Infrared Dim Star Background Suppression Method Based on Recursive Moving Target Indication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Research Status
1.2. Motivation
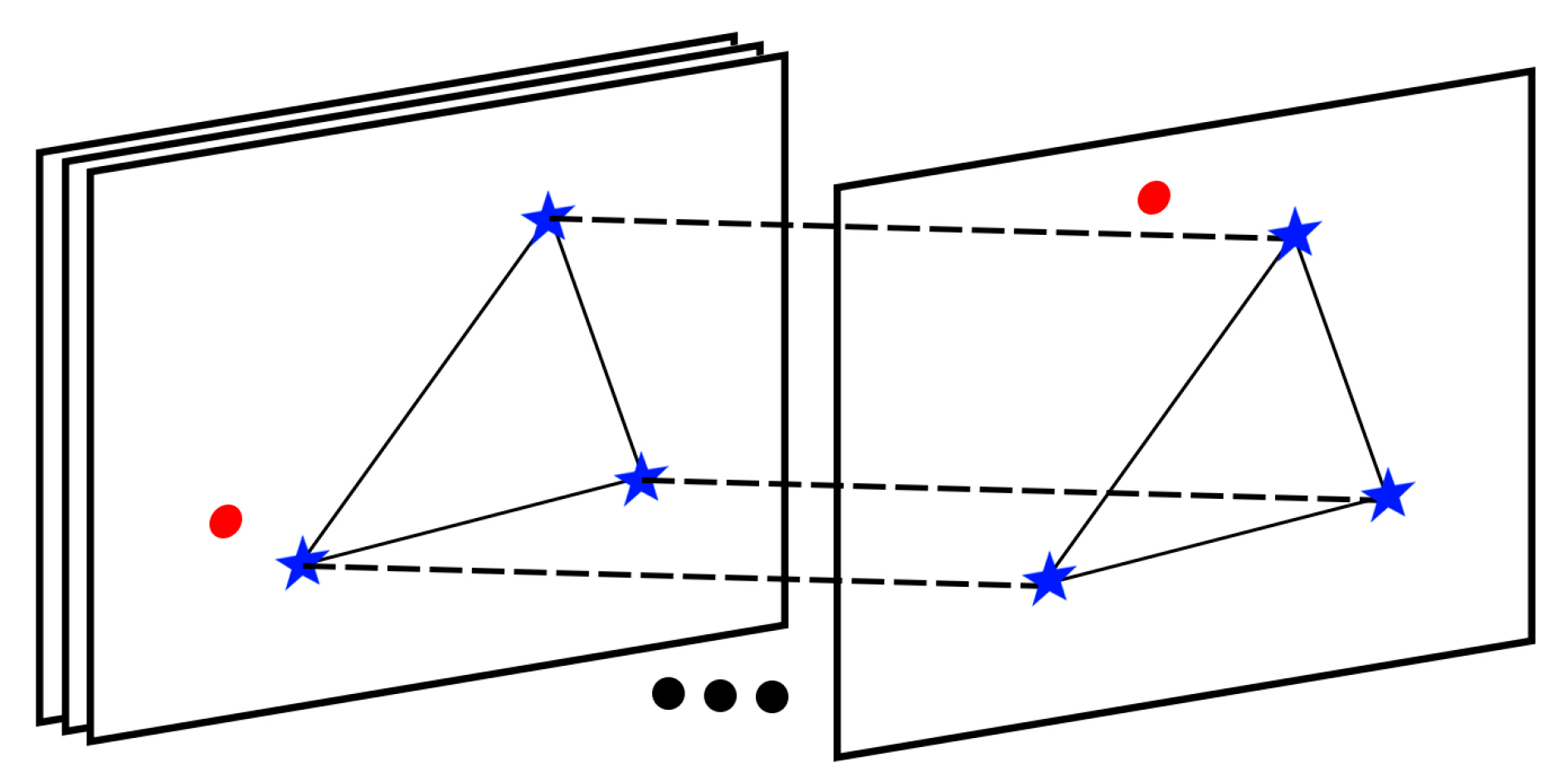
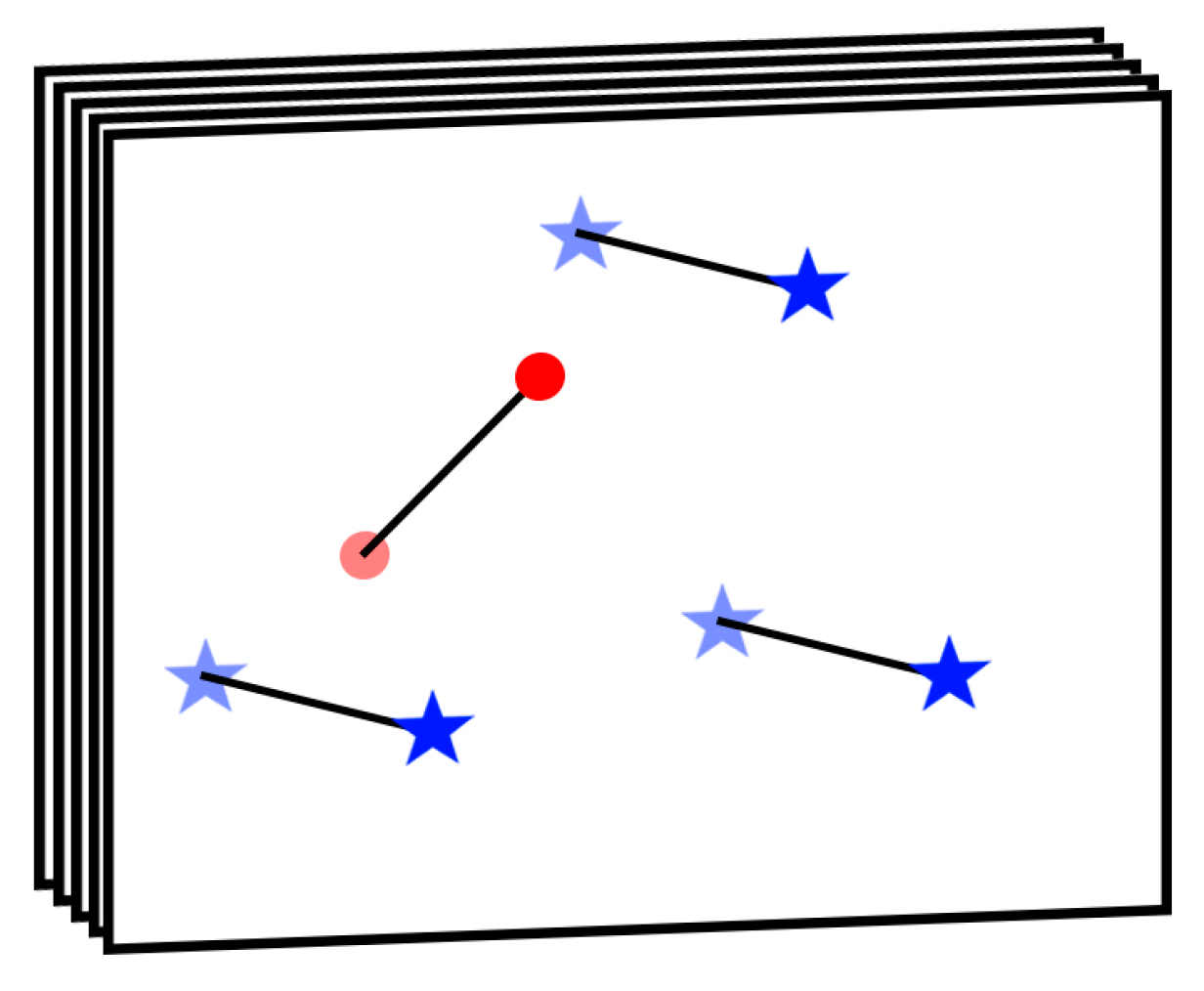
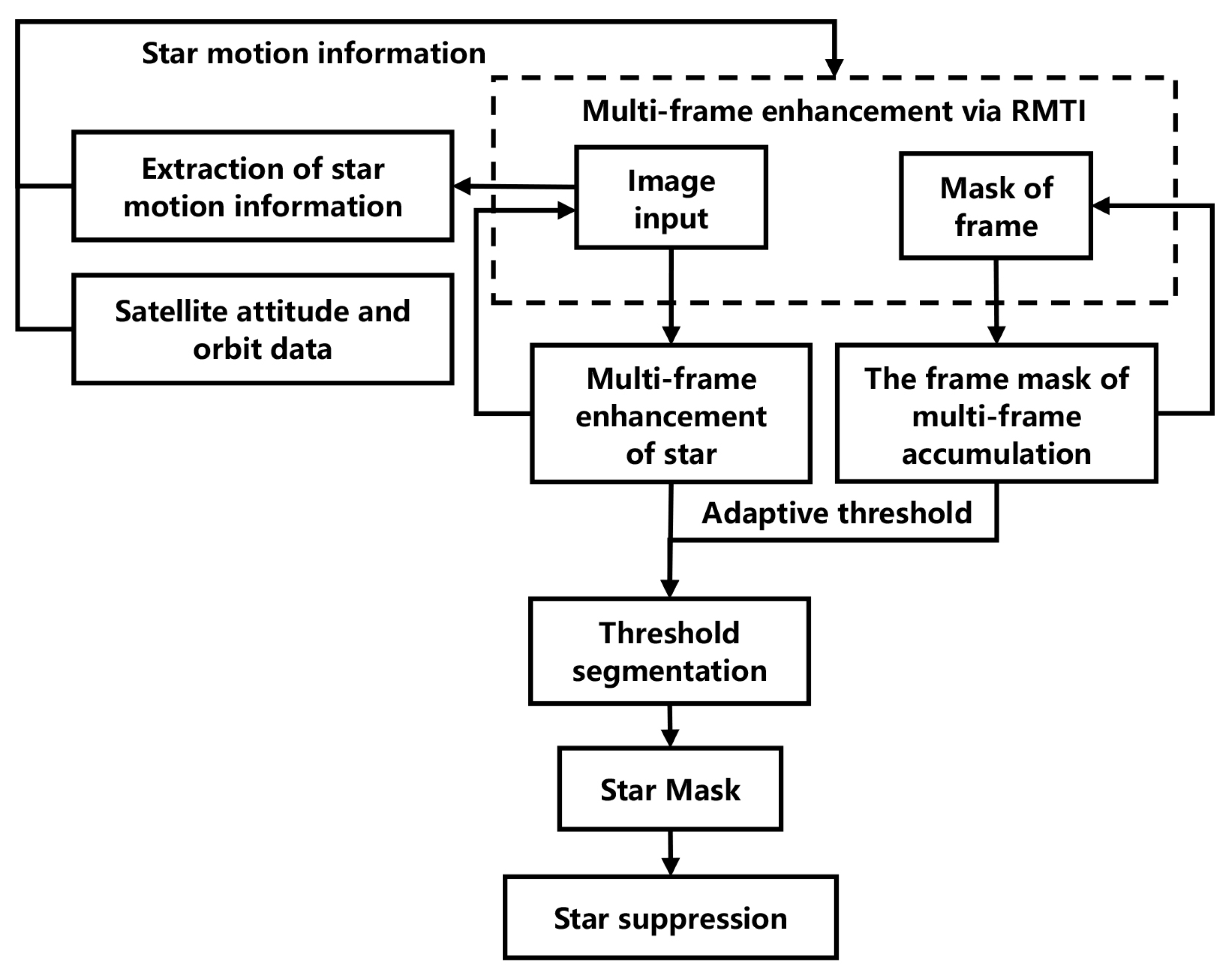
2. Methodology
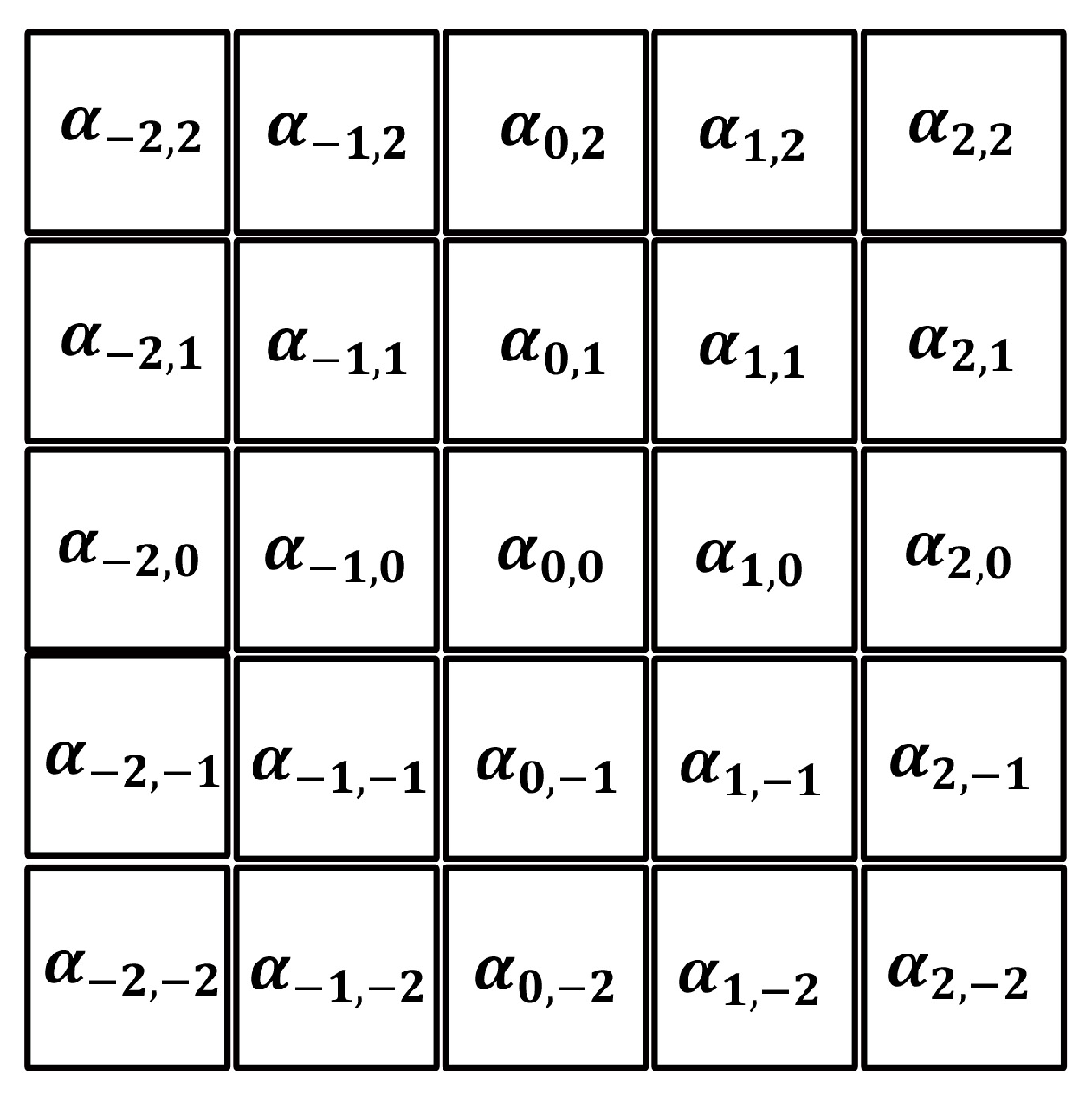
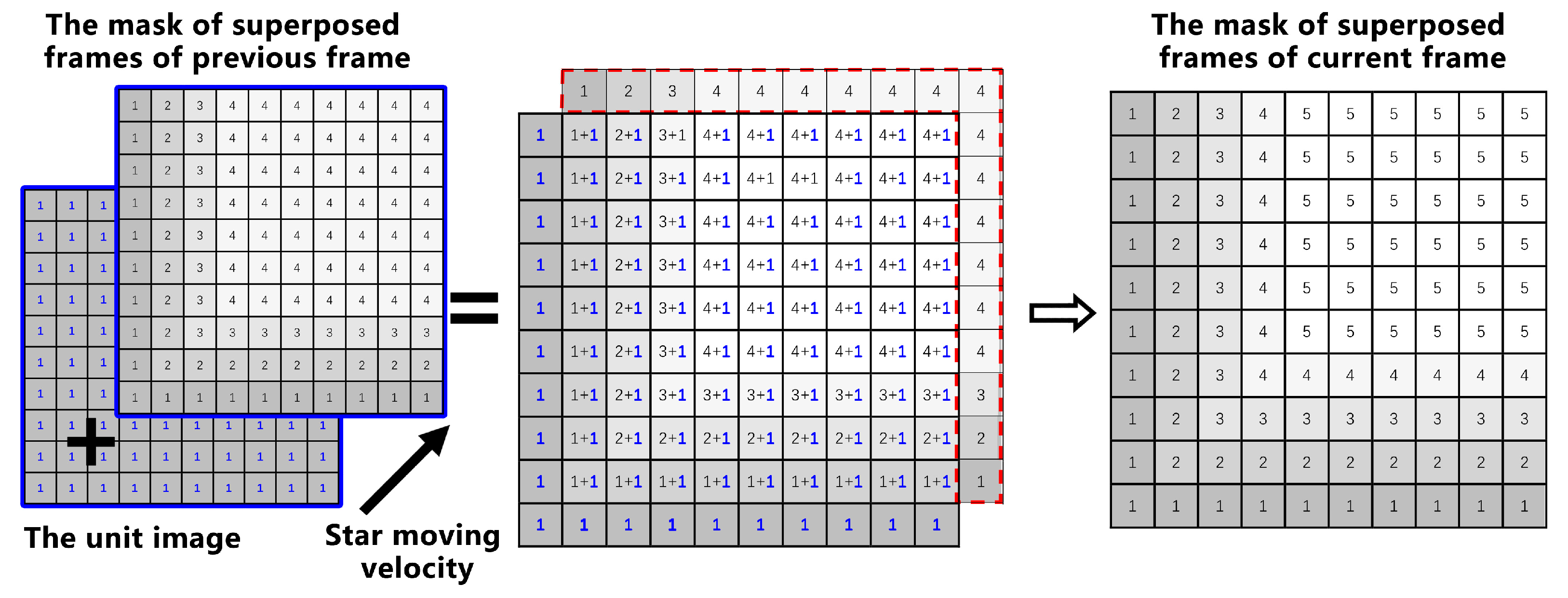
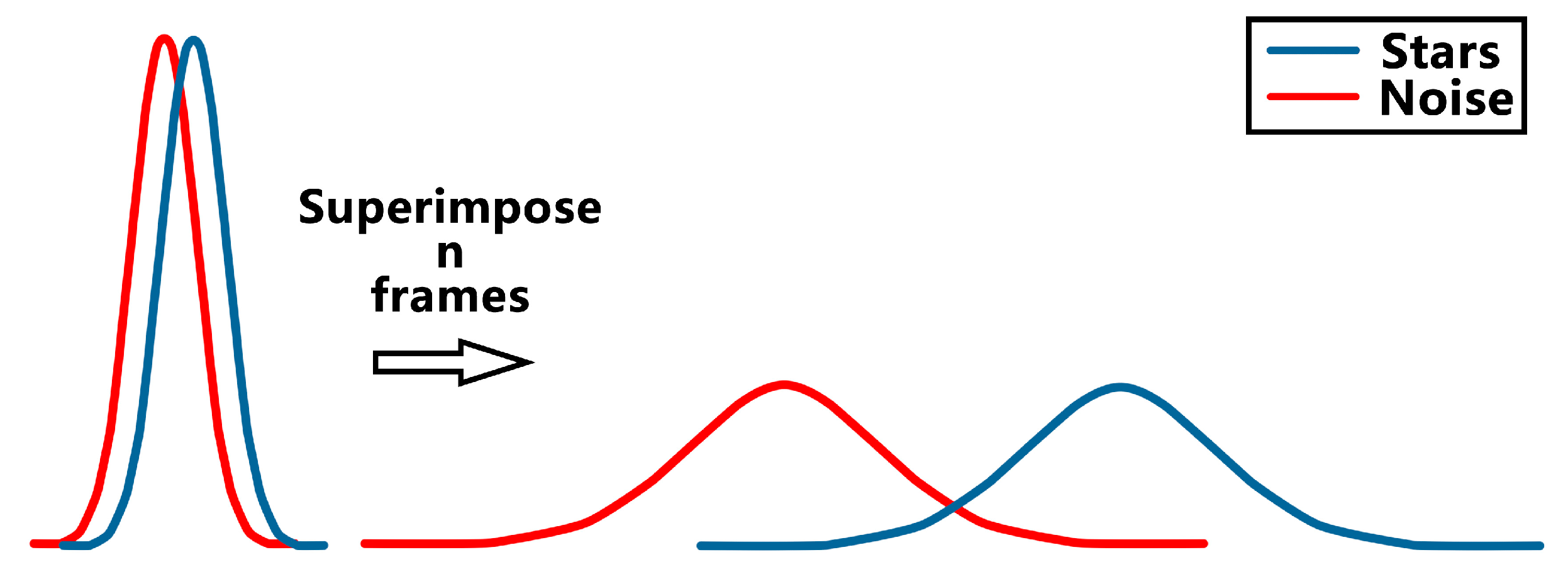
2.1. The Multi-Frame Enhancement of Advanced RMTI
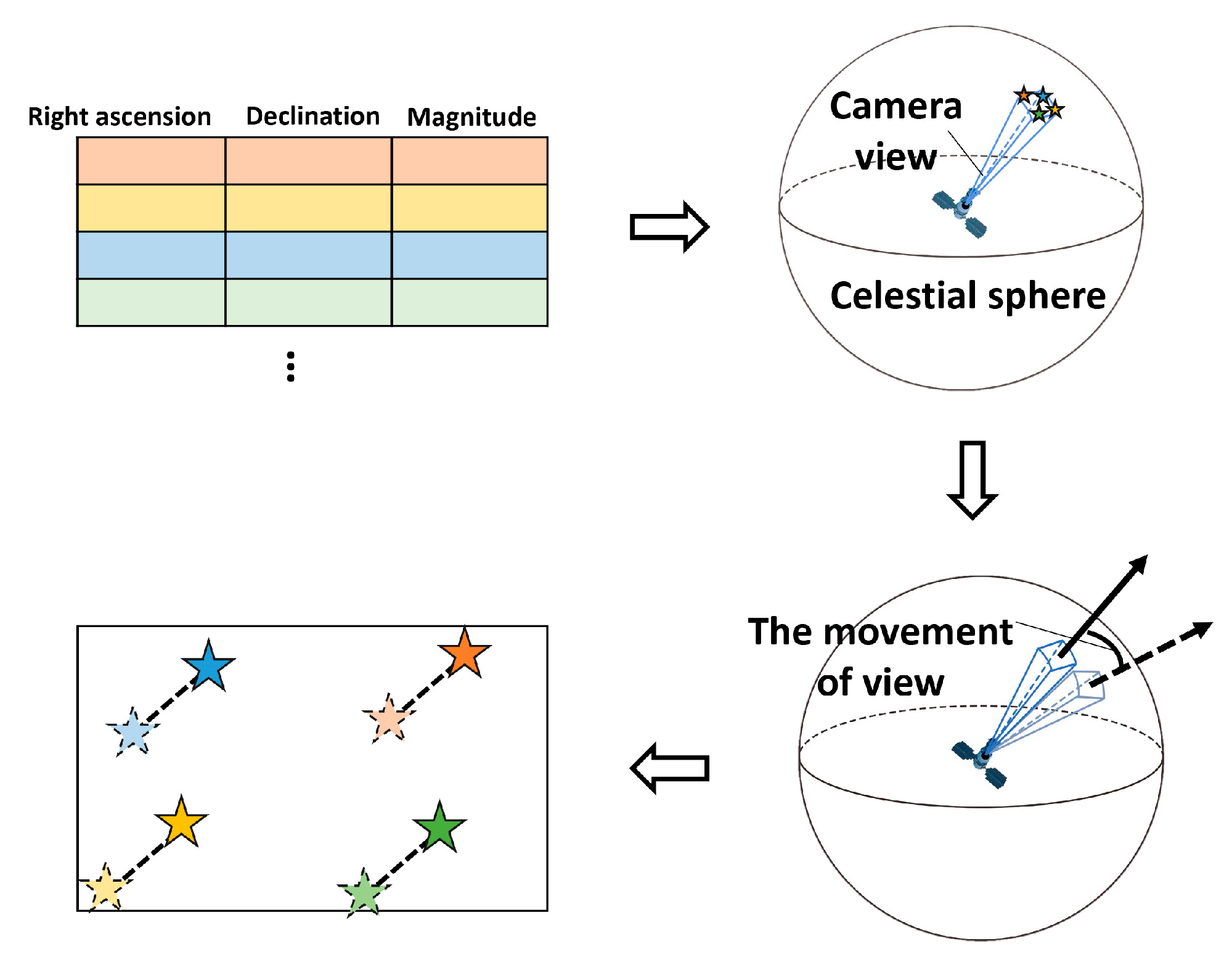
2.2. Adaptive Star Map
3. Experiment and Parameter Setting
3.1. Experimental Setup
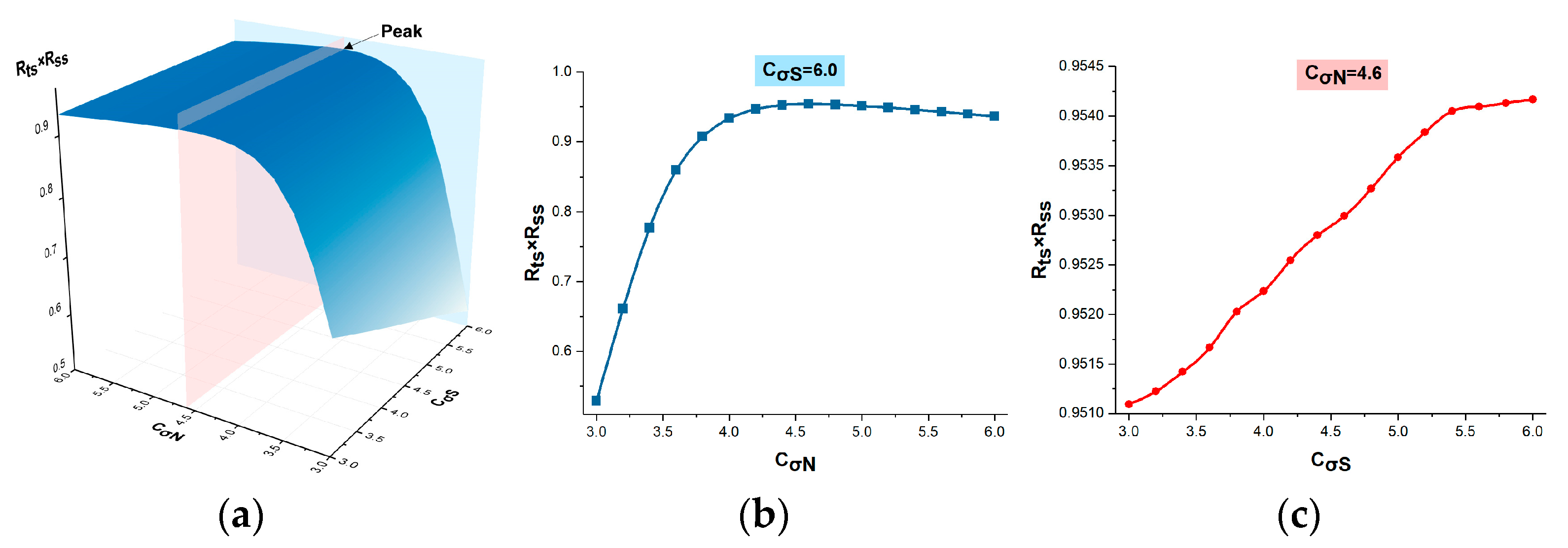
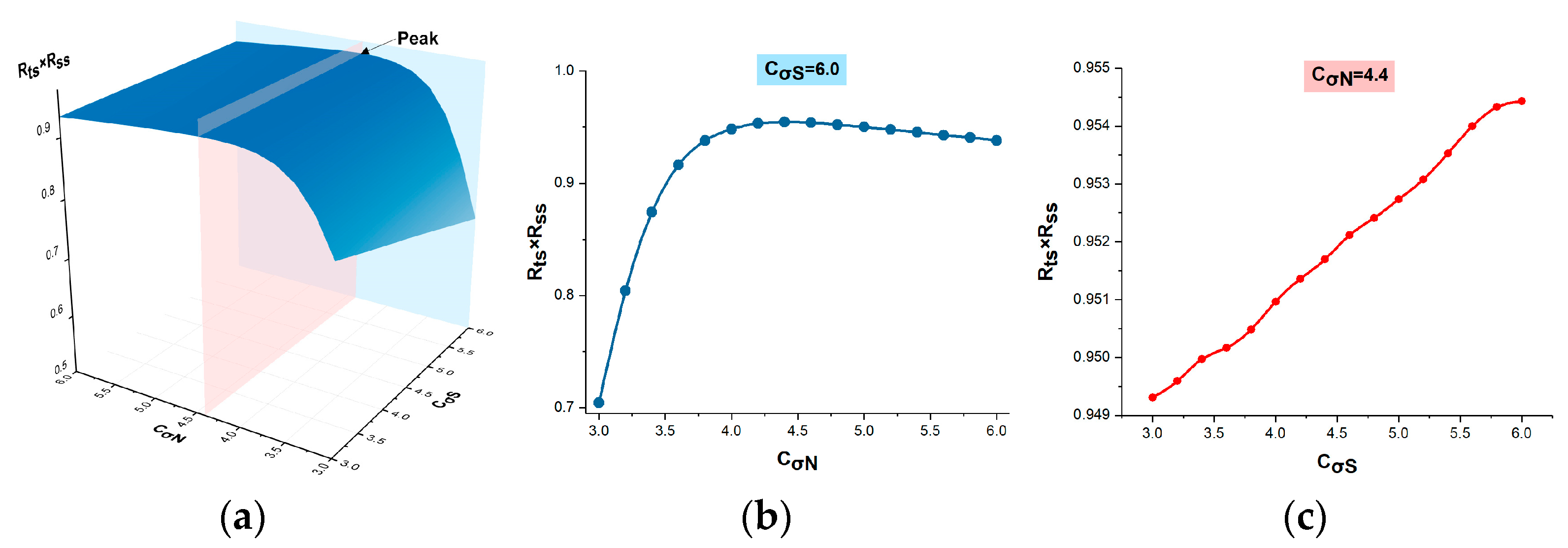
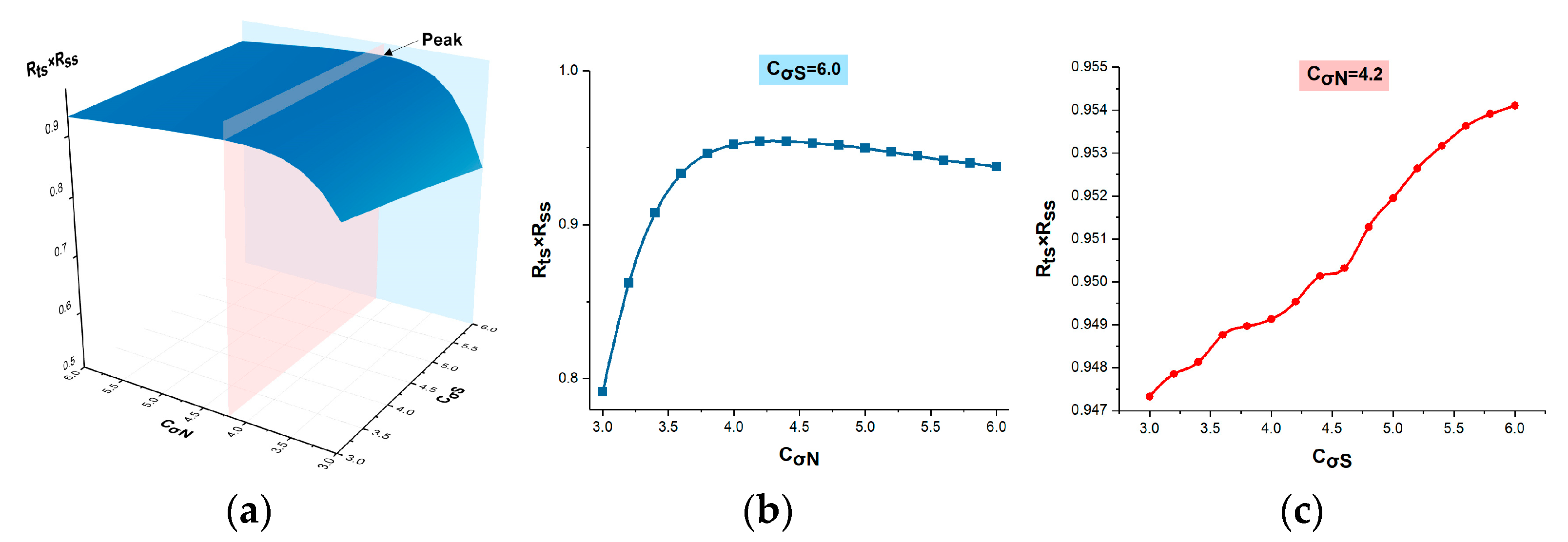
3.2. Parameter Setting
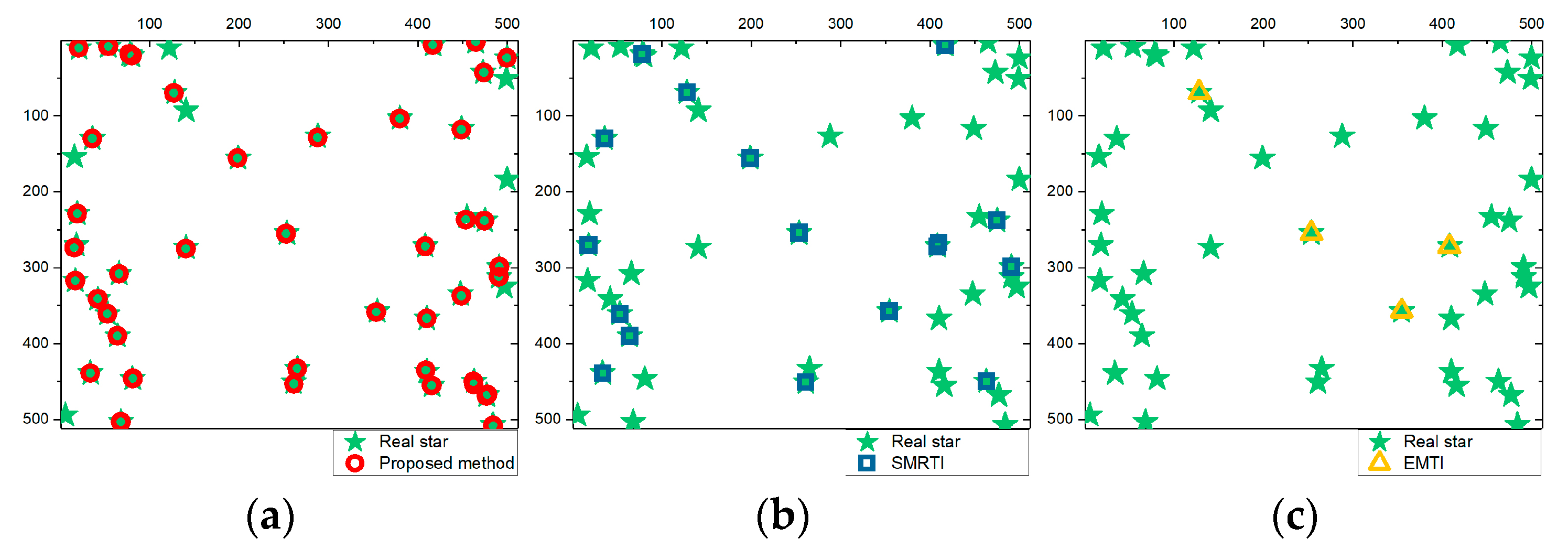
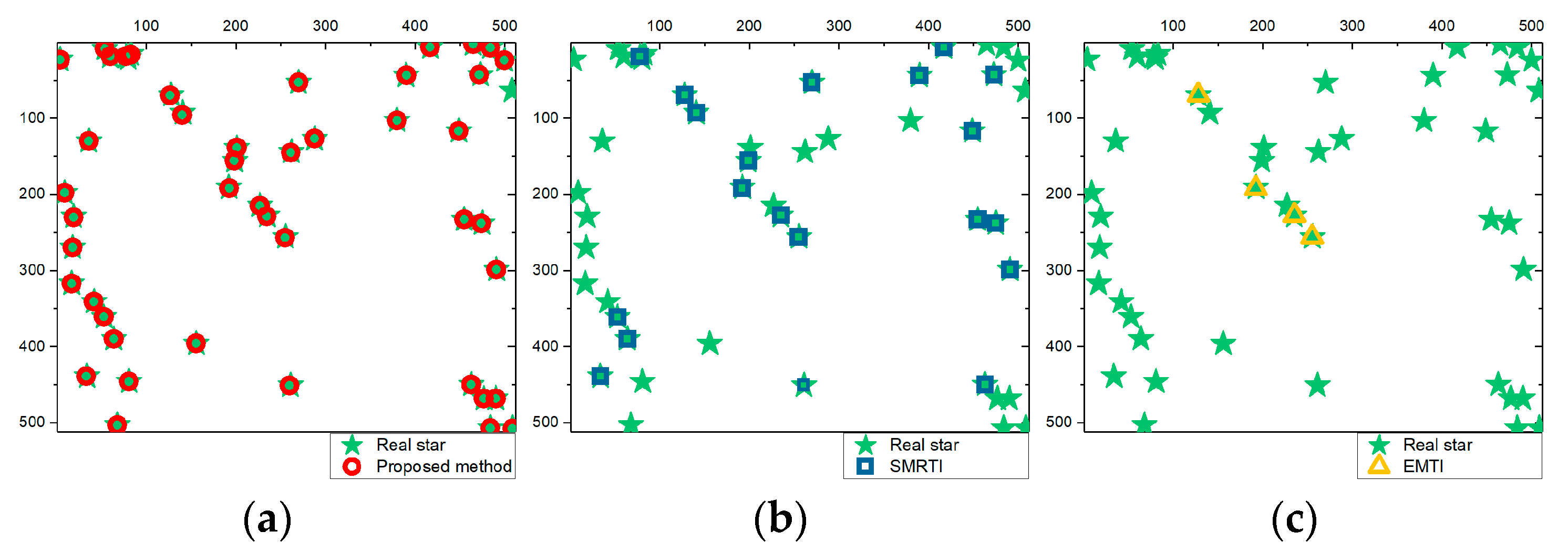
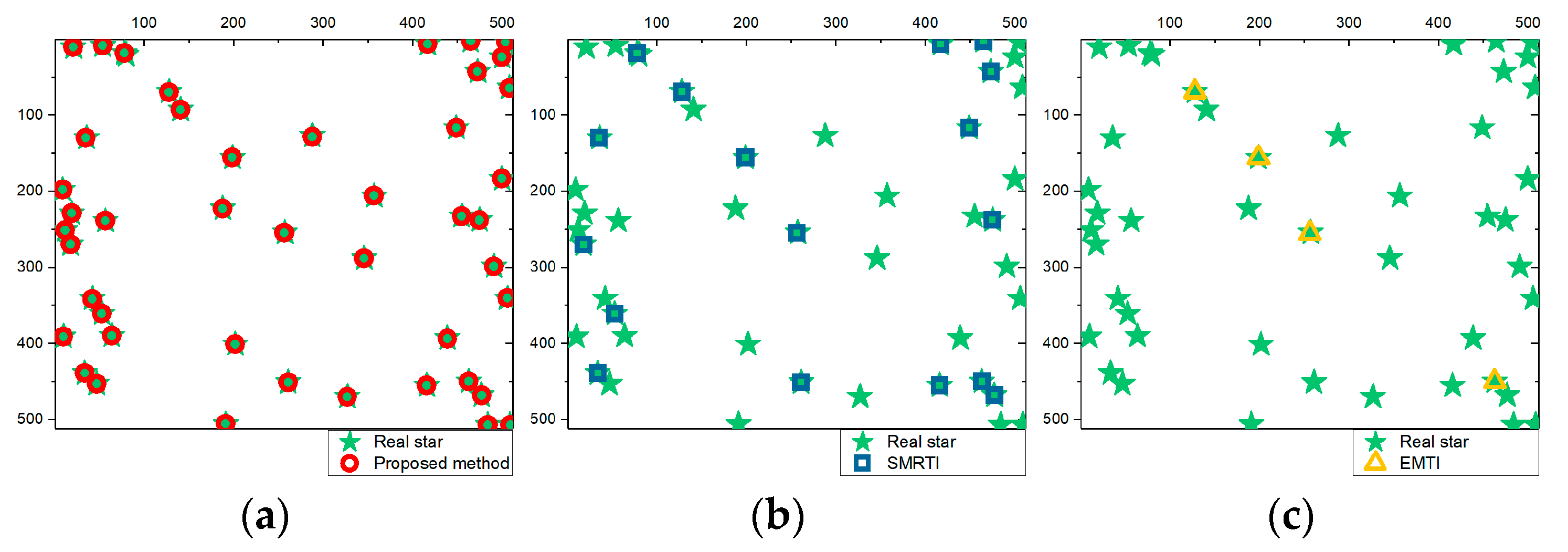
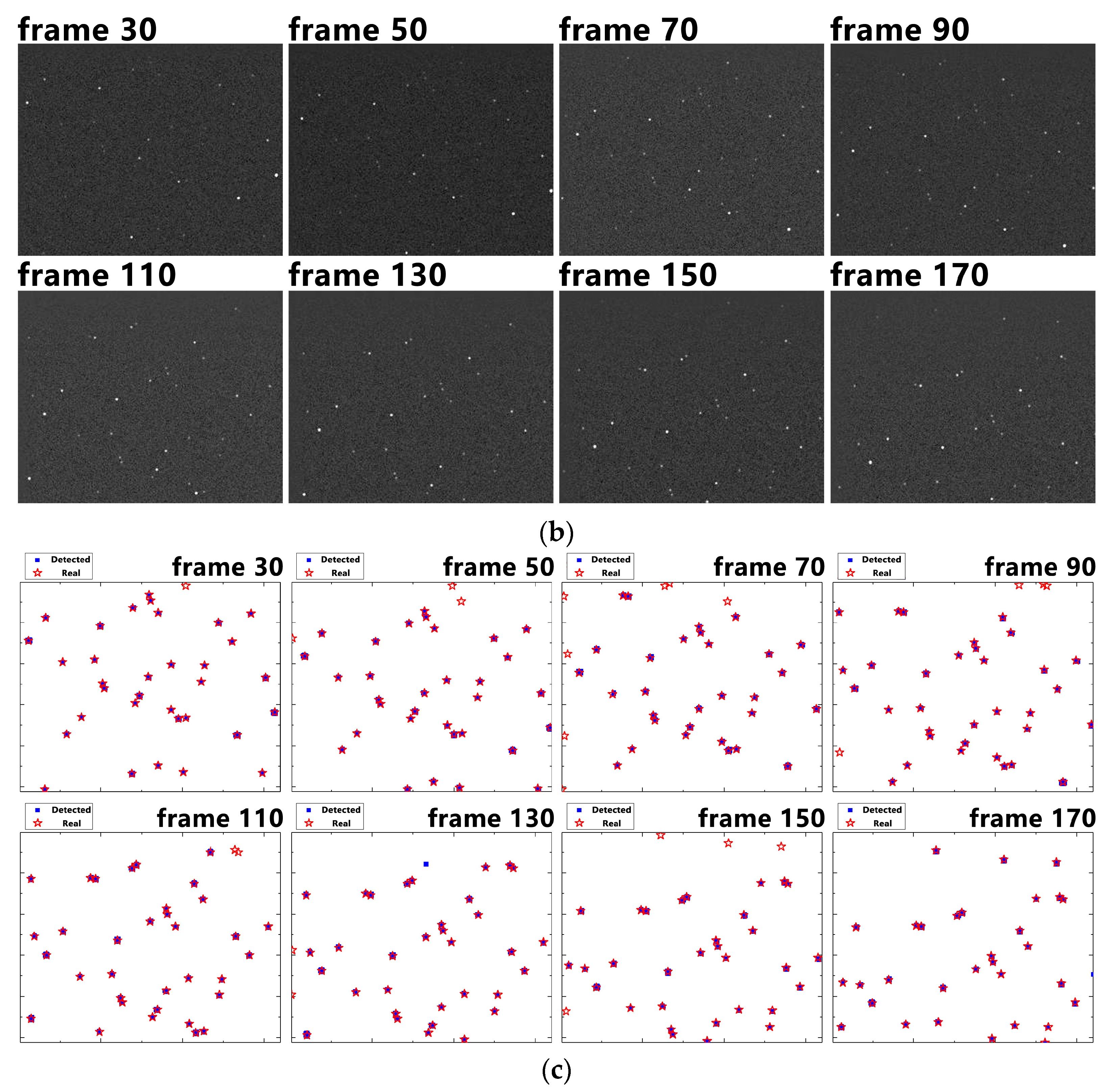
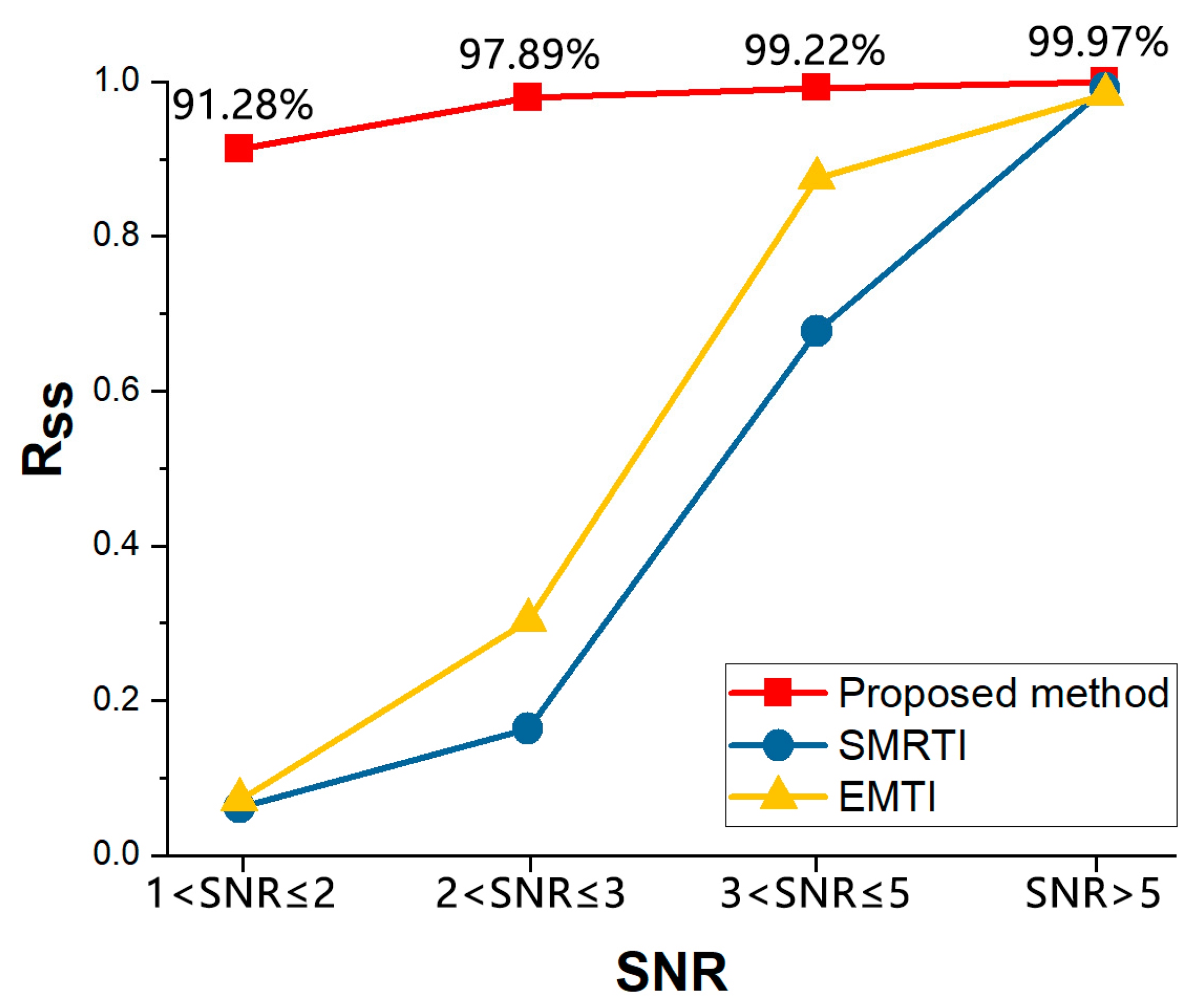
3.3. Experimental Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, B.; Nener, B.D. Multi-Sensor Space Debris Tracking for Space Situational Awareness With Labeled Random Finite Sets. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36991–37003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Y. Design and Analysis of Preload Control for Space Debris Impact Adhesion Capture Method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 203845–203853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; An, Q. Dim Space Target Detection via Convolutional Neural Network in Single Optical Image. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 52306–52318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. Space target extraction and detection for wide-field surveillance. Astron. Comput. 