How Do Underwater Cultural Heritage Sites Affect Coral Assemblages?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Three-Dimensional Photogrammetry Surveys
2.2. 3D Reconstructions and Annotations
2.3. Data Analysis
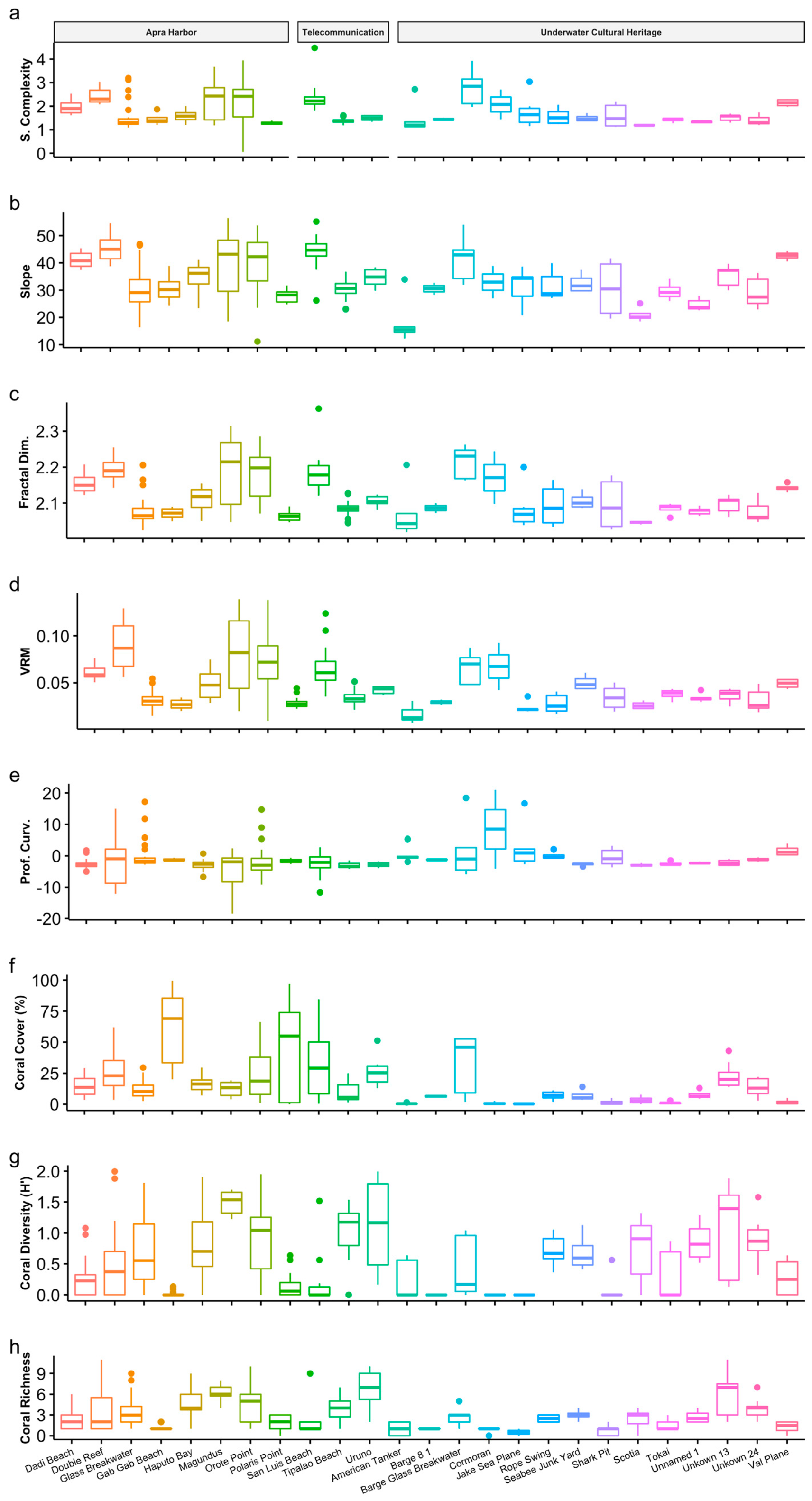
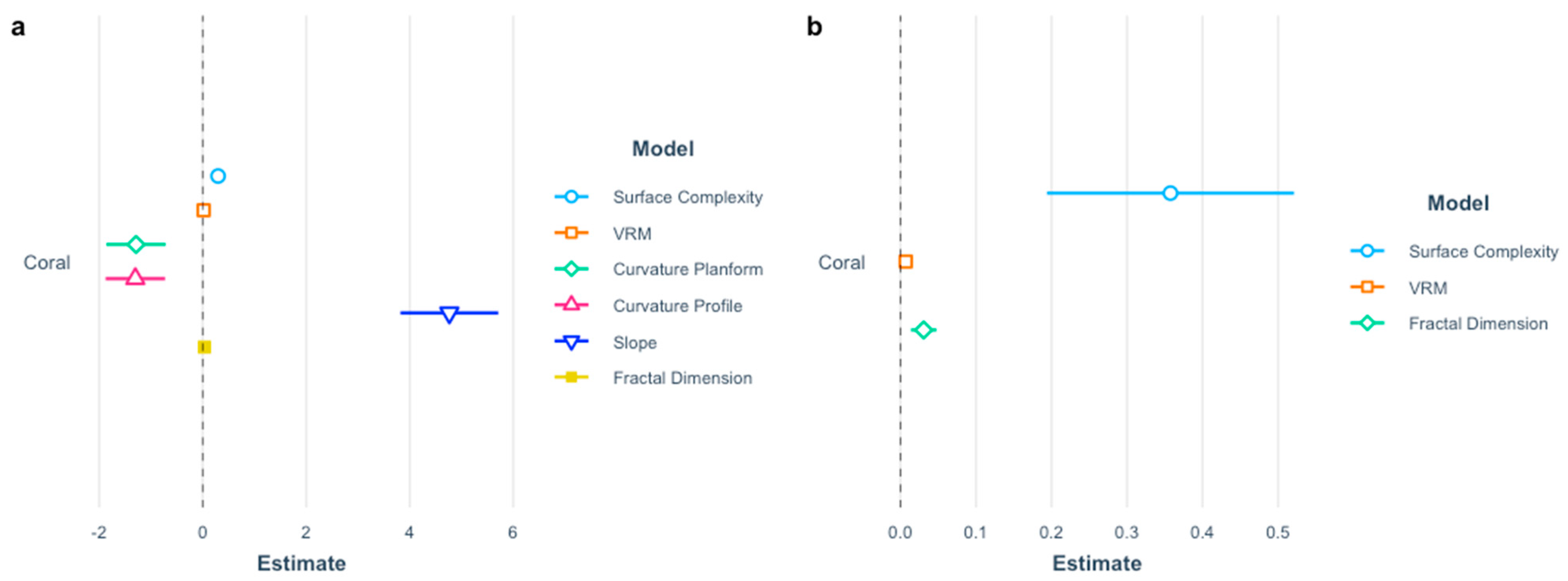
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrell, T. Submerged Cultural Resources Assessment of Micronesia; Southwest Region, Southwest Cultural Resources Center, Submerged Cultural Resources Unit; National Park Service: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 1991; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Carrell, T. Maritime History and Archaeology of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; Ships of Exploration and Discovery Research: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, P.; Martino, A.; Romeo, T.; Sinopoli, M.; Perzia, P.; Canese, S.; Vivona, P.; Andaloro, F. The effect of shipwrecks on associated fish assemblages in the central Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2015, 95, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schyff, V.; Du Preez, M.; Blom, K.; Kylin, H.; Yive, N.S.C.K.; Merven, J.; Raffin, J.; Bouwman, H. Impacts of a shallow shipwreck on a coral reef: A case study from St. Brandon’s Atoll, Mauritius, Indian Ocean. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 156, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asner, G.P.; Giardina, S.F.; Balzotti, C.; Drury, C.; Hopson, S.; Martin, R.E. Are Sunken Warships Biodiversity Havens for Corals? Diversity 2022, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.W.; Barott, K.L.; Dinsdale, E.; Friedlander, A.M.; Nosrat, B.; Obura, D.; Sala, E.; Sandin, S.A.; Smith, J.E.; Vermeij, M.J.A.; et al. Black reefs: Iron-induced phase shifts on coral reefs. ISME J. 2012, 6, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.H.R.; Bahr, K.D.; Fukunaga, A.; Swatland, D.; Kosaki, R. Innovative 3D Imaging Tools for Assessing Damages to Coral Reef Habitats Caused by Grounding Events; DOC Marine Conservation Services Series; The National Science Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga, A.; Kosaki, R.K.; Pascoe, K.H.; Burns, J.H.R. Fish assemblage structure