Abstract
With the rapid and unregulated nature of urban expansion occurring in Chattogram, Bangladesh, the adoption of urban growth restriction mechanisms such as the urban growth boundary (UGB) can provide a robust framework necessary to direct the development of built-up areas in a way that curtails the growth in environmentally sensitive areas of the city. Using a support vector machine (SVM)-based urban growth simulation model, this paper examines the areas of future contiguous expansion of the city to aid in the delineation of the UGB. Utilizing landcover, topographic, and population density data from a variety of sources for the past twenty years, the SVM method with the radial basis function (RBF) kernel is used to develop a model based on fourteen predictor variables. A grid-search is used to tune the hyperparameters and determine the best performance combination of the hyperparameters for the RBF kernel function used in the SVM. The final SVM model using the best performance combination of the hyperparameters indicates a high percentage agreement of 91.79% and a substantial agreement for the Kappa coefficient of 0.7699. The developed SVM simulation model identifies potential areas that are more likely to undergo urban expansion in Chattogram in the next twenty years and provides aids for a stringent and strict delineation of UGB for this region.
1. Introduction
Bangladesh has experienced healthy economic growth over the last several decades, largely driven by a transition from a rural agriculture-based economy towards a more modern urban economy [1]. This has resulted in a surge of migration from the rural areas into the cities [2] and rapid expansions of urban footprints, particularly among the largest cities such as Dhaka and Chattogram [3]. However, due to the lack of adequate forward-looking planning, the city’s expansion has largely taken place in an unregulated and chaotic manner [4]. For example, in Chattogram (also known as Chittagong), one of the world largest port cities and the second-largest metropolitan area in Bangladesh, large-scale housing projects and constructions have taken place without prior approval, and subdivision/sales of land lack provisions for basic amenities [4]. The encroachment of agricultural land and lowland areas is also very common to make space for housing or commercial developments. A large portion of this urban development has occurred in the form of slums and squatter settlements, which have little to no access to facilities and services [5]. This form of unregulated growth patterns has led to create negative environmental issues such as pollution, sanitation, traffic congestion, and crime, putting severe adverse pressure on the overall ecosystem of the region [4]. There is an immediate need to revisit the regulatory and policies instruments to address these concerns.
The urban growth boundary (UGB) is a planning/policy instrument that has been effectively used in various countries, such as China, Saudi Arabia, USA, and Switzerland, for urban management and to control the haphazard expansion of the city [6,7,8,9]. This paper proposes the implementation of UGB policy to address the issues of sustainable growth for the city of Chattogram and explores the methodological tools that could be potentially used to aid in the application of this policy. Particularly, the paper examines the implementation of the support vector machine (SVM)-based urban growth simulation model to aid in the delineation of the UGB for the city. The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 examines the literature and the application of UGB within developing countries, Section 3 discusses the methodological approach to delineation of UGB and the SVM, Section 4 provides the results of the urban growth simulation, and Section 5 provides a discussion and conclusion.
2. Literature Review on the Urban Growth Boundary within Developing Countries
UGBs, in simple terms, can be defined as land regulations that have been put into place, in most cases, by the local government to prohibit urban growth and development beyond a defined boundary [9,10,11]. The UGBs are designed to protect non-urban land outside the boundary and to promote compact, contiguous, and sustainable urban development [10]. The UGB, as an urban growth policy tool, has been implemented in a wide variety of cities in both the developed and the developing world. In the United States, several states, including Oregon [12], Washington [13], and Tennessee [14], have implemented UGBs for various cities within the state. Outside of North America, developed countries such as New Zealand [15], Belgium [16], The Netherlands [17,18], and Spain [19], to name a few, have also effectively utilized UGB as a prominent urban growth-restriction strategy.
The adoption of UGB in developing countries and transitioning economies [20] has been limited. To the best of our knowledge, there have only been five developing or transitioning countries where UGB has been explicitly implemented as an urban growth control mechanism: namely Albania [21], Chile [22], China [23], Saudi Arabia [24], and South Africa [25]. Although the concept of UGB remains the same in both developed and developing countries, it should be noted that the planning and implementation of the UGB for developing countries will require distinctly different approaches as compared to developed countries, particularly due to differences in the nature of urban expansion observed in these countries [26]. For developed countries, such as the US, urban sprawl has been largely signified by low-density, non-residential development, and UGBs have been used to restrict this expansion [27]. In comparison, for developing countries, urban sprawl, particularly around the periphery of megacities and emerging cities, is associated with the expansion of compact and high-density built-up areas, usually consisting of informal dwellings and slums [28,29]. Furthermore, the urban sprawl in developing countries is often linked to rapid growth of a city, leading to the inability of the city to provide sufficient services to its citizens, and hence resulting in poor, unplanned neighborhoods that lack basic necessities such as sanitation, running water, electricity, and paved roads [28,30]. Thus, when planning for a potential UGB within a developing country, such as Bangladesh, these additional issues regarding urban growth would need to be addressed in the adoption and implementation process for the UGB to be successful.
A number of studies, related to both developed and developing countries in which UGB has been implemented, have expressed concerns regarding the overall impact of UGB on urban expansion, its ability to address the sustainable growth of the city [31,32,33], and the containment of built-up urban areas within the designated boundary [34,35,36]. Specifically, amongst the developing countries, the primary reason for concern regarding the success of UGB can be attributed to the underlying issues related to urban governance and political/policy conflicts. Studies of UGBs in Chile and Albania have indicated the absence of clear regulations, inadequate supporting policies, and an unclear definition of jurisdiction as some of the leading factors related to issues with effective administration of the UGB [22,37]. These countries have also suffered from a lack of institutional capacities needed to support and enforce the property rights [38] and housing policies [39] within the UGB that have led to large tracts of land being developed outside the designated boundary. In other countries, including China and Saudi Arabia, the external influences from the business elite in the urban policymaking process, pressures for economic development-driven private businesses and political interests, as well as exploitation of loopholes and a general lack of oversight have resulted in urban buildup outside of the intended UGB in these countries [22,23,40,41]. Furthermore, in countries such as South Africa, a lack of collaborative efforts between the municipal and provincial government has created disputes over the UGB delineation, which has led to the eventual dissolution of the UGB itself [34,42].
Following these concerns regarding urban governance, particularly in initial adoption of the UGB, a lack of effective delineation of the boundary has been seen as a major concern with regards to its success. For China, the limited success of the UGB implemented in the first planning period has been attributed to the ineffective delineation that was produced solely based on the planned-economy architecture that had been used for the past several decades [35]. The archaic methodology used for delineation vastly underestimated the 10-year growth trajectory of the city, thus leading to insufficient allocation of land within the UGB and an ineffective UGB [43]. Similarly, for Saudi Arabia, the inefficiencies in the UGB have also been linked to delineation issues that have mainly arisen from technical limitations and institutional deficiencies due to the absence of trained planners, surveyors, and architects in most of the municipalities [44]. These delineation issues were further exacerbated by the use of outdated base maps and census data, hence leading to an overall inefficient UGB [44]. For Albania and Chile, the delineation process of the UGB has been largely arbitrary, with limited use of spatially explicit data used in the delineation process leading to ineffective implementation of the UGB [45,46,47].
