Abstract
In the field of computer vision, the detection of infrared small targets (IRSTD) is a crucial research area that plays an important role in space exploration, infrared warning systems, and other applications. However, the existing IRSTD methods are prone to generating a higher number of false alarms and an inability to accurately locate the target, especially in scenarios with low signal-to-noise ratio or high noise interference. To address this issue, we proposes a fully convolutional-based small target detection algorithm (FCST). The algorithm builds on the anchor-free detection method FCOS and adds a focus structure and a single aggregation approach to design a lightweight feature extraction network that efficiently extracts features for small targets. Furthermore, we propose a feature refinement mechanism to emphasize the target and suppress conflicting information at multiple scales, enhancing the detection of infrared small targets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves a detection rate of 95% and a false alarm rate of 2.32% for IRSTD tasks. To tackle even more complex scenarios, we propose a temporally-aware fully convolutional infrared small target detection (TFCST) algorithm that leverages both spatial and temporal information from sequence images. Building on a single-frame detection network, the algorithm incorporates ConvLSTM units to extract spatiotemporal contextual information from the sequence images, boosting the detection of infrared small targets. The proposed algorithm shows fast detection speed and achieves a 2.73% improvement in detection rate and an 8.13% reduction in false alarm rate relative to the baseline single-frame detection networks.
1. Introduction
Infrared small target detection (IRSTD) has been an important subject and research focus in the field of computer vision. Infrared detection has a series of advantages, such as good environmental adaptability, high concealment, and strong anti-interference ability. With the continuous improvement of the performance of infrared detection systems, infrared detection technology has been widely used in civilian fields such as medical diagnosis of diseased cells and industrial testing, as well as in military fields such as infrared warning and infrared guidance. In these fields, real-time detection of small infrared targets with high detection rates and low false alarm rates is an essential requirement. However, in most infrared imaging systems, the distance between the target to be detected and the detector is far, the signal is severely attenuated in the atmosphere, and the target has characteristics such as small imaging area, low signal-to-noise ratio, and unclear shape and texture features. Furthermore, the complex and changing background in practical scenes poses a great challenge to the detection of infrared small targets.
Currently, the mainstream infrared small target detection algorithms rely on handcrafted features for detection, which suffer from high false alarm rates and poor adaptability in complex scenes. In recent years, deep learning-based object detection techniques have rapidly developed, achieving high levels of both speed and accuracy. Deep learning-based approaches have made great progress in many areas of computer vision, such as image segmentation [1,2], action recognition [3,4], and object detection [5,6]. However, research on applying deep learning techniques to infrared small target detection tasks is relatively rare. The main challenge lies in the small size and lack of contour information of the targets, which makes it difficult for the detection network to train and converge on them. Considering the powerful feature extraction and generalization capabilities of deep learning methods, adjusting the network structure and designing detection strategies specifically for small targets could undoubtedly lead to better performance in meeting the requirements of infrared small target detection tasks.
This study addresses the issue of detecting small infrared objects, where existing deep learning-based algorithms may lose feature information due to the complex background. To overcome this, we adjust the structure of the feature extraction network and adopt feature refinement mechanisms to enhance feature representation and suppress background interference, resulting in precise detection results generated from both classification and regression subnets. For more complex scenarios, we introduce a convolutional long short-term memory network to effectively combine spatio-temporal and feature information for higher detection performance.
The key contributions of our study are:
(1) We propose a temporally-aware fully convolutional infrared small target detection (TFCST) algorithm that leverages both spatial and temporal information from sequence images to address the problem of high false alarm rate in infrared small target detection.
(2) We introduce a fully convolutional-based small target detection algorithm (FCST) to address the issue of the reduced robustness of existing IRSTD methods in complex backgrounds. Furthermore, we propose a feature refinement mechanism to emphasize the target and suppress conflicting information at multiple scales, enhancing the IRSTD.
(3) Based on the single-frame FCST, we incorporate ConvLSTM units to extract spatiotemporal contextual information from the sequence images, boosting the detection of infrared small targets.
2. Related Work
To overcome these challenges, researchers have conducted research on the detection of infrared small targets and have achieved some research results. In the process of detecting small infrared targets, detection algorithms can be divided into two categories based on the differences in their spatial and temporal handling: algorithms based on single-frame images and those based on sequence images.
2.1. Single-Frame Image-Based Infrared Small Target Detection
Based on the current state of technology, there exist four categories of infrared small target detection algorithms for a single frame image. These categories include those based on filtering, visual contrast mechanisms, image data structures, and deep learning.
Filtering-based methods can be classified into two categories: spatial-domain filtering and frequency-domain filtering. Spatial-domain filtering methods estimate the background signal of the infrared image first, then perform differential operations on the original image and the estimated background image, and finally use threshold segmentation in the differential image to achieve small infrared target detection. Typical spatial-domain filtering methods include spatial domain high-pass filtering [7], maximum mean/median filtering [8], two-dimensional least mean square (TDLMS) filtering [9], bilateral filtering [10], and top-hat transformation [11], among others.
Frequency-domain filtering methods mainly design appropriate filters in the transform domain to remove the background and noise. The earliest frequency-domain filtering methods included ideal high-pass filtering, Gaussian high-pass filtering, and Butterworth filtering.
Recently, researchers have leveraged the powerful capabilities of the human visual system (HSV) in detecting small targets in infrared images. One approach that has been successfully used is the local contrast measure (LCM) proposed by Chen et al. [12], which is based on the contrast sensitivity mechanism of human vision. Subsequently, Han et al. [13] proposed an improved version of LCM, called the improved local contrast measure (ILCM), which employs adaptive processes and attention transfer mechanisms to effectively address the over-enhancement of noise points in LCM.
In recent years, deep learning-based target detection technology has rapidly developed, and relevant research has emerged in the field of infrared small target detection. In 2019, Wang et al. used adversarial learning to balance missed detection (MD) and false alarm (FA), using two flow models processed by adversarial training for sub-tasks, with each flow focusing on reducing missed detection or false alarm, achieving good results in infrared small target detection [14]. Inspired by the unique distribution features of infrared small targets, Shi et al. [15] considered infrared small targets as “noise” and transformed the task of small target detection into a denoising problem. In 2020, Zhao et al. [16] constructed a generative adversarial network (GAN) model to automatically learn target features and directly predict target intensity. Overall, deep learning methods can more effectively extract the features of targets and background and distinguish them, which has significant advantages over traditional detection algorithms and represents a new breakthrough direction in IRSTD technology. Deep-IRTarget [17] combines frequency domain and spatial domain features to form dual-domain features, aiming to improve the accuracy of target detection. Zhang et al. [18] proposed transforming the features extracted by a pre-trained self-supervised feature extractor into a Gaussian-like distribution to reduce feature distribution mismatch.
