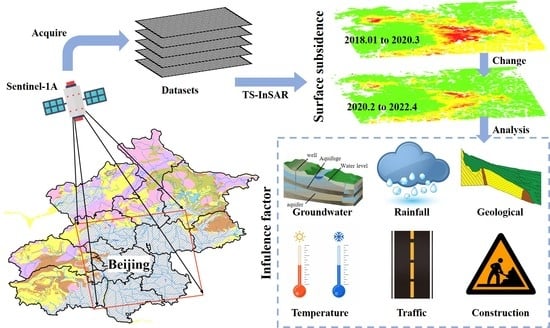
Surface Subsidence Characteristics and Causes in Beijing (China) before and after COVID-19 by Sentinel-1A TS-InSAR
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Huang, C.; Ma, S.; Xian, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F. Surface Subsidence Characteristics and Causes in Beijing (China) before and after COVID-19 by Sentinel-1A TS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051199
Sheng H, Zhou L, Huang C, Ma S, Xian L, Chen Y, Yang F. Surface Subsidence Characteristics and Causes in Beijing (China) before and after COVID-19 by Sentinel-1A TS-InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051199
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Haiquan, Lv Zhou, Changjun Huang, Shubian Ma, Lingxiao Xian, Yukai Chen, and Fei Yang. 2023. "Surface Subsidence Characteristics and Causes in Beijing (China) before and after COVID-19 by Sentinel-1A TS-InSAR" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051199
APA StyleSheng, H., Zhou, L., Huang, C., Ma, S., Xian, L., Chen, Y., & Yang, F. (2023). Surface Subsidence Characteristics and Causes in Beijing (China) before and after COVID-19 by Sentinel-1A TS-InSAR. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051199