Land Subsidence in a Coastal City Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring: A Case Study of Zhuhai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
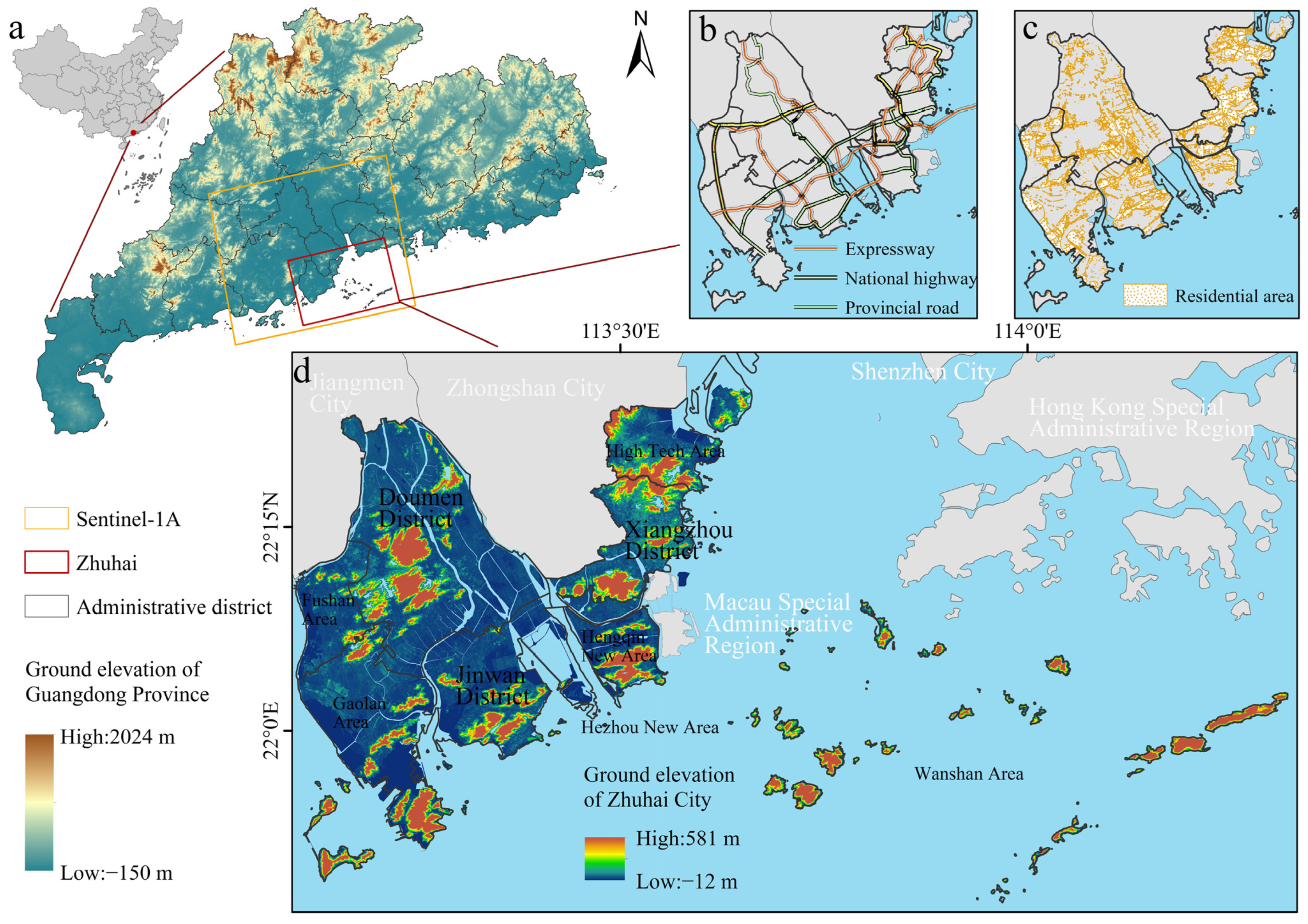
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SBAS-InSAR Technology
2.3. Research Data
2.4. Research Method
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Land Subsidence
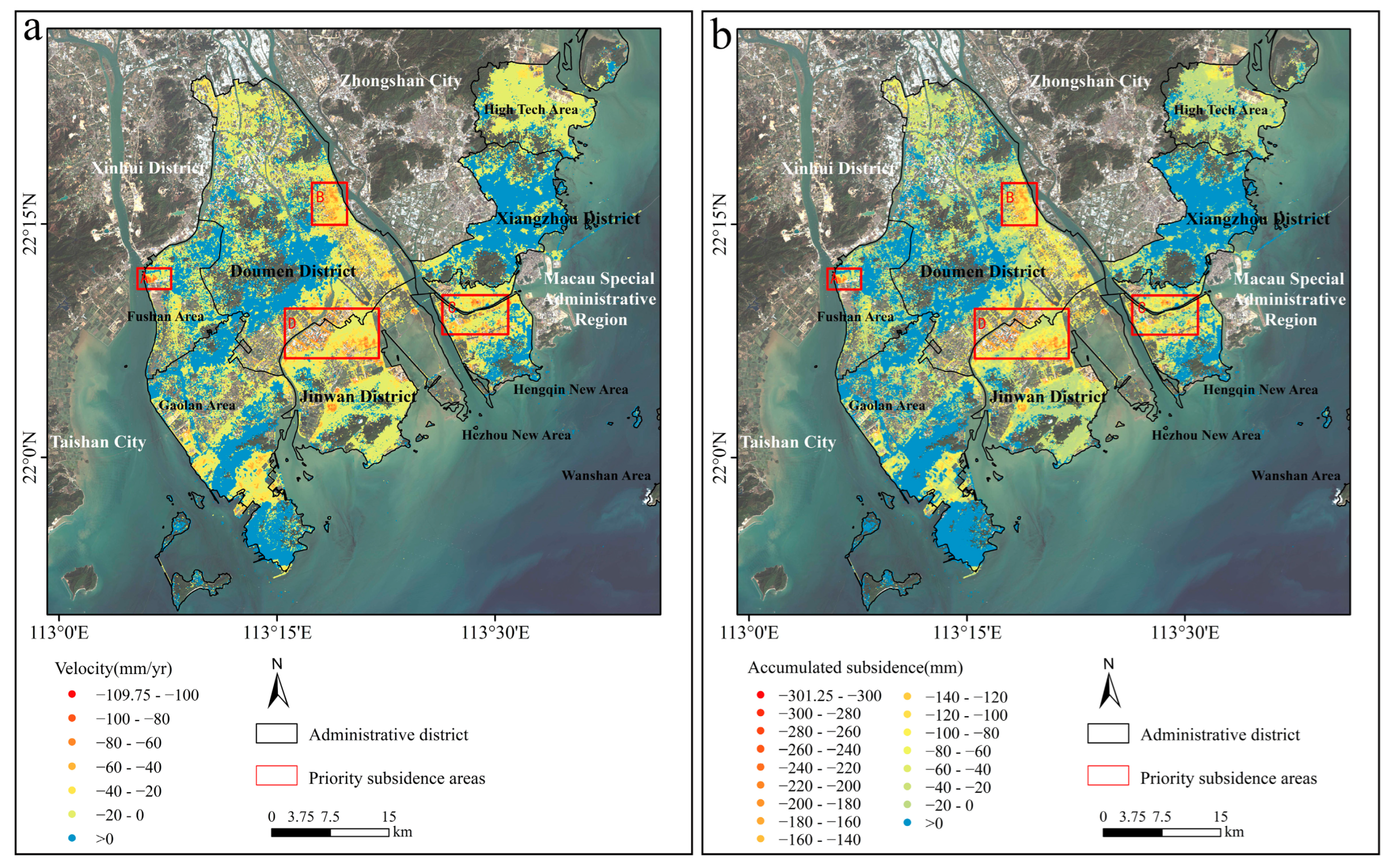
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
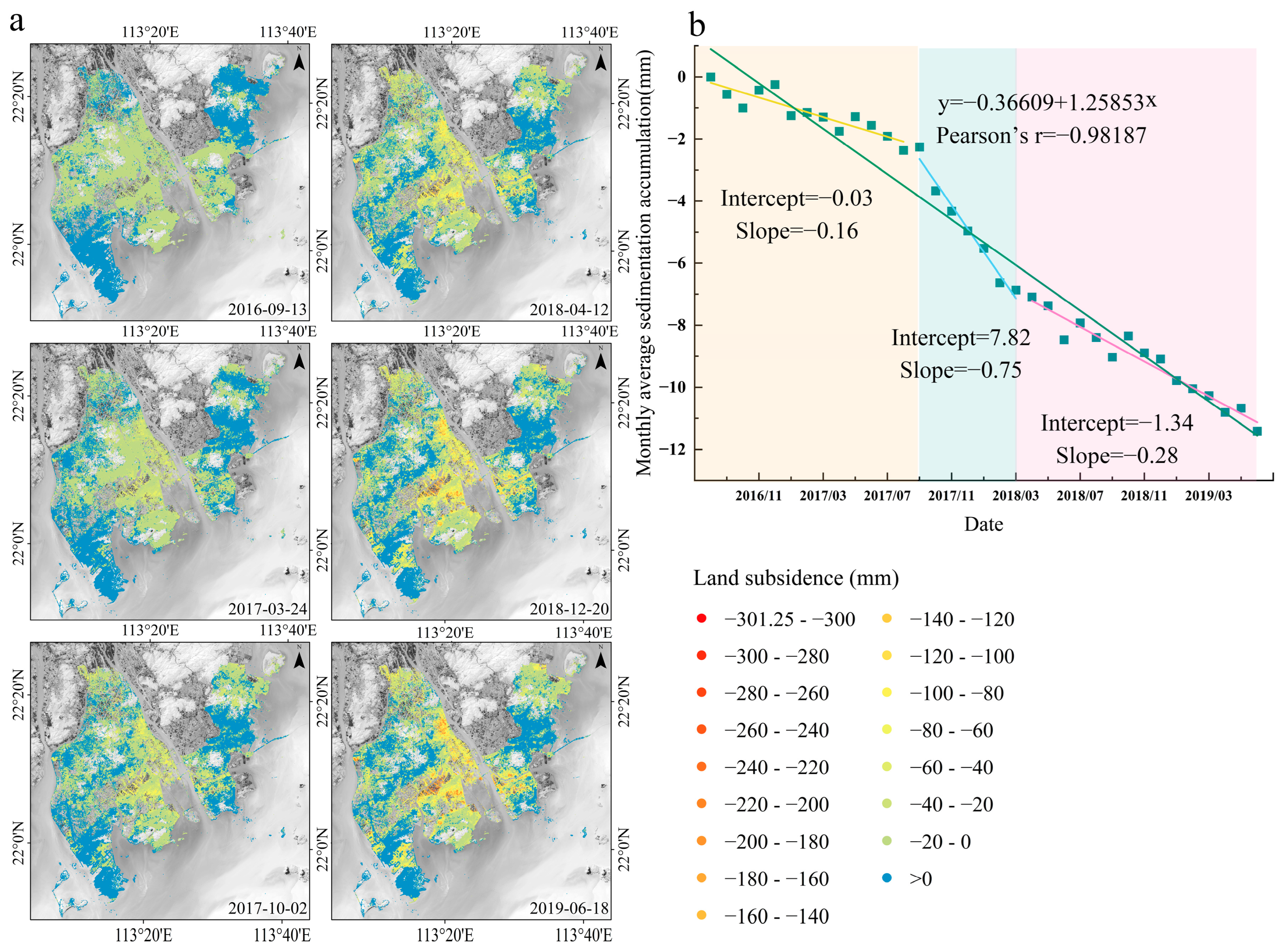
3.1.2. Time-Series Evolution Characteristics
3.2. Exploration of Subsidence Trigger Factors
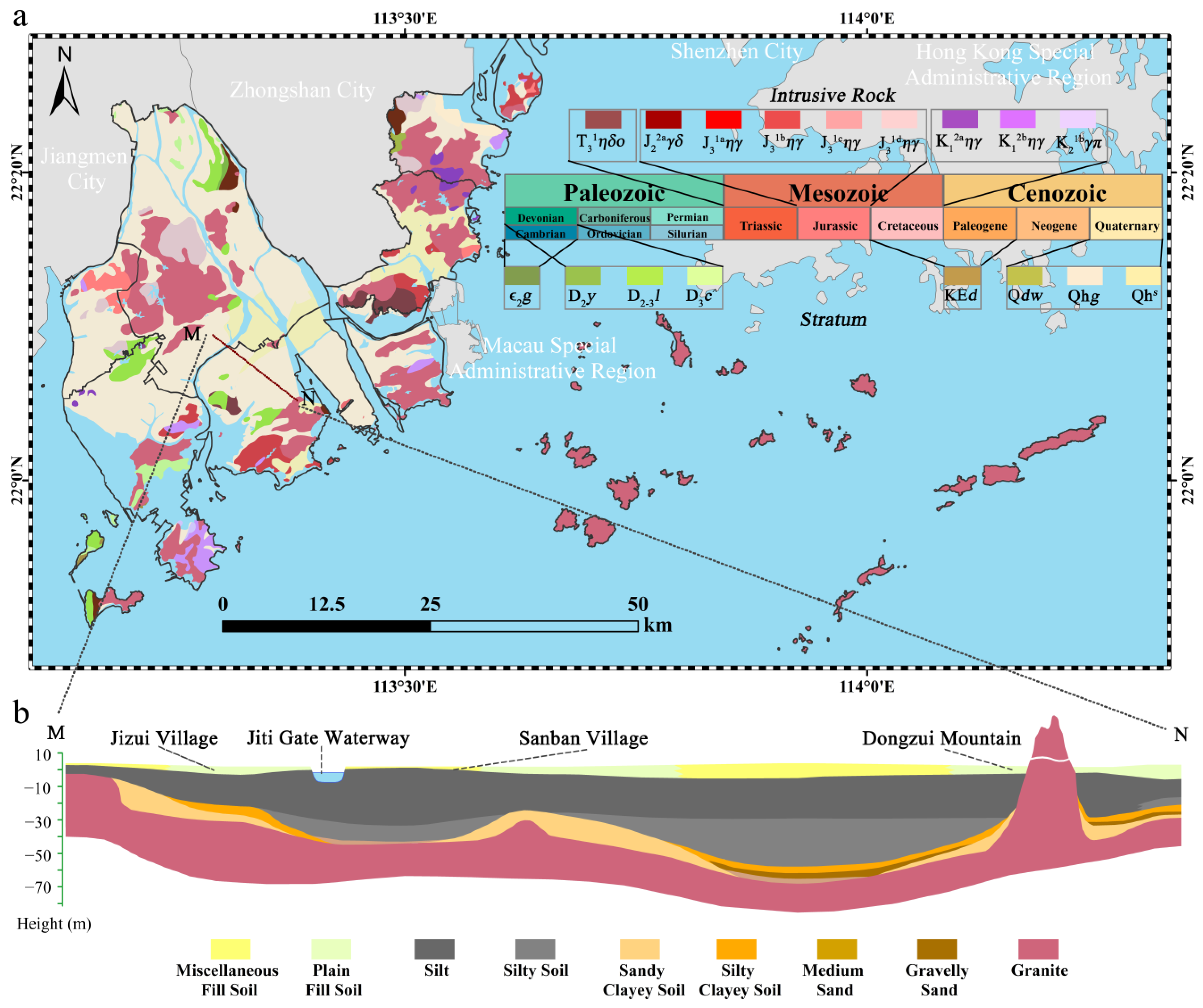
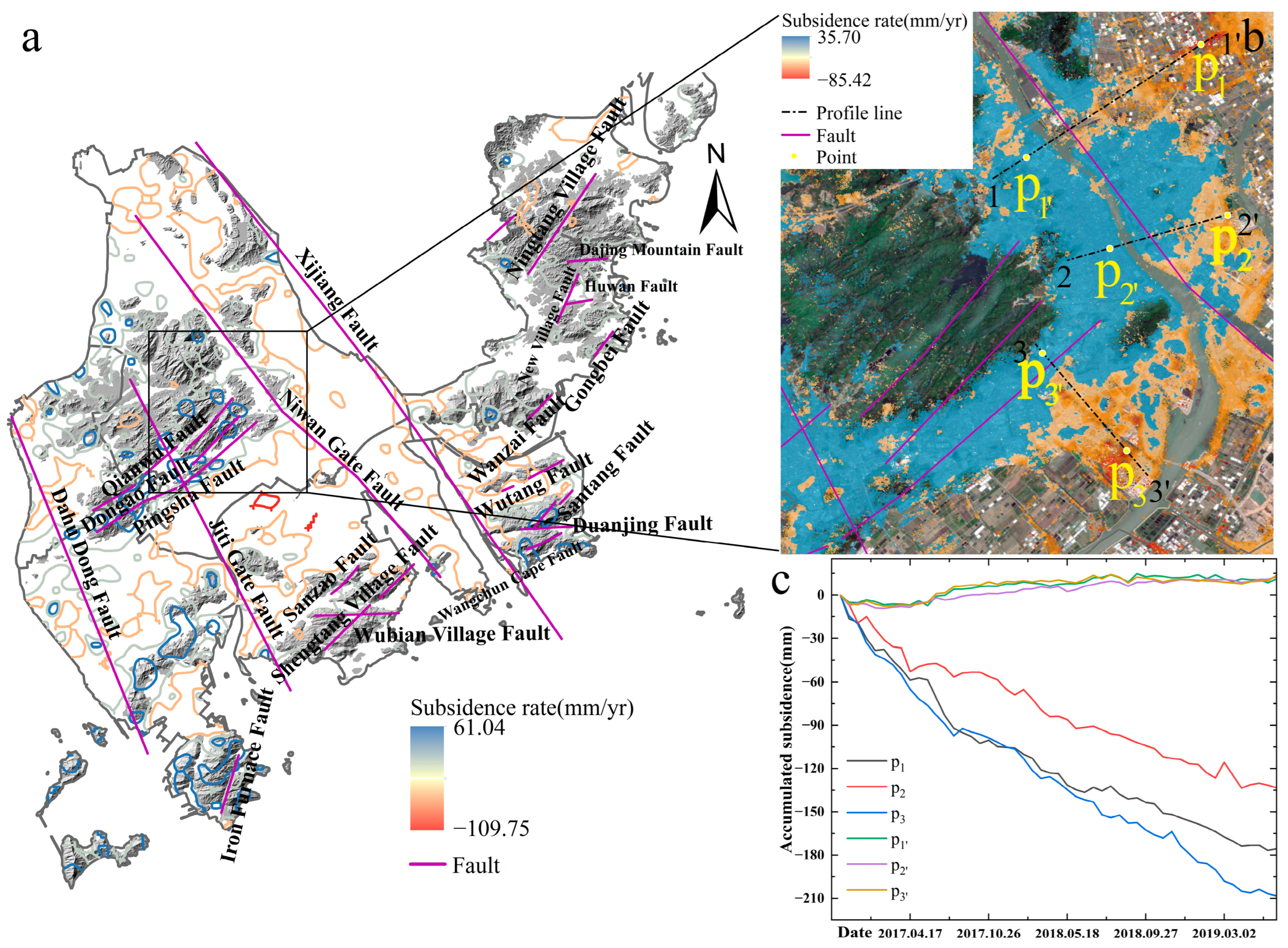
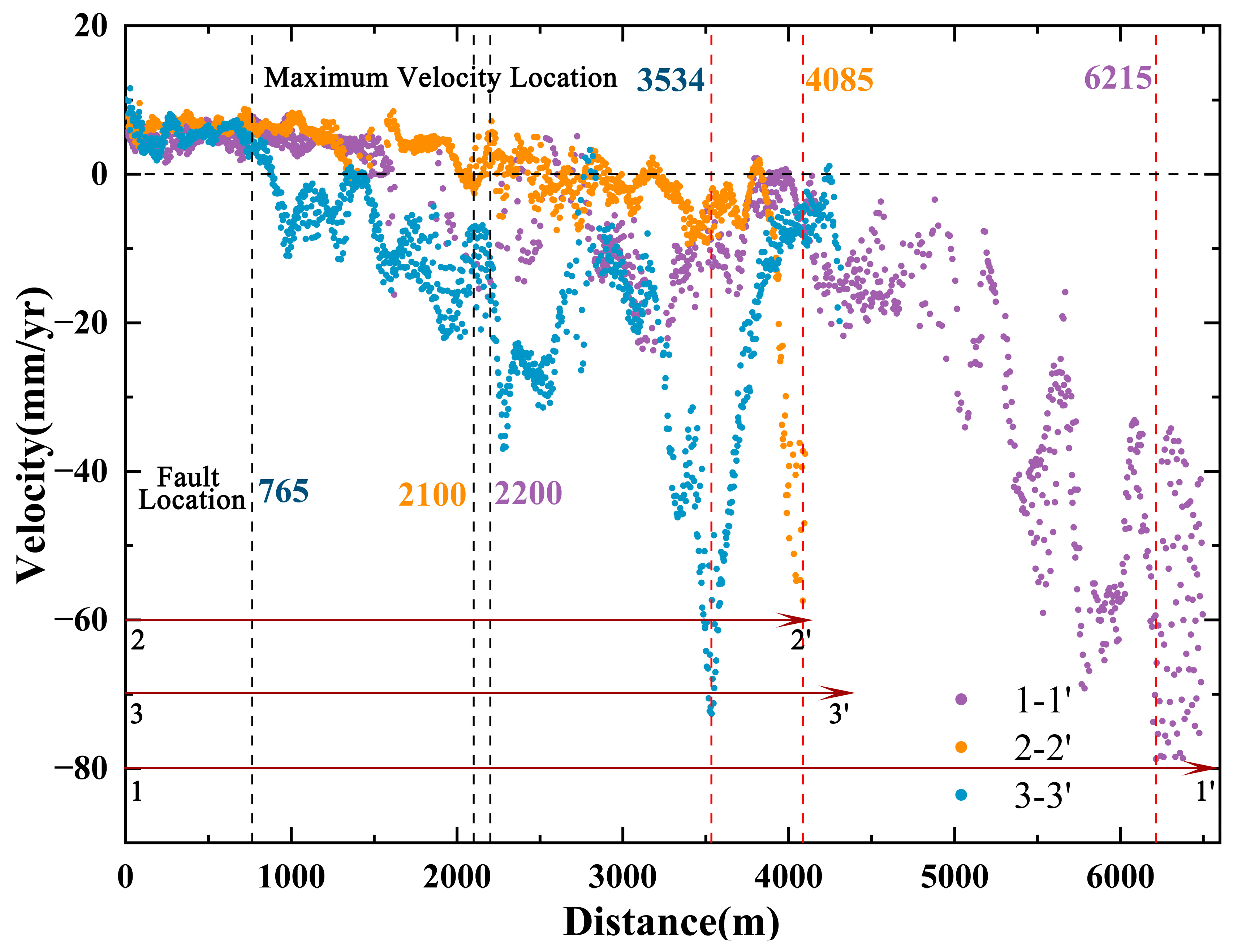
3.2.1. Fracture Structure and Land Subsidence
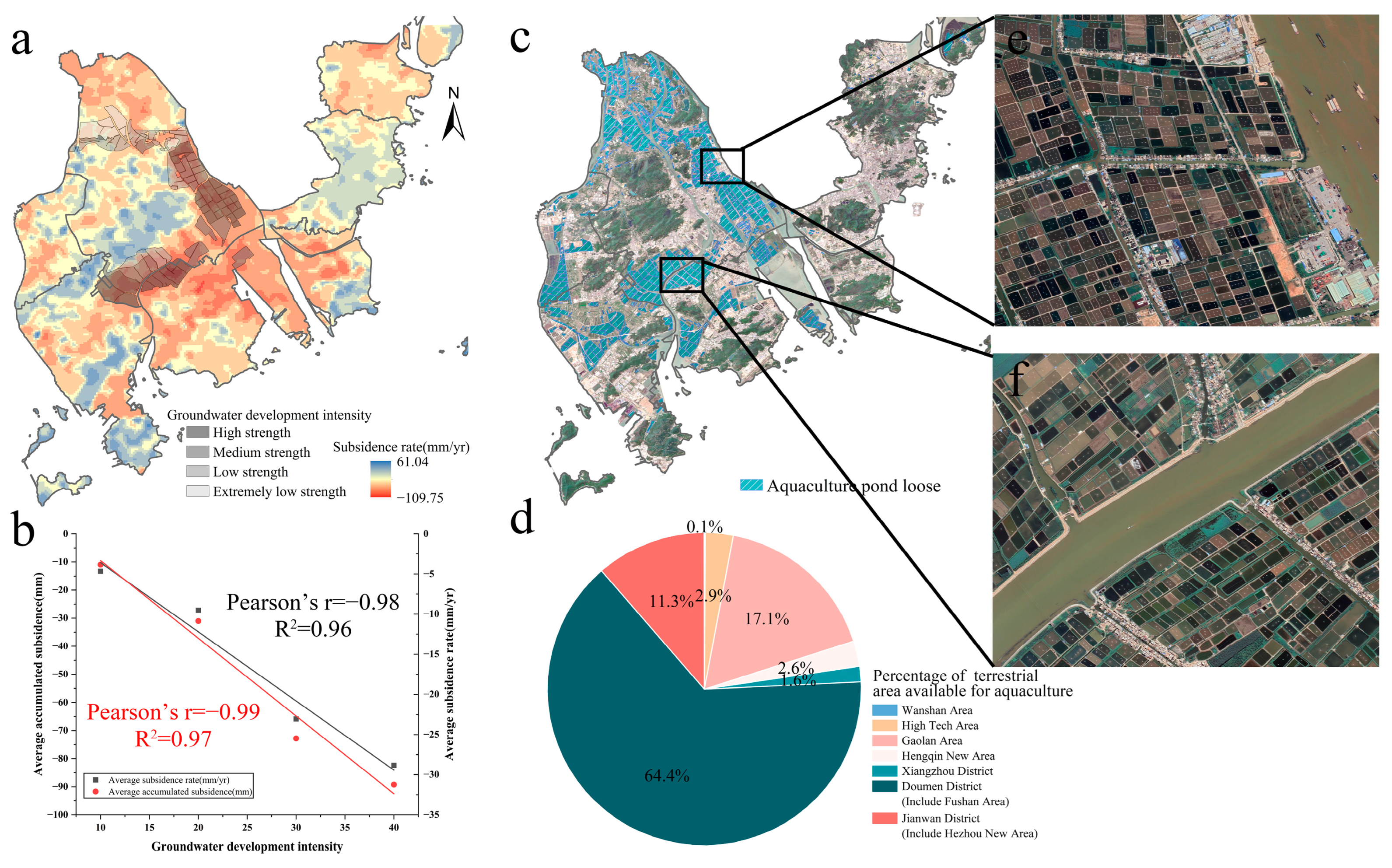
3.2.2. Soft Soil Thickness and Land Subsidence
3.2.3. Groundwater Extraction and Land Subsidence
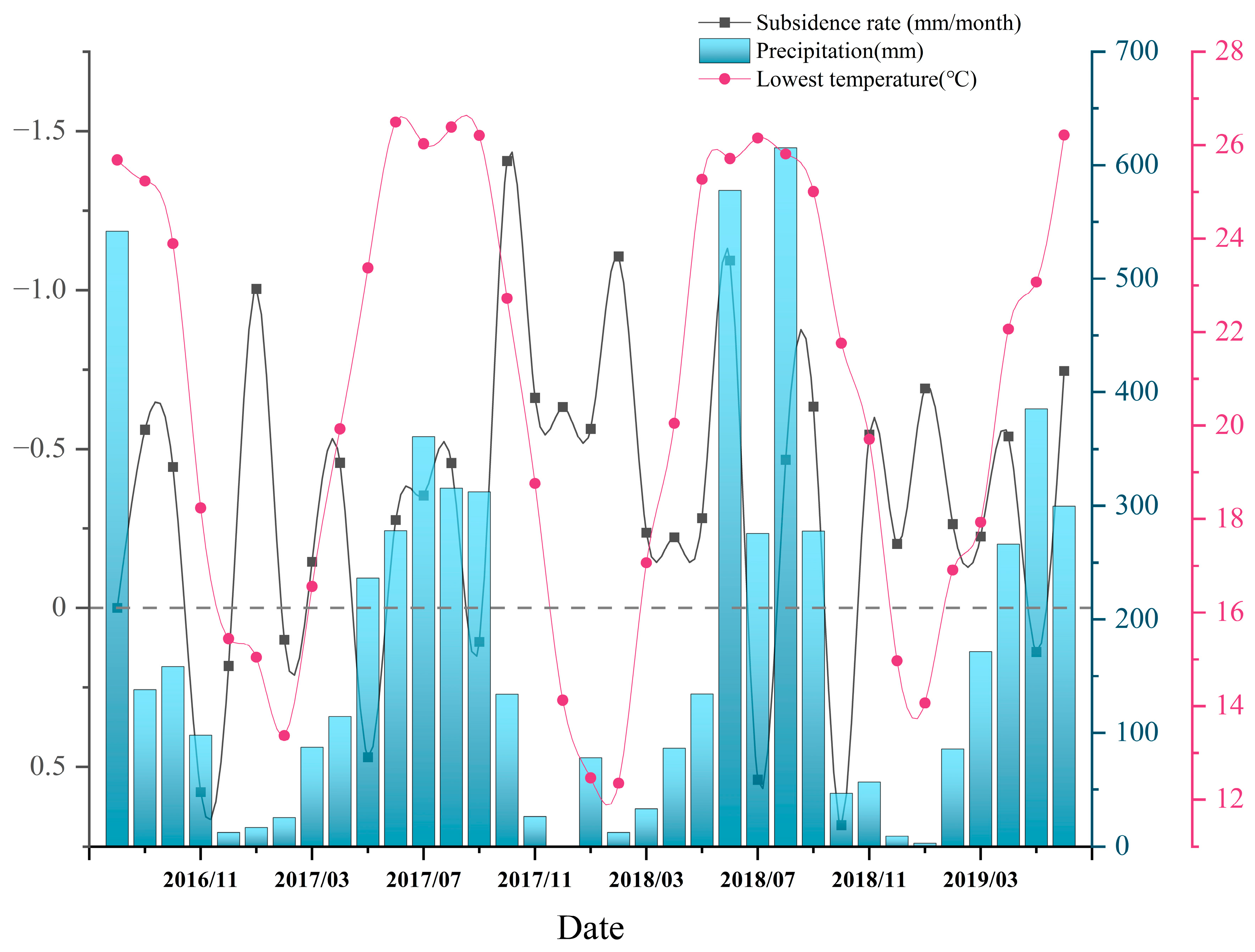
3.2.4. Atmospheric Precipitation and Land Subsidence
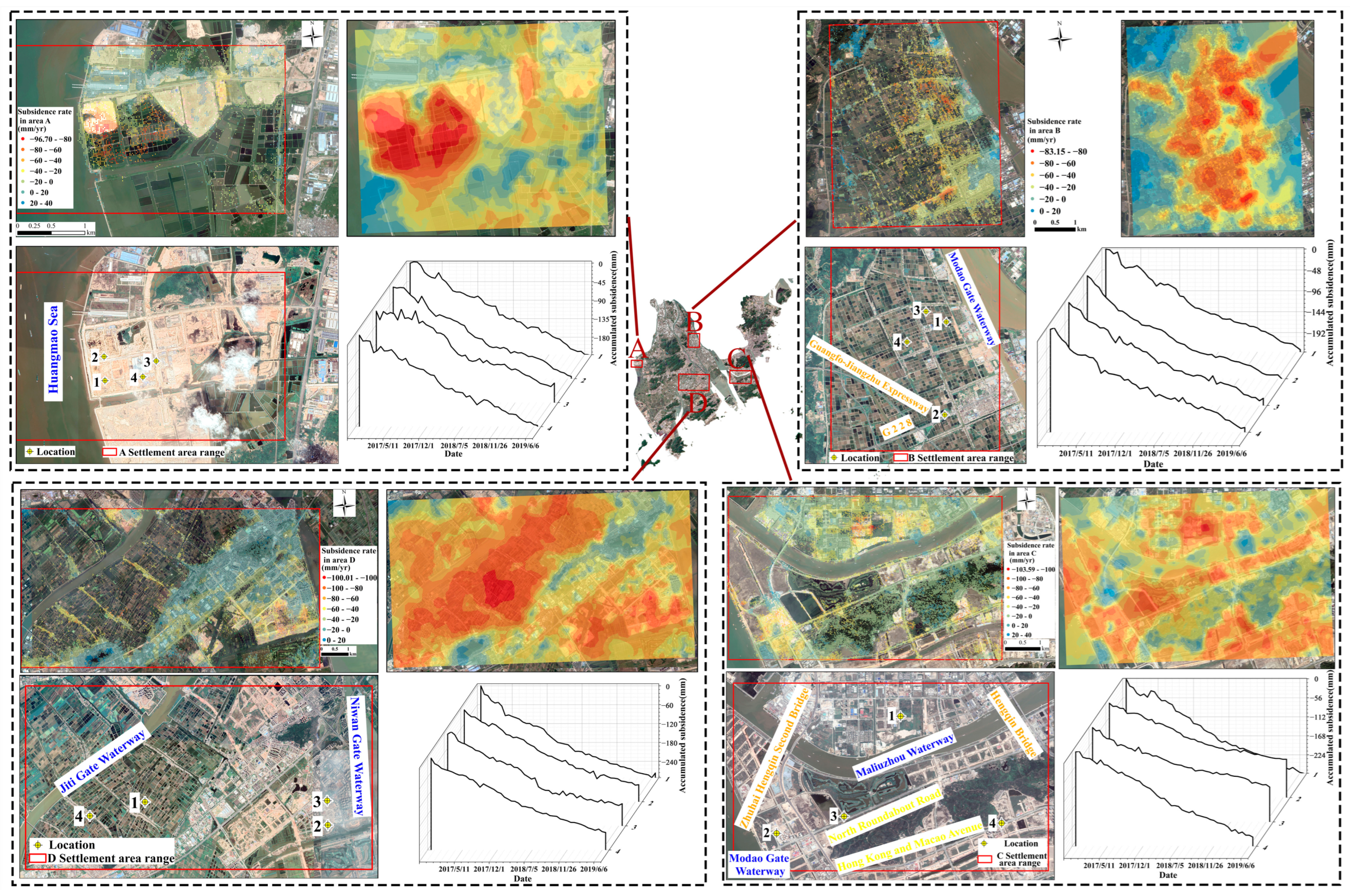
3.3. Study of Serious Subsidence Case Areas in Zhuhai
3.4. Subsidence Vulnerability Evaluation and Recommendations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catalao, J.; Raju, D.; Nico, G. Insar Maps of Land Subsidence and Sea Level Scenarios to Quantify the Flood Inundation Risk in Coastal Cities: The Case of Singapore. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Freymueller, J.; Törnqvist, T.E.; Galloway, D.L.; Dura, T.; Minderhoud, P.S.J. Measuring, modelling and projecting coastal land subsidence. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A.J.; Overeem, I.; Hutton, E.W.H.; Hannon, M.T.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Day, J.; Vorosmarty, C.; Saito, Y.; Giosan, L.; et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.N.; Brown, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Hinkel, J.; Shi, X.W.; Shi, P.J. Spatial-temporal changes of coastal and marine disasters risks and impacts in Mainland China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 139, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.G.; Zhao, Q.L.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Sturze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayuaji, L.; Sumantyo, J.T.S.; Kuze, H. ALOS PALSAR D-InSAR for land subsidence mapping in Jakarta, Indonesia. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Analysis of Permanent Scatterers in SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37120), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 2, pp. 761–763. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Qiu, H.J.; Zhu, Y.R.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.D.; Ma, S.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Efficient Identification and Monitoring of Landslides by Time-Series InSAR Combining Single- and Multi-Look Phases. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Y.; Qiu, H.J.; Zhu, Y.R.; Yang, D.D.; Tang, B.Z.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, L.Y.; Cao, M.M. Topographic Changes, Surface Deformation and Movement Process before, during and after a Rotational Landslide. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley Caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; de la Fuente, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS/PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Feng, G.C.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.; Xie, R.G.; Zhu, X.L.; Luo, S.R.; Du, Y.A. Surface deformation evolution in the Pearl River Delta between 2006 and 2011 derived from the ALOS1/PALSAR images. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.F.; Yokoya, N.; Xia, G.S.; Chanussot, J.; Zhu, X.X. X-ModalNet: A semi-supervised deep cross-modal network for classification of remote sensing data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 167, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Ding, H.X.; Zhong, Y.J.; Shi, Q. Crop Mapping Using Sentinel Full-Year Dual-Polarized SAR Data and a CPU-Optimized Convolutional Neural Network with Two Sampling Strategies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7017–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.R.; Arabameri, A.; Costache, R.; Craciun, A.; Arora, A. Land subsidence susceptibility assessment using advanced artificial intelligence models. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 18067–18093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Bai, W.W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, S.M.; Xia, K.Z. Study on engineering characteristics of large-scale deep soft soil in the central area of western Zhuhai. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng. 2019, 38, 1434–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.X.; Pei, S.P.; Jiao, J.J. Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou City, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wu, W.T.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.X. Drivers, trends, and potential impacts of long-term coastal reclamation in China from 1985 to 2010. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Z.; Zhu, T.; Cao, Y. The Consideration and Prospect of the Ecological Land Reclamation in China. Future Dev. 2013, 36, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, D.; Chen, R.S.; Meadows, M.E.; Choi, Y.R.; Banerjee, A.; Zilong, X. Mapping Trajectories of Coastal Land Reclamation in Nine Deltaic Megacities using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, B.F.; Liang, J.H.; Lu, Y.D. Impact of Soft Soils on Urban Construction in Pearl River Delta Economic Zone. In Proceedings of the Seminar on Coastal Zone Geological Environment and Urban Development, Tianjin, China, 20 December 2004; pp. 382–391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.Y.; Tang, C.; Ren, Z.Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y. Surface deformation monitoring and driving force analysis in Zhuhai city based on PS-InSAR technology. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2022, 6, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Y.; Deng, C.J. Analysis on the distribution law of soft soil and the status quo of settlement disasters in the west bank of the Pearl River Estuary. Ground Water 2021, 43, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, N.; Tang, U.W. Zhuhai. Cities 2013, 32, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Ai, K.H.; Huang, L.J. Issues of engineering characteristics and engineering construction of soft clay in Zhuhai region. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng. 2006, 25, 3372–3376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, Y.G.; Gu, R.G.; Zeng, C. Microscopic analysis of saturated soft clay in Pearl River Delta. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2011, 18, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Zhang, S.B.; Ge, X.N. Comparisons of compression index of Chinese coastal soft clay and soils from foreign regions. Rock. Soil. Mech. 2017, 38, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, B.; Huang, K.