Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach
Abstract
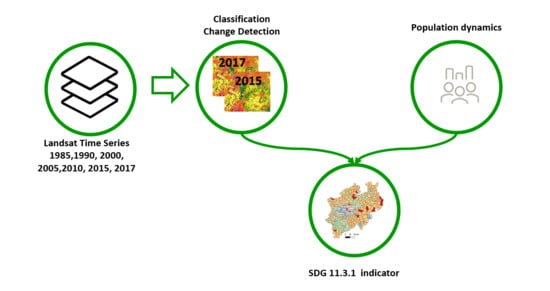
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
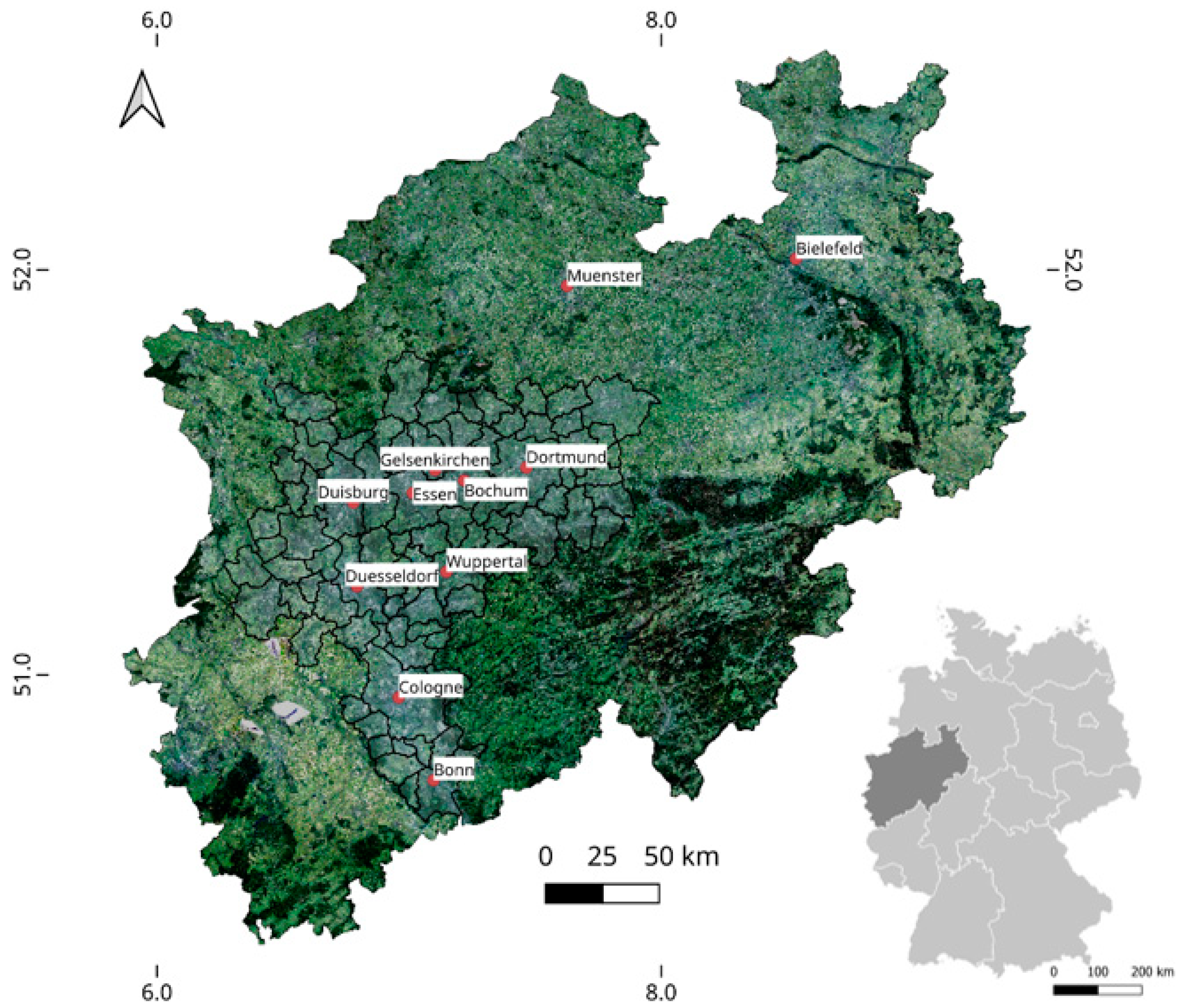
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
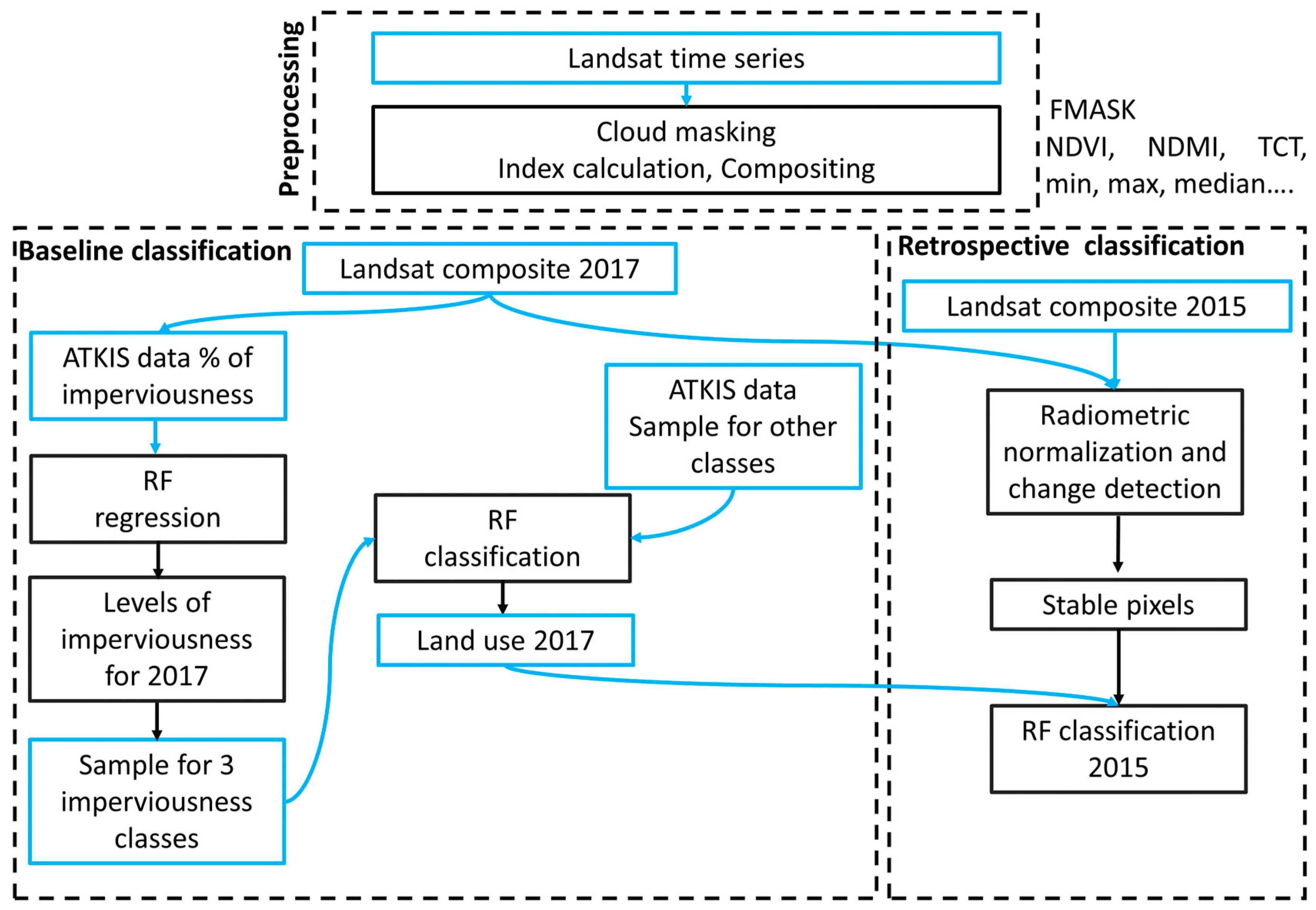
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Land Cover and Land Use Classification
3.3. Intensity Analysis and Comparison with Population Data
4. Results and Discussion
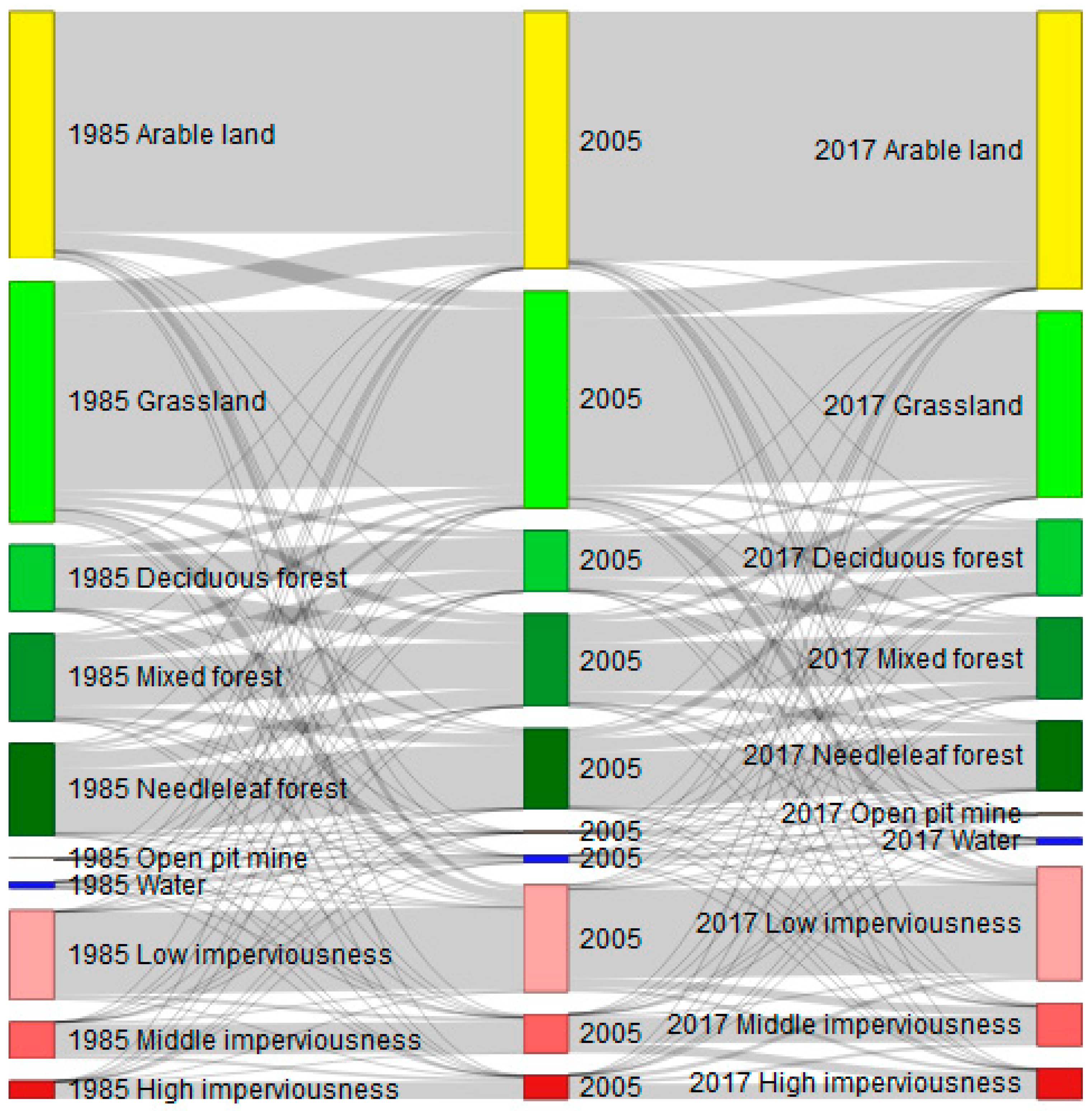
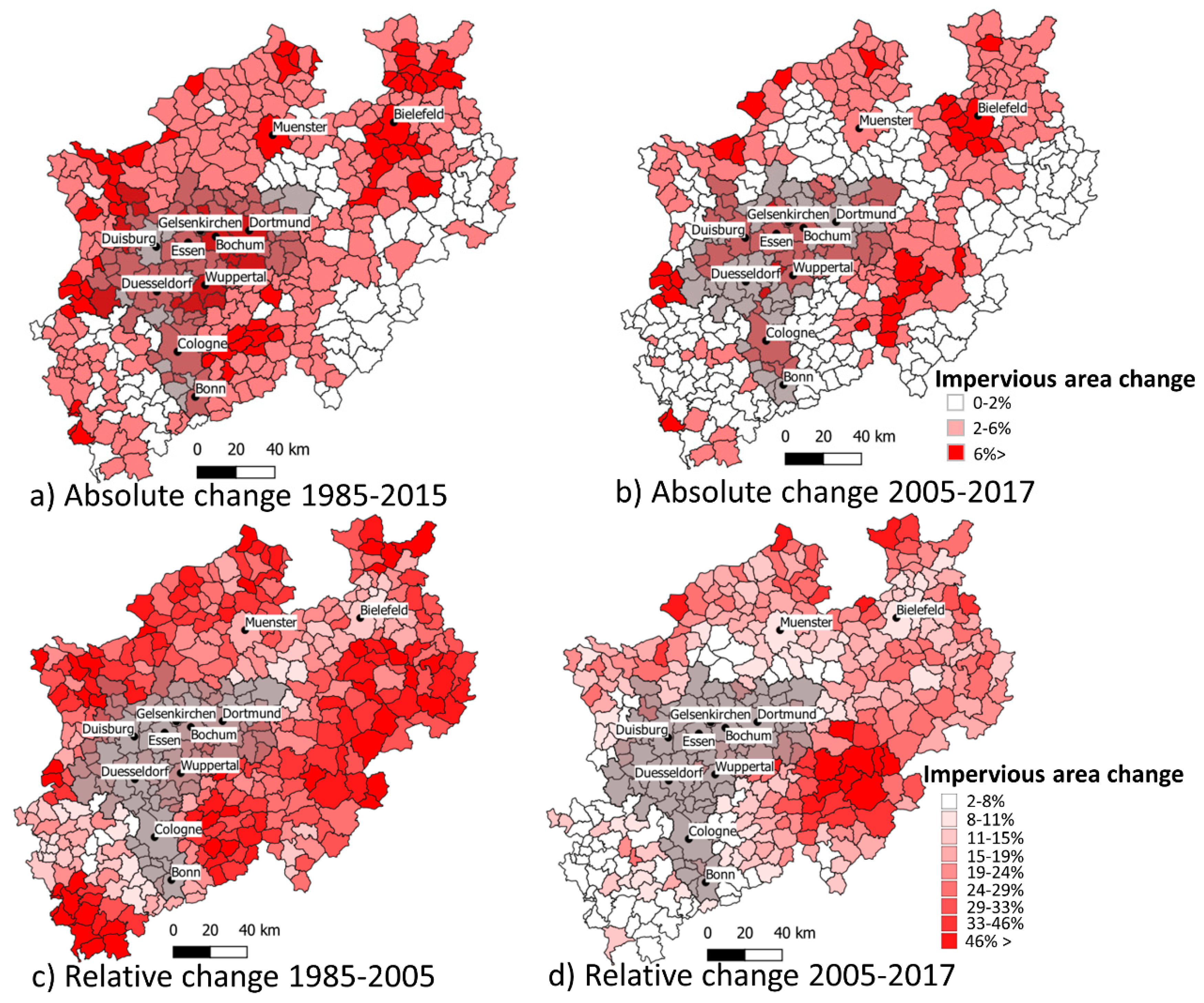
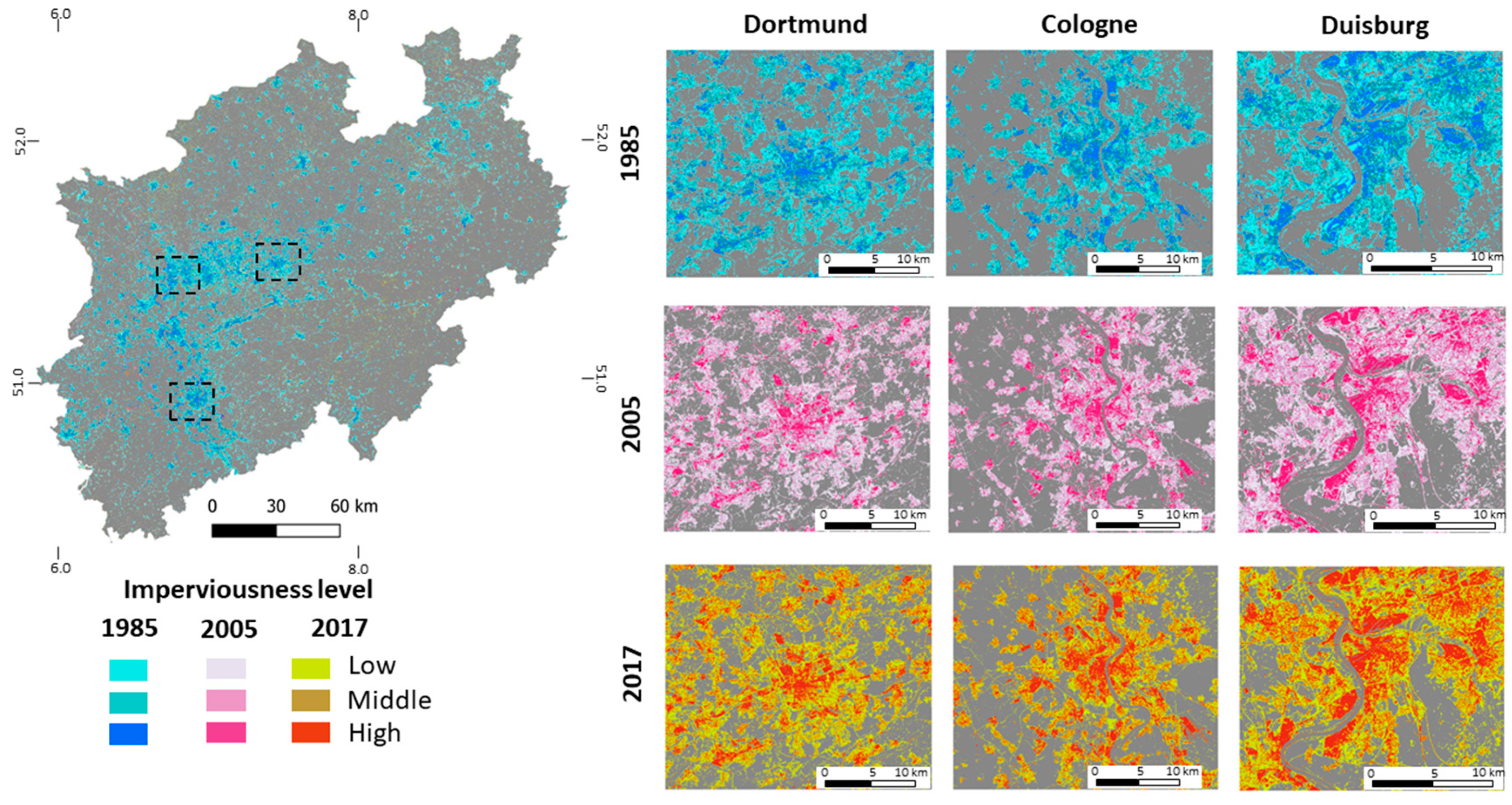
4.1. Land-Use Classification and Changes between 1985–2017
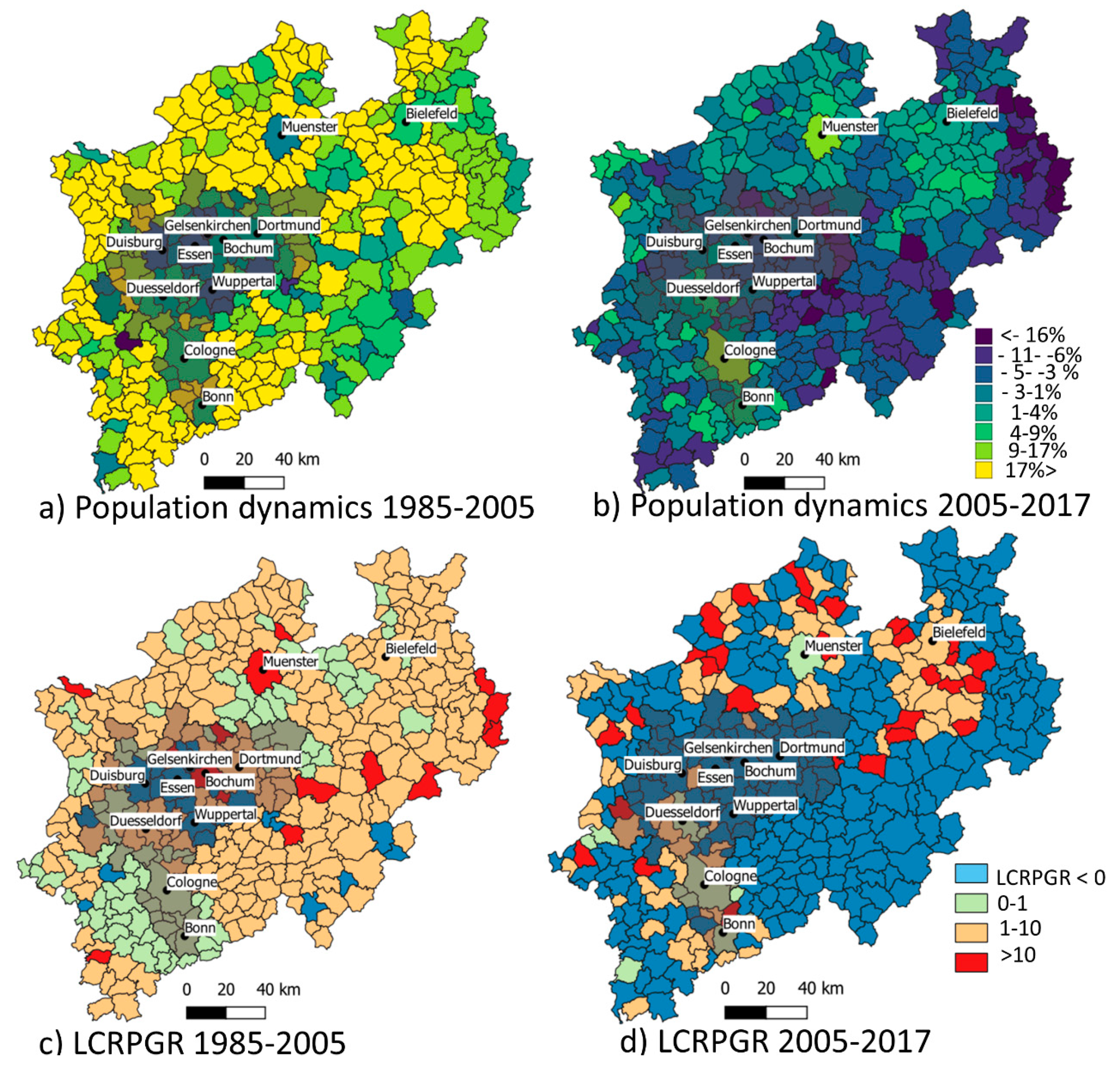
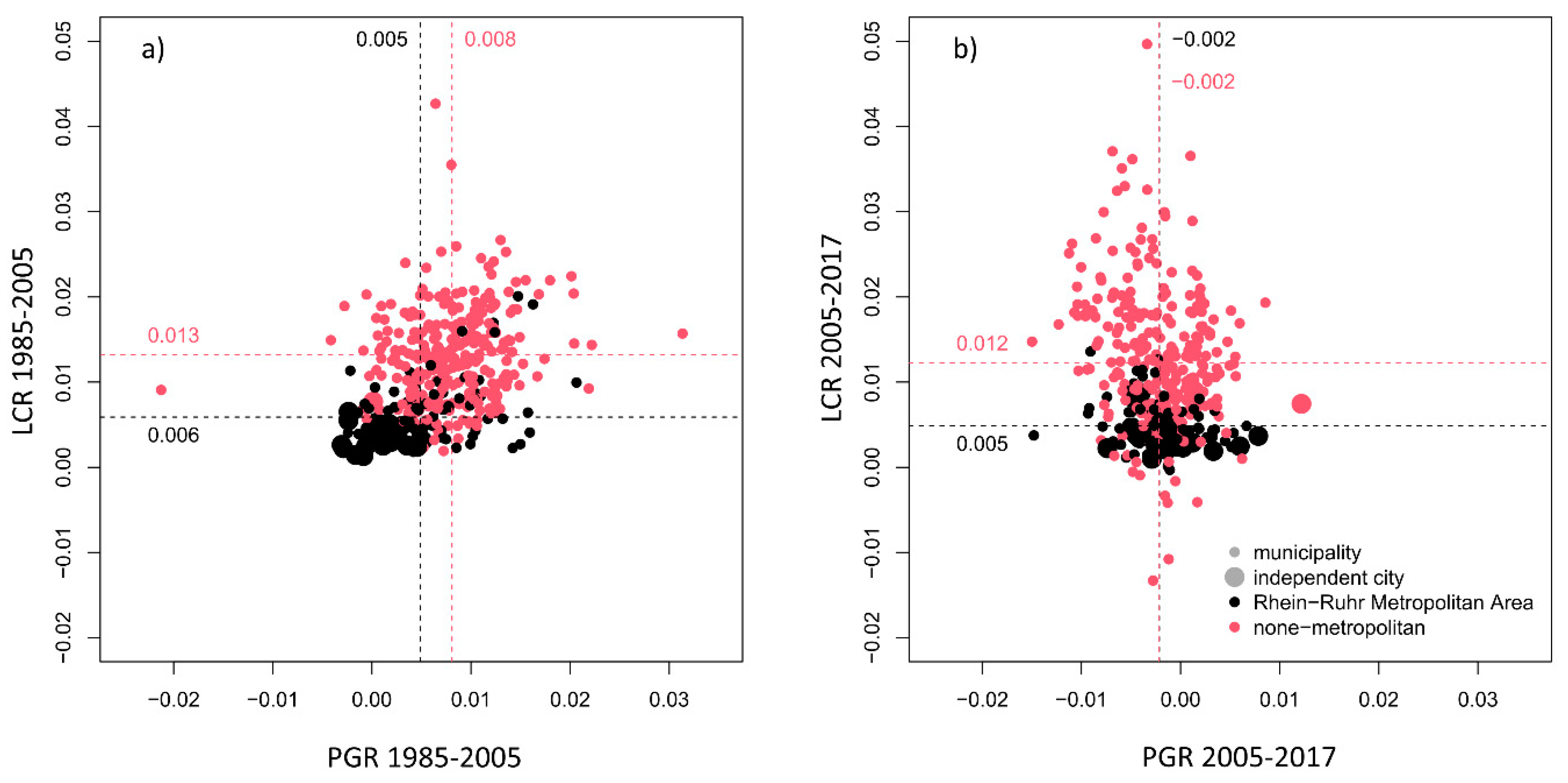
4.2. Land Consumption and Population Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.-P.; Sexton, J.O.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Townshend, J.R. Characterizing the Magnitude, Timing and Duration of Urban Growth from Time Series of Landsat-Based Estimates of Impervious Cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Qi, S.; Tao, S.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y. An Efficient Approach to Capture Continuous Impervious Surface Dynamics Using Spatial-Temporal Rules and Dense Landsat Time Series Stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DESA UN World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision, Key Facts. New York, NY, USA. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/Publications/ (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- El Mendili, L.; Puissant, A.; Chougrad, M.; Sebari, I. Towards a Multi-Temporal Deep Learning Approach for Mapping Urban Fabric Using Sentinel 2 Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Mapping Urban Impervious Surfaces by Using Spectral Mixture Analysis and Spectral Indices. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhu, Z. Continuous Subpixel Monitoring of Urban Impervious Surface Using Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 110929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote Sensing of Impervious Surfaces in the Urban Areas: Requirements, Methods, and Trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; Lakshmi, V.; Piechota, T.; Struppa, D. Earth Observation and Cloud Computing in Support of Two Sustainable Development Goals for the River Nile Watershed Countries. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Multi-Scale Estimation of Land Use Efficiency (SDG 11.3.1) across 25 Years Using Global Open and Free Data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gu, J. Using Earth Observation for Monitoring SDG 11.3.1-Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate in Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.M. Making Room for a Planet of Cities; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://www.lincolninst.edu/pubs/1880_Making-Room-for-a-Planet-of-Cities-urban-expansion (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- UNSTATS. Indicator 11.3.1. Available online: Https://Unstats.Un.Org/Sdgs/Metadata/Files/Metadata-08-05-01.Pdf (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Mudau, N.; Mwaniki, D.; Tsoeleng, L.; Mashalane, M.; Beguy, D.; Ndugwa, R. Assessment of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 and Urban Growth Trends of Major and Small Cities in South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, R.; Nascetti, A.; Cirigliano, R.V.; Di Rico, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Monti, P.; Crespi, M. Monitoring the Impact of Land Cover Change on Surface Urban Heat Island through Google Earth Engine: Proposal of a Global Methodology, First Applications and Problems. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, S.; Okujeni, A.; Canters, F.; Degerickx, J.; Heiden, U.; Hostert, P.; Priem, F.; Somers, B.; Thiel, F. Imaging Spectroscopy of Urban Environments. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henits, L.; Jürgens, C.; Mucsi, L. Seasonal Multitemporal Land-Cover Classification and Change Detection Analysis of Bochum, Germany, Using Multitemporal Landsat TM Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3439–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Lin, P.; Gong, K.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A. High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution Mapping of Global Urban Change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, M.; Staab, J.; Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. Spatial and Semantic Effects of LUCAS Samples on Fully Automated Land Use/Land Cover Classification in High-Resolution Sentinel-2 Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 88, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. Improving Impervious Surface Estimation by Using Remote Sensed Imagery Combined With Open Street Map Points-of-Interest (POI) Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4265–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersen, P.S.; Fensholt, R.; Drews, M. Using Landsat Vegetation Indices to Estimate Impervious Surface Fractions for European Cities. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8224–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.; Moul, K.; Pollini, B.; de Lamo, X.; Simonson, W. Compendium of Earth Observation Contributions to the SDG Targets and Indicators 2020. 2020. Available online: https://eo4society.esa.int/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/EO_Compendium-for-SDGs.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Deng, Y.; Fan, F.; Chen, R. Extraction and Analysis of Impervious Surfaces Based on a Spectral Un-Mixing Method Using Pearl River Delta of China Landsat TM/ETM+ Imagery from 1998 to 2008. Sensors 2012, 12, 1846–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliry, S.I.; Avdan, Z.Y.; Avdan, U. Extracting Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 Satellite Data for Urban Planning and Environmental Management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6572–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Himmler, V.; Schorcht, G.; Thiel, M.; Wehrmann, T.; Bachofer, F.; Conrad, C.; Schmidt, M.; Dech, S. Large-Area Assessment of Impervious Surface Based on Integrated Analysis of Single-Date Landsat-7 Images and Geospatial Vector Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Du, B.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L. A Post-Classification Change Detection Method Based on Iterative Slow Feature Analysis and Bayesian Soft Fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecheltjen, A.; Thonfeld, F.; Menz, G. Recent Advances in Remote Sensing Change Detection—A Review. Land Use Land Cover Mapp. Eur. 2014, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring Land Use/Land Cover Change, Urban Growth Dynamics and Landscape Pattern Analysis in Five Fastest Urbanized Cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Sun, G. Landsat-Based Land Cover Change in the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan Urban Agglomeration in 1990, 2000 and 2010. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, F.; Okujeni, A.; Hauer, J.; Hostert, P.; Nielsen, J.Ø.; van der Linden, S. Mapping Patterns of Urban Development in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, Using Machine Learning Regression Modeling with Bi-Seasonal Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Huadong, G.; Blaes, X.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Gueguen, L.; Halkia, M.; Kauffmann, M.; Kemper, T.; Lu, L.; et al. A Global Human Settlement Layer From Optical HR/VHR RS Data: Concept and First Results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2102–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Keil, M.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; Strano, E. Breaking New Ground in Mapping Human Settlements from Space—The Global Urban Footprint. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Üreyen, S.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Hanke, W.; Bachofer, F.; Zeidler, J.; Esch, T.; Gorelick, N.; Kakarla, A.; et al. Outlining Where Humans Live, the World Settlement Footprint 2015. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, A.; Sannier, C.; Corpetti, T. Monitoring Urban Areas with Sentinel-2A Data: Application to the Update of the Copernicus High Resolution Layer Imperviousness Degree. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorri, M.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Schiavina, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Unveiling 25 Years of Planetary Urbanization with Remote Sensing: Perspectives from the Global Human Settlement Layer. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedentop, S.; Fina, S. Monitoring Urban Sprawl in Germany: Towards a GIS-Based Measurement and Assessment Approach. J. Land Use Sci. 2010, 5, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environmental Agency (EEA) Urban Sprawl in Europe Joint EEA-FOEN Repor 2016; European Environmental Agency—Swiss Federal office for the Environment: Luxembourg, 2016; ISBN 978-92-9213-738-0.
- Hoymann, J.; Goetzke, R. Simulation and Evaluation of Urban Growth for Germany Including Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Measures. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J.; See, L.; Tayyebi, A. Assessing the Suitability of GlobeLand30 for Mapping Land Cover in Germany. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environmental Agency (EEA) Country Fact Sheet: Land Cover 2012. 2012. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/landuse/land-cover-country-fact-sheets/land-cover-country-fact-sheets-2012/de-germany-landcover-2012.pdf/view (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Rienow, A.; Schneevoigt, N.J.; Thonfeld, F. Quantification and Prediction of Land Consumption and Its Climate Effects in the Rhineland Metropolitan Area Based on Multispectral Satellite Data and Land-Use Modelling 1975–2030. Spat. Anal. Model. Plan. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezirksregierung Köln Erläuterung Zu Abweichungen in Der Flächenerhebung Nach Art Der Tatsächlichen Nutzung Nach Dem Umstieg von ALK/ALB Nach ALKIS in NRW; Bezirksregierung Köln: Cologne, Germany, 2020.