Despite these criticisms, there has been a growth in popularity of UGB as an urban growth-restriction tool, with China [48,49], Saudi Arabia [50,51], and South Africa [42,52] in the forefront. These countries have been in a continuous process of updating and upgrading the UGB based on the needs and requirements of the cities, with significant research being conducted on the delineation and implementation of UGB policies [6,50,53,54]. Additionally, over the last few decades, there has been a resurgence in the literature examining the adoption and delineation of UGB within other developing countries where it has not been previously implemented. Table 1 provides a list of selected literature that has examined the potential use of UGB as an urban growth control mechanism within developing countries and transitioning economies. The literature can broadly be separated into two categories. The first category comprises of research that has primarily focused on the methodological aspect of the delineation of the boundary itself. Examples of this category include research by Bhatta [55], investigating the use of Ideal Urban Radial Proximity as a delineation methodology for Kolkata, Tayyebi et al. [56], using a distance rule-based delineation method, and Ismail et al. [57], applying a Binary Urban Suitability model for UGB delineation. The second category comprises of research that examines overall application of UGB for a region rather than the boundary delineation. Examples of this category include research by the World Bank [58] examining the application of UGB in countries such as Ecuador, India, and China. Bonilla [59] conducted a cost–benefit analysis of UGB for Santa Tecla, El Salvador, and Zeković et al. [60] investigated the use of tools such as UGB to manage the urban sprawl of Belgrade.

Table 1.
Selected literature examining the use of UGB as a mechanism to contain the urban footprint within the developing countries.
The goal of this study is to combine both aspects by creating a robust framework for UGB delineation as well as providing a commentary on the application of UGB as an urban growth-restriction strategy for the city of Chattogram. If implemented properly, a policy such as UGB for Chattogram can provide a viable pathway towards sustainable urban development by restricting and directing the growth of the city and ensuring an orderly transition of undeveloped land to built-up urban land [55].
3. Delineation of UGB
3.1. Methodological Approches to the Delineation of UGB
A review of the literature showed utilization of a variety of methods for the UGB delineation process. However, there is no one consensus or a universally accepted model with regards to the delineation of the UGB [55]. Sinclair-Smith [25] divides the process in which UGBs are delineated into three approaches. For the first approach, little or no quantitative assessment was performed for boundary delineation, and it was particularly prevalent in the initial adoption of UGB. The UGB implemented in Saudi Arabia during its first iteration [40] and the UGB delineated in China during the first planning period [35] provide good examples of this approach. Due to the lack of an analytical framework supporting the design of the boundaries, spatial plans for the Chinese cities during the period have been compared to artwork by urban designers rather than a plan to establish growth boundaries [35]. In Albania, the UGB delineation was based on boundaries separating agricultural land from urban land for cities with a population greater than 10,000 [45,63,64]. Whereas in Chile, the delineation of the boundary changed numerous times based on the subsequent political principles guiding these policies [65].
The second approach to UGB delineation is defined as the conventional approach. This approach is seen as being governed through guidelines provided by planning agencies such as the American Planning Association (APA) [10] in the Growing Smart Legislative Guidebook “Model Statutes for Planning and the Management of Change” [10]. Additionally, the conventional approach has also relied on systems such as the inventory-based system, as proposed by Knaap and Hopkins [66], that applies the concept of event-driven inventory for urban growth management. A large proportion of UGBs in the United States are based on these approaches. The APA guidelines propose using a future forecast for land demand to reserve sufficient developable land for the UGB over a set time period, generally over the next 20 years [10]. It further recommends the integration of 110 to 125 percent of projected urban growth as a long-term land use planning strategy. Sinclair-Smith [25] explains that the purpose of including additional land within the UGB, than what is required, is to prevent owners from monopolizing vacant land, thus allowing for effective and competitive real estate markets. As compared to the time-driven approach, where the expansion of an established UGB to accommodate future growth occurs at a set time interval, the inventory control system proposed by Knaap and Hopkins’ [66] is an event-driven approach, where an increase in the developable land for the UGB is triggered only after the available land within the UGB is diminished to a predetermined level. The inventory control system for UGB extension was further revisited by Han and Lai [67]. They translated the inventory approach into a decision network framework, where rather than the extension of UGB being based on one single event occurring, the change in the delineation would be based on the analysis of the complex system of linked actors, problems, and solutions that have an impact on the expansion of urban areas within the city. In a comparison of the new Decision Network Framework for the time-driven approach with the event-driven inventory approach, results indicated the Decision Network Framework-supported system to be more efficient and cost-effective at UGB allocation [67].
The third category of approach used in the delineation of UGB utilized growth simulation models that included scientific and quantitative techniques to predict future growth and, based on it, delineate the appropriate UGB. This included a variety of methodologies that made use of constrained cellular automata (CA) to support the establishment of UGBs. Compared to the traditional method, the CA-based system, as used by Long et al. [35], included containment conditions such as macroeconomic, locational, institutional, and neighborhood constraints, aiding in the simulation of urban growth within the model. This in turn resulted in a more effective spatiotemporal simulation of urban expansion and an overall improvement in UGB delineation [35]. Other CA-based urban land use change modeling techniques such as SLEUTH have also been used for predicting urban growth and, based on it, the creation of urban containment policies [68,69]. Bhatta [55] utilized the Ideal Urban Radial Proximity (IURP)-based design to examine the implementation of UGB for Kolkata, India. However, IURP does not provide any simulation or modeling of urban growth processes and patterns, but rather is a theoretical construct that uses a radial distance from the city center to create a circular urban growth boundary beyond which urban growth would be restricted. The use of radial distances was also implemented for the UGB models by Tayyebi, Pijanowski, and Tayyebi [56] for the city of Tehran, Iran. The authors used artificial neural networks to predict the radial extension of urban areas in individual azimuth and, based on the growth of the urban area, an urban growth boundary for each azimuth was designated [70]. Tayyebi, Pijanowski, and Pekin [56] also used the information on the radial distance from the center of urbanized areas for individual azimuth to delineate UGB using two separate rule-based methods, the distance-dependent method (DDM) and the distance-independent method (DIM). DDM used the points on the initial urban boundary to estimate the growth of urbanized areas and predict the future UGB for subsequent time periods using percentage increments across individual azimuth. DIM, on the other hand, used rate of change in distance from the center of the urbanized areas for two different time periods within each azimuth to predict the boundary for the next time period [56]. The use of radial distance in delineating UGBs was further investigated by Tayyebi et al. [71] by using it in conjunction with spatial logistic regression (SLR). The SLR-UGB model considered the impact of spatially explicit biophysical factors such as topography to derive its impact on urban growth and hence simulate future urban growth boundary changes across each individual azimuth. Another interesting approach that has been used to allocate UGB is the application of the ant colony optimization (ACO) technique. Considering UGB as a problem of spatial optimization for land use allocation, Ma et al. [49] used the ACO method for optimizing land use for UGB delineation with the purpose of creating a balance between urban growth, planning regulation, and characteristics of the landscape. While these models provide a dramatic improvement in the methodological approach over having no systematic approach or even over having a conventional approach for delineation of UGB, it should be noted that urban development in the future more than likely will not necessarily follow historical trends of urban development, and subsequently the UGB delineation approaches might not necessarily produce the optimal UGB for the city [72]. Therefore, in addition to the delineation of the boundary, specific targets and constraints in line with the emerging trends along with supporting policies would be essential to optimize and support the UGB delineation [72].
