Quantitative Genetic Aspects of Accuracy of Tree Biomass Measurement Using LiDAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Hand-Measured Record of DBH
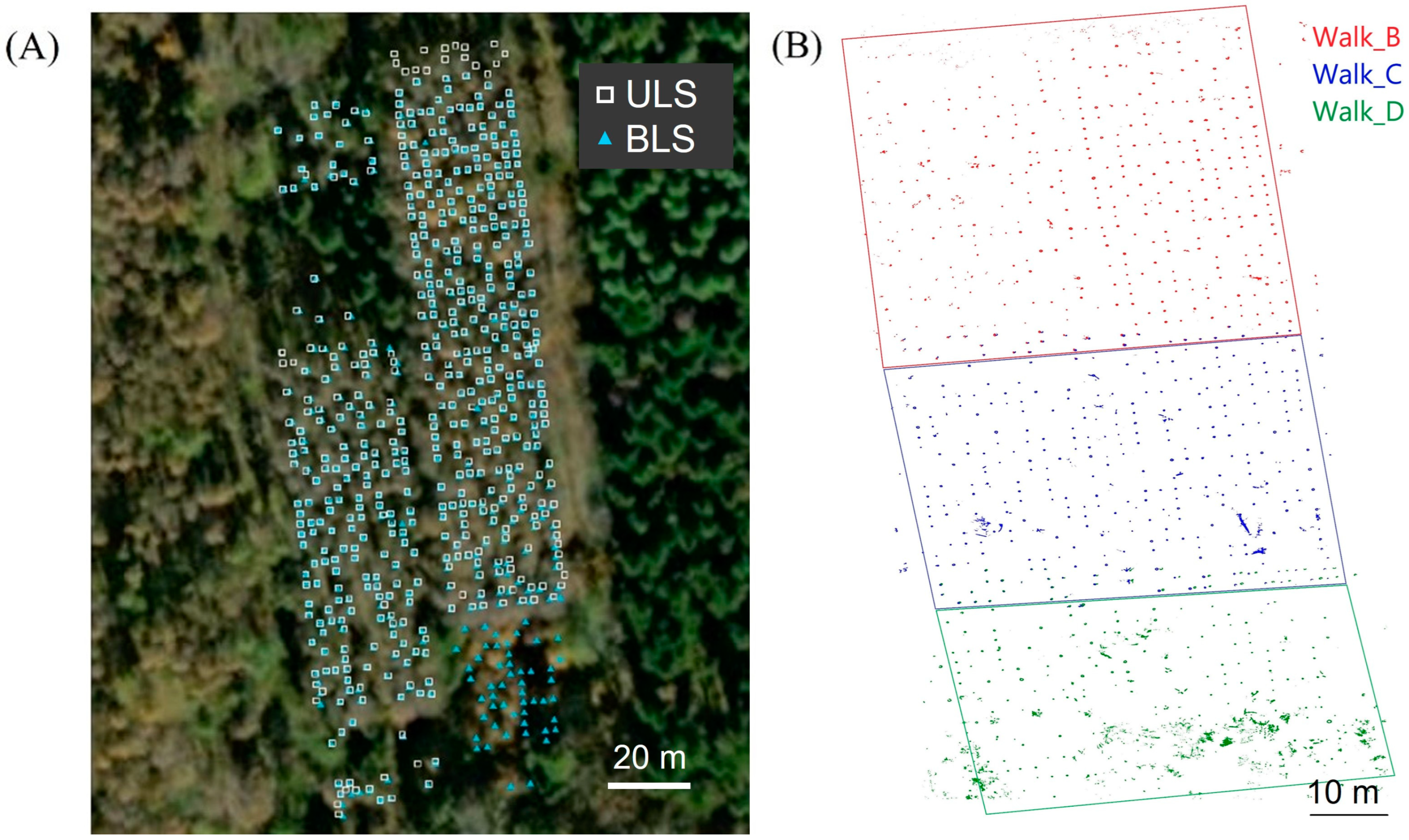
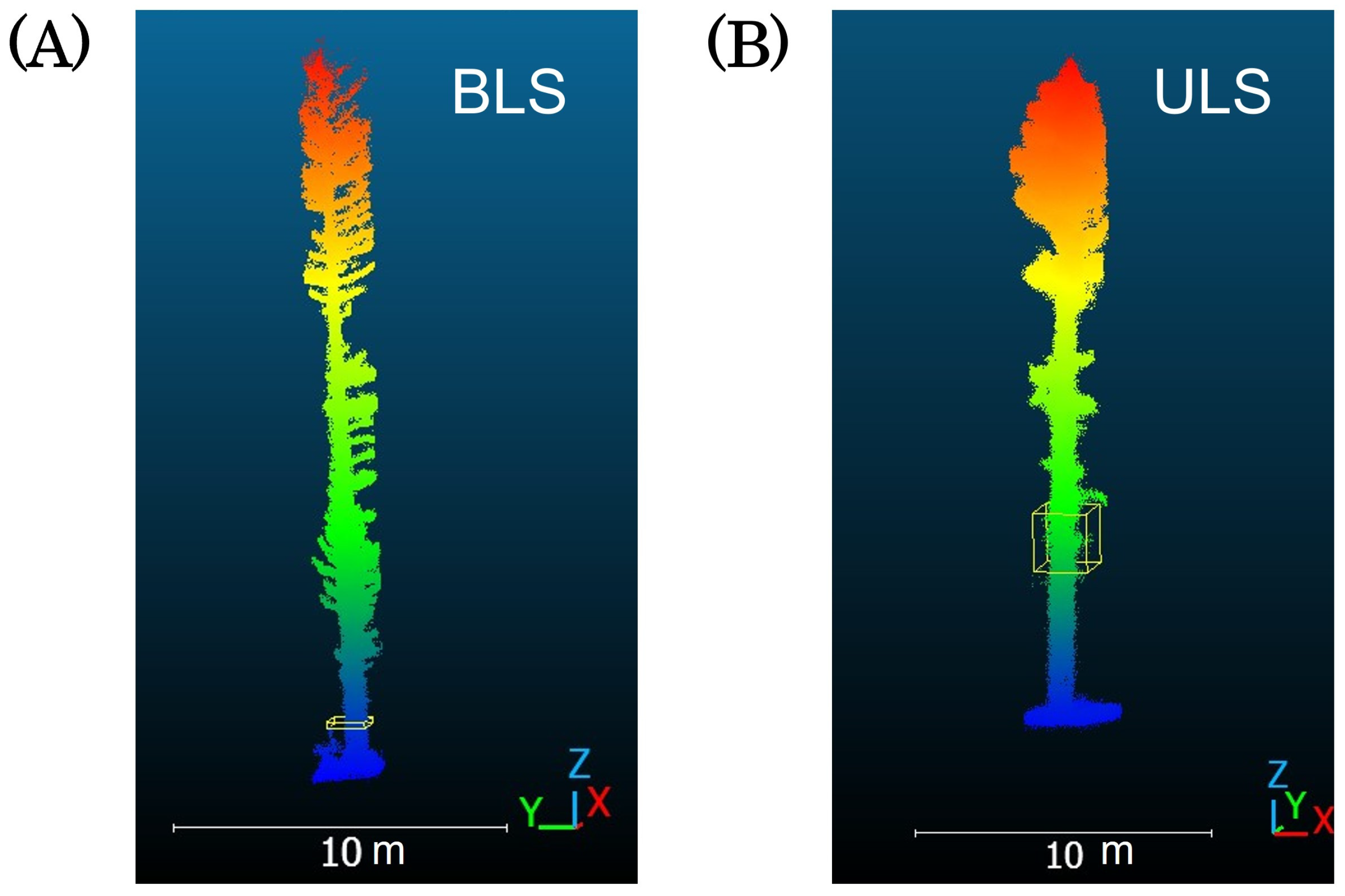
2.3. Point Cloud Data Acquisition
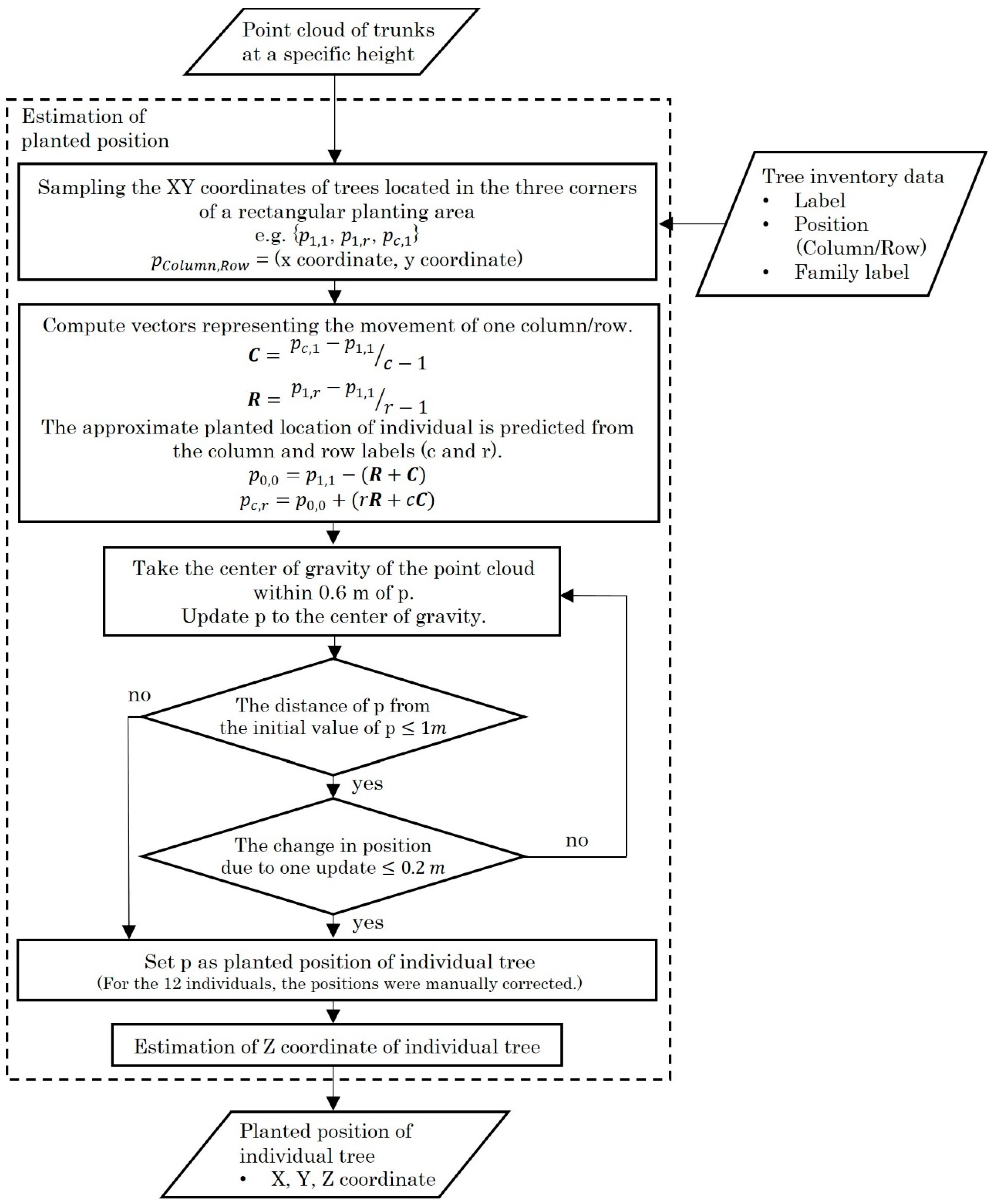
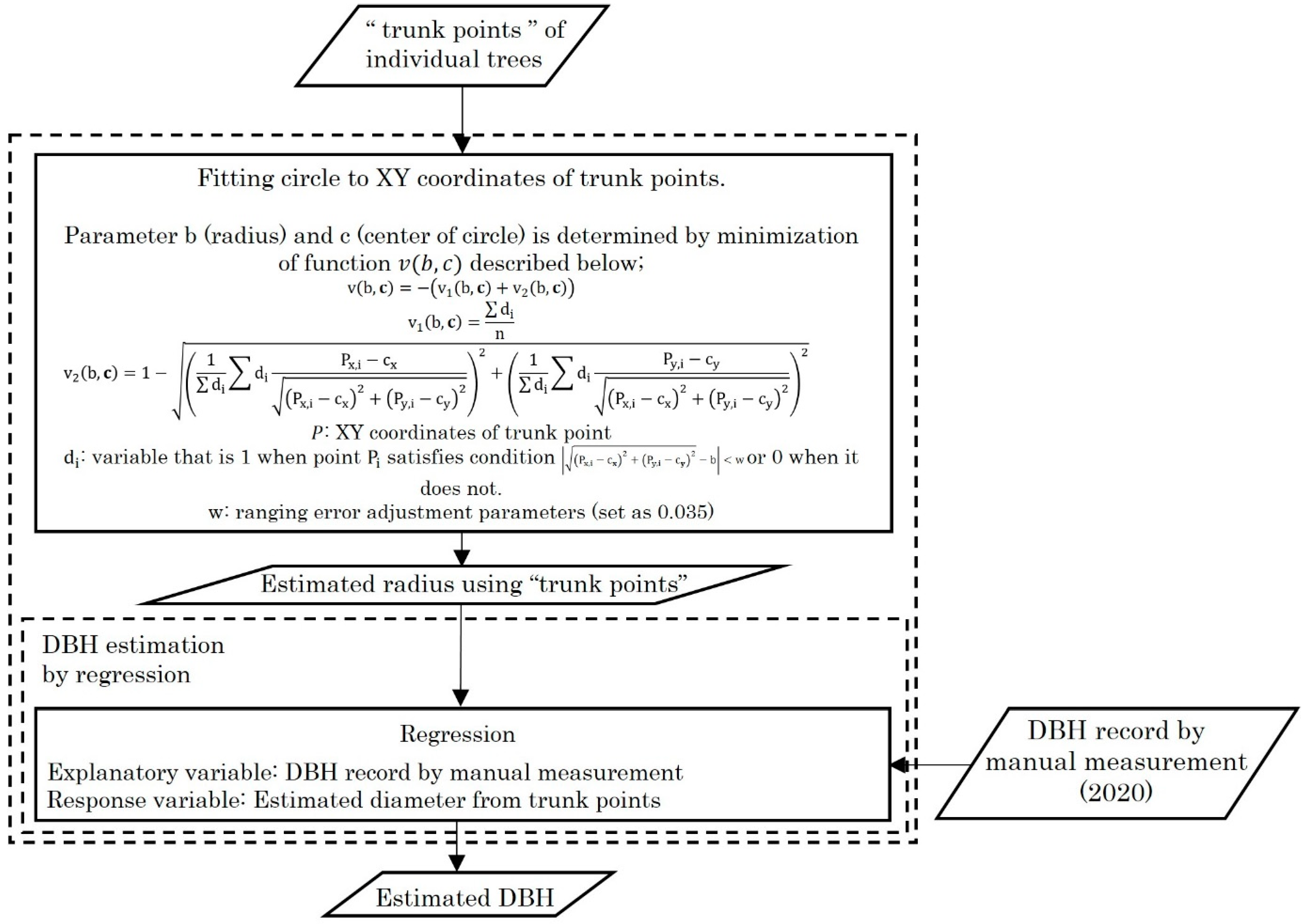
2.4. Analysis Flow of Point Cloud Data
2.5. Genotyping of Genome-Wide High-Density Markers
2.6. Estimation of Heritability
2.7. Genetic Correlation and Timber Volume Selection Accuracy
3. Results
3.1. Tree Location Estimations
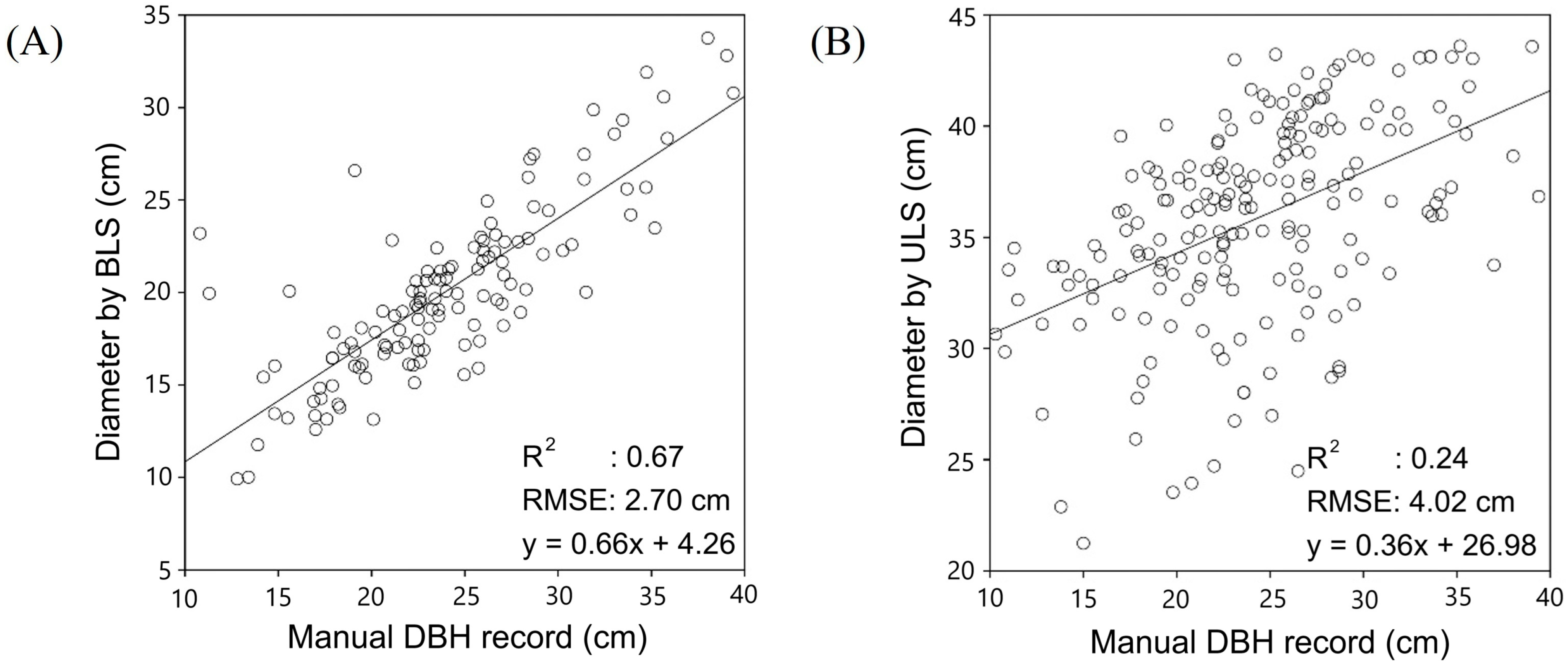
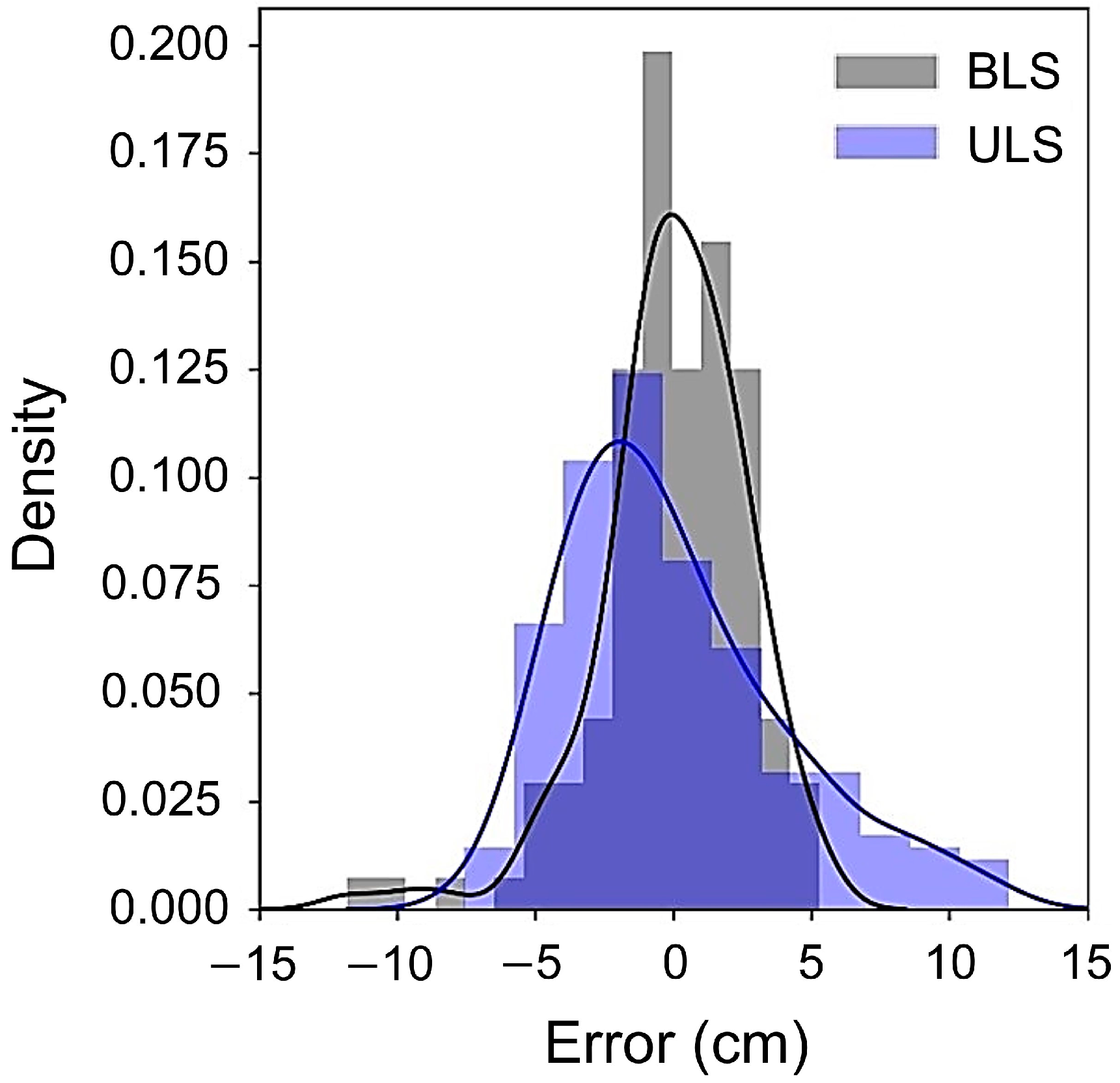
3.2. Accuracy of DBH Estimation
3.3. Heritability of DBH and Tree Height
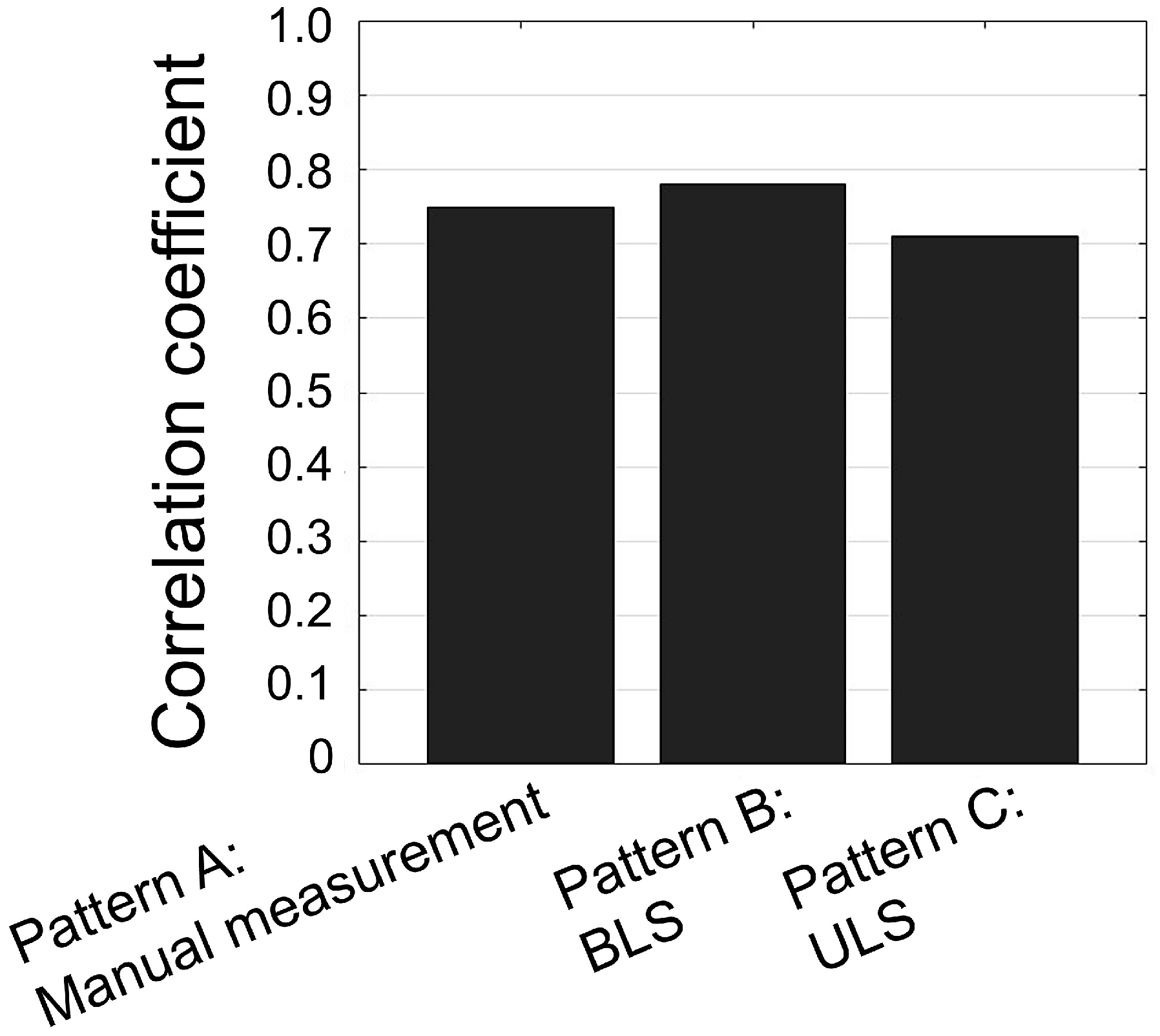
3.4. Genetic Correlation Among Traits and Accuracy of Timber Volume Selection
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Accuracy with Previous Studies
4.2. Required Accuracy Level
4.3. Potential Accuracy of Timber Volume Selection
4.4. Differences Between Platforms and Conditions for Acquiring Point Cloud Data
4.5. Significance and Comparison of Location Estimation
4.6. Applications in Forest Management and Tree Breeding
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Zhao, J.; Xie, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, K. Integrated remote sensing and model approach for impact assessment of future climate change on the carbon budget of global forest ecosystems. