A Systematic Literature Review—AI-Enabled Textile Waste Sorting
Abstract
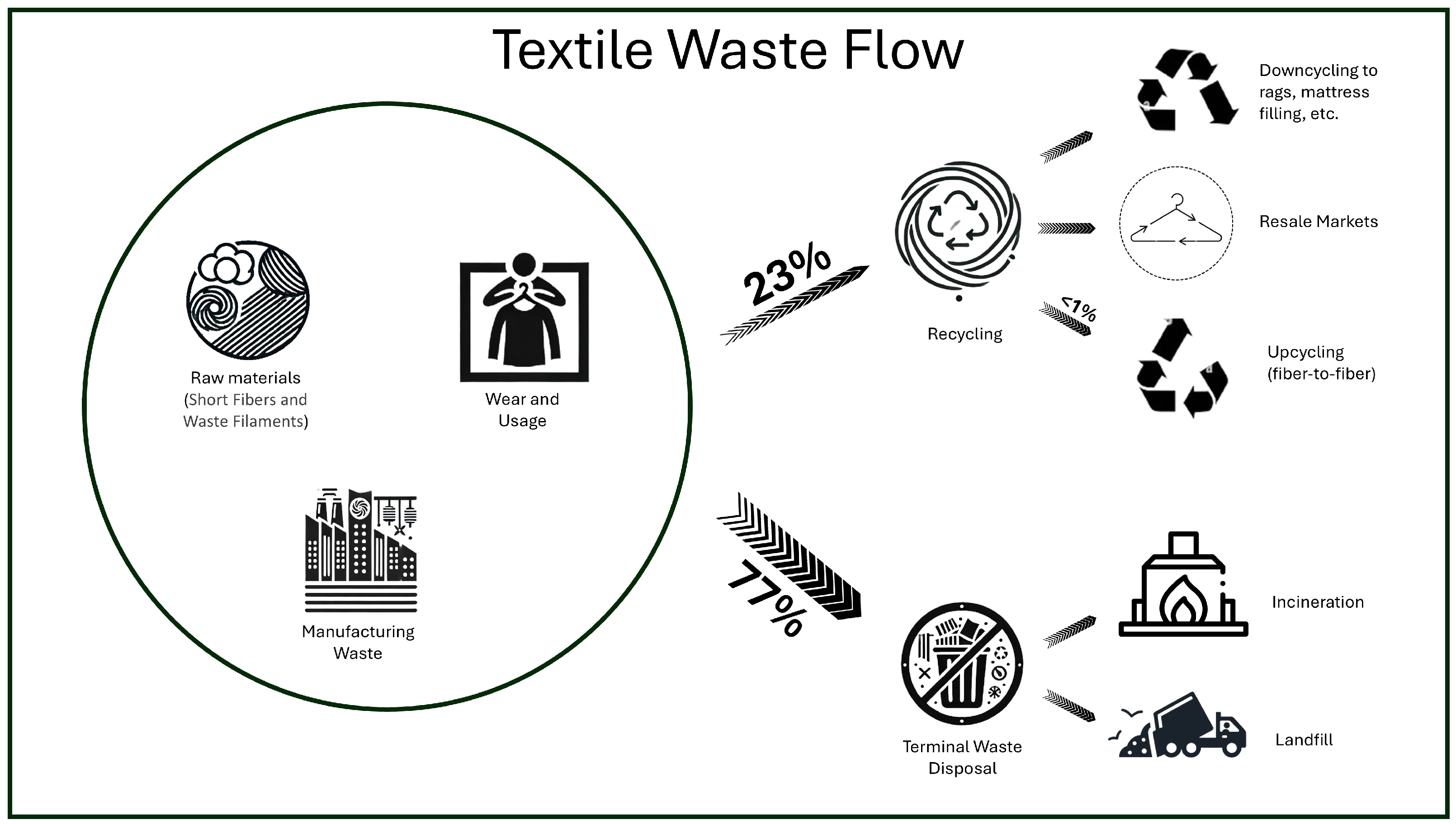
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Search
2.3. Appraisal
2.4. Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Data Input Method
3.1.1. Spectroscopy-Based Methods
3.1.2. Imaging Methods
3.1.3. Hyperspectral Imaging Method
3.2. Computer-Based Data Analysis Techniques
3.3. Metadata
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PSALSAR | Protocol, Search, Appraisal, Synthesis, Analysis, and Reporting |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| CE | Circular Economy |
| SLR | Systematic Literature Review |
| DOI | Digital Object Identifier |
| Q1-4 | Journal Quality Quartiles |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| CV | Computer Vision |
| SWIR | Short-Wave Infrared |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| HSI | Hyperspectral Imaging |
| NIR | Near-Infrared spectroscopy |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| kNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| CVA | Canonical Variate Analysis |
| Tr-Net | Textile Recycling Net |
| BP-ANN | Backpropagation Artificial Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| PNN | Probabilistic Neural Network |
| EPO | External Parameter Orthogonalization |
| 1D-CNN | One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network |
| 1D-Inception-CNN | One-Dimensional Inception-based Convolutional Neural Network |
| SPA | Successive Projections Algorithm |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| PhC Fibers | Photonic Crystal Fibers |
| PMMA | Polymethyl Methacrylate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| FDTD | Finite-Difference Time-Domain |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| RAL | Reichs-Ausschuss für Lieferbedingungen |
| SNV | Standard Normal Variate |
| k-means | K-means clustering |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| GS | Google Scholar |
References
- Sustainability. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/academic-impact/sustainability#:~:text=In%201987%2C%20the%20United%20Nations,development%20needs%2C%20but%20with%20the (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Song, K.; Ding, X.; Wu, X. Environmental sustainability of textiles and apparel: A review of evaluation methods. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, B. Textile Industry 4.0: A review of sustainability in manufacturing. Int. J. New Media Stud. 2023, 10, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelze, N. Sustainable supply chain management implementation–enablers and barriers in the textile industry. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanto, B.; Primiana, I.; Sarasi, V.; Satyakti, Y. Sustainability innovation in the textile industry: A systematic review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hachmann, J.; Iezzi, B.; Tsianou, M.; Velarde, L. Advancing the Recycling of Textiles via Efficient Sorting and Molecular Upcycling; REMADE Institute: West Henrietta, NY, USA, 2024; Available online: https://remadeinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/69_Recycling-Textiles_Alexandridis.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Tsai, P.F.; Yuan, S.M. Using Infrared Raman Spectroscopy with Machine Learning and Deep Learning as an Automatic Textile-Sorting Technology for Waste Textiles. Sensors 2025, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Acierno, D. Towards the sustainability of the plastic industry through biopolymers: Properties and potential applications to the textiles world. Polymers 2022, 14, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, K.; Aksu, İ.Ö.; Göçken, M.; Demirdelen, T. Sustainable Textile Manufacturing with Revolutionizing Textile Dyeing: Deep Learning-Based, for Energy Efficiency and Environmental-Impact Reduction, Pioneering Green Practices for a Sustainable Future. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensupa, N.; Leu, S.Y.; Hu, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, H.; Jing, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.S.K. Recent trends in sustainable textile waste recycling methods: Current situation and future prospects. In Chemistry and Chemical Technologies in Waste Valorization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 189–228. [Google Scholar]
