InfraRed Thermography and 3D-Data Fusion for Architectural Heritage: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
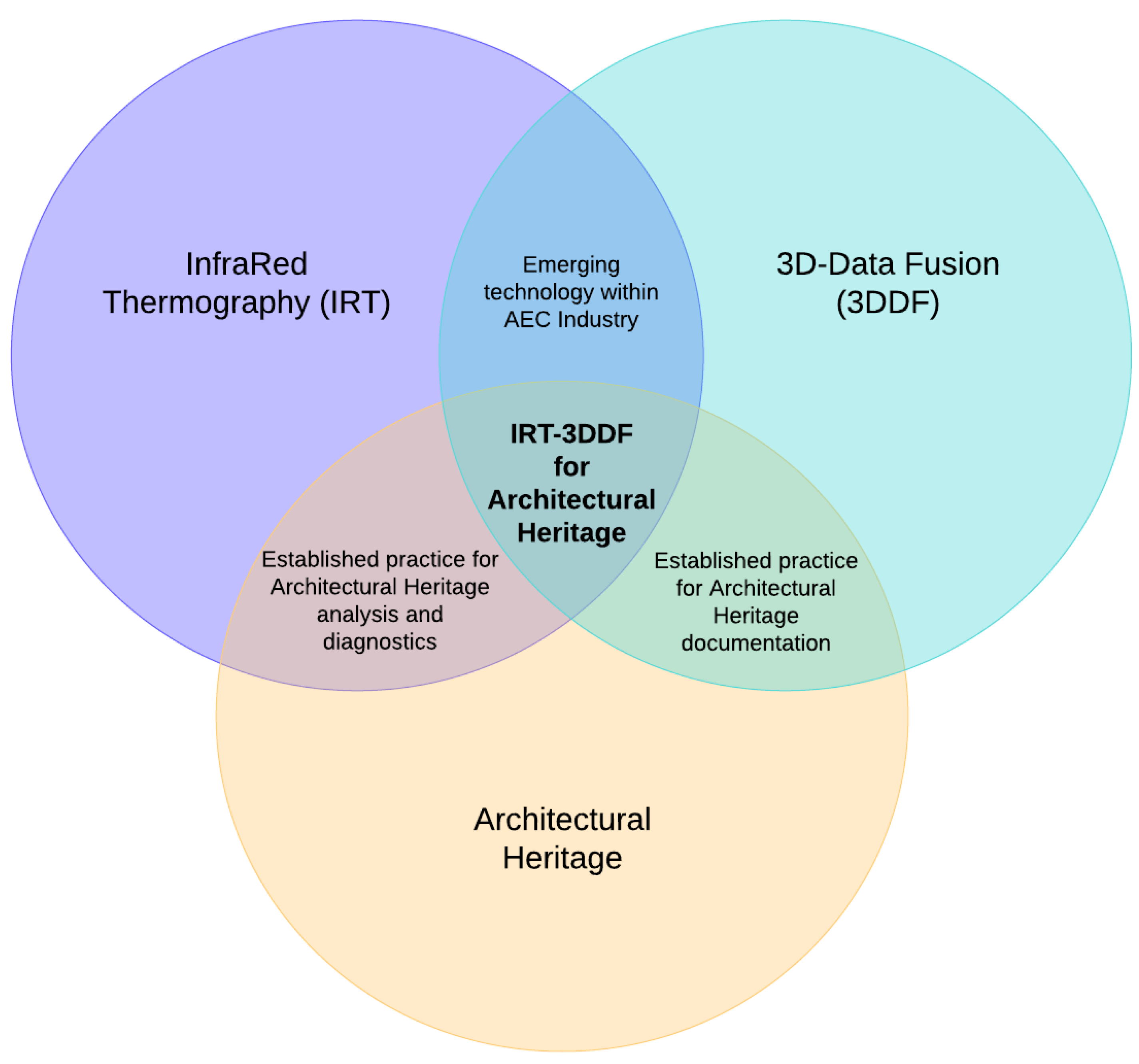
1.1. Aims and Objectives
- Undertake a systematic literature search for IRT-3DDF;
- Undertake initial bibliometric analysis for the scoping literature;
- Chart the scoping literature to underpin an accompanying thematic analysis of research gaps and emerging trends within IRT-3DDF.
1.2. Paper Structure
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scoping Review: Overview
2.1.1. Context
- Stage 1: Identifying research questions;
- Stage 2: Systematic literature search for relevant studies;
- Stage 3: Study selection through defined inclusion and exclusion criteria;
- Stage 4: Data charting;
- Stage 5: Collating, summarising, and reporting results;
- Stage 6 (Optional): Stakeholder consultation.
2.1.2. Rationale
2.2. Scoping Review: Process
2.2.1. Scoping Review Protocol and Registration
2.2.2. Research Question: Terms and Definitions
2.2.3. Literature Search: Databases and Iterative Keyword Selection
- InfraRed Thermography (Participant): “Infrared Thermography” OR IRT OR Thermography OR “Thermal Imag*” OR Thermograph*.
- 3D-Data Fusion (Concept): Photogrammetr* OR “Structure From Motion” OR SfM OR “Laser Scan*” OR TLS OR “Data Fusion” OR 3D OR Model* OR “Multi View Stereo” OR MVS OR “Sensor Fusion” OR “Data Integration”.
- Architectural Heritage (Context): “Architectural Heritage” OR “Built Heritage” OR “Historic* Building*” OR Archaeolog* OR Heritage.
2.2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Review study, conference proceedings, conference review (Exc.): All publications must present a case study of IRT-3DDF that can be analysed for its methods, results and applications.
- Publication stage (Inc.): All publications must be published.
- English language (Inc.): All publications must be available in English.
- Open access (Inc.): All publications must be open access (or granted access from the authors).
- Presence of IRT (Inc.): The presence of IRT as defined by Section 2.2.2.
- Presence of Architectural Heritage (Inc.): The presence of architectural heritage as defined by Section 2.2.2.
- Presence of IRT-3DDF (Inc.): The presence of IRT-3DDF as defined by Section 2.2.2.
2.2.5. Bibliometric Analysis
- Number of publications per year (PA).
- Bibliographic visualisation (SM).
- Keyword co-occurrence (abstract and keywords) (SM).
