Volume Loss Assessment with MT-InSAR during Tunnel Construction in the City of Naples (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
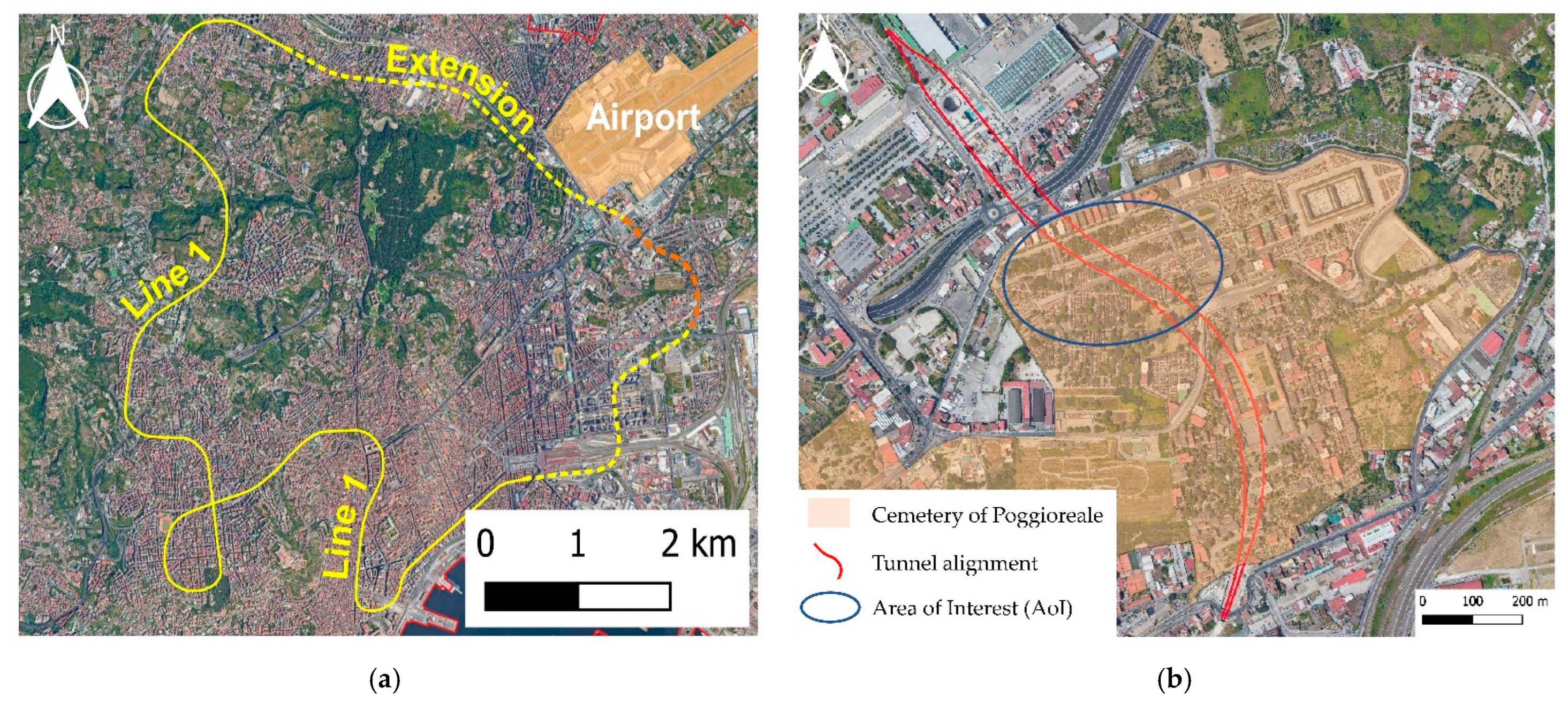
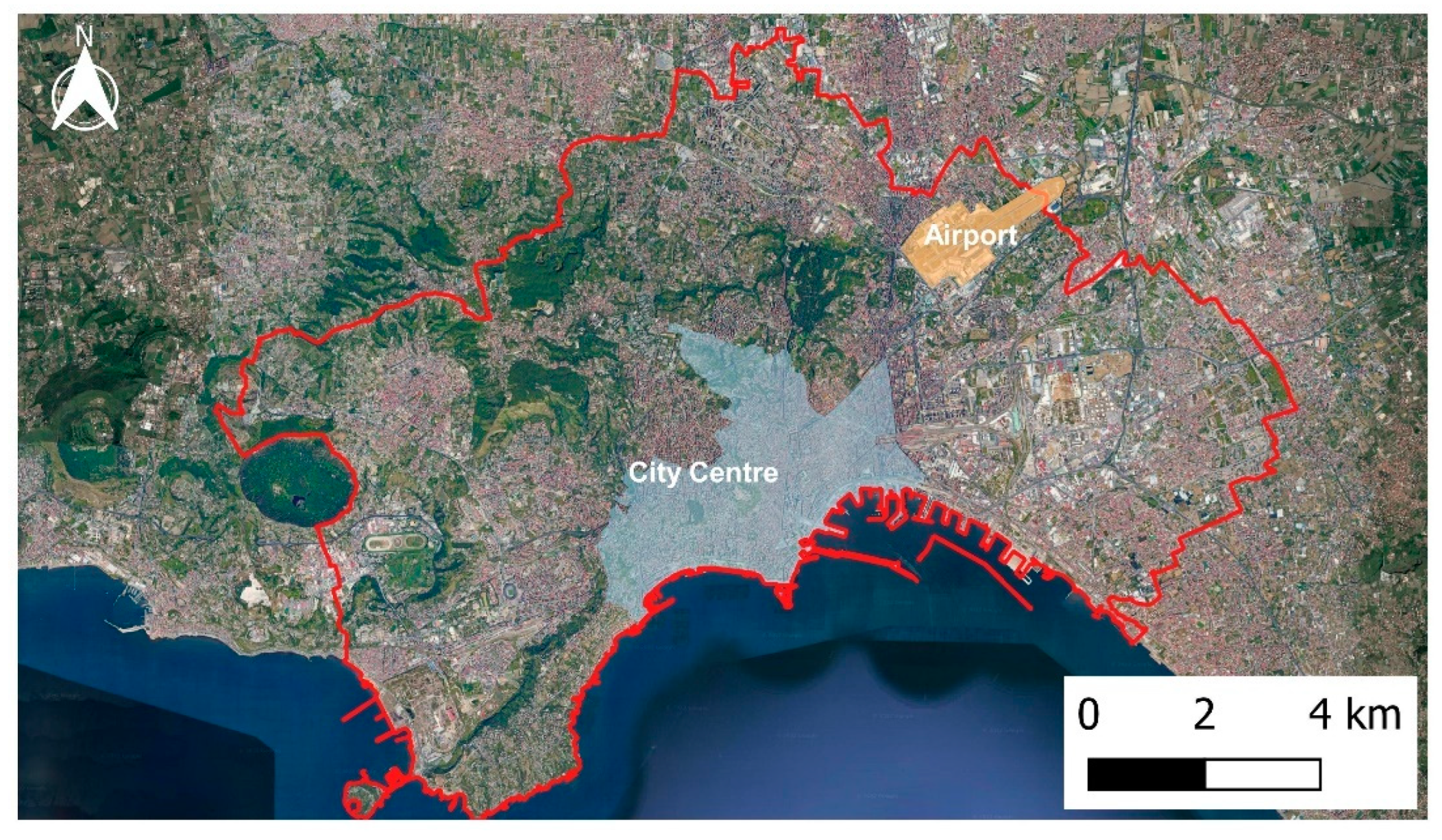
