Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
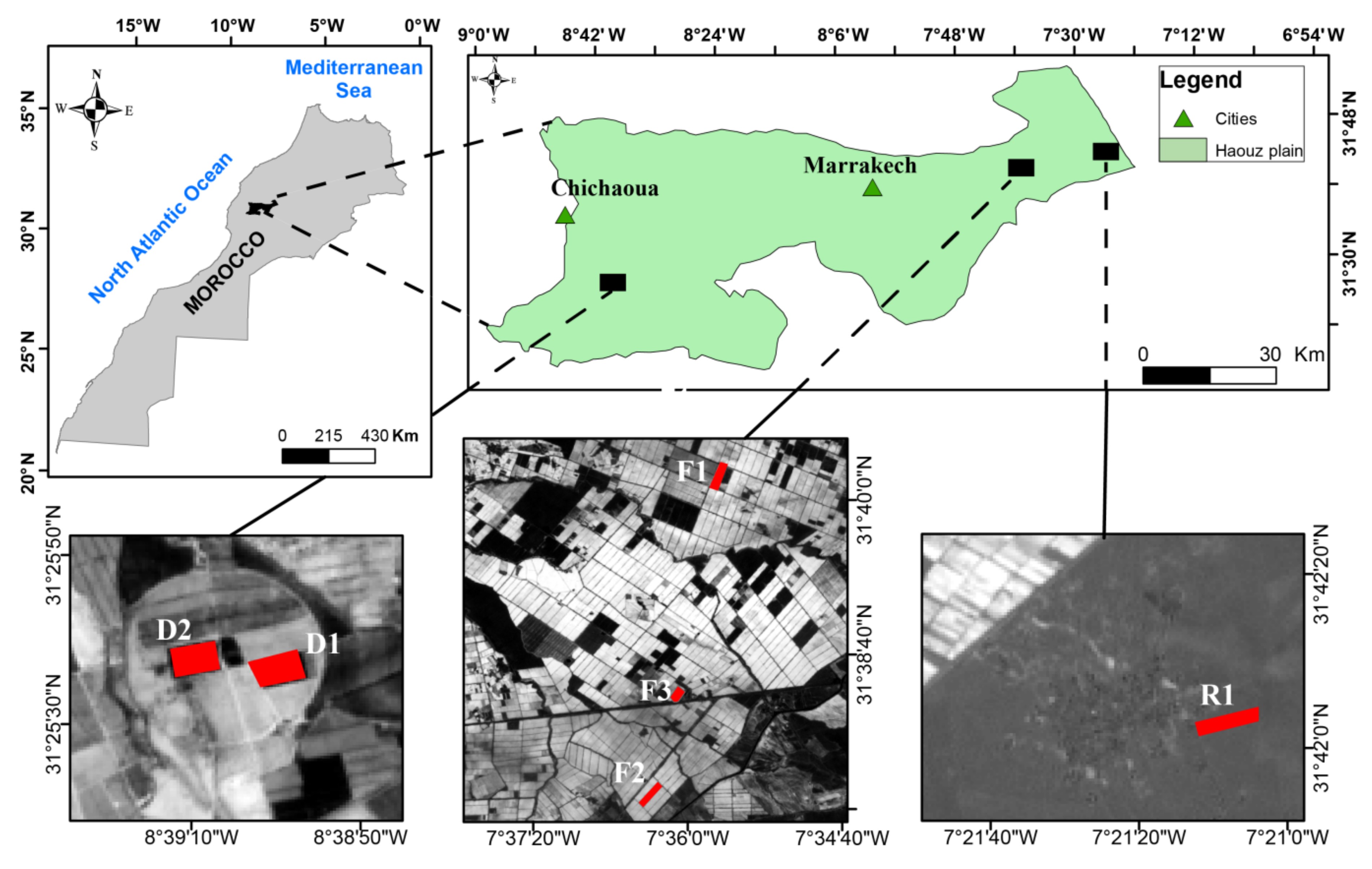
2.1. Study Region and Sites Description
2.2. In Situ Data
2.2.1. Irrigation and Meteorological Data
2.2.2. In Situ Surface Soil Moisture
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
2.3.1. Sentinel-1 SSM Product
2.3.2. Sentinel-2 Data
3. Methodology
3.1. FAO-56 Dual Crop Coefficient
3.2. Particle Filter Approach and Implementation
3.3. Experimental Design
3.3.1. Synthetic Experiments
3.3.2. In Situ SSM Assimilation
3.3.3. Satellite SSM Assimilation
3.4. Statistical Metrics
4. Results
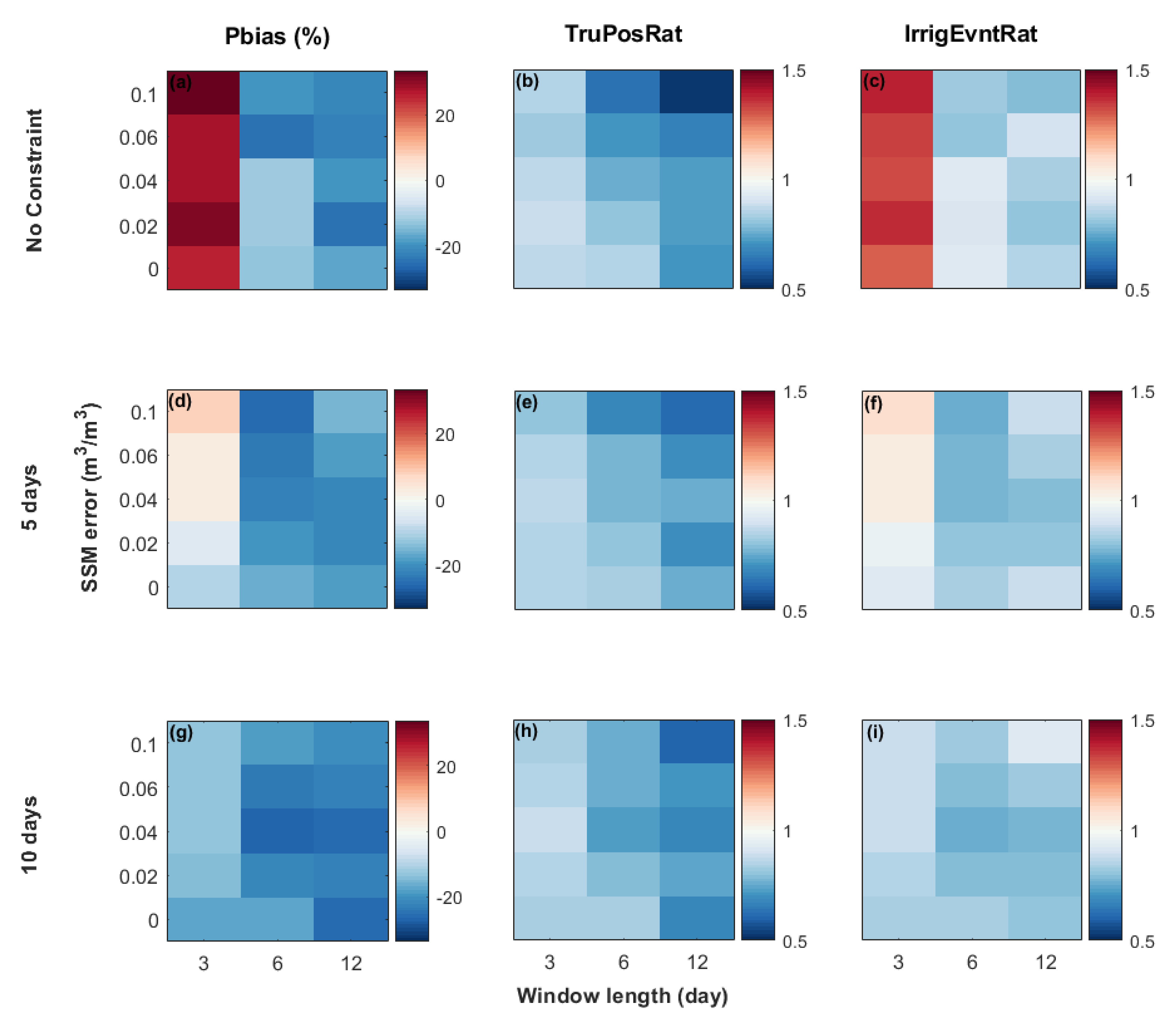
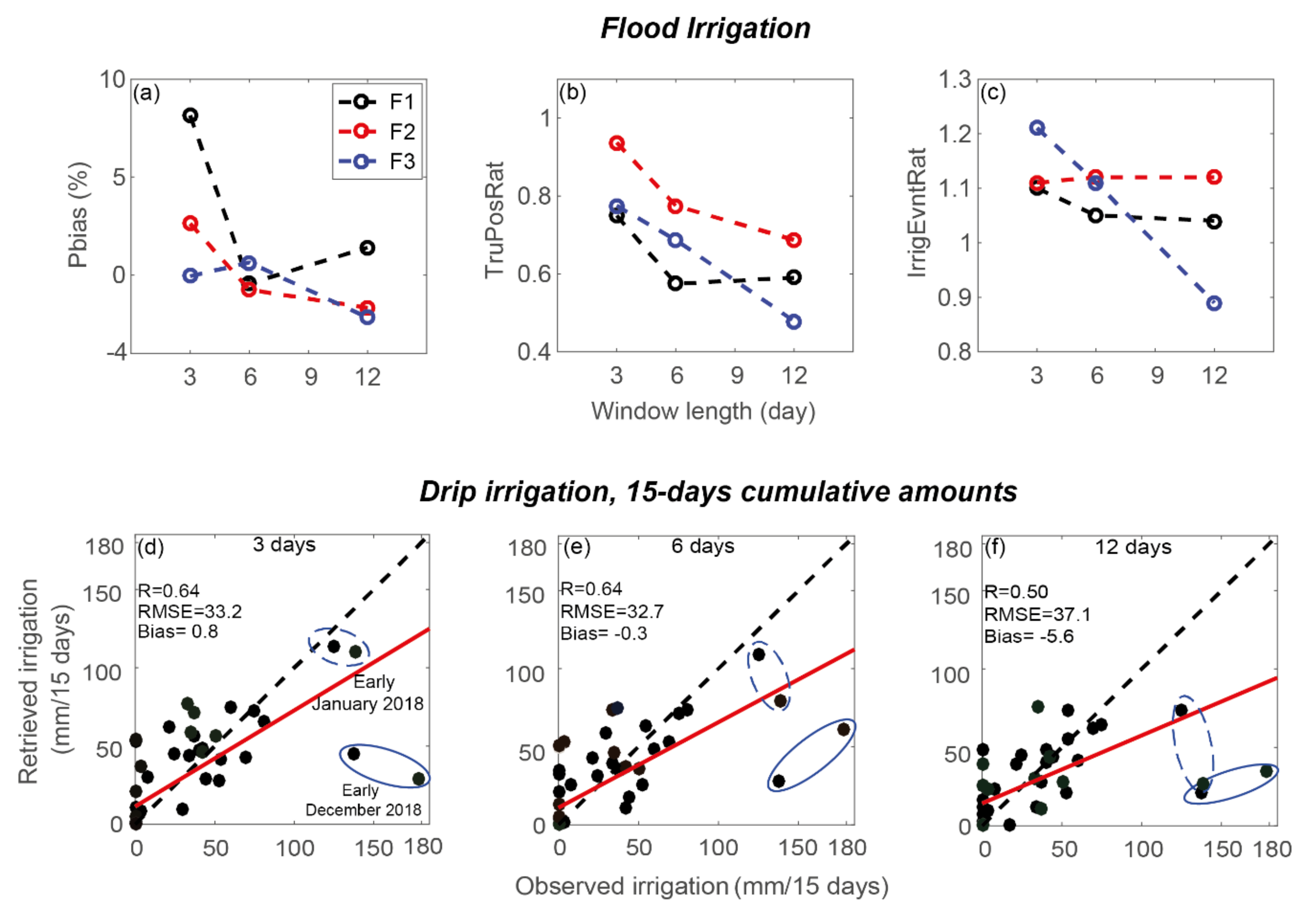
4.1. Synthetic Experiments and Sensitivity Analysis
4.1.1. Flood Irrigation
4.1.2. Drip Irrigation
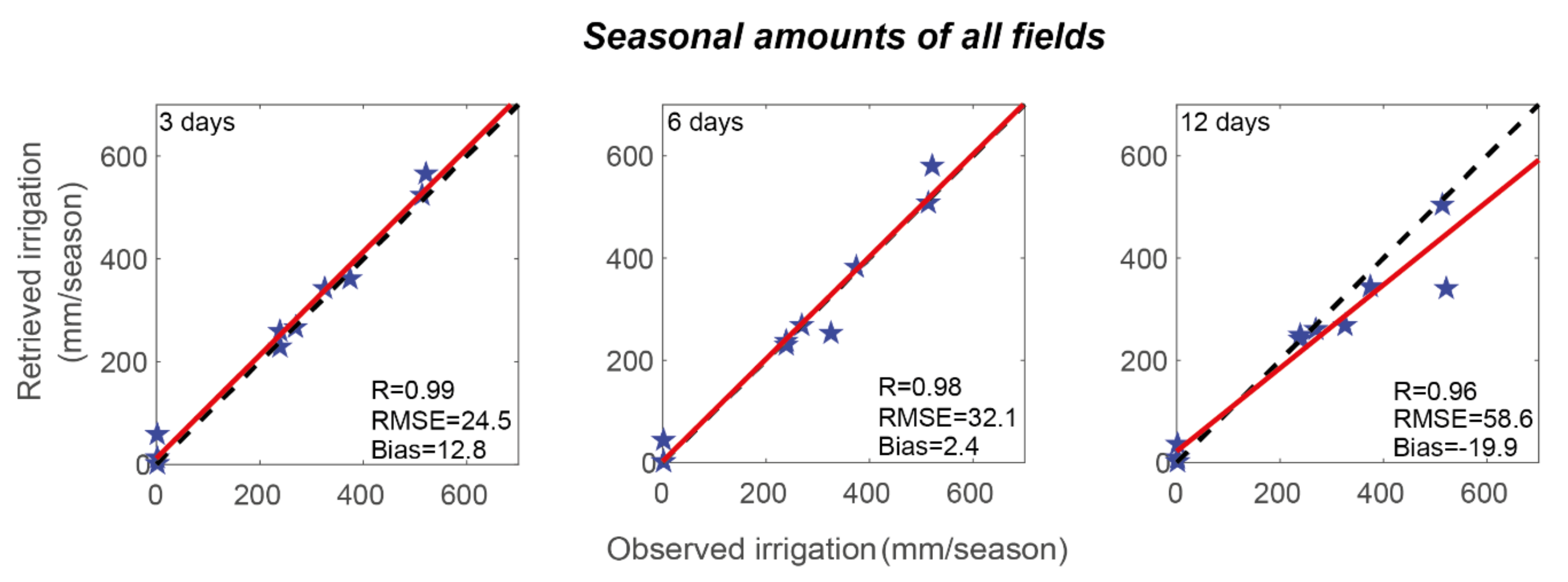
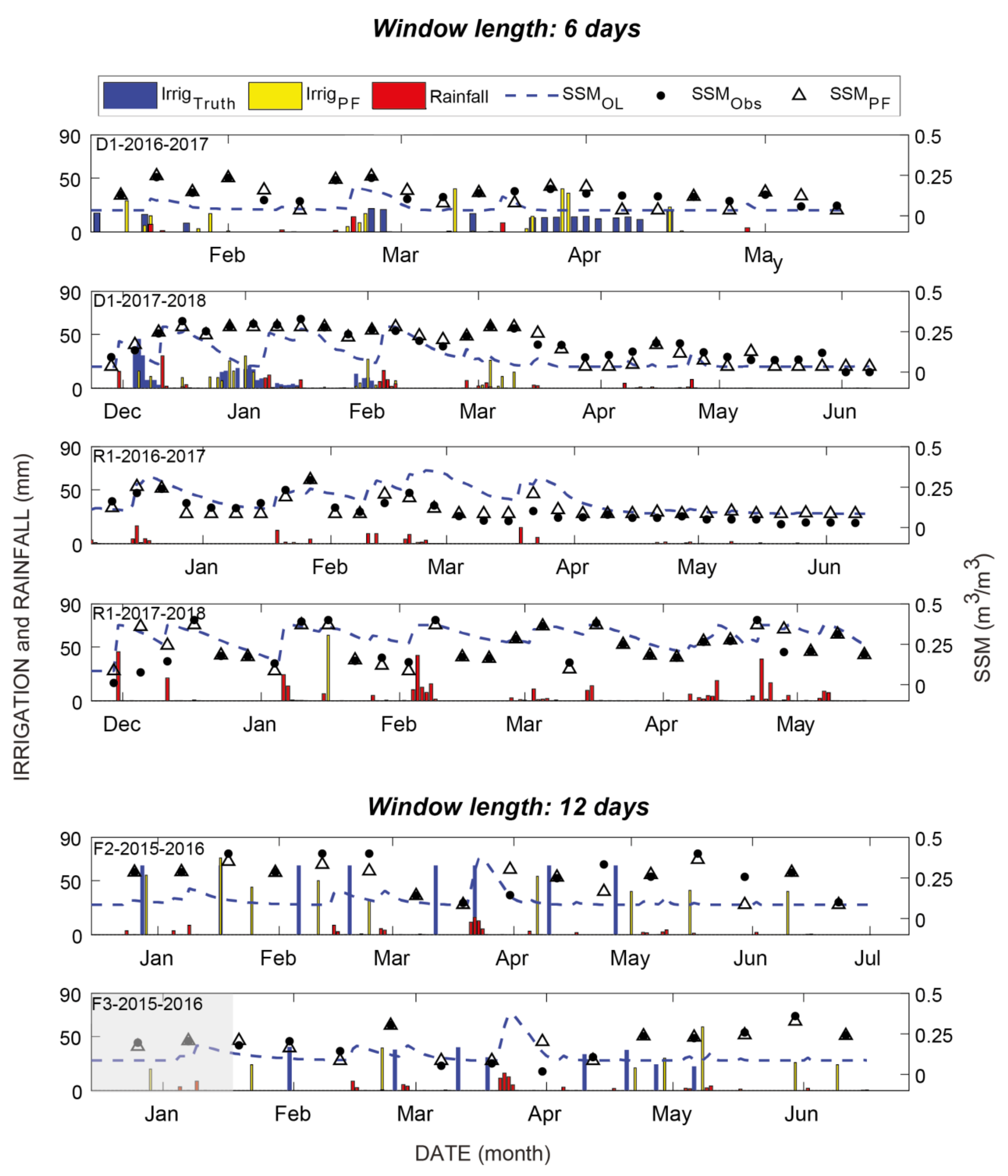
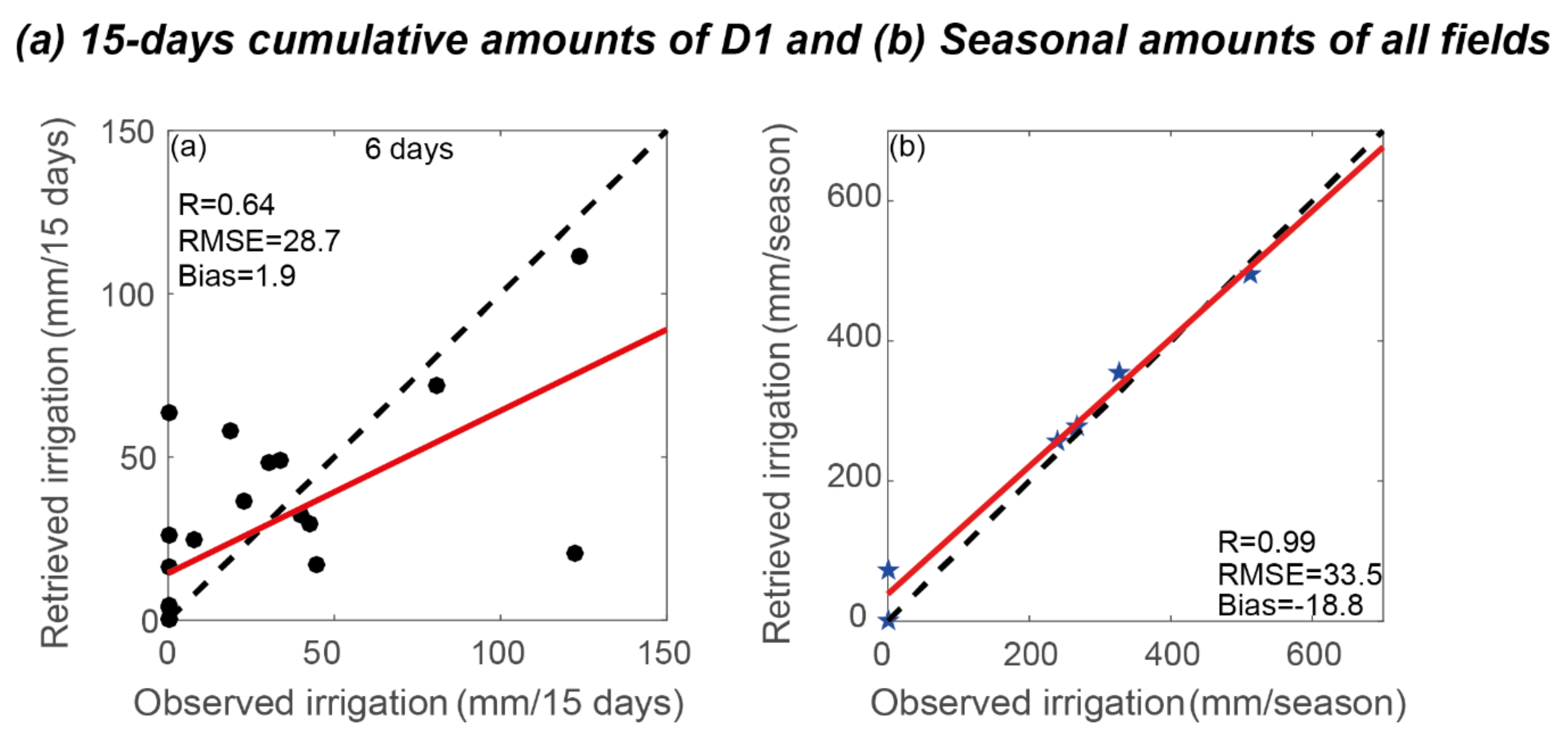
4.2. Assimilation of SSM In Situ Measurements
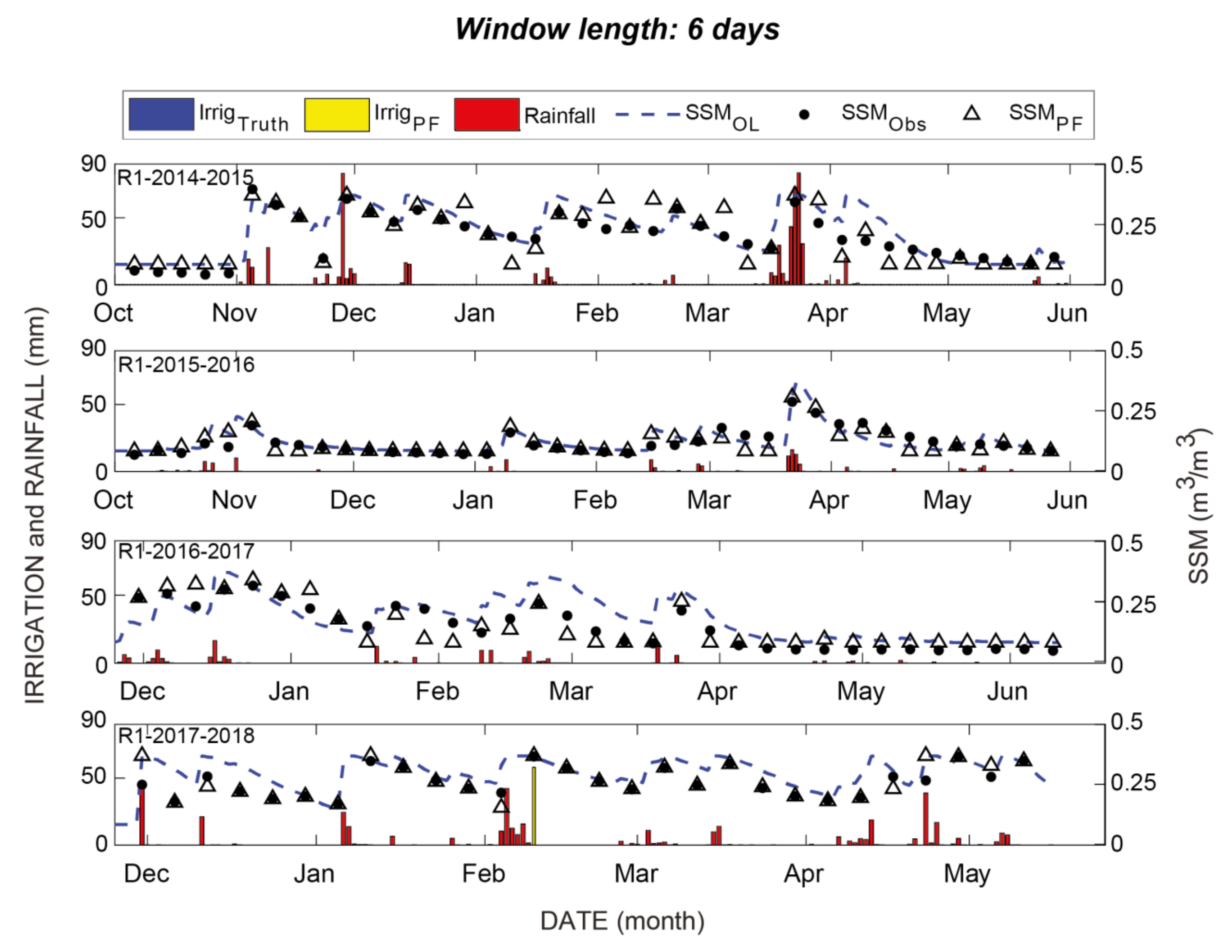
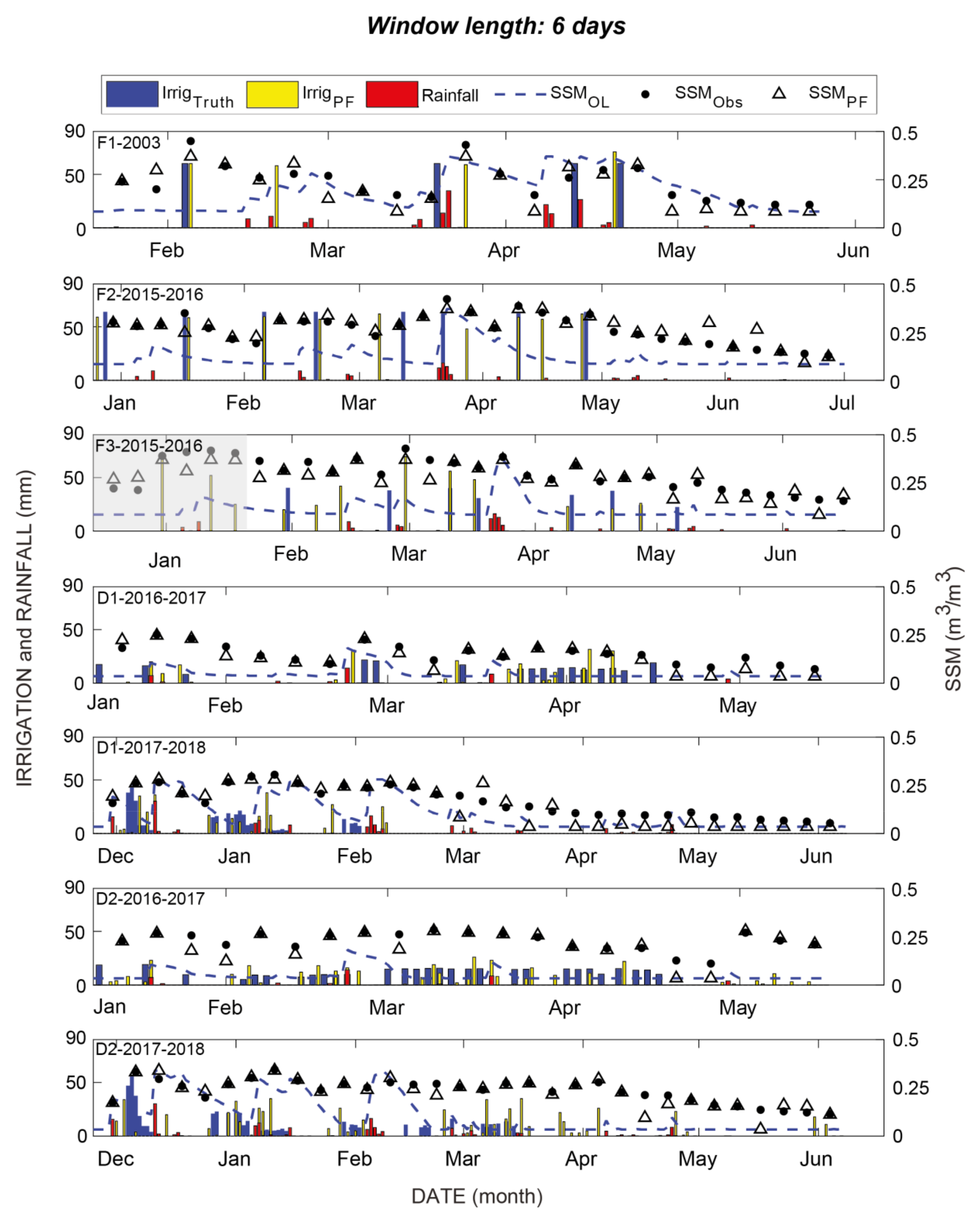
4.3. Assimilation of Sentinel-1 Derived SSM
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Field | Technique | Irrigation Period | Amount’s Range (mm) | Number of Events | Seasonal Amounts (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1-2016-2017 | Drip | Jan–Apr | 8–22 | 16 | 239.26 |
| D1-2017-2018 | Dec–Feb | 1.2–46 | 26 | 327.21 | |
| D2-2016-2017 | Jan–Apr | 7–19 | 29 | 373.02 | |
| D2-2017-2018 | Dec–Mar | 4–57 | 36 | 520.56 | |
| F1-2003 | Flood | Feb–Apr | 60 | 4 | 240 |
| F2-2015-2016 | Dec–Apr | 64 | 8 | 512 | |
| F3-2015-2016 | Jan–May | 23–50 | 8 | 267.48 |
| D1–D2 | F1–F3 | R1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| (m) | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| REW (mm) | 8 | 9 | 9 |
| (m3/m3) | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| (m3/m3) | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
References
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Xiao, C.; Xie, R.; Ming, B.; Hou, P.; Liu, G.; Xu, W.; Shen, D.; Wang, K.; et al. Optimizing water use efficiency and economic return of super high yield spring maize under drip irrigation and plastic mulching in arid areas of China. F. Crop. Res. 2017, 211, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H.; Cooley, H.; Cohen, M.J.; Morikawa, M.; Morrison, J.; Palaniappan, M. The World’s Water 2008–2009: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources. Environ. Conserv. 2009, 36, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Global Freshwater Resources: Soft-Path Solutions for the 21st Century. Science 2003, 302, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorosmarty, C.J.; Sahagian, D. Anthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle. Bioscience 2000, 50, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces-Restrepo, C.; Muñoz, G.; Vermillion, D. Irrigation Management Transfer: Worldwide Efforts and Results; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; López-Moreno, I.