Estimating Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Oak Savanna at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Resolutions. Implications for Water Resources Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- To evaluate the utility of a surface energy balance model (ALEXI/DisALEXI) and the STARFM data fusion technique, using multiple remote sensing platforms (Landsat 7/8 and MODIS), to estimate high-resolution ET in time and space over the complex canopy structure of Mediterranean oak savannas.
- (ii)
- To analyze the opportunities offered by this high-resolution product to provide information that is useful to improve the water and vegetation management of this agroforestry system at a field scale. To do that, we evaluated the water use patterns of the herbaceous stratum and other small heterogeneous vegetation patches typical of the dehesa (e.g., scrubs, humid areas, creek shore), which shape the landscape structure and reflect the existence of different micro-ecosystems and climates. Finally, the cumulative monthly ET generated by the different approaches with different spatial resolutions (1 km and 30 m) was quantified over the same vegetation patches.
2. Materials and Methods
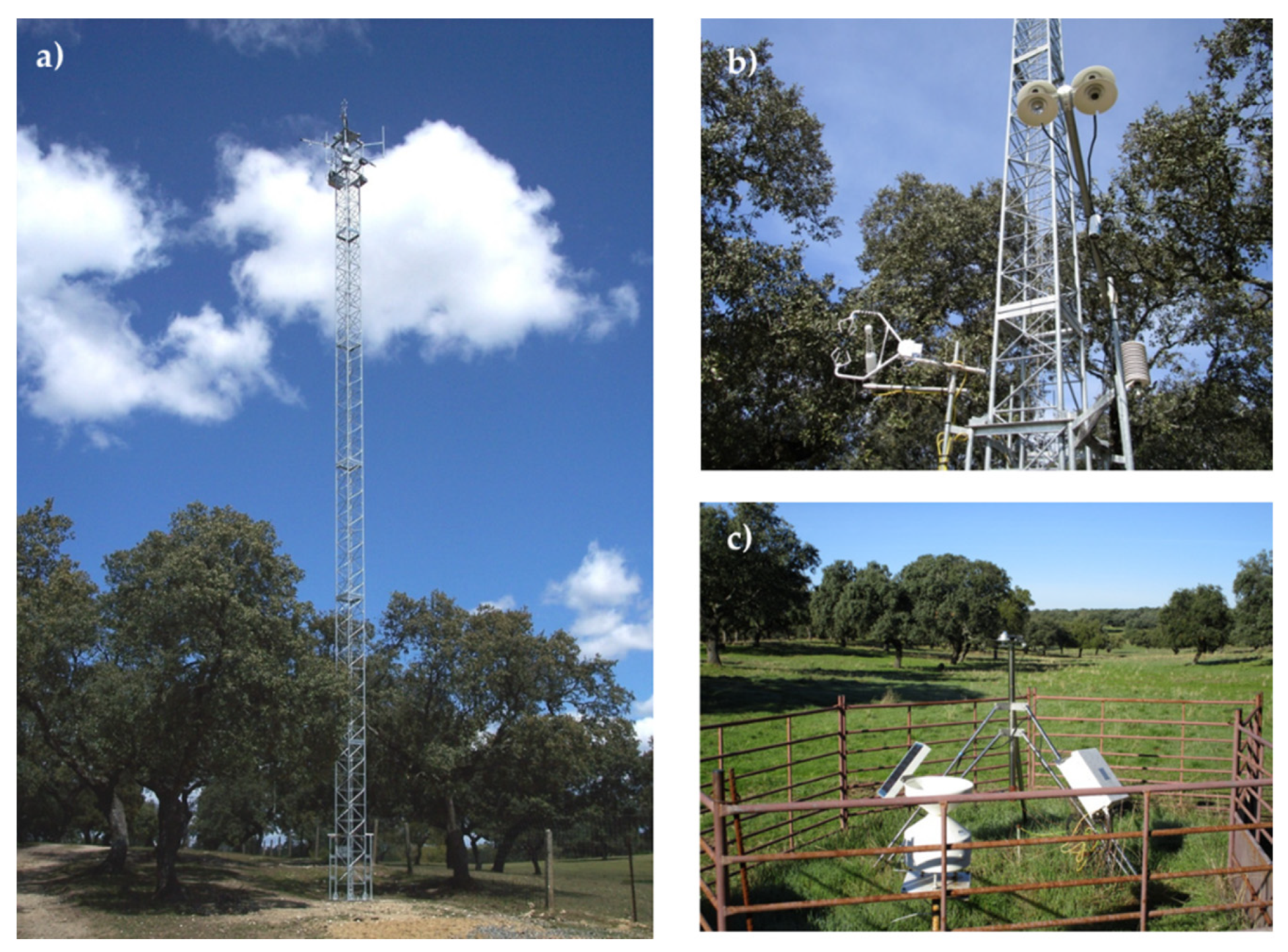
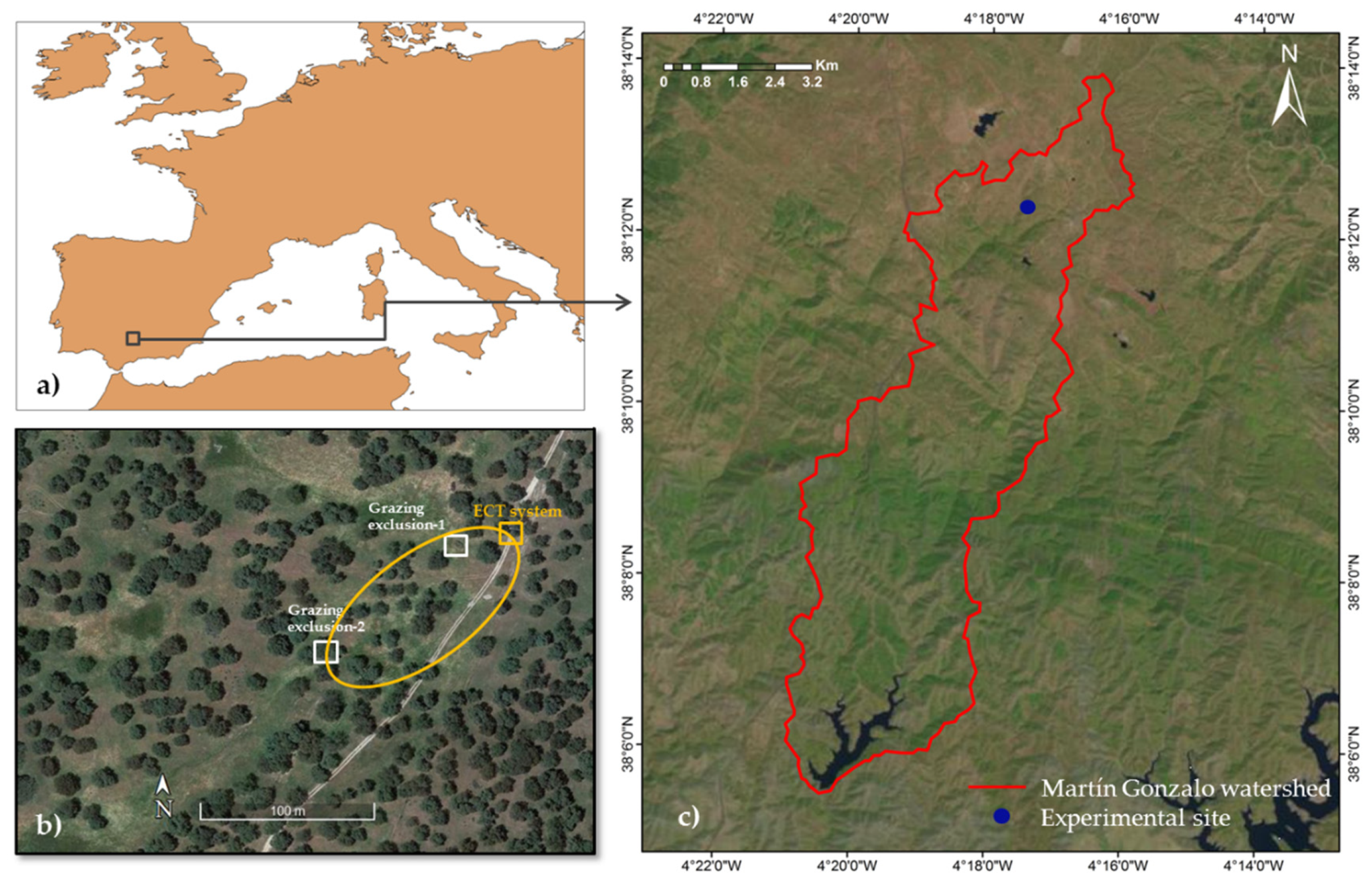
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Experimental Site
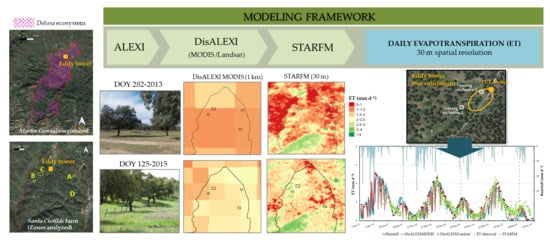
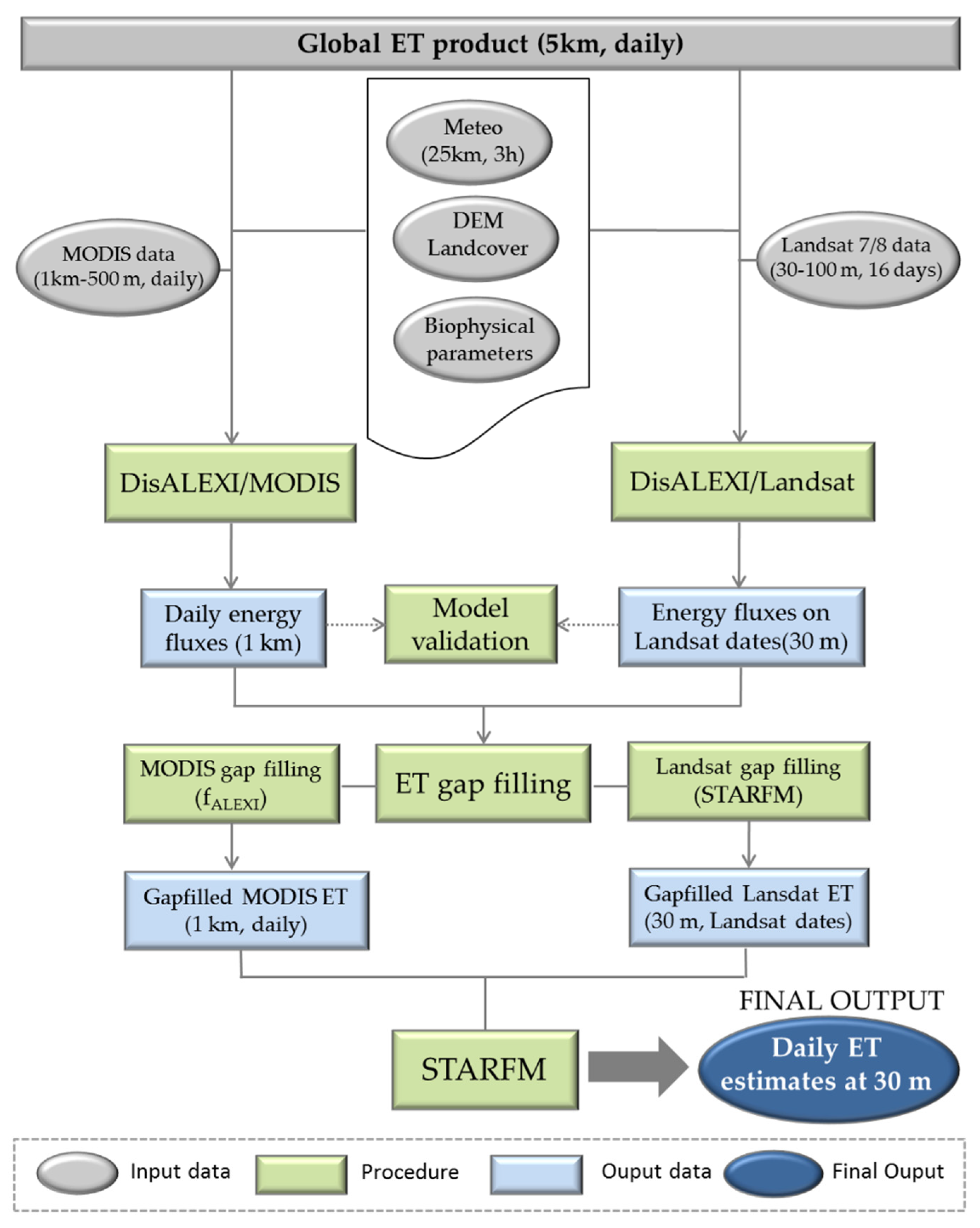
2.2. Modeling Framework
2.2.1. ALEXI/DisALEXI Model
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data Fusion Method
2.2.3. ET Data Gap Filling
2.2.4. Simple ET Interpolation Methods
2.3. Model Input Datasets
2.3.1. Landsat Data
2.3.2. MODIS Data
2.3.3. Meteorological Input Data and Vegetation Properties
2.3.4. Input Data Filtering
2.4. Global Remotely Sensed ET Product
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Surface Energy Fluxes at the Flux Tower Site
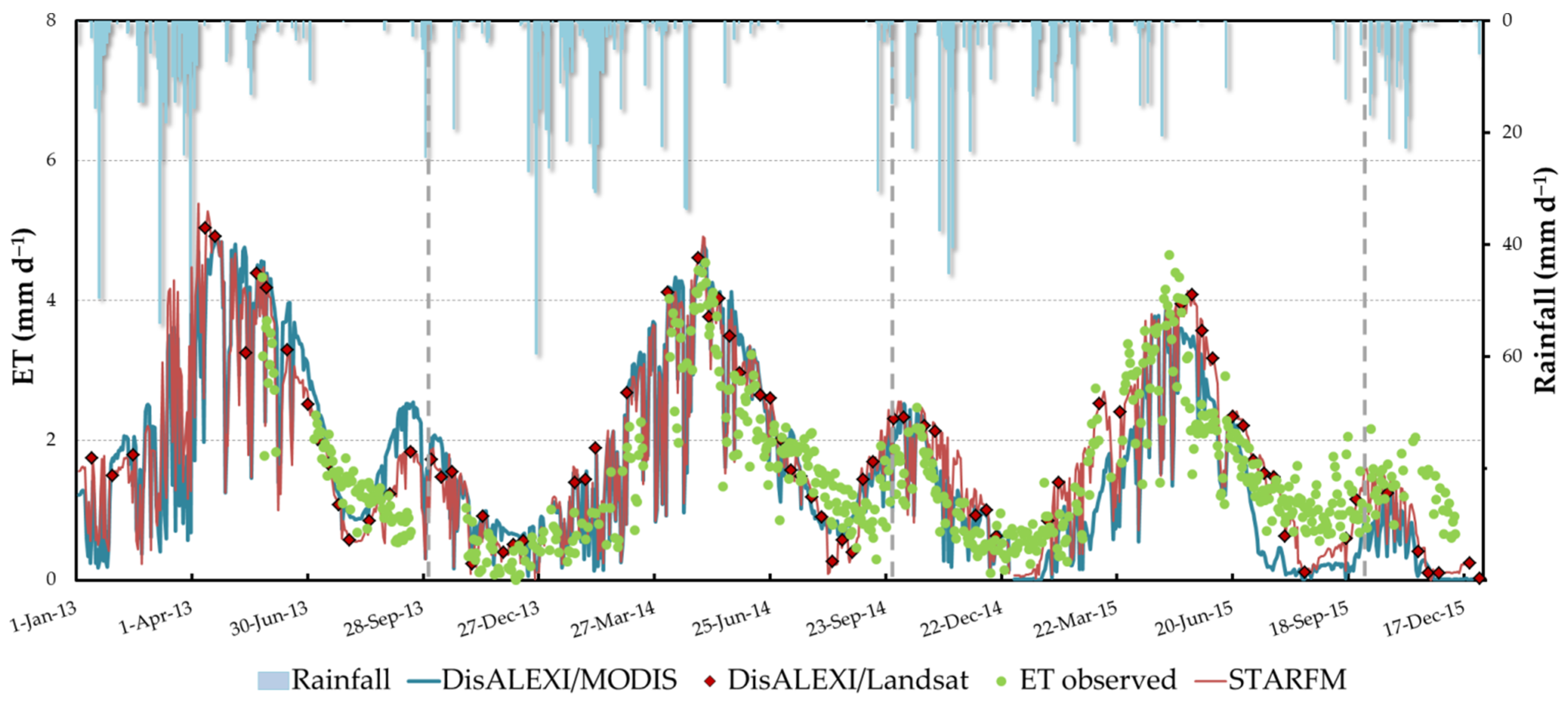
3.2. Analysis of ET Time Series from DisALEXI and STARFM
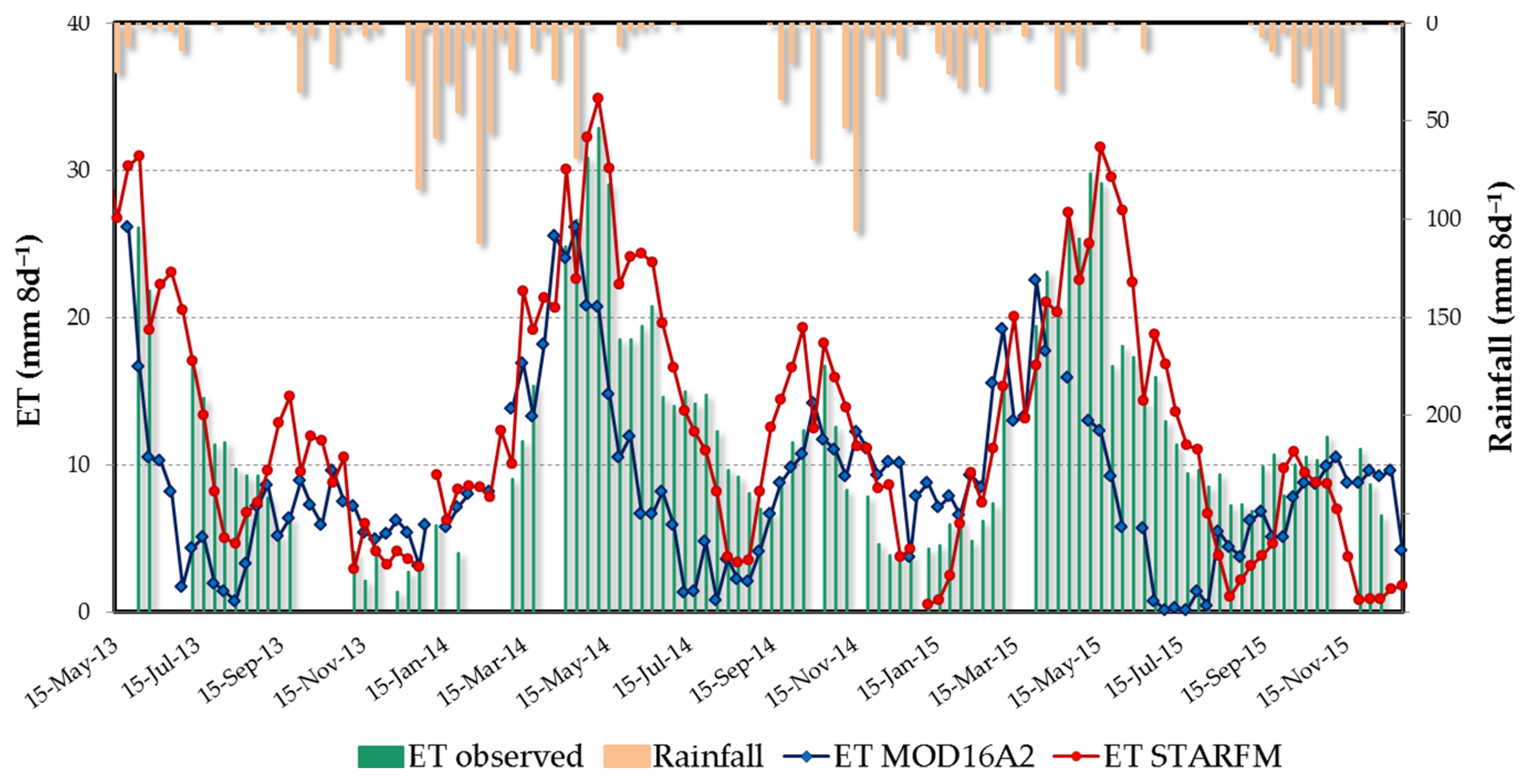
3.3. Evaluation of the MOD16A2 Global ET Product
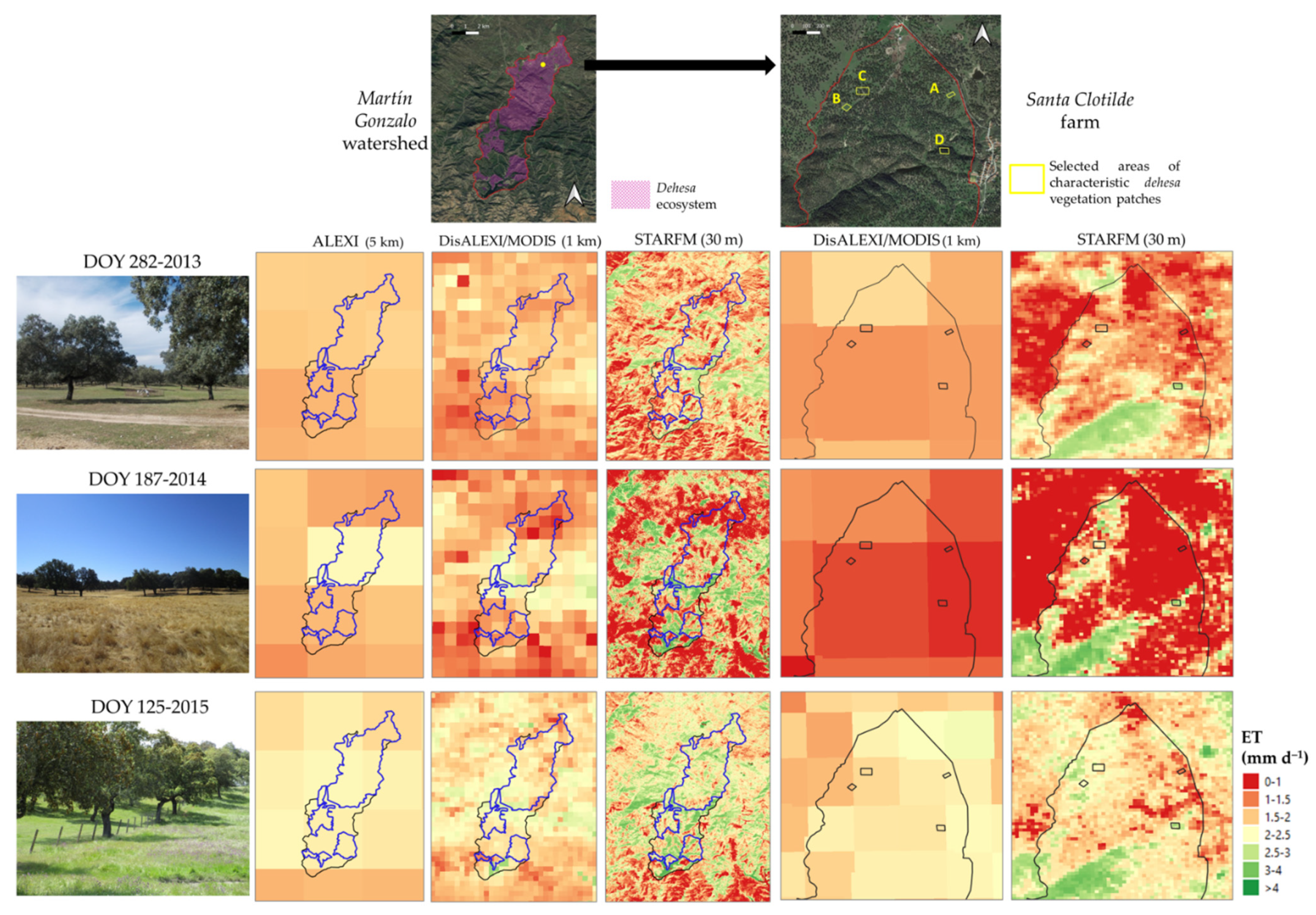
3.4. Water Resources Management at Field Scale Using High-Resolution ET Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. DisALEXI Model Validation
4.2. Temporal Patterns in ET Curves
4.3. Performance of MOD16A2 ET
4.4. Variability of Dehesa Vegetation Water Use at Field Scale