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2021, 203, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, M.J.; Johnson, B.G.; Bartowitz, K.J.; Hudiburg, T.W. Forests of the future: Climate change impacts and implications for carbon storage in the Pacific Northwest, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Piao, S.; Fang, J. Quantifying the response of forest carbon balance to future climate change in Northeastern China: Model validation and prediction. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 66, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. In Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Slade, R., Khourdajie, A.A., Diemen, R.V., McCollum, D., Pathak, M., Some, S., Vyas, P., Fradera, R., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Corte, A.P.; Rex, F.E.; Almeida, D.R.A.d.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Silva, C.A.; Moura, M.M.; Wilkinson, B.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Cunha Neto, E.M.d.; Veras, H.F.P.; et al. Measuring Individual Tree Diameter and Height Using GatorEye High-Density UAV-Lidar in an Integrated Crop-Livestock-Forest System. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Hernández, J.; Lopatin, J.; Kattenborn, G.; Fassnacht, F.E. Pilot study on the retrieval of DBH and diameter distribution of deciduous forest stands using cast shadows in UAV-based orthomosaics. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, IV, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, K.T.; Owari, T.; Furuya, N.; Hiroshima, T.; Morimoto, J. Application of UAV Photogrammetry with LiDAR Data to Facilitate the Estimation of Tree Locations and DBH Values for High-Value Timber Species in Northern Japanese Mixed-Wood Forests. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, M.; Holmgren, J.; Olofsson, K. Tree Stem Diameter Estimation from Mobile Laser Scanning Using Line-Wise Intensity-Based Clustering. Forests 2016, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, F.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, K.; Ma, Q.; Baret, F.; Jiang, D.; et al. Lidar sheds new light on plant phenomics for plant breeding and management: Recent advances and future prospects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglhaut, J.; Cabo, C.; Puliti, S.; Piermattei, L.; O’Connor, J.; Rosette, J. Structure from Motion photogrammetry in forestry: A review. Curr. For. Rep. 2019, 5, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brede, B.; Lau, A.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L. Comparing RIEGL RiCOPTER UAV LiDAR Derived Canopy Height and DBH with Terrestrial LiDAR. Sensors 2017, 17, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Krzystek, P.; Heurich, M. Tree species classification and estimation of stem volume and DBH based on single tree extraction by exploiting airborne full-waveform LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S. Estimating biomass of individual pine trees using airborne LiDAR. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, A.; Xiao, S.; Hu, S.; He, N.; Pang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. Single Tree Segmentation and Diameter at Breast Height Estimation with Mobile LiDAR. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 24314–24325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Gong, P.; Cheng, X.; Clinton, N.; Cao, C.; Ni, W.; Wang, L. Automated methods for measuring DBH and tree heights with a commercial scanning lidar. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskal, L.M.; Zheng, G. Retrieving Forest Inventory Variables with Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) in Urban Heterogeneous Forest. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kang, F.; Li, W.; Kan, J.; Zheng, Y.; He, G. Extracting Diameter at Breast Height with a Handheld Mobile LiDAR System in an Outdoor Environment. Sensors 2019, 19, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, E.; Avia, K.; Dumas, V.; Ley, L.; Reibel, N.; Butterlin, G.; Soma, M.; Lopez-Lozano, R.; Baret, F.; Merdinoglu, D.; et al. LiDAR Is Effective in Characterizing Vine Growth and Detecting Associated Genetic Loci. Plant Phenomics 2023, 5, 0116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinobu, S. Forest Tree Breeding for Japanese larch. Eurasian J. For. Res. 2005, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, T.; Hirata, R.; Fujinuma, Y.; Saigusa, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Harazono, Y.; Takada, M.; Inukai, K.; Inoue, G. CO2 and water vapor exchange of a larch forest in northern Japan. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2003, 55, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CloudCompare (Version 2.11.3 (Anoia) [64-bit]) [GPL Software]. 2023. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, G. An Easy-to-Use Airborne LiDAR Data Filtering Method Based on Cloth Simulation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarias, J.C.; Reeds, J.A.; Wright, M.H.; Wright, P.E. Convergence Properties of the Nelder-Mead Simplex Method in Low Dimensions. SIAM J. Optim. 1998, 9, 112–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Math Works Inc. MATLAB (Version R2021a) [Computer Software]. 2021. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/ (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Shirasawa, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Isobe, S. Analytical workflow of double-digest restriction site-associated DNA sequencing based on empirical and in silico optimization in tomato. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Iki, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Hirao, T.; Tamura, A.; Takahashi, M. Comprehensive collection of genes and comparative analysis of full-length transcriptome sequences from Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi) and Kuril larch (Larix gmelinii var. japonica). BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, B.L.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. Fast two-stage phasing of large-scale sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; de Los Campos, G. Genome-Wide Regression and Prediction with the BGLR Statistical Package. Genetics 2014, 198, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Quantitative Genetics; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.H. A discriminant function for plant selection. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazel, L.N.; Lush, J.L. The efficiency of three methods of selection. J. Hered. 1942, 33, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazel, L.N. The genetic basis for constructing selection indexes. Genetics 1943, 28, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Pang, S.; Zeng, H.; Shen, Z. Accuracy assessment and error analysis for diameter at breast height measurement of trees obtained using a novel backpack LiDAR system. For. Ecosyst. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, P.M.; Cook, B.D.; Sun, G.; Simard, M.; Nelson, R.F.; Ranson, K.J.; Zhang, Z.; Luthcke, S. Achieving accuracy requirements for forest biomass mapping: A spaceborne data fusion method for estimating forest biomass and LiDAR sampling error. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierzchała, M.; Gigu`ere, P.; Astrup, R. Mapping forests using an unmanned ground vehicle with 3D LiDAR and graph-SLAM. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | BLS | ULS |
|---|---|---|
| Product name | Leica Pegasus: Backpack | DJI Zenmuse L1 (+Matrice 300 RTK, D-RTK2) |
| Size | 73 × 27 × 31 cm | 15.2 × 11.0 × 16.9 cm (Zenmuse L1) 81.0 × 67.0 × 43.0 cm (Martice 300 RTK) |
| Weight | 11.9 kg | 0.93 ± 0.01 kg (Zenmuse L1) 6.3 kg (Martice 300 RTK) |
| Operating time | 4 h | 55 min (maximum flight time) |
| Number of points | 600,000 points/s | Multi-return: max. 480,000 points/s |
| Accuracy | Relative accuracy: 2−3 cm (50 m) Absolute accuracy (outdoor): 5 cm Absolute accuracy (indoors, e.g., with SLAM, without control point 1): 5−50 cm data 1 | Lidar range accuracy: 3 cm at 100 m Lidar system accuracy: 10 cm horizontally and 5 cm vertically at a distance of 50 m RTK positioning accuracy: 1 cm + 1 ppm horizontally, 1.5 cm + 1 ppm vertically |
| FOV | 270° ± 15° (horizontal) 30° ± 15° (vertical) | Non-repetitive scanning pattern: 70.4° (horizontal) × 77.2° (vertical) Repetitive scanning pattern: 70.4° (horizontal) × 4.5° (vertical) |
| GNSS | GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo | GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo |
| Laser pulse frequency | 10 Hz | 240 kHz/160 kHz |
| Maximum echo number (number of return) | 1 echo | 2 echo/3 echo |
| Flight speed | - | 5 m/s |
| Traits | DBH Manual | DBH BLS | DBH ULS |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBH BLS | 0.82 | ||
| DBH ULS | 0.57 | ||
| Tree height | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sano, H.; Miura, N.; Inamori, M.; Unno, Y.; Guo, W.; Isobe, S.; Kusunoki, K.; Iwata, H. Quantitative Genetic Aspects of Accuracy of Tree Biomass Measurement Using LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244790
Sano H, Miura N, Inamori M, Unno Y, Guo W, Isobe S, Kusunoki K, Iwata H. Quantitative Genetic Aspects of Accuracy of Tree Biomass Measurement Using LiDAR. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(24):4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSano, Haruka, Naoko Miura, Minoru Inamori, Yamato Unno, Wei Guo, Sachiko Isobe, Kazutaka Kusunoki, and Hiroyoshi Iwata. 2024. "Quantitative Genetic Aspects of Accuracy of Tree Biomass Measurement Using LiDAR" Remote Sensing 16, no. 24: 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244790
APA StyleSano, H., Miura, N., Inamori, M., Unno, Y., Guo, W., Isobe, S., Kusunoki, K., & Iwata, H. (2024). Quantitative Genetic Aspects of Accuracy of Tree Biomass Measurement Using LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 16(24), 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244790