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lasanta-Martínez, T.; Beguería, S. Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Le Page, M.; Hanich, L.; Fakir, Y.; Merlin, O.; Mangiarotti, S.; Gascoin, S.; Ezzahar, J.; et al. Remote Sensing of Water Resources in Semi- Arid Mediterranean Areas: The joint international laboratory TREMA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4879–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Page, M.; Toumi, J.; Khabba, S.; Hagolle, O.; Tavernier, A.; Hakim Kharrou, M.; Er-Raki, S.; Huc, M.; Kasbani, M.; El Moutamanni, A.; et al. A life-size and near real-time test of irrigation scheduling with a sentinel-2 like time series (SPOT4-Take5) in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11182–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurr, R.; Litke, D. Estimating Pumping Time and Ground-Water Withdrawals Using Energy–Consumption Data; (Water–Resources Investigations Report 89-4107); Dept. of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Filippucci, P.; Tarpanelli, A.; Massari, C.; Serafini, A.; Strati, V.; Alberi, M.; Raptis, K.G.C.; Mantovani, F.; Brocca, L. Soil moisture as a potential variable for tracking and quantifying irrigation: A case study with proximal gamma-ray spectroscopy data. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 136, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deines, J.M.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W. Annual Irrigation Dynamics in the U.S. Northern high plains derived from landsat satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9350–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, A.K.; Wardlow, B.; Mishra, V. Remotely sensed high resolution irrigated area mapping in India for 2000 to 2015. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.; Prasad, S.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Oliphant, A.; Poehnelt, J.; Yadav, K.; Rao, M.; Massey, R. Spectral matching techniques (SMTs) and automated cropland classification algorithms (ACCAs) for mapping croplands of Australia using MODIS 250-m time-series (2000–2015) data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 944–977. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Luo, L.; Pokhrel, Y.; Deb, K.; Huang, J.; Ran, Y. Detecting irrigation extent, frequency, and timing in a heterogeneous arid agricultural region using MODIS time series, Landsat imagery, and ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Ma, M.; Liu, W.; Dong, J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, W. Mapping irrigated areas of northeast China in comparison to natural vegetation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Ezzahar, J.; Zribi, M.; Khabba, S.; Bouras, E.; Bousbih, S.; Frison, P. Monitoring of wheat crops using the backscattering coe ffi cient and the interferometric coherence derived from Sentinel-1 in semi-arid areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. Microwave Soil Moisture Research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, R.; Liu, J. Estimation of evapotranspiration and other soil water budget components in an irrigated agricultural field of a desert oasis, using soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 21, 4347–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Dorigo, W.; Zaussinger, F.; Gruber, A.; Fernández-Prieto, D. How much water is used for irrigation? A new approach exploiting coarse resolution satellite soil moisture products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaussinger, F.; Dorigo, W.; Gruber, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Brocca, L. Estimating irrigation water use over the contiguous United States by combining satellite and reanalysis soil moisture data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Santanello, J.A.; Reichle, R.H.; Draper, C.S.; Koster, R.D.; Nearing, G.; Jasinski, M.F. Evaluating the utility of satellite soil moisture retrievals over irrigated areas and the ability of land data assimilation methods to correct for unmodeled processes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4463–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbéteau, Y.; Merlin, O.; Balsamo, G.; Er-Raki, S.; Khabba, S.; Walker, J.P.; Jarlan, L.; Malbéteau, Y.; Merlin, O.; Balsamo, G.; et al. Toward a Surface Soil Moisture Product at High Spatiotemporal Resolution: Temporally Interpolated, Spatially Disaggregated SMOS Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Biradar, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Dheeravath, V.; Li, Y.; Velpuri, M.; Gumma, M.; Gangalakunta, O.R.P.; Turral, H.; Cai, X.; et al. Global irrigated area map (GIAM), derived from remote sensing, for the end of the last millennium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3679–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; Ienco, D.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Belhouchette, H.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Demarez, V. Mapping irrigated areas using Sentinel-1 time series in Catalonia, Spain. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Gao, Q.; Fanise, P. Soil moisture and irrigation mapping in a semi-arid region, based on the synergetic use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Segui, P.Q. Irrigation mapping using Sentinel-1 time series at field scale. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Brocca, L.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Morbidelli, R. Exploiting high-resolution remote sensing soil moisture to estimate irrigation water amounts over a Mediterranean region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, E.; Tajrishy, M.; Ghazi Zadeh Hashemi, S.A.; Brocca, L. Quantification of irrigation water using remote sensing of soil moisture in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolafia-Rosenzweig, R.; Livneh, B.; Small, E.E.; Kumar, S.V. Soil Moisture Data Assimilation to Estimate Irrigation Water Use. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 3670–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappa, L.; Schlaffer, S.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Nendel, C.; Zimmerman, B.; Dorigo, W. Detection and quantification of irrigation water amounts at 500 m using sentinel-1 surface soil moisture. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Freeman, V.; Cao, S.; Paulik, C.; Schaufler, S.; Stachl, T.; Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Ciabatta, L.; Brocca, L.; et al. Toward Global Soil Moisture Monitoring with Sentinel-1: Harnessing Assets and Overcoming Obstacles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, M.J.; Quintana-Seguí, P. Comparison of remote sensing and simulated soil moisture datasets in Mediterranean landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera-Guerra, L.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S. Irrigation retrieval from Landsat optical/thermal data integrated into a crop water balance model: A case study over winter wheat fields in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Gao, Q.; Mougenot, B. Potential of sentinel-1 radar data for the assessment of soil and cereal cover parameters. Sensors 2017, 17, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; Fayad, I.; Zribi, M.; Belhouchette, H.; Demarez, V. Near real-time irrigation detection at plot scale using sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Page, M.; Jarlan, L.; El Hajj, M.M.; Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Boone, A. Potential for the detection of irrigation events on maize plots using Sentinel-1 soil moisture products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Belaud, G.; Cheviron, B.; Courault, D.; Charron, F. Soil moisture retrieval over irrigated grassland using X-band SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements, Irrigation and Drain; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abourida, A.; Simonneaux, V.; Errouane, S.; Sighir, F.; Berjami, B.; Sgir, F. Estimation des volumes d’eau pompés dans la nappe pour l’irrigation (Plaine du Haouz, Marrakech, Maroc). Comparaison d’une méthode statistique et d’une méthode basée sur l’utilisation de données de télédétection. J. Water Sci. 2008, 21, 489–501. [Google Scholar]
- Belaqziz, S.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Jarlan, L.; Le Page, M.; Kharrou, M.H.; El Adnani, M.; Chehbouni, A. A new irrigation priority index based on remote sensing data for assessing the networks irrigation scheduling. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 119, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Ezzahar, J.; Khabba, S.; Le Dantec, V.; Rafi, Z.; Zribi, M.; Frison, P.