Integrating Satellite, UAV, and Ground-Based Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Exploration of Pre-Modern Land Use in Northeastern Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
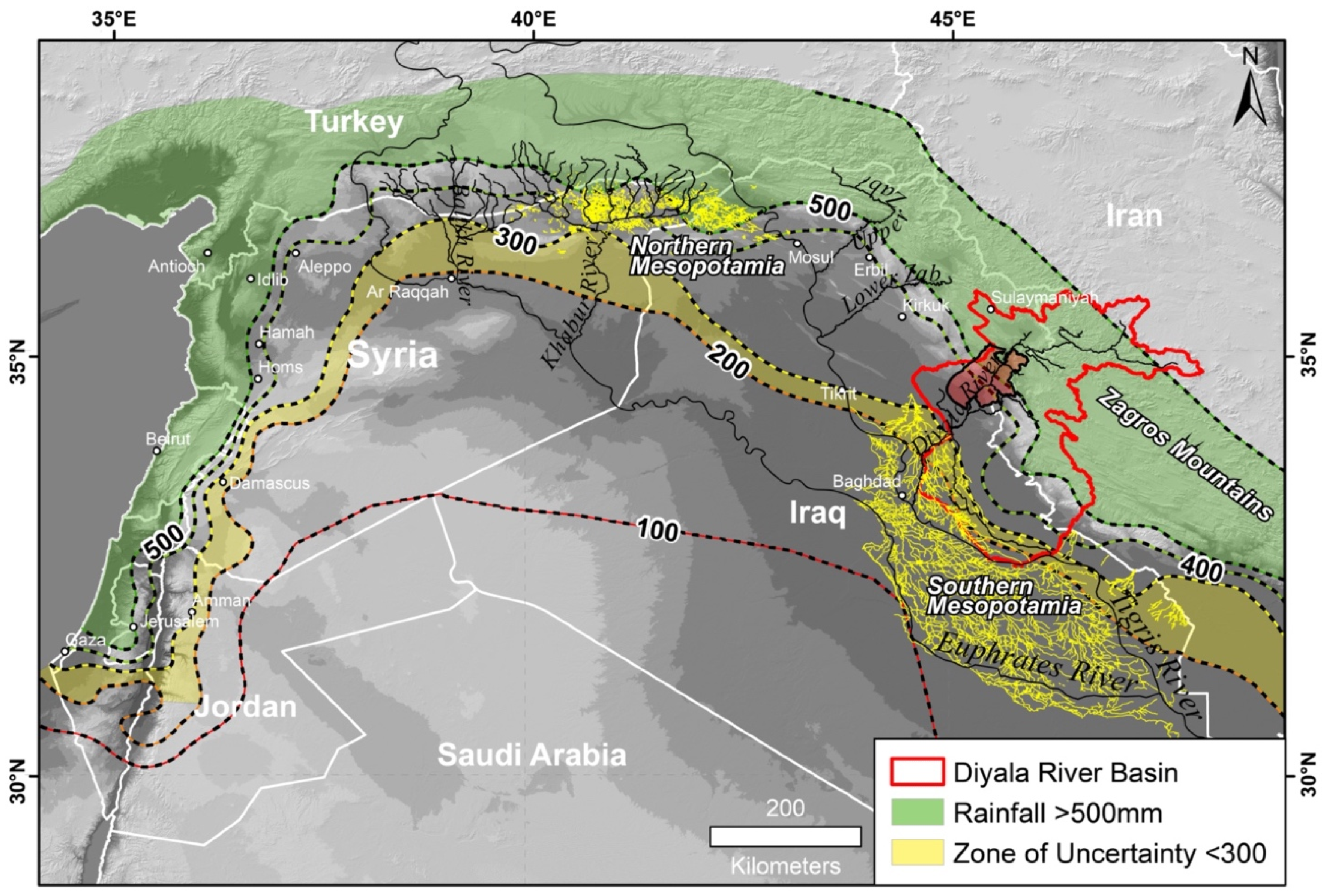
Study Region
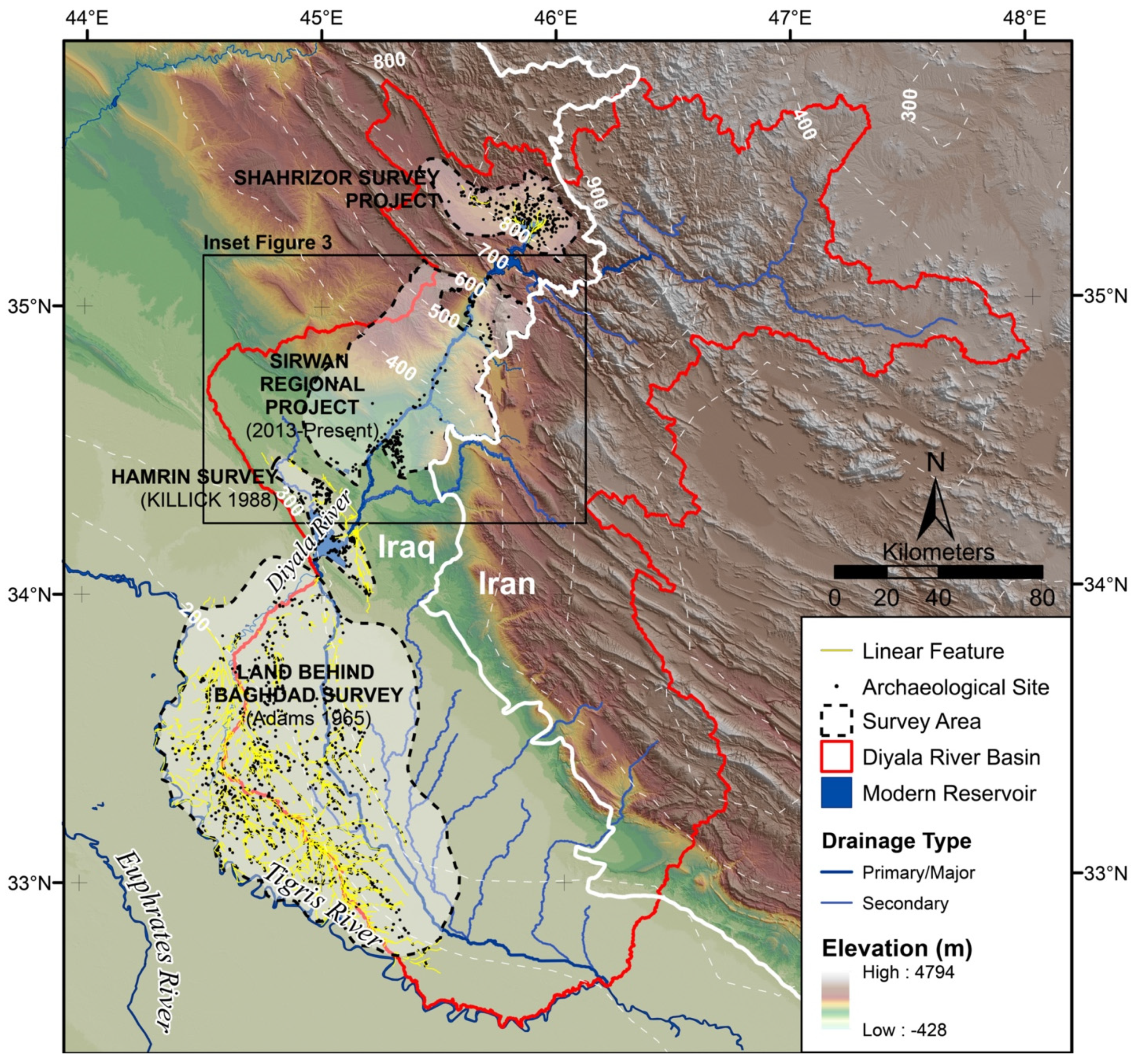
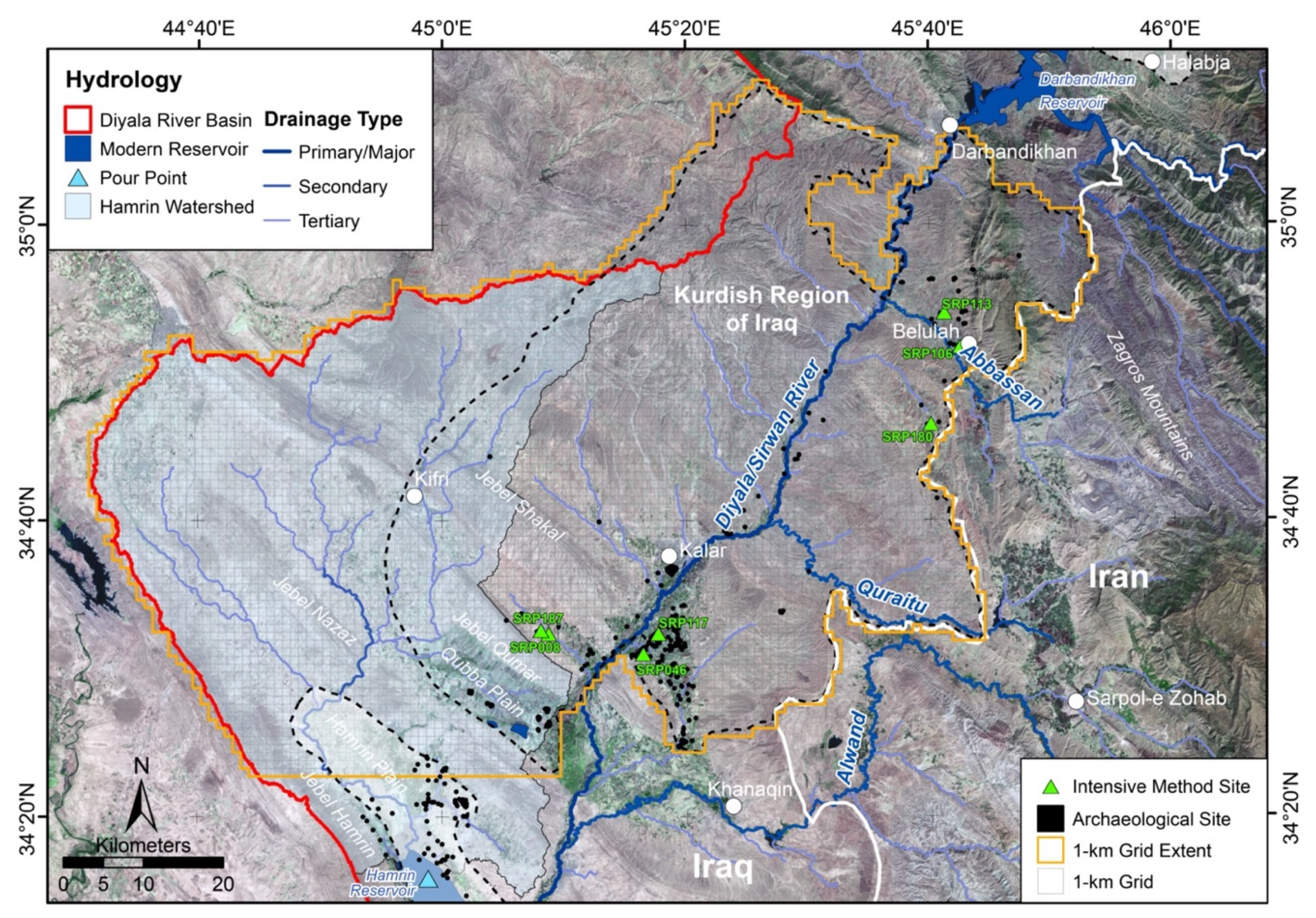
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Regional Survey
2.1.1. Feature Identification
2.1.2. DEM and Hydrology
2.2. Targeted Intensive Survey
2.2.1. Magnetic Gradiometry
2.2.2. Drone-Based Digital Elevation Models (High-Resolution Topographic Relief)
2.2.3. Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery
3. Results
3.1. Regional Survey
3.1.1. Regional Patterns in Land Use
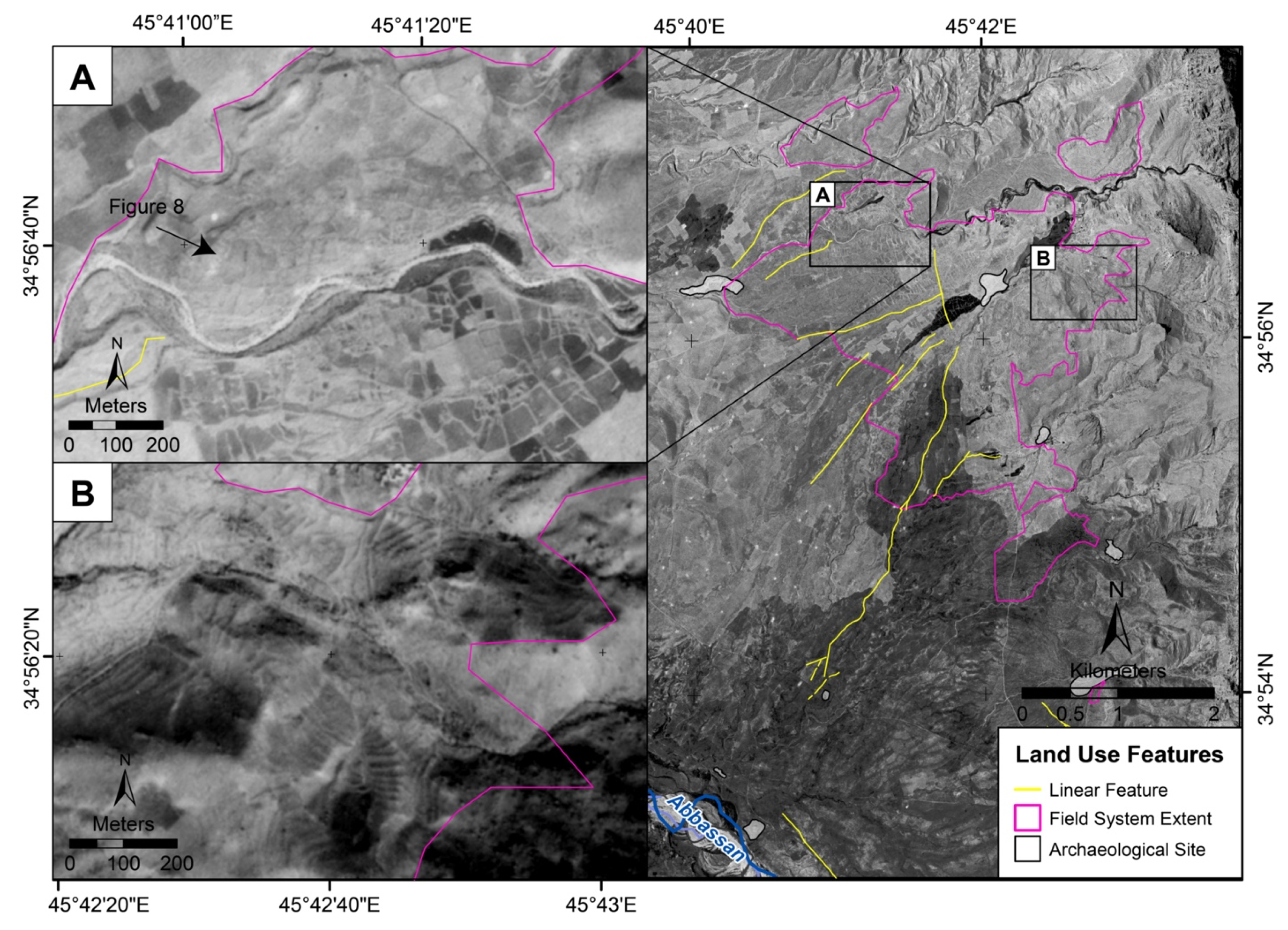
3.1.2. Constructed Field Systems
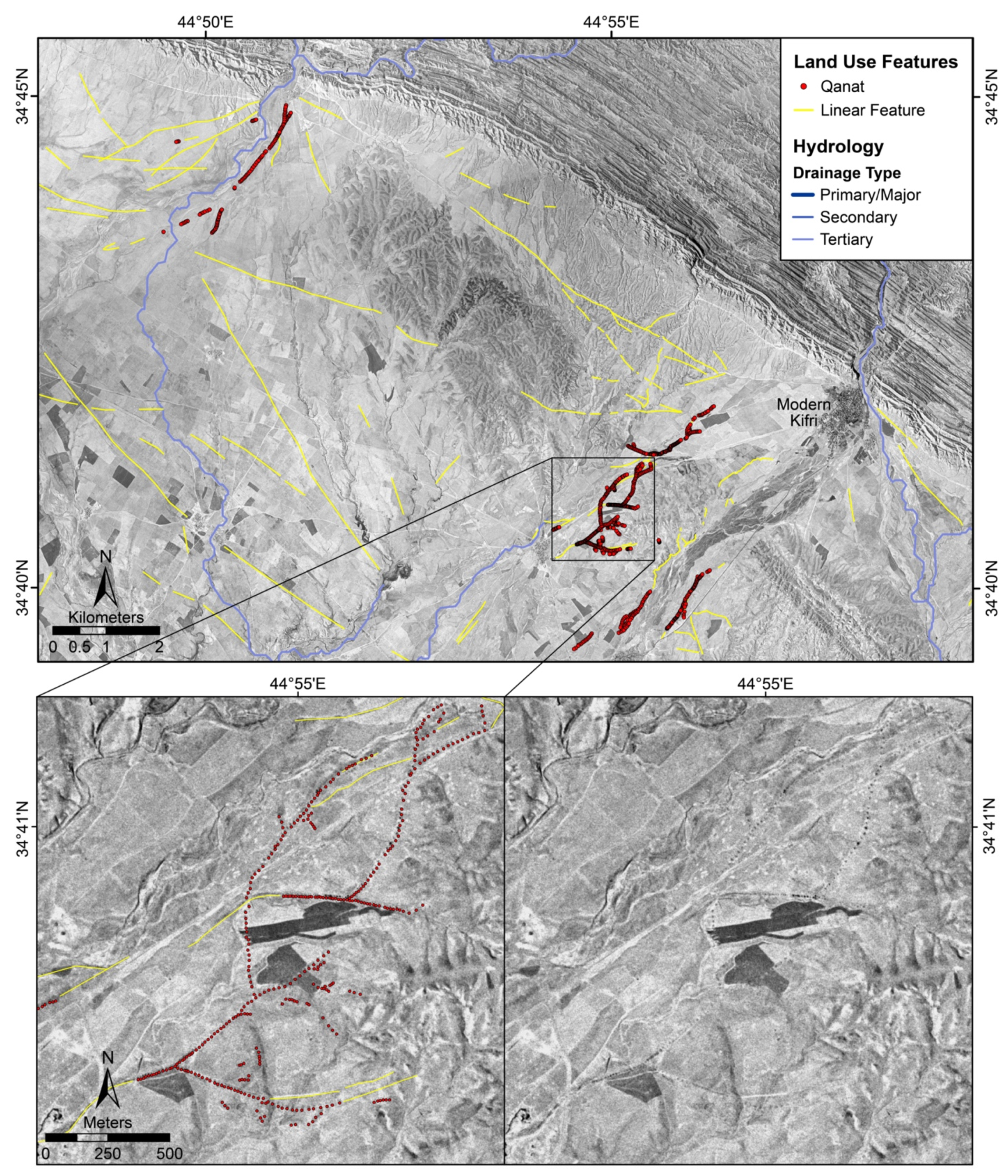
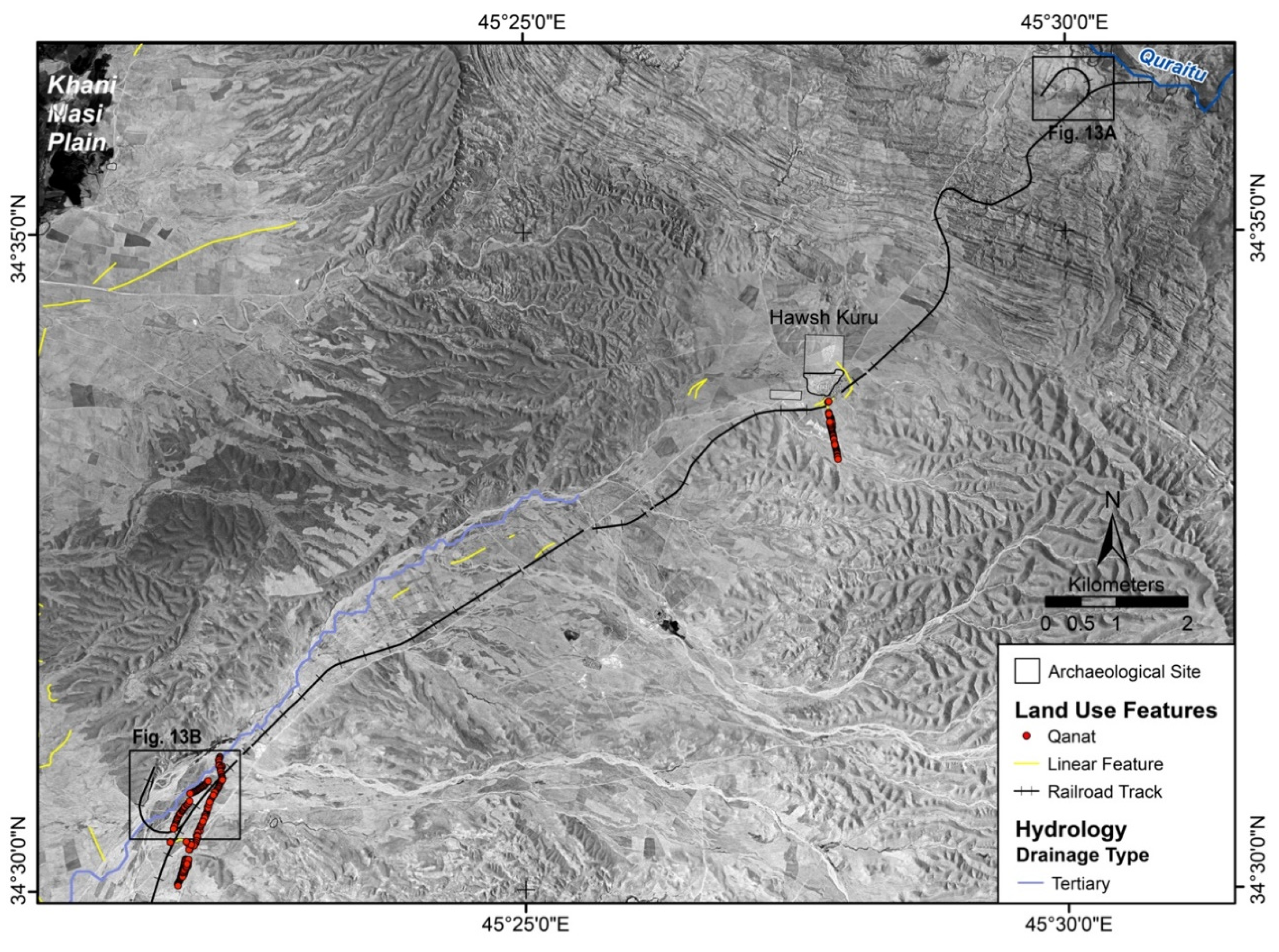
3.1.3. Water Management Features
3.1.4. Trackways and “Landscapes of Movement”
3.1.5. Hydrological Modelling
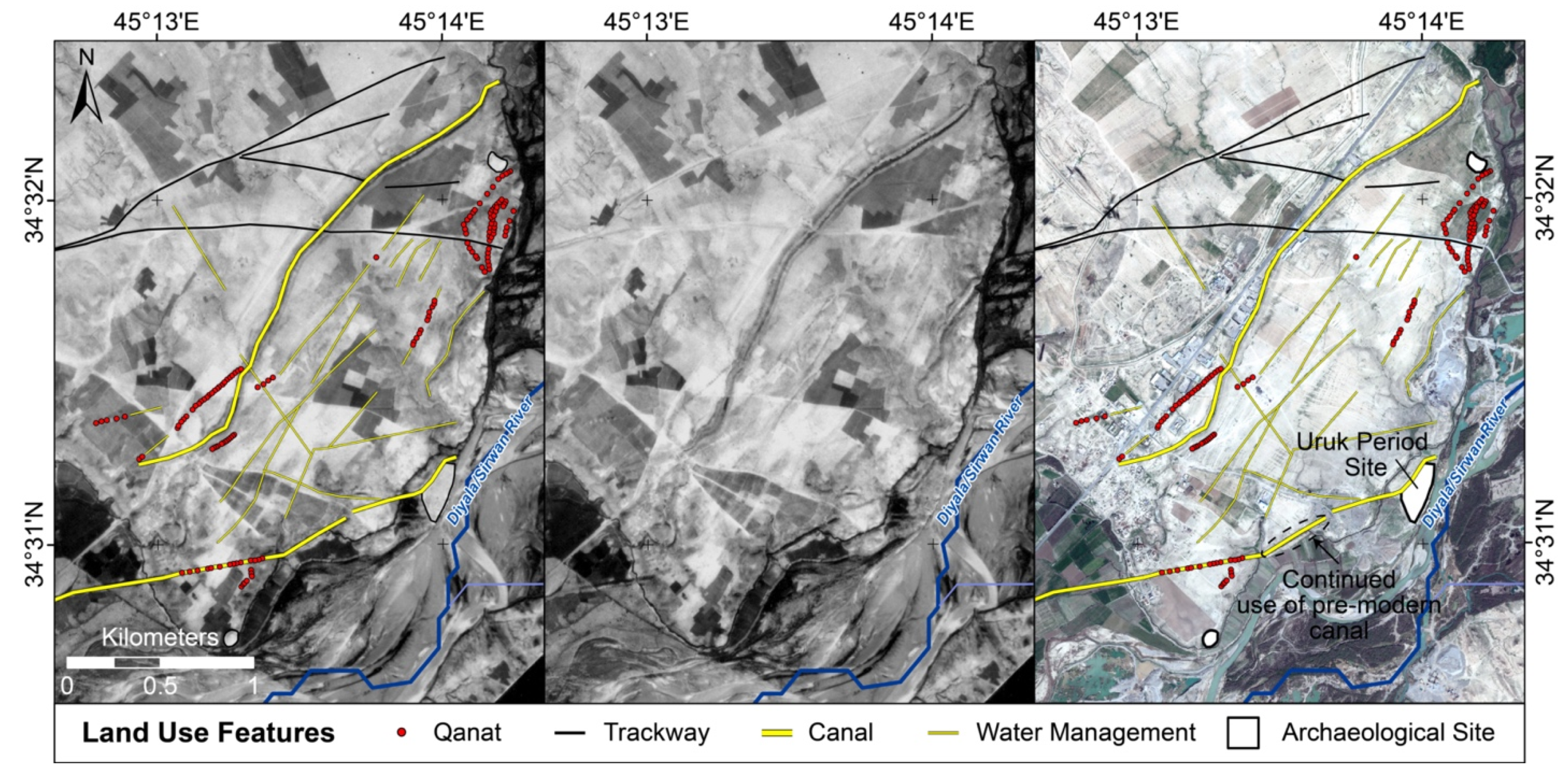
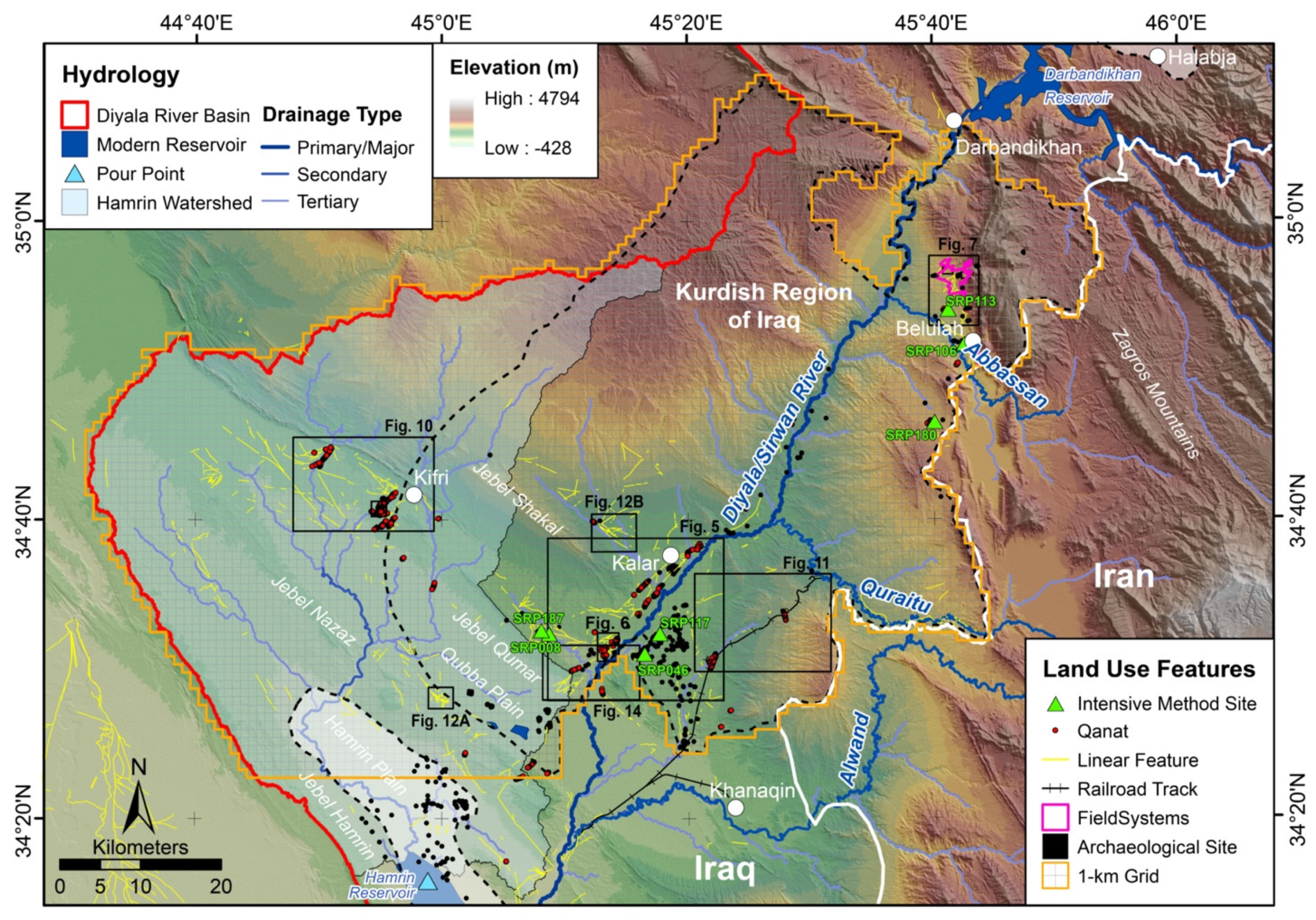
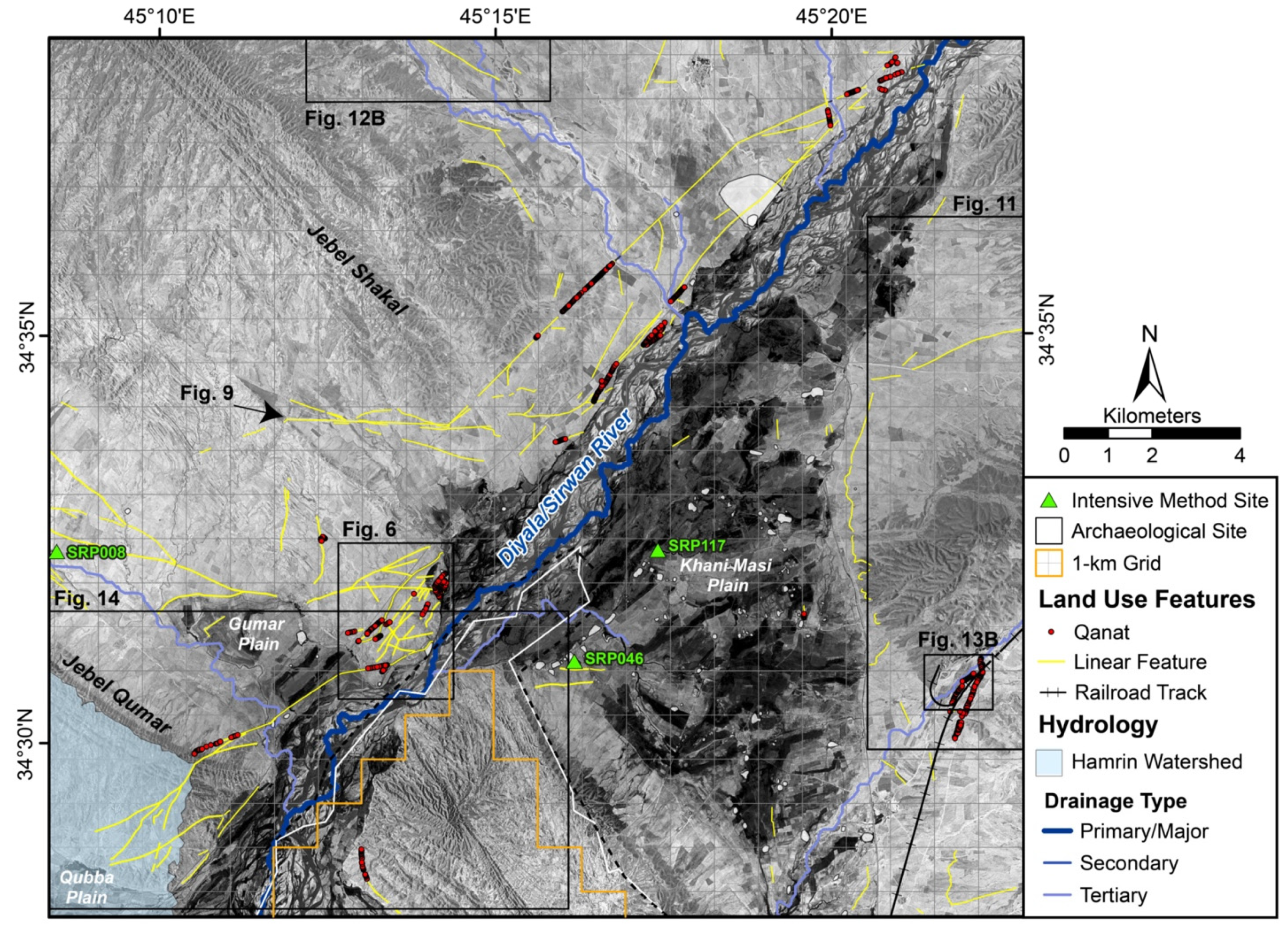



3.2. Targeted Intensive Survey
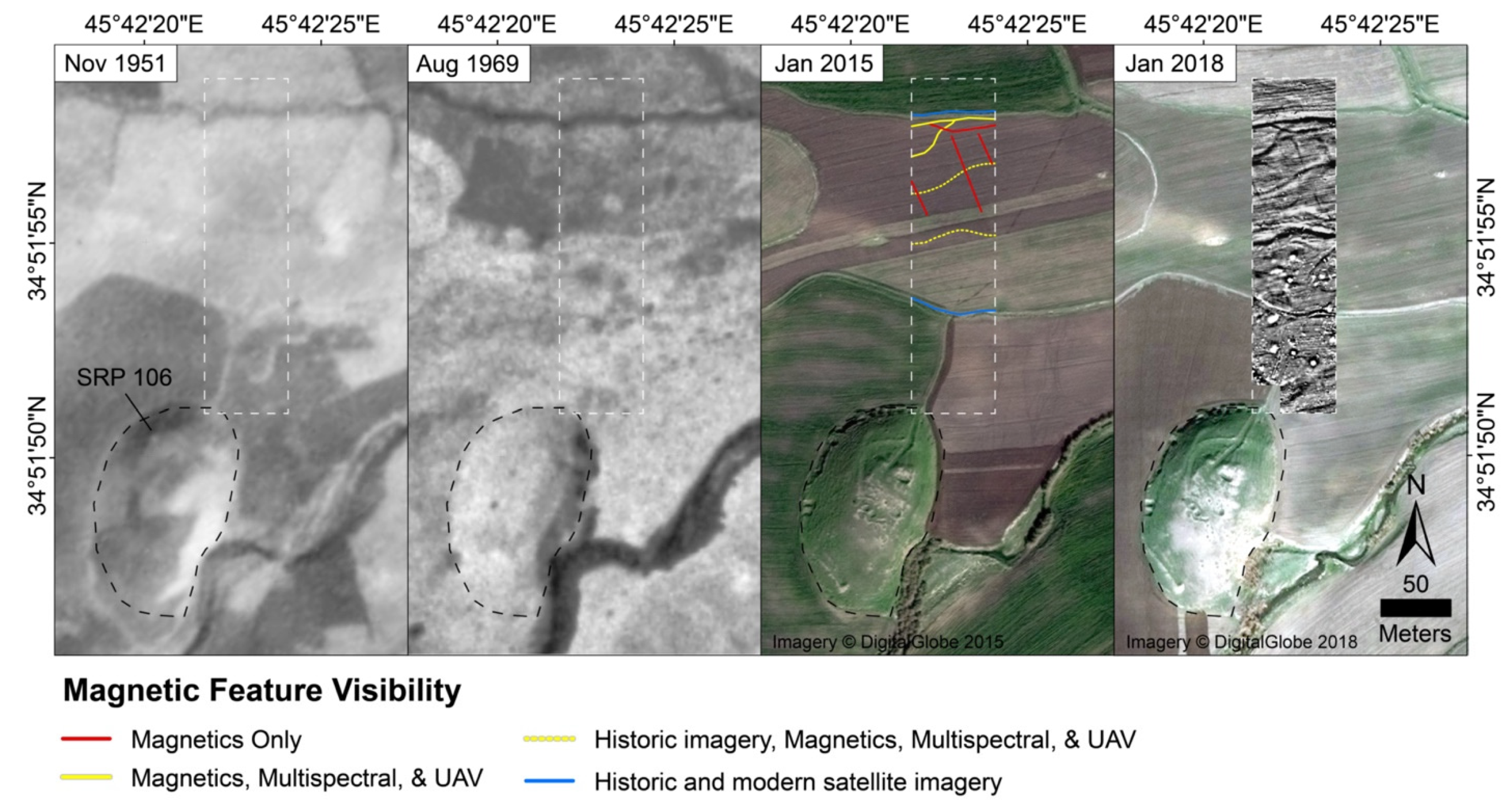
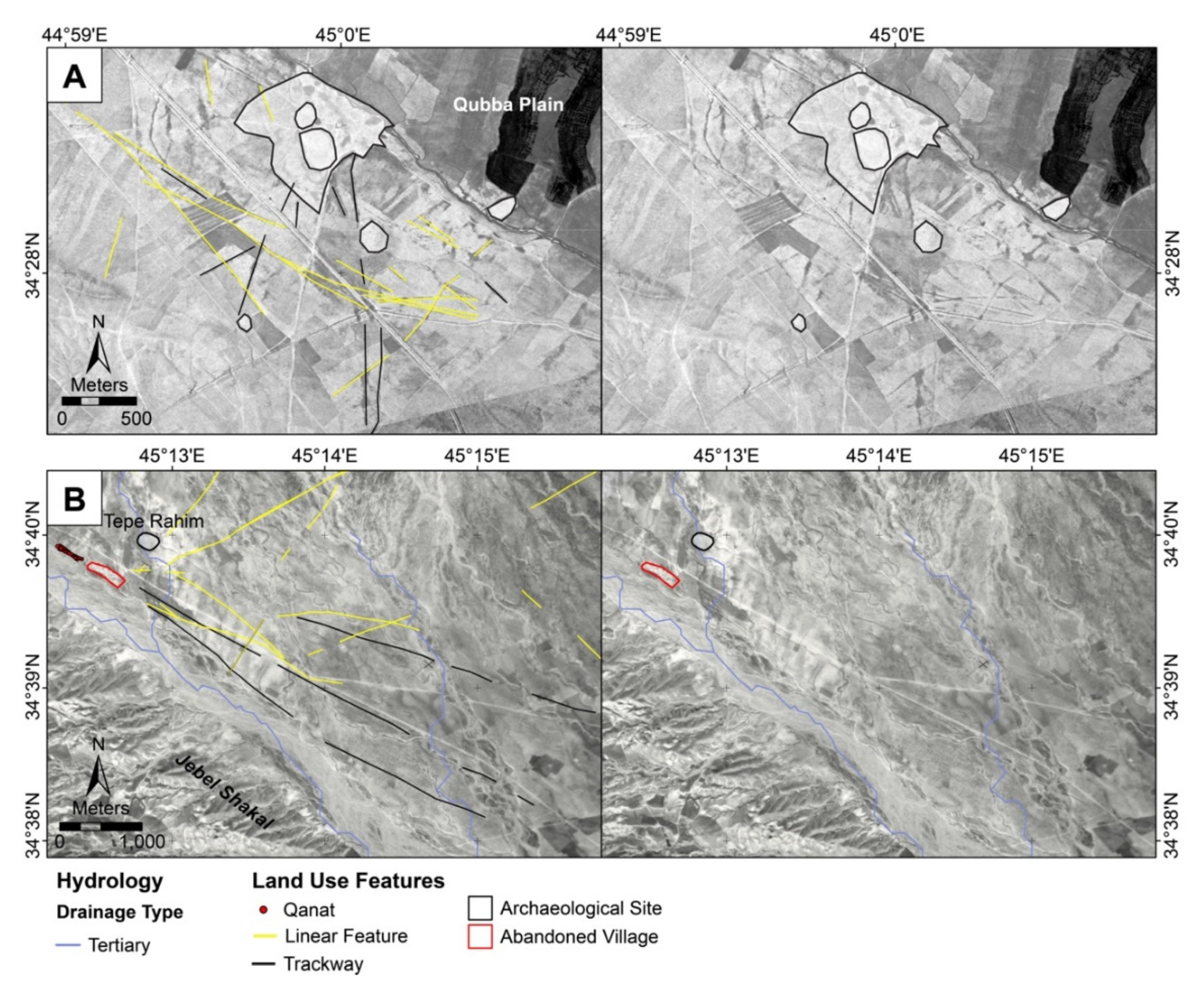
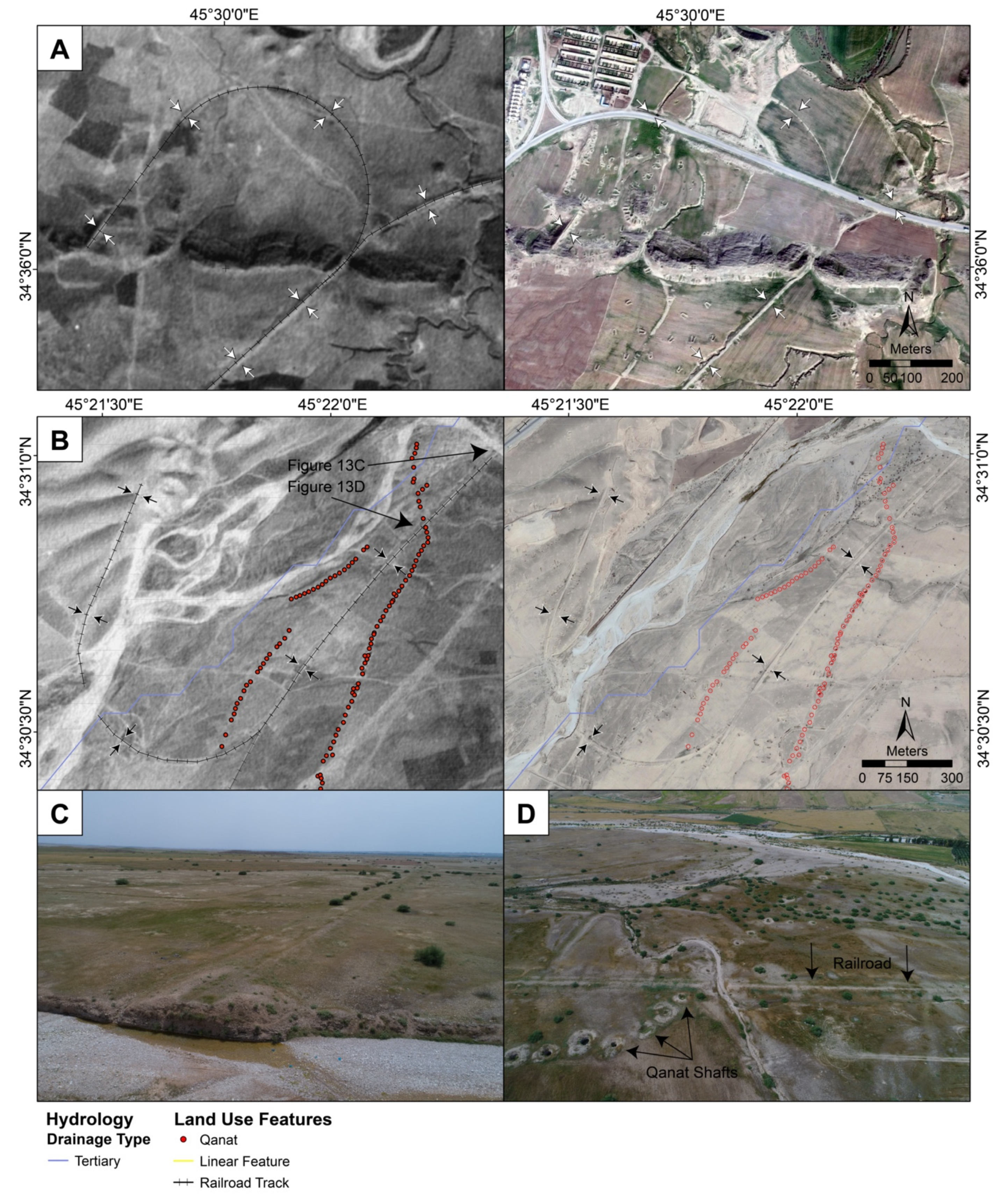
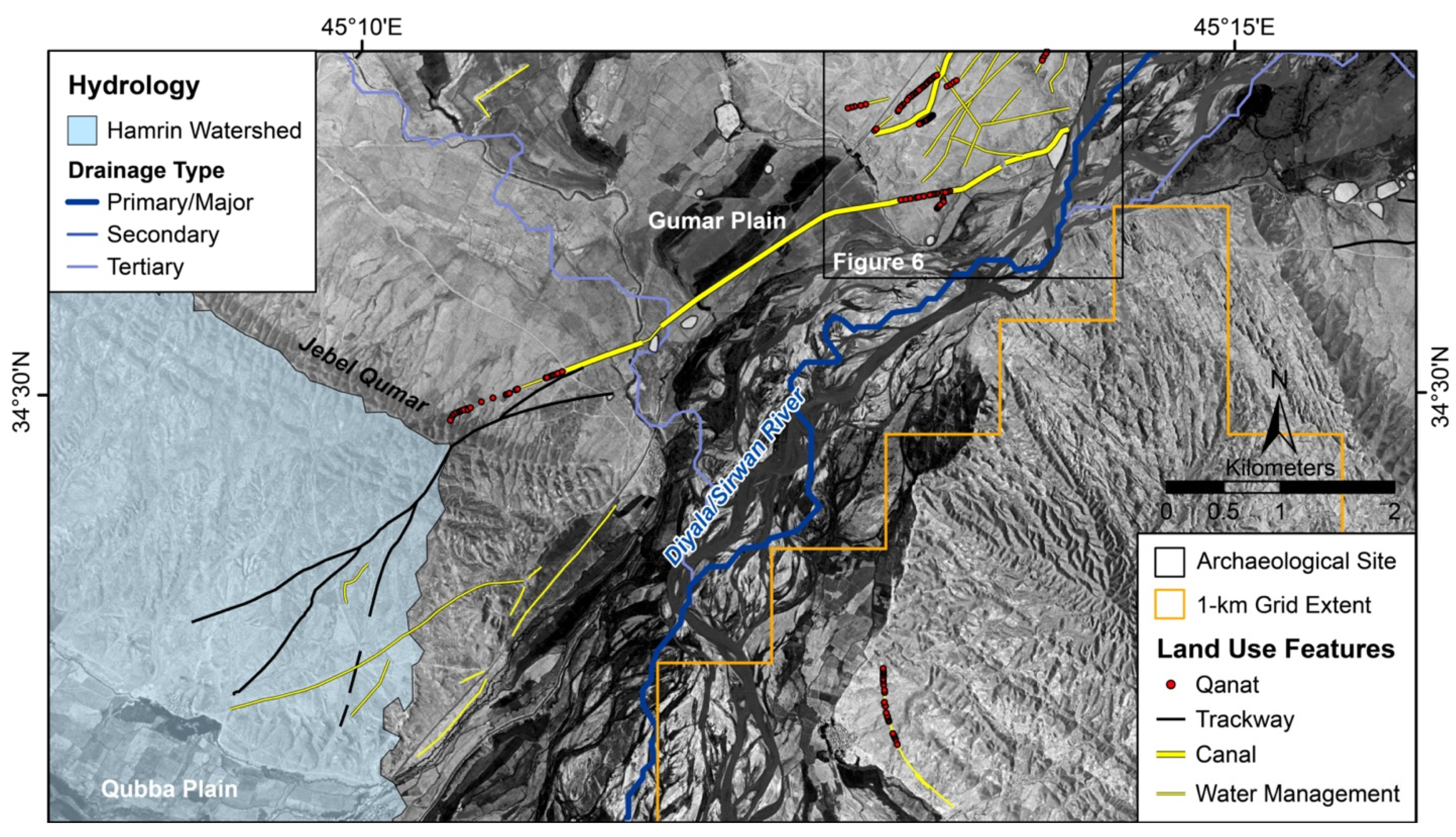
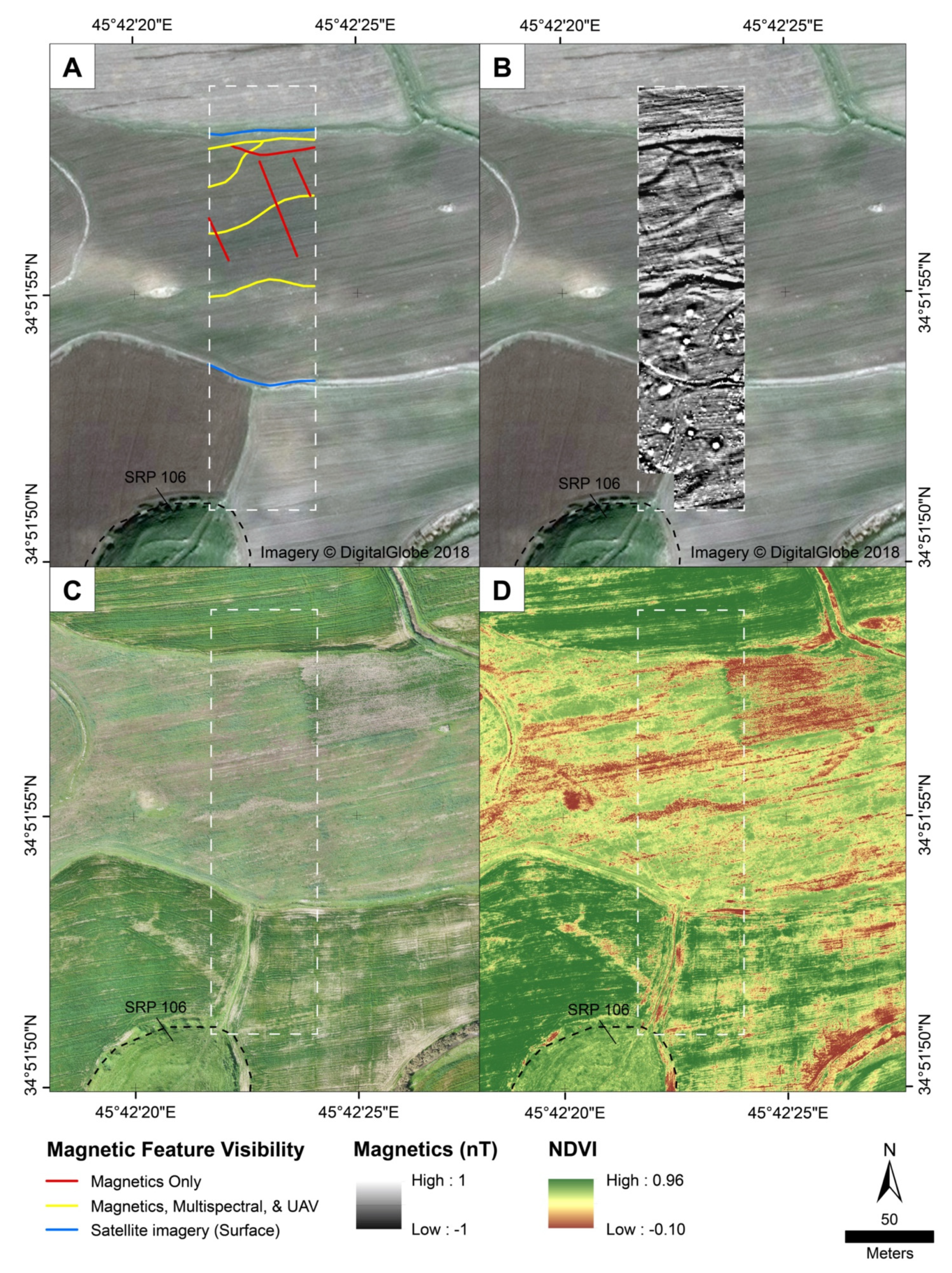

4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Patterns in Regional Land Use
4.2. The Potential of Intensive Remote Sensing Technologies in Mesopotamian Landscapes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, N.; Gleason, K. (Eds.) The Archaeology of Garden and Field; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-585-08218-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Archaeological Landscapes of the Near East; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-8165-2173-9. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J. Rethinking the Landscape: Emerging Approaches to Archaeological Remote Sensing. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2021, 50, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widell, M.; Hritz, C.; Ur, J.A.; Wilkinson, T.J. Land Use of the Model Communities. In Models of Mesopotamian Landscapes: How Small-Scale Processes Contributed to the Growth of Early Civilizations; BAR; Wilkinson, T.J., Gibson, M., Widell, M., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 56–80. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.M. Heartland of Cities: Surveys of Ancient Settlement and Land Use on the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1981; ISBN 0-226-00544-5. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.M. Land Behind Baghdad: A History of Settlement on the Diyala Plains; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Gasche, H.; Tanret, M. (Eds.) Changing Watercourses in Babylonia: Towards a Reconstruction of the Ancient Environment in Lower Mesopotamia; Mesopotamian History and Environment Series; The Oriental Institute, The University of Ghent: Chicago, IL, USA; Ghent, Belgium, 1998; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hritz, C. Tracing Settlement Patterns and Channel Systems in Southern Mesopotamia Using Remote Sensing. J. Field Archaeol. 2010, 35, 184–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritz, C.; Wilkinson, T.J. Using Shuttle Radar Topography to Map Ancient Water Channels in Mesopotamia. Antiquity 2006, 80, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jotheri, J.; Altaweel, M.; Tuji, A.; Anma, R.; Pennington, B.; Rost, S.; Watanabe, C. Holocene Fluvial and Anthropogenic Processes in the Region of Uruk in Southern Mesopotamia. Quat. Int. 2018, 483, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Hritz, C. Physical Geography, Environmental Change, and the Role of Water. In Models of Mesopotamian landscapes: How Small-Scale Processes Contributed to the Growth of Early Civilizations; BAR; Wilkinson, T.J., Gibson, M., Widell, M., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Reanalysis Version 7.0: Monthly Land-Surface Precipitation from Rain Gauges Built on GTS Based and Historic Data. Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory. 2016. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds496.0/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Ur, J.A. Emergent Landscapes of Movement in Early Bronze Age Northern Mesopotamia. In Landscapes of Movement: Trails, Paths, and Roads in Anthropological Perspective; Snead, J.E., Erickson, C.L., Darling, J.A., Eds.; University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 180–203. ISBN 978-1-934536-13-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ur, J.A. CORONA Satellite Photography and Ancient Road Networks: A Northern Mesopotamian Case Study. Antiquity 2003, 77, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jotheri, J. The Google Earth File of Archaeological Sites of Southern Mesopotamia. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Settlement and Land Use in the Zone of Uncertainty in Upper Mesopotamia. In Rainfall and Agriculture in Northern Mesopotamia; Jas, R.M., Ed.; Nederlands Historisch-Archaeologisch Instituut te Istanbul: Leiden, The Nederlands, 2000; pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pournelle, J.R.; Algaze, G. Travels in Edin: Deltaic Resilence and Early Urbanism in Greater Mesopotamia. In Preludes to Urbanism: The Late Chalcolithic of Mesopotamia; McMahon, A., Crawford, H., Eds.; McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 7–34. ISBN 978-1-902937-65-6. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J. Radial Route Systems and Agro-Pastoral Strategies in the Fertile Crescent: New Discoveries from Western Syria and Southwestern Iran. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2013, 32, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Linear Hollows in the Jazira, Upper Mesopotamia. Antiquity 1993, 67, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; French, C.; Ur, J.A.; Semple, M. The Geoarchaeology of Route Systems in Northern Syria. Geoarchaeology 2010, 25, 745–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayne, L.; Donoghue, D. A Remote Sensing Approach for Mapping the Development of Ancient Water Management in the Near East. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soroush, M.; Mehrtash, A.; Khazraee, E.; Ur, J.A. Deep Learning in Archaeological Remote Sensing: Automated Qanat Detection in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ur, J. Sennacherib’s Northern Assyrian Canals: New Insights from Satellite Imagery and Aerial Photography. Iraq 2005, 67, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, P. Qanats and Lifeworlds in Iranian Plateau Villages. In Transformation of Middle Eastern Natural Environment, Bulletin Series; Albert, J., Bernhardsson, M., Kenna, R., Eds.; ALE School of Forestry & Environmental Studies Bulletin Series 98; Yale University: New Haven, CT, USA, 1998; Volume 103, pp. 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, B.J. Toward an Understanding of Borderland Processes. Am. Antiq. 2006, 71, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.C. The Art of Not Being Governed: An Anarchist History of Upland Southeast Asia; Yale University Press: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-300-15652-2. [Google Scholar]
- Braidwood, L.S.; Braidwood, R.J.; Howe, B.; Reed, C.A.; Watson, P.J. (Eds.) Prehistoric Archeology along the Zagros Flanks; Oriental Institute Publications; Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1983; ISBN 978-0-918986-36-8. [Google Scholar]
- Braidwood, R.J.; Howe, B. (Eds.) Prehistoric Investigations in Iraqi Kurdistan; Studies in Ancient Oriental Civilization; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1960; ISBN 0-226-62404-8. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J.; Glatz, C. The Land Behind the Land Behind Baghdad: Archaeological Landscapes of the Upper Diyala (Sirwan) River Valley. Iraq 2017, 79, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankfort, H.; Jacobsen, T.; Preusser, C. Tell Asmar and Khafaje: The First Season’s Work in Eshnunna 1930/31; Oriental Institute Communications; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Frankfort, H.; Lloyd, S.; Jacobsen, T. The Gimilsin Temple and the Palace of the Rulers at Tell Asmar; Oriental Institute Publications; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Delougaz, P. The Temple Oval at Khafajah; Oriental Institute Publications; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Delougaz, P.; Hill, H.D.; Lloyd, S. Private Houses and Graves in the Diyala Region; Oriental Institute