2.2. Multi-Frame Image-Based Infrared Small Target Detection
In the detection of small infrared moving targets, the shape, grayscale variations, and motion trajectory of the targets exhibit continuity over time, a crucial characteristic for effectively distinguishing between targets and noise. Therefore, detection methods based on sequential images need to consider both spatial and temporal information.
One such method is the pipeline filtering method, which relies on the continuity of the target’s motion trajectory. The basic idea is to first detect some suspected targets in the first frame of the image and then establish a temporal pipeline along the time axis, t, in the image sequence, using these suspected targets as centers. The length of the pipeline represents the number of consecutive frames for detection, and the radius of the pipeline corresponds to the target’s neighborhood size. When the suspected target appears in the pipeline a predetermined number of times, it is judged as a real target; otherwise, it is considered interference.
When the signal strength of a target is low, direct detection methods can be challenging, while energy accumulation can effectively enhance the target’s energy and achieve the final detection. Zhang et al. proposed a representative energy-accumulation-based method for small target detection. This method first projects consecutive multiple infrared images into a two-dimensional space and then accumulates the energy of small targets along the four possible motion directions in that space. Subsequently, there have been some modified energy-accumulation-based methods [19] which achieved good detection results but with limited real-time performance.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that most existing infrared small target detection methods based on deep learning are based on single-frame images. To further improve detection performance, it is necessary to consider incorporating temporal information of the target in sequential images into detection networks.
Compared to static image object detection, the focus of research in video object detection is on how to fully utilize temporal information to reduce inter-frame redundant computation and improve detection quality. Inspired by the recurrent neural network (RNN) [20], some researchers have proposed utilizing the memory-based learning of the RNN structure to learn the spatiotemporal information in videos. Xiao and Lee developed the spatial-temporal memory network model (STMN) [21], which effectively leverages the temporal information in videos by preserving long-term appearance and motion information. Chen et al. [22] combined ConvLSTM [23] with SSD [24] to construct a correlated loss function between multiple frames of video images, strengthening the consistency of detection results across adjacent video frames and effectively improving the robustness of video object detection. Duran-Vega et al. used a quasi-recurrent neural network (QRNN) [25] to extract the temporal information in videos on the basis of Yolov5, which significantly improved the detection performance while maintaining fast detection speed.
3. Method
In this section, we first introduce the overall architecture of our TFCST. Then, we present the details of the FCST block (Section 3.2) and the temporally-aware block (Section 3.3), followed by the loss function in Section 3.4.
3.1. Overall Architecture
As shown in Figure 1, the temporally-aware fully convolutional neural network (TFCST) consists of four main components:
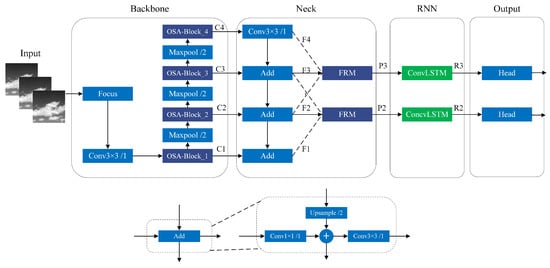
Figure 1.
The overall architecture of temporally-aware fully convolutional neural network. TFCST consists of four main components: feature extraction network, feature fusion network, recurrent neural network, and target prediction network.
(1) Feature Extraction Network: Firstly, the Focus structure is used to integrate the width and height information of the single-frame image into the channel space. Then, the OSA-Block convolutional unit, based on the single aggregation idea, is used to extract multi-scale features, with a total of four downsampling operations. This produces feature maps .
(2) Feature Fusion Network: Firstly, FPN is used to add deep semantic information to the shallow feature maps with higher resolution, which yields . Then, the feature refinement module (FRM) is used on the multi-scale features with semantic differences to filter out information that is favorable for small target detection, and the fused features are represented as .
(3) Recurrent Neural Network: The ConvLSTM units are used to model the appearance and motion information of the targets on two feature layers, and , respectively. The target information in the sequence images is then propagated and fused to produce .
(4) Target Prediction Network: The main idea of the FCOS anchor-free detection is used to predict target class, regression boxes, and centrality for the temporally-enhanced features and .
3.2. Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Infrared Small Target Detection
The model-driven IRSTD algorithm does not require learning and is easy to compute. It has achieved satisfactory detection results in some scenarios, but it can be prone to a large number of false alarms and poor robustness in complex and diverse environments. In contrast, deep learning methods possess powerful feature extraction and generalization capabilities and have demonstrated outstanding detection performance in various test environments. Therefore, deep learning is a new breakthrough direction in the field of infrared small target detection.
Based on the analysis above, we primarily investigate the method of detecting infrared small targets using deep learning. We propose a fully convolutional neural network for infrared small target detection (FCST), which is based on the anchor-free mechanism. The algorithm adopts the idea of pixel-level prediction proposed by fully convolutional one-stage object detection (FCOS) [26], which directly predicts the target’s category and regression detection box at each position of the feature map, thus avoiding the complex calculations and poor generalization caused by anchor box design. In the feature extraction stage, FCST reduces the number of downsampling operations and combines the idea of feature aggregation to ensure that the features of small targets are not lost. In the feature fusion stage, we use the feature refining mechanism to highlight the target’s characteristics and suppress conflicting information, thereby improving the detection accuracy of infrared small targets.
Modern object detection methods can be categorized into anchor-based and anchor-free methods based on whether prior boxes are used. While anchor boxes have long been considered an essential part of high-precision object detection, their mechanism is not conducive to detecting small objects. This is mainly due to the following reasons: Firstly, fixed-size, aspect ratio, and number of anchor boxes make it difficult to cover all types of objects comprehensively, which can affect the detector’s generalization ability and detection accuracy. Secondly, to achieve higher recall rates, detectors densely distribute anchor boxes on the input image, but most of them are on the background region, resulting in a severe imbalance between positive and negative samples during the training process. Lastly, the detection accuracy is sensitive to the IOU threshold when assigning training labels to anchor boxes, particularly for small objects. Therefore, recent research has focused on developing anchor-free methods that overcome these limitations and offer better performance. These methods do not rely on predefined anchor boxes and can handle objects of various sizes and aspect ratios more effectively. Additionally, they can alleviate the issue of imbalance in positive and negative samples resulting from anchor boxes’ use.
Target detection algorithms without anchor boxes are mainly based on center-based and keypoint-based methods. These approaches eliminate the need for generating anchor boxes, which leads to faster detection speeds and better generalization abilities. In recent years, one-stage fully convolutional object detection (FCOS) has become a popular anchor-box-free detection algorithm. Similar to semantic segmentation, FCOS employs pixel-level prediction to directly predict the class and regression of an object at each position on the feature map, without the need for predefined anchor boxes or candidate regions. Compared to anchor-based detection methods, FCOS is simpler and more computationally efficient, which consumes fewer computational resources.