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Porporato, A.; Laio, F.; Ridolfi, L. Plants in water-controlled ecosystems: Active role in hydrologic processes and responce to water stress I. Scope and general outline. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundel, P.W.; Arroyo, M.T.K.; Cowling, R.M.; Keeley, J.E.; Lamont, B.B.; Vargas, P. Mediterranean Biomes: Evolution of Their Vegetation, Floras, and Climate. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 383–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauquelin, T.; Michon, G.; Joffre, R.; Duponnois, R.; Génin, D.; Fady, B.; BouDagher-Kharrat, M.; Derridj, A.; Slimani, S.; Badri, W.; et al. Mediterranean forests, land use and climate change: A social-ecological perspective. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Marini, K. Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin–Current Situation and Risks for the Future; First Mediterranean Assessment Report; MedECC (Mediterranean Experts on Climate and Environmental Change); Union for the Mediterranean, Plan Bleu, UNEP/MAP: Marseille, France, 2020; ISBN 978-2-9577416-0-1. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, M.; Ruelland, D.; Fernandez, S.; Dezetter, A.; Fabre, J.; Servat, E.; Fritsch, J.M.; Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Thivet, G. Current state of Mediterranean water resources and future trends under climatic and anthropogenic changes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation between climate change in the Mediterranean region and global warming. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiébault, S.; Moatti, J.; Ducrocq, V.; Gaume, E.; Dulac, F.; Hamonou, E.; Shin, Y.; Joel, G.; Boulet, G.; Guégan, J.; et al. The Mediterranean Region under Climate Change: A Scientific Update; IRD Éditions: Marseille, France, 2016; ISBN 978-2-7099-2219-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Fader, M.; Garrabou, J.; Gattuso, J.P.; Iglesias, A.; Lange, M.A.; Lionello, P.; Llasat, M.C.; Paz, S.; et al. Climate change and interconnected risks to sustainable development in the Mediterranean. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; López-Moreno, I.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lasanta-Martínez, T.; Beguería, S. Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turco, M.; Llasat, M.C.; von Hardenberg, J.; Provenzale, A. Climate change impacts on wildfires in a Mediterranean environment. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL) 1 Formalation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Agnese, C.; Ciraolo, G.; Minacapilli, M.; Provenzano, G.; Rallo, G. Actual evapotranspiration assessment by means of a coupled energy/hydrologic balance model: Validation over an olive grove by means of scintillometry and measurements of soil water contents. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diak, G.R.; Whipple, M.S. Note on estimating surface sensible heat fluxes using surface temperatures measured from a geostationary satellite during FIFE 1989. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dugo, M.P.; Neale, C.M.U.; Mateos, L.; Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Anderson, M.C.; Li, F. A comparison of operational remote sensing-based models for estimating crop evapotranspiration. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, W.J.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; French, A.N. An intercomparison of the Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) and the Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) modeling schemes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Gao, F.; Knipper, K.; Hain, C.; Dulaney, W.; Baldocchi, D.; Eichelmann, E.; Hemes, K.; Yang, Y.; Medellin-Azuara, J.; et al. Field-scale assessment of land and water use change over the California delta using remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knipper, K.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; Alfieri, J.G.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; McKee, L.G.; Nieto, H.; et al. Evapotranspiration estimates derived using thermal-based satellite remote sensing and data fusion for irrigation management in California vineyards. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Evaluation of soil and vegetation heat flux predictions using a simple two-source model with radiometric temperatures for partial canopy cover. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 94, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, A.; Kustas, W.P.; Polo, M.J.; Carrara, A.; González-Dugo, M.P. Modeling surface energy fluxes over a dehesa (oak savanna) ecosystem using a thermal based two-source energy balance model (TSEB) I. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreu, A.; Kustas, W.P.; Polo, M.J.; Carrara, A.; González-Dugo, M.P. Modeling surface energy fluxes over a dehesa (oak savanna) ecosystem using a thermal based two source energy balance model (TSEB) II-Integration of remote sensing medium and low spatial resolution satellite images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burchard-Levine, V.; Nieto, H.; Riaño, D.; Migliavacca, M.; El-Madany, T.S.; Perez-Priego, O.; Carrara, A.; Martín, M.P. Seasonal adaptation of the thermal-based two-source energy balance model for estimating evapotranspiration in a semiarid tree-grass ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Dugo, M.; Chen, X.; Andreu, A.; Carpintero, E.; Gómez-Giraldez, P.; Carrara, A.; Su, Z. Long-term water stress and drought monitoring of Mediterranean oak savanna vegetation using thermal remote sensing. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Diak, G.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Mecikalski, J.R. A two-source time-integrated model for estimating surface fluxes using thermal infrared remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A climatological study of evapotranspiration and moisture stress across the continental United States based on thermal remote sensing: 2. Surface moisture climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; French, A.N.; Mecikalski, J.; Torn, R.; Diak, G.R.; Schmugge, T.J.; Tanner, B.C.W. Remote sensing of surface energy fluxes at 101-m pixel resolutions. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, G.; Pulido, F.J. The Functioning, Management and Persistence of Dehesas. Agrofor. Eur. 2008, 10600, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, G.; Cáceres, Y. System Report: Iberian Dehesas, Spain; AGFORWARD; Agroforestry for Europe: Plasencia, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, M.; Tietje, W.D.; Barrett, R.H. Effects of Management on Biological Diversity and Endangered Species. In Mediterranean Oak Woodland Working Landscapes; Landscape Series, 2013; Campos, P., Huntsinger., L., Oviedo, J.L., Starrs, P.F., Díaz, M., Standiford, R.B., Montero, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieninger, T.; Rolo, V.; Moreno, G. Large-scale patterns of Quercus ilex, Quercus suber, and Quercus pyrenaica regeneration in central-western Spain. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Laouina, A.; Hamza, A.; Chaker, M.; Naafa, R.; Regaya, K.; Boulet, A.-K.; Keizer, J.J.; Carvalho, T.M.M. Changes in Land Use and Land Management Practices Affecting Land Degradation within Forest and Grazing Ecosystems in the Western Mediterranean. Sustain. Agrosylvopastoral Syst. Dehesas Montados 2004, 37, 137–153. [Google Scholar]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Xu, L.; Kiang, N. How plant functional-type, weather, seasonal drought, and soil physical properties alter water and energy fluxes of an oak-grass savanna and an annual grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 123, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Xu, L. What limits evaporation from Mediterranean oak woodlands—The supply of moisture in the soil, physiological control by plants or the demand by the atmosphere? Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, R.; Rambal, S.; Damesin, C. Functional attributes in Mediterranean-type ecosystems. In Handbook of Functional Plant Ecology, 2nd ed.; Pugnaire, F.I., Valladares, F., Eds.; CRC Press Books: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Saunders, S.C.; Crow, T.R.; Naiman, R.J.; Brosofske, K.D.; Mroz, G.D.; Brookshire, B.L.; Franklin, J.F. Microclimate in Forest Ecosystem the effects of different management regimes. Bioscience 1996, 49, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnston, M.; Andreu, A.; Verfaillie, J.; Baldocchi, D.; Gonzalez-Dugo, M.P.; Moorcroft, P. Measuring surface temperatures in a woodland savanna: Opportunities and challenges of thermal imaging in an open-canopy ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.J.; De Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. A data fusion approach for mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scale. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4672–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scales over rainfed and irrigated agricultural areas using remote sensing data fusion. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semmens, K.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Gao, F.; Alfieri, J.G.; McKee, L.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Cammalleri, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Monitoring daily evapotranspiration over two California vineyards using Landsat 8 in a multi-sensor data fusion approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Semmens, K.A.; Kustas, W.P.; Noormets, A.; Wynne, R.H.; Thomas, V.A.; Sun, G. Daily Landsat-scale evapotranspiration estimation over a forested landscape in North Carolina, USA, using multi-satellite data fusion. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, P.; Huntsinger, L.; Oviedo, J.; Díaz, M.; Starrs, P.; Standiford, R.; Montero, G. Mediterranean Oak Woodland Working Landscapes: Dehesas of Spain and Ranchlands of California; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-94-007-6706-5. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpintero, E.; Andreu, A.; Gómez-Giráldez, P.J.; Blázquez, Á.; González-Dugo, M.P. Remote-sensing-basedwater balance for monitoring of evapotranspiration and water stress of a mediterranean Oak-Grass Savanna. Water 2020, 12, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, C.R.; Anderson, M.C. Estimating morning changes in land surface temperature from MODIS day/night observations: Applications for surface energy balance modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9723–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of Landsat thermal imagery in monitoring evapotranspiration and managing water resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Hain, C.R.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Schultz, L.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Cammalleri, C.; d’Urso, G.; Pimstein, A.; et al. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field to global scales using geostationary and polar orbiting satellite imagery. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 5957–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Torn, R.D.; Kustas, W.P.; Basara, J.B. A multiscale remote sensing model for disaggregating regional fluxes to micrometeorological scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Wood, J.D.; Gu, L.; Hain, C. Studying drought-induced forest mortality using high spatiotemporal resolution evapotranspiration data from thermal satellite imaging. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Alfieri, J.G.; Sharifi, A.; McCarty, G.; Yang, Y. Investigating water use over the Choptank River Watershed using a multi-satellite data fusion approach. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5298–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo: I. Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Wang, Y. Simple method for retrieving leaf area index from Landsat using MODIS leaf area index products as reference. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2012, 6, 063554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Bernstein, L.S.; Robertson, D.C. MODTRAN: A Moderate Resolution Model for LOWTRAN 7; GL-TR-89-0122; Air Force Geophysics Lab: Bedford, MA, USA, 1987; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. A data mining approach for sharpening thermal satellite imagery over land. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3287–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.I.; Katul, G.; Chi, T.W. An approximate analytical model for footprint estimation of scalar fluxes in thermally stratified atmospheric flows. Adv. Water Resour. 2000, 23, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Alfieri, J.G.; Evett, S.; Agam, N. Quantifying variability in field-scale evapotranspiration measurements in an irrigated agricultural region under advection. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajer, A.; López, S.; González, J.S.; Ranilla, M.J. Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of some Spanish browse plant species. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.; Diak, G.; Gao, F.; Knipper, K.; Hain, C.; Eichelmann, E.; Hemes, K.S.; Baldocchi, D.; Kustas, W.; Yang, Y. Impact of insolation data source on remote sensing retrievals of evapotranspiration over the California delta. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpintero, E.; Semmens, K.; Anderson, M.C.; Andreu, A.; Gao, F.; Kustas, W.P.; González-Dugo, M.P. Use of remote sensing data fusion for daily evapotranspiration monitoring at watershed scale over a dehesa ecosystem. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Recent Advances in Quantitative Remote Sensing, Valencia, Spain, 22–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carpintero, E.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Hain, C.; Nieto, H.; Gao, F.; Andreu, A.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Continuous evapotranspiration monitoring and water stress at watershed scale in a Mediterranean oak savanna. In Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XVIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; ISSN 0277-786X. ISBN 9781510604001. [Google Scholar]