Publications; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Delougaz, P.; Lloyd, S. Pre-Sargonid Temples in the Diyala Region; Oriental Institute Publications; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Killick, R.G. (Ed.) Tell Rubeidheh: An Uruk Village in the Jebel Hamrin; Hamrin Salvage Project report, 7; Iraq Archaeological Reports, 2.; Aris & Phillips: Warminster, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Altaweel, M.; Marsh, A.; Mühl, S.; Nieuwenhuyse, O.; Radner, K.; Rasheed, K.; Saber, S.A. New Investigations in the Environment, History and Archaeology of the Iraqi Hilly Flanks: Shahrizor Survey Project 2009–2011. Iraq 2012, 74, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mühl, S.; Rösch, M.; Al-Manmi, D.A.M.; Kadereit, A.; Aziz, B.Q. Irrigation in the Shahrizor Plain: The Potential of Archaeological and Geoarchaeological Archives to Reconstruct Ancient Water Management. In Water for Assyria; Kühne, H., Ed.; Studia Chaburensia; Harrassowitz Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018; Volume 7, pp. 117–136. ISBN 978-3-447-19740-3. [Google Scholar]
- Glatz, C.; Casana, J. Of Highland-Lowland Borderlands: Local Societies and Foreign Power in the Zagros-Mesopotamian Interface. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2016, 44, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panahipour, M. Land Use and Environment in a Zone of Uncertainty: A Case of the Sasanian Expansion in Eastern Iraq–Western Iran. Iran 2021, 59, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, C.; Casana, J.; Bendrey, R.; Beysal, E.; Calderbank, D.; Chelazzi, F.; Del Bravo, F.; Erskine, N.; Hald, M.M.; Laugier, E.J.; et al. Babylonian Encounters in the Upper Diyala Valley: Contextualizing the Results of Regional Survey and the 2016–2017 Excavations at Khani Masi. Am. J. Archaeol. 2019, 123, 439–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şerifoğlu, T.E.; Glatz, C.; Casana, J.; Haydar, S.M. The Sirwan (Upper Diyala) Regional Project–First Results. In The Archaeology of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq and Adjacent Regions; Konstantinos, K., MacGinnis, J., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 403–410. ISBN 978-1-78491-393-9. [Google Scholar]