In this paper, we applied the anchor-box-free detection mechanism of FCOS to design a fully convolutional neural network (FCST) for detecting small infrared targets. The structure of FCST is shown in Figure 2, and the model is designed based on two aspects: feature extraction and feature fusion networks. The target prediction network is based on the three-branch structure of FCOS.
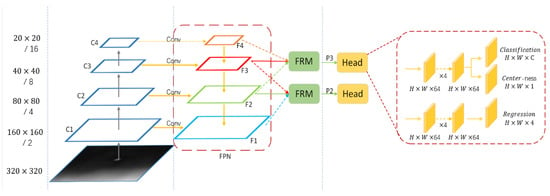
Figure 2.
The structure of fully convolutional neural network for infrared small target detection (FCST). The model is designed based on two aspects: feature extraction and feature fusion networks. The target prediction network is based on the three-branch structure of FCOS.
During the feature extraction stage, in order to prevent the loss of small target feature information caused by excessive downsampling, the network reduces the downsampling frequency and enhances the feature expression by aggregating them in a single pass, resulting in a feature map after downsampling. In the feature fusion stage, the deep semantic information is added from top to bottom into the low-level feature maps with high resolution, generating the fused feature maps . Furthermore, to address the issue of semantic conflicts caused by multi-scale feature fusion, a feature refining mechanism is employed to suppress conflicting information and reduce false alarms. Additionally, considering the differences in size between infrared small targets and general targets, FCST focuses on detecting on feature maps with downsampling rates of and , which correspond to small point targets and large patch targets with high pixel occupancy, respectively.
In the context of developing feature extraction networks, the issue of losing important target information due to downsampling has been identified. As a solution, the Focus structure has been introduced as the first layer of the feature extraction network. As shown in Figure 3, this structure slices the input data and samples it at intervals to obtain 4 feature maps, thus expanding the input channel by a factor of 4. The obtained feature maps are then subject to convolutional operations to fuse the channel information, resulting in a downsampling feature map that retains all information, without loss. This approach not only reduces the model’s parameters and computational complexity but also integrates the width and height information of the image into the channel space, thereby preserving more complete image information for subsequent feature extraction. Ultimately, this helps improve the detection performance of the network model.
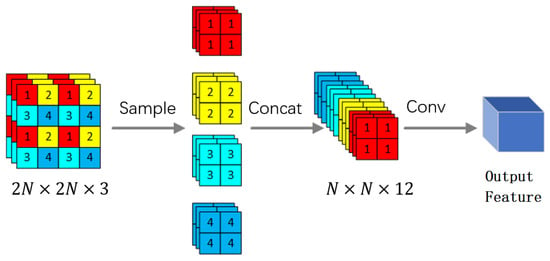
Figure 3.
The structure of the Focus block. It not only reduces the model’s parameters and computational complexity but also integrates the width and height information of the image into the channel space.
ResNet [27] is currently the most commonly used feature extractor in deep learning object detection models. Its design of residual structures enhances the information exchange between the front and back layers, which mitigates training difficulties and convergence issues that occur when the network is deepened. The ResNet structure is shown in Figure 4.
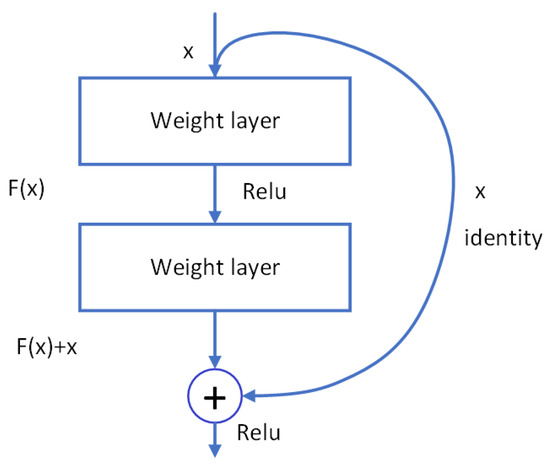
Figure 4.
The structure of the Residual block. Its design of residual structures enhances the information exchange between the front and back layers, which mitigates training difficulties and convergence issues that occur when the network is deepened.
On the other hand, DenseNet [28] establishes dense connections between all the previous layers and subsequent layers to maximize the information exchange between them in the channel dimension. This achieves better performance than ResNet, with fewer parameters and computations. Although DenseNet is effective in object detection, its speed is slow due to the high memory access cost and energy consumption caused by its dense agglomeration method. Furthermore, DenseNet causes feature redundancy because the subsequent features already learn the crucial information from earlier layers.
To overcome this information redundancy, VoVNet [29] proposed One-Shot Aggregation (OSA), which aggregates only the features from all the previous layers at the final aggregation step. In brief, OSA enhances the network’s ability to express features while still achieving higher computational efficiency than dense aggregation. Inspired by the residual connection and single-stage aggregation, the OSA-Block, which is a convolutional block, is constructed as depicted in Figure 5.
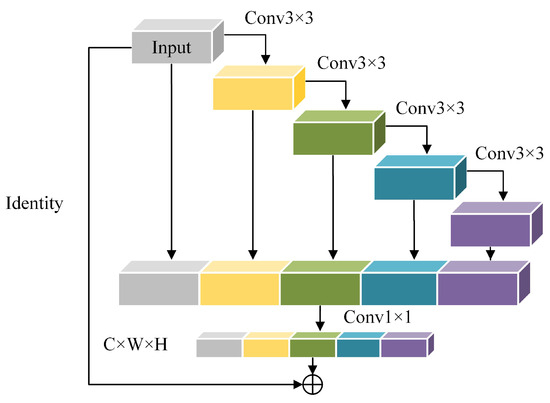
Figure 5.
The structure of the OSA-Block. OSA enhances the network’s ability to express features while still achieving higher computational efficiency than dense aggregation.
In the context of detecting small infrared targets, it is important to consider different factors when designing the feature extraction network. One major concern is the limited amount of pixel coverage that these targets occupy in the image, combined with the subtle features they possess. This means that using overly deep networks can lead to a loss of important information and increased false negatives. Additionally, large model parameters can hinder inference speed. Therefore, it is more suitable to use relatively shallow networks that can be optimized for this specific task.
The shallow feature space contains detailed spatial information, but it lacks sufficient semantic information and a comprehensive understanding of the overall scene. Therefore, using only shallow features for detecting small objects results in poor performance. On the other hand, deep features extract rich semantic information efficiently, but they sacrifice too much fine-grained information about the target. To make the most of the semantic information in deep network features, while preserving the spatial information of the shallow feature map, feature fusion between shallow and deep layers is necessary. Based on this idea, FPN [30] employs a top-down information propagation approach to fuse the semantic features in deep layers with the spatial details of shallow features through addition or concatenation. This method enhances feature representation capability without significant computational cost, and to some extent improves the detection performance of small objects. However, since different scales of features contain semantic differences, direct fusion can lead to redundancy and conflicts and weaken the expression ability of multi-scale features.