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S.; Jian, Z.; Liu, X. Comparison of Classification Algorithms for Detecting Typical Coastal Reclamation in Guangdong Province with Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2 Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.S.; Li, G.Y.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, S.S.; Wu, G.; Chai, M.T.; Tang, L.Y.; Jia, H.L.; Peng, W.L. SBAS-InSAR-Based Analysis of Surface Deformation in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 729454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, X. Landslide Detection and Mapping Based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: A Case Study in Gongjue County, Tibet, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Yang, T.; Song, S.; Yao, M.; Zhou, K.; Huang, X. Ground Deformation of the Chongming East Shoal Reclamation Area in Shanghai Based on SBAS-InSAR and Laboratory Tests. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.D.; Wang, L.; Wen, B.F.; Du, S. A New Model for three-dimensional Deformation Extraction with Single-track InSAR Based on Mining Subsidence Characteristics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 94, 102223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Xie, Z.W.; Bueh, C.; Gong, Y.F. Fidelity of the APHRODITE Dataset in Representing Extreme Precipitation over Central Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.B.; Jiang, Y.X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Xv, S.Y. Assessment and Zonation of Land Subsidence Disaster Risk of Tianjin Binhai Area. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2008, 28, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J.; Brown, S.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Meyssignac, B.; Hanson, S.E.; Merkens, J.L.; Fang, J.Y. A global analysis of subsidence, relative sea-level change and coastal flood exposure. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.C.; Wei, M.; D’Hondt, S. Subsidence in Coastal Cities Throughout the World Observed by InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Ren, X.W.; Chen, B.; Song, S.P.; Wang, J.X.; Yang, P. Study on land subsidence under different plot ratios through centrifuge model test in soft-soil territory. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Qiao, Y.L.; Zhong, Y. Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Force Analysis on Rivers and Lakes in Zhuhai City Using Remote Sensing Technologies. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 2677–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.F.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, B.W.; Wang, J.L.; Shi, G.Q.; Huang, G.Q.; Chen, F.L.; Jiang, L.M.; Lin, H. Remotely sensing large- and small-scale ground subsidence: A case study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Haque, A.; Nicholls, R.J.; Darby, S.E.; Urmi, M.T.; Dustegir, M.M.; Dunn, F.E.; Tahsin, A.; Razzaque, S.; Horsburgh, K.; et al. Sustainability of the coastal zone of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta under climatic and anthropogenic stresses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, M.S.; Yang, T.L.; Lin, J.X.; Liao, M.S. Decomposing and mapping different scales of land subsidence over Shanghai with X- and C-Band SAR data stacks. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 478–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Cao, Q.; Cao, J.; Duan, L.; Zuo, J.; Shi, M. Land Subsidence Response to Different Land Use Types and Water Resource Utilization in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbey, T.J. The influence of faults in basin-fill deposits on land subsidence, Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.L.; Gong, H.L.; Li, X.J.; Chen, B.B.; Zhou, C.F.; Shi, M.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Ni, Z.Y.; Duan, G.Y. Land Subsidence and Ground Fissures in Beijing Capital International Airport (BCIA): Evidence from Quasi-PS InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Zho, J.; Santosh, M.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, G.Z.; Guo, L.L.; Yu, S.Y.; Lan, H.Y.; et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 91–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Wu, H.; Qiu, J. Interpretation of Fault and Ground Stability Assessment Based on Remote Sensing of SPOT-5 & ETM+ in Zhuhai Area. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2008, 28, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.Q.; Zhan, W.H.; Gu, S.C.; Liu, H.L. Study on neotectonic movenent and crustal stability in pearl river delta. South China J. Seismol. 