- Perruchini, E.; Glatz, C.; Hald, M.M.; Casana, J.; Toney, J.L. Revealing Invisible Brews: A New Approach to the Chemical Identification of Ancient Beer. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2018, 100, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laugier, E.J.; Casana, J.; Glatz, C.; Sameen, S.M.; Cabanes, D. Reconstructing Agro-Pastoral Practice in the Mesopotamian-Zagros Borderlands: Insights from Phytolith and FTIR Analysis of a Dung-Rich Deposit. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 38, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotheri, J. Holocene Avulsion History of the Euphrates and Tigris Rivers in the Mesopotamian Floodplain. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2016. Available online: http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/11752/ (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Monthly Product Version 2020 at 0.25°: Monthly Land-Surface Precipitation from Rain-Gauges Built on GTS-Based and Historical Data. Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) at Deutscher Wetterdienst. 2020. Available online: https://www.doi.org/10.5676/DWD_GPCC/FD_M_V2020_025 (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Lasaponara, R.; Zong, X.; Masini, N.; Wang, G.; Shi, P.; Khatteli, H.; Chen, F.; et al. Airborne and Spaceborne Remote Sensing for Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review of the Century (1907–2017). Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritz, C. Contributions of GIS and Satellite-Based Remote Sensing to Landscape Archaeology in the Middle East. J. Archaeol. Res. 2014, 22, 229–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchoukos, N. Satellite Images and Near Eastern Landscapes. East. Archaeol. 2001, 64, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Altaweel, M.; Philip, G. (Eds.) New Agendas in Remote Sensing and Landscape Archaeology in the Near East: Studies in Honour of Tony J. Wilkinson; Archaeopress Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78969-574-8. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, B.H.; Ur, J.A. Mapping Patterns of Long-Term Settlement in Northern Mesopotamia at a Large Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E778–E787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Liere, W.; Lauffray, J. Nouvelle Prospection Archéologique Dans La Haute Jezireh Syrienne. AAS 1954, IV–V, 129–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Regional Approaches to Mesopotamian Archaeology: The Contribution of Archaeological Surveys. J. Archaeol. Res. 2000, 8, 219–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J. Global-Scale Archaeological Prospection Using CORONA Satellite Imagery: Automated, Crowd-Sourced, and Expert-Led Approaches. J. Field Archaeol. 2020, 45, S89–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casana, J.; Cothren, J. The CORONA Atlas Project: Orthorectification of CORONA Satellite Imagery and Regional-Scale Archaeological Exploration in the Near East. In Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space; Comer, D., Harrower, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 31–41. ISBN 978-1-4614-6073-2. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J.; Cothren, J. Stereo Analysis, DEM Extraction and Orthorectification of CORONA Satellite Imagery: Archaeological Applications from the Near East. Antiquity 2008, 82, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammer, E.; Ur, J. Near Eastern Landscapes and Declassified U2 Aerial Imagery. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2019, 7, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philip, G.; Donoghue, D.; Beck, A.; Galiatsatos, N. CORONA Satellite Photography: An Archaeological Application from the Middle East. Antiquity 2002, 76, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casana, J.; Cothren, J.; Kalayci, T. Swords into Ploughshares: Archaeological Applications of CORONA Satellite Imagery in the Near East. Internet Archaeol. 2012, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaqin Sheet I-38 J. 1943. Iraq and Iran Series K501. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Army Map Service. Available online: http://legacy.lib.utexas.edu/maps/ams/iraq_and_iran/ (accessed on 14 August 2019).