- IT. NRW Data Licence Germany—Attribution—Version 2.0. 2020. Available online: https://www.it.nrw/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and Expansion of the Fmask Algorithm: Cloud, Cloud Shadow, and Snow Detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juergens, C.; Meyer-Heß, M.F. Application of NDVI in Environmental Justice, Health and Inequality Studies—Potential and Limitations in Urban Environments. Preprints 2020, 2020080499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P.; Cicone, R.C. A Physically-Based Transformation of Thematic Mapper Data—The TM Tasseled Cap. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, GE-22, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzari, G.; Lobell, D.B. Landsat-Based Classification in the Cloud: An Opportunity for a Paradigm Shift in Land Cover Monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Metz, A.; Marconcini, M.; Keil, M. Combined Use of Multi-Seasonal High and Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery for Parcel-Related Mapping of Cropland and Grassland. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Egorov, A.; Potapov, P.V.; Stehman, S.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Turubanova, S.A.; Roy, D.P.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; Ju, J. Monitoring Conterminous United States (CONUS) Land Cover Change with Web-Enabled Landsat Data (WELD). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonfeld, F.; Steinbach, S.; Muro, J.; Kirimi, F. Long-Term Land Use/Land Cover Change Assessment of the Kilombero Catchment in Tanzania Using Random Forest Classification and Robust Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Clinton, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Gong, P.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Mapping Major Land Cover Dynamics in Beijing Using All Landsat Images in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Wu, C. A Review of Remote Sensing Image Classification Techniques: The Role of Spatio-Contextual Information. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 47, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random Forest Classifier for Remote Sensing Classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R. News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goetzke, R.; Judex, M.; Braun, M.; Menz, G. Evaluation of Driving Forces of Land-Use Change and Urban Growth in North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany). In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 3425–3428. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. Quantifying Annual Changes in Built-up Area in Complex Urban-Rural Landscapes from Analyses of PALSAR and Landsat Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, G. CORINE Land Cover and Land Cover Change Products. In Land Use and Land Cover Mapping in Europe: Practices & Trends; Manakos, I., Braun, M., Eds.; Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 55–74. ISBN 978-94-007-7969-3. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, A.A. The Regularized Iteratively Reweighted MAD Method for Change Detection in Multi-and Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, M.J.; Nielsen, A.A. Automatic Radiometric Normalization of Multitemporal Satellite Imagery with the Iteratively Re-Weighted MAD Transformation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marpu, P.R.; Gamba, P.; Canty, M.J. Improving Change Detection Results of IR-MAD by Eliminating Strong Changes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, M.J.; Nielsen, A.A. Linear and Kernel Methods for Multivariate Change Detection. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 38, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A Review of Assessing the Accuracy of Classifications of Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incora (Inwertsetzung von Copernicus-Daten für die Raumbeobachtung Germany 2019—Land Cover Based on Sentinel-2 Data—Mundialis. 2020. Available online: https://www.mundialis.de/de/deutschland-2019-landbedeckung-auf-basis-von-sentinel-2-daten (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Weigand, M.; Wurm, M. Land Cover DE—Sentinel-2—Germany, 2015. 2020. Available online: https://geoservice.dlr.de/data-assets/1ccmlap3mn39.htm (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Badmos, O.S.; Rienow, A.; Callo-Concha, D.; Greve, K.; Jürgens, C. Urban Development in West Africa—Monitoring and Intensity Analysis of Slum Growth in Lagos: Linking Pattern and Process. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G. Intensity Analysis to Unify Measurements of Size and Stationarity of Land Changes by Interval, Category, and Transition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Fu, Y.; Xie, T.; He, C.; Zang, J. Intensity and Stationarity Analysis of Land Use Change Based on CART Algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, R.; David, J.; Caetano, M.; Pereira, J.M.C. Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate—Analysis of Different Formulations Applied to Mainland Portugal. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBSR (Bundesinstitut für Bau-, Stadt- und Raumforschung) Studie Zum Monitoring Der Flächeninanspruchnahme—Evaluation Der Einschlägigen Datenbasis. 2020. Available online: https://www.bbsr.bund.de/BBSR/DE/forschung/programme/refo/raumordnung/2013/MonitoringFlaecheninanspruchnahme_Evaluation/01_Start.html (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Pan, J. Multi-Feature Classification of Multi-Sensor Satellite Imagery Based on Dual-Polarimetric Sentinel-1A, Landsat-8 OLI, and Hyperion Images for Urban Land-Cover Classification. Sensors 2018, 18, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canty, D.M. Mortcanty/Earthengine. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/mortcanty/earthengine (accessed on 20 April 2021).

