Wilson’s Disease in Oman: A National Cohort Study of Clinical Spectrum, Diagnostic Delay, and Long-Term Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Demographic and Family History Data
2.4. Clinical Presentation Classification
- Hepatic presentations included signs such as raised liver enzymes, jaundice, hepatomegaly, or liver failure in the absence of neurological or psychiatric features.
- Neurological presentations covered motor symptoms such as tremors, dystonia, dysarthria, or gait disturbances, without hepatic or psychiatric involvement.
- Psychiatric presentations referred to behavioral disturbances, personality changes, depression, or psychosis when they occurred alone.
- Mixed presentations were characterized by the simultaneous presence of hepatic, neurological, and/or psychiatric symptoms.
- Ophthalmologic findings, specifically the presence of Kayser–Fleischer rings, were documented separately based on slit-lamp examination results but were not used as the sole criterion for symptom classification unless accompanied by neurological involvement.
2.5. Neuropsychiatric Severity Classification
2.6. Biochemical and Genetic Data
2.7. Treatment Data
2.8. Clinical Outcomes
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological and Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Presentation and Age at Diagnosis
3.3. Severity at Diagnosis
3.3.1. Hepatic Involvement
3.3.2. Neuropsychiatric Severity
3.4. Treatment Modalities and Outcomes
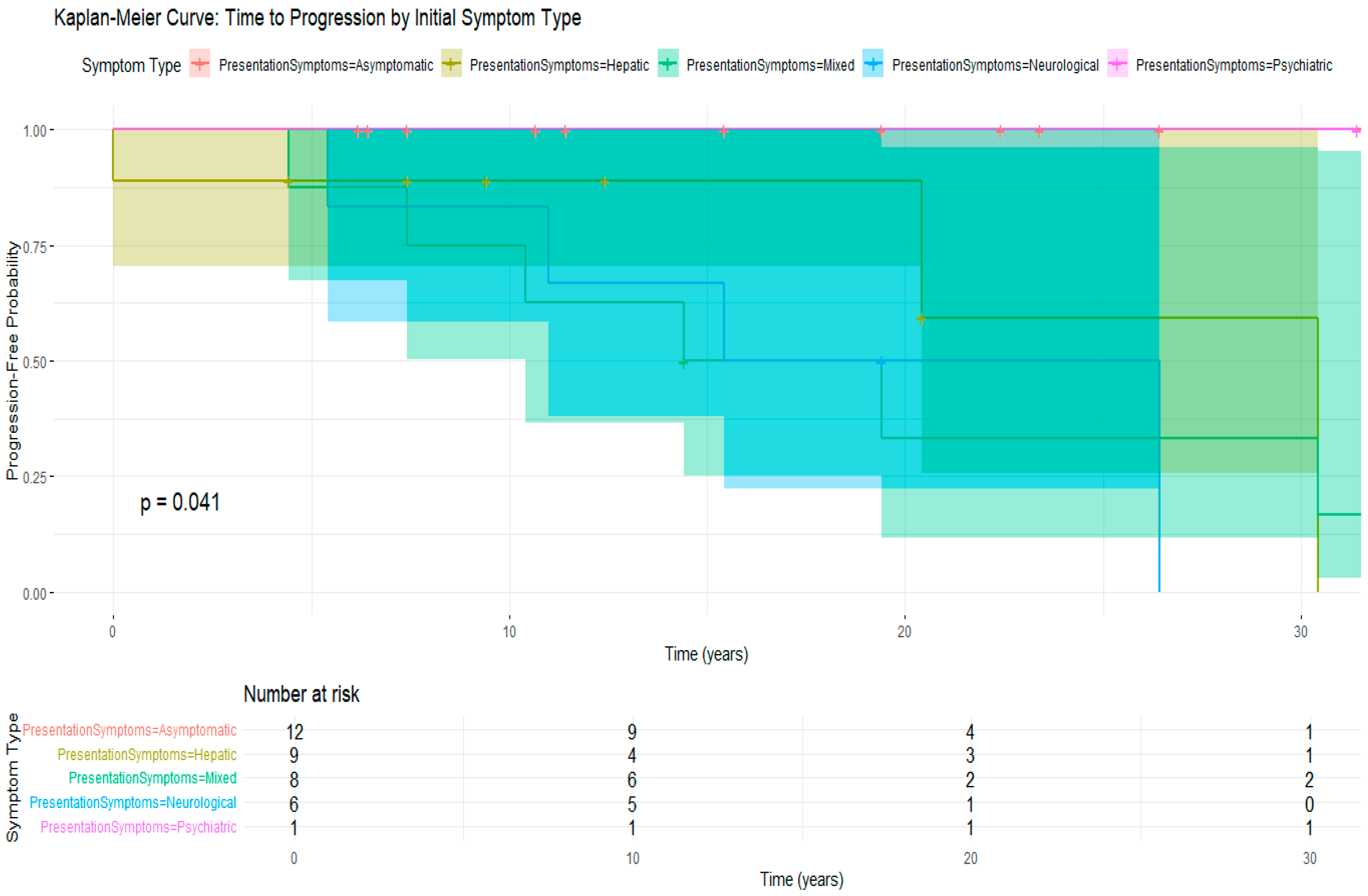
3.5. Treatment Compliance and Its Impact on Disease Progression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, G.R.; Forbes, J.R.; Roberts, E.A.; Walshe, J.M.; Cox, D.W. The Wilson disease gene: Spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Luo, K. Mutation analysis of the ATP7B gene and genotype-phenotype correlation in Chinese patients with Wilson disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza. Wilson’s disease in Oman, report of an Omani family. Oman. Med. J. 1994, 11, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.N.; Hashim, J.; Venugopalan, P. Pattern of inborn errors of metabolism in an Omani population of the Arabian Peninsula. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2002, 22, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanpong, A.; Dhawan, A. Wilson disease in children and young adults—State of the art. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzoulis, S.; Heuer, K.; Sparling, N.; Teynor, M. The patient experience of Wilson disease: A conceptual model based on qualitative research. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M. Diagnosis for Wilson disease: This disease may not be a rare disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.; Marques, M.; Liberal, R.; Cardoso, H.; Lopes, S.; Macedo, G. Wilson disease in Northern Portugal: A long-term follow-up study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Czlonkowska, A.; Stremmel, W.; Houwen, R.; Rosenberg, W.; Schilsky, M.; Jansen, P.; Moradpour, D. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilsky, M.L.; Roberts, E.A.; Bronstein, J.M.; Dhawan, A.; Hamilton, J.P.; Rivard, A.M.; Washington, M.K.; Weiss, K.H.; Zimbrean, P.C. A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Wilson Disease: 2022 Practice Guidance on Wilson Disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- João Soares, R.; Monteiro, N.; Machado, J.; Silva Marques, J.; Nunes, A. A Challenging Case of Wilson’s Disease. Cureus 2023, 15, e42655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wungjiranirun, M.; Sharzehi, K. Wilson’s Disease. Semin. Neurol. 2023, 43, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dening, T.R.; Berrios, G.E. Wilson’s Disease: Psychiatric Symptoms in 195 Cases. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1989, 46, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbrean, P.; Seniów, J. Cognitive and psychiatric symptoms in Wilson disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 142, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członkowska, A.; Litwin, T.; Dusek, P.; Ferenci, P.; Lutsenko, S.; Medici, V.; Rybakowski, J.K.; Weiss, K.H.; Schilsky, M.L. Nature Reviews Disease Primers article: Wilson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, P.; Czlonkowska, A.; Janczyk, W.; Litwin, T. Wilson’s disease—Management and long term outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudianos, G.; Gitlin, J.D. Wilson’s disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzberger, R.; Madl, C.; Ferenci, P. Wilson Disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2005, 20, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomair, R.M.; Alkiady, T.I.; Alkhamees, A.A.; Al Alyani, H.A.; Alharbi, S.S.A.; Aldalili, A.Y.A.; Alruki, K.O.A.; Almarshed, B.O.N.; Alruwaili, M.M.; Aldalbahi, T.G.T.; et al. Advancements in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson’s Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Approaches and Molecular Insights. J. Angiother. 