- NI 38-7 Khanaqin. 1957. Southwestern Asia Series K502. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Army Map Service. Available online: http://legacy.lib.utexas.edu/maps/ams/southwestern_asia/ (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Casana, J. Regional-Scale Archaeological Remote Sensing in the Age of Big Data. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. J. Soc. Am. Archaeol. 2014, 2, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, C.; Gaffney, V.; Neubauer, W.; Baldwin, E.; Chapman, H.; Garwood, P.; Moulden, H.; Sparrow, T.; Bates, R.; Löcker, K.; et al. The Stonehenge Hidden Landscapes Project. Archaeol. Prospect. 2012, 19, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J. (Ed.) Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Explicitly North American Perspective; University of Alabama Press: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-8173-5343-8. [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon, D.P.; Haley, B.S. (Eds.) Archaeological Remote Sensing in North America: Innovative Techniques for Anthropological Applications; University of Alabama Press: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-8173-1959-5. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H. Caesium-Magnetometry for Landscape-Archaeology. In Seeing the Unseen: Geophysics and Landscape Archaeology; Campana, S., Piro, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 129–165. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J.; Herrmann, J.T. Settlement History and Urban Planning at Zincirli Höyük, Southern Turkey. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2010, 23, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, C.; Gondet, S. Prospection Géophysique à Al-Rawda et Urbanisme En Syrie Au Bronze Ancien. Paléorient 2004, 30, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creekmore, A. The Structure of Upper Mesopotamian Cities: Insight from Fluxgate Gradiometer Survey at Kazane Höyük, Southeastern Turkey. Archaeol. Prospect. 2010, 17, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.M.; Brinker, C.D.; Creekmore, A.T.; Feldman, M.H.; Smith, A.; Weber, J.A. Excavations at Kurd Qaburstan, A Second Millennium BC Urban Site on the Erbil Plain. Iraq 2017, 79, 213–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvamme, K.L. Geophysical Surveys as Landscape Archaeology. Am. Antiq. 2003, 68, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E. Beneath the Euphrates Sediments: Magnetic Traces of the Mesopotamian Megacity Uruk-Warka. Anc. East ANE Today 2020, 8. Available online: https://www.asor.org/anetoday/2020/06/euphrates-sediments (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Thornley, D. Fluxgate Gradiometry Survey at Bestansur. In The Early Neolithic of The Eastern Fertile Crescent: Excavations at Bestansur and Shimshara, Iraqi Kurdistan; Matthews, R., Matthews, W., Raheem, K.R., Richardson, A., Eds.; Central Zagros Archaeological Project Czap Reports Volume 2; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, A.C.; Limp, F.; Casana, J.; Laugier, E.J.; Williamson, M. A New Era in Spatial Data Recording: Low-Cost GNSS. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2019, 7, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvamme, K.L. Remote Sensing Approaches to Archaeological Reasoning: Pattern Recognition and Physical Principles. In Archaeological Concepts for the Study of the Cultural Past; University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2008; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. Drones in Archaeology. State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Archaeol. Prospect. 2017, 24, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.T.; Glissmann, B.; Sconzo, P.; Pfälzner, P. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Survey with Commercial-Grade Instruments: A Case Study from the Eastern Ḫabur Archaeological Survey, Iraq. J. Field Archaeol. 2018, 43, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, R.; Herrmann, J. Recent Trends and Long-Standing Problems in Archaeological Remote Sensing. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2018, 1, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, D.L. Infrared Aerial Photography and Prehispanic Irrigation at Teotihuacán: The Tlajinga Canals. J. Field Archaeol. 1988, 15, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Wiewel, A.; Cool, A.; Hill, A.C.; Fisher, K.D.; Laugier, E.J. Archaeological Aerial Thermography in Theory and Practice. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2017, 5, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casana, J.; Kantner, J.; Wiewel, A.; Cothren, J. Archaeological Aerial Thermography: A Case Study at the Chaco-Era Blue J Community, New Mexico. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 45, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuldain González, J.J.; Varón Hernández, F.R. NDVI Identification and Survey of a Roman Road in the Northern Spanish Province of Álava. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, A.C.; Laugier, E.J.; Casana, J. Archaeological Remote Sensing Using Multi-Temporal, Drone-Acquired Thermal and Near Infrared (NIR) Imagery: A Case Study at the Enfield Shaker Village, New Hampshire. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLeester, M.; Casana, J.; Schurr, M.R.; Hill, A.C.; Wheeler, J.H. Detecting Prehistoric Landscape Features Using Thermal, Multispectral, and Historical Imagery Analysis at Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie, Illinois. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 21, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, C.; Cowley, D.C.; Wade, T.; Nichol, C.J. Deploying Multispectral Remote Sensing for Multi-Temporal Analysis of Archaeological Crop Stress at Ravenshall, Fife, Scotland. Archaeol. Prospect. 2019, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrot Sequoia User Guide. Available online: https://support.micasense.com/hc/en-us/articles/219325487-Quick-Start-Guide-and-User-Guide-PDF (accessed on 28 February 2018).
- Casana, J.; Laugier, E.J.; Hill, A.C.; Blakeslee, D. A Council Circle at Etzanoa? Multi-Sensor Drone Survey at an Ancestral Wichita Settlement in Southeastern Kansas. Am. Antiq. 2020, 85, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühl, S. Human Landscape-Site (Trans-) Formation in the Transigris Area. In Tells: Social and Environmental Space [Proceedings of the International Workshop “Socio-Environmental Dynamics over the Last 12,000 Years: The Creation of Landscapes II (14th-18th March 2011)” in Kiel]; Hofmann, R., Moetz, F.-K., Müller, J., Eds.; Habelt: Bonn, Germany, 2012; pp. 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Algaze, G. The Uruk World System: The Dynamics of Expansion of Early Mesopotamian Civilization, 2nd ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-226-01382-4. [Google Scholar]
- Snead, J.E.; Erickson, C.L.; Darling, J.A. Making Human Space: The Archaeology of Trails, Paths, and Roads. In Landscapes of Movement: Trails, Paths, and Roads in Anthropological Perspective; Snead, J.E., Erickson, C.L., Darling, Eds.; Penn Museum International Research Conferences; University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–19. ISBN 978-1-934536-13-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, H. Middle East Railways; The Continental Railway Circle: Harrow, UK, 1981; ISBN 978-0-9503469-7-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.T. Loyalties: Mesopotamia 1917–1920, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1936; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Boucharlat, R.; Ertsen, M.W.; Gillmore, G.; Kennet, D.; Magee, P.; Rezakhani, K.; Schacht, T.D. From Human Niche Construction to Imperial Power: Long-Term Trends in Ancient Iranian Water Systems. Water Hist. 2012, 4, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Rayne, L.; Jotheri, J. Hydraulic Landscapes in Mesopotamia: The Role of Human Niche Construction. Water Hist. 2015, 7, 397–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamali, M.; De Beaulieu, J.-L.; Miller, N.F.; Andrieu-Ponel, V.; Ponel, P.; Lak, R.; Sadeddin, N.; Akhani, H.; Fazeli, H. Vegetation History of the SE Section of the Zagros Mountains during the Last Five Millennia; a Pollen Record from the Maharlou Lake, Fars Province, Iran. Veg. Hist. Archaeobotany 2009, 18, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, P.; Fleitmann, D.; Matthews, R.; Matthews, W.; Black, S. Evidence of Resilience to Past Climate Change in Southwest Asia: Early Farming Communities and the 9.2 and 8.2 Ka Events. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 136, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.; Eastwood, W.J.; Kuzucuolu, C.; Fiorentino, G.; Caracuta, V. Climatic, Vegetation and Cultural Change in the Eastern Mediterranean during the Mid-Holocene Environmental Transition. Holocene 2011, 21, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Laugier, E.J. Satellite Imagery-Based Monitoring of Archaeological Site Damage in the Syrian Civil War. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Data Set | Date | Spatial Resolution (m2) or Scale | Coverage | Use in Study and Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historic Army Map | 1942 | 1:253,440 | 100% | Historic features [59] |
| Historic Army Map | 1957 | 1:250,000 | 100% | Historic features [60] |
| SRTM DEM | 2000 | 30 | 100% | DEM, Watershed Analysis |
| CORONA KH-4B | 3-Aug-1969 | 1.8–2.7 | 100% | Historic Imagery |
| Royal Airforce (RAF) Aerial Photography | Nov-1951 | ~2 | 40.6% | Historic Photographs |
| Google Earth Imagery | Variable | Variable | 100% | High Resolution Imagery |
| WorldView-2 Imagery | 13-Feb-2011 | 0.46 | 62.7% | High Resolution Imagery, Differential Vegetation Health, Temporal Change (DigitalGlobe) |
| Site Data | Magnetometry | Multispectral | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site No. | Site Name | Occupational Periods | No. Grids | Area Surveyed (ha) | Year Collected | Area Surveyed (ha) | Year Collected |
| SRP008 | Early–mid-3rd mill. BCE (ED) | 21 | 0.84 | 2017 | 8.29 | 2019 | |
| SRP046 | Khani Masi | 2nd mill. BCE | 90 | 3.6 | 2017 | 21.28 | 2019 |
| SRP113 | Multi-period | 8 | 0.32 | 2017 | 8.97 | 2019 | |
| SRP117 | 4th mill. BCE | 18 | 0.72 | 2017 | 8.39 | 2019 | |
| SRP106 | Tepe Shaho | Multi-period | 35 | 1.4 | 2018 | 12.06 | 2019 |
| SRP180 | Tepe Qaburstan | 3rd mill. BCE | 22 | 0.88 | 2018 | 8.26 | 2019 |
| SRP187 | Tepe Qumar | 6th–5th mill. BCE (Hassuna) | 15 | 0.6 | 2018 | 12.62 | 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laugier, E.J.; Casana, J. Integrating Satellite, UAV, and Ground-Based Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Exploration of Pre-Modern Land Use in Northeastern Iraq. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5119. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245119
Laugier EJ, Casana J. Integrating Satellite, UAV, and Ground-Based Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Exploration of Pre-Modern Land Use in Northeastern Iraq. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(24):5119. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245119
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaugier, Elise Jakoby, and Jesse Casana. 2021. "Integrating Satellite, UAV, and Ground-Based Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Exploration of Pre-Modern Land Use in Northeastern Iraq" Remote Sensing 13, no. 24: 5119. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245119
APA StyleLaugier, E. J., & Casana, J. (2021). Integrating Satellite, UAV, and Ground-Based Remote Sensing in Archaeology: An Exploration of Pre-Modern Land Use in Northeastern Iraq. Remote Sensing, 13(24), 5119. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245119






