Lightning Interferometry with the Long Wavelength Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Projection Imaging
2.3. Deconvolution
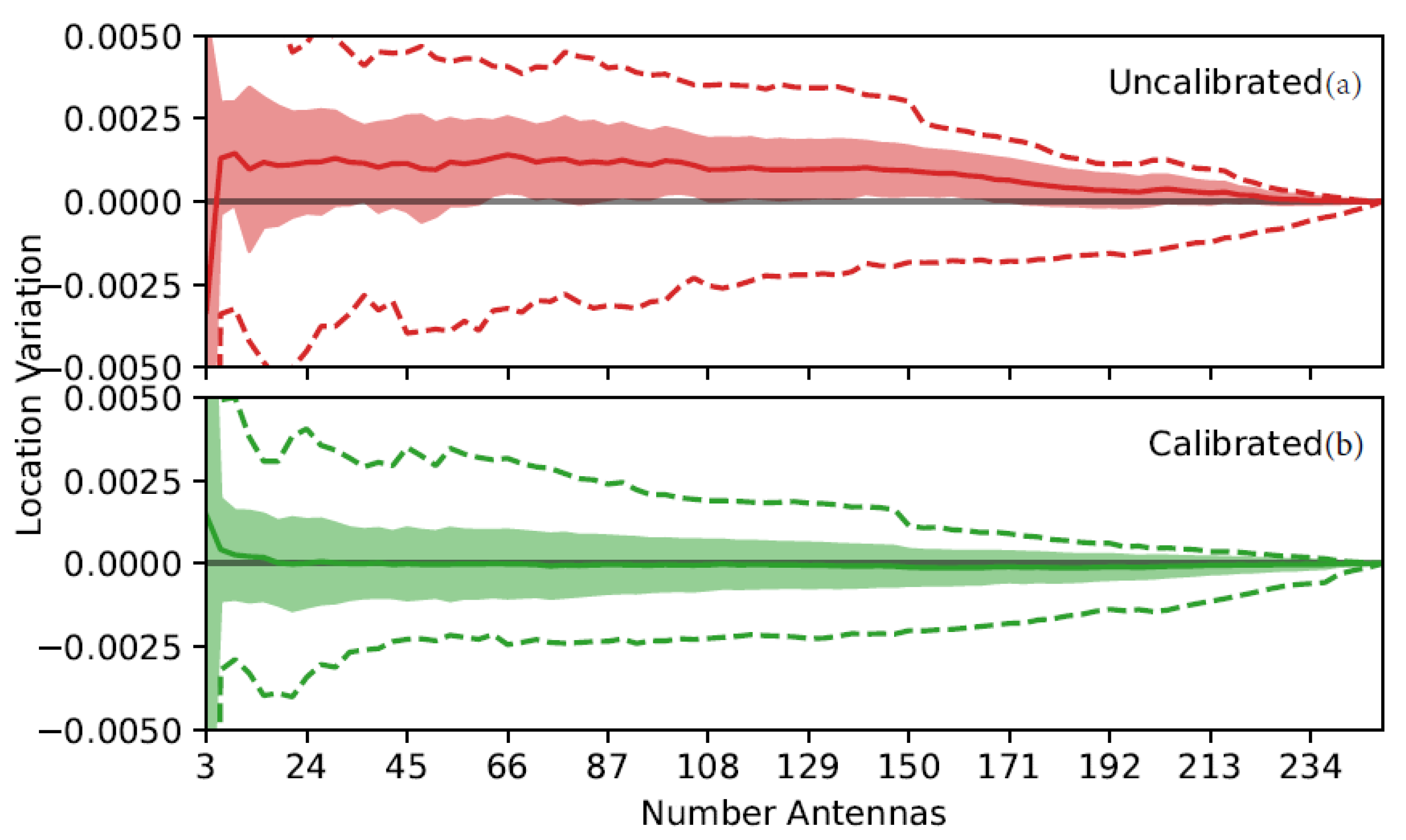
2.4. Calibration
3. Results
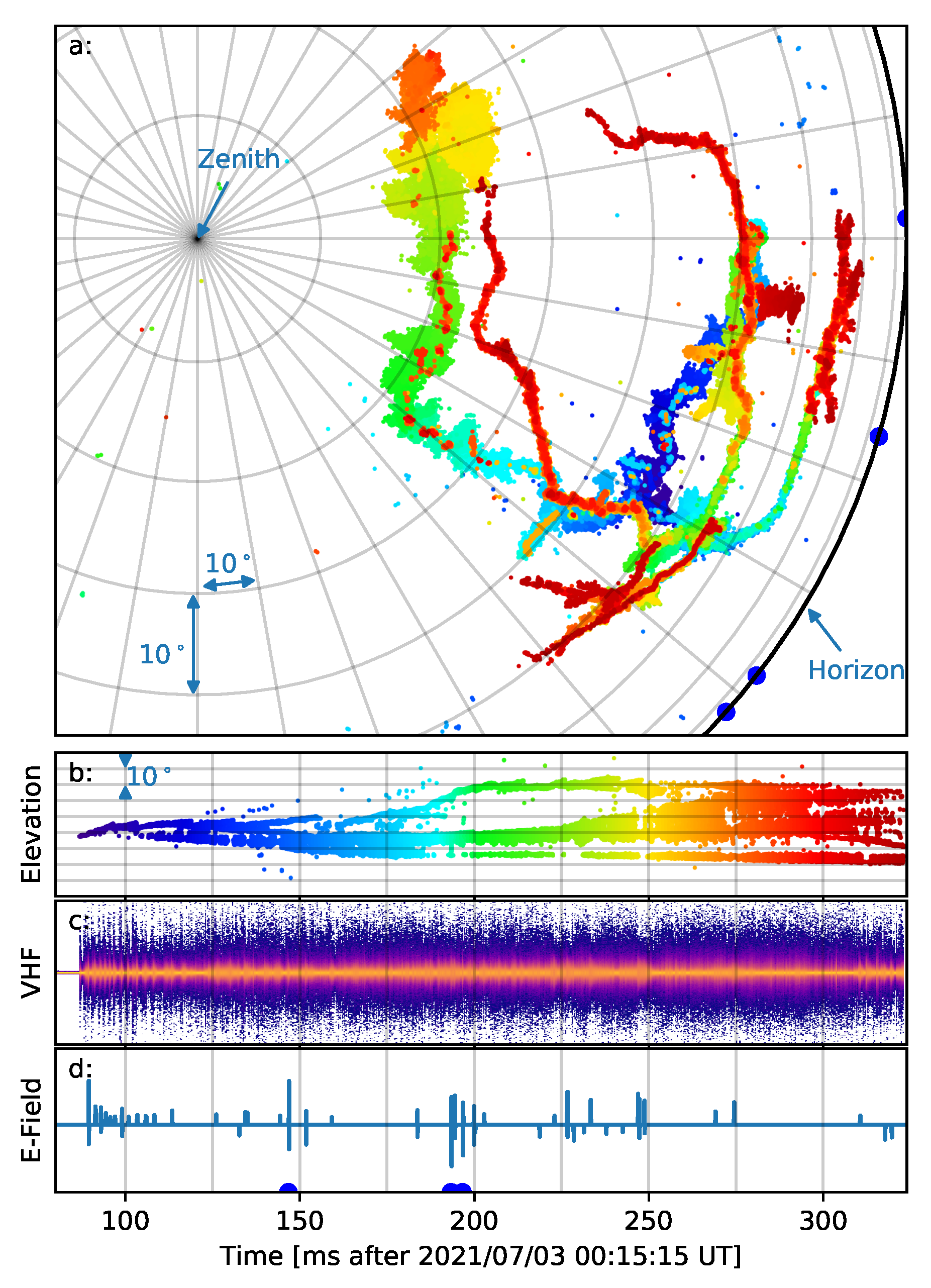
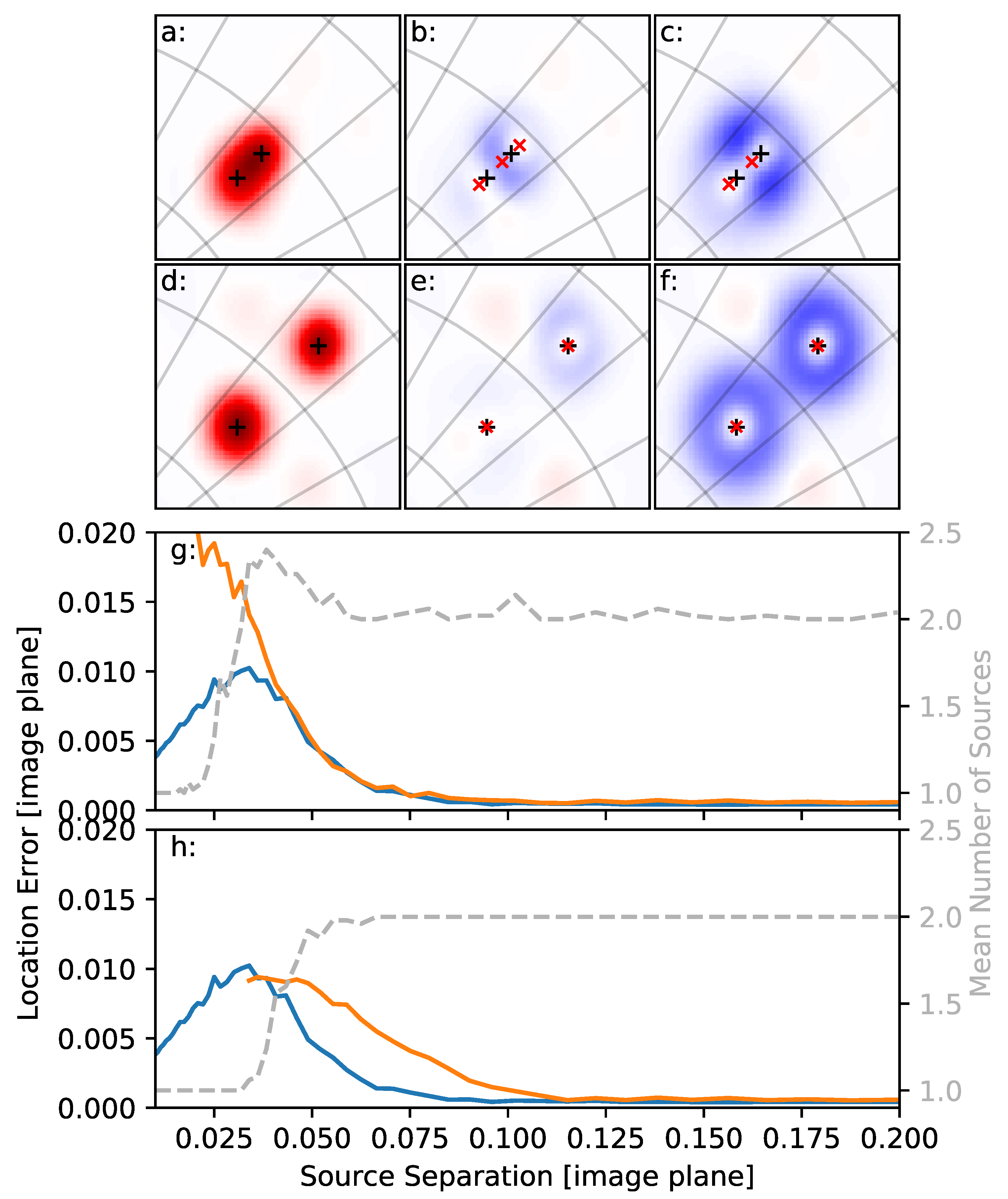
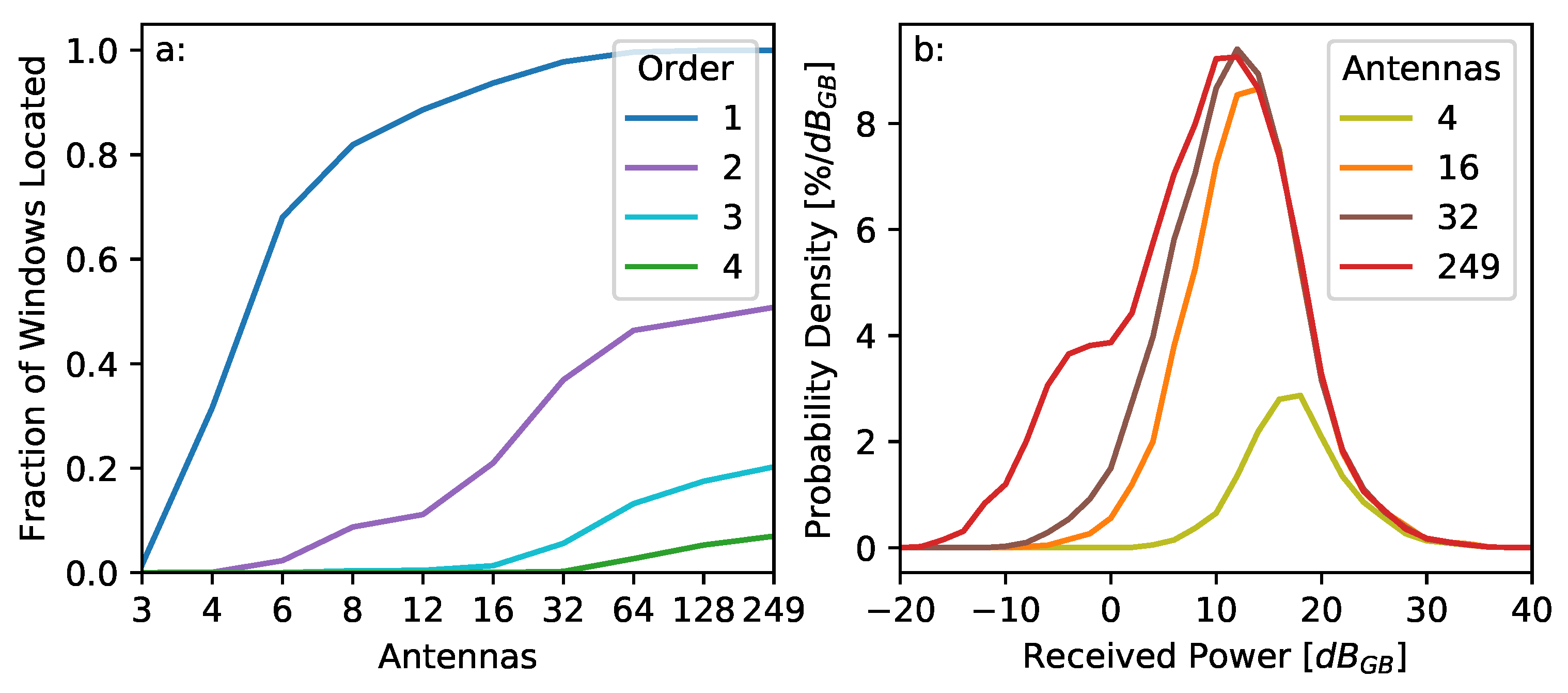
3.1. Multi-Source Detections
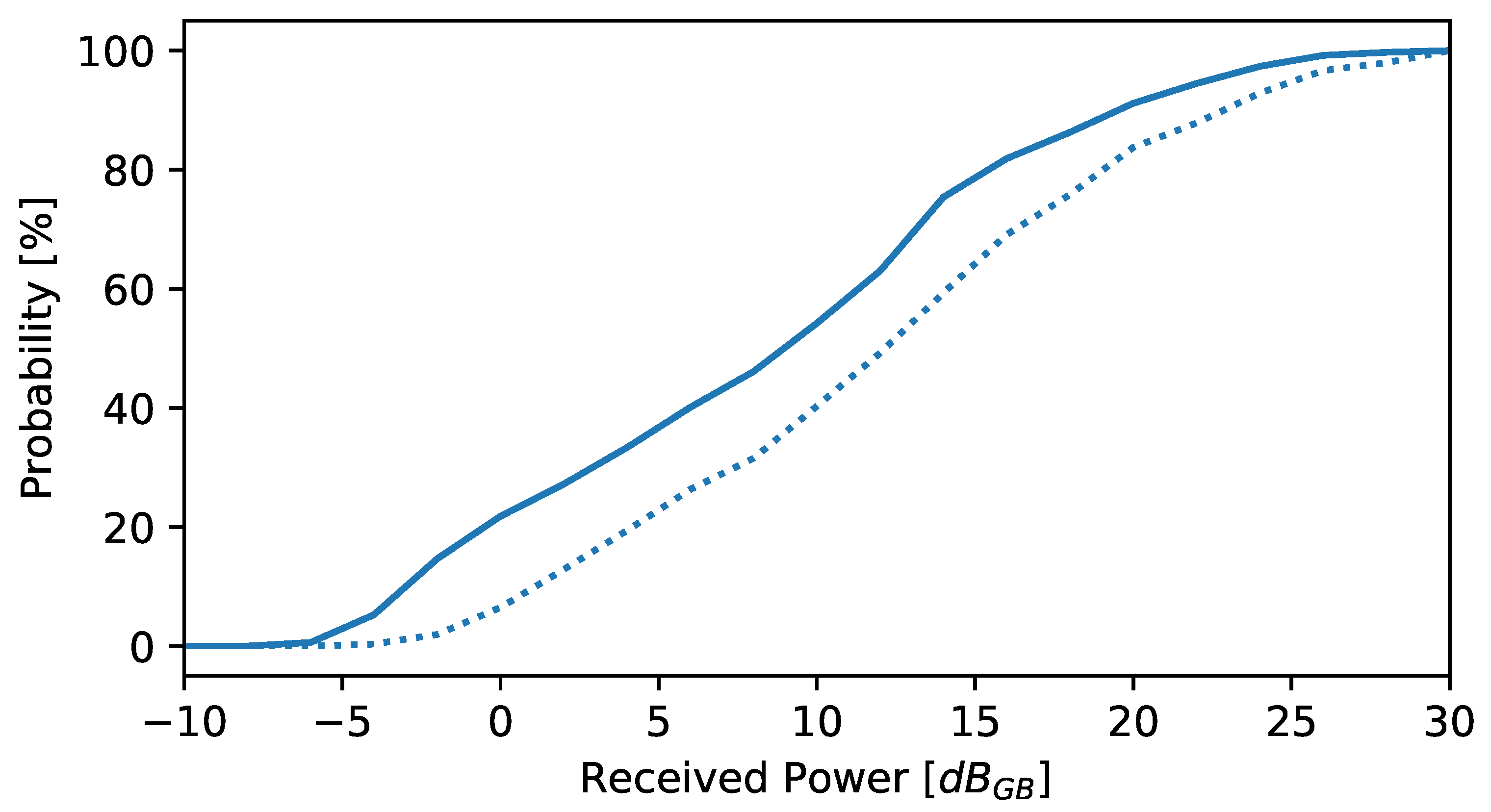
3.2. Sensitivity
3.3. Positive Leader Tips
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warwick, J.W.; Hayenga, C.O.; Brosnahan, J.W. Interferometric directions of lightning sources at 34 MHz. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1979, 84, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayenga, C.O.; Warwick, J.W. Two-dimensional interferometric positions of VHF lightning sources. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1981, 86, 7451–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P.; Auffray, G. VHF-UHF interferometric measurements, applications to lightning discharge mapping. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Krehbiel, P.R. The spatial and temporal development of intracloud lightning. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 26641–26668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Thomas, R.J.; Rison, W. Radio interferometric observations of cloud-to-ground lightning phenomena in Florida. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 2749–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Holden, D.N.; Rhodes, C.T. Broad band radio interferometry for lightning observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z.I.; Ohta, Y.; Matsuura, K. Broad band interferometric measurement of rocket triggered lightning in Japan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2769–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.G.; Akita, M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Edens, H.E.; Kawazaki, Z.; Stanley, M.A. Continuous broadband digital interferometry of lightning using a generalized cross-correlation algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3134–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Qie, X.; Jiang, R.