Abstract
Green development stands as an imperative pathway for China’s growth model. Enhancing green economic efficiency is crucial to maintaining sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin. The hierarchical governance structure of China’s economic development system inherently links competition among governments to potential impacts on the basin’s green economic efficiency, yet research in this area remains scarce. This study utilizes a panel data structured dataset containing both temporal and cross-sectional dimensions from nine provinces in the Yellow River Basin to investigate how tax competition among local governments affects green economic efficiency. The empirical results demonstrate that tax competition hinders green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, exhibiting spatial heterogeneity in its inhibitory effect. Specifically, the inhibitory effect on the middle reaches is approximately twice as significant as that observed on the upper reaches, while the inhibitory effect on the lower reaches is found to be facilitative. In addition, the upgrading of industrial structure and industrial agglomeration triggered by tax competition partially alleviate the inhibitory effect on green economic efficiency. Therefore, policymakers can promote the sustainable development of the Yellow River Basin by optimizing the tax system, implementing regional differentiation strategies, optimizing industrial layout, and promoting the development of green clusters.
1. Introduction
The Yellow River Basin serves as both an ecological barrier and an economic belt for China. However, industrialization has caused environmental pollution and ecological degradation in the Yellow River Basin. The fragility of the ecological environment and severe water pollution threaten the sustainable development of the overall economy [1]. In response to these challenges, the Chinese government has placed high importance on the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin, incorporating it into the national development strategy. The study area map for this paper is shown in Figure 1. According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the Yellow River Basin contributed 14% of China’s GDP in 2024. However, the total carbon emissions account for one-third of the national total, and the unit energy consumption is still 15.7% higher than the national average. Green economic practices now serve as a critical pathway to achieve sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin. These practices prioritize integrating environmental stewardship and resource efficiency into economic systems, fostering mutually reinforcing economic prosperity and ecological sustainability.
Figure 1.
Study area map of the Yellow River Basin.
Against the backdrop of fiscal decentralization, local governments have been granted more fiscal autonomy. Appropriate tax incentives often promote the green development of the economy [2,3]. However, a “race to the bottom” is prevalent among Chinese provinces [4], as local governments compete for tax revenue sources by relaxing environmental regulation, ultimately leading to environmental degradation [5]. Local governments, as the main drivers of regional economic development, play a significant role in the green transformation and sustainable development of the Yellow River Basin [6]. Particularly in the central and western regions of the basin, where the level of economic development is relatively low, local governments often tend to prioritize economic growth at the expense of the environment. This has undoubtedly hindered the improvement of green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Therefore, the in-depth analysis of tax competition’s impact mechanisms on green economic efficiency reveals the collaborative tensions and game-theoretic dynamics inherent in regional ecological governance. The findings can provide an empirical foundation for designing equitable ecological compensation mechanisms, facilitating a mutually reinforcing dynamic between economic growth and environmental conservation. Promoting green development in the Yellow River Basin holds crucial significance for China’s sustainable economic growth. It also offers valuable references for ecological initiatives in other major river basins worldwide.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 provides a literature review on local government tax competition and green economic efficiency. Section 3 offers a relevant theoretical analysis and proposes research hypotheses. Section 4 introduces the data sources, variables, and research model. Section 5 presents a detailed analysis of all empirical results. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the paper, draws conclusions, and proposes policy recommendations.
2. Literature Review
The “voting with their feet” theory pioneered by Tiebout reveals how resident migration patterns and local government interactions drive tax competition among jurisdictions through behavioral preference signaling [7]. Wu et al. posit that fiscal decentralization facilitates local governments’ public service investments in environmental governance [8]. Konisky contends that local governments incentivize environmental improvements to attract mobile factors who prefer high-quality environments [9], which tends to trigger a “race to the top” competition pattern. Furthermore, the intensity of competition among governments significantly impacts green technology innovation development through policy instruments and tax incentives [10]. Areas with stronger governance capacity exhibit enhanced green economic transformation efficiency. Recent research by Chen et al. highlights that under evolving political incentives prioritizing ecological performance, local governments increasingly focus on environmentally beneficial green technology innovation to boost sustainable development outcomes [11].
Numerous studies have demonstrated that tax competition distorts governmental environmental regulation implementation, significantly impacting green technology innovation and regional sustainable development [12,13]. While competition among governments drives rapid economic growth, it often results in the underprovision of public goods such as environmental protection [14]. Bierbrauer et al. argue that local governments engage in cutthroat tax competition to prevent talent outflow, ultimately eroding fiscal revenues and exacerbating environmental degradation [15]. Moreover, The Phan et al. and Cao et al. contend that competing jurisdictions frequently prioritize short-term economic gains by relaxing environmental regulations to attract investments, essentially trading ecological health for temporary growth [16,17]. This pattern creates a vicious cycle: lower environmental standards tend to attract polluting industries [18], intensifying environmental degradation. These short-sighted practices inevitably reduce public spending on environmental governance, creating a development imbalance wherein environmental infrastructure lags behind economic construction. Such systemic failures fundamentally undermine the efficiency of green production. Empirical evidence confirms that governments’ competition rivalry diminishes regional eco-efficiency, as localities sacrifice environmental quality for political advantages in competitive rankings [19]. Chinese scholars have echoed similar findings. Bai et al. argue that local governments frequently adopt lax environmental standards to attract investments for performance enhancement, often resulting in inefficient environmental policies and increased pollution [20]. Liu and Li examined tax competition’s environmental governance impacts, revealing that “destructive competition” in environmental regulation significantly degrades environmental quality [21]. Jiang demonstrates how fiscal revenue pressures exacerbate the “pollution effect” in governments’ competition [22]. Local authorities often employ industrial subsidies and tax incentives to attract enterprises, inadvertently intensifying urban pollution. Bai’s research further indicates that regional tax competition also deteriorates environmental quality in spatially connected regions [20]. In pursuing ecological conservation and high-quality development along the Yellow River Basin, local governments face dual imperatives. They must drive GDP growth to maximize economic returns while simultaneously implementing context-specific environmental policies. However, the “promotion tournament” system incentivizes officials to prioritize rapid economic growth over environmental oversight [23], constraining green innovation capacity in the basin [24]. This dilemma proves particularly pronounced in the basin’s less-developed central-western regions, where economic pressures often eclipse environmental priorities, hindering green transition and sustainable development.
