Prediction of Atmospheric Duct Conditions from a Clutter Power Spectrum Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
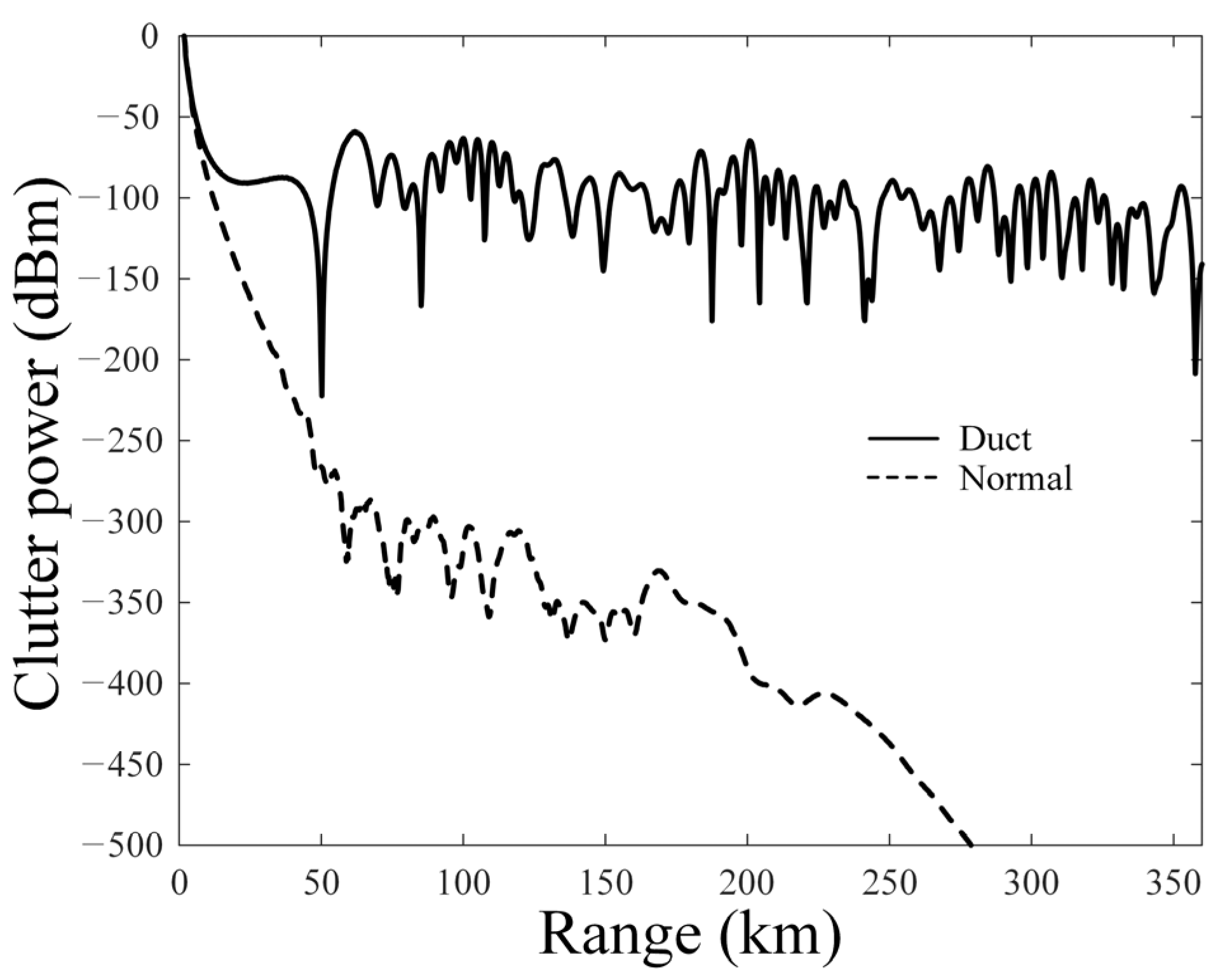
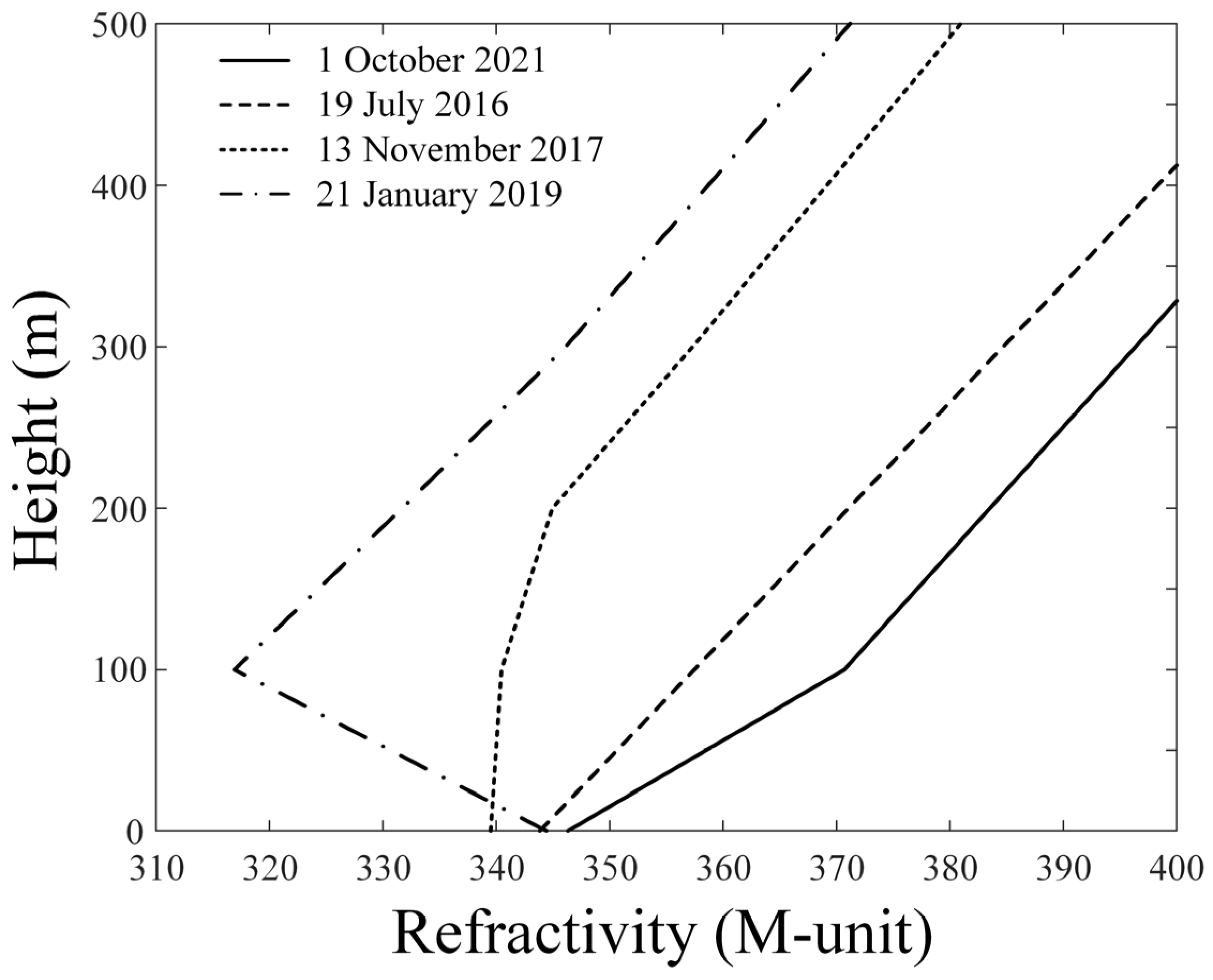
2. Calculation of Clutter Power Spectrums
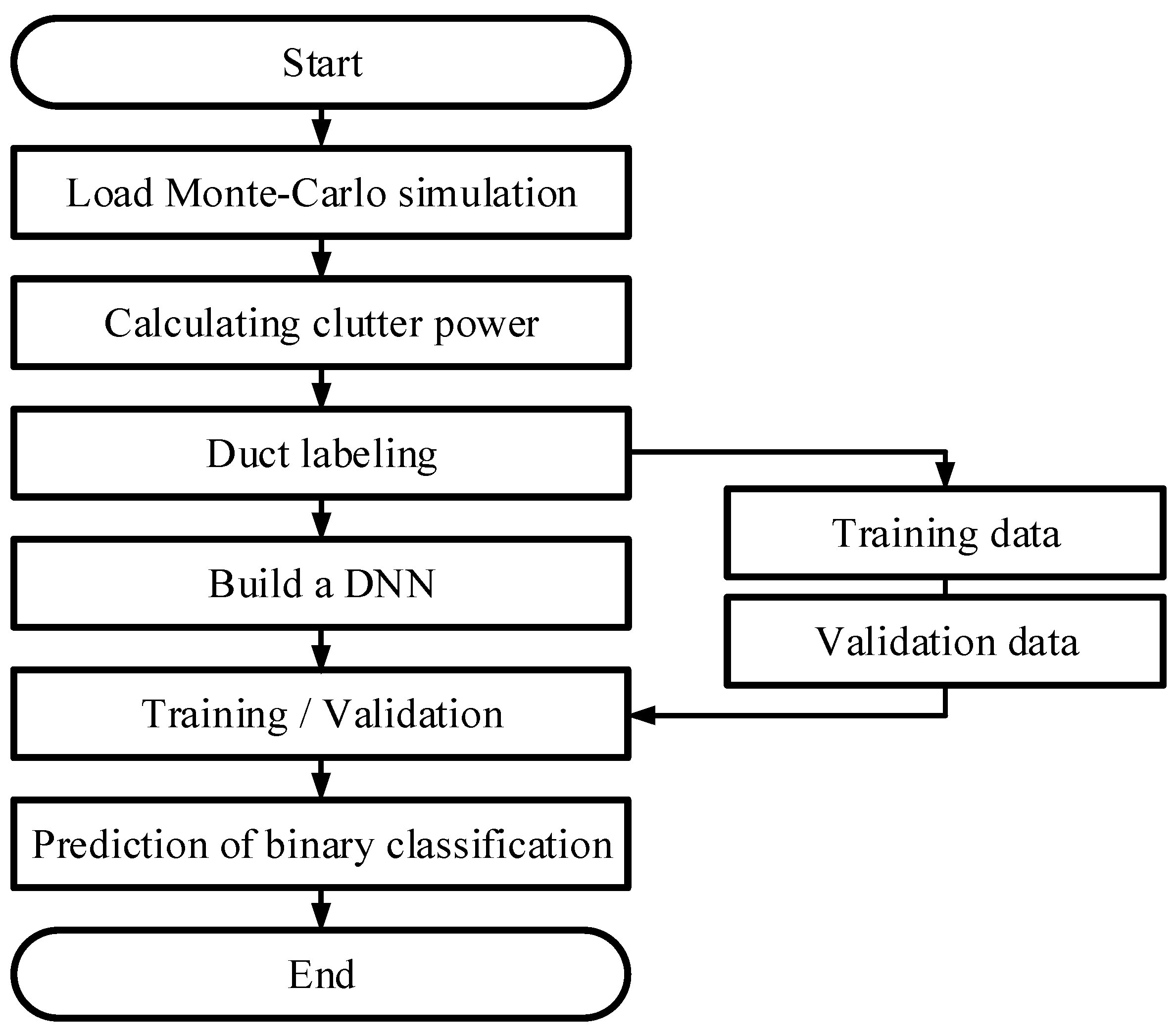
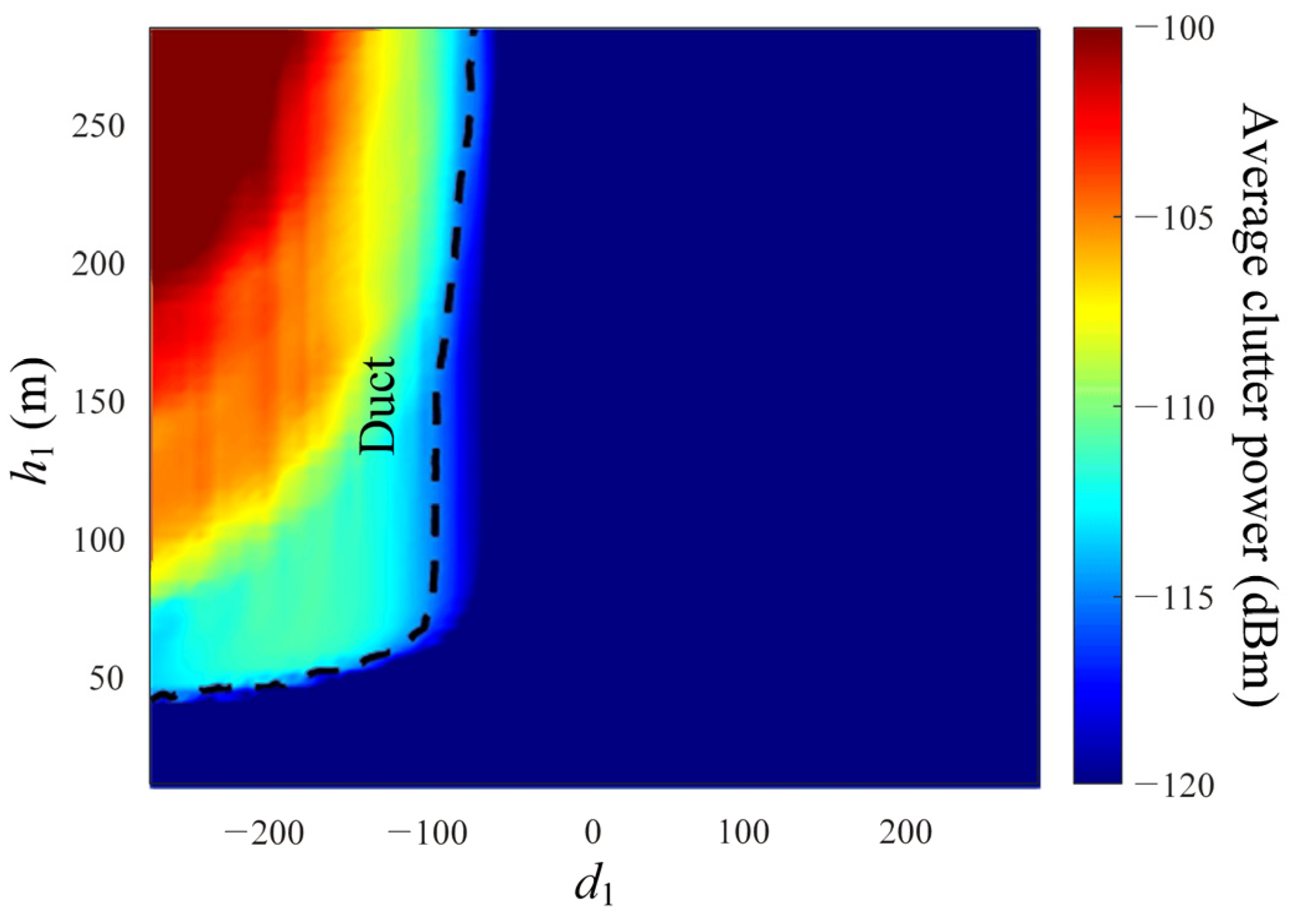
3. Estimation of an Atmospheric Refractivity Using Deep Learning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raja Abdullah, R.S.A.; Salah, A.A.; Ismail, A.; Hashim, F.H.; Rashid, N.E.A.; Aziz, N.H.A. Experimental investigation on target detection and tracking in passive radar using long-term evolution signal. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locker, C.; Vaupel, T.; Eibert, T.F. Radiation efficient unidirectional low-profile slot antenna elements for X-band application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 2765–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastkhosh, A.R.; Oskouei, H.D.; Khademevatan, G. Compact low weight high gain broadband antenna by polarization-rotation technique for X-band radar. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 743046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, R.; Su, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Suo, J.; Snoussi, H. Multiple kernelized correlation filters (MKCF) for extended object tracking using X-band marine radar data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 