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of a rocket-triggered lightning flash with large stroke number and the associated leader propagation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13388–13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rison, W.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Stock, M.G.; Edens, H.E.; Shao, X.; Thomas, R.J.; Stanley, M.A.; Zhang, Y. Observations of narrow bipolar events reveal how lightning is initiated in thunderstorms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilles, J.; Liu, N.; Stanley, M.A.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Stock, M.G.; Dwyer, J.R.; Brown, R.; Wilson, J. Fast negative breakdown in in thunderstorms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 4, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Ho, C.; Caffrey, M.; Graham, P.; Haynes, B.; Bowers, G.; Blaine, W.; Dingus, B.; Hamid Rassoul, D.M.S. Broadband RF Interferometric Mapping and Polarization (BIMAP) Observations of Lightning Discharges: Revealing New Physics Insights into Breakdown Processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 10326–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Cummer, S.A.; Qin, Z.; Chen, M. Lightning initiation processes imaged with very high frequency broadband interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Cummer, S.A. Needles and lightning leader dynamics imaged with 100–200 MHz broadband VHF interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 13556–13563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belz, J.W.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Remington, J.; Stanley, M.A.; Abbasi, R.U.; LeVon, R.; Rison, W.; Rodeheffer, D.; The Telescope Array Scientific Collaboration. Observation of the Origin of Downward Terrestrial Gamma-Ray Flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, M.; Montanyá, J.; Van der Velde, O.A.; Arcanjo, M.; López, J. Multi-Stroke Positive Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Sharing the Same Channel Observed with a VHF Broadband Interferometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N.; Yamamoto, K. A 3D interferometer-type lightning mapping array for observation of winter lightning in Japan. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Carilli, C.L.; Perley, R.A. Synthesis Imaing in Radio Astronomy II; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Haarlem, M.P.; Wise, M.W.; Gunst, A.; Heald, G.; McKean, J.P.; Hessels, J.W.; de Bruyn, A.G.; Nijboer, R.; Swinbank, J.; Fallows, R.; et al. LOFAR: The low-frequency array. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 556, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, B.M.; Scholten, O.; Buitink, S.; Dwyer; Liu, N.; Sterpka, C.; ter Veen, S. Characteristics of recoil leaders as observed by LOFAR. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 023025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, O.; Hare, B.; Dwyer, J.; Liu, N.; Sterpka, C.; Buitink, S.; Huege, T.; Nelles, A.; ter Veen, S. Time resolved 3D interferometric imaging of a section of a negative leader with LOFAR. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 063022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterpka, C.; Dwyer, J.; Liu, N.; Hare, B.; Scholten, O.; Buitink, S.; Veen, S.t.; Nelles, A. The spontaneous nature of lightning initiation revealed. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, O.; Hare, B.M.; Dwyer, J.; Liu, N.; Sterpka, C.; Kolmašová, I.; Santolík, O.; Lán, R.; Uhlíř, L.; Buitink, S.; et al. Interferometric imaging of intensely radiating negative leaders. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 062007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Scholten, O.; Dwyer, J.R.; Hare, B.M.; Sterpka, C.F.; Tilles, J.N.; Lind, F.D. Implications of Multiple Corona Bursts in Lightning Processes for Radio Frequency Interferometer Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Ellingson, S.; Kassim, N.; Craig, J.; Dowell, J.; Wolfe, C.; Hartman, J.; Bernardi, G.; Clarke, T.; Cohen, A.; et al. First light for the first station of the long wavelength array. J. Astron. Instrum. 2012, 1, 1250004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.W.; Clarke, T.E.; Cohen, A.; Craig, J.; Kassim, N.E.; Pihlstrom, Y.; Rickard, L.J.; Taylor, G.B. The long wavelength array. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.M.; Sonnenfeld, R.; Rison, B. High-time-resolution imaging of lightning with the Long Wavelength Array. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 2012, 57, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Obenberger, K.; Dowell, J.; Malins, J.; Parris, R.; Pedersen, T.; Taylor, G. Using lightning as a HF signal source to produce ionograms. Radio Sci. 2018, 53, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malins, J.; Obenberger, K.; Taylor, G.; Dowell, J. Three-dimensional mapping of lightning-produced ionospheric reflections. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranmer, M.D.; Barsdell, B.R.; Price, D.C.; Dowell, J.; Garsden, H.; Dike, V.; Eftekhari, T.; Hegedus, A.M.; Malins, J.; Obenberger, K.S.; et al. Bifrost: A Python/C++ framework for high-throughput stream processing in astronomy. J. Astron. Instrum. 2017, 6, 1750007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilles, J.N.; Liu, N.; Dowell, J.; Taylor, G.; Clem, P.G.; Edens, H.; Sonnenfeld, R.; da Silva, C. Lightning observations with the Long Wavelength Array in Sevilleta New Mexico (LWA-SV). In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, Virtual, 7–17 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.; Krehbiel, P. Multiple baseline lightning interferometry-Improving the detection of low amplitude VHF sources. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Lightning Protection (ICLP), Shanghai, China, 11–18 October 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, M.G.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Lapierre, J.; Wu, T.; Stanley, M.A.; Edens, H.E. Fast Positive Breakdown in Lightning. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 112, 8135–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilles, J.N.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Stanley, M.A.; Rison, W.; Liu, N.; Lyu, F.; Cummer, S.A.; Dwyer, J.R.; Senay, S.; Edens, H.; et al. Radio Interferometer Observations of an Energetic in-Cloud Pulse Reveal Large Currents Generated by Relativistic Discharges. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högbom, J. Aperture synthesis with a non-regular distribution of interferometer baselines. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1974, 15, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, T.C.; Stolzenburg, M.; Maggio, C.R.; Coleman, L.M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Hamlin, T.; Thomas, R.J.; Rison, W. Observed electric fields associated with lightning initiation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Introduction to Applied Linear Algebra: Vectors, Matrices, and Least Squares; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Akita, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Morimoto, T.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z.; Wang, D. What occurs in K process of cloud flashes? J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, B.M.; Scholten, O.; Dwyer, J.; Trinh, T.N.G.; Buitink, S.; ter Veen, S.; Bonardi, A.; Corstanje, A.; Falcke, H.; Hörandel, J.R.; et al. Needle-like