The impact of tax competition among local governments on green economic efficiency exhibits regional heterogeneity. Qiao et al. reveal that the impact of green taxation on the efficiency of green innovation in industrial enterprises exhibits an inverted U-shaped curve, characterized by an initial enhancement followed by a subsequent suppression of performance [25]. Han Yancui’s research demonstrates distinct geographical disparities in fiscal decentralization’s influence—while exerting insignificant negative effects in western regions, it actively promotes green economic efficiency in central and eastern areas [26]. This dual nature manifests through two mechanisms. On one hand, central government evaluation systems drive local administrations to optimize resource allocation through foreign capital attraction, capital inflows, and innovation investments, potentially enhancing green efficiency. On the other hand, governments’ competition frequently distorts fiscal expenditure structures, exemplified by redundant infrastructure projects that undermine sustainable development. He et al. contextualize this paradox within an analytical framework incorporating tax competition, revenue decentralization, and environmental pollution [27]. Their findings highlight a critical east–west divergence: while eastern China’s tax competition demonstrates environmental benefits, central-western regions experience environmental degradation through similar competitive practices.
A review of the relevant literature reveals growing scholarly attention to the impacts of local governments’ competition on green development. These works have laid a solid foundation for our research. Most of the research mainly focuses on analyzing how local government behaviors impact environmental governance and green innovation. In contrast, studies exploring the influence of tax competition on green economic efficiency are relatively scarce. Particularly, studies specifically targeting the Yellow River Basin are even more limited in quantity. Existing studies on local governance behaviors regarding green economic transformation and environmental pollution provide valuable references for understanding this nexus. Building upon these foundations, this study contributes to the field in four key dimensions: (1) Methodologically, it integrates tax competition and green economic efficiency into a unified analytical framework. This approach examines their interaction in the Yellow River Basin context, addressing existing research gaps. (2) Constructing an indicator system from the “economic–social–environmental” dimensions and using the Super-SBM model that includes undesirable outputs to measure green economic efficiency in the basin. (3) Employing a mediation effect model to investigate the transmission mechanisms and pathways. (4) Considering the current development context of the Yellow River Basin, we propose targeted policy recommendations to steer local governments’ competition toward sustainable practices.
3. Research Hypotheses
Rational behavior assumptions suggest that local governments prioritize fiscal maximization strategies [28]. Local governments implement tax competition to enhance revenue streams. Their methodology focuses on incentives for enterprises to broaden the tax base [29], which is particularly critical in advancing the Yellow River Basin’s sustainable development agenda. Fiscal competition drives regional economic strategies. Many local governments aggressively cut tax rates while offering disproportionate tax incentives to attract enterprises. This pattern increasingly manifests as a systemic race to the bottom in public finance management [14]. Excessive tax competition disrupts fundamental market mechanisms. This phenomenon induces distorted resource allocation and redundant infrastructure development. These distortions systematically reduce resource utilization efficiency while hindering green economic efficiency improvements.
Tax competition among local governments carries significant social welfare implications. Governments might compromise labor protections to reduce operational costs for businesses, prioritizing investment attraction over worker rights. This regulatory erosion directly diminishes social welfare standards while creating systemic workforce vulnerabilities [30]. Furthermore, such competition exacerbates regional developmental disparities. Jurisdictions with weaker fiscal positions experience tax base shrinkage and stunted growth trajectories. Meanwhile, tax-advantaged regions accumulate disproportionate economic benefits, widening regional disparities [31]. These structural imbalances within the Yellow River Basin fundamentally constrain green economic efficiency optimization.
Tax competition among local governments exerts substantial ecological impacts across the Yellow River Basin. The Yellow River Basin faces multiple challenges, including water scarcity, fragile ecosystems, and relatively lagging economic development. Excessive tax competition among local governments drives policymakers to prioritize investment attraction through lowered environmental standards, relaxing entry requirements while weakening regulatory enforcement [16,17]. This dynamic creates conditions conducive to the rapid expansion of pollution-intensive industries [18]. The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis postulates an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic development and environmental degradation, where ecological damage initially intensifies before potential mitigation at higher income levels.
The upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin feature underdeveloped economies with limited industrialization, while maintaining notable agricultural and pastoral production sectors. Intense tax competition among local governments drives excessive natural resource extraction in the upper reaches. This overexploitation degrades local ecosystems while transmitting environmental pressures to the middle reaches and lower reaches, collectively constraining green economic efficiency improvements across the basin. The middle reaches, characterized by dense populations and significant agro-industrial output, face distinct risks. Under tax competition pressures, these areas develop excessive reliance on resource-dependent industries, prioritizing economic returns at the expense of ecological preservation. The lower reaches receive cumulative ecological impacts from upper basin activities. Pollution transmission mechanisms manifest through deteriorating water quality and compromised environmental sustainability, creating systemic barriers to a green transition. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 1:
Tax competition among local governments has a negative impact on green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin.