2.2.6. Data Charting
- Contextual:
- (a)
- Study Location(s)
- (b)
- Study Building(s)
- (c)
- Architectural Style(s)
- (d)
- Primary Research Focus
- Methodological:
- (a)
- Fusion Method
- (b)
- Thermal Camera
- (c)
- Thermography Type
- Practical:
- (a)
- Thermal Outputs
- (b)
- Thermal Findings
- (c)
- Future Developments
2.2.7. Thematic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Bibliometric Analysis
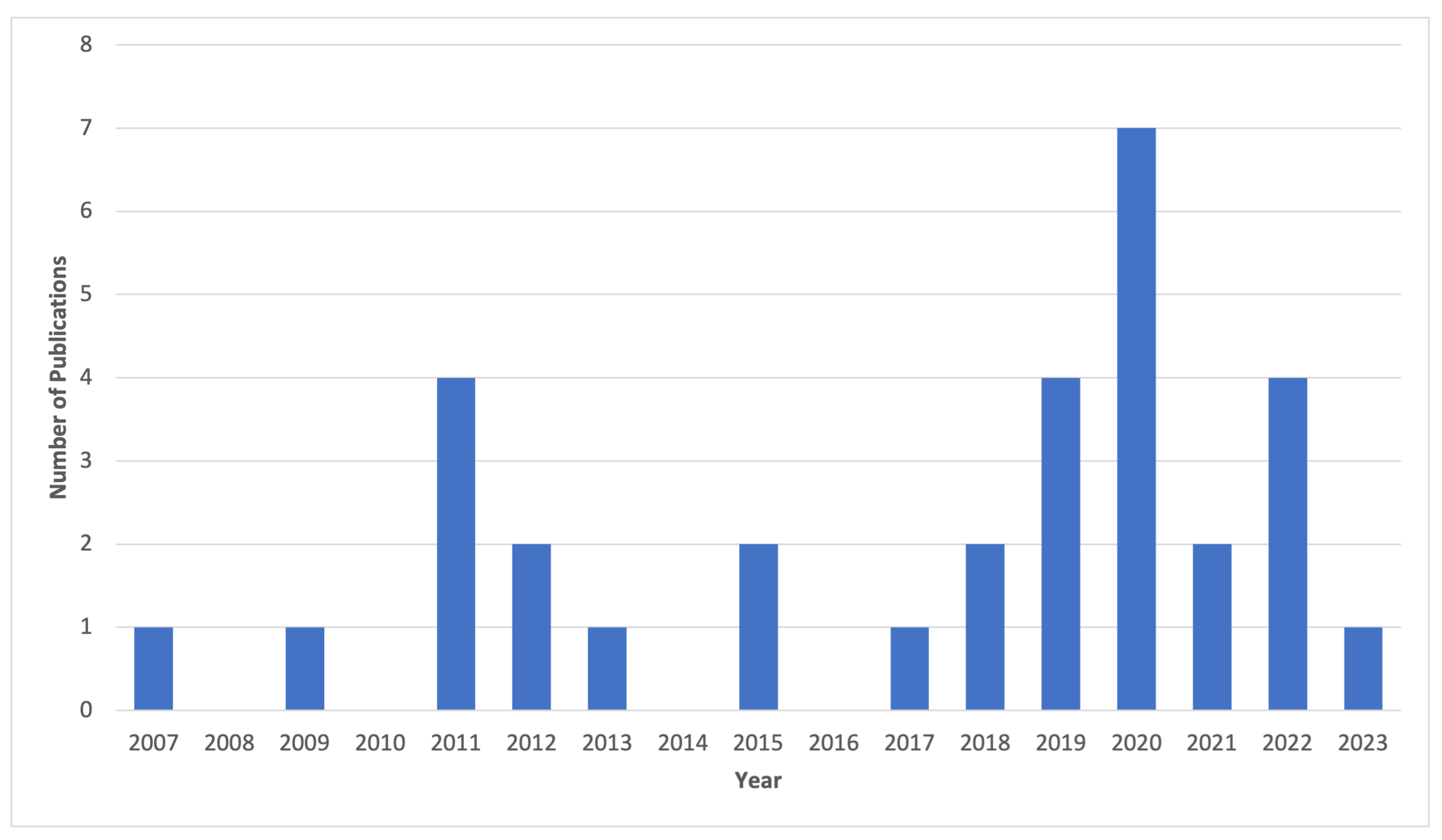
3.2.1. Publications per Year
3.2.2. Bibliographic Visualisation
3.2.3. Keyword Co-Occurrence
4. Data Charting and Thematic Analysis
4.1. Contextual Data Charting
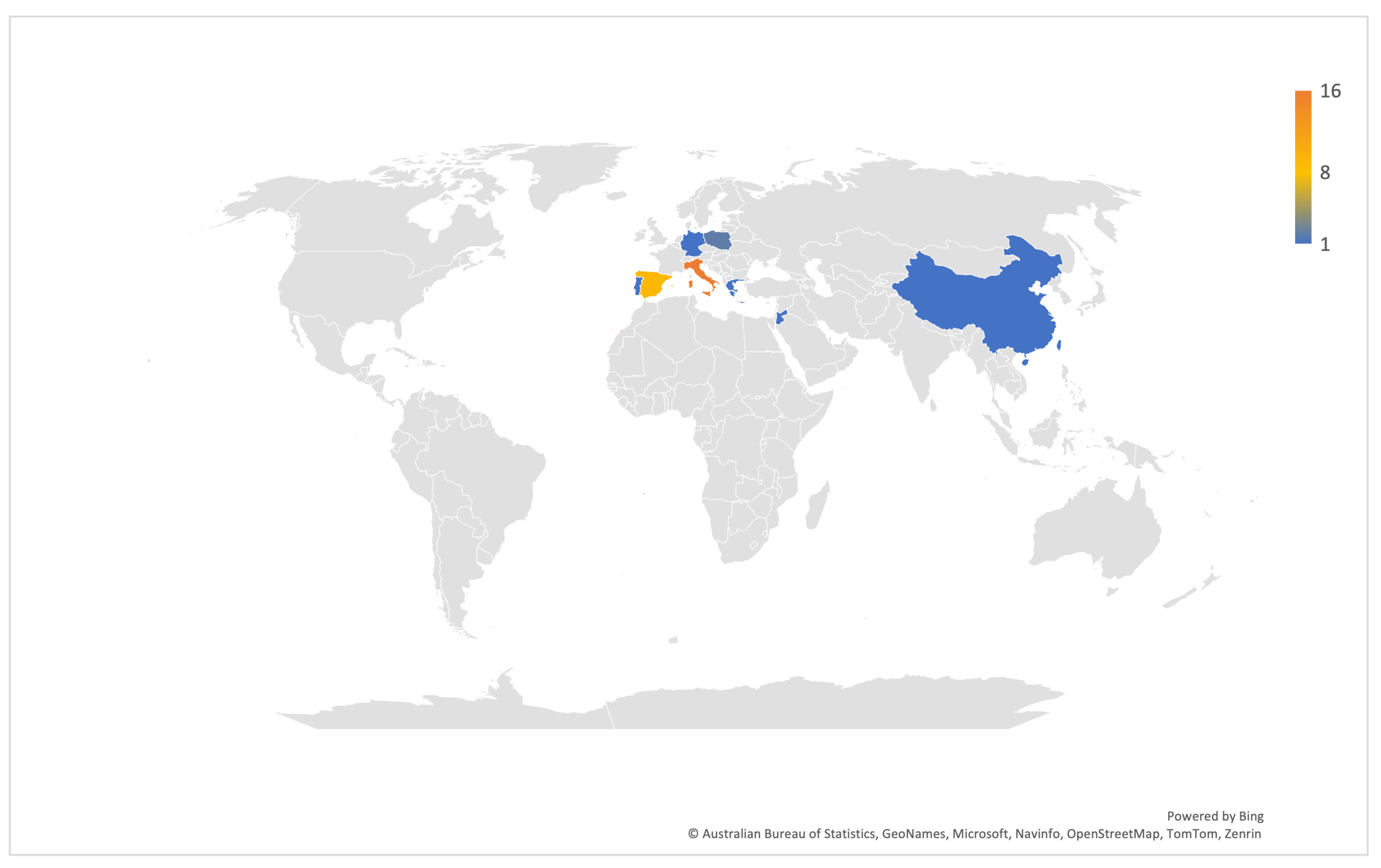
4.1.1. Study Location(s)
4.1.2. Study Building(s)
4.1.3. Architectural Style(s)
| Authors | Study Location(s) | Study Building(s) | Architectural Style(s) | Primary Research Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020a [76] | Turin, Italy | Castello del Valentino | 16th Century Suburban Mansion | Method Development |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020b [70] | Turin, Italy | Castello del Valentino | 16th Century Suburban Mansion | Method Development |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2021 [68] | Turin, Italy | Castello del Valentino | 16th Century Suburban Mansion | Method Development |
| Adan et al., 2020 [77] | Valencia, Spain | Church of Santos Juanes | Main nave | Method Development |
| Alba et al., 2011 [78] | Milan, Italy | Rectorate Office and The “Trifoglio” Building, Politecnico di Milano University | Classical revival style; Italian modernism | Building Diagnostics |
| Artese et al., 2019 [79] | Valencia, Spain | Church of Escuelas Pias | Hemispherical dome | Building Diagnostics |
| Barbieri et al., 2023 [60] | Bologna, Italy | Library Tower, Faculty of Engineering, University of Bologna | 20th Century Rationalist Architecture | Holistic Management |
| Brumana et al., 2013 [80] | Lombardy, Italy | Isola Comacina | Archaeological site | Method Development |
| Brumana et al., 2018 [81] | Cremona, Italy | Magio Grasselli Palace | 18th Century brick cloister vaults | Holistic Management |
| Cabrelles et al., 2009 [63] | Petra, Jordan | Djinn Block No. 9, Petra UNESCO World Heritage Site | Archaeological tomb | Building Diagnostics |
| Costanzo et al., 2015 [65] | Cosenza, Italy | St. Augustine Monumental Compound | Vernacular church and monastery | Method Development |
| Fang et al., 2022 [82] | Nanjing, China | Beamless Hall of Linggu Temple | Series of barrel vaults and arches | Holistic Management |
| Griffo et al., 2019 [62] | Rome, Italy | Nymphaeum of Egeria, Caffarella Park | Caved grotto | Method Development |
| Laguela et al., 2011 [59] | Galicia, Spain | School of Technical Industrial Engineering, Vigo | 1930s educational centre | Method Development |
| Lewinska and Maciuk, 2020 [83] | Kraków, Poland | AGH-UST University of Science and Technology; Barbican Fortified Outpost | Vernacular wooden and masonry architecture | Holistic Management |
| Maierhofer et al., 2011 [67] | Magdeburg, Germany | Cathedral of Saint Mauritius and Saint Katharina | Sandstone column | Method Development |
| Martín-Lerones et al., 2021 [84] | Valladolid, Spain | The Castle of Torrelobatón | Middle-Age European Castle | Holistic Management |
| Merchán et al., 2020 [71] | Almadenejos, Spain | Baritel de San Carlos | Archaeological mine and mill | Building Diagnostics |
| Mileto et al., 2015 [85] | Monzón, Spain | Monzón Castle | 10th Century castle and fortress | Building Diagnostics |
| Napolitano et al., 2019 [66] | Florence, Italy | Sala degli Elementi, Palazzo Vecchio | Internal wall | Building Diagnostics |
| Patrucco et al., 2020 [72] | Lazio, Italy; Turin, Italy | Santa Maria delle Grazie church; Bout du Col | Coffered wooden ceiling; Abandoned alpine village | Method Development |
| Patrucco et al., 2022a [75] | Valencia, Spain | Palacio de Colomina | Decorative classical architecture | Holistic Management |
| Patrucco et al., 2022b [74] | Cuneo, Italy; Torino, Italy | Rural Chapel; Comprehensive School; Parabolic Arch of Morano sul Po | Varied architectural heritage | Method Development |
| Paziewska and Rzonca, 2022 [73] | Porąbka, Poland | Parish of the Birth of the Blessed Virgin Mary | Church and stone towers | Building Diagnostics |
| Previtali et al., 2012 [86] | Milan, Italy | Politecnico di Milano University | Classical and modern façades | Method Development |
| Puente et al., 2018 [61] | Bande, Spain | “Aquis Querquennis” Roman Fort and Camp | Archaeological site | Building Diagnostics |
| Scaioni et al., 2012 [87] | Milan, Italy | Politecnico di Milano University | Classical and modern façades | Method Development |
| Scaioni et al., 2017 [64] | Milan, Italy | The Church of St. Pio X; Milanese residential building | Concrete church; 1960s protected buildings | Method Development |
| Solla et al., 2020 [69] | Leiria, Portugal | The Monastery of Batalha | Masonry façades | Holistic Management |
| Rizzi et al., 2007 [88] | Verona, Italy | Palazzo Barbieri | Neoclassical palace | Method Development |
| Tsilimantou et al., 2019 [89] | Rhodes Island, Greece | Acropolis of Erimokastro | Deserted castle and fortifications | Building Diagnostics |
| Zalama et al., 2011 [90] | Valladolid, Spain | Iglesia conventual de San Pablo | Isabelline style church façade | Method Development |
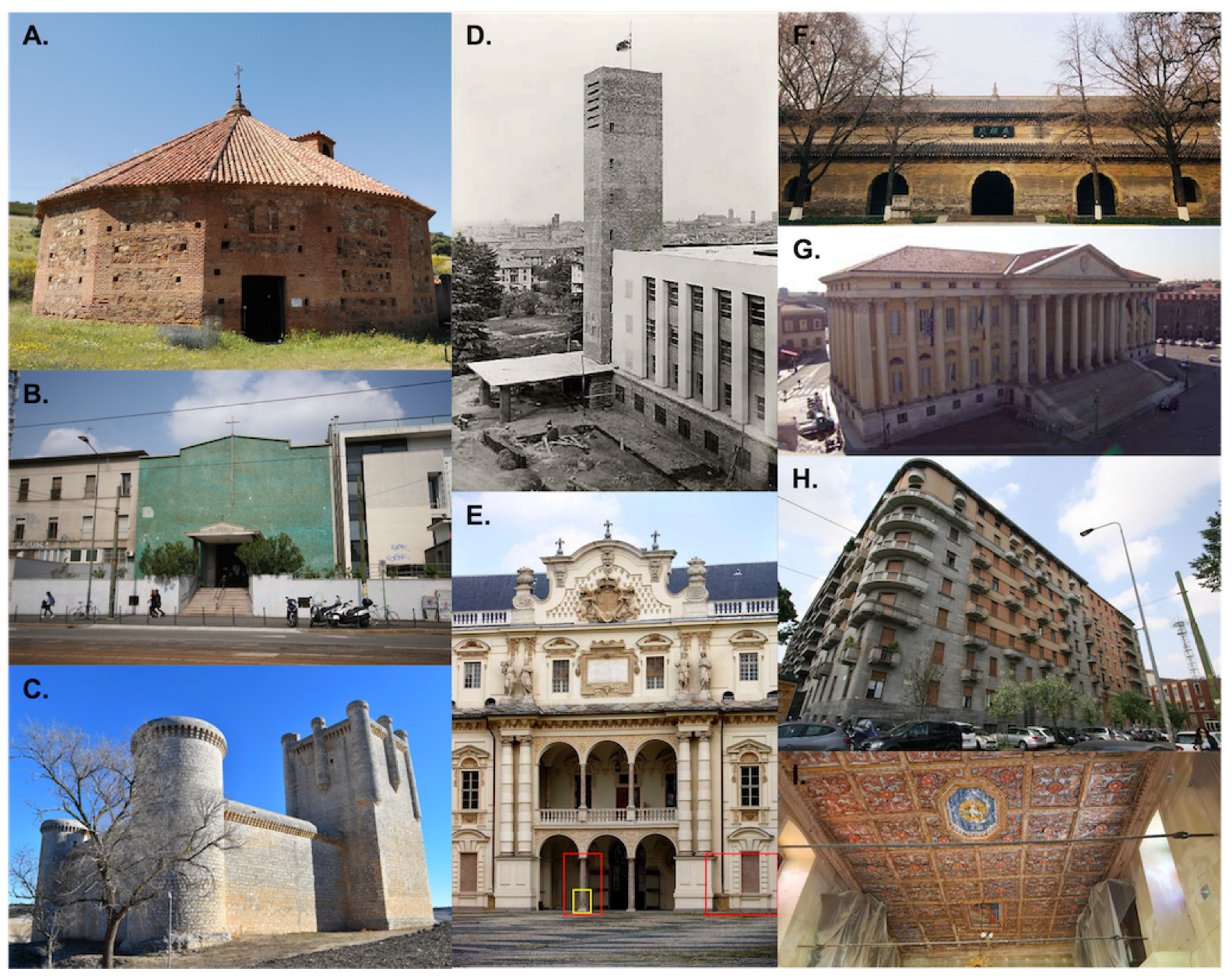

4.1.4. Primary Research Focus
4.2. Methodological Data Charting
4.2.1. Fusion Method
4.2.2. Thermal Cameras
4.2.3. Thermography Type
4.3. Practical Data Charting
4.3.1. Thermal Outputs
4.3.2. Thermal Findings
4.3.3. Future Developments
5. Discussion