structures discovered on positively charged lightning branches. Nature 2019, 568, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, J.L.; Sonnenfeld, R.G.; Edens, H.E.; Stock, M. On the relationship between continuing current and positive leader growth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12479–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Velocities of positive leaders in intracloud and negative cloud-to-ground lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9983–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, M.M.F.; Cummins, K.L.; Warner, T.A.; Krider, E.P.; Campos, L.Z.S.; Ballarotti, M.G.; Pinto, O., Jr.; Fleenor, S.A. Positive leader characteristics from high-speed video observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Biagi, C.J.; Rakov, V.A.; Hill, J.D.; Stapleton, M.V.; Jordan, D.M.; Uman, M.A.; Morimoto, T.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z. Three-dimensional imaging of upward positive leaders in triggered lightning using VHF broadband digital interferometers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Wolf, A.; Hoover, S.; Vieregg, A.; Gorham, P.; Allison, P.; Barwick, S.; Baughman, B.; Beatty, J.; Belov, K.; Besson, D.; et al. An interferometric analysis method for radio impulses from ultra-high energy particle showers. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 60, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Stock, M.; Bitzer, P. A new approach to map lightning channels based on low-frequency interferometry. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, M.; Stock, M.; Kawasaki, Z.; Krehbiel, P.; Rison, W.; Stanley, M. Data processing procedure using distribution of slopes of phase differences for broadband VHF interferometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6085–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, V.