Petty–Clark’s Law states that labor shifts from primary and secondary industries to more advanced industries, driving continuous industrial structure upgrading [32]. Industrial structure restructuring also serves as a critical channel through which economic growth impacts the environment [33]. Studies confirm that industrial structure upgrading enhances regional green development by improving resource efficiency, reducing emissions, and stimulating green growth [34]. Collaboration and competition among firms further optimize industrial structures [35]. The manufacturing industry, especially, notably boosts green economic progress in the Yellow River Basin [36]. Tax competition among local governments exerts dual effects on industrial structure upgrading. On the one side, Ye et al. demonstrate that tax competition incentives lower production costs and encourage innovation, optimizing industrial layouts [37]. Fiscal decentralization also supports green industrial transitions [38]. On the other side, excessive tax competition attracts resources to identical industries, causing misallocation. Li and Mao showed that tax competition rationalizes structures through market interventions, but also aggravates the distortion of industrial structure [39]. Excessive tax competition accelerates low-end manufacturing, distorts industrial systems, and hinders green efficiency [40]. Accurately assessing how tax competition shapes industrial upgrading in the Yellow River Basin is vital for advancing regional sustainability.
New economic geography posits that industrial agglomeration can create external benefits, known as “agglomeration rents”. When a large number of enterprises cluster in a region, they can obtain agglomeration rents through knowledge and technology spillover effects, which serve as the driving force behind industrial agglomeration [41]. Many scholars argue that industrial agglomeration is an essential path for achieving green industrial development [42]. Acs and Varga argue that agglomeration enhances knowledge spillovers among firms, fostering green technological innovation [43]. Dense firm networks within clusters facilitate technical collaboration and joint R&D and provide critical innovation momentum for green transitions [44,45]. Cross-industry cooperation along supply chains further enables resource recycling and efficiency gains. However, Marshallian externalities theory warns that agglomeration effects may enter non-economic zones, triggering negative impacts [46]. Brülhart and Mathys demonstrate that industrial agglomeration exacerbates congestion and regional pollution [47]. Yang, using China’s provincial data, reveals an inverted U-shaped relationship between agglomeration and environmental pollution [48]. Local governments’ competition often fosters protectionism, reducing resource allocation efficiency [32]. Tax competition for enterprise resources leads to industrial spatial decentralization, undermining industrial synergies and economies of scale. Shi and Shen note that governments prioritize firm quantity and investment scale over inter-firm linkages, resulting in agglomerations with limited genuine technology spillovers [49]. In the Yellow River Basin, such competition risks industrial homogenization. Congestion effects from clustered low-end industries drive redundant construction and fragmented supply chains, lowering resource efficiency and impeding green economic progress.
Accordingly, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 2:
Tax competition among local governments impacts green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin through industrial structure upgrading.
Hypothesis 3:
Tax competition among local governments impacts green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin through industrial agglomeration.
The theoretical framework diagram of the mechanism of tax competition is shown in Figure 2.
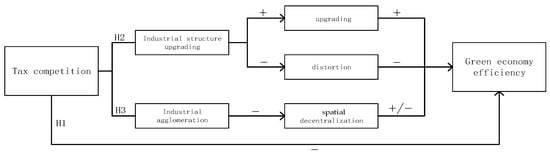
Figure 2.
Theoretical framework diagram of the mechanism of tax competition.
4. Research Design
4.1. Green Economic Efficiency Measurement
Green economic efficiency describes the process of achieving economic gains while minimizing resource consumption and environmental damage, thereby advancing sustainable development. As environmental challenges have escalated, the efficiency of the green economy has become the focus of academic circles. Current studies primarily examine two dimensions: determinant factors and measurement methodologies. In terms of determinant factors, technological progress [50,51], environmental regulation, and industrial structure upgrading have a positive impact on the efficiency of the green economy [52,53,54]. However, resource dependence [55], government intervention, and human capital mismatch have a negative effect on the efficiency of the green economy [10,56]. In addition, the relationship between economic growth and green economic efficiency presents an “inverted U-shaped” nonlinear relationship [57]. In measurement approaches, data envelopment analysis (DEA) remains predominant [58], though some studies employ stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) and other techniques [59]. However, with further research, traditional DEA models face limitations. The traditional DEA models fail to differentiate efficiency variations among fully efficient DMUs (those with efficiency scores of 1) and inadequately address slack issues associated with non-expected output. The super-efficiency SBM model has overcome the above shortcomings, and has been widely used in the evaluation of energy efficiency [60], ecological efficiency, and green economic efficiency [52,61].
In accordance with the principles of traditional economic efficiency, green economic efficiency comprehensively considers resource utilization and environmental loss, which is an important index reflecting the development level of the green economy. Referring to previous studies [62,63], this paper selects relevant variables from three dimensions of “economy, society, and environment”, and classifies them into input, expected output, and unexpected output. The super-efficiency stochastic block model (Super-SBM model) and Matlab R2021b software are used to calculate green economic efficiency. The Super-SBM model overcomes the disadvantage that the efficiency value of the traditional DEA model is limited between 0 and 1. When multiple decision units are effective, values can still be ranked and compared. The Super-SBM model can consider both expected output and unexpected output. It integrates undesirable outputs, including environmental pollutants, into green efficiency measurements. This method enhances the assessment precision of economic activity–environmental performance interdependencies. The Super-SBM model provides a holistic framework for evaluating regional performance in resource efficiency, pollution mitigation, and green transition efforts, offering an innovative methodological perspective for advancing sustainability assessments in these fields. is closely linked to the secondary sector, and data are more readily available. Referring to previous studies [62,64], emissions were chosen as the indicator instead of emissions. The index system is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Construction of the green economic efficiency index system.
The main formula of the Super-SBM model is as follows:
where n represents the number of provinces, and it equals nine in this paper; represents input; represents expected output; represents unexpected output; , , represent the slack variable of input, expected output, and unexpected output, respectively; represents the weight vector.