5.1. IRT-3DDF Scoping Review: Reflections and Efficacy
5.2. Infrared Thermography: Principles and Practices for IRT-3DDF
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kioussi, A.; Karoglou, M.; Labropoulos, K.; Bakolas, A.; Moropoulou, A. Integrated documentation protocols enabling decision making in cultural heritage protection. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, e141–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Ioannides, M.; Previtali, M. Holistic Heritage Building Information Modelling (HHBIM): From Nodes to Hub Networking, Vocabularies and Repositories. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, E.; Rinaudo, F. 3D Interpretation and Fusion of Multidisciplinary Data for Heritage Science: A Review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 42, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Historic England. Energy Efficiency and Historic Buildings How to Improve Energy Efficiency: Advice Note 14; Technical Report; Historic England: Swindon, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Denard, H. The London Charter for the Computer-based Visualisation of Cultural Heritage (Version 2.1, February 2009). In Paradata and Transparency in Virtual Heritage, 1st ed.; Bentkowska-Kafel, A., Denard, H., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Masri, Y.; Rakha, T. A scoping review of non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques in building performance diagnostic inspections. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, B.; Lucchi, E.; Bienvenido-Huertas, D.; Nardi, I. Non-destructive techniques (NDT) for the diagnosis of heritage buildings: Traditional procedures and futures perspectives. Energy Build. 2022, 263, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usamentiaga, R.; Venegas, P.; Guerediaga, J.; Vega, L.; Molleda, J.; Bulnes, F. Infrared Thermography for Temperature Measurement and Non-Destructive Testing. Sensors 2014, 14, 12305–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylili, A.; Fokaides, P.A.; Christou, P.; Kalogirou, S.A. Infrared Thermography (IRT) Applications for Building Diagnostics: A Review. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jarzabek-Rychard, M.; Tong, X.; Maas, H.G. Fusion of Thermal Imagery with Point Clouds for Building Façade Thermal Attribute Mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahaghin, M.; Samadzadegan, F.; Dadrass Javan, F. Precise 3D Extraction of Building Roofs by Fusion of UAV-based Thermal and Visible Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 7002–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavaš, H.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Buljan, I.H.; Barić, T. Locating Hidden Elements in Walls of Cultural Heritage Buildings by Using Infrared Thermography. Buildings 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisegna, F.; Ambrosini, D.; Paoletti, D.; Sfarra, S.; Gugliermetti, F. A Qualitative Method for Combining Thermal Imprints to Emerging Weak Points of Ancient Wall Structures by Passive Infrared Thermography—A Case Study. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.; Erazo-Aux, J.; Lagüela, S.; Sfarra, S.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Pivarčiová, E.; Gargiulo, G.; Maldague, X.; Arias, P. Introduction of Deep Learning in Thermographic Monitoring of Cultural Heritage and Improvement by Automatic Thermogram Pre-Processing Algorithms. Sensors 2021, 21, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadelano, G.; Bison, P.; Bortolin, A.; Ferrarini, G.; Peron, F.; Girotto, M.; Volinia, M. Monitoring of Historical Frescoes by Timed Infrared Imaging Analysis. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2015, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Tortora, M.; Arrizza, L.; Cerichelli, G.; Nardi, I.; Maldague, X. Diagnostics of Wall Paintings: A Smart and Reliable Approach. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 18, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Perilli, S.; Scozzafava, M.; Avdelidis, N.P.; Maldague, X.P.V. Precious Walls Built in Indoor Environments Inspected Numerically and Experimentally within Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) and Radio Regions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1083–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdelidis, N.P.; Moropoulou, A. Applications of infrared thermography for the investigation of historic structures. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.; Lagüela, S.; Otero, R.; Arias, P. Thermographic methodologies used in infrastructure inspection: A review—Data acquisition procedures. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Remondino, F. Data fusion in cultural heritage—A review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 40, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chane, C.S.; Mansouri, A.; Marzani, F.S.; Boochs, F. Integration of 3D and multispectral data for cultural heritage applications: Survey and perspectives. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gonzálvez, P.; Muñoz-Nieto, A.L.; DelPozo, S.; Sanchez-Aparicio, L.J.; Gonzalez-Aguilera, D.; Micoli, L.; Barsanti, S.G.; Guidi, G.; Mills, J.; Fieber, K.; et al. 4D Reconstruction and Visualization of Cultural Heritage: Analyzing our Legacy Through Time. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 42, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osello, A.; Lucibello, G.; Morgagni, F. HBIM and Virtual Tools: A New Chance to Preserve Architectural Heritage. Buildings 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, M.; Lagüela, S.; Riveiro, B.; Lorenzo, H. Non-Destructive Testing for the Analysis of Moisture in the Masonry Arch Bridge of Lubians (Spain). Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2013, 20, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxepare, L.; Leon, I.; Sagarna, M.; Lizundia, I.; Uranga, E.J. Advanced Intervention Protocol in the Energy Rehabilitation of Heritage Buildings: A Miñones Barracks Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, E.; Rinaudo, F. Close-Range Sensing and Data Fusion for Built Heritage Inspection and Monitoring—A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, I.S.; Flores-Colen, I.; Silva, A. Critical analysis about emerging technologies for Building’s façade inspection. Buildings 2021, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adán, A.; Quintana, B.; García Aguilar, J.; Pérez, V.; Castilla, F.J. Towards the Use of 3D Thermal Models in Constructions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, A.; Adán, A.; Javier Castilla, F. Thermal point clouds of buildings: A review. Energy Build. 2022, 274, 112425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.; Golparvar-Fard, M. An Automated Vision-Based Method for Rapid 3D Energy Performance Modeling of Existing Buildings Using Thermal and Digital Imagery. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2013, 27, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Ham, Y.; Golpavar-Fard, M. 3D as-is building energy modeling and diagnostics: A review of the state-of-the-art. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszczuk, D.; Stilla, U. Camera Pose Refinement by Matching Uncertain 3D Building Models with Thermal Infrared Image Sequences for High Quality Texture Extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 132, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Mobile Thermal Mapping for Matching of Infrared Images with 3D Building Models and 3D Point Clouds. Quant. Infrared Thermogr. J. 2018, 15, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natephra, W.; Motamedi, A.; Yabuki, N.; Fukuda, T. Integrating 4D Thermal Information with BIM for Building Envelope Thermal Performance Analysis and Thermal Comfort Evaluation in Naturally Ventilated Environments. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarza̧bek-Rychard, M.; Lin, D.; Maas, H.G. Supervised Detection of Façade Openings in 3D Point Clouds with Thermal Attributes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, M.; Volk, R.; Soibelman, L. Investigation on Performance of RGB Point Cloud and Thermal Information Data Fusion for 3D Building Thermal Map Modeling Using Aerial Images under Different Experimental Conditions. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moropoulou, A.; Avdelidis, N.; Karoglou, M.; Delegou, E.; Alexakis, E.; Keramidas, V. Multispectral Applications of Infrared Thermography in the Diagnosis and Protection of Built Cultural Heritage. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchi, E. Applications of the infrared thermography in the energy audit of buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3077–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquhoun, H.L.; Levac, D.; O’Brien, K.K.; Straus, S.; Tricco, A.C.; Perrier, L.; Kastner, M.; Moher, D. Scoping reviews: Time for clarity in definition, methods, and reporting. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. Theory Pract. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’brien, K.K. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miake-Lye, I.M.; Hempel, S.; Shanman, R.; Shekelle, P.G. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, H.; Tricco, A.C. Differentiating between mapping reviews and scoping reviews in the evidence synthesis ecosystem. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 149, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Health Research (NIHR). PROSPERO: International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews; National Institute of Health Research (NIHR): Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation. Convention Concerning The Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage; Technical Report; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Harzing, A.W.; Alakangas, S. Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: A ongitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Chàfer, M.; Mata, É. Comparative analysis of web of science and scopus on the energy efficiency and climate impact of buildings. Energies 2020, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkūnaitė, Z.; Kalibatas, D.; Kalibatienė, D. A bibliometric data analysis of multi-criteria decision making methods in heritage buildings. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2019, 25, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.J.; Lerones, P.M.; Llamas, J.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Zalama, E. A Review of Heritage Building Information Modeling (H-BIM). Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Palacios, J.B.; Morabito, D.; Remondino, F. Access to complex reality-based 3D models using virtual reality solutions. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 23, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Herrera-Avellanosa, D.; Del Pero, C.; Troi, A. What are the Implications of Climate Change for Retrofitted Historic Buildings? A Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual: Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.8. 2018. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.8.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Martínez-Molina, A.; Tort-Ausina, I.; Cho, S.; Vivancos, J.L. Energy Efficiency and Thermal Comfort in Historic Buildings: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagüela, S.; Martínez, J.; Armesto, J.; Arias, P. Energy efficiency studies through 3D laser scanning and thermographic technologies. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Franzoni, E.; Lambertini, A.; Pizzigatti, C.; Trevisiol, F.; Bitelli, G. 3D Data Management and Thermographic Studies as a Knowledge Base for the Conservation of a Rationalist Architecture; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, I.; Solla, M.; Lagüela, S.; Sanjurjo-Pinto, J. Reconstructing the Roman site “Aquis Querquennis” (Bande, Spain) from GPR, T-LiDAR and IRT Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffo, M.; Cimadomo, P.; Menconero, S. Integrative IRT for Documentation and Interpretation of Archaeological Structures. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2019, 42, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrelles, M.; Galcerá, S.; Navarro, S.; Lerma, J.L.; Akasheh, T.; Haddad, N. Integration of 3D Laser Scanning, Photogrammetry and Thermography to Record Architectural Monuments. In Proceedings of the 22nd CIPA Symposium, International Archives of the Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Kyoto, Japan, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Scaioni, M.; Rosina, E.; L’erario, A.; Dìaz-Vilariño, L. Integration of infrared thermography & photogrammetric surveying of built andscape. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 42, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, A.; Minasi, M.; Casula, G.; Musacchio, M.; Buongiorno, M.F. Combined use of terrestrial laser scanning and IR Thermography applied to a historical building. Sensors 2015, 15, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, R.; Hess, M.; Glisic, B. Integrating Non-Destructive Testing, Laser Scanning, and Numerical Modeling for Damage Assessment: The Room of the Elements. Heritage 2019, 2, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maierhofer, C.; Krankenhagen, R.; Röllig, M.; Schlichting, J.; Schiller, M.; Seidl, T.; Mecke, R.; Kalisch, U.; Hennen, C.; Meinhardt, J. Investigating Historic Masonry Structures with a Combination of Active Thermography and 3D Laser Scanner. Quant. Infrared Thermogr. J. 2011, 8, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, E.; Colombero, C.; Comina, C.; Rinaudo, F.; Volinia, M.; Girotto, M.; Ardissono, L. Integrating Multiband Photogrammetry, Scanning, and GPR for Built Heritage Surveys: The Façades of Castello del Valentino. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, M.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Gonçalves, G.; Francisco, C.; Puente, I.; Providência, P.; Gaspar, F.; Rodrigues, H. A Building Information Modeling Approach to Integrate Geomatic Data for the Documentation and Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, E.; Volinia, M.; Girotto, M.; Rinaudo, F. Three-Dimensional Thermal Mapping from IRT Images for Rapid Architectural Heritage NDT. Buildings 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, P.; Merchán, M.J.; Salamanca, S.; Adán, A. Application of Multisensory Technology for Resolution of Problems in the Field of Research and Preservation of Cultural Heritage. In Advances in Digital Cultural Heritage; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ioannides, M., Martins, J., Žarnić, R., Lim, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10754, pp. 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrucco, G.; Cortese, G.; Giulio Tonolo, F.; Spanò, A. Thermal and optical data fusion supporting built heritage analyses. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewska, J.; Rzonca, A. Integration of Thermal and RGB Data Obtained by Means of a Drone for Interdisciplinary Inventory. Energies 2022, 15, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrucco, G.; Giulio Tonolo, F.; Sammartano, G.; Spanò, A. SFM-Based 3D Reconstruction of Heritage Assets using UAV Thermal Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrucco, G.; Gómez, A.; Adineh, A.; Rahrig, M.; Lerma, J.L. 3D Data Fusion for Historical Analyses of Heritage Buildings Using Thermal Images: The Palacio de Colomina as a Case Study. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, E.; Rinaudo, F.; Volinia, M.; Girotto, M. Multispectral Sensing and Data Integration for the Study of Heritage Architecture. Eng. Process. 2020, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Adán, A.; Pérez, V.; Vivancos, J.L.; Aparicio-Fernández, C.; Prieto, S.A. Proposing 3D thermal technology for heritage building energy monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, M.I.; Barazzetti, L.; Scaioni, M.; Rosina, E.; Previtali, M. Mapping Infrared Data on Terrestrial Laser Scanning 3D Models of Buildings. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1847–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artese, S.; Lerma, J.L.; Aznar Molla, J.; Sánchez, R.M.; Zinno, R. Integration of Surveying Techniques to Detect the Ideal Shape of a Dome: The Case of the Escuelas Pías Church in Valencia. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Oreni, D.; Van Hecke, L.; Barazzetti, L.; Previtali, M.; Roncoroni, F.; Valente, R. Combined Geometric and Thermal Analysis from UAV Platforms for Archaeological Heritage Documentation. In Proceedings of the XXIV International CIPA Symposium, ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Strasbourg, France, 2–6 September 2013; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Brumana, R.; Condoleo, P.; Grimoldi, A.; Banfi, F.; Landi, A.G.; Previtali, M. HR LOD based HBIM to detect influences on geometry and shape by stereotomic construction techniques of brick vaults. Appl. Geomat. 