- Cubera, E.; Morena, G. Effect of single Quercus ilex trees upon spatial and seasonal changes in soil water content in dehesas of central western Spain. Ann. For. Sci. 2007, 64, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, G.; Obrador, J.J.; Cubera, E.; Dupraz, C. Fine root distribution in Dehesas of Central-Western Spain. Plant Soil. 2005, 277, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.F. How Oaks Respond to Water Limitation. In Proceedings of the Seventh California Oak Symposium: Managing Oak Woodlands in a Dynamic World; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Alés, R. Response of Mediterranean grassland species to changing rainfall. A reply to Figueroa and Davy. Orsis 1993, 8, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- David, T.S.; Henriques, M.O.; Kurz-Besson, C.; Nunes, J.; Valente, F.; Vaz, M.; Pereira, J.S.; Siegwolf, R.; Chaves, M.M.; Gazarini, L.C.; et al. Water-use strategies in two co-occurring Mediterranean evergreen oaks: Surviving the summer drought. Tree Physiol. 2007, 27, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burba, G.; Anderson, D. Eddy Covariance Flux Measurements. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 18, 211. [Google Scholar]
- Seguin, B.; Becker, F.; Phulpin, T.; Gu, X.F.; Guyot, G.; Kerr, Y.; King, C.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Ottlé, C.; Stoll, M.P.; et al. IRSUTE: A minisatellite project for land surface heat flux estimation from field to regional scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, L.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J. Monitoring evapotranspiration of irrigated crops using crop coefficients derived from time series of satellite images. I. Method validation. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, F.L.M.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Gavilán, P.; Domínguez, J. Integration of vegetation indices into a water balance model to estimate evapotranspiration of wheat and corn. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, I.; Villodre, J.; Carrara, A.; Calera, A. Remote sensing-based soil water balance to estimate Mediterranean holm oak savanna (dehesa) evapotranspiration under water stress conditions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwongsitanon, N.; Suwawong, T.; Thianpopirug, S.; Williams, J.; Jia, L.; Bastiaanssen, W. Validation of seven global remotely sensed ET products across Thailand using water balance measurements and land use classifications. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 30, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, D.; Jamshidi, S.; Smith, D.; Kellner, O. Evapotranspiration Climatology of Indiana, USA Using In Situ and Remotely Sensed Products. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 2093–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, A.; Flores, H.; Crespo, G.; Marín, M.I.; Campos, I.; Calera, A. Performance Assessment of MOD16 in Evapotranspiration Evaluation in Northwestern Mexico. Water 2018, 10, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Comparison of MOD16 and LSA-SAF MSG evapotranspiration products over Europe for 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, S.; Zand-Parsa, S.; Pakparvar, M.; Niyogi, D. Evaluation of Evapotranspiration over a Semiarid Region Using Multiresolution Data Sources. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, R.; Rambal, S. How tree cover influences the water balance of Mediterranean rangelands. Ecology 1993, 74, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

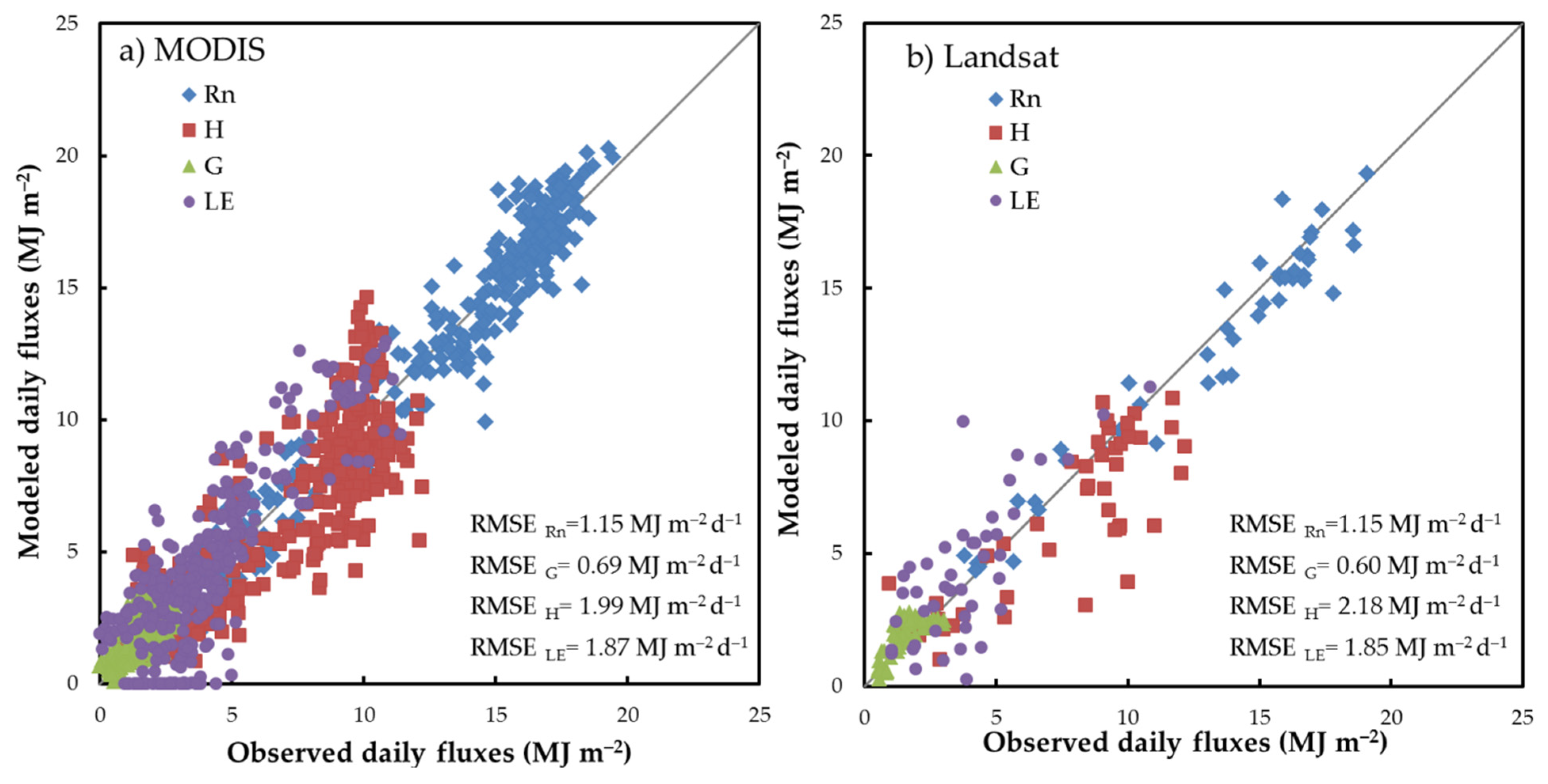


| Flux | Ō (MJ m−2 d−1) | MAE (MJ m−2 d−1) | RMSE (MJ m−2 d−1) | MBE (MJ m−2 d−1) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS | Rn | 12.93 | 0.91 | 1.15 | 0.11 | 0.95 |
| G | 1.59 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.35 | 0.52 | |
| H | 7.34 | 1.64 | 1.99 | −0.60 | 0.69 | |
| LE | 4.01 | 1.54 | 1.87 | 0.37 | 0.69 | |
| Landsat | Rn | 12.90 | 0.91 | 1.15 | −0.33 | 0.94 |
| G | 1.52 | 0.46 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.60 | |
| H | 7.52 | 1.56 | 2.18 | −1.16 | 0.68 | |
| LE | 3.86 | 1.46 | 1.85 | 0.50 | 0.56 |
| MODIS | MODIS-Landsat (STARFM) | Interpolated Landsat (Using FPET) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (mm d−1) | 0.589 | 0.539 | 0.596 |
| RMSE (mm d−1) | 0.737 | 0.673 | 0.749 |
| MBE (mm d−1) | 0.005 | 0.103 | 0.158 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpintero, E.; Anderson, M.C.; Andreu, A.; Hain, C.; Gao, F.; Kustas, W.P.; González-Dugo, M.P. Estimating Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Oak Savanna at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Resolutions. Implications for Water Resources Management. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183701
Carpintero E, Anderson MC, Andreu A, Hain C, Gao F, Kustas WP, González-Dugo MP. Estimating Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Oak Savanna at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Resolutions. Implications for Water Resources Management. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183701
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpintero, Elisabet, Martha C. Anderson, Ana Andreu, Christopher Hain, Feng Gao, William P. Kustas, and María P. González-Dugo. 2021. "Estimating Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Oak Savanna at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Resolutions. Implications for Water Resources Management" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183701
APA StyleCarpintero, E., Anderson, M. C., Andreu, A., Hain, C., Gao, F., Kustas, W. P., & González-Dugo, M. P. (2021). Estimating Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Oak Savanna at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Resolutions. Implications for Water Resources Management. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183701