As demonstrated in Table 2, the findings concerning the green economic efficiency of the nine provinces and regions in the Yellow River Basin are measured. Overall, it shows an upward trend. However, it is evident that there are discernible regional variations. The green economic efficiency of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Qinghai Province, Shandong Province, and Henan Province has been consistently high. The green economic efficiency of Shanxi Province is suboptimal, and that of Shaanxi Province has instead declined.

Table 2.
The results of green economic efficiency measurement.
Based on administrative divisions, this paper categorizes the Yellow River Basin into the upper, middle, and lower reaches. Since the economic center of Henan Province is concentrated in the lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin, this study classifies Henan Province as part of the lower reaches. The upper reaches include five provincial-level regions: Qinghai Province, Sichuan Province, Gansu Province, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. The middle reaches comprise Shanxi Province and Shaanxi Province. The lower reaches encompass Henan Province and Shandong Province. The lower reaches have demonstrated strong performance due to their strategic geographic advantages, robust economic infrastructure, and advanced technological innovation capabilities. Similarly, the upper reaches benefit from favorable conditions. However, the middle reaches face persistent challenges in advancing green economy development. These challenges stem from three main issues: overdependence on heavy industry, inefficient use of resources, and significant ecological pressure [65,66]. Addressing these issues requires a coordinated approach to the development of the upper, middle, and lower reaches. The focus is on accelerating the green transformation of industries in the middle reaches and promoting balanced efficiency improvements across the basin.
4.2. Model Construction
Informed by a theoretical analysis examining how tax competition in the Yellow River Basin affects green economic efficiency, we developed a benchmark regression model to assess this relationship. Firstly, the Hausman test was used, and the test result was found to be p < 0.05. The original hypothesis was rejected, so a Two-way fixed effect model was used. In order to study the effect of tax competition on green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, the following fixed effect model was set up:
where stands for green economic efficiency in year t of region i and stands for the intensity of tax competition in year t of region i. represents the control variable. and stand for the individual fixed effect and the time fixed effect, respectively. is the random perturbation term. is the model intercept term. and represent the coefficients.
This study investigates the mediating roles of industrial agglomeration and industrial structure upgrading in shaping the transmission mechanism. To empirically test these pathways, we propose the following mediation model:
where refers to the industrial agglomeration level. and stand for the model intercept item. , , , , and stand for the coefficients. If tax competition in formula (3) has a significant impact on green economic efficiency, then formula (4) and formula (5) are returned. If and are significantly not 0, it indicates that local government tax competition has an impact on the efficiency of green economy in the Yellow River Basin through industrial agglomeration.
4.3. Description of Variables
4.3.1. The Explained Variable
Green economic efficiency (Gee) is the explained variable. The efficiency values measured by the Super-SBM model are adopted as proxy variables.
4.3.2. Core Explanatory Variable
The core explanatory variable is tax competition (Taxc). Following China’s tax-sharing reform, tax competition among local governments has emerged as a pivotal mechanism driving environmentally sustainable economic transformation. Tax competition intensity quantifies regional competitive pressures and tax incentive implementation. Referring to Liu and Li [21], this paper uses the ratio of provincial tax revenues to regional GDP to measure tax competition. Its formula is expressed as follows:
4.3.3. Mechanism Variables
(1) Industrial structure upgrading (Ins): Industrial structure upgrading drives regional economic restructuring and fosters long-term high-quality development. Given our focus on the Yellow River Basin’s transition from primary and secondary industries to tertiary sectors, this study employs the industrial structure hierarchy coefficient as the measurement metric [62,67]. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the proportion of value added by the i-th industry to the regional GDP. A higher value indicates a more optimized industrial structure, demonstrating a greater shift of the region’s industrial composition toward the tertiary sector.
(2) Industrial agglomeration (Ind): Industrial agglomeration can reflect the concentration of economic activities within a region, thereby influencing resource utilization efficiency and environmental benefits. Industrial agglomeration facilitates resource sharing and technological spillovers among firms, accelerating green technological innovation. These dynamics enhance green economic efficiency and support sustainable regional development. The existing literature proposes diverse metrics for measuring agglomeration. Referring to previous studies [14,42], this study adopts location entropy to quantify regional industrial agglomeration. Since the industrial structure of the Yellow River Basin is dominated by industry, and industrial activities have a greater impact on the environment, the value added of industry used in the calculation of industrial agglomeration can better reflect regional economic activities. This approach better reflects localized economic patterns while accounting for ecological implications. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the proportion of the industrial added value of the province i in year t to the local industrial added value of the nine provinces. represents the proportion of the GDP of province i in year t to the total GDP of the nine provinces.
A higher value of the location entropy indicates a higher level of industrial agglomeration in the Yellow River Basin. The larger the value of , the higher the level of industrial agglomeration in the Yellow River Basin.
4.3.4. Control Variables
Referring to previous studies and following a systematic assessment of key determinants influencing green economic efficiency and building upon established scholarly work [5,62,68], this study incorporates the following control variables:
(1) Environmental Regulation (Er): Environmental regulation can protect the environment by limiting pollution emissions, but it may also have short-term negative effects on economic development by increasing corporate costs. Green and sustainable economic development requires moderate regulation to ensure a harmonious balance between environmental protection and economic growth.
(2) Per Capita GDP (Pgdp): This metric serves as a composite indicator of regional economic capacity, resident welfare standards, and sustainable development potential.
(3) Industrialization Level (Il): The industrialization level reflects the degree of industrialization and modernization in a region. Excessive industrialization may lead to environmental pollution and resource consumption, affecting the progress of green economic development. The improvement of new industrialization levels promotes green economic efficiency.
(4) GDP Growth Rate (Growth): The GDP growth rate reflects the vitality of the regional economy. Sustained and stable economic expansion corresponds to healthy development patterns. Paradoxically, excessively high GDP growth rates may trigger detrimental consequences such as resource overexploitation and environmental degradation, ultimately impeding environmentally sustainable economic growth.