2018, 10, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, Z. High-Definition Survey of Architectural Heritage Fusing Multisensors—The Case of Beamless Hall at Linggu Temple in Nanjing, China. Sensors 2022, 22, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinska, P.; Maciuk, K. Thermal and Spatial Data Integration for Recreating Rebuilding Stages of Wooden and Masonry Buildings. Photogramm. Rec. 2020, 35, 402–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Lerones, P.; Olmedo, D.; López-Vidal, A.; Gómez-García-bermejo, J.; Zalama, E. BIM Supported Surveying and Imaging Combination for Heritage Conservation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileto, C.; Vegas, F.; Lerma, J.L. Multidisciplinary Studies, Crossreading and Transversal Use of Thermography: The Castle of Monzón (Huesca) as a case study. In Proceedings of the Defensive Architecture of the Mediterranean—XV to XVIII Centuries; Rodriguez-Navarro, P., Ed.; Editorial Universitat Politecnica de Valencia: Valencia, Spain, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, M.; Erba, S.; Rosina, E.; Redaelli, V.; Scaioni, M.; Barazzetti, L. Generation of a GIS-based Environment for Infrared Thermography Analysis of Buildings. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8511, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaioni, M.; Rosina, E.; Barazzetti, L.; Previtali, M.; Redaelli, V. High-Resolution Texturing of Building Facades with Thermal Images. In Proceedings of the Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXIV; Burleigh, D., Stockton, G., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8354, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, A.; Voltolini, F.; Girardi, S.; Gonzo, L.; Remondino, F. Digital Preservation, Documentation and Analysis of Paintings, Monuments and Large Cultural Heritage with Infrared Technology, Digital Cameras and Range Sensors. In Proceedings of the XXI International CIPA Symposium, International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Athens, Greece, 1–6 October 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tsilimantou, E.; Delegou, T.E.; Bourexis, F.; Tapeinaki, S.; Soile, S.; Ioannidis, C.; Moropoulou, A. Combination of Geometric Documentation and Infrared Thermography Results for Preservation Purposes in Archaeological Sites. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Transdisciplinary Multispectral Modelling and Cooperation for the Preservation of Cultural Heritage; Osman, A., Moropoulou, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalama, E.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Llamas, J.; Medina, R. An Effective Texture Mapping Approach for 3D Models Obtained from Laser Scanner Data to Building Documentation. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Condoleo, P.; Grimoldi, A.; Landi, A.G.; Attico, D.; Turrina, A.; Banfi, F.; Previtali, M. HBIM Feeding Open Access Vault Inventory Through GeoDB HUB. In Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection: 7th International Conference, EuroMed 2018, Nicosia, Cyprus, 29 October–3 November 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11196, pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, F. BIM Orientation: Grades of Generation and Information for Different Type of Analysis and Management Process. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, D.; Pa-squaloni, G.; Paoletti, D. Comparative examples of the evolution of thermal cameras in artwork diagnostics: An experimental perspective. In The Future of Heritage Science and Technologies: Design, Simulation and Monitoring; Florence Heri-Tech 2022. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. 169; Furferi, R., Governi, L., Volpe, Y., Gherardini, F., Seymour, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Colyer, M.; Arnold, B. Building Thermography (UKTA Resources). Available online: https://ukta.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/building-thermography-ukta.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Usamentiaga, R.; Garcia, D.F.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X. Highly accurate geometric calibration for infrared cameras using inexpensive calibration targets. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2017, 112, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Marcucci, E.; Ambrosini, D.; Paoletti, D. Infrared exploration of the architectural heritage: From passive infrared thermography to hybrid infrared thermography (HIRT) approach. Mater. Constr. 2016, 66, 07415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Robson, S.; MacDonald, L.; Garside, D.; Evans, R. Spectral and 3D Cultural Heritage Documentation Using a Modified Camera. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-2, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maset, E.; Fusiello, A.; Crosilla, F.; Toldo, R.; Zorzetto, D. Photogrammetric 3D Building Reconstruction from Thermal Images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, IV-2/W3, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.P.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, S.; Nozick, V.; Saito, H. Registration of RGB and Thermal Point Clouds Generated by Structure From Motion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocobelli, D.P.; Boehm, J.; Bryan, P.; Still, J.; Grau-Bové, J. BIM for Heritage Science: A Review. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtiyoso, A.; Grussenmeyer, P. Virtual Disassembling of Historical Edifices: Experiments and Assessments of an Automatic Approach for Classifying Multi-Scalar Point Clouds into Architectural Elements. Sensors 2020, 20, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, H.