3.2. Use of SVM in Aiding the Deliniation of UGB
In this study, we investigate the use of support vector machines (SVM) to aid in UGB delineation through the simulation of future contiguous built-up urban footprint expansion for the city of Chattogram over the next 20 years. SVM is a well-established methodology that has previously been used in a wide variety of research related to monitoring machine condition and faults [73], language and speech recognition [74], diagnosis of diseases [75], and recognizing human motion patterns [76]. Additionally, SVM has also been extensively used in examining and modeling urban growth [77,78,79,80]. The primary reason for using SVM in this study is due to the exceptional performance of this methodology as a classifier [81], and specifically in forecasting land use change and urban growth as compared to other methodologies, such as the logistic regression approach [78] or the artificial neural network or decision tree [82].
Factors that have a significant impact on urban growth were used as the input parameters for the SVM model, and the past 20 years of data on these factors were used to train the model. This trained SVM model was then used to simulate the future expansion of the urban footprints for Chattogram. Unlike the UGB delineation methodologies discussed previously, the outcome of the simulation is not used as a delineation of the UGB itself, instead, it is used as a robust methodology that can be employed as a part of the overall UGB delineation process. The goal is to utilize the SVM approach to provide an insight on potential areas that are more likely to undergo urban expansion. This information would be valuable for planners and decision-makers to optimize the delineation of UGB. Results obtained from the simulation would act as a guide for planners by highlighting the type of current land cover that is likely to change into urban built-up areas, identifying areas that are at a higher environmental risk, restricting/regulating growth in these areas, and subsequently allowing for expansion in areas with lower environmental risk as well as access to essential services for a more effective delineation of UGB. Additionally, the urban built-up simulation would provide planners and decision-makers a roadmap to propose policies directed at addressing these concerns related to sustainable urban expansion of the city.
3.3. SVM
SVM was initially proposed by Vapnik and Lerner [83] as a new generation of machine learning algorithms inspired by statistical learning theory and designed as a linear classifier, which was later extended to include regression [84]. SVM operates by projecting the input data into Hilbert space, where it can be separated by an optimal separating hyperplane situated in a multi-dimensional space, maximizing the margin between the closest data classes to the plane [78,85]. This maximization of the margin between the two classes allows for minimizing the upper bound of the generalization error [80]. This approximate implementation of the structural risk minimization (SRM) principle provides a good generalization performance of the SVM [86]. Furthermore, an n-class classification in SVM is achieved as a sequence of one-versus-all binary classification to reach the final decision [87]. In this study, the SVM-based classification approach was used to provide a binary classification on areas that would expand into urban built-up areas and those that would not in the future.
For a linear case of SVM, let us assume a training dataset consisting of k datapoints that are separable into two classes, as represented by:
with the parameters x ∈ Rn in an n-dimensional space and its corresponding class label y ∈ {+1, −1} [84].
In the training phase, SVM was used to generate the hyperplane that best separates the two classes, +1 and −1. This hyperplane can be represented by H1: and H2: , where a majority of class +1 lies above H1 and a majority of class −1 lies below H2 . Here, H1 and H2 are the supporting vectors or decision boundaries responsible for determining the optimal hyperplane, w′ is the transpose of the n dimensional coefficient vector which determines the orientation of the hyperplane w, and b is the offset or the bias [80]. The hyperplane itself can be represented as H: [88].
In Figure 1, while there are no datapoints between the H1 and H2 decision boundaries, the points that are located on H1 and H2 are the support vectors determining the optimal hyperplane, while other points on the training dataset do not contribute towards defining the hyperplane [86,88].
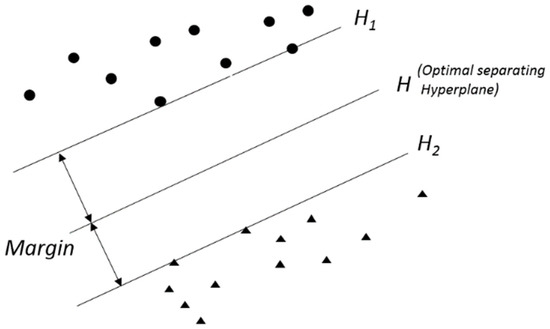
Figure 1.
Binary classifier with optimal separating hyperplane separating two categories circles and triangles.
Scaling the coefficient vector and the offset for all datapoints, we get for positive examples, , i.e., those points lying above H1 when i = 1, 2, n, and for negative examples, , i.e., those points lying below H2 when i = 1, 2, n. This is equivalent to [86], .
The distance of a point xi from the hyperplane (H:) is given by [86]:
Based on this, the distance between H1 and H2 can be denoted by:
Maximization of the distance between H1 and H2 can be obtained by minimizing the norm of .
The optimal hyperplane separating the two separable training data classes satisfies the following [86]:
Minimize:
Subject to: i = 1, 2 …, n
In practice, however, as not all training datasets are perfectly linearly separable by a hyperplane, these imperfect separations are accounted for by a non-negative slack variable, ξ, that is incorporated into the constraints to consider the misclassification errors [86].
Minimize:
Subject to: i = 1, 2 …, n;
Here, is the positive slack variable representing the distance between the misclassified points, and C is the penalty parameter representing the trade-off between the margin size and the number of misclassified training points. To minimize the misclassification error and to maximize the margin size, Lagrange multipliers α and β are introduced and solved for the saddle point of the Lagrangian function [84].
Minimize:
Subject to: , 0c, i = 1, 2 …, n
Additionally, to extend the linear machine learning to non-linear cases in SVM, the kernel method is used to map the non-linearly separable classes to higher dimensional feature spaces, where they can be separated using a linear optimal hyperplane [86]. As all the training data that appear in the previous equation are in dot product, the kernel function defined as is introduced, resulting in [89]:
Some of the common kernel functions include the linear function K, polynomial function K, and radial basis function (RBF) K, where q and are the parameters for the polynomial and RBF kernel functions, respectively [86].
3.4. Study Area
The city of Chattogram in Bangladesh was used as the study area for this research. Located in southeastern Bangladesh, nestled between the Karnaphuli river in the east and the Bay of Bengal to the west, Chattogram is the second-largest city in the country. It is also the commercial capital of Bangladesh, having the busiest seaport in the country, accounting for 92% of import/export cargo [90] and holding around 40% of the country’s large-scale industries [91]. It contributes 50% of the tax revenue and around 11% of the GDP for Bangladesh [1]. With a population of just over 4 million, the city of Chattogram accounts for 9.07% of the overall population and 20% of the overall built-up area of all the municipalities in Bangladesh [3,92]. This alarming rate of increase in the urban footprint of Chattogram is driven by industrial growth, infrastructural development, and a massive rural to urban in-migration, which has come at a cost of a loss of surrounding agricultural land, vegetation, and lowlands [4].
3.5. Data Collection and Preparation
The expansion of the city’s urban footprint depends on the interaction between a variety of environmental, socioeconomic, and topographic parameters. In this study, we used 14 parameters (Table 2) to estimate urban growth and simulate a future pattern of urban expansion of Chattogram using SVM. Selection of the 14 parameters used in the simulation was based on findings from past literature that drew from urban theory and models identifying key drivers that directly or indirectly influence urban expansion.

Table 2.
Parameters used in SVM for simulation of future contiguous urban expansion.