(5) Human Capital (Hc): Human capital includes workers’ knowledge, skills, and education levels, representing the quality and productivity of the labor force. Talent is a crucial factor in promoting technological innovation and industrial upgrading, and improving human capital levels is particularly important for driving green industrial transformation.
(6) Infrastructure Construction Level (ICL): Robust infrastructure systems constitute a critical foundation for socio-economic advancement. Well-developed infrastructure can enhance a region’s appeal and competitiveness, thereby attracting more talent and investment inflows.
The relevant variables and their descriptions are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Descriptions of related variables.
4.4. Data Source
This paper selects data from nine provinces (autonomous regions) in the Yellow River Basin between 2004 and 2022 as research samples. The analysis focuses on revealing the impact mechanism of tax competition among local governments on green economic efficiency in the basin. The nine provinces (autonomous regions) in the Yellow River Basin include the following: Shanxi Province, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Shandong Province, Henan Province, Sichuan Province, Shaanxi Province, Gansu Province, Qinghai Province, and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. The original data for the indicators were primarily sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook (2005–2023), the China Environmental Statistical Yearbook (2005–2023), the National Bureau of Statistics database, the Wind database, the CSMAR database, and relevant provincial statistical yearbooks. Missing data were supplemented using interpolation methods. Descriptive statistics for each variable are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics.
5. Results
5.1. Baseline Regression Results
This paper examines the direct impact of local government tax competition on the green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Based on Equation (1), the Two-way fixed effects model is employed, and the regression results are presented in Table 5. Column (1) includes only core variables, where the linear term coefficient of tax competition is −5.440, which is statistically significant at the 1% level with a negative sign. Column (2) incorporates control variables, and the tax competition coefficient remains significantly negative at −5.979 (1% significance level). These results indicate that local government tax competition exerts a significant inhibitory effect on the green economic efficiency of the Yellow River Basin. Hypothesis 1 is confirmed. Local governments prioritize tax incentives for energy-intensive industries to attract investment. This practice inadvertently stifles the growth of the green industry by diverting resources from sustainable sectors. Meanwhile, interjurisdictional tax competition often leads to weakened environmental regulations as localities vie for fiscal revenues. Such regulatory erosion directly undermines the Yellow River Basin’s transition toward eco-friendly development models, consequently constraining improvements in green economic productivity.

Table 5.
Baseline regression results.
5.2. Robustness Test
To verify the robustness of the finding that local government tax competition inhibits the green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, this paper adopts four methods: replacing the core explanatory variable, replacing the explained variable, lagging the explanatory variable by one period, and narrowing the sample interval. The regression analysis is conducted again, and the results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Robustness test results.
(1) Replacing the measurement method and recalculating the core explanatory variable: The tax competition intensity index is calculated as the ratio of the national average tax rate to a region’s effective tax rate, and its formula is expressed as follows:
In which represents the ratio of the total tax revenue of the nine provinces (regions) in the Yellow River Basin in year t to the sum of their regional GDP in the same year. represents the ratio of the tax revenue of province i in year t to its regional GDP. When a region offers more substantial tax incentives, the more intense the tax competition, the lower the actual tax rate in that region, and the higher the tax competition intensity index (Com); conversely, the smaller the index.
(2) Replacing the measurement method and recalculating the explained variable to ensure objective results: We employ a combined approach using the entropy method and Super-SBM model. Specifically, the entropy method is first applied to assign weights to three indicator categories in the green economic efficiency evaluation system: input metrics, desired output metrics, and undesired output metrics. This weighted framework then serves as the basis for recalculating green economic efficiency.
(3) Lagging the explanatory variable by one period: Since the impact of policy implementation tends to be lagged, the effect of tax competition on green economic efficiency may take some time to materialize. This study examines the explanatory variable lagged by one year to test whether tax competition precedes changes in green economic efficiency over time, thereby strengthening the inference of causality.
(4) Excluding the impact of the pandemic to enhance model robustness: It is imperative that the repercussions of the pandemic on economic activity be given due consideration. During this period, a sudden drop in industrial production led to abnormal fluctuations in economic and environmental indicators. It is evident that such movements are unrelated to tax competition mechanisms and are statistical artefacts of exogenous shocks. To eliminate the influence of the pandemic, the sample data from 2020 to 2022 are removed, and the regression is re-run.
The results from all four columns indicate that tax competition among local governments still has a significant negative impact on the green economic efficiency of the Yellow River Basin, further confirming that the baseline regression results are highly robust.
5.3. Endogeneity Test
Although robustness checks can mitigate potential endogeneity issues present in this study, they cannot entirely eliminate errors arising from omitted variables and other related problems. Moreover, the enhancement of green economic efficiency generates economic benefits while improving resource utilization and reducing environmental pollution. These combined benefits strengthen regional competitiveness, potentially altering local fiscal policymaking and intensifying tax competition among local governments. Therefore, there may be a bidirectional causal relationship between tax competition and the green economic efficiency of the Yellow River Basin. This study employs instrumental variables to strengthen the robustness of the baseline regression findings. The number of provincial-level administrative regions serves as an ideal instrument due to two key characteristics. First, it exhibits strong exogeneity. The number is easily observable and is not affected by the level of tax competition and economic conditions. Second, while it bears no direct causal link to green economic efficiency, it systematically correlates with tax competition among local governments. To address potential endogeneity, we construct an instrumental variable by interacting the number of provincial-level administrative regions with one-period lagged tax competition measures. Empirical validation is conducted through the two-stage least squares (2SLS) method. The results are presented in Table 7. The results indicate that the coefficient for tax competition remains consistent with the baseline regression estimates. Furthermore, the instrumental variables pass both the underidentification test and weak instrument test, demonstrating that potential endogeneity issues do not undermine the robustness of the estimation outcomes.