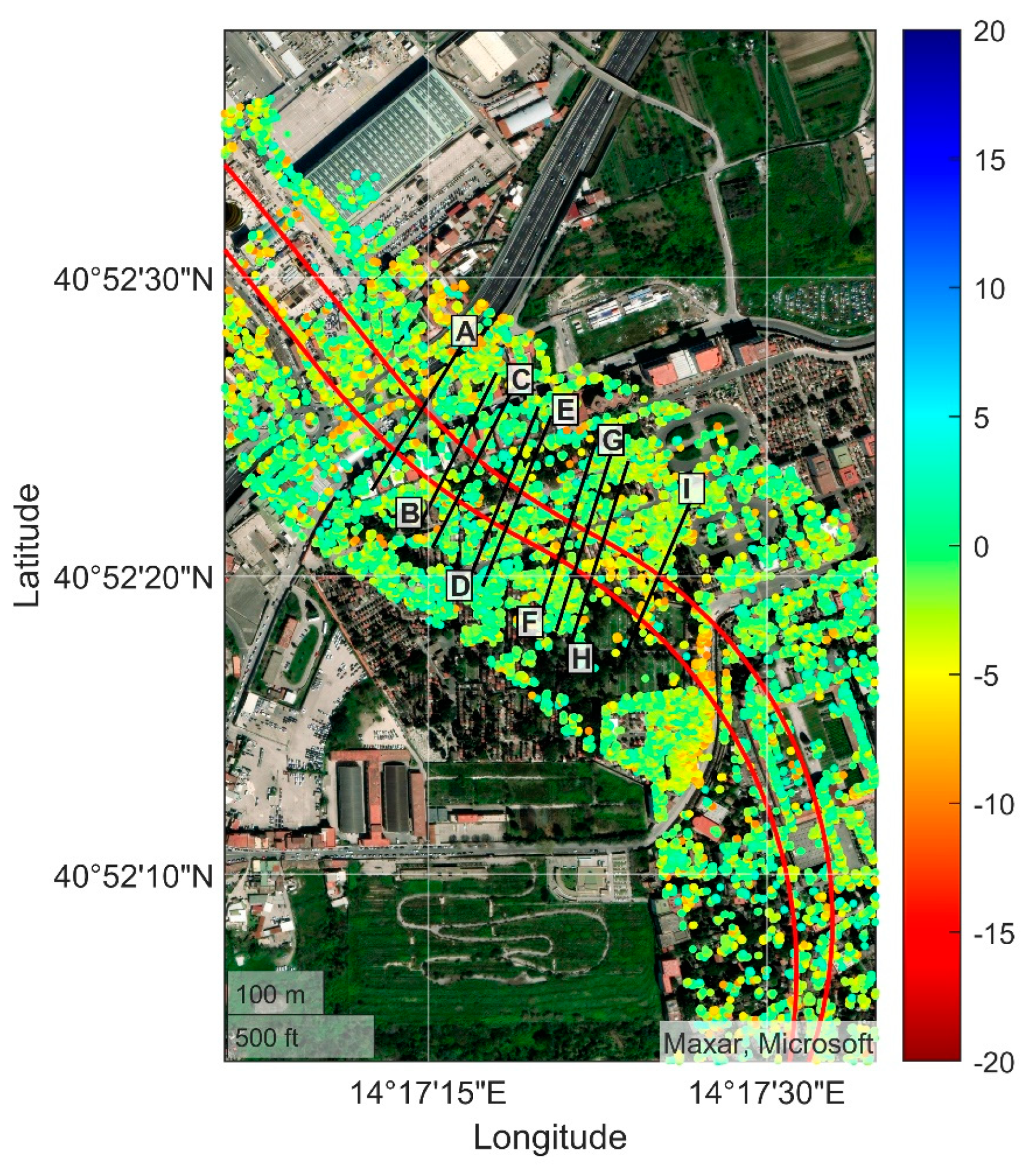
2. Area of Interest and Dataset
3. Methodology
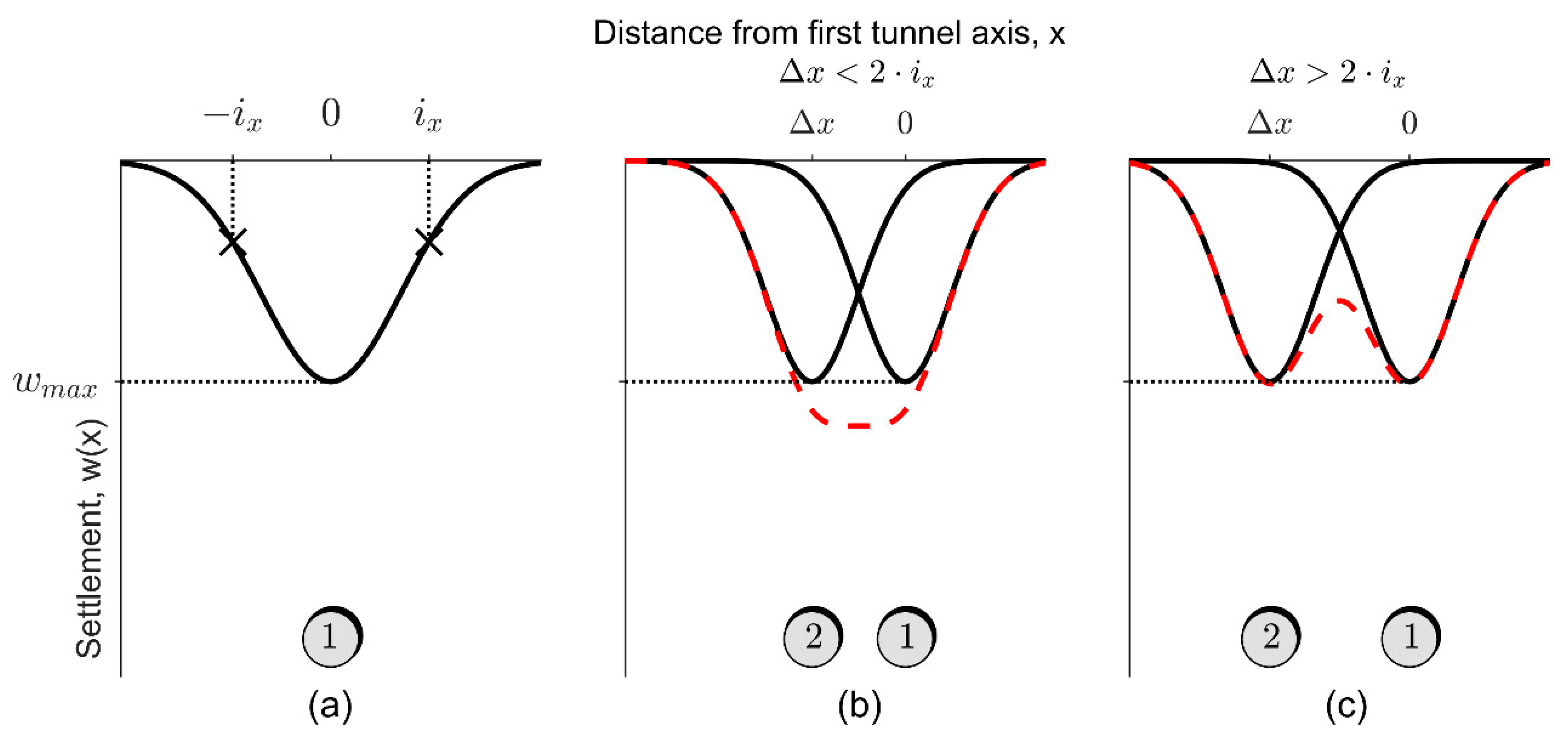
3.1. Empirical Method for Tunnel-Induced Vertical Displacements
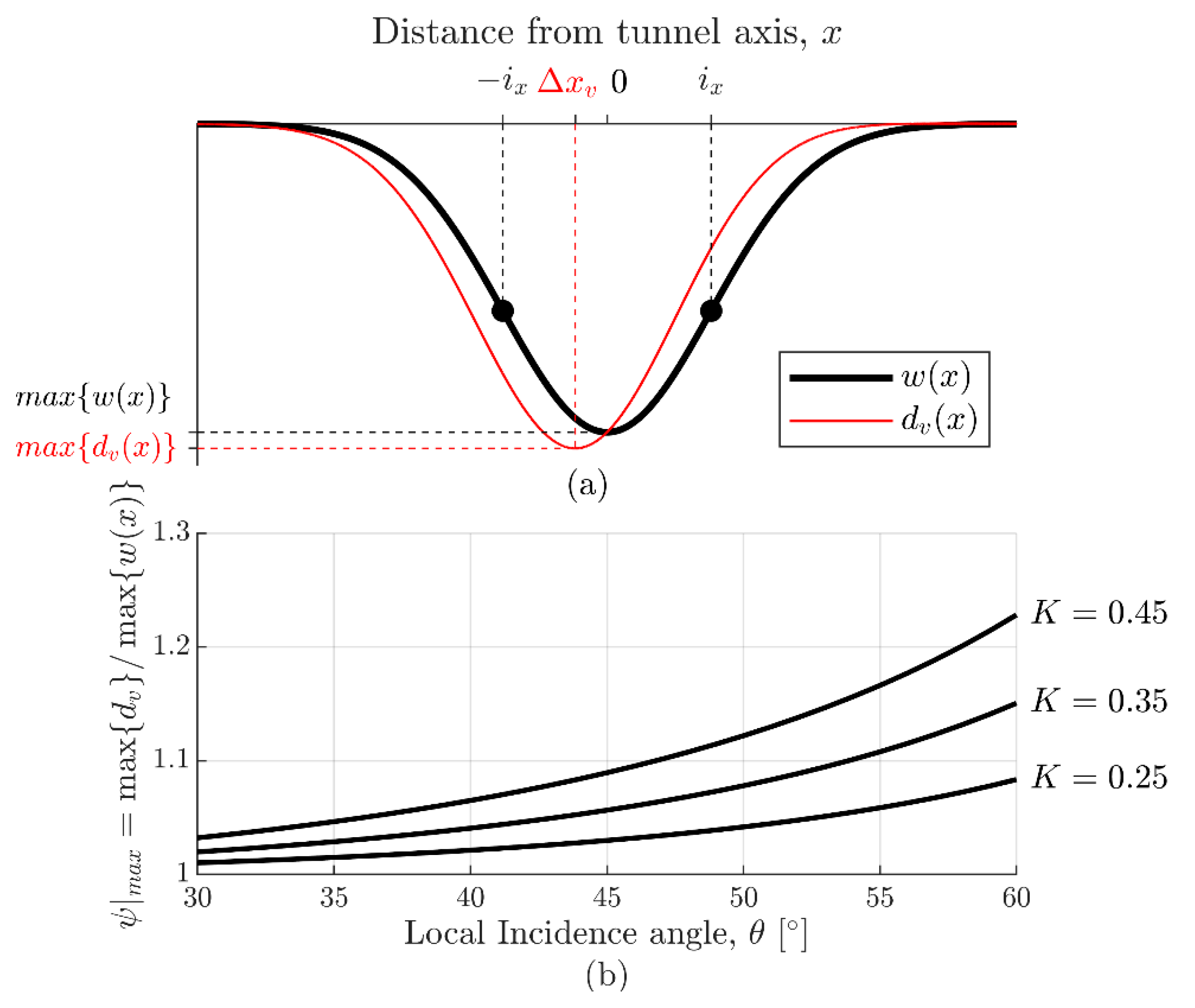