The pressure from increasing population density is a critical driver of urban expansion of an area [93], and thus was also included in the analysis. The topography of a particular region also significantly affects the potential for future urban build-up [94]. When considering a location for urban expansion, there is a higher likelihood of new urban build-up occurring in areas that are flatter as compared to areas with steeper slopes [95]. As a result, the slope parameter was considered in this study. Availability of transportation and access to transportation have also been identified in numerous studies as important drivers of outward urban growth, with a higher degree of urban build-up occurring along with transportation nodes and routes [96,97]. Taking this into consideration, in this study we used distance to major roads and distance to major railroads within Chattogram as transportation parameters. With regards to economic factors, proximity to job sites and infrastructures, particularly in and around the central business districts, have been seen as prime drivers of urban expansion [98]. To account for this, distance to big commercial areas and industrial parks within Chattogram were also included in the analysis. Environmental factors such as access to greenspaces [70] and water bodies such as rivers and canals [99] have been an important draw for urban growth. In order to incorporate these environmental factors into the analysis, distance to the Karnaphuli river, upon which banks Chattogram lies, distances to the numerous ponds, an important part of the landscape that are scattered throughout Chattogram, and the distance to Kerfa Bagan forest were considered in the study. Neighborhood characteristics also play a critical role in understanding the probability of land converting to urban areas [100]. Additionally, with current land cover also having a significant influence on the future land cover of a region [80], land cover information on Chattogram for 1990, 2000, and 2019 (Figure 2) that was derived previously from Google Earth Engine using Landsat data was used in the analysis (see [2]). The 3 × 3 Moore’s Neighborhood of each cell for each of the land cover classes was then calculated and used in the analysis. Finally, areas where urbanization is not allowed (i.e., areas that are not protected areas, areas that are not a water feature, and areas designated for parks) were identified and excluded from the analysis. The remaining areas were designated as areas where urbanization is allowed and were included in the analysis.
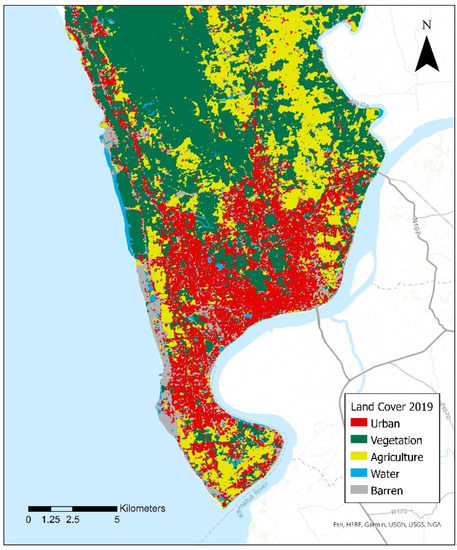
Figure 2.
Land cover classification of Chattogram for 2019 (Source: Bajracharya and Sultana [3]).
With contiguity of urban areas being an important part of the UGB [101], contiguous urban patches were created using cells classified as urban in the land cover data. Due to the scattered pattern of built-up urban areas, particularly around the fringes of the city core of Chattogram, isolated patches of built-up urban areas were disregarded, and the largest contiguous patch was selected for the analysis [70]. Cells within the contiguous built-up urban areas were allocated the value of +1 and all other areas were allocated the value of −1. This variable was taken as the target variable for the SVM.
One of the limitations of this simulation has been the minimal use of socioeconomic parameters in the analysis, particularly due to the limited availability of spatially explicit, fine-scale data for the region. Inclusion of these parameters, such as GDP per capita [102], migration patterns [103], along with availability of schools, hospitals [104], and other amenities/civic institutions [105,106] discussed in the literature that drive land use change, could provide a better understanding of externalities that trigger urban expansion [107]. Further research would be essential to collect such socioeconomic data that would aid in future urban expansion simulation and the subsequent delineation of the UGB for Chattogram.
Although the availability of up-to-date, high-resolution, spatially explicit data and digital maps for developing countries including Bangladesh has been limited [4], all the data used in this study were collected through freely available sources. Preparation of the spatial data, including computation of Moore Neighborhood, calculation of Euclidean distances for proximity, conversion from DEM to slope, extraction of contiguous areas, and reclassification of data, was performed using ArcGIS 10.7 software [108]. All the datasets were converted into 30 by 30 m resolution (Figure 3) and exported in ASCII format. However, the large water bodies surrounding Chattogram (Karnaphuli river and Bay of Bengal) were excluded from the analysis. As the scale of the feature vectors has a significant influence on the SVM results, and with normalization of the features providing a considerable superior generalization performance [109], normalization between the values of 0 and 1 was performed for all the predictor datasets. To train the SVM, as classifiers tend to perform poorly in an imbalanced training dataset [110], a balanced training dataset was created containing an equal number of randomly selected cells that changed to urban cells from 2000 to 2010, and those that remained the same over the given time period.
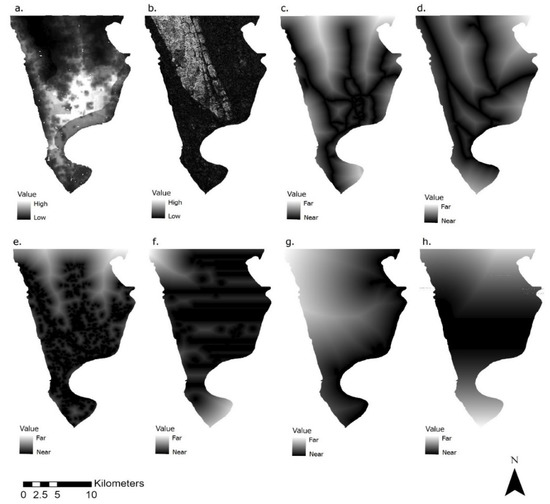
Figure 3.
(a) Population density, (b) slope, (c) distance to roads, (d) distance to rail, (e) distance to commercial areas, (f) distance to ponds, (g) distance to rivers, (h) distance to forest and parks.
3.6. Model Implementation
The SVM model for this study was developed using Kernlab [111], a kernel-based machine learning library available through the R library. Past literature indicates that the RBF kernel is a widely implemented kernel function in land cover and urban growth simulation [80,89,112] and performs better than other kernel functions [79,113,114,115]; thus, the RBF kernel function was used for the analysis. The RBF kernel function requires the use of two hyperparameters, C and [80]. These hyperparameters used in the model have a significant impact on the model [116]. The C hyperparameter is the penalty parameter that adds a penalty for misclassification of datapoints. A lower value of C indicates a smaller penalty for misclassified datapoints, so a larger decision boundary is chosen in the model at the expense of misclassification of datapoints. A higher value of C indicates a larger penalty for misclassified datapoints, so a smaller decision boundary is chosen in the model to minimize the misclassification of datapoints. Very low values of C will likely underfit the training data and very high values of C will likely overfit the training data [116]. The hyperparameter impacts the distance of influence of the training datapoints. A lower value of indicates a larger radius with more datapoints grouped together, while a higher value of indicates a smaller radius with fewer datapoints being grouped together. Very high values of decrease the accuracy of the training dataset [116].