Table 7.
Endogeneity test results.
5.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
The analysis of green economic efficiency across the Yellow River Basin reveals distinct regional patterns: the middle reaches underperform compared to the upper and lower regions. As shown in Table 8, tax competition exerts spatially heterogeneous impacts. Columns (1)–(3) present the impacts of tax competition on green economic efficiency in the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin. The results indicate that tax competition in the upper reaches significantly inhibits green economic efficiency improvement. This inhibitory effect is notably stronger in the middle reaches, approximately twice that of the upper regions, likely due to the concentration of pollution-intensive and resource-dependent industries in these areas. In contrast, tax competition in the lower reaches demonstrates a positive effect on green economic efficiency, possibly attributable to the region’s advanced industrial structure and thriving emerging industries. The tax incentives in the lower reaches appear to effectively stimulate technological efficiency, thereby enhancing green economic performance. However, statistically insignificant results in the middle and lower reaches may stem from limited subregional sample sizes, reducing analytical power. These findings underscore the dual role of fiscal policies in balancing industrial growth and environmental sustainability across diverse economic landscapes.

Table 8.
Heterogeneity analysis results.
5.5. Mechanism Analysis
This paper further examines underlying mechanisms, with results presented in Table 9. Column (1) shows that tax competition among local governments suppresses green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, evidenced by a tax competition coefficient of −5.979. Columns (2)–(5) reveal that the inhibitory effect is partially masked through two mediating pathways.

Table 9.
Mechanism analysis results.
The first is industrial structure upgrading. Tax competition indirectly enhances green efficiency by promoting industrial structure upgrading (indirect effect: 1.534). The increased tax competition coefficient indicates that there is a suppression effect of industrial structure upgrading. Tax competition operates through targeted fiscal instruments, particularly tax reductions tailored for green industries and high-tech sectors. These preferential policies generate competitive pressures in factor markets, which subsequently compel resource-intensive industries to engage in technological innovation [69]. Ultimately, such market-driven mechanisms facilitate industrial transformation toward higher value-added activities with improved cost efficiency. However, this positive influence remains insufficient to offset the overall negative impact.
The second is industrial agglomeration. Tax competition improves green economic efficiency by restraining industrial agglomeration (indirect effect: 0.874). The increased tax competition coefficient indicates that there is a suppression effect of industrial agglomeration. Tax competition disrupts optimal industrial clustering, as firms prioritize tax havens over regions with mature industrial chains or resource advantages [70]. This leads to fragmented spatial distribution and weak agglomeration economies. Notably, the agglomeration of pollution-intensive industries in the Yellow River Basin may intensify environmental degradation, hindering the improvement of green economic efficiency. However, given the region’s heavy reliance on traditional industries, suppressing industrial clustering through tax competition generates limited environmental benefits. These benefits are dwarfed by the dominant efficiency-reducing effects of tax competition itself.
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Exploring the impact of tax competition on economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin could help realize the major national strategy of ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. This is of great theoretical significance and practical value in promoting the green and synergistic development of the Yellow River Basin as well as its long-term sustainable development. Similarly, it can also provide a reference for the sustainable development of other large river basins with similarities. This paper explores the impact of tax competition among local governments on green economic efficiency in the Yellow River Basin using panel data from nine provinces (regions) in the Yellow River Basin from 2004 to 2022. In addition, a robustness test, endogeneity test, heterogeneity analysis, and mechanism test are also conducted. The main findings are as follows: (1) Tax competition among local governments in the Yellow River Basin significantly inhibits the improvement of green economic efficiency. After the robustness test and endogeneity test, the above conclusions are reliable. (2) According to the analysis of green economic efficiency measurements across the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin, the lower reaches exhibit the highest green economic efficiency, and the middle reaches show the lowest efficiency. Heterogeneity analyses further reveal that tax competition has a more pronounced dampening effect on green economic efficiency in the middle reaches, about twice as much as it does in the upper reaches. However, tax competition promotes green economic efficiency in the lower reaches. (3) The upgrading of the industrial structure in the Yellow River Basin helps to promote green economic efficiency, while industrial agglomeration is not conducive to the promotion of green economic efficiency. The industrial agglomeration and structural upgrading triggered by tax competition partially offset the inhibitory effect of tax competition on green economic efficiency, but not enough to reverse the overall negative trend. Similarly, some major rivers in other countries or regions are experiencing the same trouble as the Yellow River Basin. Examples include the Rhine and the Mississippi [71,72]. We hope that our study will serve as a reference for other regions in similar situations.
Based on the above findings, this paper proposes the following policy recommendations: (1) The government should optimize the tax system in the Yellow River Basin. Local governments can implement green tax reforms and provide fiscal incentives to green industries to curb “competition to the bottom”. In addition, it is extremely important to strengthen the vertical financial supervision mechanism. The central government can establish a mechanism for assessing the environmental impact of tax policies, and incorporate environmental performance into the assessment system of local governments, so as to provide local governments with a clear direction for green development. (2) Implement differentiated strategies. In response to the low green economic efficiency as well as stronger inhibition in the middle reaches, a strategy of compensation and development can be adopted in parallel. First, a special ecological compensation system can be established according to the cost of pollution control and the need for green industry transformation. For example, enterprises can apply for compensation according to performance, such as the green patent growth rate and the comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste, which can provide a strong impetus for green development. Secondly, corresponding tax support policies can be formulated to provide advantages to different regions. (3) Optimize the industrial layout and promote the development of green industry clusters. Increase investment in infrastructure construction in industrial clusters, especially in green infrastructure, such as sewage treatment and clean energy supply, to support the green transformation of enterprises. In addition, local government cooperation can be strengthened to jointly promote the green development of industrial parks. Cross-regional green development alliances can institutionalize common sustainable development goals, coordinated policy frameworks, and technology exchange platforms to form industrial chains for resource recycling and green technology sharing.
