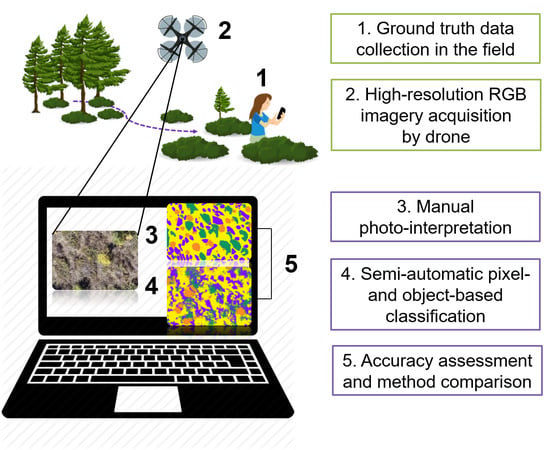
Using UAV Imagery to Detect and Map Woody Species Encroachment in a Subalpine Grassland: Advantages and Limits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
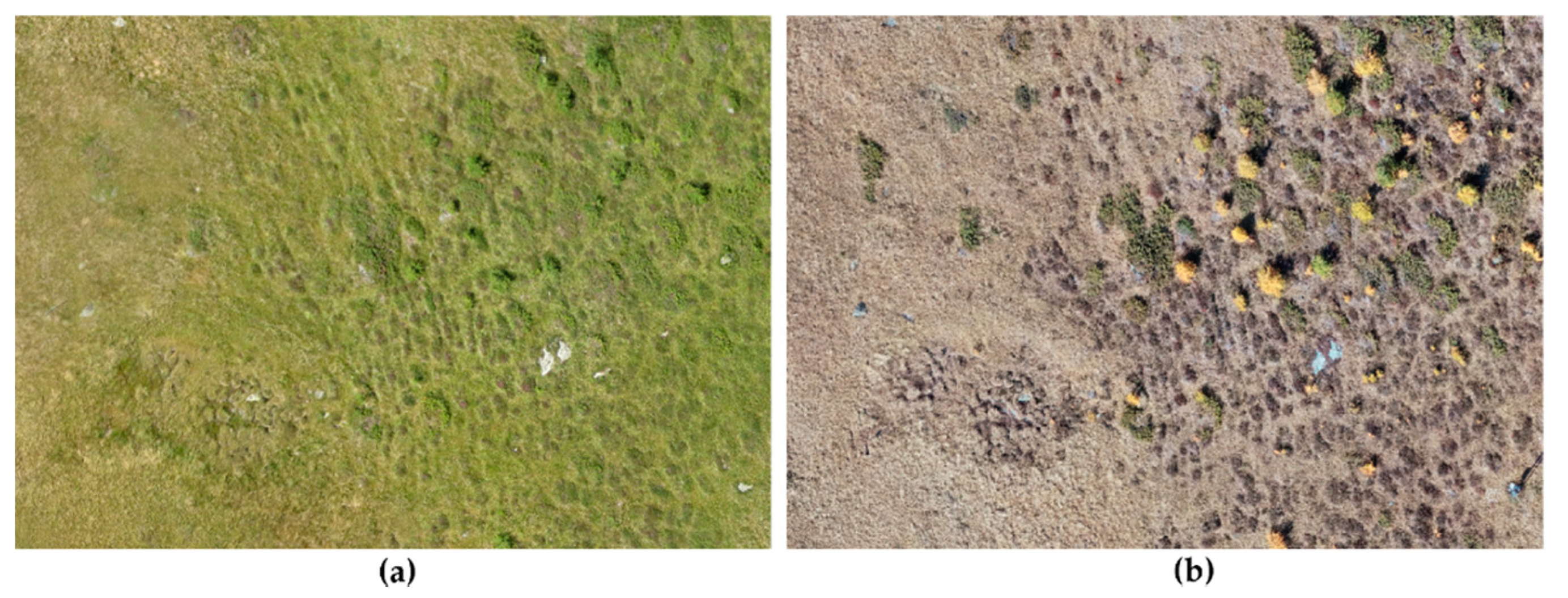
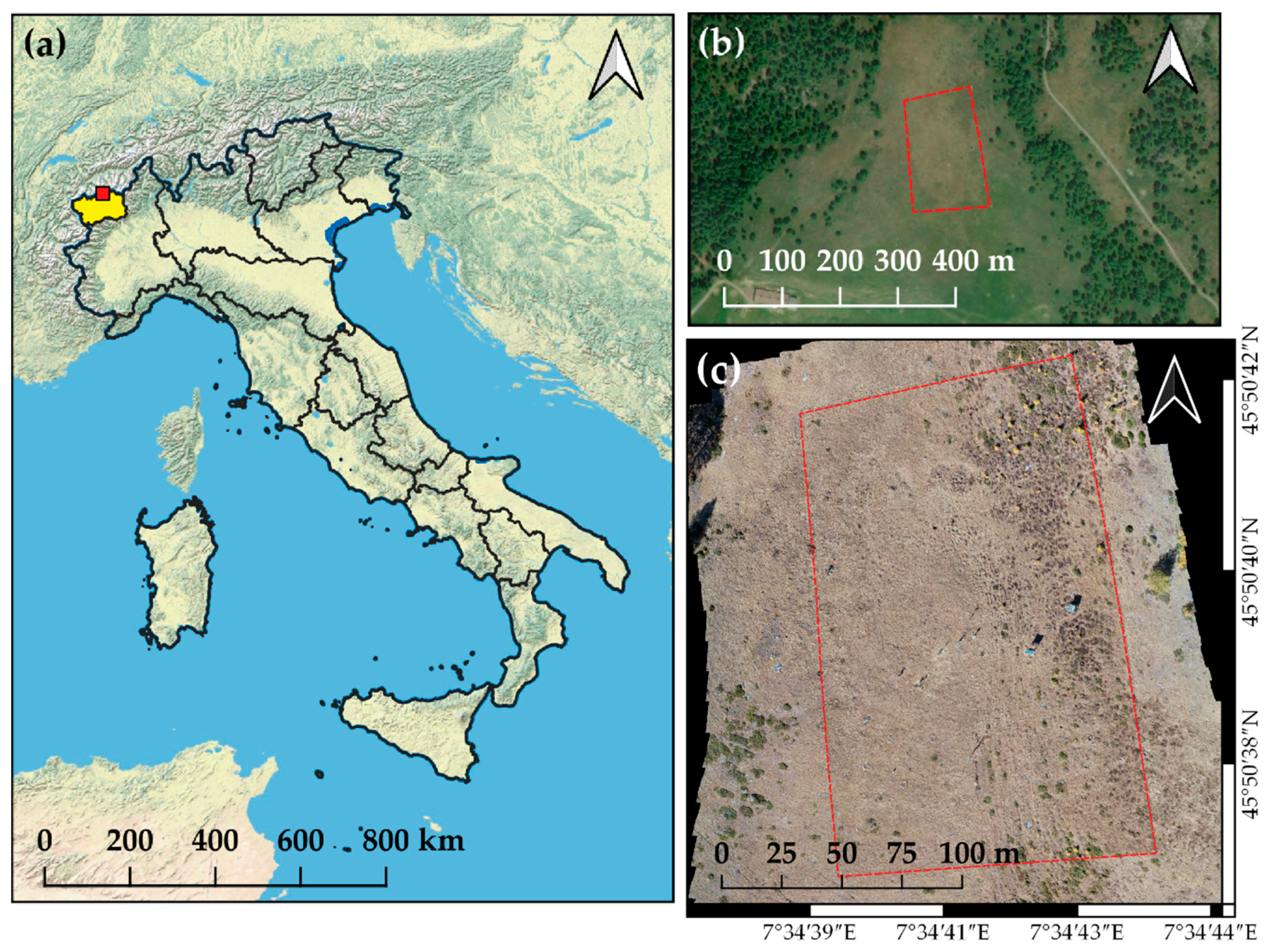
2.1. Study Area and Vegetation Characteristics
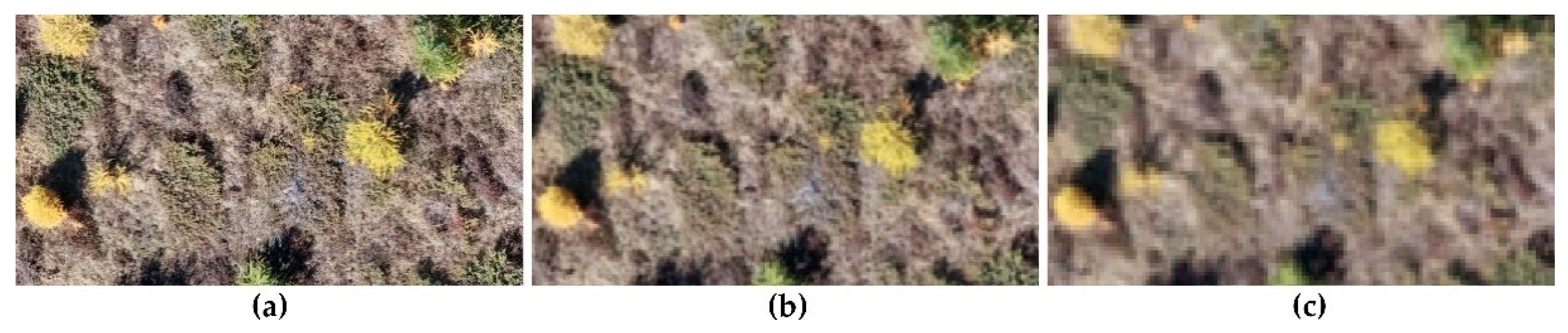
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Photogrammetric Data Processing
2.4. Ground Truth
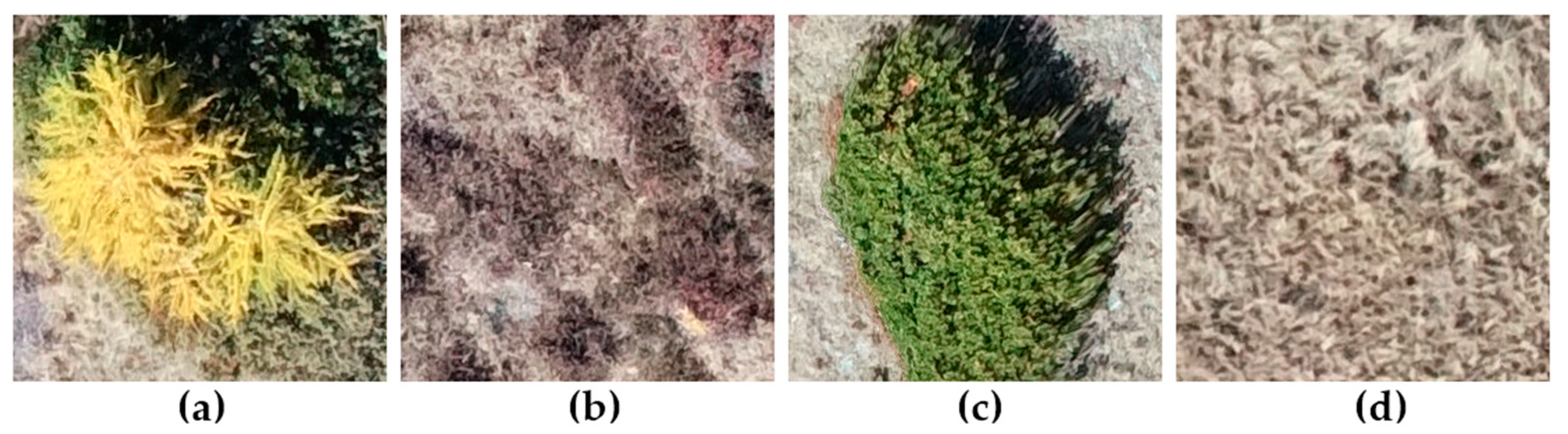
2.5. Reference Data: Sampling and Response Design
2.6. Image Classification
2.7. Analyses
3. Results
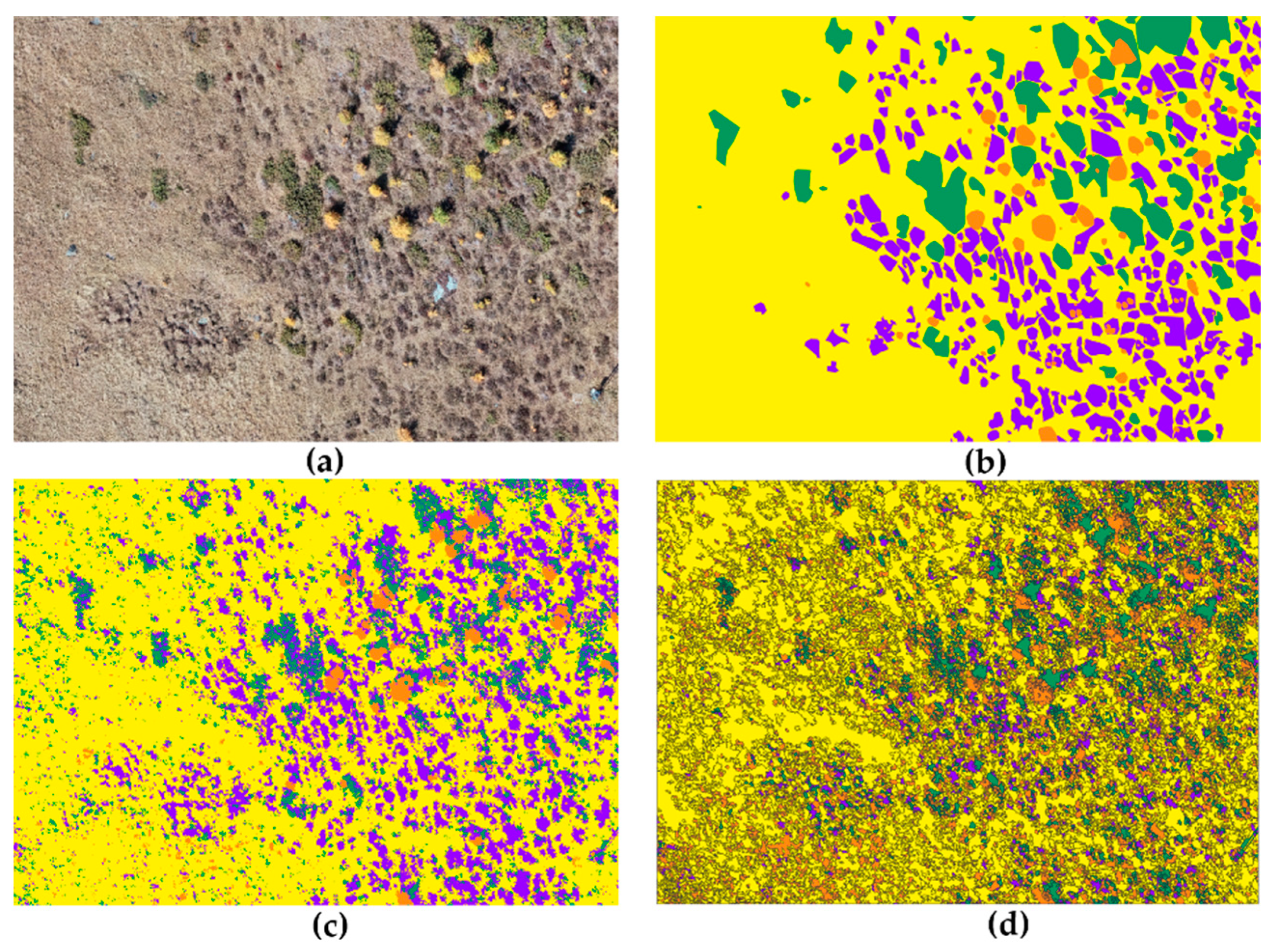
3.1. Photo-Interpretation
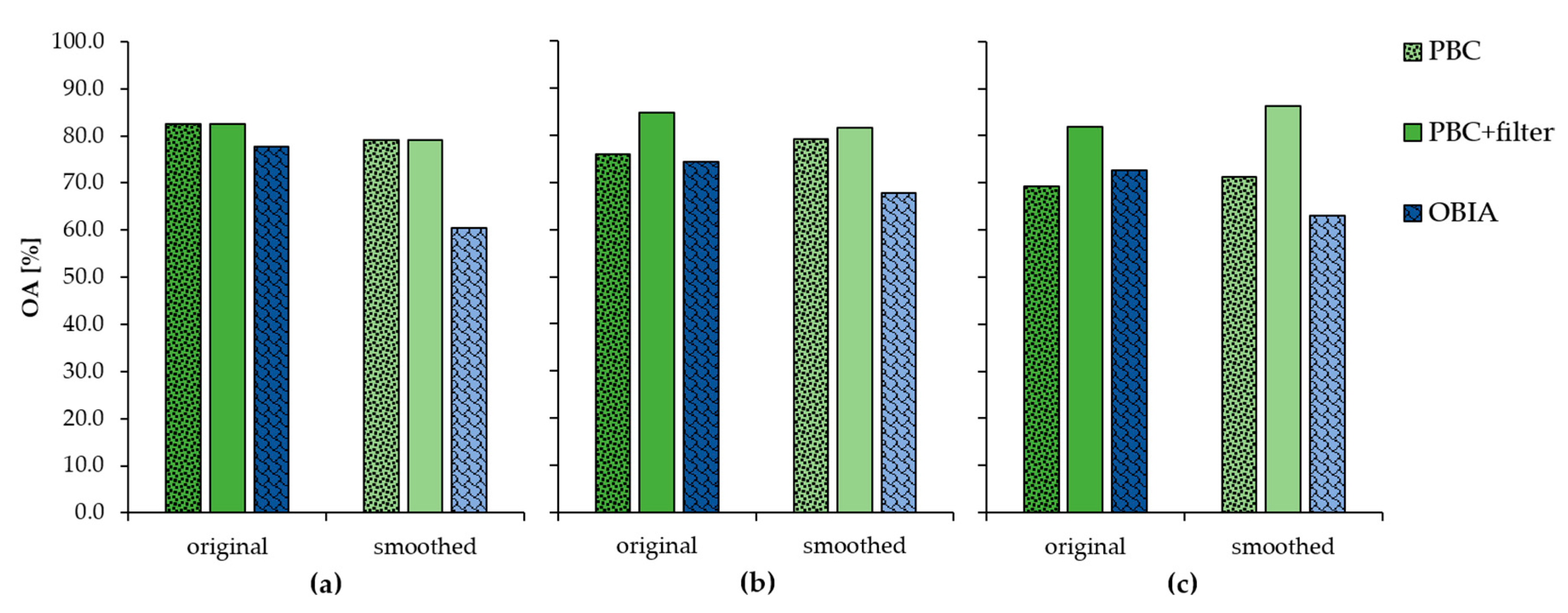
3.2. Semi-Automatic Classification Methods
3.3. Land Cover Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.; et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickebusch, S. Modelling Tree Population Dynamics at the Alpine and Boreal Thee-Line Ecotones in Response to Climate and Land-Use Change. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lausanne (UNIL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Didier, L. Invasion patterns of European larch and Swiss stone pine in subalpine pastures in the French Alps. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 145, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullinger, S.; Dirnböck, T.; Grabherr, G. Patterns of Shrub Invasion into High Mountain Grasslands of the Northern Calcareous Alps, Austria. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2003, 35, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quétier, F. Vulnérabilité des Écosystèmes Semi-Naturels Européens aux Changements D’utilisation des Terres: Application aux Prairies Subalpines de Villar D’arène, France. Ph.D. Thesis, École Nationale Supérieure Agronomique (ENSA), Montpellier, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kräuchi, N.; Brang, P.; Schönenberger, W. Forests of mountainous regions: Gaps in knowledge and research needs. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 132, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthelme, F.; Villaret, J.-C.; Brun, J.-J. Shrub encroachment in the Alps gives rise to the convergence of sub-alpine communities on a regional scale. J. Veg. Sci. 2007, 18, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, M.; Davies, A.B.; Parr, C.L.; Eggleton, P.; Robertson, M.P. Woody encroachment slows decomposition and termite activity in an African savanna. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, N.N.; Archer, S.R.; Campbell, J.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Morton, J.A.; Knapp, A.K. Woody plant proliferation in North American drylands: A synthesis of impacts on ecosystem carbon balance. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappeiner, U.; Cernusca, A. Alpine meadows and pastures after abandonment. Results of the Austrian MAB programme and the EC-STEP project INTEGRALP. Pirineos 1993, 141–142, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görzen, E.; Borisova, K.; Fenesi, A.; Ruprecht, E.; Donath, T.W. Effects of woody species encroachment and fire on vegetation and the soil seed bank in dry grasslands of Transylvania. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2019, 22, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.; Liu, T.; Hu, H.; et al. Soil organic carbon components in inner Mongolian shrub-encroached grasslands. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieninger, T.; Hui, C.; Gaertner, M.; Huntsinger, L. The impact of land abandonment on species richness and abundance in the Mediterranean Basin: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terziyska, T.S.; Tsakalos, J.; Bartha, S.; Apostolova, I.; Sopotlieva, D.; Zimmermann, M.Z.; Szabo, G.; Wellstein, C. Species and functional differences between subalpine grasslands with and without dwarf shrub encroachment. Plant Biosyst. 2020, 154, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.H.B.; Arieira, J.; Parolin, P.; da Cunha, C.N.; Junk, W.J. Shrub encroachment influences herbaceous communities in flooded grasslands of a neotropical savanna wetland. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2016, 19, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliveres, S.; Maestre, F.T.; Eldridge, D.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Quero, J.L.; Bowker, M.A.; Gallardo, A. Plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality peak at intermediate levels of woody cover in global drylands. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleery, R.; Monadjem, A.; Baiser, B.; Fletcher, R.; Vickers, K.; Kruger, L. Animal diversity declines with broad-scale homogenization of canopy cover in African savannas. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 226, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, R.A.; Boone, W.W.; Soto-Shoender, J.; Fletcher, R.J.; Blaum, N.; McCleery, R.A. Shrub encroachment and vertebrate diversity: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmel, J.; Mantilla-Contreras, J.; Gauger, D.; Blindow, I. Carabid beetles as indicators for shrub encroachment in dry grasslands. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellis, G.; Chiti, T.; Rey, A.; Yuste, J.C.; Trotta, C.; Papale, D. The ecosystem carbon sink implications of mountain forest expansion into abandoned grazing land: The role of subsoil and climatic factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, L.M.; Esch, E.H.; Kopp, C.W.; Cleland, E.E. Warming and shrub encroachment decrease decomposition in arid alpine and subalpine ecosystems. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2018, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, O.; Saravesi, K.; Ninot, J.M.; Geml, J.; Markkola, A.; Ahonen, S.H.K.; Peñuelas, J. Encroachment of shrubs into subalpine grasslands in the Pyrenees modifies the structure of soil fungal communities and soil properties. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wilson, S.D. Facilitation among woody plants establishing in an old field. Ecology 1998, 79, 2694–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunstler, G.; Curt, T.; Bouchaud, M.; Lepart, J. Indirect facilitation and competition in tree species colonization of sub-Mediterranean grasslands. J. Veg. Sci. 2006, 17, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coop, J.D.; Givnish, T.J. Spatial and temporal patterns of recent forest encroachment in montane grasslands of the Valles Caldera, New Mexico, USA. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.H.; Thuiller, W.; Lavorel, S.; Davies, I.D.; Garbolino, E. Land-use change and subalpine tree dynamics: Colonization of Larix decidua in French subalpine grasslands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wich, S. Drones and conservation. In Drones and Aerial Observation: New Technologies for Property Rights, Human Rights, and Global Development. A Primer; New America Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzichetto, M.; Malavasi, M.; Barták, V.; Acosta, A.T.R.; Moudrý, V.; Carranza, M.L. Modeling plant invasion on Mediterranean coastal landscapes: An integrative approach using remotely sensed data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 171, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chignell, S.M.; Luizza, M.W.; Skach, S.; Young, N.E.; Evangelista, P.H. An integrative modeling approach to mapping wetlands and riparian areas in a heterogeneous Rocky Mountain watershed. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 4, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, E.; Reese, H.; Ecke, F. Combining spectral data and a DSM from UAS-images for improved classification of non-submerged aquatic vegetation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinel, S.; Hubert-Moya, L.; Clémentb’, B. Combined use of lidar data and multispectral earth observation imagery for wetland habitat mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 37, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prošek, J.; Šímová, P. UAV for mapping shrubland vegetation: Does fusion of spectral and vertical information derived from a single sensor increase the classification accuracy? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetz, W.; McGeoch, M.A.; Guralnick, R.; Ferrier, S.; Beck, J.; Costello, M.J.; Fernandez, M.; Geller, G.N.; Keil, P.; Merow, C.; et al. Essential biodiversity variables for mapping and monitoring species populations. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissling, W.D.; Walls, R.; Bowser, A.; Jones, M.O.; Kattge, J.; Agosti, D.; Amengual, J.; Basset, A.