For this study, the SVM model was first trained using predictor variables from the 2000 dataset and the built-up urban area target variable for the 2010 datasets using the RBF kernel function. Next, the trained model was applied to the 2010 predictor dataset to simulate the built-up urban area target variable for 2019. The hyperparameters for the RBF kernel function used in the SVM model were tuned through a grid search process for each pair of C ∈ {0.1, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100} and ∈ {0.1, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100} to determine the best performance combination of these hyperparameters for the model. Lastly, the best performance combination of the hyperparameters obtained from the grid search was used to create the final SVM model, which was applied to the 2019 predictor data to simulate the growth of built-up urban areas for 2040. A detailed representation of the model is shown in Figure 4.
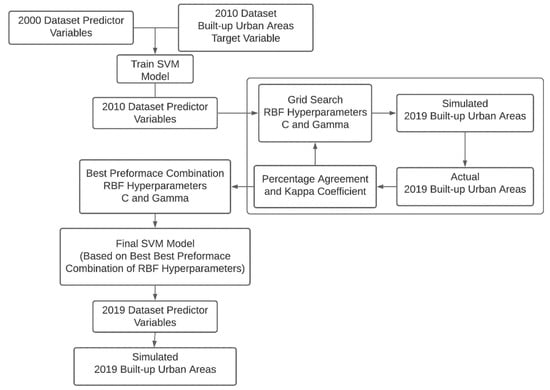
Figure 4.
Diagram of SVM-based simulation of built-up urban areas for 2040.
4. Results of Urban Growth Simulation
For the SVM model, the best performance assessment of the RBF kernel hyperparameters was conducted by comparing the percent agreement of the built-up urban areas simulated by the model for 2019 with the actual built-up urban areas for 2019 and its Cohen’s Kappa statistics [117]. The percent agreement indicated the overall accuracy of the correct predictions made by the model, while Cohen’s Kappa coefficients indicated the magnitude of agreement between the two beyond those that occur due to chance [118]. Results from the hyperparameter turning showed that a C value of 5 (Table 3) and a value of 0.1 (Table 4) provided the best performance combination for the model. This combination produced an overall percentage agreement of 91.79% and a Cohen’s Kappa coefficient of 0.7699, showing a substantial agreement [119].

Table 3.
Results from the grid search examining percentage agreement between predicted built-up urban areas for 2019 and actual built-up areas for 2019, with best performance of value shown in italics.

Table 4.
Results from the grid search examining Cohen’s Kappa coefficient between predicted built-up urban areas for 2019 and actual built-up areas for 2019, with best performance of Kappa value shown in italics.
The SVM model based on the best performance combination of the hyperparameters was applied to the 2019 dataset, using it as the predictor variable to simulate the future built-up urban areas for 2040 in Chattogram. Keeping in mind the overall goal of the UGB to promote contiguous urban growth, isolated patches of built-up urban areas simulated by the model that appeared outside of the largest contiguous built-up urban area were excluded from the analysis. The results from the SVM model-based simulation for 2040 (Figure 5) predicted an increase of 18.27 km2 of contiguous built-up urban areas from base 2019 levels over the next twenty-year time period for the city of Chattogram. A majority of growth in the built-up urban areas is expected to occur in the north-eastern region (5.33 km2) and along the south-western region (3.81 km2) of Chattogram (Figure 6). Alarmingly, a large portion of this expansion in the south-western corner of Chattogram is expected to occur in areas with a high risk of flooding due to its proximity to the bay. The other regions of the city showed limited expansion of built-up urban areas. When examining the land cover change (Figure 7), current agricultural land cover, with 6.07 km2, is predicted to be the biggest land cover type to be converted into the contiguous built-up urban land cover. This is followed by the inclusion of 5.28 km2 of built-up urban land cover, that were previously scattered outside of the contiguous area and are now included as a part of the contiguous region for 2040, and nearly equal amounts of vegetated (3.76 km2) and barren (3.75 km2) land cover being converted as a part of the contiguous built-up urban region.
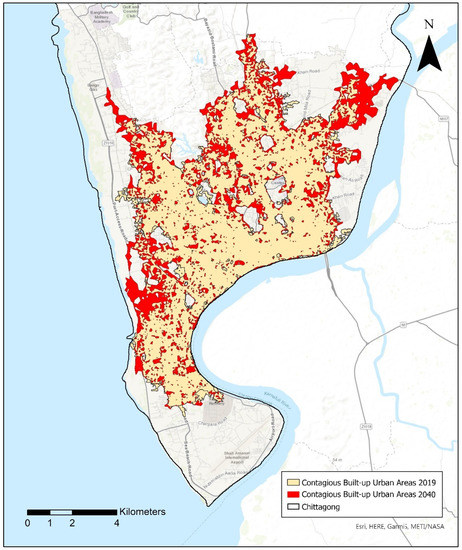
Figure 5.
Simulation of contagious built-up urban areas to aid in the delineation of the potential urban growth boundary for Chattogram.
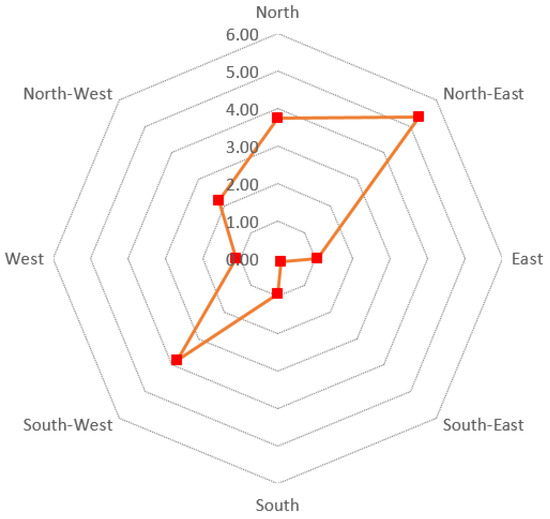
Figure 6.
Directional expansion of contiguous built-up urban footprint for Chattogram with area presented in km2.
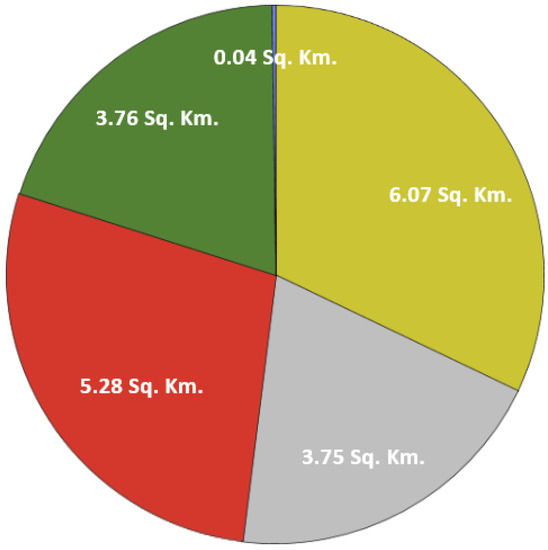
Figure 7.
Land cover type in 2019 that is predicted to be converted into built-up urban land cover in 2040.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
With Chattogram experiencing increasing population growth and rapidly and uncontrollably expanding urban build up areas, adoption of UGBs for the city could provide the robust forward-looking policy/regulatory framework necessary to curtail this haphazard growth by restricting and directing the expansion of built-up urban areas while emphasizing sustainable urban growth. The areas highlighted in red in Figure 5, the contiguous built-up urban areas, provide a strong foundation and an excellent starting point for city planners and decision-makers to examine an establishment of a potential UGB for Chattogram for the next 20-year time period. This simulation of future contiguous urban growth for year 2040 was specifically created based on the business-as-usual assumption, without accounting for any unforeseen future influences from unprecedented changes in population, economy, environment, policies, or politics [55]. Additionally, the urban growth simulation was performed using only land cover data, topographic features, and population density information due to limited availability of free datasets.