Despite the contributions of the research in this paper, there are still some limitations that provide opportunities for future research. Firstly, due to the difficulty of sourcing the latest data for variables such as industrial wastewater emissions, the data for this paper are only available up to 2022. Future research could explore the identification of more appropriate variables to replace them. Secondly, the study utilized provincial data; future research could employ municipal data to generate more accurate and pertinent results. Furthermore, it is possible to explore the use of novel metrics for the assessment of green economic efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and X.S.; methodology, J.S.; software, Y.W.; formal analysis, X.S.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S., X.S. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, J.S.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Province Social Science Planning Research Project, grant number 24CGLJ12.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wohlfart, C.; Kuenzer, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Social–Ecological Challenges in the Yellow River Basin (China): A Review. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yao, Y.; Xu, K. Can Environmental Regulation Improve the Industrial Ecology Efficiency? Evidence from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Peng, X. The Unintended Energy Efficiency Gain from Tax Incentives for Investment: Micro-evidence from Quasi-natural Experiments in China. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2024, 28, 310–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Baskaran, A. Regional Economic Growth, Digital Economy and Tax Competition in China: Mechanism and Spatial Assessment. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2024, 1, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Lin, Z.-H.; Yang, P.-L. Decoding the Impact of Fiscal Decentralization on Urban Pollution Intensity in China: A Spatial Econometric Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, R.; He, S. How Does Technological Innovation Affect Carbon Emission Efficiency in the Yellow River Economic Belt: The Moderating Role of Government Support and Marketization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63864–63881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiebout, C.M. A Pure Theory of Local Expenditures. J. Political Econ. 1956, 64, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xu, N.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. Empowering Local Governments: How Environmental Fiscal Federalism Affects Greenhouse Gas Emissions in China? J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konisky, D.M. Regulatory Competition and Environmental Enforcement: Is There a Race to the Bottom? Am. J. Political Sci. 2007, 51, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Iqbal, W.; Ahmad, W.; Marie, M. Nexus between Government Spending’s and Green Economic Performance: Role of Green Finance and Structure Effect. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhong, K. Do Environmental Regulations of Carbon Emissions and Air Pollution Foster Green Technology Innovation: Evidence from China’s Prefecture-Level Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, X.; Hashmi, S.M.; Hu, H.; Wong, W.-K. Tax Competition, Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development: An Empirical Test Based on Spatial Durbin Model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 982159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.; Gong, F.; Zhu, K. Tax Competition among Local Governments: Evidence from the Spillovers of Location-Based Tax Incentives in China. China Econ. Rev. 2023, 82, 102077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lyu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Industrial Agglomeration Externalities, Local Governments’ Competition and Environmental Pollution: Evidence from Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierbrauer, F.; Brett, C.; Weymark, J.A. Strategic Nonlinear Income Tax Competition with Perfect Labor Mobility. Games Econom. Behav. 2013, 82, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Phan, C.; Jain, V.; Purnomo, E.P.; Islam, M.D.M.; Mughal, N.; Guerrero, J.W.G.; Ullah, S. Controlling Environmental Pollution: Dynamic Role of Fiscal Decentralization in CO2 Emission in Asian Economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65150–65159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ren, W.; Yue, L. Environmental Regulation and Carbon Emissions: New Mechanisms in Game Theory. Cities 2024, 149, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B.; Shadbegian, R.J. ‘Optimal’ Pollution Abatement—Whose Benefits Matter, and How Much? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2004, 47, 510–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.N.; Karmakar, A.K. Analytical Issues in Trade, Development and Finance: Essays in Honour of Biswajit Chatterjee; India Studies in Business and Economics; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; ISBN 978-81-322-1650-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Lu, J.; Li, S. Fiscal Pressure, Tax Competition and Environmental Pollution. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 73, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W. Environmental Pollution and Intergovernmental Tax Competition in China: Based on Spatial Panel Data Model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S. Air Pollution and Economic Growth under Local Government Competition: Evidence from China, 2007–2016. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Fu, J. Economic Growth, Environmental Sustainability and China Mayors’ Promotion. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. Impact of Environmental Regulation Intensity on Green Innovation Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. The Double Impact Effect of Green Taxation on the Green Innovation Efficiency of Industrial Enterprises. J. Financ. Dev. Res. 2020, 12, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y. Promoting Green Economy Efficiency through Fiscal Decentralization and Environmental Regulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 11675–11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, Y. Tax Competition, Revenue Decentralization and China’s Environmental Pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. The Influence of China’s Local Fiscal Revenue Targets on House Price Growth. Hous. Policy Debate 2023, 33, 699–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, L.; Lester, R.; Raghunandan, A. Tax Subsidy Disclosure and Local Economic Effects. J. Account. Res. 2025, 63, 547–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, X. Veto and Versatile: Understanding the Local Implementation of Environmental Policies in China. Local Gov. Stud. 2025, 51, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellofatto, A.A.; Besfamille, M. Tax Decentralization notwithstanding Regional Disparities. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 123, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Hao, Y.; Ikram, M.; Wu, H.; Akram, R.; Rauf, A. Assessment of the Public Acceptance and Utilization of Renewable Energy in Pakistan. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yang, Z.; Irfan, M.; Ding, C.J.; Hu, M.; Hu, J. Toward Low-carbon Sustainable Development: Exploring the Impact of Digital Economy Development and Industrial Restructuring. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 2159–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Feridun, M. The Impact of Growth, Energy and Financial Development on the Environment in China: A Cointegration Analysis. Energy Econ. 2011, 33, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Cen, Y. How Does Manufacturing Agglomeration Affect Green Economic Efficiency? Energy Econ. 2020, 92, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Gao, Y.; Dong, F.; Feng, Y. Research on the Spatial Spillover Effect of Industrial Agglomeration on the Economic Growth in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H. Impacts of Strengthening Competition Policy and Industrial Policy Transformation on Market Efficiency-The Analysis of the Efficient Market and Effective Government. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 1, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Cao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Sun, H. Fiscal Decentralization, Government Environmental Preference and Industrial Green Transformation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mao, J. Local Government’s Tax Competition, Industrial Structure Adjustment and Regional Green Development in China. Financ. Trade Econ. 2018, 39, 142–157. [Google Scholar]