3676–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Krishnamurthy, V. Signal interpretation of multifunction radars: Modeling and statistical signal processing with Stochastic Context Free Grammar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jang, D.; Kim, Y.; Choo, H. Design of S/X-Band dual-loop shared-aperture 2 × 2 array antenna. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2022, 22, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.H.; Go, M.; Seo, C.; Choo, H. Analysis of the target detection performance of Air-to-Air airborne radar using long-range propagation simulation in abnormal atmospheric conditions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Choo, H. Prediction of target detection probability based on air-to-air long-range scenarios in anomalous atmospheric environments. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, L. Photonic-radar based multiple-target tracking under complex traffic-environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 225845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.-H. Theoretical minimum detection range for a rapidly moving target and an experimental evaluation. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2021, 21, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.P.; Dockery, G.D. Influence of evaporation ducts on radar sea return. IEE Proc. F (Radar Signal Process.) 1990, 137, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.F.; Liu, C.G.; Wang, H.G.; Zhu, Q.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, Q.N. Experimental analysis of atmospheric ducts and navigation radar over-the-horizon detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Wang, J.R. Atmospheric correction of AMSR-E brightness temperatures for dry snow cover mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Racette, P.; Triesky, M.E.; Browell, E.V.; Ismail, S.; Chang, L.A. Profiling of atmospheric water vapor with MIR and LASE. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2002, 40, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkemeier, W.P.; Duvosin, P.F.; Fontaine, A.B.; Thomson, D.W. Indirect atmospheric measurements utilizing rake tropospheric scatter techniques—Part II: Radiometeorological interpretation of rake channel-sounding observations. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvenot, R.; Fabbro, V. On the knowledge of radar coverage at sea using real time refractivity from clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 4, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvenot, R.; Fabbro, V.; Gerstoft, P.; Bourlier, C.; Saillard, J. Real time refractivity from clutter using a best fit approach improved with physical information. Radio Sci. 2010, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Tracking refractivity from clutter using Kalman and Particle filters. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Estimation of radio refractivity from radar clutter using Bayesian Monte Carlo analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.B.; Choo, H. Study of an Atmospheric Refractivity Estimation from a Clutter Using Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Z.S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.G. Retrieving evaporation duct heights from radar sea clutter using particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Progress Electromagn. Res. M 2009, 9, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-X.; Zhao, X.-F.; Sheng, Z. Refractivity estimation from radar sea clutter. Chin. Phys. B 2009, 18, 5084–5090. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Yin, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Joint inversion of evaporation duct based on radar sea clutter and target echo using deep learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, J. Deep learning for solving inversion problem of atmospheric refractivity estimation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Cha, H.; Wei, M.; Tian, B.; Ren, X. An atmospheric refractivity inversion method based on deep learning. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.Y.; Zhang, Y. Deep Learning Method for Evaporation Duct Inversion Based on GPS Signal. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Refractive Prediction System (AREPS); Ver. 3.6; The Space and Naval Warfare System: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005.