-L. Water Stress Detection Over Irrigated Wheat Crops in Semi-Arid Areas using the Diurnal Differences of Sentinel-1 Backscatter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Mediterranean and Middle-East Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (M2GARSS), Tunis, Tunisia, 9–11 March 2020; pp. 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Hssaine, B.; Merlin, O.; Rafi, Z.; Ezzahar, J.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er-raki, S. Calibrating an evapotranspiration model using radiometric surface temperature, vegetation cover fraction and near-surface soil moisture data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 257, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, Z.; Merlin, O.; Le, V.; Khabba, S.; Mordelet, P.; Er-raki, S.; Amazirh, A.; Olivera-guerra, L.; Ait, B. Partitioning evapotranspiration of a drip-irrigated wheat crop: Inter- comparing eddy covariance- sap flow- lysimeter- and FAO-based methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzahar, J.; Ouaadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Elfarkh, J.; Aouade, G.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Chehbouni, A.; Jarlan, L. Evaluation of Backscattering Models and Support Vector Machine for the Retrieval of Bare Soil Moisture from Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Bazzi, H. Synergic use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 images for operational soil moisture mapping at high spatial resolution over agricultural areas. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Chahbi, A.; Shabou, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Duchemin, B.; Baghdadi, N.; Amri, R.; Chehbouni, A. Soil surface moisture estimation over a semi-arid region using ENVISAT ASAR radar data for soil evaporation evaluation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Su, Z. First assessment of Sentinel-1A data for surface soil moisture estimations using a coupled water cloud model and advanced integral equation model over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Pascual, D.V.; Dedieu, G. A multi-temporal and multi-spectral method to estimate aerosol optical thickness over land, for the atmospheric correction of FormoSat-2, LandSat, VENμS and Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hssaine, B.A.; Merlin, O.; Ezzahar, J.; Ojha, N.; Er-raki, S.; Khabba, S. An evapotranspiration model self-calibrated from remotely sensed surface soil moisture, land surface temperature and vegetation cover fraction: Application to disaggregated SMOS and MODIS data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 1781–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, A.; Jarlan, L.; Er-Raki, S.; Le Page, M.; Aouade, G.; Tavernier, A.; Boulet, G.; Ezzahar, J.; Merlin, O.; Khabba, S. Performance of the two-source energy budget (TSEB) model for the monitoring of evapotranspiration over irrigated annual crops in North Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, B.; Hadria, R.; Erraki, S.; Boulet, G.; Maisongrande, P.; Chehbouni, A.; Escadafal, R.; Ezzahar, J.