in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands is associated with the architectural complexity of coral-reef habitats. Diversity 2020, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, K.H.; Fukunaga, A.; Kosaki, R.K.; Burns, J.H.R. 3D assessment of a coral reef at Lalo Atoll reveals varying responses of habitat metrics following a catastrophic hurricane. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, A.-F.; Dulvy, N.K.; Gill, J.A.; Côté, I.M.; Watkinson, A.R. Flattening of Caribbean coral reefs: Region-wide declines in architectural complexity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 3019–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, N.A.J.; Nash, K.L. The importance of structural complexity in coral reef ecosystems. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.A.J.; Jennings, S.; MacNeil, M.A.; Mouillot, D.; Wilson, S.K. Predicting climate-driven regime shifts versus rebound potential in coral reefs. Nature 2015, 518, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.S.; Burns, J.H.R.; Liu, G.; Steward, K.; Gutlay, T.N.; Kenyon, J.; Eakin, C.M.; Kosaki, R.K. Mass coral bleaching due to unprecedented marine heatwave in Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument (Northwestern Hawaiian Islands). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O.; MacArthur, R.H. The Theory of Island Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, J.F. Habitat modification and facilitation in benthic marine communities. In Marine Community Ecology; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Filip, L.; Dulvy, N.K.; Côté, I.M.; Watkinson, A.R.; Gill, J.A. Coral identity underpins architectural complexity on Caribbean reefs. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, R.D.; Ainsworth, T.D. The nature and taxonomic composition of coral symbiomes as drivers of performance limits in scleractinian corals. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 408, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Burns, J.H.R.; Pascoe, K.H.; Kosaki, R.K. Associations between benthic cover and habitat complexity metrics obtained from 3D reconstruction of coral reefs at different resolutions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, N.K.; Burns, J.H.R.; Green, S.J. Intra-habitat structural complexity drives the distribution of fish trait groups on coral reefs. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P.J.; Hooten, A.J.; Steneck, R.S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C.D.; Sale, P.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Caldeira, K.; et al. Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 2007, 318, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S.; Trapon, M.; Berumen, M.L.; Chong-Seng, K. Recent disturbances augment community shifts in coral assemblages in Moorea, French Polynesia. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magel, J.M.T.; Burns, J.H.R.; Gates, R.D.; Baum, J.K. Effects of bleaching-associated mass coral mortality on reef structural complexity across a gradient of local disturbance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Gamiño, J.L.; Hanson, K.M.; Stat, M.; Gates, R.D. Phenotypic plasticity of the coral Porites rus: Acclimatization responses to a turbid environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 434, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.H.R.; Delparte, D.; Kapono, L.; Belt, M.; Gates, R.D.; Takabayashi, M. Assessing the impact of acute disturbances on the structure and composition of a coral community using innovative 3D reconstruction techniques. Methods Oceanogr. 2016, 15, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.H. Final Report [Apra Harbor, Guam]; California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.S.; McManus, J.; Richmond, R.H.; King, D.B., Jr.; Gailani, J.Z.; Lackey, T.C.; Bryant, D. Predicting dredging-associated effects to coral reefs in Apra Harbor, Guam–Part 2: Potential coral effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 168, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schils, T.; Houk, P.; Biggs, J.; Donaldson, T.; Kense, A.; McLean, M. Marine Resources Surveys of Naval Base Guam and Naval Support Activity Andersen Air Force Base; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 158. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.H.R.; Delparte, D.; Gates, R.D.; Takabayashi, M. Integrating structure-from-motion photogrammetry with geospatial software as a novel technique for quantifying 3D ecological characteristics of coral reefs. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueira, W.; Ferrari, R.; Weatherby, E.; Porter, A.; Hawes, S.; Byrne, M. Accuracy and precision of habitat structural complexity metrics derived from underwater photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16883–16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Burns, J.H.R.; Craig, B.K.; Kosaki, R.K. Integrating three-dimensional benthic habitat characterization techniques into ecological monitoring of coral reefs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G. Getting computer vision airborne: Using structure from motion for accurate orthophoto production. RSPSoc Archaeol. Spec. Interest Group Meet. Spring 2012, 2012, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijbom, O.; Edmunds, P.J.; Roelfsema, C.; Smith, J.; Kline, D.I.; Neal, B.P.; Dunlap, M.J.; Moriarty, V.; Fan, T.Y.; Tan, C.J.; et al. Towards automated annotation of benthic survey images: Variability of human experts and operational modes of automation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Burns, J.H.R. Metrics of coral reef structural complexity extracted from 3D mesh models and digital elevation models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- McArdle, B.H.; Anderson, M.J. Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 2001, 82, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Chapman, M.G. On resemblance measures for ecological studies, including taxonomic dissimilarities and a zero-adjusted Bray–Curtis coefficient for denuded assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in marine communities. Approach Stat. Anal. Interpret. 2001, 2, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.B.C. Adaptation and diversity of reef corals. BioScience 1991, 41, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, G.J.; Smith, J.E.; Conklin, E.J.; Gove, J.M.; Sala, E.; Sandin, S.A. Benthic communities at two remote Pacific coral reefs: Effects of reef habitat, depth, and wave energy gradients on spatial patterns. PeerJ 2013, 1, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Pascoe, K.H.; Pugh, A.R.; Kosaki, R.K.; Burns, J.H.R. Underwater photogrammetry captures the initial recovery of a coral reef at Lalo Atoll. Diversity 2022, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzhardinge, R.C.; Bailey-Brock, J.H. Colonization of artificial reef materials by corals and other sessile organisms. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 567–579. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, L.S. If you build it, will they come? Toward a concrete basis for coral reef gardening. In Coral Reef Restoration Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 119–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ninio, R.; Meekan, M. Spatial patterns in benthic communities and the dynamics of a mosaic ecosystem on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 2002, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, K.S.; Wu, B.-J.; Fang, L.-S.; Fan, T.-Y. Dynamics of a coral reef community after mass mortality of branching Acropora corals and an outbreak of anemones. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
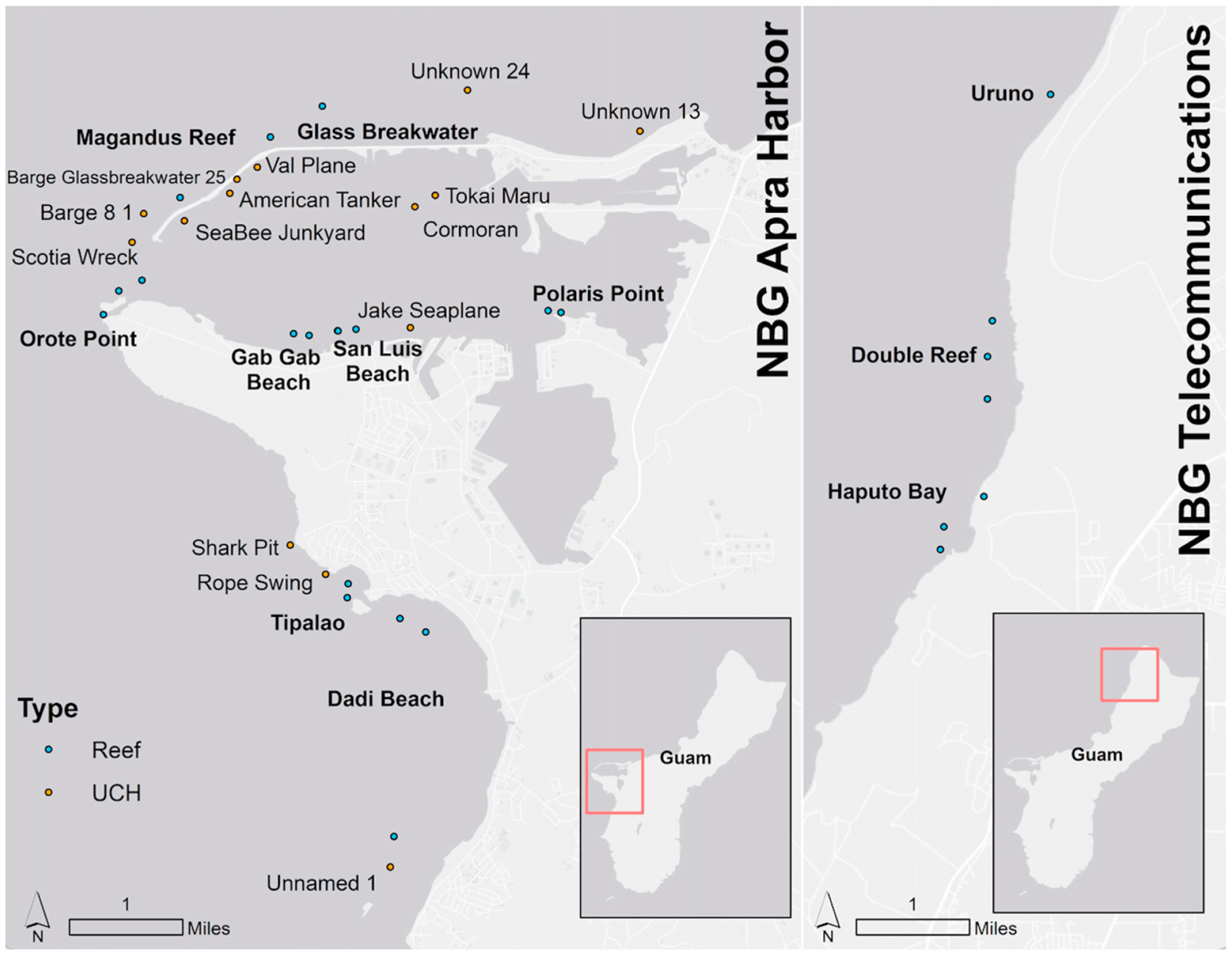


| UCH Site | Submerged Date | Era | Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Tanker | 09/30/1944 | WWII | Ferro Cement |
| Barge 8 1 | unknown | WWII | Steel |
| Barge Glass Breakwater | 09/24/1944 | WWII | Ferro Cement |
| Cormoran | 04/7/1917 | WWI | Steel, Wood |
| Jake Sea Plane | 05/1944–07/1944 | WWII | Aluminum |
| Rope Swing | 09/1945 | WWII | Mixed (War Debris) |
| Seabee Junk Yard | 09/1945 | WWII | Mixed (War Debris) |
| Shark Pit | 09/1945 | WWII | Mixed (War Debris) |
| Scotia | 03/11/1904 | 1904 | Iron, Wood |
| Tokai Maru | 08/27/1943 | WWII | Steel |
| Unnamed 1 (Amtrac) | 06/21/1944 | WWII | Steel |
| Unknown 13 | unknown | - | unknown metal |
| Unknown 24 | unknown | - | unknown metal |
| Val Plane | 06/19/1944 | WWII | Aluminum |
| (a) AP vs. UCH | |||||
| Genus | Av.Abund (AP) | Av.Abund (UCH) | Av.Diss | Diss/SD | Contrib% |
| Porites | 23.79 | 5.03 | 52.76 | 1.76 | 68.98 |
| Leptastrea | 0.88 | 0.92 | 5.34 | 0.81 | 6.99 |
| Montipora | 0.75 | 0.20 | 3.97 | 0.53 | 5.19 |
| Astreopora | 0.48 | 0.62 | 3.39 | 0.62 | 4.44 |
| Pocillopora | 0.35 | 0.39 | 2.40 | 0.77 | 3.13 |
| Leptoria | 0.27 | 0.05 | 1.37 | 0.80 | 1.79 |
| (b) TS vs. UCH | |||||