1996, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, J.R.; Huang, H.; Deng, J.; Chen, A. Analysis on the Dynamics of Coastline and Reclamation in Pearl River Estuary in China for Nearly Last Half Century. Water 2022, 14, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, R.; Herrera, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente, F.; Cuenca, A.; Mallorquí, J.J. Study of the land subsidence in Orihuela City (SE Spain) using PSI data: Distribution, evolution and correlation with conditioning and triggering factors. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.L.; Li, C.; Yang, S.L. The microscopic characteristics of Shanghai soft clay and its effect on soil body deformation and land subsidence. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, X.X.; Jie, J.; Yang, T.L.; Wu, J.Z.; Wang, H.S. Analysis on factors affecting ground settlement in plain area of Pearl River Delta. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2019, 30, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.W.; Wei, C.Z. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Aquaculture Ponds in Coastal Cities of Guangdong Province: An Empirical Study Based on Sentinel-1 Data during 2015–2019. Trop. Geogr. 2021, 41, 622–634. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Chen, C.M. Characteristics and Estimation of Water Resources Variation in Resent 50-years in Zhuhai City. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2005, 44, 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Fan, Q.; Si, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, M. Interpretation of the Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Land Deformation in Beijing during 2003–2020 Using Sentinel, ENVISAT, and Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Ayyub, B.M.; Zhang, D.M.; Huang, H.W.; Saadat, Y. Impact of Water Level Rise on Urban Infrastructures: Washington, DC, and Shanghai as Case Studies. Risk Anal. 2019, 39, 2718–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.Q.; Qiu, H.J.; Yang, D.D.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, S.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Cao, M.M.; Wufuer, W. Increasing landslide activity in the Taxkorgan River Basin (eastern Pamirs Plateau, China) driven by climate change. Catena 2023, 223, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Z.; Xie, H.; Chen, B. Land Subsidence in Qingdao, China, from 2017 to 2020 Based on PS-InSAR. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Li, H. Application of SBAS technology to the surface deformation based on Sentinel-1A radar image. Eng. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 27, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Huzang, Z.M. The Strength Calculation Method of Foundation Treated with Sand Well. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 919, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Fan, C.; Xu, H.; Hou, X.Y. Spatial and temporal characteristics analysis for land subsidence in Shanghai coastal reclamation area using PS-InSAR method. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1000523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashra, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigna, F.; Osmanoglu, B.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Dixon, T.H.; Avila-Olivera, J.A.; Garduno-Monroy, V.H.; DeMets, C.; Wdowinski, S. Monitoring land subsidence and its induced geological hazard with Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A case study in Morelia, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.; Kaiser, M.; Koch, M.; Gaber, A. Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A. Review: Advances in delta-subsidence research using satellite methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.T. InSAR Time Series Deformation Monitoring and Analysis in the Peral River Delta. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2022, 45, 132–135. [Google Scholar]




| Subsidence Severity (mm/yr) | Low >−10 | Relatively Low −30~−10 | Medium −50~−30 | Relatively High −80~−50 | High <−80 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of monitoring points | 553,219 | 269,167 | 68,554 | 13,928 | 499 | 905,367 |
| Percentage | 61.10% | 29.73% | 7.57% | 1.54% | 0.06% | 100% |
| Severe Subsidence Area | Geographical Location | Average Subsidence Rate (mm/yr) | Maximum Subsidence Rate (mm/yr) | Average Cumulative Subsidence (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 113°09′36″~113°13′24″E, 22°17′91″~22°20′19″N | −12.11 | −96.70 | −29.23 |
| B | 113°29′48″~113°33′58″E, 22°24′58″~22°29′16″N | −28.48 | −83.15 | −89.15 |
| C | 113°44′33″~113°51′96″E, 22°12′68″~22°16′97″N | −18.65 | −103.59 | −50.65 |
| D | 113°26′21″~113°37′07″E, 22°10′27″~22°25′71″N | −22.35 | −100.01 | −70.17 |