- ITU. The Radio Refractive Index: Its Formula and Refractivity Data. ITU-R P.453. 2019. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-P.453/en (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Liu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.Y. Atmospheric ducting effect in wireless communications: Challenges and opportunities. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2021, 6, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, J. The investigation of cooperation diversity for communication exploiting evaporation ducts in the south China Sea. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 8337–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, T.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H. Statistical modeling of evaporation duct channel for maritime broadband communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 10228–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, C. Long-range microwave links guided by evaporation ducts. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 60, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.H.; Wang, S.; Chong, Y.J.; Park, Y.B.; Ko, J.; Choo, H. High altitude ducts causing abnormal wave propagation in coastal area of Korea. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Fan, H.; Guo, L. A Random Forest Algorithm Combined with Bayesian Optimization for Atmospheric Duct Estimation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, F.H.; Sole, R.L.; Bedford, B.L.; Franc, D.; Pawlowitz, T. Effects of RF Interference on Radar Receiver; Institute for Telecommunication Sciences: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Compaleo, J.; Yardim, C.; Xu, L. Refractivity-from-clutter capable, software-defined, coherent-on-receive marine radar. Radio Sci. 2021, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, F.E.; Reilly, J.P.; Cohen, M. Radar Design Principles, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, E.; Shams, M.Y.; Hikal, N.A.; Elmougy, S. The effect of choosing optimizer algorithms to improve computer vision tasks: A comparative study. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 16591–16633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamin, A.; Humeau-Heurtier, A. (Multiscale) cross-entropy methods: A review. Entropy 2019, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.N.; Chung, K.S.; Feng, Y.C.; Lin, P.L.; Tsai, B.A. Assimilation of Radar-Derived Refractivity and Radar Data in the Context of Ensemble Kalman Filter: Cases Study of the Southwest Monsoon Experiment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 149, 1365–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiles, S.M.; Painter, T.; Okin, G.S. A method to retrieve the spectral complex refractive index and single scattering optical properties of dust deposited in mountain snow. J. Glaciol. 2017, 6, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hyperparameter | Number of Neurons | Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epochs | 30 | Layer 1 | 128 | Activation | ReLU |
| Minibatch size | 128 | Layer 2 | 64 | Last classification | Softmax |
| Learning rate | 0.01 | Layer 3 | 32 | ||
| Optimizer | Adam | Layer 4 | 8 | loss | Cross-entropy |
| Total Number of Data Items | Validation Accuracy | Prediction Accuracy with the Heuksando Data |
|---|---|---|
| 2800 | 94.35% | 98.31% |
| 5600 | 95.99% | 98.36% |
| 8400 | 96.63% | 98.53% |
| 11,200 | 97.43% | 98.43% |
| 14,000 | 97.77% | 98.84% |
| 28,000 | 98.20% | 99.06% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, T.; Cho, J.; Jang, D.; Choo, H. Prediction of Atmospheric Duct Conditions from a Clutter Power Spectrum Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16040674
Jin T, Cho J, Jang D, Choo H. Prediction of Atmospheric Duct Conditions from a Clutter Power Spectrum Using Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(4):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16040674
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Taekyeong, Jeongmin Cho, Doyoung Jang, and Hosung Choo. 2024. "Prediction of Atmospheric Duct Conditions from a Clutter Power Spectrum Using Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 16, no. 4: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16040674
APA StyleJin, T., Cho, J., Jang, D., & Choo, H. (2024). Prediction of Atmospheric Duct Conditions from a Clutter Power Spectrum Using Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 16(4), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16040674