Results from the SVM-based simulation indicate the north, north-east, and south-west as regions where the majority of future expansion of the city is expected to occur. A large portion of the north-east region is already experiencing urban expansion through the development of scattered urban built-up areas and is expected to continue with this trend. Most of the expansion of the urban footprint in this region is expected to occur over agricultural areas and around the scattered urban built-up areas. Similarly, in the south-west region, a large portion of the expansion is also expected to occur over agricultural land, scattered urban buildup, and baren lands adjacent to the beach. In this situation, delineation of UGB would need to be targeted at restraining the current buildup of scattered settlements and encouraging the urban development within the boundary. UGB delineation could be effectively used to guide the direction of future urban growth of the region, with the aim to lower the overall environmental cost of the development while providing access to the essential services in the region.
The future expansion of the urban footprint of the city in the north is particularly alarming due to its proximity to the hill and forested areas. Most of the expansion in this region is expected to occur over vegetated areas, thus resulting in issues of encroachment and further degradation of forested hill areas that continue to plague the region [4]. Taking this into consideration, there would need to be a stringent and strict delineation of UGB for this region to limit the damage to the environment. While a complete restriction in development and urban expansions of an economically vibrant city such as Chattogram is impossible, the goal of UGB is to direct the growth of the city towards areas that are more sustainable and less detrimental to the overall environment.
For the actual delineation of UGB and successful implantation of the policy for Chattogram, in addition to the simulation of future expansion of the urban footprint, further investigation into the social, economic, and environmental aspects of the city would need to be considered. Supplemental research in terms of collecting social and economic datasets, including data on slum settlement, industrial/economic activities and how they could be incorporated as a part of the UGB policy, and of knowledge-based boundary delineation processes, would be needed. A successful implementation and realization of a multifaceted and complex policy tool such as a UGB would require a holistic approach involving cooperation and coordination from different levels of government, non-government, and the private sector [120]. The success of a policy such as UGB for Chattogram will be contingent on the formulation of supporting policies inspiring good urban governance that complement and work in synergy with the proposed UGB [121]. Furthermore, these supporting policies will need to address underlying issues related to the haphazard and uncontrolled urban expansion within Chattogram, such as management of informal settlements and strict enforcement of these boundary lines. These supporting policies and regulations will be essential in strengthening the UGB and ensuring its overall success.
Moreover, along with the physical variables used in this study to simulate future urban growth, the urban expansion of Chattogram is likely to be highly impacted by other exogenous and unforeseen factors that are difficult to account for in the model, such as influences from private developers and political influences. As a result, although the simulation of future built-up urban areas that was based on past trends would provide a good approximation, the actual urban expansion would not strictly follow these historical trends [72]. Thus, the UGB policy and the delineation would inherently need to be dynamic in nature. It would require frequent monitoring and adjustments to the delineation based on any changes to the various factors impacting the expansion of built-up urban areas. These changes would need to be in adherence to the concepts of sustainability and sustainable urban growth. Finally, it is more than likely that the delineation of UGB for the city of Chattogram, if actually adopted, will look different from the boundaries projected in this study. However, the lessons learned and the insights gained from this study will certainly be valuable for planners and policy-makers and encourage the debate on the need for sustainable urban growth for the city of Chattogram.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B.; Formal analysis, P.B.; Investigation, P.B.; Resources, S.S.; Supervision, S.S.; Validation, P.B.; Writing—original draft, P.B.; Writing—review & editing, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data used to support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Muzzini, E.; Aparicio, G. Bangladesh: The Path to Middle-Income Status from an Urban Perspective; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/13113 (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Uddin, M.; Firoj, M. Causes and Consequences of Rural-Urban Migration in Bangladesh: An Empirical Study in Chittagong City. Int. J. Ethics Soc. Sci. 2013, 1, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, P.; Sultana, S. Rank-Size Distribution of Cities and Municipalities in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Nazem, M.N.I. Examination of Land Use/Land Cover Changes, Urban Growth Dynamics, and Environmental Sustainability in Chittagong City, Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 18, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, N. Assessing Urban Sustainability of Slum Settlements in Bangladesh: Evidence from Chittagong City. J. Urban Manag. 2018, 7, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhayyal, Z. Urban Growth Change Analysis of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: 2005–2015. Pap. Resour. Anal. 2017, 20. Available online: http://www.gis.smumn.edu/GradProjects/AlkhayyalZ.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Gennaio, M.-P.; Hersperger, A.M.; Bürgi, M. Containing Urban Sprawl—Evaluating Effectiveness of Urban Growth Boundaries Set by the Swiss Land Use Plan. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.; Tu, Y.; Shu, X. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Urban Growth Boundaries Using Human Mobility and Activity Records. Cities 2015, 46, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendall, R.; Martin, J.; Fulton, W. Holding The Line: Urban Containment in the United States; The Brookings Institution Center on Urban and Metropolitan Policy, 2002; Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/research/holding-the-line-urban-containment-in-the-united-states/ (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- American Planning Association. Growing Smart Legislative Guidebook—Model Statutes for Planning and the Management of Change; Meck, S., Ed.; American Planning Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-844829-67-8. Available online: https://www.huduser.gov/portal/publications/polleg/growingsmart.html (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Brueckner, J.K. Urban Growth Boundaries: An Effective Second-Best Remedy for Unpriced Traffic Congestion? J. Hous. Econ. 2007, 16, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, A.C.; Duncan, J.B. Growth Management Principles and Practices; Planners Press, American Planning Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-918286-92-5. [Google Scholar]
- Washington State Legislature Comprehensive Plans—Urban Growth Areas. 2018; Vol. 36.70A.110. Available online: http://app.leg.wa.gov/RCW/default.aspx?cite=36.70A.110 (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- TACIR, Tennessee’s Growth Policy Act: A Vision for the Future; Tennessee Advisory Commission on Intergovernmental Relations; 2000. Available online: https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/tacir/documents/annexation00.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Grimes, A.; Liang, Y. Spatial Determinants of Land Prices: Does Auckland’s Metropolitan Urban Limit Have an Effect? Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2009, 2, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boussauw, K.; Allaert, G.; Witlox, F. Colouring Inside What Lines? Interference of the Urban Growth Boundary and the Political–Administrative Border of Brussels. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2013, 21, 1509–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabielek, K. The Compact City: Planning Strategies, Recent Developments and Future Prospects in the Netherlands. In Proceedings of the AESOP 26th Annual Congress Ankara, Ankara, Turkey, 11–15 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vasili, Z. Urban Containment Policies in European Regions. The Case Studies of Randstad and Greater London. Master’s Thesis, Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paül, V.; McKenzie, F.H. Peri-Urban Farmland Conservation and Development of Alternative Food Networks: Insights from a Case-Study Area in Metropolitan Barcelona (Catalonia, Spain). Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations World Economic Situation and Prospects; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-92-1-109177-9.