- European Protection Agency. Facts and Figures About Materials, Waste and Recycling. 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/facts-and-figures-about-materials-waste-and-recycling/textiles-material-specific-data (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Sivaram, N.; Gopal, P.; Barik, D. Toxic waste from textile industries. In Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, S.; Sandin, G.; Zamani, B.; Peters, G. Environmental assessment of Swedish fashion consumption. In Five Garments—Sustainable Futures; Mistra Future Fashion: Stockholms Lan, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Environmental Agency. Textiles in Europe’s Circular Economy. 2023. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/textiles-in-europes-circular-economy/textiles-in-europe-s-circular-economy (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. A New Textiles Economy: Redesigning Fashion’s Future; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Cowes, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/publications/a-new-textiles-economy-redesigning-fashions-future (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Baloyi, R.B.; Gbadeyan, O.J.; Sithole, B.; Chunilall, V. Recent advances in recycling technologies for waste textile fabrics: A review. Text. Res. J. 2024, 94, 508–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanga-Labayen, J.P.; Labayen, I.V.; Yuan, Q. A review on textile recycling practices and challenges. Textiles 2022, 2, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, G.; Hole, A.S. Recycling as the way to greener production: A mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudisch, K.; Jüngling, S.; Carrillo Mendoza, R.; Woggon, U.K.; Budde, I.; Malzacher, M.; Pufahl, K. Paving the road to a circular textile economy with AI. In Proceedings of the INFORMATIK 2021, Gesellschaft für Informatik, Bonn, Germany, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Spyridis, Y.; Argyriou, V.; Sarigiannidis, A.; Radoglou, P.; Sarigiannidis, P. Autonomous AI-enabled Industrial Sorting Pipeline for Advanced Textile Recycling. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 29 April–1 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Han, X. Efficient recognition and automatic sorting technology of waste textiles based on online near infrared spectroscopy and convolutional neural network. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank. 2024. Available online: https://www.scimagojr.com/ (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Wu, T.W.; He, P.J.; Lan, D.Y.; Lu, F.; Long, J.S.; Zhang, H. Application of XGBoost for fast identification of typical industrial organic waste samples with near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. ACS ES&T Eng. 2023, 3, 841–850. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Sun, L.; Zhu, R.; Gao, S.; Ma, B.; Gao, T.; He, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, X. Comprehensive Analysis of the Preparation of Regenerated ε-Caprolactam Based on Solvent-Free Alkali-Catalyzed Depolymerization of Colored Waste Polyamide 6/Polyurethane Blended Textiles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 8482–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncu, M.; Özdemir, H. Optical coherence tomography imaging can identify Merino lambs’ wool using automatic machine learning vision. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 4611–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, H.; Ngo, H.Q.T. Toward a sustainable transition in automated production: Enabling the vision-based approach and synchronous control for textile surface inspection systems. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 5391–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Wang, N. Landfill Waste Segregation Using Transfer and Ensemble Machine Learning: A Convolutional Neural Network Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwais, N.; Alabdulkreem, E.; Mahmood, K.; Marzouk, R.; Assiri, M.; Abdelmageed, A.A.; Abdelbagi, S.; Drar, S. Hybrid mutation moth flame optimization with deep learning-based smart fabric defect detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seçkin, M.; Seçkin, A.Ç.; Demircioglu, P.; Bogrekci, I. FabricNET: A microscopic image dataset of woven fabrics for predicting texture and weaving parameters through machine learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengstermann, M.; Hasan, M.M.B.; Scheffler, C.; Abdkader, A.; Cherif, C. Development of a new hybrid yarn construction from recycled carbon fibres for high-performance composites: Part III: Influence of sizing on textile processing and composite properties. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2021, 34, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Chen, Y. Deep learning for demand forecasting in the fashion and apparel retail industry. Forecasting 2022, 4, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, M.A.; Repon, M.R.; Jurkonienė, S.; Haji, A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Shukhratov, S. Valorization of pineapple leaves: Effective conversion of agro waste to textile materials. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, K.R.; Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Belal, M.A.; Pakawanit, P.; Vittayakorn, N.; Bowen, C.; Khanbareh, H.; Kim, H.J. Triboelectrification Based on the Waste Waterproof Textiles for Multisource Energy Harvesting. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024; Early View. [Google Scholar]
- Kronberg, S.; Baghaei, B. Transforming Polycotton Textile Waste into New Bicomponent Fibers: An Investigative Study. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2024, 2024, 5239028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarreta-Andrés, J.; Melià-Seguí, J.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Vilajosana, X.; Sarma, S.E. Toward low-cost RF-Based bulk fabric classification for the textile industry. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 16586–16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukovska-Popovska, I.; Ivert, L.K.; Jónsdóttir, H.; Dreyer, H.C.; Kaipia, R. The supply and demand balance of recyclable textiles in the Nordic countries. Waste Manag. 2023, 159, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkka, V.; Aminoff, A.; Palmgren, R.; Heikkilä, P.; Harlin, A. Investigating postponement and speculation approaches to the end-of-life textile supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulou-Kalkavoura, V.; Fijoł, N.; Lombardo, S.; Ruiz-Caldas, M.X.; Mathew, A.P. In Situ Functionalisation and Upcycling of Post-Consumer Textile Blends into 3D Printable Nanocomposite Filaments. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 8, 2400132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, H.M.; Bai, C.; Zaman, S.I.; Quayson, M.; Garcia, C. Enabling the Integration of Industry 4.0 and Sustainable Supply Chain Management in the Textile Industry: A Framework and Evaluation Approach. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 14704–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Rehman, M.; Baffo, I. Digital and Sustainable Transition in Textile Industry through Internet of Things Technologies: A Pakistani Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Kang, Y.T.; Yang, S.G.; Zhao, W.B.; Kang, Y.S.; Im, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Do Noh, S. Cyber physical energy system for saving energy of the dyeing process with industrial internet of things and manufacturing big data. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2020, 7, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhi, C.; Guo, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Sun, R.; Dong, Z.; Yu, L. ChatGPT for textile science and materials: A perspective. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hua, T. Antibacterial, scalable manufacturing, skin-attachable, and eco-friendly fabric triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13356–13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Rahman, S.; Habib, M.A.B.; Tanjil, M. A sustainable approach to utilize an agro-based weedy plant “Urena lobata” in blend yarn manufacturing in short-staple ring spinning. Cellulose 2023, 30, 9815–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.; Akinlabi, S.; Jen, T.C.; Dunmade, I. A machine learning approach for investigating the impact of seasonal variation on physical composition of municipal solid waste. J. Reliab. Intell. Environ. 2023, 9, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soekoco, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Fauzi, A.; Tasya, H.; Diandra, P.; Tasa, I.; Yuliarto, B. Fabrication of Recycled Polycarbonate Fibre for Thermal Signature Reduction in Camouflage Textiles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.B.; Rocha, M.C.G.; de Andrade, M.C.; Junior, F.L.S.; Peripolli, S.B.; de Campos, J.B. Effect of reduced graphene oxide on thermal property of recycled textile polyamide. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3941–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.; Smith, P.; Frame, P.; Jones, K.; Qiang, Z. Direct Upcycling of Woven Polypropylene Fabrics to Carbon-Based Joule Heaters. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 8, 2300332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, K.; Buldu, A.; Demetgul, M. A thermal-based defect classification method in textile fabrics with K-nearest neighbor algorithm. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 45, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machnowski, W.; Wąs-Gubała, J. Evaluation of selected thermal changes in textile materials arising in the wake of the impact of heat radiation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, F.; Lavasani, M.R.B. Improvement of the mechanical and thermal properties of polyester nonwoven fabrics by PTFE coating. Turk. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. State of the art in textile waste management: A review. Textiles 2023, 3, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Wei, Z. Qualitative classification of waste textiles based on near infrared spectroscopy and the convolutional network. Text. Res. J. 2020, 90, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.R.; Cantero, R.; Canals, T.; Puig, R. Circular economy of post-consumer textile waste: Classification through infrared spectroscopy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cura, K.; Rintala, N.; Kamppuri, T.; Saarimäki, E.; Heikkilä, P. Textile recognition and sorting for recycling at an automated line using near infrared spectroscopy. Recycling 2021, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S. Qualitative identification of waste textiles based on near-infrared spectroscopy and the back propagation artificial neural network. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.R.; Cantero, R.; Riba-Mosoll, P.; Puig, R. Post-consumer textile waste classification through near-infrared spectroscopy, using an advanced deep learning approach. Polymers 2022, 14, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.P.; He, P.J.; Lan, D.Y.; Xian, H.Y.; Lü, F.; Zhang, H. Rapid determination of moisture content of multi-source solid waste using ATR-FTIR and multiple machine learning methods. Waste Manag. 2022, 153, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Gong, Y. Moisture insensitive analysis of polyester/viscose waste textiles using Near-Infrared spectroscopy and Orthogonalization of external parameters algorithm. J. Ind. Text. 2023, 53, 15280837231187671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, B.; Coon, A.; Cantley, L.; Perkins, B.; Doran, E.; Wang, T.; Rothschild, M.; Shtein, M. Polymeric Photonic Crystal Fibers for Textile Tracing and Sorting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.A.; Zhao, H.; Gattrell, M.; Lockhart, J.; Cranston, E.D. Identification of common textile microplastics via autofluorescence spectroscopy coupled with k-means cluster analysis. Analyst 2024, 149, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, G.; Gasbarrone, R.; Palmieri, R.; Serranti, S. A characterization approach for end-of-life textile recovery based on short-wave infrared spectroscopy. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Fu, C.C. Applying image processing to the textile grading of fleece based on pilling assessment. Fibers 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.T.; Ho, D.D.; Nguyen, H.N. An approach for designing an optimal CNN model based on auto-tuning GA with 2D chromosome for defect detection and classification. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Jeong, J. Design and implementation of machine vision-based quality inspection system in mask manufacturing process. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogar, M.; Petrak, S.; Mahnić Naglić, M. Digital Technologies in the Sustainable Design and Development of Textiles and Clothing—A Literature Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.K. Recycled clothing classification system using intelligent IoT and deep learning with AlexNet. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 5544784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furferi, R.; Servi, M. A machine vision-based algorithm for color classification of recycled wool fabrics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Lv, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.; Xu, Z. Qualitative classification of waste garments for textile recycling based on machine vision and attention mechanisms. Waste Manag. 2024, 183, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Khan, H.S.; Yousaf, A.; Khurshid, K.; Abbas, A. Modern trends in hyperspectral image analysis: A review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 14118–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B. Hyperspectral imaging in medical applications. In Data Handling in Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 32, pp. 523–565. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, L.M.; Thewis, A.; Boudry, C.; Rotar, I.; Dardenne, P.; Baeten, V.; Pierna, J.A.F. Hyperspectral imaging applications in agriculture and agro-food product quality and safety control: A review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 48, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Rissanen, M.; Sixta, H. Machine vision estimates the polyester content in recyclable waste textiles. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, H.; Lv, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Non-destructive detection and classification of textile fibres based on hyperspectral imaging and 1D-CNN. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1224, 340238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, G.; Gasbarrone, R.; Palmieri, R.; Serranti, S. End-of-life textile recognition in a circular economy perspective: A methodological approach based on near infrared spectroscopy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waste Management. Waste Management Home Page. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/waste-management (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Textile Research Journal. Textile Research Journal Home Page. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/home/trj (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Resources, Conservation and Recycling. Resources, Conservation and Recycling Home Page. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/resources-conservation-and-recycling (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- MDPI. Sustainability Journal. 2024. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- MDPI. Sensors Journal. 2024. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience Home Page. Available online: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.prox.lib.ncsu.edu/journal/8483 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Polymers. Polymers Home Page. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/polymers (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Journal of Cleaner Production. Journal of Cleaner Production Home Page. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-cleaner-production (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Journal of Industrial Textiles. Journal of Industrial Textiles Home Page. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/home/jit (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Analyst. Analyst Home Page. Available online: https://www.rsc.org/journals-books-databases/about-journals/analyst/ (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Advanced Materials Technologies. Advanced Materials Technologies Home Page. Available online: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/2365709X#pane-01cbe741-499a-4611-874e-1061f1f4679e01 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Analytica Chimica Acta. Analytica Chimica Acta Home Page. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/analytica-chimica-acta (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Applied Sciences. Applied Sciences Home Page. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/applsci (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Recycling. Recycling Home Page. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/recycling (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Waste and Biomass Valorization. Waste and Biomass Valorization Home Page. Available online: https://link.springer.com/journal/12649 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Exchange, T. Materials Market Report. 2024. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/knowledge-center/reports/materials-market-report-2024/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Babaarslan, O.; Shahid, M.A.; Okyay, N. Investigation of the performance of cotton/polyester blend in different yarn structures. AUTEX Res. J. 2023, 23, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
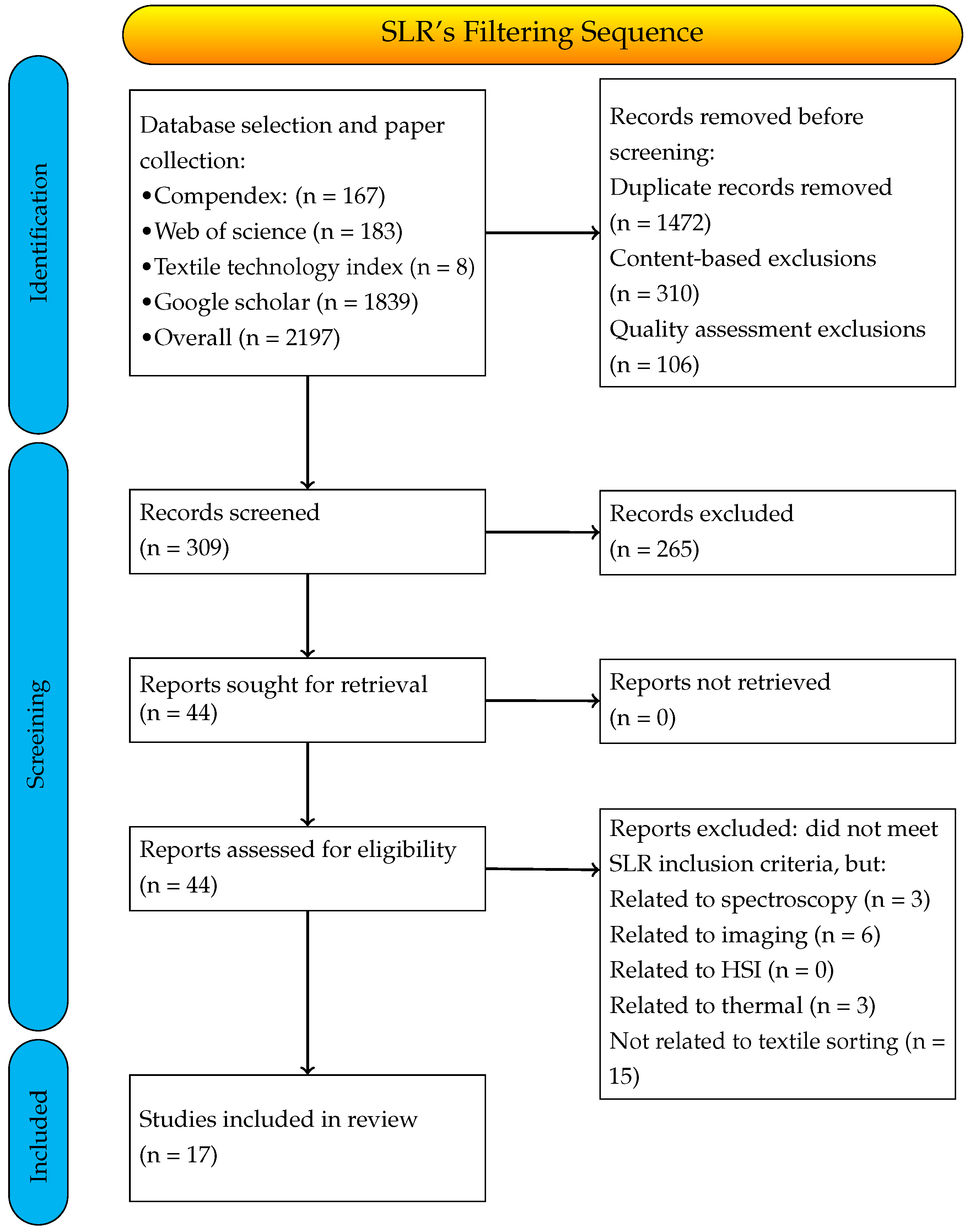

| DB 1 | Searching String and Searching Terms | #Articles | Date 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compendex | ( (( (((textile recycling) OR (textile lifecycle) OR (clothing lifecycle) OR (textile waste sorting) OR (automated waste sorting) OR (textiles sustainability)) WN TI) OR (((textile recycling) OR (textile lifecycle) OR (clothing lifecycle) OR (textile waste sorting) OR (automated waste sorting) OR (textiles sustainability)) WN AB)) AND ((((Automated) OR (Automation) OR (Automatic) OR (Machine learning) OR (computer vision) OR (CNN) OR (image processing)) WN TI) OR (((Automated) OR (Automation) OR (Automatic) OR (Machine learning) OR (computer vision) OR (CNN) OR (image processing)) WN AB))) AND (((2025 OR 2024 OR 2023 OR 2022 OR 2021 OR 2020) WN YR) AND (ja WN DT) AND (cpx WN DB) AND (english WN LA)) ) | 167 | 15 December 2024 |
| Web of Science | ( ((TI = (clothing lifecycle OR Textile lifecycle OR Textile recycling OR Textiles Sustainability OR AutomatedWaste Sorting OR TextileWaste Sorting)) OR (AB = (clothing lifecycle OR Textile lifecycle OR Textile recycling OR Textiles Sustainability OR AutomatedWaste Sorting OR TextileWaste Sorting)) ) AND ( ( (TI = (Automated OR Automation OR Automatic OR Machine Learning OR CNN OR Computer Vision OR Image processing)) OR (AB = (Automated OR Automation OR Automatic OR Machine Learning OR CNN OR Computer Vision OR Image processing)) ) AND ( (PY = (“2024” OR “2023” OR “2022” OR “2021” OR “2020”)) AND (DT = (“ARTICLE” OR “PROCEEDINGS PAPER”)) AND (LA = (“ENGLISH”)) NOT (DT = (“REVIEW”)))) ) | 183 | 18 December 2024 |
| Textile technology index | ( (TI Textile lifecycle OR TI textile recycling OR TI clothing lifecycle OR TI Textiles Sustainability OR TI Automated Waste Sorting OR TI Textile Waste Sorting) OR ((AB Textile lifecycle OR AB textile recycling OR AB clothing lifecycle OR AB Textiles Sustainability OR AB Automated Waste Sorting OR AB Textile Waste Sorting))) AND ( (TI Automated OR TI Automation OR TI Automatic OR TI Machine Learning OR TI CNN OR TI Computer Vision OR TI Image processing) OR (AB Automated OR AB Automation OR AB Automatic OR AB Machine Learning OR AB CNN OR AB Computer Vision OR AB Image processing) ) | 8 | 20 December 2024 |