| Genus | Av.Abund (TS) | Av.Abund (UCH) | Av.Diss | Diss/SD | Contrib% |
| Porites | 14.89 | 5.03 | 46.35 | 1.96 | 61.97 |
| Montipora | 3.05 | 0.20 | 10.13 | 1.30 | 13.55 |
| Leptastrea | 0.71 | 0.92 | 3.61 | 1.22 | 4.83 |
| Millepora | 0.59 | 0.39 | 2.39 | 1.27 | 3.20 |
| Astreopora | 0.21 | 0.62 | 2.14 | 0.45 | 2.86 |
| Leptoria | 0.54 | 0.05 | 1.72 | 1.32 | 2.31 |
| Goniastrea | 0.50 | 0.06 | 1.57 | 0.89 | 2.10 |
| (a) AP | ||||
| Genus | Av.Abund | Av.Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% |
| Porites | 23.79 | 35.73 | 1.50 | 82.9 |
| Leptastrea | 0.88 | 1.86 | 0.46 | 4.33 |
| Montipora | 0.75 | 1.36 | 0.75 | 3.15 |
| (b) TS | ||||
| Genus | Av.Abund | Av.Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% |
| Porites | 14.89 | 53.22 | 15.98 | 82.05 |
| Montipora | 3.05 | 4.84 | 0.67 | 7.46 |
| (c) UCH | ||||
| Genus | Av.Abund | Av.Sim | Sim/SD | Contrib% |
| Porites | 5.03 | 9.63 | 0.67 | 55.8 |
| Leptastrea | 0.92 | 2.9 | 0.42 | 16.8 |
| Astreopora | 0.62 | 1.85 | 0.58 | 10.72 |
| Lobophyllia | 0.09 | 1.15 | 0.20 | 6.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burns, J.H.R.; Pascoe, K.H.; Ferreira, S.B.; Kane, H.; Kapono, C.; Carrell, T.L.; Reyes, A.; Fukunaga, A. How Do Underwater Cultural Heritage Sites Affect Coral Assemblages? Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082130
Burns JHR, Pascoe KH, Ferreira SB, Kane H, Kapono C, Carrell TL, Reyes A, Fukunaga A. How Do Underwater Cultural Heritage Sites Affect Coral Assemblages? Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(8):2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082130
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurns, John H. R., Kailey H. Pascoe, Sofia B. Ferreira, Haunani Kane, Clifford Kapono, Toni L. Carrell, Andres Reyes, and Atsuko Fukunaga. 2023. "How Do Underwater Cultural Heritage Sites Affect Coral Assemblages?" Remote Sensing 15, no. 8: 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082130
APA StyleBurns, J. H. R., Pascoe, K. H., Ferreira, S. B., Kane, H., Kapono, C., Carrell, T. L., Reyes, A., & Fukunaga, A. (2023). How Do Underwater Cultural Heritage Sites Affect Coral Assemblages? Remote Sensing, 15(8), 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082130