| Input | Description | Compositing |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index | |
| NDWI | Normalized difference water index | |
| TCC | Tasseled Cap Components (greenness, wetness, and brightness) | Minimum, maximum, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 80th and 90th percentile, mean over growing season (April-September) and year |
| Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI bands | Green, Blue, Red, NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2 |
| Year | OA | PA for Low, Middle, and High Imperviousness Class | UA for Low, Middle, and High Imperviousness Class | Accuracies for Aggregated Urban Area | Accuracies for Aggregated Non-Urban Areas | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | UA | PA | UA | ||||
| 2017 | 89.0% | 89.3 90.5 94.4 | 89.4 90.5 94.4 | 96.3 | 93.04 | 92.7 | 96.2 |
| 2015 | 87.0% | 77.9 93.9 90.1 | 81.5 90.7 90.1 | 94.6 | 91.3 | 90.9 | 94.7 |
| 2010 | 80.0% | 62.9 77.9 90.5 | 69.3 83.2 87.5 | 93.1 | 90.7 | 91.2 | 92.3 |
| 2005 | 79.1% | 82.9 76.2 89.9 | 78.2 92.4 82.6 | 94.8 | 92.1 | 94.6 | 96.7 |
| 2000 | 80.2% | 63.1 78.1 90.2 | 69.1 83.5 87.8 | 93.1 | 96 | 96.2 | 93.3 |
| 1990 | 75.3% | 54.9 67.6 90.1 | 65.1 79.7 80.8 | 91.3 | 95.8 | 95.8 | 91.4 |
| 1985 | 77.3% | 61.1 69.8 87.4 | 74.5 75.7 82.9 | 87.7 | 95.9 | 96.1 | 88.3 |
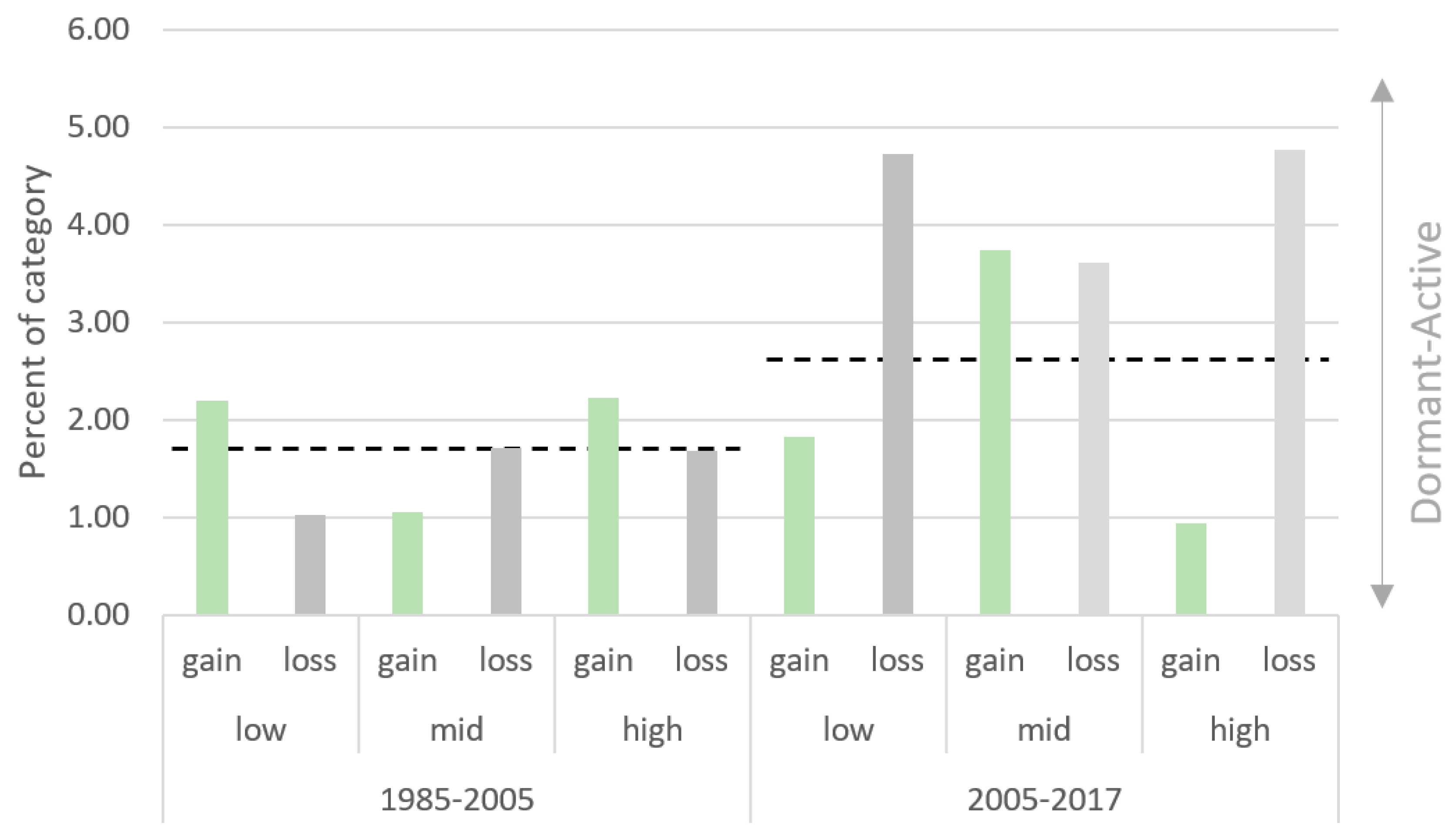
| Intensity Change Category | Time Interval | Annual Intensity of Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Interval level | 1985–2005 | 1.71 |
| 2005–2017 | 2.72 | |
| Transition level | 1985–2005 | From Low to middle 0.49 From low to high 0.32 From middle to high 1.16 |
| 2005–2017 | From low to middle 1.38 From low to high 0.24 From middle high 0.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghazaryan, G.; Rienow, A.; Oldenburg, C.; Thonfeld, F.; Trampnau, B.; Sticksel, S.; Jürgens, C. Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091694
Ghazaryan G, Rienow A, Oldenburg C, Thonfeld F, Trampnau B, Sticksel S, Jürgens C. Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091694
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhazaryan, Gohar, Andreas Rienow, Carsten Oldenburg, Frank Thonfeld, Birte Trampnau, Sarah Sticksel, and Carsten Jürgens. 2021. "Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091694
APA StyleGhazaryan, G., Rienow, A., Oldenburg, C., Thonfeld, F., Trampnau, B., Sticksel, S., & Jürgens, C. (2021). Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091694