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; et al. Towards global data products of Essential Biodiversity Variables on species traits. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettorelli, N.; Wegmann, M.; Skidmore, A.; Mücher, S.; Dawson, T.P.; Fernandez, M.; Lucas, R.; Schaepman, M.E.; Wang, T.; O’Connor, B.; et al. Framing the concept of satellite remote sensing essential biodiversity variables: Challenges and future directions. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 2, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.M.; Ferrier, S.; Walters, M.; Geller, G.N.; Jongman, R.H.G.; Scholes, R.J.; Bruford, M.W.; Brummitt, N.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Essential biodiversity variables. Science 2013, 339, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broich, M.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.; Adusei, B.; Lindquist, E.; Stehman, S.V. Time-series analysis of multi-resolution optical imagery for quantifying forest cover loss in Sumatra and Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, L.P.; Wich, S.A. Dawn of drone ecology: Low-cost autonomous aerial vehicles for conservation. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2012, 5, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, L.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Saran, S.; Tolpekin, V.A.; Raju, P.L.N. Markov random field-based method for super-resolution mapping of forest encroachment from remotely sensed ASTER image. Geocarto Int. 2016, 31, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suess, S.; van der Linden, S.; Okujeni, A.; Griffiths, P.; Leitão, P.J.; Schwieder, M.; Hostert, P. Characterizing 32 years of shrub cover dynamics in southern Portugal using annual Landsat composites and machine learning regression modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Bryson, M.; Sukkarieh, S. Multi-class predictive template for tree crown detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 68, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haest, B.; Borre, J.V.; Spanhove, T.; Thoonen, G.; Delalieux, S.; Kooistra, L.; Mücher, C.A.; Paelinckx, D.; Scheunders, P.; Kempeneers, P. Habitat mapping and quality assessment of NATURA 2000 heathland using airborne imaging spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, M.; Mariscal, A.; Padbury, M.; Cane, T.; Kniveton, D.; Chinchero, M.A. Identifying tropical Ecuadorian Andean trees from inter-crown pixel distributions in hyperspatial aerial imagery. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2012, 15, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneque-Gálvez, J.; McCall, M.K.; Napoletano, B.M.; Wich, S.A.; Koh, L.P. Small drones for community-based forest monitoring: An assessment of their feasibility and potential in tropical areas. Forests 2014, 5, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; He, Y. Species classification using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-acquired high spatial resolution imagery in a heterogeneous grassland. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Taboada, F.; Paredes, C.; Julián-Pelaz, J. Mapping of the invasive species Hakea sericea using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and worldview-2 imagery and an object-oriented approach. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, S.; Moat, J.; Whaley, O.; Boyd, D.S. Identifying species from the air: UAVs and the very high resolution challenge for plant conservation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räpple, B.; Piégay, H.; Stella, J.C.; Mercier, D. What drives riparian vegetation encroachment in braided river channels at patch to reach scales? Insights from annual airborne surveys (Drôme River, SE France, 2005–2011). Ecohydrology 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, D.; Dillon, C.; Shemrock, A.; Weissflog, N.; Sager, E.P.S. An object-based image analysis workflow for monitoring shallow-water aquatic vegetation in multispectral drone imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, P.; Müllerová, J.; Bartaloš, T.; Brůna, J. Unmanned aerial vehicles for alien plant species detection and monitoring. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllerová, J.; Brůna, J.; Bartaloš, T.; Dvořák, P.; Vítková, M.; Pyšek, P. Timing is important: Unmanned aircraft vs. Satellite imagery in plant invasion monitoring. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoux, J.; Bogaert, P. Good practices for object-based accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.J.; Tarasoff, C.; Whitworth, G.E.; Baron, J.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Church, J.S. Utility of unmanned aerial vehicles for mapping invasive plant species: A case study on yellow flag iris (Iris pseudacorus L.). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2083–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, P.J.; Schwieder, M.; Suess, S.; Okujeni, A.; Galvão, L.S.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Monitoring natural ecosystem and ecological gradients: Perspectives with EnMAP. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13098–13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraitis, P. Multiple Stable States in Natural Ecosystems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780191810084. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Klouček, T.; Prošek, J. The potential of Unmanned Aerial Systems: A tool towards precision classification of hard-to-distinguish vegetation types? Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 71, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Hay, G.J.; Kelly, M.; Lang, S.; Hofmann, P.; Addink, E.; Queiroz Feitosa, R.; van der Meer, F.; van der Werff, H.; van Coillie, F.; et al. Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis—Towards a new paradigm. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X. A new segmentation method for very high resolution imagery using spectral and morphological information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Gong, P.; Clinton, N.; Biging, G.; Kelly, M.; Schirokauer, D. Object-based detailed vegetation classification with airborne high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagno, M.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Cremonese, E.; Rossini, M.; Colombo, R.; Filippa, G.; Julitta, T.; Manca, G.; Siniscalco, C.; Di Cella, U.M.; et al. Phenology and carbon dioxide source/sink strength of a subalpine grassland in response to an exceptionally short snow season. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvánek, D.; Janák, M. Managment of Natura 2000 Habitats. 6230* Species-Rich Nardus Grasslands; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2019. Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgu, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, D.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Sarma, K.K.; Kalita, R.; Sudhakar, S. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Classifications: A Perspective Survey. Trans. GIS 2016, 20, 463–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Gill, L.; Ghosh, B. Drone image segmentation using machine and deep learning for mapping raised bog vegetation communities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Lucieer, A.; Podobnikar, T.; Carni, A. Mapping invasive Fallopia japonica by combined spectral, spatial, and temporal analysis of digital orthophotos. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 19, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Joshi, P.K. A comparison of selected classification algorithms for mapping bamboo patches in lower Gangetic plains using very high resolution WorldView 2 imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Joshi, P.K.; Kochb, B. A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: Role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Ørka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Gianelle, D.; Næsset, E. Tree species classification in boreal forests with hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2632–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.W.; Paelinckx, D. Evaluation of Random Forest and Adaboost tree-based ensemble classification and spectral band selection for ecotope mapping using airborne hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznanovic, A.J.; Falkowski, M.J.; Maclean, A.L.; Smith, A.M.S.; Evans, J.S. An accuracy assessment of tree detection algorithms in juniper woodlands. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, N.; Wainwright, H.; Dafflon, B.; Léger, E.; Peterson, J.; Steltzer, H.; Wilmer, C.; Rowland, J.C.; Williams, K.H.; Hubbard, S.S. Investigating microtopographic and soil controls on a mountainous meadow plant community using high-resolution remote sensing and surface geophysical data. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 1618–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosan, T.M.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Oliveras, I.; Phillips, O.L.; Malhi, Y.; Gloor, E.; Wagner, F.H. Extensive 21st-century woody encroachment in South America’s savanna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, N.; Ochoa, C.G.; Mata-Gonzalez, R. The use of low-altitude UAV imagery to assess western juniper density and canopy cover in treated and untreated stands. Forests 2019, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwaimana, M.; Satyanarayana, B.; Otero, V.; Muslim, A.M.; Muhammad Syafiq, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Raymaekers, D.; Koedam, N.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F. The advantages of using drones over space-borne imagery in the mapping of mangrove forests. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Estimating the age and population structure of encroaching shrubs in arid/semiarid grasslands using high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; Cheng, L.; Du, P.; Liu, Y. A review of supervised object-based land-cover image classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Rango, A.; Havstad, K.M.; Paris, J.F.; Beck, R.F.; McNeely, R.; Gonzalez, A.L. Object-oriented image analysis for mapping shrub encroachment from 1937 to 2003 in southern New Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippelli, S.K.; Vogeler, J.C.; Falkowski, M.J.; Meneguzzo, D.M. Monitoring conifer cover: Leaf-off lidar and image-based tracking of eastern redcedar encroachment in central Nebraska. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Archer, S.R.; McClaran, M.P.; Marsh, S.E. Shrub encroachment into grasslands: End of an era? PeerJ 2018, 2018, e5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopeć, D.; Sławik, Ł. How to effectively use long-term remotely sensed data to analyze the process of tree and shrub encroachment into open protected wetlands. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 125, 102345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatesta, L.; Tardella, F.M.; Tavoloni, M.; Postiglione, N.; Piermarteri, K.; Catorci, A. Land use change in the high mountain belts of the central Apennines led to marked changes of the grassland mosaic. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2018, 22, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Mechanisms, monitoring and modeling of shrub encroachment into grassland: A review. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, S.M.; Webb, R.H.; Belnap, J.; Andrew Hubbard, J.; Swann, D.E.; Rutman, S. Forecasting climate change impacts to plant community composition in the Sonoran Desert region. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, M.; Chetty, K.; Bulcock, H. A review of hyperspectral remote sensing and its application in vegetation and water resource studies. Water SA 2007, 33, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