2021, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, P.; Kwaśniewska, P.K.; Wilewska, A.; Borowiec, K.; Borowiec, A.; Biernikiewicz, J.; Alabrudziński, K.; Biernikiewicz, M.; Pomirski, B.; Pomirska, A. The Wilson’s disease—Etiology, symptoms in various organs, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis. J. Educ. Health Sport 2025, 77, 56733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, P.; Jańczyk, W.; Zanetto, A.; Burra, P.; Czlonkowska, A.; Debray, D.; Ferenci, P.; Merle, U.; Nicastro, E.; Poujois, A.; et al. EASL-ERN Clinical Practice Guidelines on Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 690–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursitoglu, M.; Cikrikcioglu, M.A.; Danalioglu, A.; Tukek, T. Wilson’s disease. Cent. Eur. J. Med. 2010, 5, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, C.; Denk, H. Wilson disease. Virchows. Archiv. 2004, 445, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.; Schwarz, C.; Burghart, L.; Pfisterer, N.; Bauer, D.; Hübl, W.; Mandorfer, M.; Gschwantler, M.; Reiberger, T. Late-stage presentation with decompensated cirrhosis is alarmingly common but successful etiologic therapy allows for favorable clinical outcomes. PLoS ONE 2023, 1, e0290352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, S.L. Key Insights and Clinical Pearls in the Identification and Management of Cirrhosis and Its Complications. Am. J. Med. 2024, 137, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shribman, S.; Warner, T.T.; Dooley, J.S. Clinical presentations of Wilson disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7 (Suppl. 2), 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Serper, M. Screening for advanced liver disease in the general population. Lancet 2023, 402, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Yopp, A.C.; Singal, A.G. Diagnostic delays are common among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2015, 13, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deme, P.; Sheffield, A.; Alick-Lindstrom, S. Wilson’s disease: Neuropsychiatric presentation and delayed diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e246296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Ganaraja, V.H.; Sharma, V.K. Wilson’s disease. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2025, 4, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korga, M.; Pawlik, P.; Zaroda, P.; Wawrzkowicz, J.; Niewinna, P.; Dąda, P.; Mańdziuk, D.; Żuchowski, M.; Kołodziej, K.; Kolodziej, W.J. Wilson’s disease—Clinical picture, factors influencing disease progression, treatment methods. Qual. Sport 2024, 15, 51826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, T.; Dzieżyc, K.; Członkowska, A. Wilson disease-treatment perspectives. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7 (Suppl. 2), 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, U.; Schaefer, M.; Ferenci, P.; Stremmel, W. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and long-term outcome of Wilson’s disease: A cohort study. Gut 2007, 56, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloh, T.; Annunziato, R.A. Transition of Care and Adherence in Patients with Wilson Disease. In Clinical and Translational Perspectives on WILSON DISEASE; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Wilson’s Disease. Semin. Neurol. 2007, 27, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.M.; Lu, X.; Shao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Sheng, H.; Guan, Z.; et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of early diagnosed Wilson’s disease: A large cohort study. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Age at First Presentation (years) | Median: 13 (IQR: 6.75–25.0) |
| Age at Diagnosis (years) | Median: 14.5 (IQR: 9.0–27.0) |
| Sex | |
| 16 (44.4%) |
| 20 (55.6%) |
| Family History of WD | 32 (88.9%) |
| Parental Consanguinity | 2 (5.6%) |
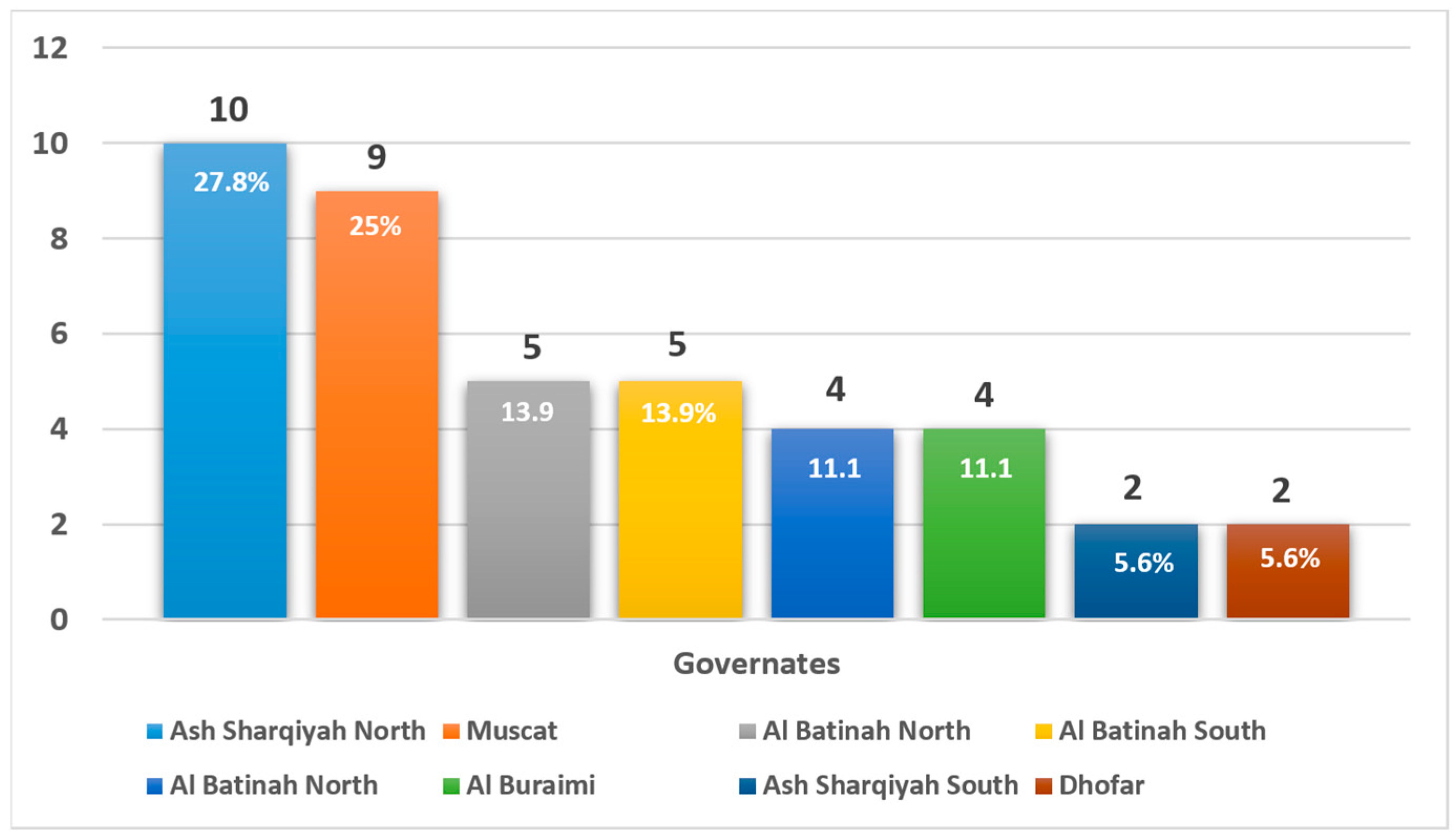
| Region of Origin | |
| 10 (27.8%) |
| 9 (25.0%) |
| 6 (16.7%) |
| 11 (30.5%) |
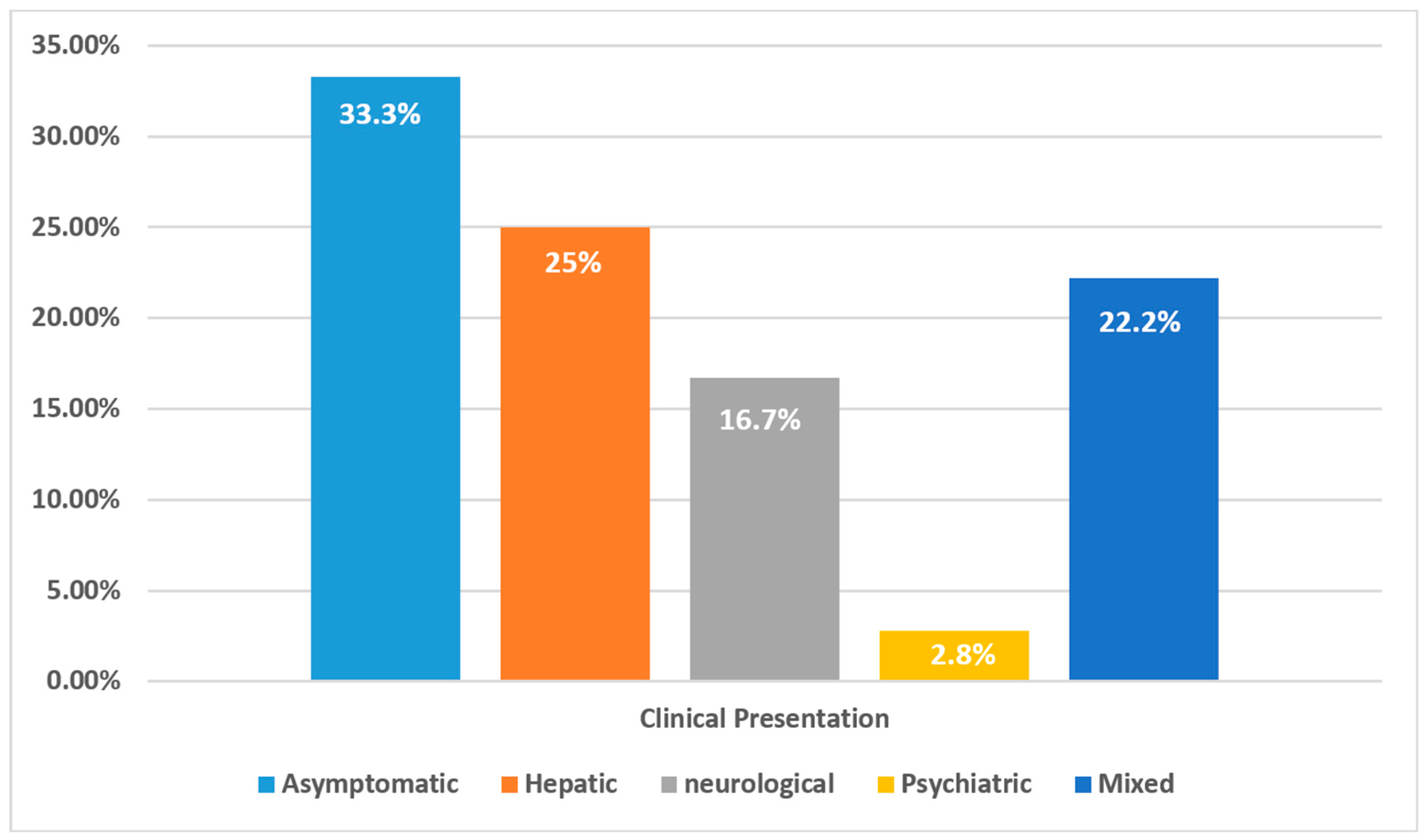
| Clinical Presentation | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Asymptomatic (via Family Screening) | 12 (33.3%) |
| Pure Hepatic Symptoms | 9 (25.0%) |
| Pure Neurological Symptoms | 6 (16.7%) |
| Hepatic + Neurological | 4 (11.1%) |
| Neurological + Psychiatric | 2 (5.6%) |
| Hepatic + Neurological + Psychiatric | 2 (5.6%) |
| Pure Psychiatric Symptoms | 1 (2.8%) |