3.2. Empirical Method for Tunnel-Induced Horizontal Displacements
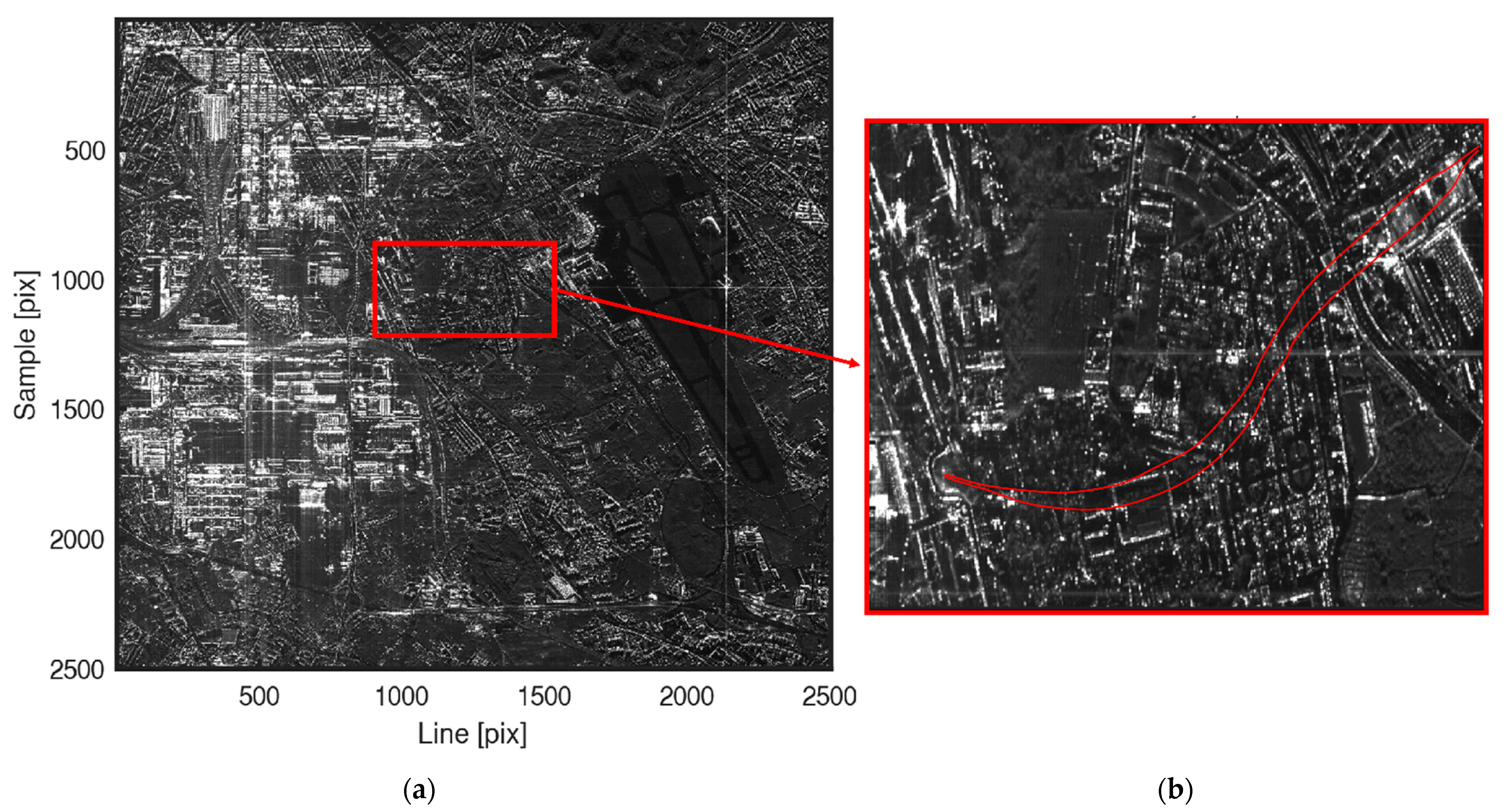
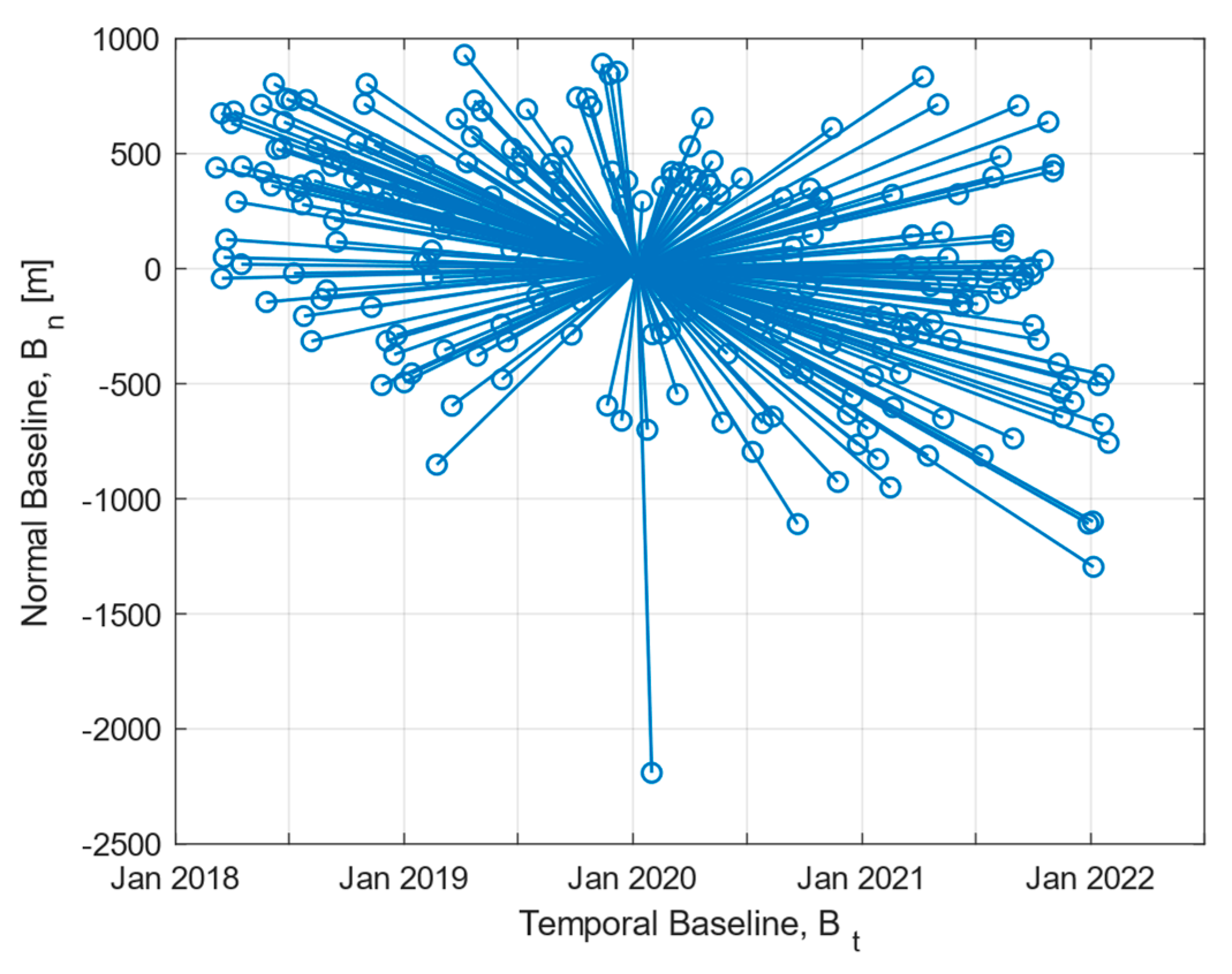
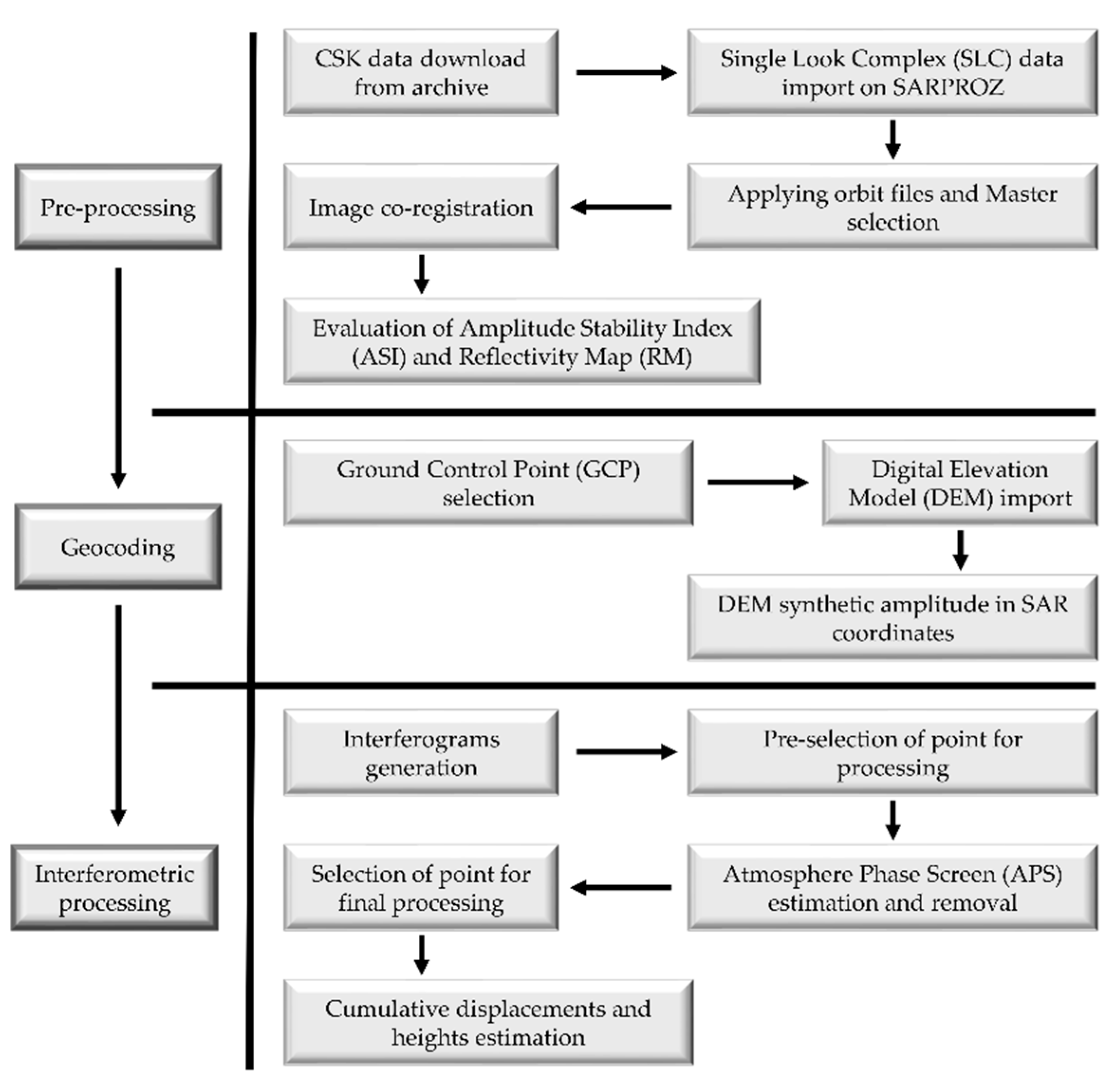
3.3. Multi Temporal InSAR
- -
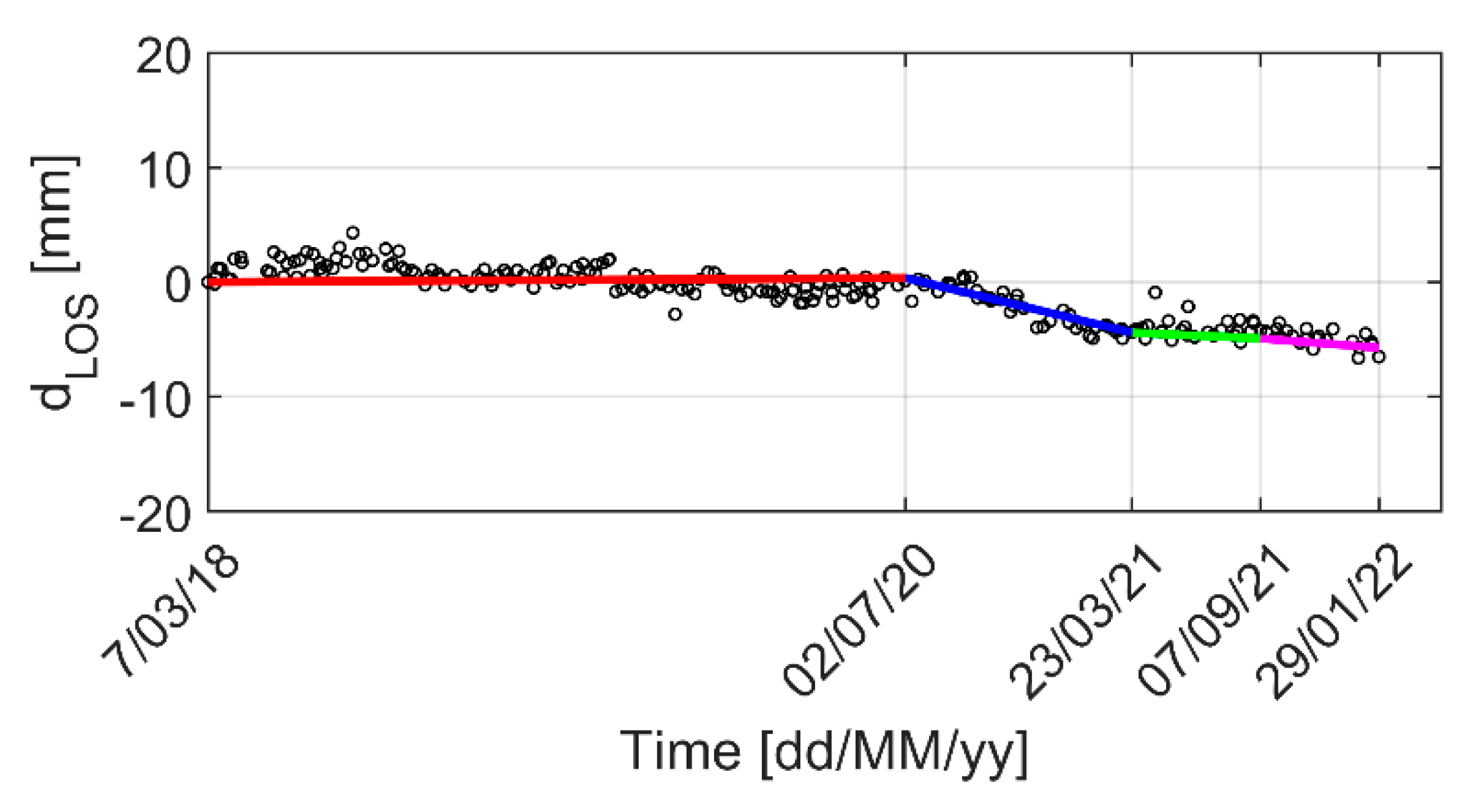
- 7 March 2018 to 2 July 2020 (i.e., from beginning of the analysis to prior to the first excavation);
- -
- 2 July 2020 to 23 March 2021 (i.e., from the beginning to the end of the first excavation);
- -
- 23 March 2021 to 7 September 2021 (i.e., from the end of the first excavation to the beginning of the second excavation);
- -
- 7 September 2021 to 29 January 2022 (i.e., from the beginning of the second excavation to the end of the analysis).