2020, 32, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Budavari, B. Enhancing small moving target detection performance in low-quality and long-range infrared videos using optical flow techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Verma, S.K.; Kumar, Y. Review on recent development in infrared small target detection algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Dong, L. Reverse Procedure Detection of Space Target Streaks Based on Motion Parameter Estimation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 21823–21831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Shao, S.; Zhang, E.; Lin, G. Infrared moving small-target detection via spatiotemporal consistency of trajectory points. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, G.; Yan, D.; Zhao, Z. Two Algorithms for the Detection and Tracking of Moving Vehicle Targets in Aerial Infrared Image Sequences. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Jin, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, C. Infrared blind-pixel compensation algorithm based on generative adversarial networks and Poisson image blending. Signal Image Video Process 2020, 14, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchendjou, G.T.; Simeu, E. Detection, location and concealment of defective pixels in image sensors. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2021, 9, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gu, G.; Chen, Q. Infrared small target tracking via gaussian curvature-based compressive convolution feature extraction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 7000905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.J.; Gu, G.H.; Cao, E.C.; Hu, X.B.; Qian, W.X.; Ren, K. In-frame and inter-frame information based infrared moving small target detection under complex cloud backgrounds. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Qin, F.; Peng, Z. Mask Sparse Representation Based on Semantic Features for Thermal Infrared Target Tracking. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N. Infrared radiation characteristic measure method of point target. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2015, 34, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Rao, P.; Chen, X.; Qiu, S. On-Board Flickering Pixel Dynamic Suppression Method Based on Multi-Feature Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, X. Stray Light Suppression of Wide-Field Surveillance in Complicated Situations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, D.; Yan, C.; Hu, C. Stray light nonuniform background correction for a wide-field surveillance system. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 10719–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.R.; Sentovich, M.F.; Ho, C.q. Star Background Cancellation for Deep Space Surveillance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1981, AES-17, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dim small target detection based on convolutinal neural network in star image. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 4681–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Z.; Hongjian, Z.; Dakai, S.; Li, W.; Yanpeng, W.; Chunyan, L. High sensitive automatic detection technique for space objects. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, J. An algorithm of small and dim target detection in deep space background. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Information and Automation, Zhuhai, China, 22–24 June 2009; pp. 985–989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhou, J.; Duan, F.; Sun, J.; Jiang, L. A new starry images matching method in dim and small space target detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fifth International Conference on Image and Graphics, Xi’an, China, 20–23 September 2009; pp. 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Gao, Z.; Xie, C. Improved GM-PHD filter based on threshold separation clusterer for space-based starry-sky background weak point target tracking. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 103, 102766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xiaoliang, X.; Tongsheng, S. Space small targets detection based on maximum projection and quick registration. Infrared Laser Eng. 2016, 45, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Yuan, J.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, L. Space target detection based on the invariance of inter-satellite topology. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 June 2022; pp. 2151–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Lei, Z.; Yu, Q.; Liu, X. Small target detection using main directional suppression high pass filter. Optik 2014, 125, 3017–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianlin, L.; Xijian, P.; Debao, M. A novel method of drift-scanning stars suppression based on the standardized linear filter. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optoelectronic Imaging and Processing Technology, Beijing, China, 28 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Rao, P.; Jia, L.; Chen, X. Dim moving infrared target enhancement based on precise trajectory extraction. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 128, 104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkang, D.; Zongxi, S. Detection and tracking of multi-space junks in star images. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2016), Chengu, China, 20–22 May 2016; p. 100330N. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Yan, W.; Zhao, L. Moving space target detection algorithm based on trajectory similarity. In Proceedings of the SPIE/COS Photonics Asia, Beijing, China, 11 October 2018; p. 108161B. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Qin, S.; Dai, D. A Star Identification Algorithm based on Radial Basis Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation (IAECST), Guangzhou, China, 9–11 December 2022; pp. 1274–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, J. Fast and Robust Star Identification Using Color Ratio Information. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 20401–20412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.S.; Chen, S.; Low, K.S. A Rotation-Invariant Additive Vector Sequence Based Star Pattern Recognition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupon, J.; Czakon, N.; Bosch, J.; Komiyama, Y.; Medezinski, E.; Miyazaki, S.; Oguri, M. The bright-star masks for the HSC-SSP survey. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 70, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Pei, H.; Huang, Z.; Huang, T.; Qin, S. Non-cooperative Space Target High-Speed Tracking Measuring Method Based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Xi’an, China, 26–28 July 2022; pp. 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Xiao, H. Background Suppression Method of Star Image Based on Improved CBDNet. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning & International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications (CVIDL & ICCEA), Changchun, China, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Su, Y. Infrared target tracking based on improved particle filtering. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 2154015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Rao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, X. Low-SNR Infrared Point Target Detection and Tracking via Saliency-Guided Double-Stage Particle Filter. Sensors 2022, 22, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barniv, Y. Dynamic Programming Solution for Detecting Dim Moving Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1985, AES-21, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; Long, G.; Yu, Q. Real-time visual enhancement for infrared small dim targets in video. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Rosenfeld, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Hough-transform detection of lines in 3-D space. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2000, 21, 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Kultanen, P.; Xu, L.; Oja, E. Randomized Hough transform (RHT). In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 16–21 June 1990; Volume 631, pp. 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, I.S.; Gagliardi, R.M.; Stotts, L.B. Optical moving target detection with 3-D matched filtering. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1988, 24, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.S.; Gagliardi, R.M.; Stotts, L.B. A recursive moving-target-indication algorithm for optical image sequences. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1990, 26, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yu, Q.F.; Lei, Z.H.; Liu, X.C. A block-based improved recursive moving-target-indication algorithm. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongfu, H.; Jinzhen, W.; Zengping, C. Motion characteristics analysis of space target and stellar target in opto-electronic observation. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2012, 39, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; González, D.; Klein, M.; Pilla, M.; Vallerand, S.; Maldague, X. Infrared image processing and data analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2004, 46, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Choi, G.B.; Baek, R.H.; Kang, H.S.; Jung, S.W.; Jeong, Y.H. Low-Temperature Performance of Nanoscale MOSFET for Deep-Space RF Applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2008, 29, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.L.; Eisenhardt, P.R.M.; Mainzer, A.K.; Ressler, M.E.; Cutri, R.M.; Jarrett, T.; Kirkpatrick, J.D.; Padgett, D.; McMillan, R.S.; Skrutskie, M.; et al. The Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE): Mission Description and Initial On-orbit Performance. Astron. J. 2010, 140, 1868–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Star Identification; Nation Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, B.; Arulampalam, S.; Gordon, N. Detection and tracking of stealthy targets. In Beyond the Kalman Filter Particle Filters for Tracking Applications; Barton, D.K., Ed.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2004; pp. 240–251. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Format | 512 × 512 |
| The angle resolution of pixel | 0.02464° |
| The angle of field of view | 12.6° × 12.6° |
| Framerate | 20 Hz |
| Bits per pixel | 14 bits |
| Spectrum | 2.1~3.3 μm |