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Shao, X.M. Correlated high-speed video and radio interferometric observations of a cloud-to-ground lightning flash. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 25731–25753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, M.M.; Campos, L.Z.; Krider, E.P.; Pinto, O., Jr. High-speed video observations of positive ground flashes produced by intracloud lightning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.D.; Uman, M.A.; Jordan, D.M. High-speed video observations of a lightning stepped leader. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.A.; Orville, R.E.; Marshall, J.; Huggins, K. Spectral (600–1050 nm) time exposures (99.6 μs) of a lightning stepped leader. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenburg, M.; Marshall, T.C.; Karunarathne, S.; Karunarathna, N.; Orville, R.E. Leader observations during the initial breakdown stage of a lightning flash. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12198–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, H.E.; Eack, K.B.; Eastvedt, E.M.; Trueblood, J.J.; Winn, W.P.; Krehbie, P.R.; Aulich, G.D.; Hunyady, S.J.; Murray, W.C.; Rison, W.; et al. VHF lightning mapping observations of a triggered lightning flash. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velde, O.A.; Montanyá, J. Asymmetries in bidirectional leader development of lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 13504–13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilles, J.N. Broadband Radio Mapping and Imaging of Lightning Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Cummer, S.; Pu, Y. Lightning Initiation from Fast Negative Breakdown is Led by Positive Polarity Dominated Streamers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Cummer, S.A.; Liu, N. VHF radio spectrum of a positive leader and implications for electric fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazelyan, E.M.; Raizer, Y.P. Lightning Physics and Lightning Protection; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, J.R. Terrestrial gamma-ray flashes initiated by positive leaders. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 043012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, N.; Brook, M. A comparison of intracloud and cloud-to-ground lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 1960, 65, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.L.; Winn, W.P.; Taylor, M.C.; Aulich, G.D.; Hunyady, S.J.; Eack, K.B.; Edens, H.E.; Sonnenfeld, R.G.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Eastvedt, E.M.; et al. Polarity asymmetries in rocket-triggered lightning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023. Submitted for Publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Ho, C.; Bowers, G.; Blaine, W.; Dingus, B. Lightning interferometry uncertainty, beam steering interferometry, and evidence of lightning being ignited by a cosmic ray shower. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD032273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stock, M.; Tilles, J.; Taylor, G.B.; Dowell, J.; Liu, N. Lightning Interferometry with the Long Wavelength Array. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143657
Stock M, Tilles J, Taylor GB, Dowell J, Liu N. Lightning Interferometry with the Long Wavelength Array. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(14):3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143657
Chicago/Turabian StyleStock, Michael, Julia Tilles, Greg B. Taylor, Jayce Dowell, and Ningyu Liu. 2023. "Lightning Interferometry with the Long Wavelength Array" Remote Sensing 15, no. 14: 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143657
APA StyleStock, M., Tilles, J., Taylor, G. B., Dowell, J., & Liu, N. (2023). Lightning Interferometry with the Long Wavelength Array. Remote Sensing, 15(14), 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143657