4. Results
- -
- The stability of the AoI is assessed;
- -
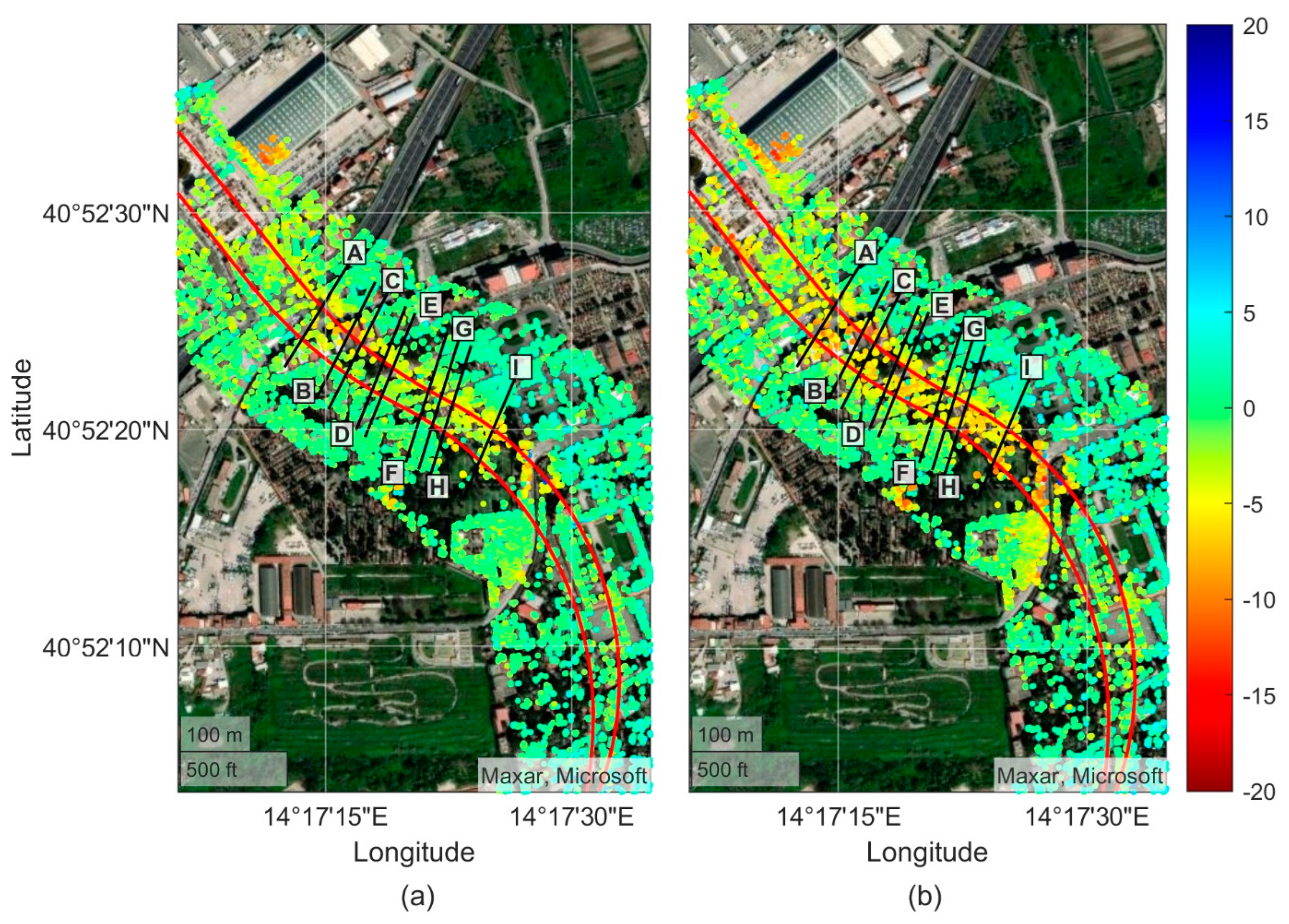
- The displacement maps right after the excavation of the first and second excavation are presented;
- -
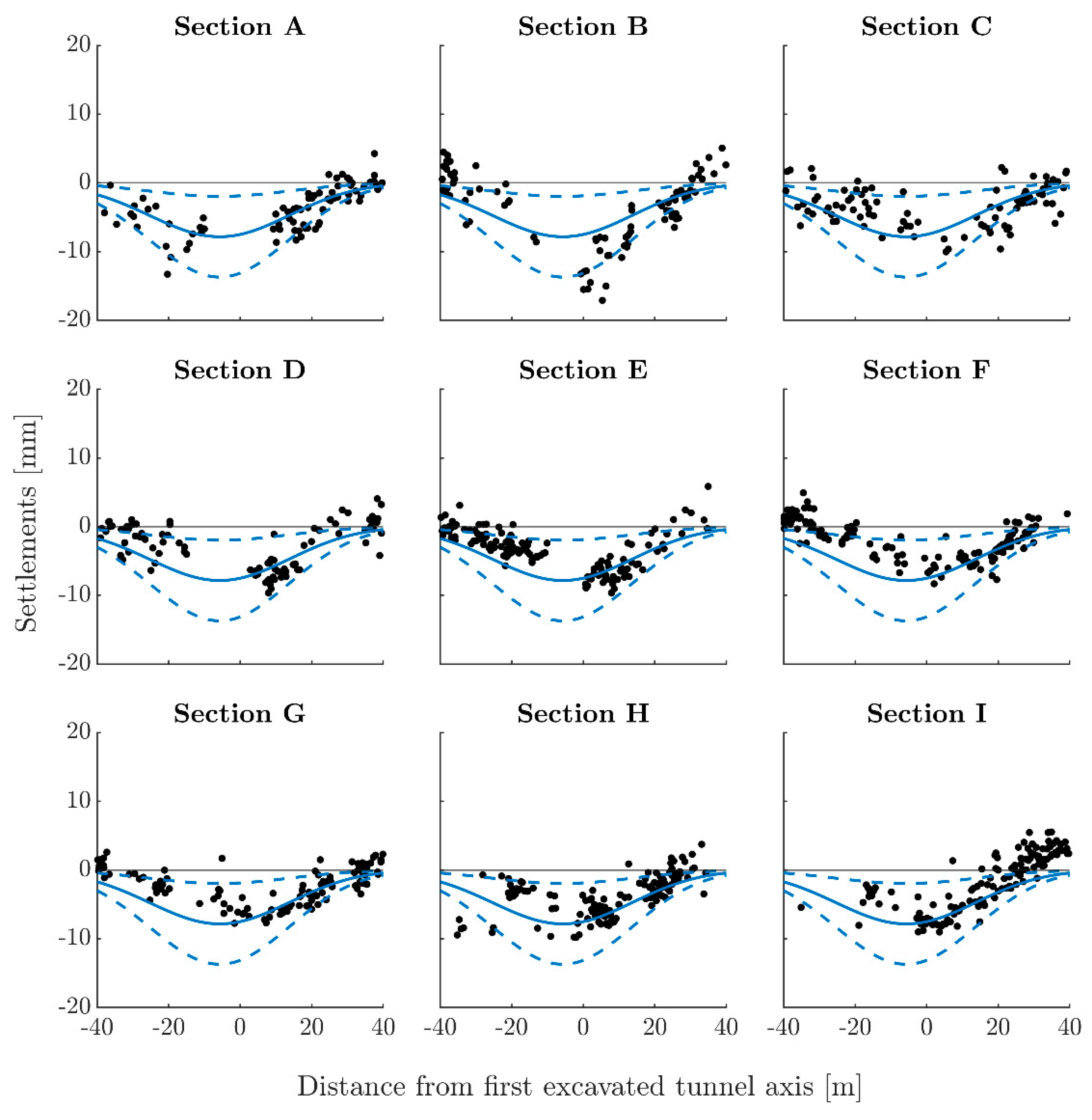
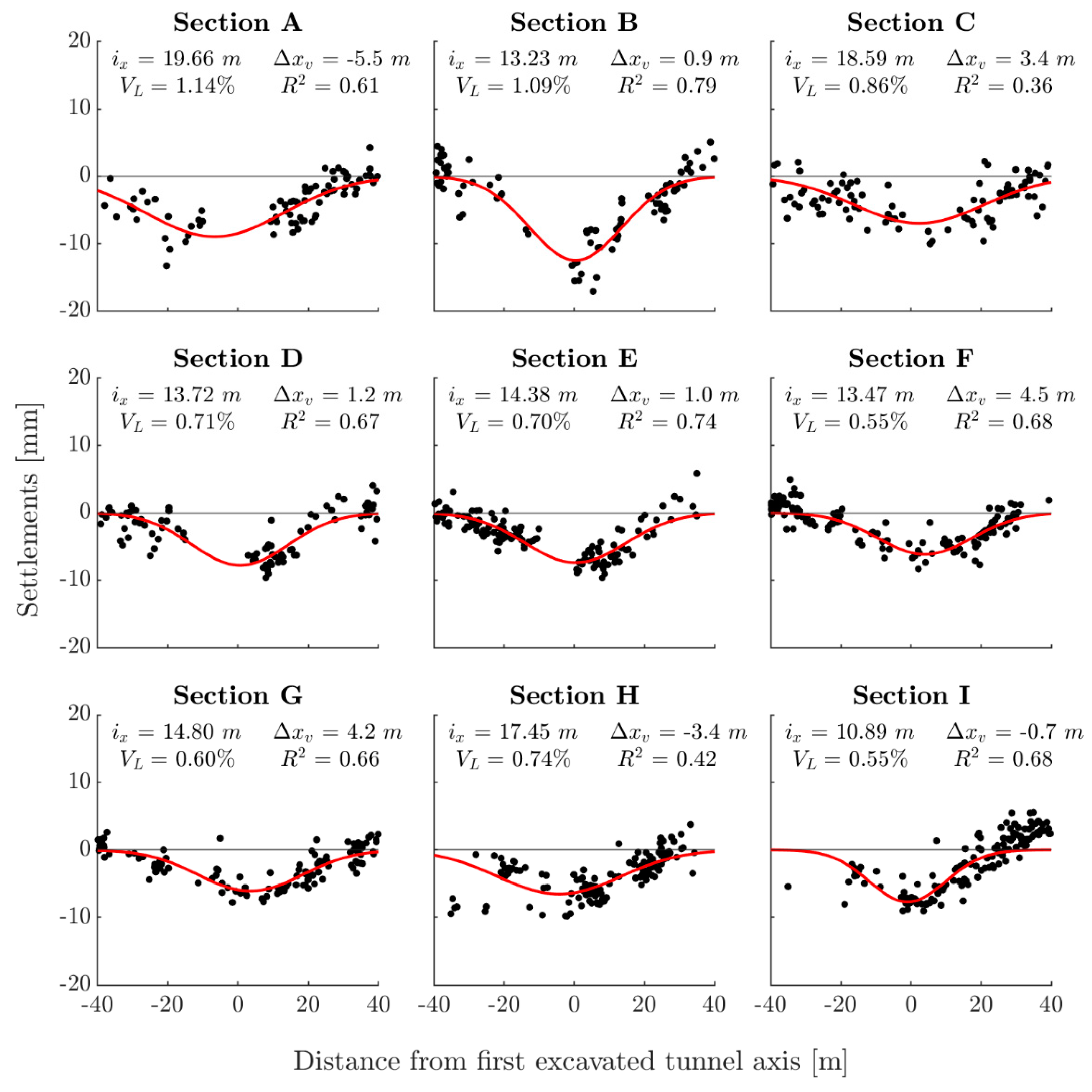
- Predicted settlement profiles obtained using Equation (15) are compared to those retrieved from MT-InSAR to assess the reliability of the measurements;
- -
- Monitored data from MT-InSAR, which lie on cross sections orthogonal to the first excavated tunnel axis (the one further east in Figure 2b), are interpolated to gain information on VL and ix. The latter are then used to predict the settlement caused by the second excavation, taking into account the influence of the second excavation on the first one using the superimposition of the effects.
4.1. Assessment of the AoI before the Excavations
4.2. Displacements Maps after the Excavation Processes
4.3. Settlements’ Prediction and Comparison to Monitored Data
4.4. Volume Loss Assessment and Settlement Prediction for the Second Excavation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
(1 + x·tan(ϑ)/z0)·VL·π·D2/4 − ∫tan(ϑ)/z0·VL·π·D2/4·dx =
VL·π·D2/4 + x·tan(ϑ)/z0·VL·π·D2/4 − x·tan(ϑ)/z0·VL·π·D2/4 =
VL·π·D2/4 = V∗L·π·D2/4 (Equation (A2)) → VL = V∗L.
References
- Vollset, S.E.; Goren, E.; Yuan, C.W.; Cao, J.; Smith, A.E.; Hsiao, T.; Bisignano, C.; Azhar, G.S.; Castro, E.; Chalek, J.; et al. Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: A forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 1285–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A. Inequality, the Urban-Rural Gap, and Migration. Q. J. Econ. 2013, 128, 1727–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, J.B.; Worth, C.P. Settlement of Buildings and Associated Damage. No. CP 33/75. 1975. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248646701_Settlement_of_Buildings_and_Associated_Damage (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Boscardin, M.D.; Cording, E.J. Building response to excavation-induced settlement. J. Geotech. Eng. 1989, 115, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, F.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, I.; Parsons, I.; Wright, T.J.; Funning, G.J. Post-seismic motion following the 1997 Manyi (Tibet) earthquake: InSAR observations and modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 169, 1009–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronin, A.A. Satellite remote sensing in seismology. A review. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 124–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, E.J.; Blom, R.G.; Goldstein, R.M. Detection and monitoring of rapid subsidence over Lost Hills and Belridge oil fields by SAR interferometry. Appl. Geol. Remote Sens. Int. Conf. 1997, 1, I-84. [Google Scholar]
- Tomàs, R.; Romeo, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorquì, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; Gonzàlez, P.J.; Fernàndez, J.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Mann, D.; Freymueller, J.T.; Meyer, D.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry of Okmok volcano, Alaska: Radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 10791–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.; Froger, J.L. The role of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar in detecting, mapping, monitoring, and modelling the volcanic activity of Piton de la Fournaise, La Réunion: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barla, G.; Tamburini, A.; Del Conte, S.; Giannico, C. InSAR monitoring of tunnel induced ground movements. Geomech. Tunn. 2016, 9, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Giardina, G.