- Felstehausen, H. Urban Growth And Land Use Changes In Tirana, Albania: With Cases Describing Urban Land Claims; Working Papers; University of Wisconsin-Madison, Land Tenure Center: Madison, WI, USA, 1999; Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/uwltwp/12806.html (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Hölzl, C.; Nuissl, H. Urban Policy and Spatial Planning in a Globalized City—A Stakeholder View of Santiago de Chile. Plan. Pract. Res. 2014, 29, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegras, C.; Gakenheimer, R. Urban Growth Management for Mobility: The Case of the Santiago, Chile Metropolitan Region; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 172. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/czegras/www/Zegras_Gakenheimer_Stgo_growth_mgmt.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Al-Hathloul, S. Riyadh Development Plans in the Past Fifty Years (1967-2016). Curr. Urban Stud. 2017, 5, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinclair-Smith, K. Methods and Considerations for Determining Urban Growth Boundaries—an Evaluation of the Cape Town Experience. Urban Forum 2014, 25, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengston, D.N.; Fletcher, J.O.; Nelson, K.C. Public Policies for Managing Urban Growth and Protecting Open Space: Policy Instruments and Lessons Learned in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B. Causes and Consequences of Urban Growth and Sprawl. In Analysis of Urban Growth and Sprawl from Remote Sensing Data; Advances in Geographic Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 17–36. ISBN 978-3-642-05298-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.L. Compact City Policies for Megacities: Core Areas and Metropolitan Regions. In Compact Cities; Routledge: London, UK, 2002; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in Developing Countries: Current Trends, Future Projections, and Key Challenges for Sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-H.; Poudyal, N.; Lambert, D.M. Estimating Spatially Varying Effects of Urban Growth Boundaries on Land Development and Land Value. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.-J. The Effects of Portland’s Urban Growth Boundary on Urban Development Patterns and Commuting. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kline, J.D.; Alig, R.J. Does Land Use Planning Slow the Conversion of Forest and Farmlands? Growth Change 1999, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A. The Life & Death of Urban Growth Management in the Gauteng Province. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.; Lai, S.-K.; Mao, Q. Urban Growth Boundaries of the Beijing Metropolitan Area: Comparison of Simulation and Artwork. Cities 2013, 31, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pllumbi, D. Mirroring Tirana Reflections on Tirana’s Urban Context and Perspectives. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 2, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, P.A. Spatial Segregation in Complex Urban Systems: Housing and Public Policy in Santiago, Chile, UT Austin. 2009. Available online: https://repositories.lib.utexas.edu/handle/2152/18450 (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Valletta, W.; Hamza, E.; Laha, M.; Kelm, K. Status of Land Reform and Real Property Markets in Albania; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 1–125. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/815161468002656300/Status-of-land-reform-and-real-property-markets-in-Albania (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Rojas, E. Housing Policies, Quality of Housing and Urban Development. Lessons from the Latin American Experience 1960–2010. In Proceedings of the World Bank Conference on Land and Poverty, Washington, DC, USA, 23–27 March 2015; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mubarak, F.A. Urban Growth Boundary Policy and Residential Suburbanization: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Habitat Int. 2004, 28, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lü, B.; Roo, G. de Performance and Dilemmas of Urban Containment Strategies in the Transformation Context of Beijing. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2010, 53, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, V.; Sutherland, C.; Scott, D. Pushing the Boundaries–Urban Edge Challenges in EThekwini Municipality. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2016, 98, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lai, S.-K.; Dang, A.; Tan, Z.; Wu, C. Effectiveness of Urban Construction Boundaries in Beijing: An Assessment. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hathloul, S.; Mughal, M.A. Urban Growth Management-the Saudi Experience. Habitat Int. 2004, 28, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allkja, L. Changing Planning Cultures: The Case of Albania. Master’s Thesis, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2012. Available online: http://theses.ubn.ru.nl/handle/123456789/3412 (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Aquino, F.L.; Gainza, X. Understanding Density in an Uneven City, Santiago de Chile: Implications for Social and Environmental Sustainability. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5876–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dino, B.; Karimi, K.; Griffiths, S. Autocratic Planning Systems Challenged by Unregulated Urbanisation: Urban Transformation in Post-Socialist Tirana, Albania; Portland Urban Architecture Research Laboratory: Portland, OR, USA, 29 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Tan, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y. Modeling Urban Growth Boundary Based on the Evaluation of the Extension Potential: A Case Study of Wuhan City in China. Habitat Int. 2018, 72, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, X.; Cai, Y. Delimiting the Urban Growth Boundaries with a Modified Ant Colony Optimization Model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 62, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshebli, A. Towards Making Urban Planning Practices More Effective amid Rapid Urban Growth in Riyadh-Saudi Arabia. Master’s Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FSCP. Urban Planning Reviews: Governance of Planning Local Planning Urban Management; FSCP: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2016; Available online: https://www.futuresaudicities.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Urban-Planning-Reviews_Output-1_Governance.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Horn, A.; Van Eeden, A. The Application of an Urban Sprawl Index for Comparative Purposes in Towns and Cities in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geomat. 2018, 7, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Ma, S. Simulating Urban Growth Boundaries Using a Patch-Based Cellular Automaton with Economic and Ecological Constraints. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Song, Y.; Han, H. Bringing Conservation Priorities into Urban Growth Simulation: An Integrated Model and Applied Case Study of Hangzhou, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B. Modelling of Urban Growth Boundary Using Geoinformatics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2009, 2, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Pekin, B. Two Rule-Based Urban Growth Boundary Models Applied to the Tehran Metropolitan Area, Iran. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.A.; Ludin, A.N.M.; Hosni, N. Delineating Urban Growth Limit for Managing Urbanisation in Iskandar Malaysia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 169, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Exploring Urban Growth Management: The Case of Three Cities; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTURBANDEVELOPMENT/Resources/336387-1169585750379/Urban_Growth_June_2008.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Bonilla, A.I.M. Assessing Urban Containment Policies for Managing the Urban Growth of Santa Tecla City, El Salvador. Ph.D. Thesis, Ohio University, Athens, OH, USA, 2007. Available online: https://etd.ohiolink.edu/pg_10?0::NO:10:P10_ETD_SUBID:60672 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Zeković, S.; Vujošević, M.; Bolay, J.-C.; Cvetinović, M.; Miljković, Ž.J.; Maričić, T. Planning and Land Policy Tools for Limiting Urban Sprawl: The Example of Belgrade. Spatium 2015, 33, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, A.; Orenstein, D.E. Can Urban Growth Management Work in an Era of Political and Economic Change? International Lessons From Israel. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2012, 78, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-K.; Wang, L.-G.W. Effects of Urban Construction Boundaries on Development Decisions; National Taipei University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abitz, J. Post-Socialist City Development in Tirana; Roskilde University: Roskilde, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, H.M.; Craig, W. Albanian Law on City Planning: Critical Summary of Its Major Provisions; Albania Series; Land Tenure Center University of Wisconsin—Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; p. 33. Available online: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/12770/1/ltcwp04.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Jirón, L.A.C.; Padzerka, C.M. Urban Form at the Fringe of Metropolitan Santiago (Chile). A Result of a Normative or Profitability Plan? 1999. Available online: https://web.uchile.cl/vignette/revistaurbanismo/n1/13.html (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Knaap, G.J.; Hopkins, L.D. The Inventory Approach to Urban Growth Boundaries. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2001, 67, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lai, S.