Chlorophyll-Specific Absorption Coefficient of Phytoplankton in World Oceans: Seasonal and Regional Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
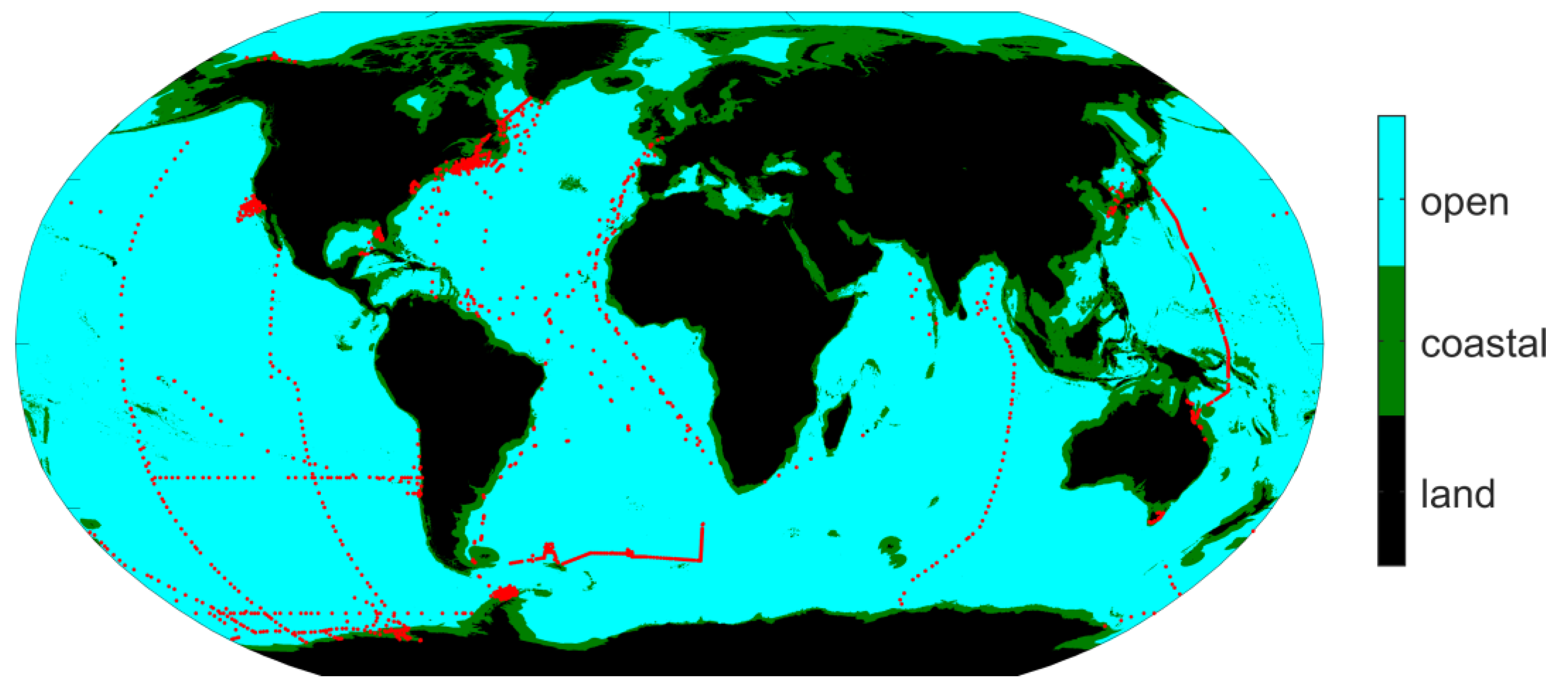
2.1. Domain of Study
2.2. Satellite Ocean Color Data
2.3. Analyses of Data
2.4. In Situ Data to Assist Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Multi-Year Averages
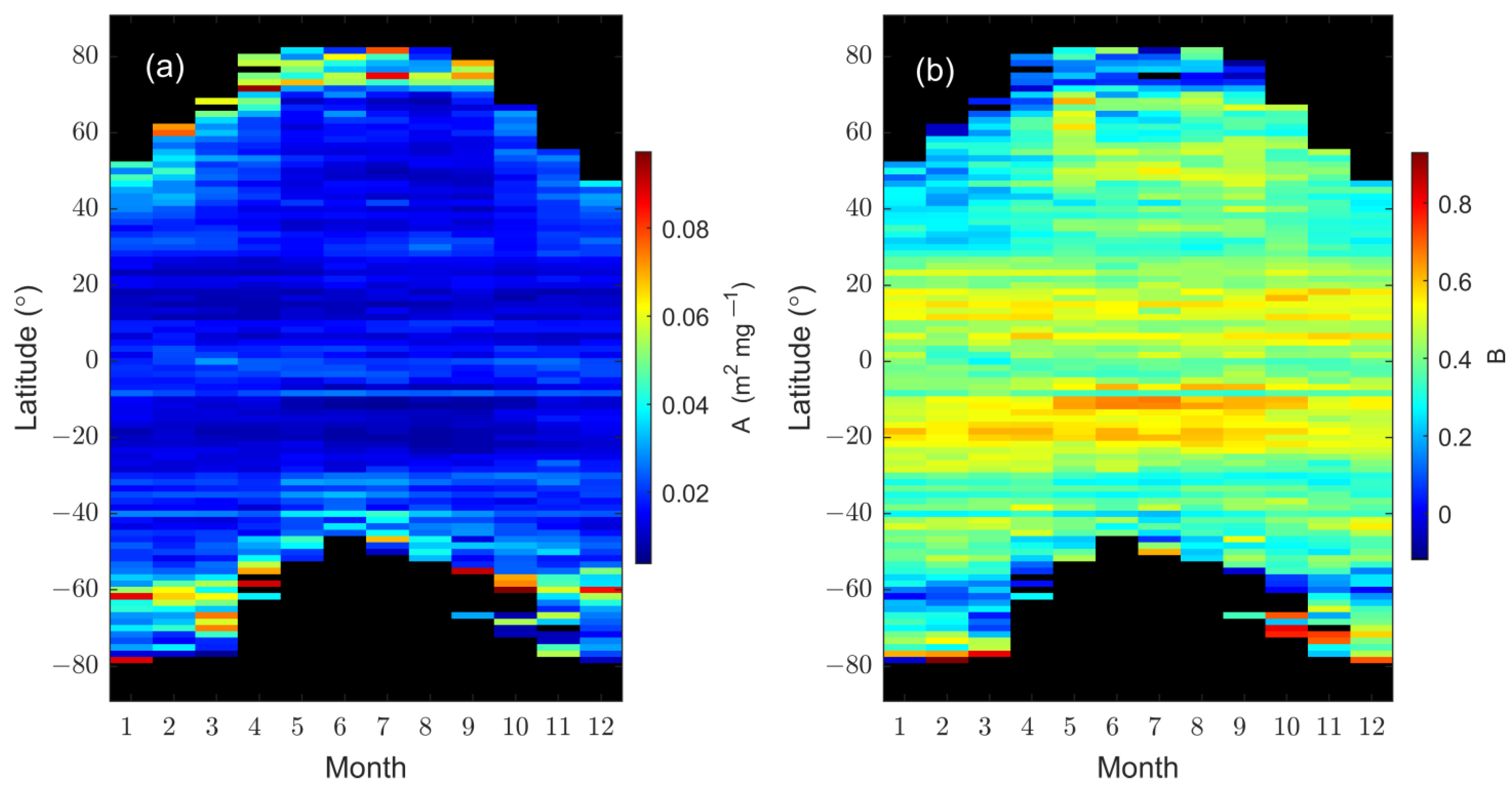
3.2. Temporal Variation in Monthly
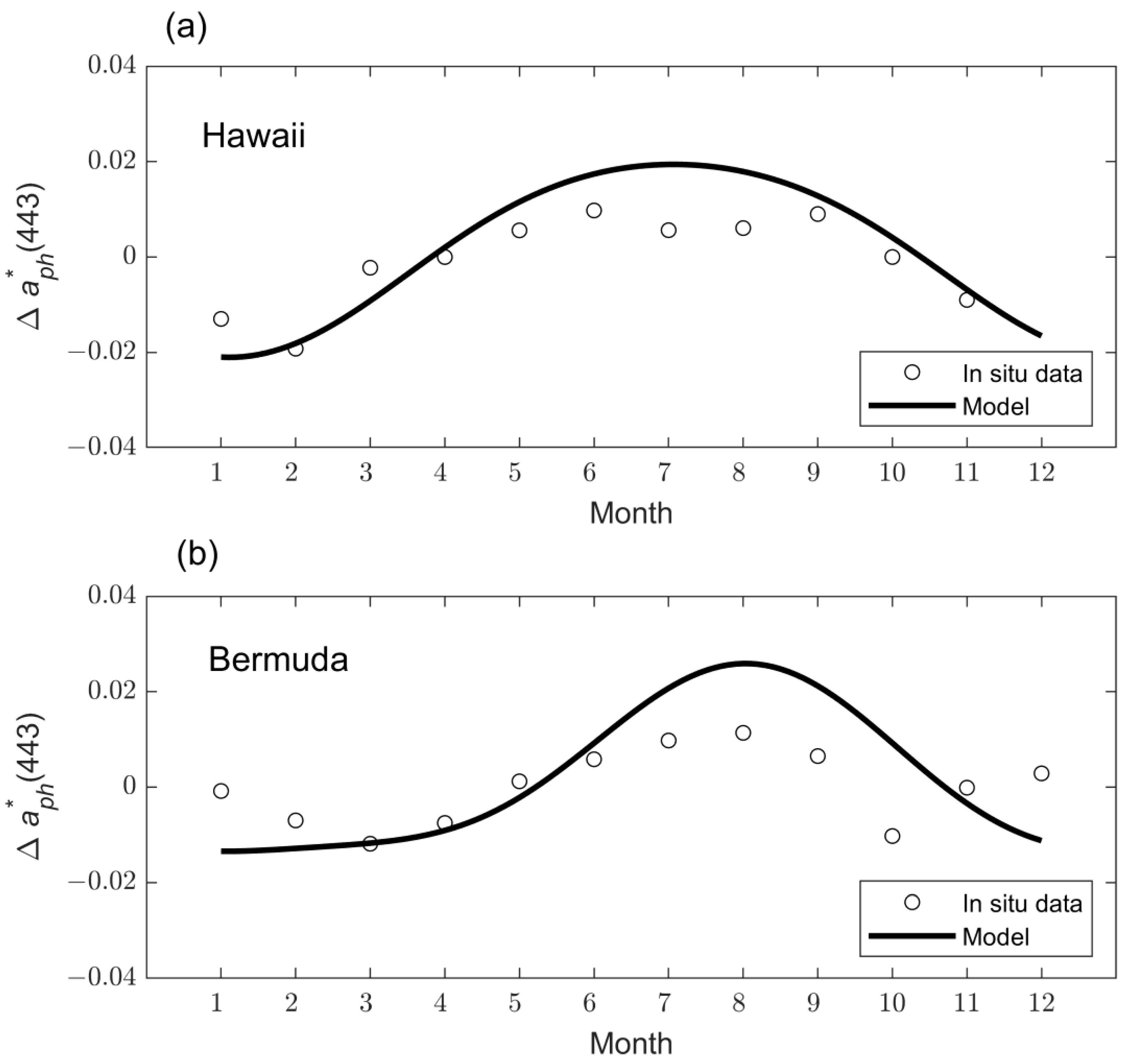
3.2.1. Example Time Series Data
3.2.2. Goodness of Fit
3.2.3. Seasonal Variability
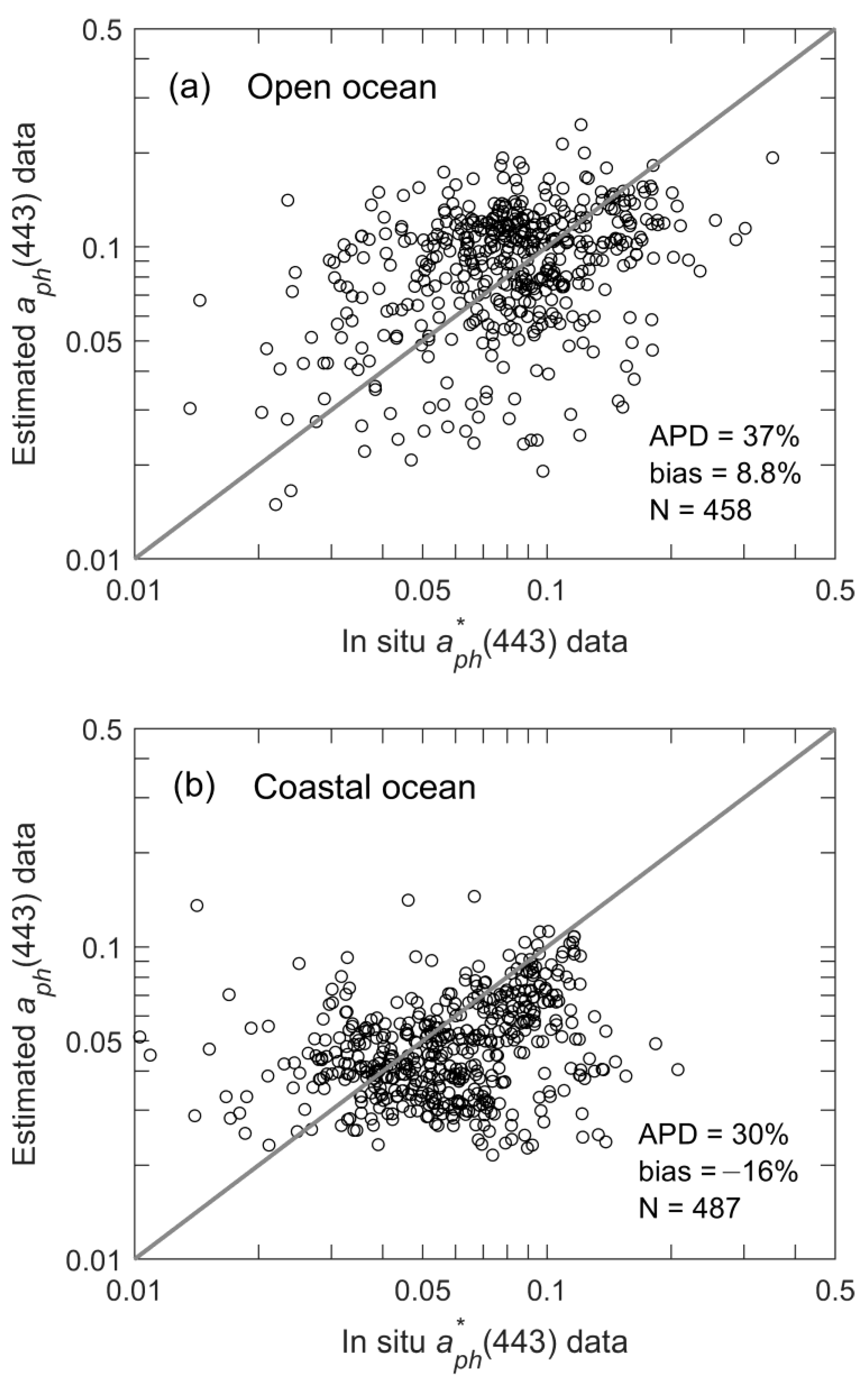
3.3. Dependence of on Chl-a Concentration
3.4. Estimation of as a Function of Geolocation and Time
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, D.A.; Buesseler, K.O.; Doney, S.C.; Sailley, S.F.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boyd, P.W. Global assessment of ocean carbon export by combining satellite observations and food-web models. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Forget, M.-H.; White, G.N., III; Caverhill, C.; Bouman, H.; Devred, E.; Son, S. Operational estimation of primary production at large geographical scales. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3437–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoepffner, N.; Sathyendranath, S. Effect of pigment composition on absorption properties of phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 73, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Mikelsons, K.; Jiang, L.; Kratzer, S.; Lee, Z.P.; Moore, T.; Sosik, H.M.; Van der Zande, D. Global satellite water classification data products over oceanic, coastal, and inland waters. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, L.; Sathyendranath, S. An optical classification of coastal and oceanic waters based on the specific spectral absorption curves of phytoplankton pigments, dissolved organic matter, and other particulate materials. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Claustre, H. Variability in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: Analysis and parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13321–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Babin, M.; Allali, K.; Claustre, H. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: Analysis and implications for bio-optical models. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 31033–31044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Stramski, D.; Ferrari, G.M.; Claustre, H.; Bricaud, A.; Obolensky, G.; Hoepffner, N. Variations in the light absorption coefficients of phytoplankton, nonalgal particles, and dissolved organic matter in coastal waters around Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, J.S. Regional models for phytoplankton absorption as a function of chlorophyll a concentration. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13333–13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Feldman, G.C.; Boss, E.; Brando, V.E.; Dowell, M.; Hirata, T.; Lavender, S.J.; Lee, Z.P.; et al. Generalized ocean color inversion model for retrieving marine inherent optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Peters, S.W.M.; van der Woerd, H.J.; Eleveld, M.A.; Ruddick, K.; Schönfeld, W.; Krasemann, H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Röttgers, R.; et al. Variability in specific-absorption properties and their use in a semi-analytical ocean colour algorithm for MERIS in North Sea and Western English Channel Coastal Waters. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; DiGiacomo, P.M. Remote sensing of chlorophyll-a in coastal waters based on the light absorption coefficient of phytoplankton. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carder, K.L.; Chen, F.R.; Lee, Z.P.; Hawes, S.K.; Kamykowski, D. Semianalytic Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectrometer algorithms for chlorophyll-a and absorption with bio-optical domains based on nitrate-depletion temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 5403–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A. Light and marine photosynthesis: A spectral model with geochemical and climatological implications. Prog. Oceanogr. 1991, 26, 263–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitz, J.; Claustre, H.; Gentili, B.; Stramski, D. Phytoplankton class-specific primary production in the world's oceans: Seasonal and interannual variability from satellite observations. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, GB3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidigare, R.R.; Ondrusek, M.E.; Morrow, J.H.; Kiefer, D.A. In vivo absorption properties of algal pigments. In Ocean Optics X; Society of Photo Optical: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1990; pp. 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Letelier, R.M.; White, A.E.; Bidigare, R.R.; Barone, B.; Church, M.J.; Karl, D.M. Light absorption by phytoplankton in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Boss, E.; Chase, A.; Xi, H.; Zhang, X.; Röttgers, R.; Pan, Y.; Bracher, A. Retrieval of phytoplankton pigments from underway spectrophotometry in the Fram Strait. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, T.A.; Rufty, K.M.; Moisan, J.R.; Linkswiler, M.A. Satellite observations of phytoplankton functional type spatial distributions, phenology, diversity, and ecotones. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, A.M.; Bricaud, A. Retrievals of a size parameter for phytoplankton and spectral light absorption by colored detrital matter from water-leaving radiances at SeaWiFS channels in a continental shelf region off Brazil. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2006, 4, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Bouman, H.; Platt, T. The global distribution of phytoplankton size spectrum and size classes from their light-absorption spectra derived from satellite data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Cao, W.; Shen, F. Retrieval of phytoplankton cell size from chlorophyll a specific absorption and scattering spectra of phytoplankton. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 8362–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Devred, E.; Sathyendranath, S.; Lavender, S.J.; Hardman-Mountford, N.J. Model of phytoplankton absorption based on three size classes. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 4535–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitz, J.; Huot, Y.; Bruyant, F.; Babin, M.; Claustre, H. Relating phytoplankton photophysiological properties to community structure on large scales. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devred, E.; Perry, T.; Massicotte, P. Seasonal and decadal variations in absorption properties of phytoplankton and non-algal particulate matter in three oceanic regimes of the Northwest Atlantic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 932184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilova, T.; Suslin, V.; Krivenko, O.; Efimova, T.; Moiseeva, N.; Mukhanov, V.; Smirnova, L. Light absorption by phytoplankton in the upper mixed layer of the Black Sea: Seasonality and parametrization. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, J.M.; Gómez-Jakobsen, F. Seasonal variability in phytoplankton light absorption properties: Implications for the regional parameterization of the chlorophyll a specific absorption coefficients. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 232, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, A.; Hill, V.; Huot, Y.; Babin, M.; Bricaud, A. Seasonal variability in the light absorption properties of western Arctic waters: Parameterization of the individual components of absorption for ocean color applications. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Miyamura, T.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Ishizaka, J. Seasonal variation of absorption by particles and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Funka Bay, southwestern Hokkaido, Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Stuart, V.; Irwin, B.D.; Maass, H.; Savidge, G.; Gilpin, L.; Platt, T. Seasonal variations in bio-optical properties of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1999, 46, 633–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, L.; Hu, C.; Varela, R.; Arias, G.; Guzmán, L.; Muller-Karger, F. Bio-optical characteristics of Cariaco Basin (Caribbean Sea) waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Son, S. The VIIRS ocean color product algorithm theoretical basis document version 1.0. In NOAA NESDIS STAR Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD); NOAA NESDIS Center for Satellite Applications and Research: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Shi, W.; Rausch, K.; Voss, K.J. Impacts of VIIRS SDR performance on ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean Color Products, 10th ed.; International Ocean Color Coordinating Group: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, M. Improved