To address the aforementioned issues, a Feature Refinement Module (FRM) is proposed, as illustrated in Figure 6. The FRM generates adaptive weights on both spatial and channel dimensions in two parallel branches, which filter multiple scale features and preserve useful information. Before extracting adaptive weights, the feature dimensions of different scales need to be consistent. Let denote the feature of the m-th layer, and and denote the adjacent layer features. For high-level features with smaller resolutions , a convolution is first used to adjust the channels to be consistent with and then upsampled to the same size as by nearest neighbor interpolation. For shallow features with larger resolutions , a convolution with a stride of 2 is applied to simultaneously adjust the channels and resolutions.
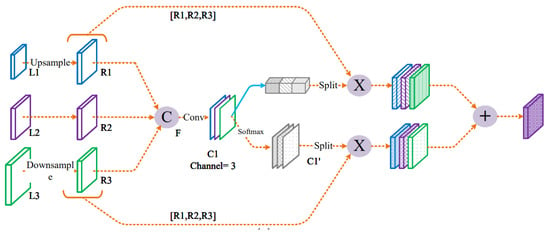
Figure 6.
Illustration of feature refinement module (FRM). The FRM generates adaptive weights on both spatial and channel dimensions in two parallel branches, which filter multiple scale features and preserve useful information.
Let be the result of adjusting the feature dimension of layer n to layer m. Then the process of channel-wise feature refinement is defined as follows:
In the above equation, is the feature vector located at () of layer m, and a, b, c represent adaptive channel fusion weights with a dimension of . The idea of obtaining these weights is to combine adaptive average pooling and maximum pooling on the spatial dimension to compress the input features and aggregate spatial information that can represent global characteristics of the image. The computation can be expressed as follows:
where F denotes the output of multi-scale features concatenation, as shown in Figure 7, and is the sigmoid operation, while and represent adaptive average pooling and maximum pooling, respectively.
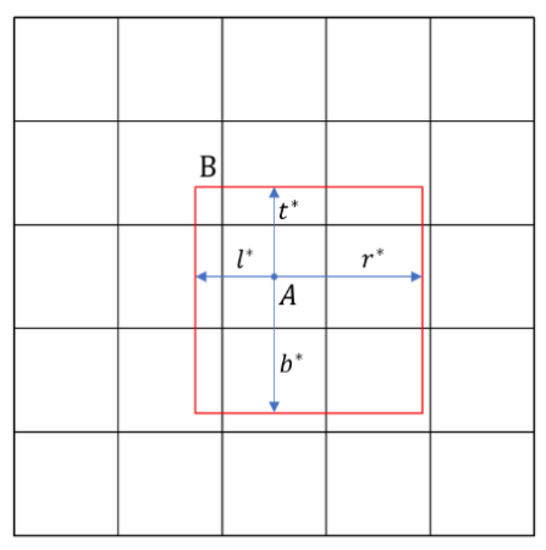
Figure 7.
Regression diagram of FCOS, where A is the ground-truth target point, B represents the predicted target box and are used for regression calculation. The target prediction network also outputs a four-dimensional vector, which represent the distances to the four edges of the detection box.
The process of spatial-wise feature refinement for multi-scale features can be defined as follows:
In the above equation, x and y represent spatial positions in the feature map, and k represents the channels. is the output of spatial refinement features at (). The attention weights for the spatial dimension are denoted as , and , which can be computed as follows:
where is used to normalize the features along the channel direction to obtain the relative weights of different channel directions at the same spatial position.
The overall output of FRM is a combination of refined features along the channel and spatial dimensions, which is expressed as follows:
By using this method, multi-scale features are fused under the guidance of adaptive weights, enhancing the feature representation of small targets and suppressing background information. Finally, is obtained by fusing , , and , and , , and are used as inputs for the target detection network.
In Figure 2, we can see that the structure of the object detection network, which is based on the anchor box, is similar to that of RetinaNet [30]. The target prediction network has two branches on each detection layer (which consist of four consecutive convolutional layers), one for category prediction and the other for detection box regression. However, unlike traditional anchor-based approaches, the idea of the anchor-free mechanism is to treat each pixel on the feature map as a sample and directly predict both the class and detection box regression without relying on fix-sized and fixed-number anchor boxes.
During the training phase, each position on the feature map with a downsampling rate of s is mapped back to the original image through calculations. Only if the predicted class label is consistent with the true class label and the detection box regression falls within the range of the true annotation box is it regarded as a positive sample. Otherwise, it is a negative sample. Compared to the traditional method of IOU threshold-based division, this positive and negative sample selection method is more conducive to improving the recall rate for small object detection, which is also one of the significant reasons why we constructed the network based on FCOS.
In addition to class prediction, the target prediction network also outputs a four-dimensional vector, , for the regression calculation of the detection box at that position, where it represent the distances to the four edges of the detection box, as shown in Figure 7. If the sample at that position is associated with detection box , then the regression target trained at that position is defined as follows:
Furthermore, the approach of predicting on multiple feature maps can increase the recall rate of object detection, but it can also introduce many low-quality prediction boxes that deviate from the true boxes. To address this issue, FCOS proposes a simple yet effective strategy without introducing any hyperparameters. Specifically, the network adds an additional “center-ness” branch in parallel with the classification branch, which measures the offset of the predicted location relative to the center of the object and adds a new loss term based on center-ness. The formula for center-ness is as follows:
As can be seen from the formula, the center-ness value ranges from 0 to 1, with a higher value indicating a prediction closer to the true box center, and vice versa. During the testing phase, the final score of the detection box is obtained by multiplying the object class score and the center-ness value. Therefore, center-ness can reduce the score of prediction boxes that deviate from the true box center and improve the detection accuracy by filtering them out through a non-maximum suppression (NMS) process.
3.3. Temporally-Aware Fully Convolutional Neural Network
In typical detection systems, video sequences rather than static images are acquired, and relying solely on spatial information from a single frame may not be sufficient for detecting infrared small targets in scenes with complex backgrounds and weak target signals. To achieve more robust detection capabilities, it is necessary to consider incorporating both temporal and spatial information from sequence images. While existing infrared small target detection methods based on sequence images have demonstrated high detection accuracy by processing multiple frames simultaneously, they often sacrifice detection speed and require significant computational resources, making it challenging to apply them in real-time settings.
We presents a novel approach for detecting infrared small targets by combining a fully convolutional neural network with a recurrent neural network. Inspired by RNN-based video object detection methods, we extended a single-stage anchor-free detection network to create the temporally-aware fully convolutional neural network for infrared small target (TFCST), which effectively utilizes the ConvLSTM [23] architecture to propagate and refine features across frames. As a result, TFCST exhibits enhanced detection accuracy in more complex scenarios, while also remaining capable of real-time online detection tasks. This was demonstrated through various experiments conducted on the proposed method.