-K. Reformulation and Assessment of the Inventory Approach to Urban Growth Boundaries. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Cheng, Q.; Gong, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.; Lu, J.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. Using Urban Development Boundaries to Constrain Uncontrolled Urban Sprawl in China. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2016, 106, 1321–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhuang, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, D. A New Perspective for Urban Development Boundary Delineation Based on SLEUTH-InVEST Model. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Tayyebi, A.H. An Urban Growth Boundary Model Using Neural Networks, GIS and Radial Parameterization: An Application to Tehran, Iran. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Perry, P.C.; Tayyebi, A.H. Predicting the Expansion of an Urban Boundary Using Spatial Logistic Regression and Hybrid Raster–Vector Routines with Remote Sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, X. Exploring Smart Growth Boundaries of Urban Agglomeration with Land Use Spatial Optimization: A Case Study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan City Group, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, A.; Yang, B.-S. Support Vector Machine in Machine Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2007, 21, 2560–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Reynolds, D.A.; Singer, E.; Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A. Support Vector Machines for Speaker and Language Recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 2006, 20, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartakhti, J.S.; Zangooei, M.H.; Mozafari, K. Hepatitis Disease Diagnosis Using a Novel Hybrid Method Based on Support Vector Machine and Simulated Annealing (SVM-SA). Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 108, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuldt, C.; Laptev, I.; Caputo, B. Recognizing Human Actions: A Local SVM Approach. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2004, Cambridge, UK, 26 August 2004; Volume 3, pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, P.; Hostert, P.; Gruebner, O.; van der Linden, S. Mapping Megacity Growth with Multi-Sensor Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xie, C.; Tay, R. Support Vector Machines for Urban Growth Modeling. Geoinformatica 2010, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Sultana, S.; Babakan, A.S.; Suthaharan, S. An Enhanced Support Vector Machine Model for Urban Expansion Prediction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 75, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardžić-Petrović, M.; Dragićević, S.; Kovačević, M.; Bajat, B. Modeling Urban Land Use Changes Using Support Vector Machines. Trans. GIS 2016, 20, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiantis, S.B.; Zaharakis, I.; Pintelas, P. Supervised Machine Learning: A Review of Classification Techniques. Emerg. Artif. Intell. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2007, 160, 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Samardžić-Petrović, M.; Kovačević, M.; Bajat, B.; Dragićević, S. Machine Learning Techniques for Modelling Short Term Land-Use Change. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vapnik, V. Pattern Recognition Using Generalized Portrait Method. Autom. Remote Control 1963, 24, 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Shi, X. Cellular Automata for Simulating Land Use Changes Based on Support Vector Machines. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C. Support Vector Machines for Land Use Change Modeling; UCGE Reports; Citeseer: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Belousov, A.I.; Verzakov, S.A.; Von Frese, J. Applicational Aspects of Support Vector Machines. J. Chemom. A J. Chemom. Soc. 2002, 16, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statnikov, A. A Gentle Introduction to Support Vector Machines in Biomedicine: Theory and Methods; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An Assessment of Support Vector Machines for Land Cover Classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.M.I. The Role of Port of Chittagong on the Economy of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. Available online: https://Thesis.Eur.Nl/Pub/40492 (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Mia, M.A.; Nasrin, S.; Zhang, M.; Rasiah, R. Chittagong, Bangladesh. Cities 2015, 48, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBS. Bangladesh Population and Housing Census 2011—National Volume2: Union Statistics; Statistics and Informatics Division, Ministry of Planning: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2014. Available online: http://www.bbs.gov.bd/WebTestApplication/userfiles/Image/National%20Reports/Union%20Statistics.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Meyer, W.B.; Turner, B.L. Human Population Growth and Global Land-Use/Cover Change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.M.; Shrestha, M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S.; Harrington, J.A.; Prebyl, T.J.; Swann, A.; Agar, M.; Antolin, M.F.; Nolen, B. Land Fragmentation under Rapid Urbanization: A Cross-Site Analysis of Southwestern Cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2011, 14, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.C.; Gaydos, L.J. Loose-Coupling a Cellular Automaton Model and GIS: Long-Term Urban Growth Prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1998, 12, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cervero, R. Linking Urban Transport and Land Use in Developing Countries. J. Transp. Land Use 2013, 6, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, S.; Weber, J. The Nature of Urban Growth and the Commuting Transition: Endless Sprawl or a Growth Wave? Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 544–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Srinivasan, S. Urban Land Use Change and Regional Access: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Mountrakis, G. Integration of Urban Growth Modelling Products with Image-Based Urban Change Analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5468–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.-O. Neural-Network-Based Cellular Automata for Simulating Multiple Land Use Changes Using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2002, 16, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.; Moore, T. Development inside Urban Growth Boundaries: Oregon’s Empirical Evidence of Contiguous Urban Form. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1998, 64, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Cao, X.; Imura, H. Application of an Integrated System Dynamics and Cellular Automata Model for Urban Growth Assessment: A Case Study of Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 91, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ye, C.; Cai, Y.; Xing, X.; Chen, Q. The Impact of Rural Out-Migration on Land Use Transition in China: Past, Present and Trend. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C. The Meds and Eds in Urban Economic Development. J. Urban Aff. 2003, 25, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.N.; Lloyd, R.; Wong, K.K.; Jain, P. Amenities Drive Urban Growth. J. Urban Aff. 2002, 24, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heying, C.H. Civic Elites, Civic Institutions, and the Urban Growth Dynamic. Ph.D. Thesis, Citeseer, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- de Noronha Vaz, E.; Nijkamp, P.; Painho, M.; Caetano, M. A Multi-Scenario Forecast of Urban Change: A Study on Urban Growth in the Algarve. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESRI ArcMap 10.7; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.7/get-started/introduction/whats-new-in-arcgis.htm (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Herbrich, R.; Graepel, T. A PAC-Bayesian Margin Bound for Linear Classifiers: Why SVMs Work. Adv. Neural Inf. Processing Syst. 2001, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Akbani, R.; Kwek, S.; Japkowicz, N. Applying Support Vector Machines to Imbalanced Datasets. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Karatzoglou, A.; Smola, A.; Hornik, K.; Karatzoglou, M.A. Package ‘Kernlab’. Technical Report, CRAN, 03 2016. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/kernlab/index.html (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- Huang, B.; Xie, C.; Tay, R.; Wu, B. Land-Use-Change Modeling Using Unbalanced Support-Vector Machines. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2009, 36, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Colkesen, I. A Kernel Functions Analysis for Support Vector Machines for Land Cover Classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Bui, H.Q.; Lasko, K.; Nguyen, T.N.T. Improvement of Land-Cover Classification over Frequently Cloud-Covered Areas Using Landsat 8 Time-Series Composites and an Ensemble of Supervised Classifiers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwuashi, O.; McConchie, J.; Nwilo, P.; Isong, M.; Eyoh, A.; Nwanekezie, O.; Eyo, E.; Ekpo, A.D. Predicting Future Land Use Change Using Support Vector Machine Based GIS Cellular Automata: A Case of Lagos, Nigeria. J. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Cao, C.; Lee, S.E. Applying Support Vector Machines to Predict Building Energy Consumption in Tropical Region. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popescu, L.-G. From a Holistic Approach of Public Policy to Co-Governance. Theor. Appl. Econ. 2013, 20, 584. [Google Scholar]
- Aminuzzaman, S.M. Dynamics of Public Policy: Determinants of Policymaking and Implementation in Bangladesh. Public Organ. Rev. 2013, 13, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).