| Google Scholar | Group 1: (“Textile Waste Sorting”, “Textile Lifecycle”, “Textile Recycling”, “Clothing Lifecycle”, “Textiles Sustainability”, “Automated Waste Sorting”) Group 2: (“Automated”, “Automation”, “Automatic”, “Machine Learning”, “Computer Vision”, “CNN”, “Image Processing”) *Each subject in Group 1 will be ANDed with each subject in Group 2. This means a search will be conducted for publications that contain both a subject from Group 1 and a subject from Group 2 within the 2020–2025 period. | 1839 | 22 December 2024 |
| Eligibility Criteria | Decision |
|---|---|
| Keywords exist in the article’s title or the abstract section of the paper | Inclusion |
| Is published in a peer-reviewed journal | Inclusion |
| Studies published post-2020 | Inclusion |
| Written in English | Inclusion |
| Is duplicated within the search documents | Exclusion |
| Papers published in Q3/Q4 journal quality quartiles | Exclusion |
| Conference papers, practice materials, reviews, books, or thesis documents | Exclusion |
| Articles lacking a pair of Group 1 a and Group 2 b keywords in the title or abstract | Exclusion |
| Automated Sorting Method | Description | SLR Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Spectroscopy | Uses spectroscopy techniques to capture spectral data for identifying textile materials in automated sorting. | Studies must apply spectroscopy techniques with computer-based automation (e.g., ML 1, DL 2, CV 3) in the textile waste management domain, focusing on the sorting process. |
| Imaging | Uses traditional imaging methods, such as RGB cameras, to classify textiles based on color and texture differences. However, this approach lacks detailed spectral information for precise material identification. | Studies should employ traditional imaging (e.g., RGB-based) with computer-based automation to assist textile sorting in recycling. |
| HSI 4 | HSI captures both spatial and spectral data, analyzing each pixel across multiple narrow spectral bands. This enables precise material differentiation beyond what traditional imaging can achieve. | Studies should employ HSI with computer-based automation for textile waste sorting, allowing material classification based on spectral signatures. |
| Thermal | Employs thermal methods to detect material differences for automated textile classification. | Studies must utilize thermal-based approaches integrated with computer-based automation for textile waste sorting in the recycling stage. |
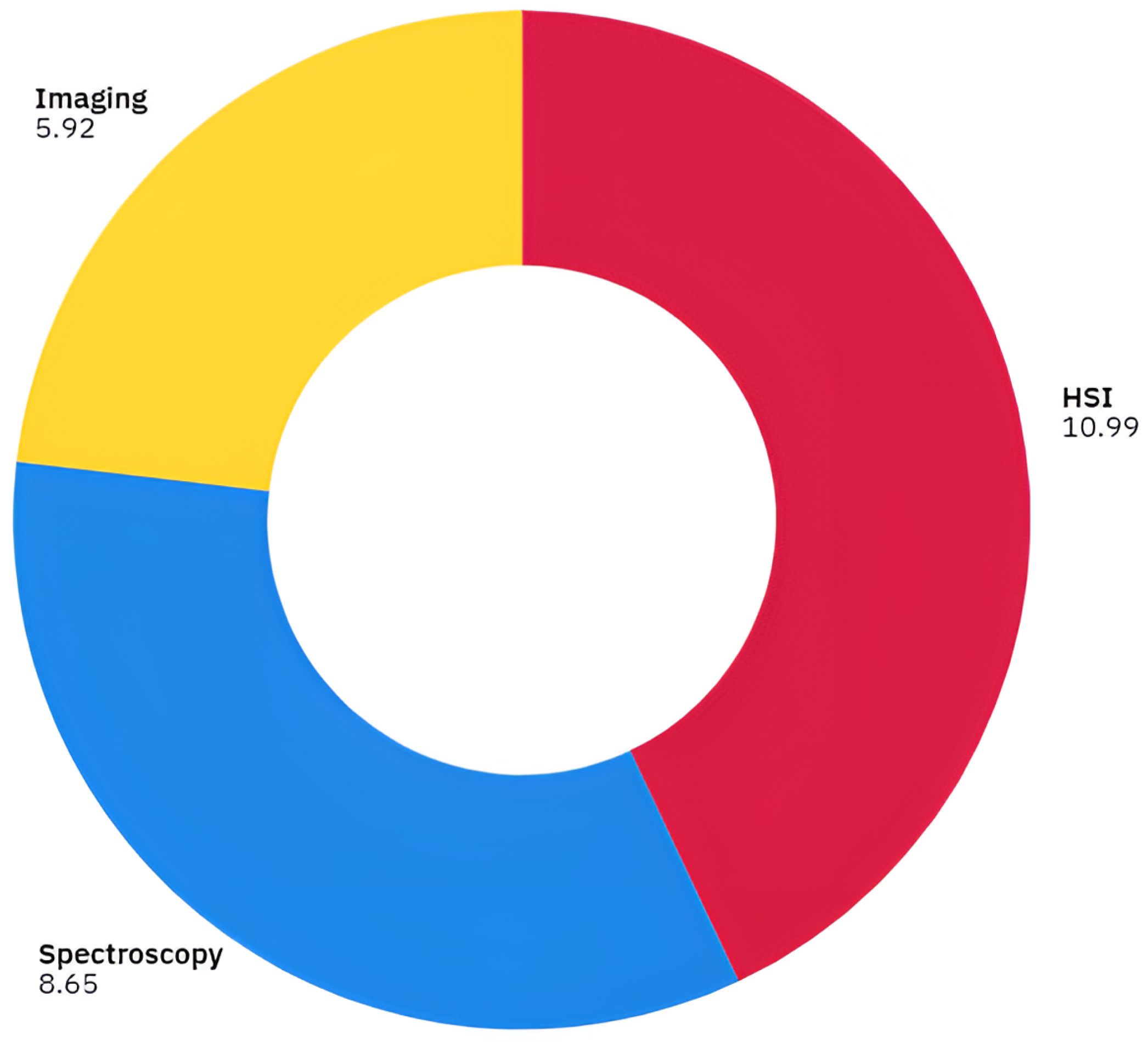
| Domain | Screened | SLR Included |
|---|---|---|
| Spectroscopy | 14 | 11 |
| Imaging | 9 | 3 |
| HSI | 3 | 3 |
| Thermal | 3 | 0 |
| Not Related to Textile Sorting 1 | 15 | 0 |
| Total | 44 | 17 |
| Classification Techniques | Number of Appearance | Included Articles |
|---|---|---|
| Neural Networks | 10 | [8,22,56,59,60,62,70,71,72,77] |
| Statistical Classifiers | 5 | [62,65,76,77,78] |
| Distance-Based and Kernel Classifiers | 5 | [8,56,57,62,77] |
| Tree-Based | 4 | [8,61,62,77] |
| k-Means clustering | 1 | [64] |
| Feature Extraction Techniques | Number of Appearance | Included Articles |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensionality Reduction | 5 | [8,57,60,76,78] |
| Regression | 2 | [61,76] |
| Technical Preprocessing | 1 | [78] |
| Simulation/Interpretation Tools | 1 | [63] |
| Authors | Data Input Method | Data Analysis Technique(s) | Highest Accuracy | Limitation(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu [56] | Spec. 1 | CNN (Tr-Net) *, SVM, MLP | 96.2% | Small dataset; CNN refinement needed; blend robustness limited. |
| Riba [57] | Spec. | PCA, CVA, kNN * | 100% | No blended fabrics; contact-based sensor limits scalability. |
| Cura [58] | Spec. | Spectral Matching | 73% | Coating, aging, thin fabrics, and blend ratios affected performance. |
| Li [59] | Spec. | BP-ANN | >99% | Poor results for <5% blends; excluded coated/core fibers. |
| Riba [60] | Spec. | CNN *, PCA, CVA | 100% | Weaker performance for cotton blends; small dataset. |