near-infrared ocean reflectance correction algorithm for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 21657–21678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Ocean reflectance spectra at the red, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared from highly turbid waters: A study in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Ondrusek, M.; Gilerson, A.; Goes, J.; Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Voss, K.J.; Ladner, S.; Lance, V.P.; et al. Satellite ocean color validation. In Field Measurements for Passive Environmental Remote Sensing: Instrumentation, Intensive Campaigns, and Satellite Applications; Nalli, N., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 351–374. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Yu, X.; Lee, Z.P.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Improving low-quality satellite remote sensing reflectance at blue bands over coastal and inland waters. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaing, S.; Harmel, T.; Gilerson, A.; Foster, R.; Weidemann, A.D.; Arnone, R.; Wang, M.; Ahmed, S. Evaluation of the VIIRS ocean color monitoring performance in coastal regions. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrusek, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Stengel, E.; Kovach, C.; Gilerson, A.; Herrera, E.; Malinowski, M.; Goes, J.I.; Gomes, H.d.R.; et al. Report for dedicated JPSS VIIRS ocean color calibration/validation cruise: Gulf of Mexico in April 2021. In NOAA Technical Report NESDIS 157; NOAA National Environmental Satellite, Data Information, Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Mikelsons, K.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. Statistical evaluation of satellite ocean color data retrievals. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. On the interplay between ocean color data quality and data quantity: Impacts of quality control flags. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.B.; Cannizzaro, J.P.; English, D.C.; Hu, C. Validation of VIIRS and MODIS reflectance data in coastal and oceanic waters: An assessment of methods. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Watanabe, S. Satellite-measured water properties in high altitude Lake Tahoe. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S. VIIRS-derived chlorophyll-a using the ocean color index method. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.P.; Franz, B. Chlorophyll a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2156–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. A blended inherent optical property algorithm for global satellite ocean color observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2019, 17, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multi-band quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.W.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications, 5th ed.; International Ocean Color Coordinating Group: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2006; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.W.; Blaisdell, J.M.; Darzi, M. Level-3 SeaWiFS Data Products: Spatial and Temporal Binning Algorithms; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1995; p. 104566. [Google Scholar]