| Data and Method | Severe Subsidence Area | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Time | Data | Quantity | Method | Location | Velocity (mm/yr) | Accumulated Subsidence (mm) | |
| 2006~ 2011 | ALOS1/ PALSAR | 162 | SBAS | Gaolan Port | MAX: −87 | - | [13] |
| 2016~ 2019 | Sentinel-1A | 51 | SBAS | Most of Gaolan Port | AVG: −3.15 MAX: −93.27 | AVG: −4.94 MAX: −238.45 | This study |
| 2018~ 2019 | Sentinel-1A | 39 | SBAS + PS | Jinwan District | MAX: Approx. −110 | MAX: Approx. −110 | [67] |
| 2016~ 2019 | Sentinel-1A | 51 | SBAS | Jinwan District + Part of Gaolan Area | AVG: −7.14 MAX: −104.98 | AVG: −12.98 MAX: −285.24 | This study |
| 2018~ 2020 | Sentinel-1A | 63 | PS | Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Zhuhai Link | MAX: −23.89 | MAX: Approx. −60 | [23] |
| 2016~ 2019 | Sentinel-1A | 51 | SBAS | Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Zhuhai Link | AVG: −0.96 MAX: −29.95 | AVG: −4.98 MAX: −75.74 | This study |
| 2016~ 2017 | Sentinel-1A | 32 | SBAS | Gaolan Area Part | MAX: −75.04 | MAX: Approx. −80 | [60] |
| 2016~ 2019 | Sentinel-1A | 51 | SBAS | Gaolan Area Part | AVG: −11.21 MAX: −69.97 | AVG: −14.14 MAX: −189.62 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Peng, H.; Zeng, M.; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Pi, P.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, A.; Liu, F. Land Subsidence in a Coastal City Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring: A Case Study of Zhuhai, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092424
Sun H, Peng H, Zeng M, Wang S, Pan Y, Pi P, Xue Z, Zhao X, Zhang A, Liu F. Land Subsidence in a Coastal City Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring: A Case Study of Zhuhai, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092424
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Huimin, Hongxia Peng, Min Zeng, Simiao Wang, Yujie Pan, Pengcheng Pi, Zixuan Xue, Xinwen Zhao, Ao Zhang, and Fengmei Liu. 2023. "Land Subsidence in a Coastal City Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring: A Case Study of Zhuhai, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092424
APA StyleSun, H., Peng, H., Zeng, M., Wang, S., Pan, Y., Pi, P., Xue, Z., Zhao, X., Zhang, A., & Liu, F. (2023). Land Subsidence in a Coastal City Based on SBAS-InSAR Monitoring: A Case Study of Zhuhai, China. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092424