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. From Point Clouds to Building Information Models: 3D Semi-Automatic Reconstruction of Indoors of Existing Buildings. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, E.; Remondino, F. Classification of 3D Digital Heritage. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M.; Van Genechten, B. Automated Classification of Heritage Buildings for As-Built BIM Using Machine Learning Techniques. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, IV-2/W2, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Building Facade Object Detection from Terrestrial Thermal Infrared Image Sequences Combining Different Views. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, II-3/W4, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, H.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. Automation of Thermal Point Clouds Analysis for the Extraction of Windows and Thermal Bridges of Building Facades. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B2-2, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Maas, H.G. Unsupervised Window Extraction from Photogrammetric Point Clouds with Thermal Attributes. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, IV-2/W5, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.; Coley, D.; Goodhew, S.; De Wilde, P. Thermography methodologies for detecting energy related building defects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirashrafi, S. The Hill House: Collaborative Scientific Conservation in Action. 2019. Available online: https://blog.historicenvironment.scot/2019/03/hill-house/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Brooke, C. Thermal Imaging for the Archaeological Investigation of Historic Buildings. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




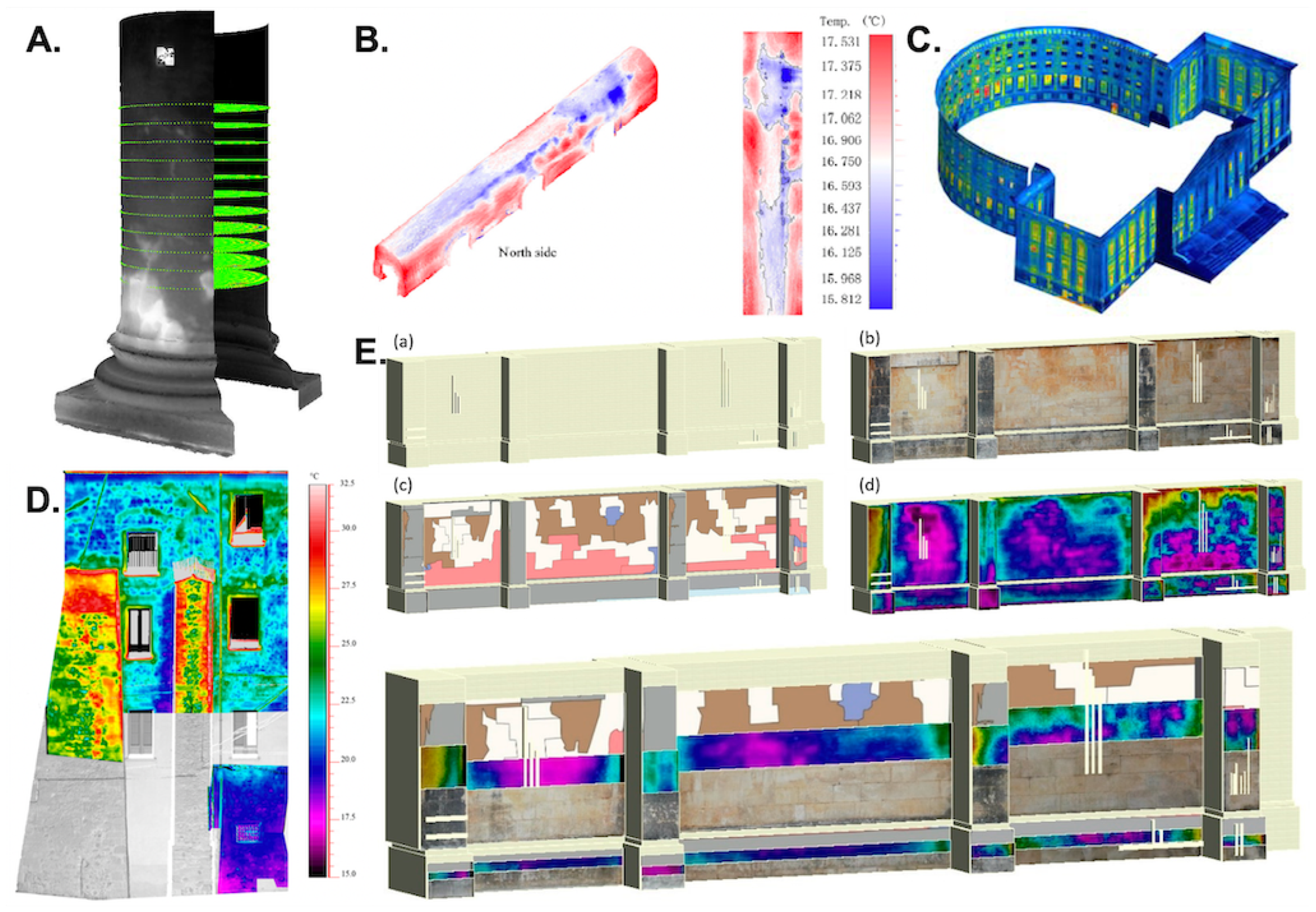
| Authors | Fusion Method | Thermal Camera | Thermography Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020a [76] | Thermal alignment onto 2D RGB ortho-mosaic | FLIR T1030sc (1024 × 768) * | Passive |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020b [70] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh | FLIR T1030sc (1024 × 768) * | Passive |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2021 [68] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | FLIR T1030sc (1024 × 768) * | Passive |
| Adan et al., 2020 [77] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS point cloud | FLIR A65 (640 × 512) | Passive |
| Alba et al., 2011 [78] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | AVIO (320 × 240); NEC H2640 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Artese et al., 2019 [79] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | - | Passive |
| Barbieri et al., 2023 [60] | Thermal texturing of 3D parametric model | FLIR P620 (640 × 480) * | Active |
| Brumana et al., 2013 [80] | Thermal alignment onto 2D RGB ortho-mosaic | FLIR TAU (640 × 512) | Passive |
| Brumana et al., 2018 [81] | Thermal texturing of 3D parametric model | AVIO TVS-500 (320 × 240); FLIR T640 (640 × 480) * | Active |
| Cabrelles et al., 2009 [63] | Thermal alignment onto 2D TLS mesh | FLIR ThermaCAM B4 (320 × 240) | Passive |
| Costanzo et al., 2015 [65] | Thermal alignment onto 2D TLS reflectance mesh | AVIO (NEC) R300SR-S (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Fang et al., 2022 [82] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS point cloud | Zoller+Fröhlich T-Cam (382 × 288) | Passive |
| Griffo et al., 2019 [62] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB point cloud | Testo 875i (320 × 240) * | Passive |
| Laguela et al., 2011 [59] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS point cloud | AVIO (NEC) TH9260 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Lewinska and Maciuk, 2020 [83] | Thermal texturing of 3D parametric model | FLIR ThermaCAM P60 (320 × 240) * | Passive |
| Maierhofer et al., 2011 [67] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | Infratec VarioCAM HR (640 × 480) * | Active |
| Martín-Lerones et al., 2021 [84] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS point cloud | FLUKE Ti32 (320 × 240) * | Passive |
| Merchán et al., 2020 [71] | Thermal texturing of TLS point cloud | FLIR AX5 (640 × 512) | Passive |
| Mileto et al., 2015 [85] | Thermal alignment onto 2D TLS mesh | - | Passive |
| Napolitano et al., 2019 [66] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | FLIR A615 (640 × 512) * | Passive |
| Patrucco et al., 2020 [72] | Thermal alignment onto 2D RGB orth-mosaic: Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh | FLIR SC660 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Patrucco et al., 2022a [75] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | FLIR ThermaCAM B4 (320 × 240) | Passive |
| Patrucco et al., 2022b [74] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh; Thermal texturing of 3D RGB point cloud | DJI Zenmuse XT2 (640 × 512) * | Passive |
| Paziewska and Rzonca, 2022 [73] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh | DJI Zenmuse H20T (640 × 512) * | Passive |
| Previtali et al., 2012 [86] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | - | Passive |
| Puente et al., 2018 [61] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS point cloud | - | Passive |
| Scaioni et al., 2012 [87] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | AVIO (NEC) H2640 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Scaioni et al., 2017 [64] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh | FLIR P640 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Solla et al., 2020 [69] | Thermal texturing of 3D parametric model | FLIR T335 (320 × 240) * | Passive |