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Kharrou, M.H.; et al. Monitoring wheat phenology and irrigation in Central Morocco: On the use of relationships between evapotranspiration, crops coefficients, leaf area index and remotely-sensed vegetation indices. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er-Raki, S.; Chehbouni, A.; Duchemin, B. Combining satellite remote sensing data with the FAO-56 dual approach for water use mapping in irrigated wheat fields of a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Morris, J.; Martin, E. Particle filters for state and parameter estimation in batch processes. J. Process Control 2005, 15, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Morris, J.; Martin, E. Particle filters for dynamic data rectification and process change detection. Fault Detect. Superv. Saf. Tech. Process. 2007, 1, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, P.J. Particle filtering in geophysical systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 4089–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.S.; Fletcher, S.J. Data assimilation in numerical weather prediction and sample applications. In Solar Energy Forecasting and Resource Assessment; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 319–355. ISBN 9780123971777. [Google Scholar]
- Yozevitch, R.; Ben-Moshe, B. Advanced Particle Filter Methods. In Heuristics and Hyper-Heuristics: Principles and Applications; BoD: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sircoulomb, V.; Hoblos, G.; Chafouk, H.; Ragot, J.; Sircoulomb, V.; Hoblos, G.; Chafouk, H.; Analysis, J.R. Analysis and Comparison of Nonlinear Filtering Methods; Advanced Control and Diagnosis Workshop: Nancy, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, A.; Wolinski, D.; Pettré, J.; Manocha, D. Realtime pedestrian tracking and prediction in dense crowds. In Group and Crowd Behavior for Computer Vision; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 391–415. ISBN 9780128092804. [Google Scholar]
- Arulampalam, M.S.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/nongaussian bayesian tracking. Bayesian Bounds Param. Estim. Nonlinear Filter. Track. 2007, 50, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervan, A.; Murphey, T. Algorithmic materials: Embedding computation within material properties for autonomy. In Robotic Systems and Autonomous Platforms; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 197–221. ISBN 9780081022603. [Google Scholar]
