The Changes in Nighttime Lights Caused by the Turkey–Syria Earthquake Using NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. NTL Changes at Different Scales
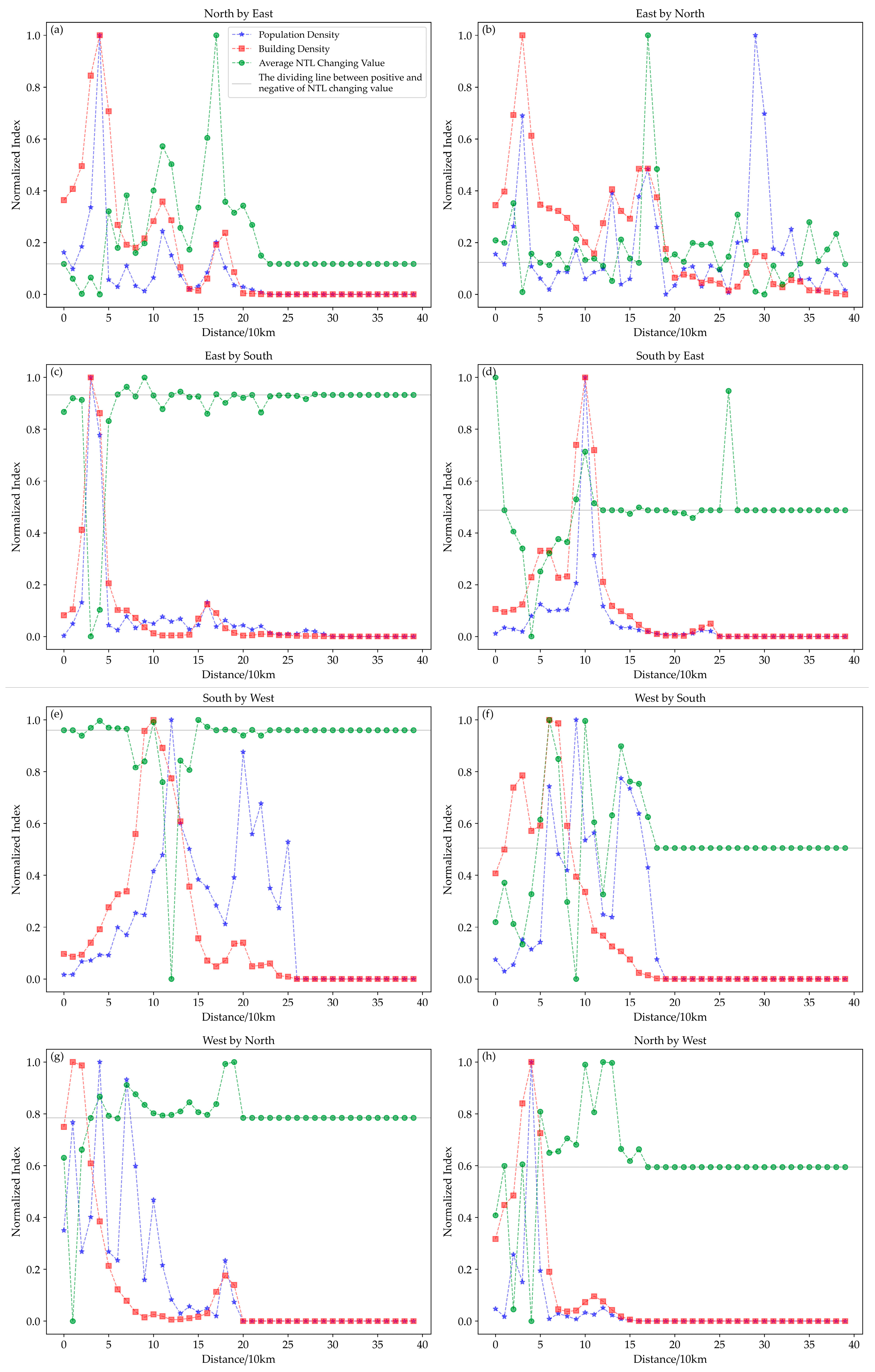
3.2. Changes in NTL Intensity for Different Directions and Distances
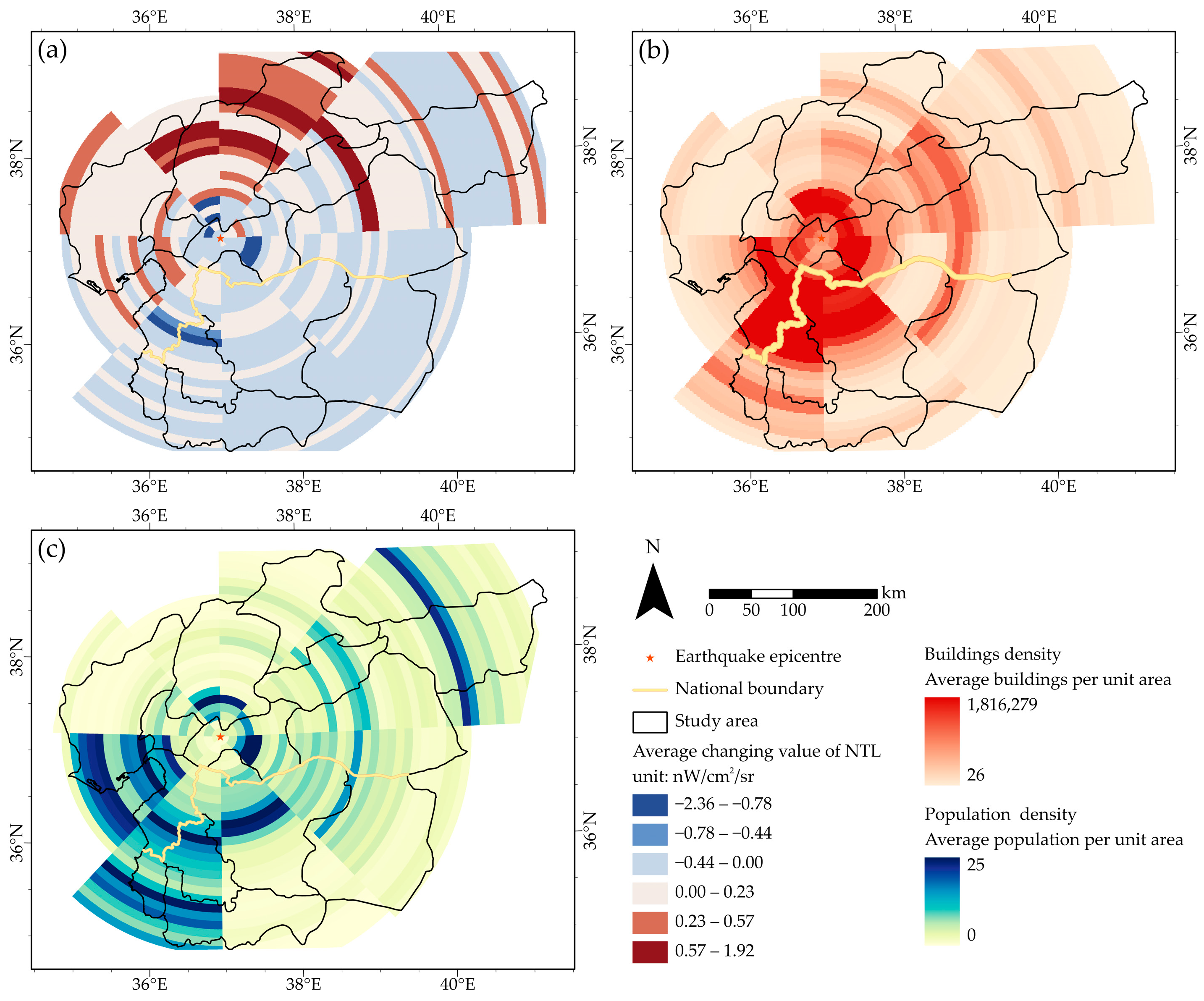
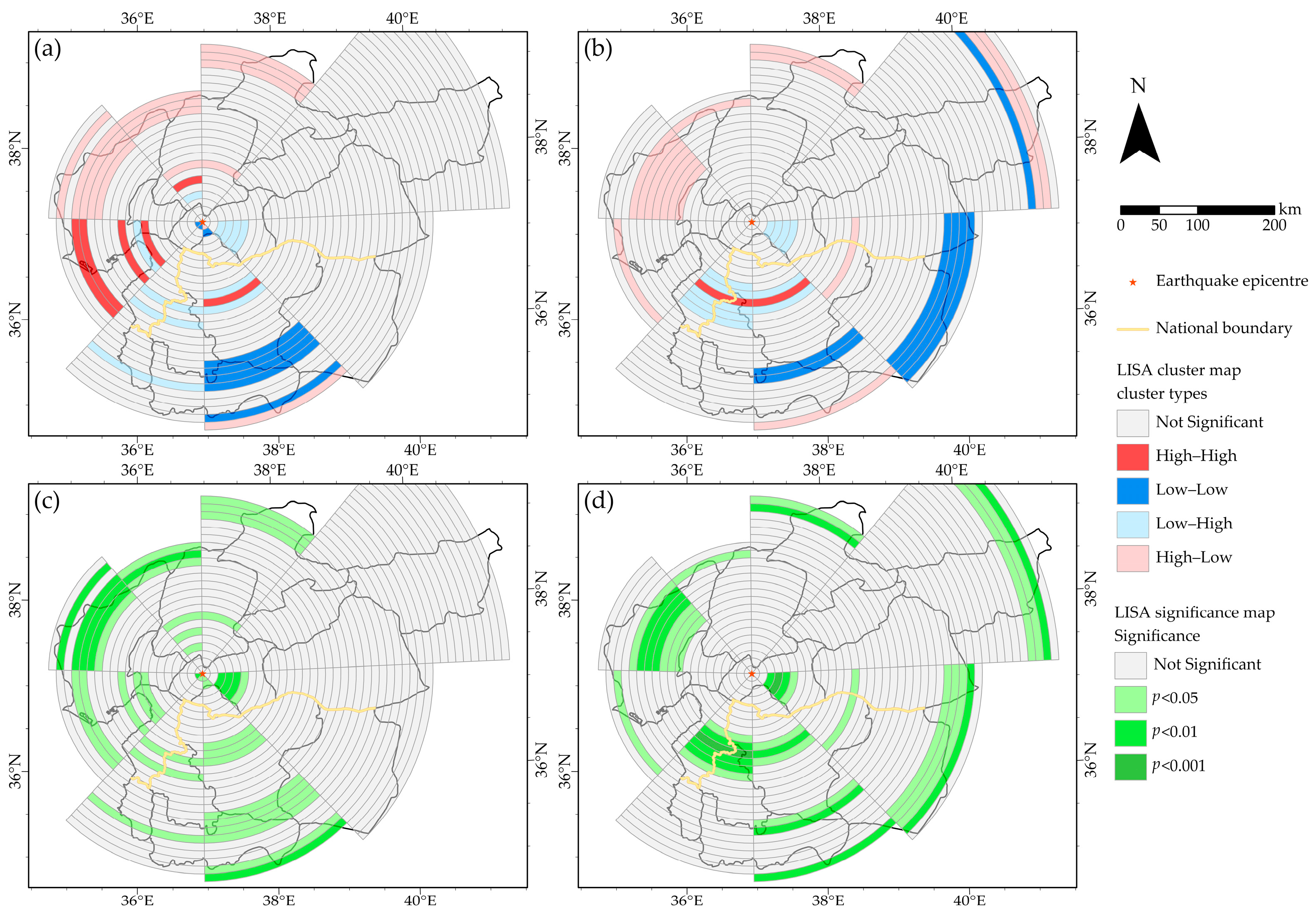
3.3. Spatial Correlation between NTL Changes and Population Density or Building Density
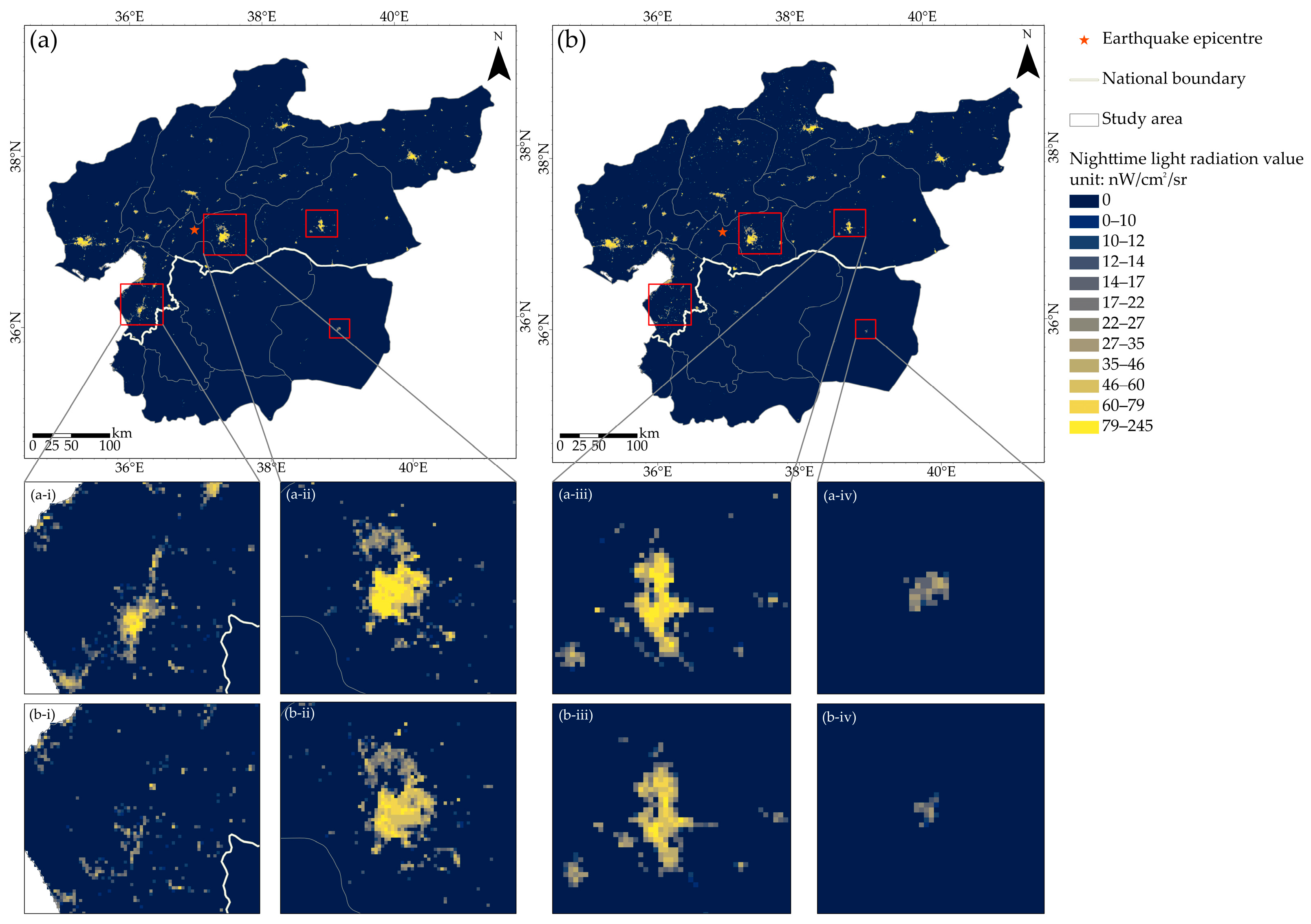
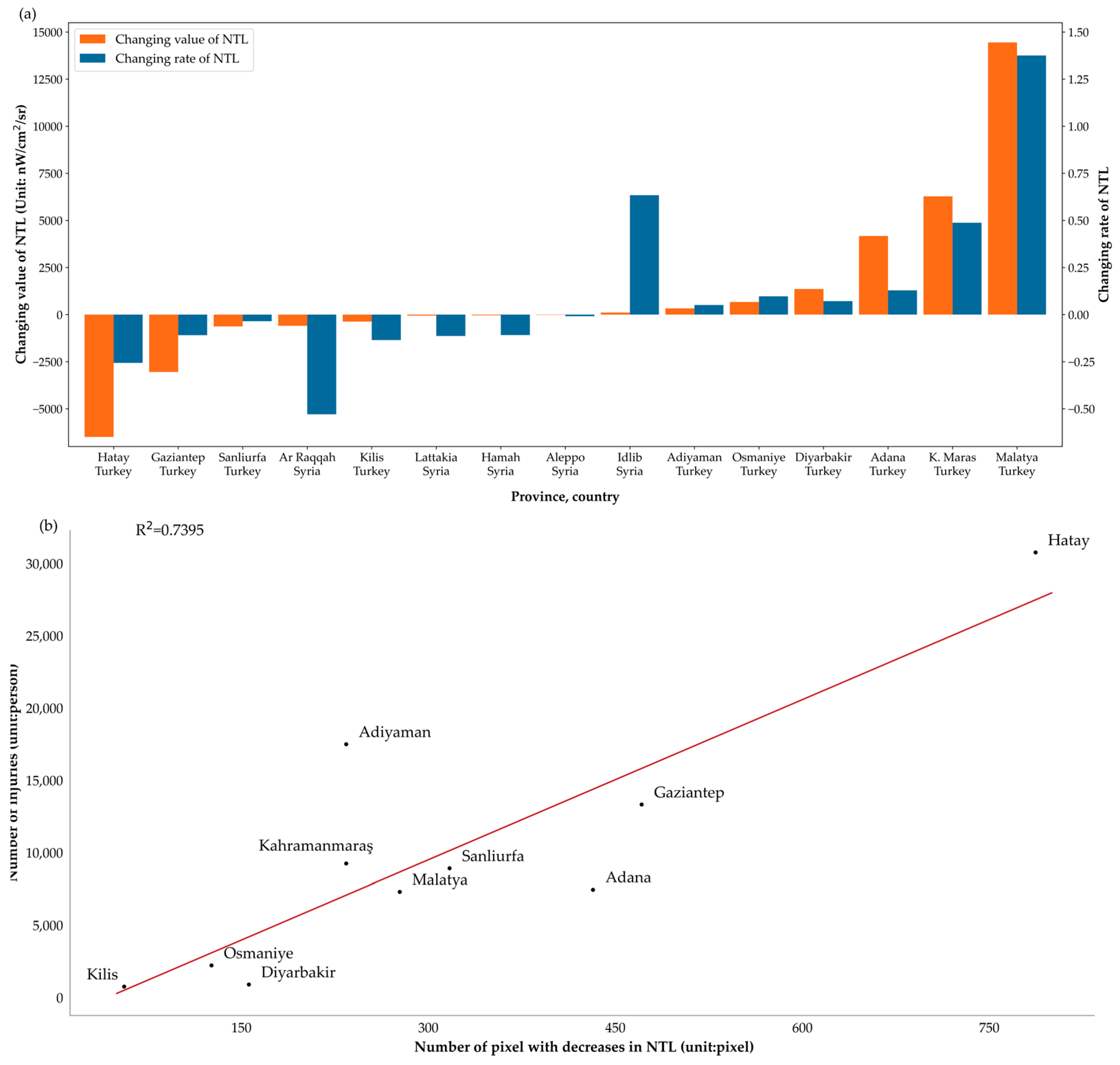
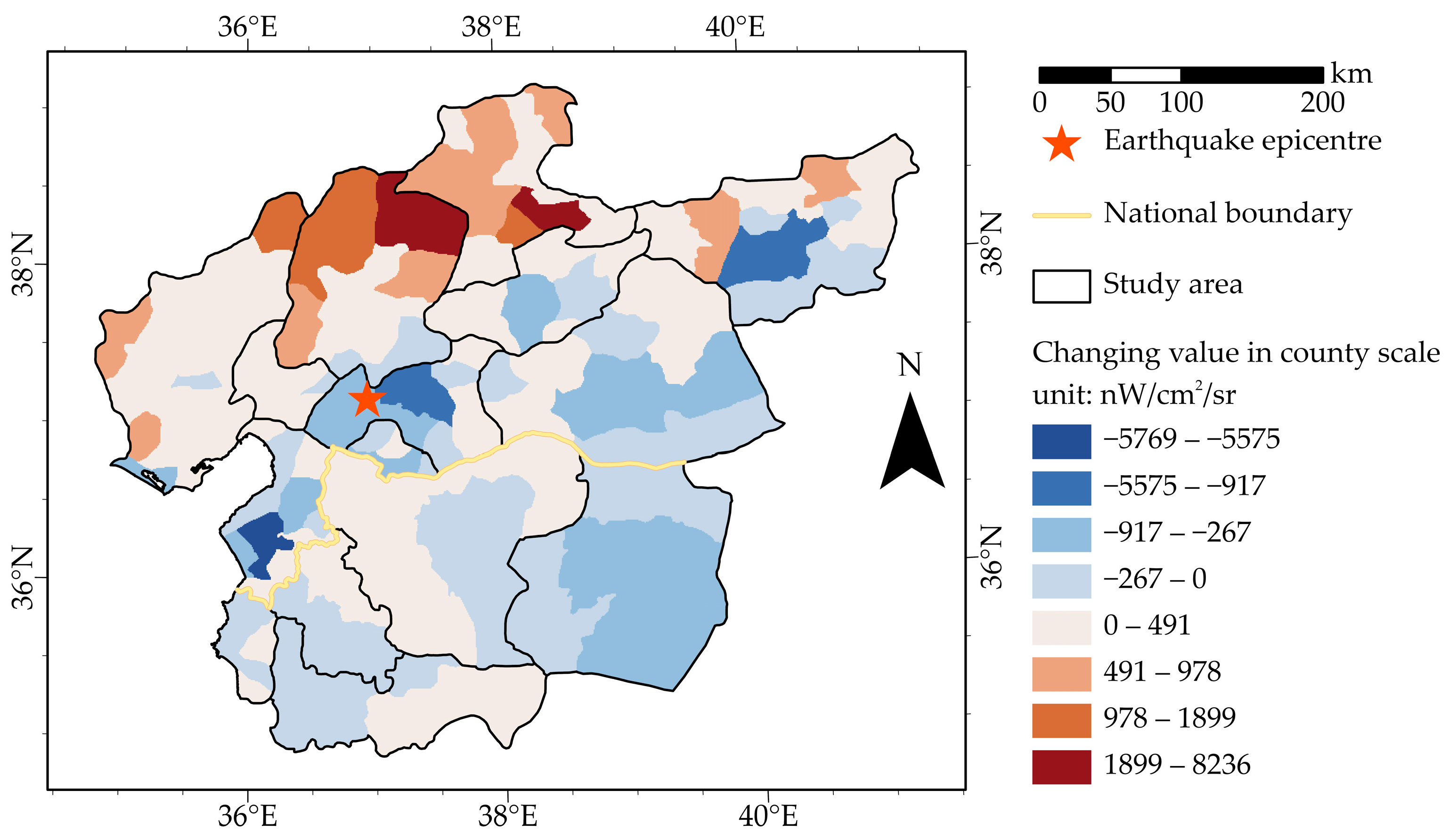
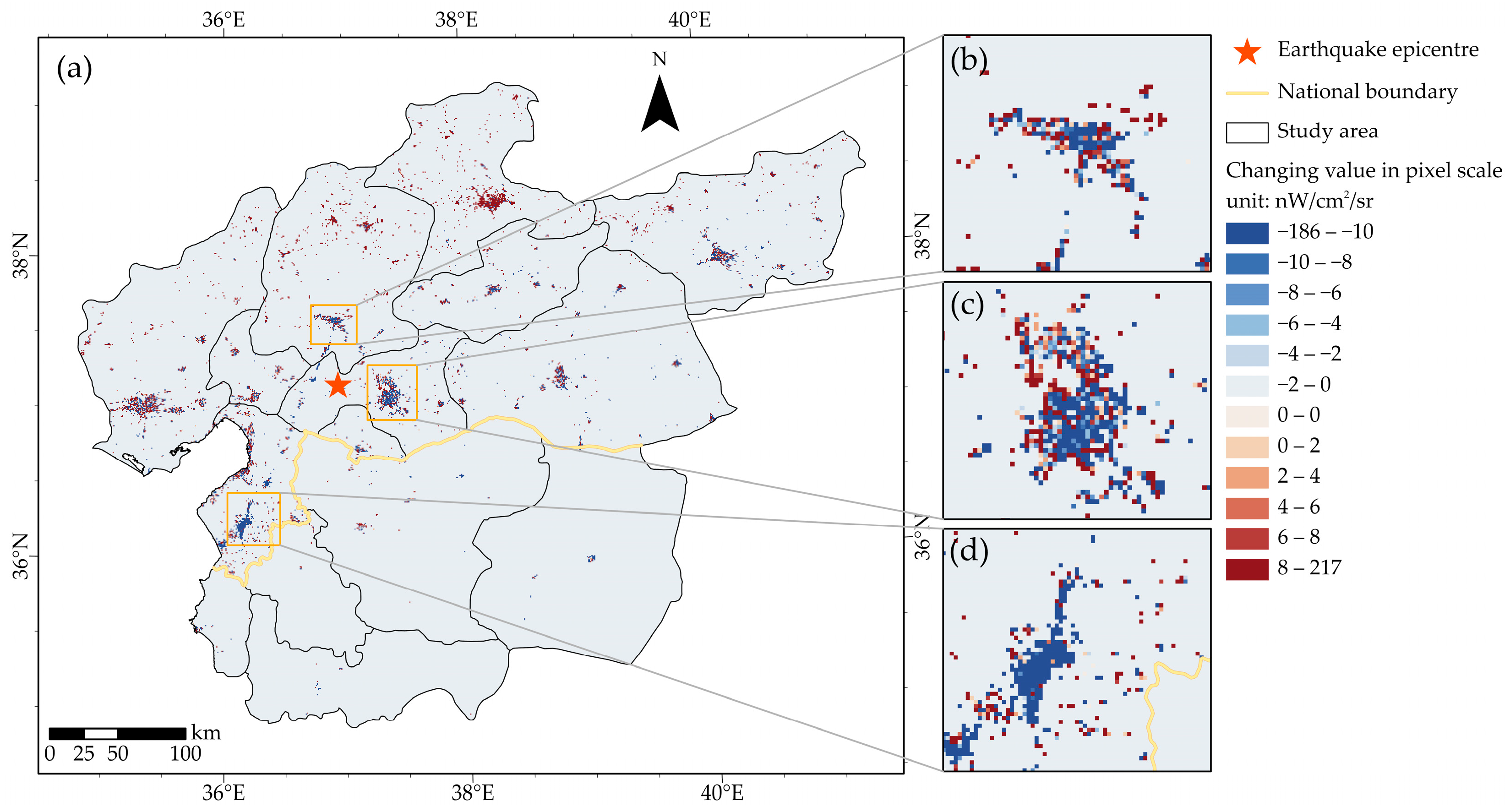
4. Results
4.1. NTL Changes at Different Scales
4.2. Relationship between NTL, Population, and Building Density in Different Directions and Distances
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naddaf, M. Turkey–Syria Earthquake: What Scientists Know. Nature 2023, 614, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ReliefWeb. Türkiye Earthquake February 2023, Bi-Weekly Highlights—03/03/2023—Türkiye. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/turkiye/turkiye-earthquake-february-2023-bi-weekly-highlights-03032023 (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Alvarez, D.A.; Hurtado, J.E.; Bedoya-Ruíz, D.A. Prediction of Modified Mercalli Intensity from PGA, PGV, Moment Magnitude, and Epicentral Distance Using Several Nonlinear Statistical Algorithms. J. Seismol. 2012, 16, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Guo, H. Assessing Changes in Nighttime Lighting in the Aftermath of the Turkey-Syria Earthquake Using SDGSAT-1 Satellite Data. Innovation 2023, 4, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Gupta, R.; Fobi Nsutezo, S.; Pound, E.; Ortiz, A.; Rosa, M.; White, K.; Dodhia, R.; Zolli, A.; Birge, C.; et