| Rizzi et al., 2007 [88] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | FLIR P640 (640 × 480) * | Passive |
| Tsilimantou et al., 2019 [89] | Thermal texturing of 3D RGB mesh | FLIR B200 (240 × 180) * | Passive |
| Zalama et al., 2011 [90] | Thermal texturing of 3D TLS mesh | - | Passive |
| Authors | Thermal Outputs | Thermal Findings | Future Developments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020a [76] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics | Material decay; Previous restoration; Structural integrity | Data integration |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2020b [70] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal mesh model | - | Method development |
| Adamopoulos et al., 2021 [68] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay; Moisture detection | Data integration |
| Adan et al., 2020 [77] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal mesh model | Thermal comfort assessment | Method development; Data integration (seasonal) |
| Alba et al., 2011 [78] | 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay; Structural integrity | Method development; Research application |
| Artese et al., 2019 [79] | 3D thermal mesh model | Crack detection | On-going conservation |
| Barbieri et al., 2023 [60] | 3D thermal H-BIM model | Treatment failure | Data management (H-BIM) |
| Brumana et al., 2013 [80] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics | Archaeological investigation; Hidden structures | Data integration |
| Brumana et al., 2018 [81] | 3D thermal H-BIM model | Construction age; Structural integrity | Data management (H-BIM); Structural simulation (FEM) |
| Cabrelles et al., 2009 [63] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay | Inform conservation practices |
| Costanzo et al., 2015 [65] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics | Crack detection; Material decay; Previous restoration; Structural integrity; | Data integration |
| Fang et al., 2022 [82] | 3D thermal point cloud | Moisture detection; Structural integrity | Data management (BIM); Data integration (GPR) |
| Griffo et al., 2019 [62] | 3D thermal point cloud | - | Augmented reality |
| Laguela et al., 2011 [59] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaic; 3D thermal point cloud | - | Method development |
| Lewinska and Maciuk, 2020 [83] | 3D thermal parametric model | Previous restoration | Data management (H-BIM) |
| Maierhofer et al., 2011 [67] | 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay | On-going conservation |
| Martín-Lerones et al., 2021 [84] | 3D thermal point cloud; 3D thermal parametric model | Crack detection | Data management (H-BIM) |
| Merchán et al., 2020 [71] | 3D thermal point cloud | - | H-BIM creation; Segmentation |
| Mileto et al., 2015 [85] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaic | Construction age; Material decay; Material density | On-going conservation |
| Napolitano et al., 2019 [66] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaic; 3D thermal FEM model | Crack Detection; Material Decay; Structural integrity | Simulation; Numerical modelling |
| Patrucco et al., 2020 [72] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaic; 3D thermal mesh model | Hidden structures | Archaeological investigation |
| Patrucco et al., 2022a [75] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal mesh model | Hidden structures; Previous restoration | Data management (H-BIM) |
| Patrucco et al., 2022b [74] | 3D thermal point cloud; 3D thermal mesh model | - | Method development |
| Paziewska and Rzonca, 2022 [73] | 3D thermal mesh model | Heat eakage | Energy modelling; Method development |
| Previtali et al., 2012 [86] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics | Material decay | Method development |
| Puente et al., 2018 [61] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics; 3D thermal point cloud | Material decay; Previous restoration | Visualisation |
| Scaioni et al., 2012 [87] | 2D thermal ortho-mosaics | Material decay | Method development |
| Scaioni et al., 2017 [64] | 3D thermal mesh model | - | Method development |
| Solla et al., 2020 [69] | 3D thermal H-BIM model | Material Decay; Moisture detection | Data management (H-BIM) |
| Rizzi et al., 2007 [88] | 3D thermal mesh model | - | Method development |
| Tsilimantou et al., 2019 [89] | 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay; Structural integrity | On-going conservation |
| Zalama et al., 2011 [90] | 3D thermal mesh model | Material decay; Moisture detection | Method development |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutherland, N.; Marsh, S.; Priestnall, G.; Bryan, P.; Mills, J. InfraRed Thermography and 3D-Data Fusion for Architectural Heritage: A Scoping Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092422
Sutherland N, Marsh S, Priestnall G, Bryan P, Mills J. InfraRed Thermography and 3D-Data Fusion for Architectural Heritage: A Scoping Review. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092422
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutherland, Neil, Stuart Marsh, Gary Priestnall, Paul Bryan, and Jon Mills. 2023. "InfraRed Thermography and 3D-Data Fusion for Architectural Heritage: A Scoping Review" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092422
APA StyleSutherland, N., Marsh, S., Priestnall, G., Bryan, P., & Mills, J. (2023). InfraRed Thermography and 3D-Data Fusion for Architectural Heritage: A Scoping Review. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092422