Sequential image data consists of both temporal and spatial information. To learn spatiotemporal features in near-term precipitation forecasting, the convolutional long short-term memory (ConvLSTM) [23] model was proposed based on the long short-term memory (LSTM) [21] architecture. The basic unit of LSTM is referred to as a memory block, which consists of three gate units and a memory cell. The three gate units are the input gate, output gate, and forget gate, which are responsible for controlling the flow of information. The memory cell is used to store the current state of the network. During forward propagation, the input gate controls the flow of information into the memory cell, while the output gate controls the flow of information from the memory cell to other memory blocks. During backpropagation, the output gate regulates the flow of error and gradients into the memory cell, whereas the input gate controls the flow of error and gradients out of the memory cell. The forget gate determines the extent of information retention and governs the internal recurrent state of the memory cell. The ConvLSTM takes the input at time t and the memory block output, concatenates them, and performs a convolution operation to extract spatiotemporal features.
As shown in Figure 8, ConvLSTM has the same structure as the LSTM unit, which includes input gates, forget gates, output gates, and memory cells. However, what sets ConvLSTM apart from LSTM is that the input at time t and the output from the memory block at time t-1 are concatenated and then convolved, which is crucial for extracting spatiotemporal information. ConvLSTM can be described as follows:
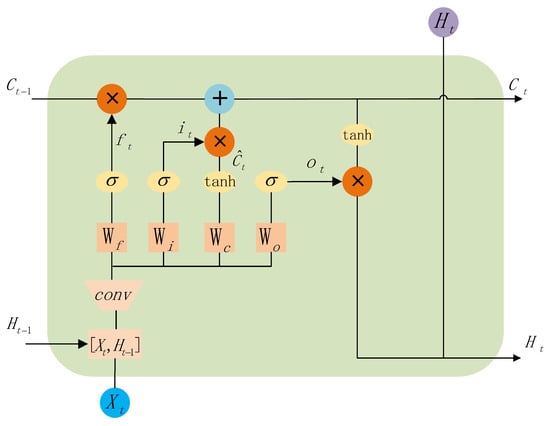
Figure 8.
The architecture of ConvLSTM. The block is utilized to save the temporal contextual status information of historical frames. ConvLSTM extends LSTM by incorporating convolutional operations into the LSTM structure. It introduces convolutional layers within the LSTM cells, enabling the network to process both spatial and temporal dependencies in sequential data simultaneously.
The aim of this study is to detect infrared small targets in sequence images quickly and robustly. Building upon the single-frame detector FCST, we introduce a novel infrared small target detection model, TFCST. In the detection process, the main idea is to use a recurrent neural network structure to propagate and refine features across frames, enabling the network to have a temporal aware ability. Given the extremely fast detection speed of the basic network FCST, in order to fully utilize the temporal and spatial information of sequence images, TFCST performs detection on each frame and uses ConvLSTM to save the temporal contextual status information of historical frames. Then, based on this temporal contextual information, the features of the current frame are enhanced to improve the small target detection performance. It is worth noting that the idea of TFCST is not to post-process the results of single-frame detection, but to directly propagate temporal contextual information between feature layers, which can achieve online detection, as illustrated in Figure 9.
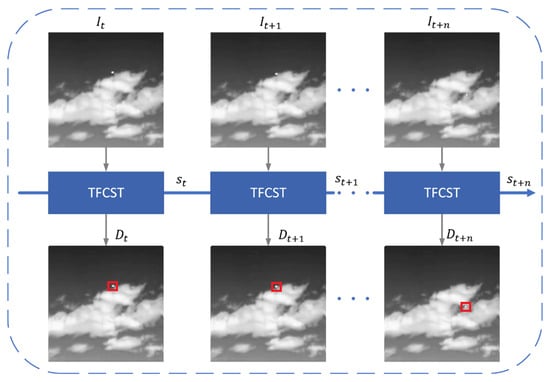
Figure 9.
The detection idea of TFCST. TFCST directly propagates temporal contextual information between feature layers, which can achieve online detection.
The goal of the network model for infrared sequence with n frames is to output the correct detection results for each frame, where is a set of multiple detection boxes and target class prediction results are obtained on a single frame , relying only on the image data between frames. The small target detection model TFCST based on the sequence images can be represented as function , where represents the state information extracted by the network in the first k frames. Based on the structure of single-frame image detection model FCST, TFCST approximates the equation above by adding m ConvLSTM units with memory characteristics. The ConvLSTM unit takes the previous state vector extracted from the historical frames as input and outputs the current state vector at the current detection moment. During the detection process of the infrared sequence images, running the TFCST detector on each frame in chronological order will yield the detection results for the entire sequence.
In consideration of the different sizes of infrared small targets with various shapes, such as point sources and patchy ones, TFCST still employs a multi-scale detection approach, mainly conducting the detection on two down-sampled feature layers at and scales, respectively. Furthermore, to propagate temporal and spatial contextual information among frames at each scale, TFCST incorporates ConvLSTM on each feature layer after feature fusion.
3.4. Loss Function
During the training stage of the network, loss functions need to be calculated separately for the categories, detection boxes, and centrality of the targets to optimize the network parameters. For the category prediction of infrared small targets, the Focal Loss [31] is used to calculate the loss, mainly due to the small proportion of target pixels. Focal Loss was first proposed in RetinaNet to alleviate the problem of imbalanced positive and negative samples during training. The formula is as follows:
In the above formula, is used to adjust the weight of the positive and negative sample loss values, is used to adjust the proportion of easy-to-classify samples in the total samples, and is the predicted target confidence score.
Regarding regression loss, higher requirements are imposed on the location prediction in small target detection. Therefore, this study adopts the [32] to perform positional regression on the targets, which can reflect the proximity relationship between the predicted box and the target box and effectively avoid the problem of zero gradients in the loss function due to the predicted box not intersecting with the actual box. The calculation formula for is as follows:
In the above formula, represents the ground truth box of the target, represents the predicted box, and B represents the minimum bounding rectangle that can surround and . The definition of GIOU Loss is:
For the calculation of centrality loss, the centrality loss can be calculated using binary cross-entropy loss. Therefore, the loss function of the target detection model can be expressed as a joint loss of classification loss , regression loss , and centrality loss :
4. Experiments
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods, we conducted comprehensive experiments on both FCST and TFCST. In this section, we first introduce the experimental data and training parameters. Subsequently, we performed ablation experiments and comparative experiments. The experiments were conducted on a computer equipped with a 2.90-GHz Intel Core i7-10 700 CPU, an RTX 3090 GPU, and 32-GB RAM. Python 3.7 was utilized as the programming language for all experiments.