- Moisan, J.R.; Moisan, T.A.H.; Linkswiler, M.A. An inverse modeling approach to estimating phytoplankton pigment concentrations from phytoplankton absorption spectra. J. Geophys. Res. -Ocean. 2011, 116, C09018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarcq, H.; Reygondeau, G.; Alvain, S.; Vantrepotte, V. Monitoring marine phytoplankton seasonality from space. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandonneau, Y.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Loisel, H.; Blanchot, J.; Montel, Y.; Thieuleux, F.; Bécu, G. Seasonal and interannual variability of ocean color and composition of phytoplankton communities in the North Atlantic, equatorial Pacific and South Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Mao, Z.; Jamet, C.; Linderman, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Seasonal cycles of phytoplankton expressed by sine equations using the daily climatology from satellite-retrieved chlorophyll-a concentration (1997–2019) over global ocean. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, J.A.; O'Reilly, J.E.; Barnard, A.H.; Moore, T.S.; Ruhsam, C.M. Variability in coastal zone color scanner (CZCS) Chlorophyll imagery of ocean margin waters off the US East Coast. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 1191–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, B.; Dera, J.; Ficek, D.; Majchrowski, R.; Kaczmarek, S.; Ostrowska, M.; Koblentz-Mishke, O.I. Modelling the influence of acclimation on the absorption properties of marine phytoplankton. Oceanologia 1999, 41, 187–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zoffoli, M.L.; Lee, Z.; Marra, J.F. Regionalization and dynamic parameterization of quantum yield of photosynthesis to improve the ocean primary production estimates from remote sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Bricaud, A.; Carder, K.L.; Cleveland, J.; Ferrari, G.M.; Gould, R.; Kahru, M.; Kishino, M.; Maske, H.; Moisan, T.; et al. Determination of Spectral Absorption Coefficients of Particles, Dissolved Material, and Phytoplankton for Discrete Water Samples; Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA: Greenbelt, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 125–153. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, A.; Sathyendranath, S.; Brotas, V.; Groom, S.; Grant, M.; Taberner, M.; Antoine, D.; Arnone, R.; Balch, W.M.; Barker, K.; et al. A compilation of global bio-optical in situ data for ocean-colour satellite applications—Version two. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1037–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, J.; Bailey, S.W. The SeaWiFS Bio-Optical Archive and Storage System (SeaBASS): Current Architecture and Implementation; NASA/TM-2002-211617; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.; Fargion, G.; McClain, C.R. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Validation, Revision 4, Volume IV: Inherent Optical Properties: Instruments, Characterizations, Field Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, C.R.; Signorini, S.R.; Christian, J.R. Subtropical gyre variability observed by ocean-color satellites. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2004, 51, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, R.; Stuart, V.; Lutz, V.; Sessions, H.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T.; Kyewalyanga, M.; Clementson, L.; Fukasawa, M.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Seasonal pigment patterns of surface phytoplankton in the subtropical southern hemisphere. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvain, S.; Moulin, C.; Dandonneau, Y.; Loisel, H. Seasonal distribution and succession of dominant phytoplankton groups in the global ocean: A satellite view. Glob. Biogeochem Cycles 2008, 22, GB3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A. Ecological Geography of the Sea; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; p. 398. [Google Scholar]
- Organelli, E.; Nuccio, C.; Melillo, C.; Massi, L. Relationships between phytoplankton light absorption, pigment composition and size structure in offshore areas of the Mediterranean Sea. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2011, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Babin, M.; Claustre, H.; Ras, J.; Tieche, F. Light absorption properties and absorption budget of Southeast Pacific waters. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C08009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Partensky, F.; Vaulot, D.; Claustre, H. Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus: A comparative study of their optical properties in relation to their size and pigmentation. J. Mar. Res. 1993, 51, 617–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, K.; Bricaud, A.; Claustre, H. Spatial variations in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of phytoplankton and photosynthetically active pigments in the equatorial Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 12413–12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meler, J.; Ostrowska, M.; Ficek, D.; Zdun, A. Light absorption by phytoplankton in the southern Baltic and Pomeranian lakes: Mathematical expressions for remote sensing applications. Oceanologia 2017, 59, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.J.; Roesler, C.S. Unraveling phytoplankton optical variability in the Gulf of Maine during the spring and fall transition period. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 61–62, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Larouche, P.; Tang, S.; Michel, C. Seasonal variability of light absorption properties and water optical constituents in Hudson Bay, Canada. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 3087–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nababan, B. Bio-Optical Variability of Surface Waters in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico; University of South Florida: Tampa, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sapiano, M.R.P.; Brown, C.W.; Schollaert Uz, S.; Vargas, M. Establishing a global climatology of marine phytoplankton phenological characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C08026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelsons, K.; Wang, M. Optimal satellite orbit configuration for global ocean color product coverage. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A445–A457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; Antoine, D.; D'Ortenzio, F.; de Boyer Montégut, C. Phytoplankton spring and fall blooms in the North Atlantic in the 1980s and 2000s. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Phytoplankton biomass dynamics in the Arabian Sea from VIIRS observations. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 227, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, S.A.; Carton, J.A.; McClain, C.R. Variability of upwelling and chlorophyll in the equatorial Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L03610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, C.B.; Larouche, P.; Gosselin, M. Variability of phytoplankton light absorption in Canadian Arctic seas. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C00G17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, V.A.; Sathyendranath, S.; Head, E.J.H. Absorption coefficient of phytoplankton: Regional variations in the North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 135, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, A.M.; Marlon, R.L.; Cullen, J.J. Assessment of the relationships between dominant cell size in natural phytoplankton communities and the spectral shape of the absorption coefficient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, D.; Chami, M.; Brown, I.; Calzado, V.S.; Doxaran, D.; Cunningham, A. Role of measurement uncertainties in observed variability in the spectral backscattering ratio: A case study in mineral-rich coastal waters. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 4663–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Campbell, J.W.; Dowell, M.D. A class-based approach to characterizing and mapping the uncertainty of the MODIS ocean chlorophyll product. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; O'Malley, R.T.; Siegel, D.A.; McClain, C.R.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Feldman, G.C.; Willigan, A.J.; Falkowski, P.G.; Letelier, R.M.; Boss, E.S. Climate-driven trends in contemporary ocean productivity. Nature 2006, 444, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yu, J.; Ho, T.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Kong, L.; Liu, H. Dynamics of phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea in response to the East Asian aerosol input. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Gap Filling of Missing Data for VIIRS Global Ocean Color Products Using the DINEOF Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2018, 56, 4464–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Global daily gap-free ocean color products from multi-satellite measurements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Satellite Data (2014–2017) | In Situ Data | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Min. | Max. | STD | CV | Range of Variation | Observation Time | ||
| Open Ocean | North Atlantic Gyre | 0.114 | 0.090 | 0.141 | 0.015 | 13% | 0.13 [72] | — |
| South Atlantic Gyre | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.159 | 0.017 | 13% | — | ||
| North Pacific Gyre | 0.147 | 0.120 | 0.172 | 0.021 | 14% | 0.070–0.140 [17] | January–December | |
| South Pacific Gyre | 0.155 | 0.117 | 0.189 | 0.025 | 16% | 0.070–0.100 [71] | October–December | |
| Indian Ocean Gyre | 0.125 | 0.093 | 0.161 | 0.020 | 16% | — | ||
| Equatorial Pacific | 0.115 | 0.106 | 0.137 | 0.007 | 6% | 0.080–0.130 [73] | November | |
| South China Sea | 0.104 | 0.079 | 0.125 | 0.012 | 12% | — | — | |
| Gulf of Mexico | 0.093 | 0.073 | 0.116 | 0.012 | 13% | — | — | |
| Mediterranean Sea | 0.062 | 0.038 | 0.084 | 0.011 | 18% | 0.023–0.165 [70] | September–November | |
| Coastal Ocean | Baltic Sea | 0.043 | 0.034 | 0.097 | 0.013 | 30% | 0.016–0.124 [74] | March–May, August–October |
| Black Sea | 0.036 | 0.022 | 0.056 | 0.009 | 25% | 0.030–0.115 [26] | August–September, November–December | |
| Gulf of Maine | 0.048 | 0.036 | 0.110 | 0.016 | 33% | 0.040–0.079 [75] | April, October | |
| Hudson Bay | 0.048 | 0.031 | 0.170 | 0.034 | 71% | 0.019–0.125 [76] | July, September–October | |
| Long Island Sound | 0.035 | 0.023 | 0.058 | 0.010 | 29% | — | — | |
| Gulf of Mexico | 0.054 | 0.040 | 0.079 | 0.009 | 17% | 0.020–0.150 [77] | April–May, July–August, November | |
| Yellow Sea | 0.045 | 0.023 | 0.062 | 0.010 | 22% | — | — | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Mikelsons, K.; Jiang, L. Chlorophyll-Specific Absorption Coefficient of Phytoplankton in World Oceans: Seasonal and Regional Variability. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092423
Wei J, Wang M, Mikelsons K, Jiang L. Chlorophyll-Specific Absorption Coefficient of Phytoplankton in World Oceans: Seasonal and Regional Variability. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092423
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jianwei, Menghua Wang, Karlis Mikelsons, and Lide Jiang. 2023. "Chlorophyll-Specific Absorption Coefficient of Phytoplankton in World Oceans: Seasonal and Regional Variability" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092423
APA StyleWei, J., Wang, M., Mikelsons, K., & Jiang, L. (2023). Chlorophyll-Specific Absorption Coefficient of Phytoplankton in World Oceans: Seasonal and Regional Variability. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092423