- Margulis, S.A.; Girotto, M.; Cortés, G.; Durand, M. A particle batch smoother approach to snow water equivalent estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1752–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losa, S.N.; Kivman, G.A.; Schro, J.; Wenzel, M. Sequential weak constraint parameter estimation in an ecosystem model. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 43, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fearnhead, P.; Papaspiliopoulos, O.; Roberts, G.O.; Stuart, A. Random-weight particle filtering of continuous time processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2010, 72, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, P.J.; Evensen, G. Data assimilation and inverse methods in terms of a probabilistic formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1996, 124, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; Johansen, A.M. A Tutorial on Particle Filtering and Smoothing: Fifteen Years Later; The Institute of Statistical Mathematics: Tokyo, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Douc, R.; Cappé, O.; Moulines, E. Comparison of resampling schemes for particle filtering. Int. Symp. Image Signal Process. Anal. 2005, 2005, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-gaussian Bayesian state estimation. IEE Proc. Part F Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, D.; Del Moral, P.; Lyons, T. Discrete Filtering Using Branching and Interacting Particle Systems. Markov Process. Relat. Fields 1999, 5, 293–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, G. Monte Carlo filter and smoother for non-gaussian nonlinear state space models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Chen, R. Blind deconvolution via sequential imputations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J.D.; Schön, T.B.; Gustafsson, F. On resampling algorithms for particle filters. NSSPW Nonlinear Stat. Signal Process. Work. 2006 2006, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicely, M.A.; Wells, B.E. Improved parallel resampling methods for particle filtering. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47593–47604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.; Clifford, P.; Fearnhead, P. Improved particle filter for nonlinear system state. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1999, 146, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.; Liu, J.S.; Wong, W.H. Sequential imputations and Bayesian missing data problems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T. Stochastic methods for sequential data assimilation in strongly nonlinear systems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2001, 129, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.E. Hidden Markov Models and the Variants. ESAIM Proc. Surv. 2015, 51, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Martinuzzi, J.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T. Performance metrics for soil moisture retrievals and application requirements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, G.; Albergel, C.; Al-Yaari, A.; Brocca, L.; Calvet, J.C.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.; Crow, W.; Dorigo, W.; et al. Validation practices for satellite soil moisture retrievals: What are (the) errors? Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 118061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ceos Database: Mission Summary—Sentinel-1 C. Available online: http://database.eohandbook.com/database/missionsummary.aspx?missionID=577 (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Hengl, T.; De Jesus, J.M.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. SoilGrids250m: Global gridded soil information based on machine learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Shangguan, W.; Wei, N.; Xin, Q.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, D.; Yan, F. A review of the global soil property maps for Earth system models. Soil 2019, 5, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Liu, P.; Mahanama, S.P.P.; Njoku, E.G.; Owe, M. Comparison and assimilation of global soil moisture retrievals from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for the Earth Observing System (AMSR-E) and the Scanning Multichannel Microwave Radiometer (SMMR). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Modanesi, S.; Dari, J.; Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, M.G.J.; Girotto, M.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Le Page, M.; Jarlan, L. A review of irrigation information retrievals from space and their utility for users. Remote Sens. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, K.; Wagner, W. Explaining Anomalies in SAR and Scatterometer Soil Moisture Retrievals from Dry Soils with Subsurface Scattering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jeu, R.A.M.; Wagner, W.; Holmes, T.R.H.; Dolman, A.J.; van de Giesen, N.C.; Friesen, J. Global soil moisture patterns observed by space borne microwave radiometers and scatterometers. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 3 Days | 6 Days | 12 Days | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.65 |
| RMSE (mm/15 days) | 23.6 | 24.8 | 27.1 |
| bias (mm/15 days) | 0.24 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| TruPosRat (4 Days) | TruPosRat (5 Days) | IrrigEvntRat | Pbias | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F4 | F5 | F4 | F5 | F4 | F5 | F4 | F5 |
| 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 1.15 | 1.09 | −3.14 | 3.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Ezzahar, J.; Le Page, M.; Merlin, O. Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142667
Ouaadi N, Jarlan L, Khabba S, Ezzahar J, Le Page M, Merlin O. Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142667
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuaadi, Nadia, Lionel Jarlan, Saïd Khabba, Jamal Ezzahar, Michel Le Page, and Olivier Merlin. 2021. "Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142667
APA StyleOuaadi, N., Jarlan, L., Khabba, S., Ezzahar, J., Le Page, M., & Merlin, O. (2021). Irrigation Amounts and Timing Retrieval through Data Assimilation of Surface Soil Moisture into the FAO-56 Approach in the South Mediterranean Region. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142667