4.1. Data Introduction
In order to verify the effectiveness of TFCST, we present a sequential image infrared small target dataset. The training set consists of 144 infrared sequences, comprising a total of 11,551 frames, while the test set consists of 42 sequences, comprising a total of 3268 frames. The length of each sequence varies between 50 and 260 frames. In these datasets, some targets are real, some are simulated, and the simulated targets were generated by our own target simulation system, in which the three-dimensional motion trajectory of the targets are projected to obtain its 2D positions in the images. In the target simulation system, the camera frame rate, the optical system point-spread-function, and the target signal-to-noise ratio can be set. The different motion rate of the target on the image can be simulated by setting different frame rates, and the intensity of the target can be calculated by the set target signal-to-noise ratio.
Additionally, considering the diversity of infrared small targets in practical scenarios, random rotation and scale adjustments were added during the construction of target images, making the targets exhibit various shapes such as points, spots, and stripes. The background samples mainly come from the single-frame infrared small target dataset proposed before. When constructing infrared sequential data, background images with more clutter interference were specifically selected. Some of the images are shown in Figure 10.
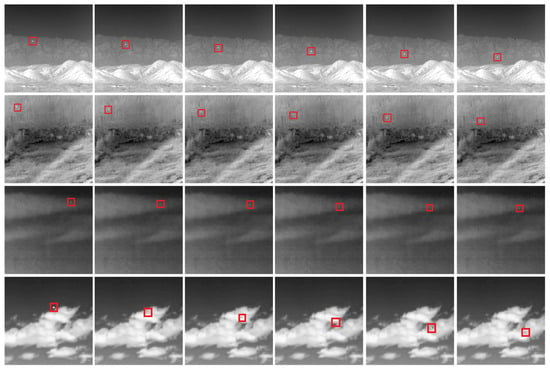
Figure 10.
Illustration of the dataset. When constructing infrared sequential data, background images with more clutter interference were specifically selected.
4.2. Training Parameter
Considering the poor diversity of sequence image datasets, the TFCST network first pre-trains the FCST single-frame detector model and then further trains it on the constructed infrared sequence image dataset. During training, the weights of the feature extraction network and feature fusion network are frozen, and the ConvLSTM and the remaining parts of the network are trained using the Adam optimizer. The learning rate is adaptively adjusted based on the size of the loss function value, with an initial value of . The tolerance for the network performance to remain unchanged is three times, and a total of 100 rounds of training are performed with a batch size of 4. After training is completed, the best evaluation result is selected as the final model.
4.3. Ablation Experiment
First, the impact of extracting continuous frame image information of length seq_len on detection performance during network training was studied, and the experimental results are shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12.
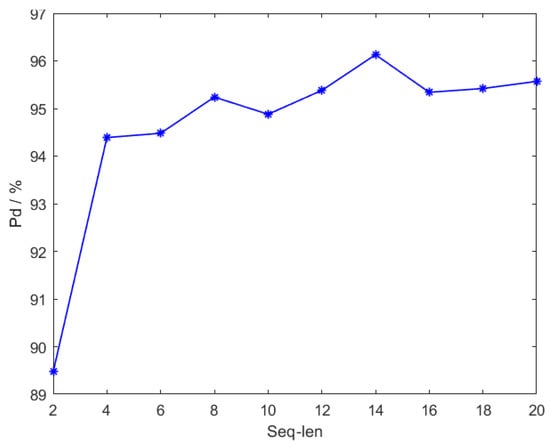
Figure 11.
Illustration of the positive detection () performance. is the ratio of the number of positive targets detected to the total number of all positive targets.
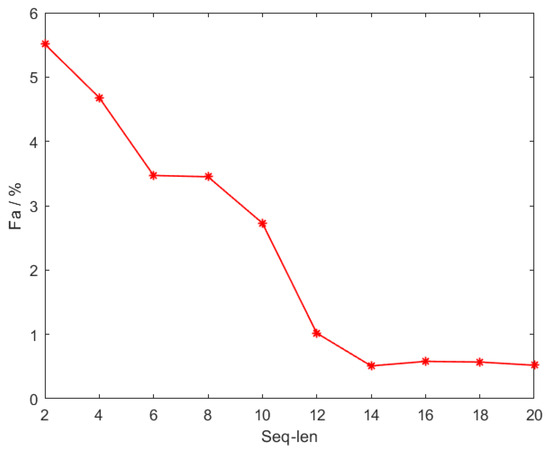
Figure 12.
Illustration of the false alarm () performance. is the ratio of the number of false targets detected to the total number of targets detected.
From Figure 11 and Figure 12, it can be seen that during network training, the more video frames that the network can utilize, the more sufficient is the spatiotemporal information extracted by the ConvLSTM, which is more conducive to the detection of infrared small targets. However, when the selected length of continuous frames reaches a certain value, the network’s performance also reaches saturation. In the experiment, when seq_len = 14, the detection rate of the TFCST network in the test set of sequence image infrared small targets is 96.13%, and the false alarm rate is 0.51%, which achieves the best detection effect. When increasing the length of seq_len, the detection performance of the network is difficult to further improve.
It is worth noting that as the length of seq_len increases, the overall trend of false alarm rate changes is constantly decreasing, indicating that the combination of the ConvLSTM based on the single-frame detector can improve the problem of high false alarm rate of the infrared small target detection algorithm in complex backgrounds. The trend of the detection rate, however, does not always increase, and fluctuates with the increase of seq_len. The reason may be related to the random jumping sampling strategy adopted during network training. In some cases, the samples extracted from the infrared sequence are more conducive to the ConvLSTM learning, and the feature information extracted from the historical frames can be more conducive to the detection of targets in the current frame.
Next, the impact of different temporal models on network detection performance was studied. In the experiment, two RNN variants, ConvGRU [33] and Bottleneck-LSTM [34], were selected. ConvGRU is a recurrent network model built on the basis of gated recurrent units (GRU) [35]. Compared with LSTM, GRU optimizes the structure of the memory cells, reduces parameters, and accelerates the training speed. Bottleneck-LSTM is a more efficient RNN structure proposed on the basis of ConvLSTM, which uses depth-separable convolution and reduces the number of related convolution operations in memory cells.
In the experiment, the length of the continuous frame in the sequence image during the training stage was uniformly set to 14, and multiple sets of experiments were repeated to obtain more stable results, and the statistical results were averaged. In addition, we also compared the detection speed of different RNNs with frames per second and model parameter count. The detection results of the TFCST network on the test set when different RNN models are used are shown in Table 1, where positive detection (Pd), false alarm (Fa), frames per second (FPS), and model parameter count are included.

Table 1.
The detection performance of TFCST with different RNNs.