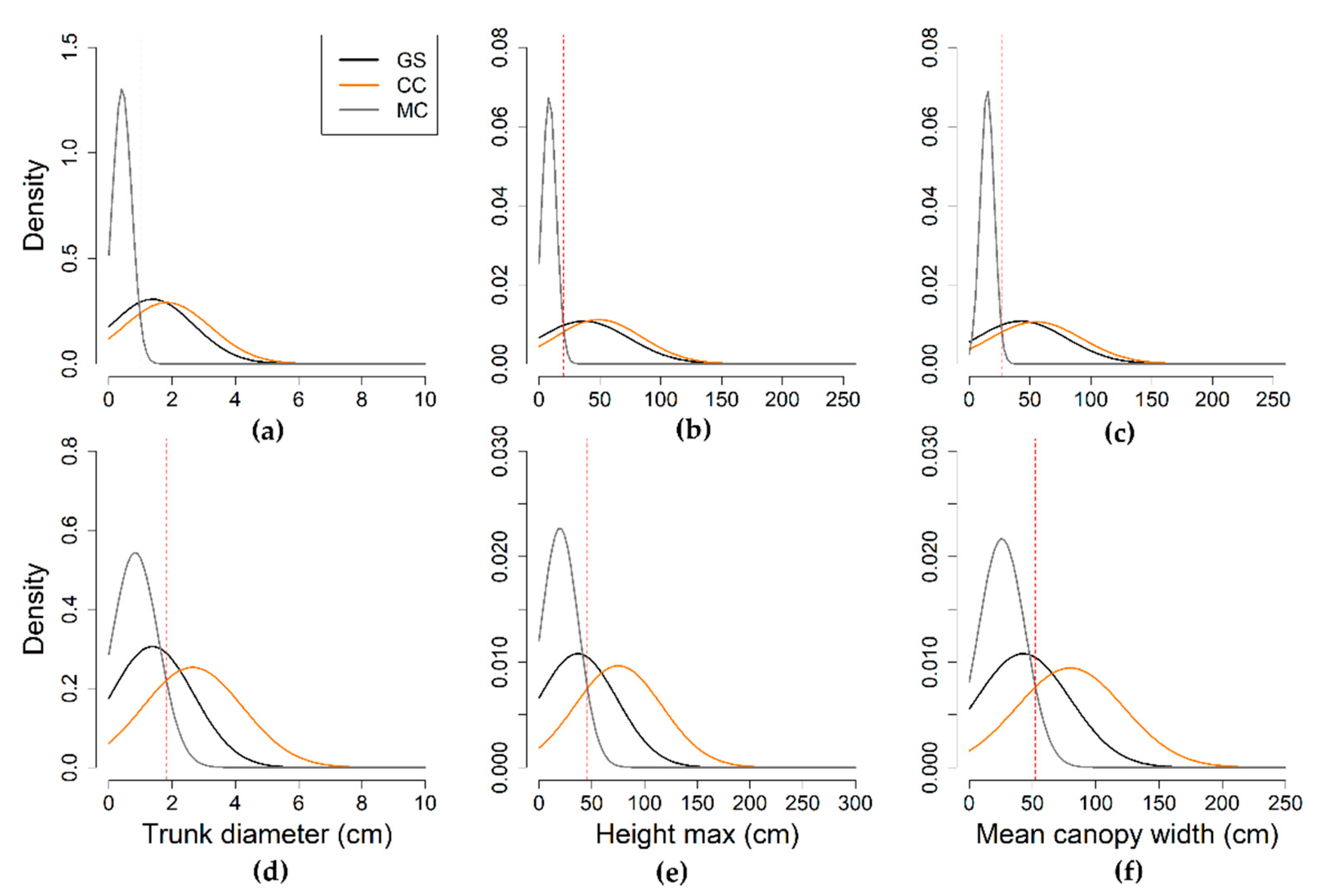
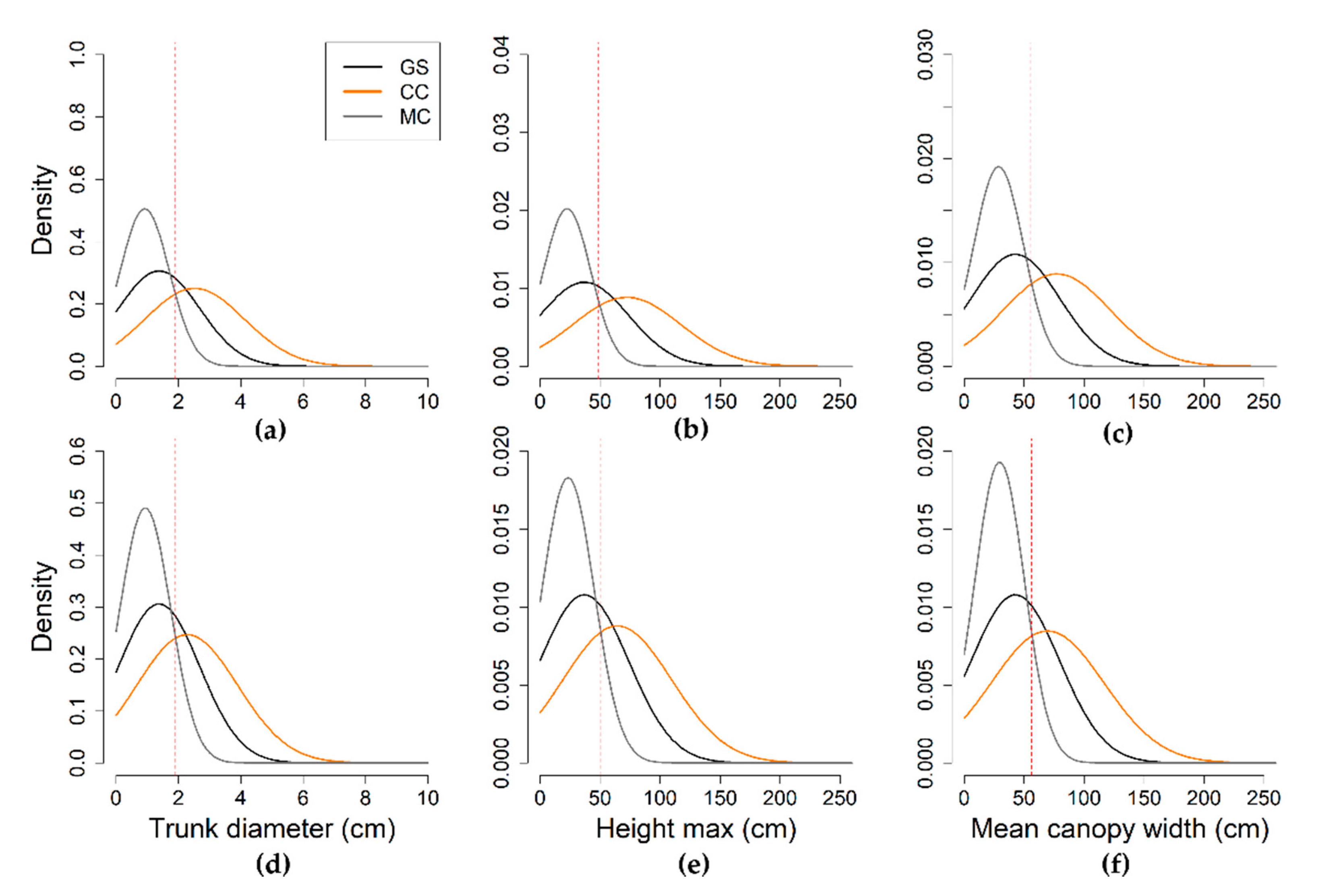
| Parameter | Statistics | GS | LR | HR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | MC | CC | MC | |||
| (n = 531) | (n = 135) | (n = 335) | (n = 320) | (n = 134) | ||
| Trunk diameter (cm) | min | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| median | 1.1 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | |
| mean | 1.4 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0.4 | |
| max | 9.1 | 9.1 | 5.8 | 9.1 | 2.3 | |
| Height max (cm) | min | 1.0 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 1.0 |
| median | 26.0 | 60.0 | 14.0 | 39.5 | 7.0 | |
| mean | 36.8 | 75.1 | 19.8 | 48.8 | 8.3 | |
| max | 260.0 | 260.0 | 140.0 | 260.0 | 40.0 | |
| Mean crown width (cm) | min | 5.0 | 30.0 | 5.0 | 11.0 | 5.0 |
| median | 34.0 | 65.0 | 21.0 | 45.0 | 14.0 | |
| mean | 42.7 | 79.8 | 25.8 | 54.8 | 14.8 | |
| max | 250.0 | 250.0 | 200.0 | 250.0 | 36.0 | |
| Method | Resolution | OA [%] | PA [%] | UA [%] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| PI | HR | 99.3 | 49.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 100 | 99.3 |
| PI | LR | 88.5 | 14.1 | 45.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 93.5 | 95.6 | 85.5 |
| Method | G | G→S | S→G | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | 84.6% | 6.5% | 2.2% | 6.7% |
| PBC | 63.1% | 12.3% | 13.3% | 11.3% |
| OBIA | 70.8% | 8.2% | 12.5% | 8.4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oddi, L.; Cremonese, E.; Ascari, L.; Filippa, G.; Galvagno, M.; Serafino, D.; Cella, U.M.d. Using UAV Imagery to Detect and Map Woody Species Encroachment in a Subalpine Grassland: Advantages and Limits. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071239
Oddi L, Cremonese E, Ascari L, Filippa G, Galvagno M, Serafino D, Cella UMd. Using UAV Imagery to Detect and Map Woody Species Encroachment in a Subalpine Grassland: Advantages and Limits. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(7):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071239
Chicago/Turabian StyleOddi, Ludovica, Edoardo Cremonese, Lorenzo Ascari, Gianluca Filippa, Marta Galvagno, Davide Serafino, and Umberto Morra di Cella. 2021. "Using UAV Imagery to Detect and Map Woody Species Encroachment in a Subalpine Grassland: Advantages and Limits" Remote Sensing 13, no. 7: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071239
APA StyleOddi, L., Cremonese, E., Ascari, L., Filippa, G., Galvagno, M., Serafino, D., & Cella, U. M. d. (2021). Using UAV Imagery to Detect and Map Woody Species Encroachment in a Subalpine Grassland: Advantages and Limits. Remote Sensing, 13(7), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071239