| Field direction | Seq.1: De = 340.668 Ra = −46.885 Seq.2: De = 298.808 Ra = −59.196 Seq.3: De = 252.166 Ra = −69.028 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Format | 320 × 256 |
| The angle resolution of pixel | 0.01784° |
| The angle of field of view | 4.568° × 5.710° |
| Framerate | 30 Hz |
| Bits per pixel | 14 bits |
| Spectrum | 3 μm |
| Minimum detectable magnitude (corresponding SNR = 1) | 9.56 |
| 1 | 4.2~4.8 | 5.5~6.0 |
| 1.5 | 4.0~4.6 | 5.6~6.0 |
| 2 | 4.0~4.4 | 5.8~6.0 |
| Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | 98.72% | 98.82% | 0.0031 s |
| SMRTI | 98.19% | 69.88% | 0.2490 s |
| EMTI | 98.59% | 73.28% | 0.0640 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Rao, P.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Jia, L. Infrared Dim Star Background Suppression Method Based on Recursive Moving Target Indication. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4152. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174152
Zhang L, Rao P, Hong Y, Chen X, Jia L. Infrared Dim Star Background Suppression Method Based on Recursive Moving Target Indication. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4152. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174152
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Peng Rao, Yang Hong, Xin Chen, and Liangjie Jia. 2023. "Infrared Dim Star Background Suppression Method Based on Recursive Moving Target Indication" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4152. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174152
APA StyleZhang, L., Rao, P., Hong, Y., Chen, X., & Jia, L. (2023). Infrared Dim Star Background Suppression Method Based on Recursive Moving Target Indication. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4152. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174152