It can be observed that when using ConvGRU and Bottleneck-LSTM, the number of model parameters is smaller. However, the detection rate, false alarm rate, and even the detection speed were inferior to the performance when using ConvLSTM. Since TFCST is built on the basis of the lightweight single-frame detector FCST, if we do not consider the constraints of computing resources and model weight size, using ConvLSTM is a better choice as it can more fully extract spatiotemporal information in sequence images compared to other optimized RNN models.
4.4. Contrast Test
To thoroughly compare the performance of the FCST network with other detection methods, we compared it with a total of nine different types of detection algorithms. Among them, in the model-driven methods, we selected the morphological filtering algorithms TopHat [11], MPCM [36], based on visual contrast mechanism, IPI [37], based on image data structure, NRAM [38], based on matrix optimization, and PSTNN [39], based on tensor optimization. For data-driven methods, considering detection speed, we primarily selected one-stage object detection algorithms. Among them, for anchor-based methods, we chose Retinanet [30] and YOLOv3 [40], while for anchor-free detection methods, we selected YOLOX [41].
We selected four typical infrared scenes, and the detection results of each algorithm are shown in Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16. In the figures, the red boxes represent correct detections, the yellow boxes represent missed detections, and the blue boxes represent false alarms. From the figure, it can be observed that traditional infrared small object detection algorithms exhibit significant variations in detection performance across different scenes. Specifically, the model-driven methods showed excellent detection performance in Scene 2 but exhibited a higher number of missed detections in Scenes 3 and 4. The TopHat algorithm had a high number of false alarms in Scene 1 but showed higher detection rates compared to other model-driven methods in Scenes 3 and 4. The reason for these issues is that model-driven methods rely on fixed hyperparameters and segmentation thresholds, leading to poor adaptability across different scenes. On the other hand, data-driven object detection algorithms, as compared to model-driven methods, generally demonstrated better detection performance. Among them, Retinanet had false alarms and missed detections in Scenes 1 and 4, YOLOv3 only predicted one false object in Scene 2, while the anchor-free detection algorithm YOLOX and the proposed FCST achieved accurate detection of small objects across different scenes.
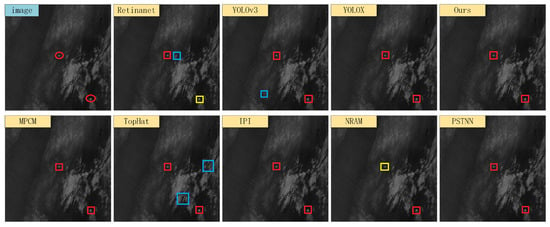
Figure 13.
Illustration of detection results on Scene 1. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets and, false alarms.
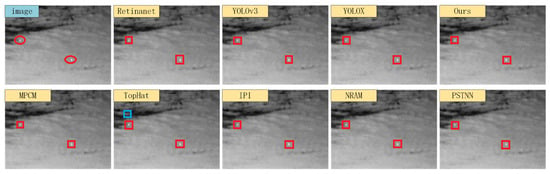
Figure 14.
Illustration of detection results on Scene 2. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
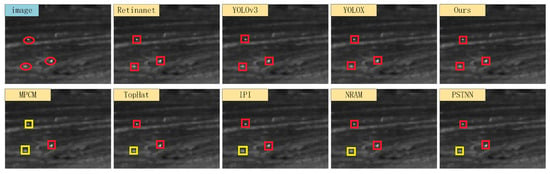
Figure 15.
Illustration of detection results on Scene 3. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
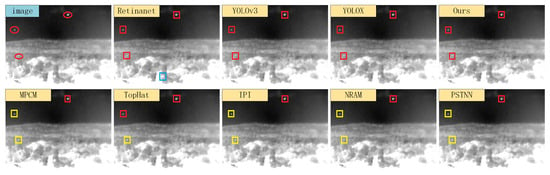
Figure 16.
Illustration of detection results on Scene 4. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
We conducted experiments on a test set consisting of 600 infrared images to evaluate the performance of each detection algorithm. Specifically, we compared these methods based on three metrics, , , and FPS, which are defined as follows:
(1) Detection rate () and false alarm rate () are defined as follows:
where represents the number of detected true targets, represents the total number of true targets, represents the number of false detections, and represents the total number of detected targets.
(2) Frames per second (FPS) denotes the processing speed of the detection algorithm, measured in frames processed per second.
We obtained the experimental results, which are summarized in Table 2. These results provide insights into the performance of each algorithm in terms of detection accuracy (Pd), false alarm rate (Fa), and processing speed (FPS). It is evident that the FCST algorithm achieved the highest Pd and lowest Fa among the tested methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in accurately detecting targets in the infrared images. Moreover, it maintained a competitive processing speed of 66.4 FPS, ensuring real-time performance.

Table 2.
The detection performance of FCST with different methods.
To analyze and demonstrate the advantages of TFCST over FCST, we selected four complex infrared image sequences from the test set for experimental comparison, and their descriptions are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Description of image sequences. We selected a change of images to conduct the experiment.
In the experiment, FCST was also trained on the constructed sequence infrared image dataset based on pre-trained weights. The visual detection results of the two detection networks on four sequences are shown in Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19 and Figure 20, where the red box represents correct detection, the yellow box represents missed detection, and the blue box represents false alarm.

Figure 17.
Illustration of detection results on Sequence 1. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
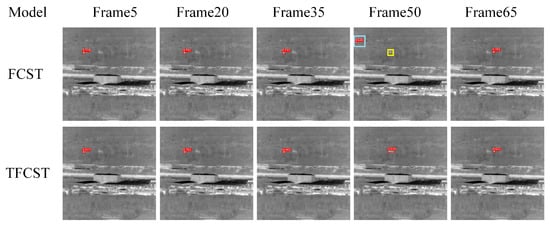
Figure 18.
Illustration of detection results on Sequence 2. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
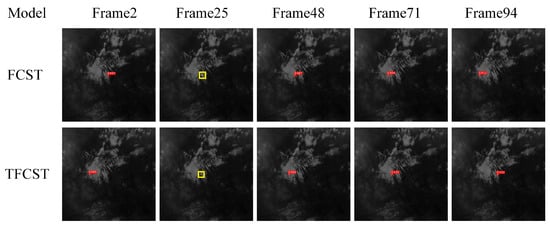
Figure 19.
Illustration of detection results on Sequence 3. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
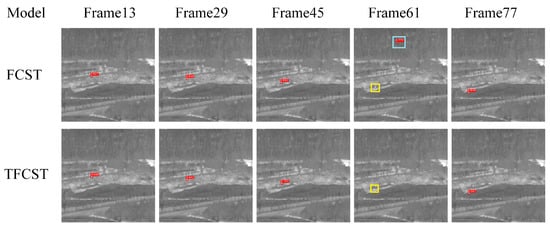
Figure 20.
Illustration of detection results on Sequence 4. Boxes in red, yellow, and blue respectively signify true positive targets with corresponding confidence scores, miss detected targets, and false alarms.
