smallest; for rotation parameters (such as RX, RY, and RZ), all show relatively large values, which may be related to the limited number of available satellite laser ranging stations during this period;
- (5)
- After considering constellation translation and rotation, the orbital accuracy under different prior constraints remains at the same level. The RMS shows that the orbital accuracy of the IGSO satellites in three directions is better than 20 cm, while the accuracy of the MEO satellites in along-track, cross-track, and radial directions is better than 10 cm, 8 cm, and 5 cm, respectively.
Author Contributions
W.X. conceived the idea and designed the experiments with Z.L.; Z.W., S.G. and L.F. organized and analyzed the data; Y.C. checked the data. All authors participated in writing and revising this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U20A0193.
Data Availability Statement
Data related to this article are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, Z. Performance analysis and progress of inter-satellite-link of Beidou system. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Cai, H.; Meng, Y.; Geng, C.; Jia, X.; Mao, Y.; Geng, T.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X. BDS-3 RNSS technical characteristics and service performance. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 810–821. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, C. Globalization highlight: Orbit determination using BeiDou inter-satellite ranging measurements. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Cai, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y. Precise orbit determination for BDS-3 satellites using satellite-ground and inter-satellite link observations. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Evaluation of BDS-3 Orbit Determination Strategies Using Ground-Tracking and Inter-Satellite Link Observation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shang, L.; Lic, G. The research on system error of Inter-Satellite-Link (ISL) measurements for autonomous navigation of Beidou system. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, T. Orbit Determination of the Next-Generation Beidou Satellites with Intersatellite Link Measurements and a Priori Orbit Constraints. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Hu, G.; Li, X.; et al. Initial results of centralized autonomous orbit determination of the new-generation BDS satellites with inter-satellite link measurements. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, J. Orbit and clock analysis of BDS-3 satellites using inter-satellite link observations. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Precise orbit determination for BDS satellites. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, W.; Xi, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, X. Improving integrated precise orbit determination of GPS, GLONASS, BDS and Galileo through integer ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, P.A.; Michalak, G.; Knig, R. Precise orbit determination of low Earth orbiters using carrier phase cycle slip fixing over long data gaps—An alternative to GNSS phase bias products based ambiguity resolution. In Proceedings of the 43rd COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Sydney, Australia, 28 January–4 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.; Zhao, Q. Determining orbit of COMPASS-M1 Using International laser ranging data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Han Univ. 2009, 34, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Sun, B.; Yang, X.; Cao, F.; He, Z.; Yang, H. Precision analysis of BeiDou broadcast ephemeris by using SLR data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Han Univ. 2017, 42, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; He, B. Satellite laser ranging station classification for GNSS satellite orbit accuracy validation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Validation of BeiDou precision orbit products using satellite laser ranging measurements. Geomat. Technol. Equip. 2022, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Jiao, W. GLONASS orbit determination by using SLR data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2003, 28, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Jia, X.; Yang, Z. Determination of Navigation Satellite Clock Bias Using SLR and GPS dual frequency phase-smoothed pseudo-range data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 33, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Jia, X.; Qin, X. Validating clock bias of satellite using SLR and pseudorange data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2007, 32, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Jiao, W.; Chen, L.; Huo, L. Evaluation of CHAMP satellite orbit with SLR measurements. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2005, 30, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Peng, H.; Wu, B. The precise orbit determination for HY2A satellite using GPS, DORIS and SLR data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2015, 40, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, E.; Wang, L.; Jin, S.; Liu, J. Estimation of ERP with combined observations of GNSS and SLR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2014, 39, 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Research on Earth Rotation Parameters of GNSS/VLBI/SLR Mutli-Source Data Fusion Epoch Reference Frame. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Technology University, Qingdao, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Precise Orbit Determination and Geodetic Parameter Calculation by Combining GNSS and SLR Data from Multiple Satellites. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; He, B.; Hu, X. Precise orbit determination using satellite laser ranging and inter-satellite link observations for BDS-3 satellites. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, R.; Jia, X.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Huyan, Z.; Li, J.; Wei, Z. Orbit determination and time synchronization for BDS-3 satellites with raw inter-satellite link ranging observations. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Guo, S.W.; Fan, L.; Gu, S.; Fang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Li, W.; et al. GSTAR: An innovative software platform for processing space geodetic data at the observation level. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Lin, H.; Fan, L.; Ye, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F. Research on in-orbit characteristics of inter-satellite links phase center offsets based on whole-network estimation. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 45, 4060–4071. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, W.; Fan, L.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F. Impact of ambiguity resolution on phase center offsets and hardware delay estimation for BDS-3 inter-satellite links. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1154159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P.; Lutz, S. Impact of earth radiation pressure on GPS position estimates. J. Geod. 2011, 86, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schär, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. Code’s new solar radiation pressure model for GNSS orbit determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizouard, C.; Lambert, S.; Gattano, C.; Becker, O.; Richard, J.Y. The IERS EOP 14C04 solution for earth orientation parameters consistent with Itrf 2014. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. The Impact of Attitude, Solar Radiation and Function Model on Precise Orbit Determination for GNSS Satellites. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rebischung, P.; Schmid, R. Igs14/Igs14.Atx: A new framework for the LGS products. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions (2010); IERS Technical Note, No. 36; International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service Central Bureau: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Sun, L. In-orbit performance assessment of BeiDou intersatellite link ranging. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Cai, H.; Meng, Y. Assessment of BDS-3 terrestrial reference frame realized by broadcast ephemeris: Comparison with GPS/Galileo. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.P.; Tsai, Y.H.; Hsieh, P.J. Characterization of Galileo yaw attitude on tidal loading and range bias in SLR-based orbit validation. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindorfer, M.A.; Koidl, F.; Kirchner, G.; Wang, P.; Dilssner, F.; Schoenemann, E.; Strangfeld, A.; Gonzalez, F. Satellite laser ranging to Galileo satellites: Symmetry conditions and improved normal point formation strategies. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K. Determination of global geodetic parameters using satellite laser ranging to Galileo, GLONASS, and BeiDou satellites. Satell. Navig. 2024, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fan, L.; Shi, C. Impact of different range bias corrections on orbit and Earth rotation parameters determination using BDS-3 satellite laser ranging observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 016325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, T. Constellation rotation error analysis and control in long-term autonomous orbit determination for navigation satellite. J. Astronaut. 2008, 29, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.T. Eliminating constellation rotation error of autonomous orbit determination using differential anchor stations. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2013, 38, 920–924. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, F.; Liu, W.; Fang, R. Analysis and control method for constellation rotation in navigation satellite autonomous orbit determination. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2009, 34, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).