- Gennaioli, N.; La Porta, R.; Lopez-de-Silanes, F.; Shleifer, A. Human Capital and Regional Development *. Q. J. Econ. 2013, 128, 105–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Increasing Returns and Economic Geography. J. Political Econ. 1991, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tong, L.; Mei, L. The Effect of Industrial Agglomeration on Green Development Efficiency in Northeast China since the Revitalization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acs, Z.J.; Varga, A. Entrepreneurship, Agglomeration and Technological Change. Small Bus Econ. 2005, 24, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Song, S.; Duan, R. Industrial Symbiotic Agglomeration and Green Economic Growth: A Spatial Difference-in-Differences Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Q. Effect of Green Technology Innovation on Green Total Factor Productivity in China: Evidence from Spatial Durbin Model Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.V. Marshall’s Scale Economies. J. Urban Econ. 2003, 53, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brülhart, M.; Mathys, N.A. Sectoral Agglomeration Economies in a Panel of European Regions. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2008, 38, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R. Whether Industrial Agglomeration Can Reduce Environmental Pollution or Not. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2015, 25, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Shen, K. Tax Competition, Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development: An Empirical Test Based on Spatial Durbin Model. Front. Public Health 2013, 6–18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H. Overall Optimization Model of Efficiency and Performance of Green Technology Innovation. Sustain. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2021, 30, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Rasool, Z.; Nazar, R.; Anser, M.K. Towards a Greener Future: How Green Technology Innovation and Energy Efficiency Are Transforming Sustainability. Energy 2024, 290, 129891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tang, M.; Chao, X.; Li, P. How Environmental Regulation Influences the Green Economy Efficiency of Resource-Based Cities: An Empirical Study from China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 27249–27276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Guo, Q.; Yu, C. Spatial Effect of Green Economic Efficiency in China from the Perspective of Informatization. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2023, 31, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, L. Green Economic Efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta: Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2019, 5, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Cao, M.; Han, Y.; Pan, Y.; Feng, Y. The Road to Inclusive Green Growth in China: Exploring the Impact of Digital-Real Economy Integration on Carbon Emission Efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Peng, L.; Fang, N. The Impact of Human Capital Misallocation on Green Economy Efficiency: Empirical Analysis of Chinese Urban Agglomerations. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Li, M.; Erum, N.; Hussain, A.; Xie, H.; Ud Din Khan, H.S. Revisiting Environmental Kuznets Curve in Relation to Economic Development and Energy Carbon Emission Efficiency: Evidence from Suzhou, China. Energies 2021, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Ye, B.; Qin, Q. A Novel Stochastic Semi-Parametric Frontier-Based Three-Stage DEA Window Model to Evaluate China’s Industrial Green Economic Efficiency. Energy Econ. 2023, 119, 106566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Fang, D.; Sun, L.; Luo, Q. Natural Resources Utilization Efficiency under the Influence of Green Technological Innovation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Mahendru, M.; Ma, X.; Rao, A.; Shang, Y. Impacts of Environmental Regulations on Green Economic Growth in China: New Guidelines Regarding Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency. Renew. Energy 2022, 187, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, N. Eco-Efficiency in China’s Loess Plateau Region and Its Influencing Factors: A Data Envelopment Analysis from Both Static and Dynamic Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, M. Did China’s Energy Consumption Permit Trading Scheme Improve Green Economic Efficiency? Prefecture-Level Evidence from China. Energy 2024, 308, 132744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Yang, B.; Quan, T.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y. Internet Development and Green Economic Efficiency in China: A New Perspective of Government’s Dual Goal Constraints and Citizens’ Green Lifestyle. J. Int. Dev. 2024, 36, 2844–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, R.; Duan, H.; Jiang, P. A Comparative Study of Green Growth Efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin between 2010 and 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, G.; Feng, H. The Logic and Practice of Digital High-end Enabling the Green Development of the Manufacturing Industry: Exploratory Case Study on the Multiple Heterogeneity of the Yellow River Basin. J. Manag. 2024, 37, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Li, X.; Fu, Y. Coupling Coordination Analysis and Obstacle Factors of Water-Energy-Environment-Economy in the Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shao, X.; Liu, W.; Kong, J.; Zuo, G. The Impact of the Pilot Program on Industrial Structure Upgrading in Low-Carbon Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Zhang, H.; Quan, T.; Yu, Y. China’s Agricultural Land Transfer: Carbon Emissions Driver or Opportunity? The Pivotal Role of Rural Human Capital Revealed. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1480636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Hao, Y. Echoes of Dependency: The Impact of Resource Reliance on Green Industry Transformation in China. Resour. Policy 2024, 96, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.; De Mooij, R.; Liu, L. International Corporate Tax Avoidance: A Review of the Channels, Magnitudes, and Blind Spots. J. Econ. Surv. 2020, 34, 660–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenten, T.; Dieperink, C. Governance Conditions for a Successful Restoration of Riverine Ecosystems, Lessons from the Rhine River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Xu, Y.J.; Keim, B.D.; Brown, V.M.; Giosan, L.; Mann, M.E.; Stephens, J.R. Emerging Climate Threats to the Mississippi River Delta: Moving from Restoration to Adaptation. One Earth 2024, 7, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).