al. Turkey Earthquake Report; Microsoft: Redmond, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N. Using Night Lights from Space to Assess Areas Impacted by the 2023 Turkey Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Jendryke, M.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Night-Time Light Dynamics during the Iraqi Civil War. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tralli, D.M.; Blom, R.G.; Zlotnicki, V.; Donnellan, A.; Evans, D.L. Satellite Remote Sensing of Earthquake, Volcano, Flood, Landslide and Coastal Inundation Hazards. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2005, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.E.; Belliss, S.E.; Samsonov, S.V.; McNeill, S.J.; Glassey, P.J. A Review of the Status of Satellite Remote Sensing and Image Processing Techniques for Mapping Natural Hazards and Disasters. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiß, C.; Taubenböck, H. Remote Sensing Contributing to Assess Earthquake Risk: From a Literature Review towards a Roadmap. Nat. Hazards 2013, 68, 7–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, Y.; Cao, H. Rapid response to Turkey-Syria earthquake using night-time light remote sensing. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual Maps of Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A Global Map of Urban Extent from Nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Small, C.; Shu, S.; Wu, J. Evolution of Urban Spatial Clusters in China: A Graph-Based Method Using Nighttime Light Data. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2022, 112, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Su, J.; Xia, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, R. Spatial Mismatches between Nighttime Light Intensity and Building Morphology in Shanghai, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 81, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, M.; Yang, H.; Ge, W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, L.; Chen, X. Detecting Zimbabwe’s Decadal Economic Decline Using Nighttime Light Imagery. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4551–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, F. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Venezuela’s Nighttime Light During the Socioeconomic Crisis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2396–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Han, W.; Faouzi, B.; Washaya, P.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H.; Wu, C. Evaluating Algeria’s Social and Economic Development Using a Series of Night-Time Light Images between 1992 to 2012. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 9228–9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Wu, Q.; Hong, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NOAA-20 Monthly Composite Data for Socioeconomic Indicators Estimation and Urban Area Extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, J. Estimation of Poverty Using Random Forest Regression with Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Yu, B. A Building Volume Adjusted Nighttime Light Index for Characterizing the Relationship between Urban Population and Nighttime Light Intensity. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 99, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling Spatiotemporal CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Emission Dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS Nighttime Stable Light Data Using Panel Data Analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X. China’s City-Level Energy-Related CO2 Emissions: Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces. Appl. Energy 2017, 200, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Qiu, B.; Yu, B. The Potential of Nighttime Light Remote Sensing Data to Evaluate the Development of Digital Economy: A Case Study of China at the City Level. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 92, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lian, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. NPP-VIIRS DNB Daily Data in Natural Disaster Assessment: Evidence from Selected Case Studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, L.; Gong, A. Post-Earthquake Night-Time Light Piecewise (PNLP) Pattern Based on NPP/VIIRS Night-Time Light Data: A Case Study of the 2015 Nepal Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Long-Term Resilience Curve Analysis of Wenchuan Earthquake-Affected Counties Using DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10854–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, M.; Hayashi, H.; Nagata, S. Monitoring Spatial Distribution of Population and Buildings Using DMSP Night-Time Imagery and Its Application for Earthquake Damage Assessment. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003, 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 4, pp. 2430–2432. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Nie, G.; Deng, Y.; An, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Rapid Detection of Earthquake Damage Areas Using VIIRS Nearly Constant Contrast Night-Time Light Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2386–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Meng, Q. Assessment of the Impact of the 2010 Haiti Earthquake on Human Activity Based on DMSP/OLS Time Series Nighttime Light Data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 044515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhan, C.; Tao, J.; Li, L. Long-Term Monitoring of the Impacts of Disaster on Human Activity Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the 2008 Wenchuan, China Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Román, M.O.; Sun, Q.; Molthan, A.L.; Schultz, L.A.; Kalb, V.L. Monitoring disaster-related power outages using nasa black marble nighttime light product. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII–3, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Zhizhin, M.; Bazilian, M. The Dimming of Lights in China during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sha, D.; Liu, W.; Houser, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, R.; Lan, H.; Flynn, C.; Lu, M.; Hu, T.; et al. Spatiotemporal Patterns of COVID-19 Impact on Human Activities and Environment in Mainland China Using Nighttime Light and Air Quality Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Calabria, M.; Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Martín-Ruiz, S.; Ortiz, J.-L.; Vílchez, J.M.; Pelegrina, A.; García, A.; Zamorano, J.; Bennie, J.; Gaston, K.J. Effects of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Urban Light Emissions: Ground and Satellite Comparison. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Levin, N.; Jendryke, M. Tracing Cultural Festival Patterns Using Time-Series of VIIRS Monthly Products. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Stokes, E.C. Holidays in Lights: Tracking Cultural Patterns in Demand for Energy Services. Earths Future 2015, 3, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wu, B.; Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Yu, B. A Monthly Night-Time Light Composite Dataset of NOAA-20 in China: A Multi-Scale Comparison with S-NPP. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 7931–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000–2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Ta, N.; Shi, K.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Deng, S.; Wu, J. Delineating Seasonal Relationships between Suomi NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light and Human Activity Across Shanghai, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, B. Analyzing Parcel-Level Relationships between Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Intensity and Artificial Surface Features across Shanghai, China: A Comparison with NPP-VIIRS Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 85, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveit, T.; Skoufias, E.; Strobl, E. Using VIIRS Nightlights to Estimate the Impact of the 2015 Nepal Earthquakes. Geoenviron. Disasters 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Zilio, L.; Ampuero, J.-P. Earthquake Doublet in Turkey and Syria. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS). VIIRS Radiometric Calibration Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD). Available online: https://nsidc.org/sites/nsidc.org/files/technical-references/JPSS-ATBD-VIIRS-SDR-C.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Mi, J. GISD30: Global 30-m Impervious Surface Dynamic Dataset from 1985 to 2020 Using Time-Series Landsat Imagery on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1831–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M 7.8—Pazarcik Earthquake, Kahramanmaras Earthquake Sequence. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us6000jllz/executive (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Bao, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Tong, G.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, B. Improving Risk Management by Using the Spatial Interaction Relationship of Heavy Metals and PAHs in Urban Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, D. Can Night-Time Light Images Play a Role in Evaluating the Syrian Crisis? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6648–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Under the Rubble: Gasps of Air, Protein Powder and Miraculous Rescues. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/02/14/world/europe/turkey-earthquake-rescue.html (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- ReliefWeb. Türkiye—Earthquake Response 2023: Malatya Humanitarian Snapshot (As of 27 April 2023)—Türkiye. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/turkiye/turkiye-earthquake-response-2023-malatya-humanitarian-snapshot-27-april-2023 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- ABC News. Miraculous Moments as Survivors Pulled from Earthquake Rubble in Turkey, Syria. Available online: https://abcnews.go.com/International/dramatic-rescues-survivors-pulled-earthquake-rubble-turkey-syria/story?id=96960014 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Euronews. ‘Slow Humanitarian Response’ to Rebel-Controlled Syria after Earthquake Is ‘Deadly’: HWR|Euronews. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20230216041647/https://www.euronews.com/2023/02/16/slow-humanitarian-response-to-rebel-controlled-syria-after-earthquake-is-deadly-hwr (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Sawah, L.; Alkheder, K.; Kibrasli, F. Modern Mechanisms for Restoring the National Economy of Syria. In Education Excellence and Innovation Management: A 2025 Vision to Sustain Economic Development During Global Challenges; Soliman, K.S., Ed.; Int Business Information Management Assoc-Ibima: Norristown, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 9435–9445. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Dou, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Liang, D. SDGSAT-1: The World’s First Scientific Satellite for Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, B. The Changes in Nighttime Lights Caused by the Turkey–Syria Earthquake Using NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133438
Yuan Y, Wang C, Liu S, Chen Z, Ma X, Li W, Zhang L, Yu B. The Changes in Nighttime Lights Caused by the Turkey–Syria Earthquake Using NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133438
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yuan, Congxiao Wang, Shaoyang Liu, Zuoqi Chen, Xiaolong Ma, Wei Li, Lingxian Zhang, and Bailang Yu. 2023. "The Changes in Nighttime Lights Caused by the Turkey–Syria Earthquake Using NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133438
APA StyleYuan, Y., Wang, C., Liu, S., Chen, Z., Ma, X., Li, W., Zhang, L., & Yu, B. (2023). The Changes in Nighttime Lights Caused by the Turkey–Syria Earthquake Using NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band Data. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133438