It is observed that in Infrared Image Sequence 1, the artificial structure (crane) in the background has a high-intensity interference section, which is very similar to the small infrared target, making it difficult for the detection algorithm to distinguish effectively. The single-frame image-based detection algorithm FCST showed false alarms in frames 50 and 65 of sequence 1. However, the TFCST based on the sequence images utilized the state information extracted from historical frames by the detector, thus enhancing the robustness of the detection during the current frame, and hence no occasional false detections occurred during the detection process. In the Infrared Image Sequence 2, the target passes through a region with severe clutter interference during its motion. The detection method FCST, which only uses spatial information in the infrared image, cannot detect the target correctly in this situation. A missed detection occurred in frame 38 of sequence 2, and the clutter interference in the image was misjudged as a target, indicating comparatively poor robustness. In contrast, TFCST correctly detected the targets in all consecutive frames, with stable output of detection results, exhibiting better detection performance.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that even with the utilization of temporal information in the detection algorithm, TFCST, when the target is heavily mixed in the background clutter region, there may still be missed detections due to low target confidence, as shown in frame 25 of Infrared Image Sequence 3 and frame 61 of Infrared Image Sequence 4. To comprehensively compare the performance of the two detection methods tested, we further calculated the detection results for 60 infrared sequences (3050 frames in total) in the test dataset, as presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Detection results of FCST compared with TFCST. The table compares positive detection (Pd), false alarm (Fa), and frames per second (FPS).
From Table 4, it is evident that TFCST, with a slightly lower inference speed, achieved a 2.73% increase in detection rate compared to the FCST network, significantly reducing the number of false target predictions, with a false alarm rate of only 0.51%. This result confirms that by combining the extraction of spatiotemporal domain information using ConvLSTM, the performance of a single-frame detector can be effectively enhanced. Moreover, TFCST also has extremely fast detection speed and hence meets the requirements for real-time detection.
5. Conclusions
To address the problems of high false alarm rates and poor robustness of existing infrared small target detection algorithms, a fully convolutional-based approach is proposed. Built upon a mechanism without anchor boxes, the algorithm avoids issues related to anchor box design and unfavorable effects on small target detection by pixel-level prediction. To address the issue of losing small target feature information with a deep network, a lightweight feature extraction network is designed, incorporating reduced downsampling and single-stage aggregation that efficiently extract small target features. Additionally, a feature refinement mechanism is proposed to deal with semantic conflicts when fusing features of different scales. By learning adaptive fusion weights in both spatial and channel dimensions, this mechanism enhances small target feature representation while suppressing background information. To cope with the infrared small target detection task in more complicated backgrounds with weaker target signals, a time-series-aware fully convolutional-based infrared small target detection approach is proposed. Built upon the mechanism without anchor boxes, the algorithm combines ConvLSTM to model the target’s appearance and movement information in sequential images, thus propagating and fusing temporal and spatial contextual information. This mechanism enhances the detection accuracy of infrared small targets in more complex scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and L.Z.; Methodology, Z.Z., J.X. and P.H.; Software, J.X. and P.H.; Validation, L.Z., P.H. and J.X.; Formal analysis, L.Z. and J.X.; Investigation, Z.Z. and P.H.; Resources, Z.Z.; Data curation, P.H. and J.X.; Writing—original draft, P.H. and L.Z.; Writing—review and editing, P.H., Z.Z. and L.Z.; Visualization, J.X. and P.H.; Supervision, Z.Z.; Project administration, L.Z.; Funding acquisition, Z.Z. and L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, J. Show, Match and Segment: Joint Weakly Supervised Learning of Semantic Matching and Object Co-Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 3632–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadinia, H.; Sadeghi, F.; Divvala, S.; Hajishirzi, H.; Choi, Y.; Farhadi, A. Segment-Phrase Table for Semantic Segmentation, Visual Entailment and Paraphrasing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Li, G. Spatial-Temporal Context-Aware Online Action Detection and Prediction. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Gu, Q. Class-wise boundary regression by uncertainty in temporal action detection. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 3854–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wei, J.; Peng, C.; Qin, H. Depth-Quality-Aware Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2350–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappriya, S.; Priyadarsini, M.; Stateczny, A.; Puttamadappa, C.; Parameshachari, B. Cascade Object Detection and Remote Sensing Object Detection Method Based on Trainable Activation Function. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhao, K.; Kong, X. Discussion on the suppression and method of background noise of small target infrared image. Opt. Optoelectron. Technol. 2004, 2, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, S.; Deshpande, S.; Er, M.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3809, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hadhoud, M.; Hadhoud, M.; Thomas, D. The Two-Dimensional Adaptive LMS (TDLMS) Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1988, 35, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.; Bae, T.; Sohng, K. Small Target Detection Using Bilateral Filter Based on Edge Component. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2010, 31, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M. The design of top-hat morphological filter and application to infrared target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2006, 48, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y. A Local Contrast Method for Small Infrared Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Han, J.; Yong, M.; Bo, Z. A Robust Infrared Small Target Detection Algorithm Based on Human Visual System. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. Miss Detection vs. False Alarm: Adversarial Learning for Small Object Segmentation in Infrared Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision 2019, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8508–8517. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Shi, M.; Wang, H. Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection Based on Denoising Autoencoder Network. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, B.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Han, Z. A Novel Pattern for Infrared Small Target Detection With Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xu, M. Deep-IRTarget: An automatic target detector in infrared imagery using dual-domain feature extraction and allocation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, F. Graph-based few-shot learning with transformed feature propagation and optimal class allocation. Neurocomputing 2022, 470, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Bai, K.; Wang, Y. Infrared dim and small target detection based on three-dimensional collaborative filtering and spatial inversion modeling. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 101, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsoy, O.; Cardie, C. Opinion mining with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing 2014, Doha, Qatar, 26–28 October 2014; pp. 720–728. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y. Video Object Detection with an Aligned Spatial-Temporal Memory. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 485–501. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lu, C.; Tang, C. Online video object detection using association LSTM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2344–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.; Wong, W.; Woo, W. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning apporach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Infromation Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Wei, K.; Fu, Y.; Huang, H. 3-d quasi-recurrent neural network for hyperspectral image denoising. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9626–9635. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Laurens, V. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Bae, Y.; Park, J. An Energy and GPU-Computation Efficient Backbone Network for Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Lin, T.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Lin, T.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 99, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Ballas, N.; Ballas, N.; Yao, L.; Pal, C.; Courville, A. Delving Deeper into Convolutional Networks for Learning Video Representations. Comput. Sci. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, M. Mobile Video Object Detection with Temporally-Aware Feature Maps. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Cho, K.; Van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. Comput. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared Small Target Detection via Non-Convex Rank Approximation Minimization Joint l2,1 Norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).