| Qi [61] | Spec. | ATR, SVR, RF, PLSR, SPA-SVR * | R2 = 0.966 | Textile-specific insights limited; contamination interference; small ATR-FTIR detection area. |
| Du [22] | Spec. | CNN | 97.1% | Blend and coated fabric confusion; reflectance issues. |
| Qiu [62] | Spec. | EPO, CNN, SVM, RF *, PLS | R2 = 0.83 | Limited to polyester–viscose blends; generalization not tested. |
| Iezzi [63] | Spec. | Simulation (Lumerical) | — | Only PE and nylon tested; durability and scalability untested. |
| Johns [64] | Spec. | k-means clustering | 71% | No blend analysis; influenced by dyes and aging; moderate accuracy. |
| Bonifazi [65] | Spec. | PLS-DA | 98.4% overall | Lower sensitivity for blends; limited surface-level detection. |
| Tsai [8] | Spec. | PCA, kNN, SVM, RF, ANN *, CNN | 96.9% | Small dataset; dope-dyed textiles excluded; imbalanced classes. |
| Noh [70] | Imaging | CNN (AlexNet) | 68.28%; 74.2% (clean); 53.3% (crumpled) | Garment-type classification only; no fiber analysis; low crumpled fabric accuracy. |
| Furferi [71] | Imaging | PNN | 83.2% | Misclassified black/gray fabrics; not ideal for multicolored textiles. |
| Tian [72] | Imaging | CNN | >90% | No fiber detection; single garment per image; limited throughput. |
| Mäkelä [76] | HSI | PCA, PLS-R * | 2.2–4.5% APE 2 | Small sample set; surface/layering effects caused error in outliers. |
| Huang [77] | HSI | CNN *, PLS-DA, SVM, RF | 98.6% | Limited fiber types; blend/treated fabric generalization not assessed. |
| Bonifazi [78] | HSI | PCA, PLS-DA * | >99.2% | Spectral overlap in blends; limited samples; needs broader fiber variety. |
| Publisher | n |
|---|---|
| Elsevier | 6 |
| MDPI | 5 |
| SAGE Publishing | 3 |
| Hindawi | 1 |
| RSC Publishing | 1 |
| Wiley-Blackwell | 1 |
| Springer Nature | 1 |
| Journal | n |
|---|---|
| Waste Management [79] | 2 |
| Textile Reseach Journal [80] | 2 |
| Resources, Conservation and Recycling [81] | 2 |
| Sustainability [82] | 1 |
| Sensors [83] | 1 |
| Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience [84] | 1 |
| Polymers [85] | 1 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production [86] | 1 |
| Journal of Industrial Textiles [87] | 1 |
| Analyst [88] | 1 |
| Advanced Materials Technologies [89] | 1 |
| Analytica Chimica Acta [90] | 1 |
| Applied Sciences [91] | 1 |
| Recycling [92] | 1 |
| Waste and Biomass Valorization [93] | 1 |
| Article | Citation Count | Publication Year | Citation Rate 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Riba et al. [57] | 122 | 2020 | 24.40 |
| Du et al. [22] | 65 | 2022 | 21.60 |
| Cura et al. [58] | 71 | 2021 | 17.75 |
| Mäkelä et al. [76] | 70 | 2020 | 14.00 |
| Huang et al. [77] | 37 | 2022 | 12.33 |
| Liu et al. [56] | 46 | 2020 | 9.20 |
| Sun-Kuk Noh [70] | 33 | 2021 | 8.25 |
| Tian et al. [72] | 7 | 2024 | 7.00 |
| Li et al. [59] | 27 | 2021 | 6.75 |
| Riba et al. [60] | 20 | 2022 | 6.66 |
| Qi et al. [61] | 18 | 2022 | 6.00 |
| Bonifazi et al. [78] | 20 | 2022 | 6.66 |
| Bonifazi et al. [65] | 6 | 2024 | 6.00 |
| Johns et al. [64] | 3 | 2024 | 3.00 |
| Furferi et al. [71] | 5 | 2023 | 2.50 |
| Iezzi et al. [63] | 4 | 2023 | 2.00 |
| Qiu et al. [62] | 1 | 2023 | 0.50 |
| Tasi et al. [8] | 0 | 2024 | 0.00 |
| Published Year | n |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 3 |
| 2021 | 3 |
| 2022 | 5 |
| 2023 | 3 |
| 2024 | 4 |
| Total | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faghih, E.; Saki, Z.; Moore, M. A Systematic Literature Review—AI-Enabled Textile Waste Sorting. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104264
Faghih E, Saki Z, Moore M. A Systematic Literature Review—AI-Enabled Textile Waste Sorting. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104264
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaghih, Ehsan, Zahra Saki, and Marguerite Moore. 2025. "A Systematic Literature Review—AI-Enabled Textile Waste Sorting" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104264
APA StyleFaghih, E., Saki, Z., & Moore, M. (2025). A Systematic Literature Review—AI-Enabled Textile Waste Sorting. Sustainability, 17(10), 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104264