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Multi-temporal InSAR structural damage assessment: The London Crossrail case study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, G.; Milillo, P.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Evaluation of InSAR monitoring data for post-tunnelling settlement damage assessment. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2018, 26, e2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, V.; Bilotta, E.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M.; Russo, G. An application of A-DInSAR for monitoring tunnelling induced displacements in urban area. The case study of the Naples Metro Line 6 stretch Mergellina-Chiaia. Gallerie Grandi Opere Sotter. 2021, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Giardina, G.; Milillo, P.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Example Applications of Satellite Monitoring for Post-tunneling Settlement Damage Assessment for the Crossrail Project in London. In Structural Analysis of Historical Constructions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 2225–2235. [Google Scholar]
- Macchiarulo, V.; Milillo, P.; DeJong, M.J.; Marti, J.G.; Sanchez, J.; Giardina, G. Integrated InSAR monitoring and structural assessment of tunnelling-induced building deformations. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, S.; Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Mazzanti, P.; Rocca, A. Assessment of landslide pre-failure monitoring and forecasting using satellite SAR interferometry. Geosciences 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Iglesias, R.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: Potential, limits and initial C-and X-band comparison. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. The SARPROZ InSAR tool for urban subsidence/manmade structure stability monitoring in China. In Proceedings of the ISRSE, Sidney, Australia, 10–15 April 2011; p. 1015. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, R.B. Deep excavations and tunneling in soft ground. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Mexico City, Mexico, 1969; Available online: https://discovered.ed.ac.uk/discovery/fulldisplay?vid=44UOE_INST:44UOE_VU2&tab=Everything&docid=alma991421573502466&lang=en&context=L&query=sub,exact,%20Soil%20mechanics%20--%20Congresses (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Schmidt, B. Settlements and Ground Movements Associated with Tunneling in Soil. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (ISTAT). Available online: https://www.istat.it/it/archivio/232137 (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Metropolitana di Napoli s.p.a. Available online: https://www.metropolitanadinapoli.it/tunnel-capodichino-poggioreale-visita-sindaco (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Metropolitana di Napoli s.p.a. Available online: https://www.metropolitanadinapoli.it/metropolitana-linea-1-prima-galleria-da-capodichino-a-poggioreale/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Di Pace, M.; Cocchi, R.; De Gugliemo, M.L. Scavo Meccanizzato: TBM a spasso per Napoli. Le Strade 2021, 1568, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mair, R.J.; Taylor, R.N. Bored tunnelling in the urban environments. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 12 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- di Prisco, C.; Callari, C.; Barbero, M.; Bilotta, E.; Russo, G.; Boldini, D.; Desideri, A.; Flessati, L.; Graziani, A.; Luciani, A.; et al. Assessment of excavation-related hazards and design of mitigation measures. In Handbook on Tunnels and Underground Works; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 247–316. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, M.P.; New, B.M. Settlements above tunnels in the United Kingdom—Their magnitude and prediction. In Proceedings of the Tunnelling 82, Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium, Brighton, UK, 1 January 1982; pp. 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, R.; Lei, H.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Z. Relating twin-tunnelling-induced settlement to changes in the stiffness of soil. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwansawat, S.; Einstein, H.H. Describing settlement troughs over twin tunnels using a superposition technique. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2007, 133, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, F.H.; Shahrour, I. Numerical analysis of the interaction between twin-tunnels: Influence of the relative position and construction procedure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwell, P.B. Ground movements caused by tunnelling in soil. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Large Movements and Structures, Cardiff, UK, July, 1978; pp. 812–948. [Google Scholar]
- Cording, E.J.; Hansmire, W.H. Displacements around soft ground tunnels. In Proceedings of the 5th Pan American Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1975; pp. 571–632. Available online: https://books.google.com.au/books/about/5th_Panamerican_Conference_on_Soil_Mecha.html?id=tWHAoAEACAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Rankin, W.J. Ground movements resulting from urban tunnelling: Predictions and effects. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 1988, 5, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 3, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansoti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-Gonzàlez, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

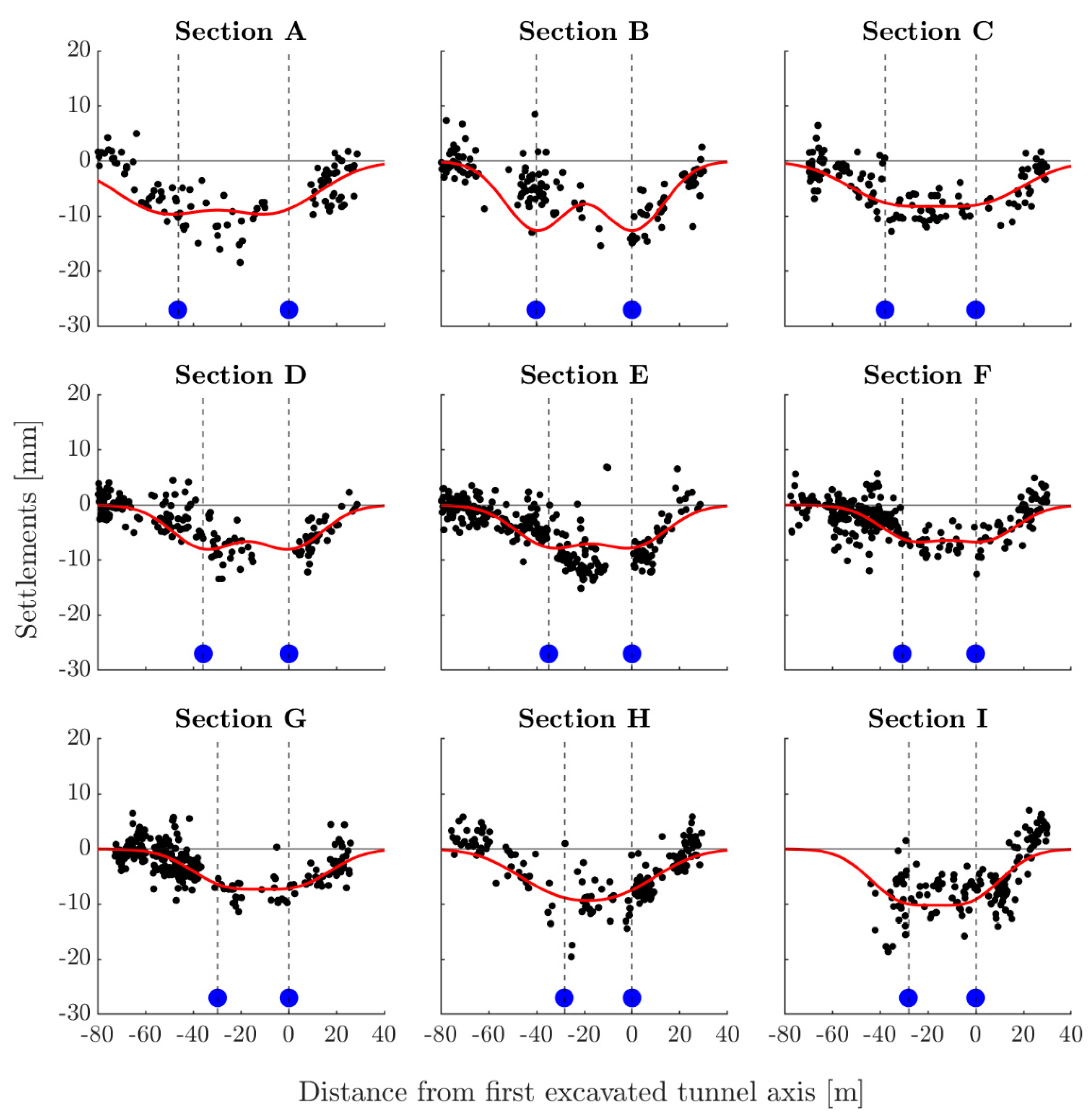
| % of Monitored Scatters that Fall within the Expected Range | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I |
| 64% | 53% | 67% | 59% | 78% | 55% | 64% | 79% | 54% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Della Ragione, G.; Rocca, A.; Perissin, D.; Bilotta, E. Volume Loss Assessment with MT-InSAR during Tunnel Construction in the City of Naples (Italy). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102555
Della Ragione G, Rocca A, Perissin D, Bilotta E. Volume Loss Assessment with MT-InSAR during Tunnel Construction in the City of Naples (Italy). Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102555
Chicago/Turabian StyleDella Ragione, Gianluigi, Alfredo Rocca, Daniele Perissin, and Emilio Bilotta. 2023. "Volume Loss Assessment with MT-InSAR during Tunnel Construction in the City of Naples (Italy)" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102555
APA StyleDella Ragione, G., Rocca, A., Perissin, D., & Bilotta, E. (2023). Volume Loss Assessment with MT-InSAR during Tunnel Construction in the City of Naples (Italy). Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102555