| Presentation Symptoms | n | Mean_Age | SD_Age | Median Age at Diagnosis (IQR) * | Min_Age | Max_Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic | 12 | 11.8 | 7.8 | 11.0 ** | 0.8 | 25.0 |
| Hepatic | 9 | 16.0 | 9.4 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 30.0 |
| Mixed | 8 | 19.0 | 6.7 | 17.0 | 13.0 | 32.0 |
| Neurological | 6 | 25.3 | 7.5 | 24.5 ** | 16.0 | 35.0 |
| Psychiatric | 1 | 11.0 | NA | 11.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
| Severity Level | |
|---|---|
| Hepatic Severity at Diagnosis | n (%) |
| 13 (36.1%) |
| 14 (38.9%) |
| 6 (16.7%) |
| 3 (8.3%) |
| Neuropsychiatric Severity at Diagnosis | n (%) |
| 22 (61.1%) |
| 7 (19.4%) |
| 7 (19.4%) |
| A. Treatment Regimens at Last Follow-Up | |
|---|---|
| Treatment Regimen | n (%) |
| Trientene + Zinc sulfate | 12 (33.3%) |
| Penicillamine + Zinc sulfate | 8 (22.2%) |
| Zinc sulfate only | 6 (16.7%) |
| Penicillamine only | 4 (11.1%) |
| All three drugs | 4 (11.1%) |
| Trientene only | 2(5.6%) |
| B. Treatment and Follow-Up Outcomes | |
| Outcome | n (%) |
| Regular follow-up | 34 (94.4%) |
| Deaths | 2 (5.6%) |
| Survival Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Median survival time (years) | 14.4 |
| 25th percentile (Q1, years) | 5.6 |
| 75th percentile (Q3, years) | 18.7 |
| Interquartile range (IQR, years) | 13.1 |
| Estimated Survival Probability (%) | |
| At 5 years | 91.4% |
| At 10 years | 88.3% |
| At 15 years | 70.1% |
| At 20 years | 61.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Busafi, S.A.; Al Julandani, J.N.; Alismaeili, Z.; Al Raisi, J.J. Wilson’s Disease in Oman: A National Cohort Study of Clinical Spectrum, Diagnostic Delay, and Long-Term Outcomes. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15080144
Al-Busafi SA, Al Julandani JN, Alismaeili Z, Al Raisi JJ. Wilson’s Disease in Oman: A National Cohort Study of Clinical Spectrum, Diagnostic Delay, and Long-Term Outcomes. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(8):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15080144
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Busafi, Said A., Juland N. Al Julandani, Zakariya Alismaeili, and Juhaina J. Al Raisi. 2025. "Wilson’s Disease in Oman: A National Cohort Study of Clinical Spectrum, Diagnostic Delay, and Long-Term Outcomes" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 8: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15080144
APA StyleAl-Busafi, S. A., Al Julandani, J. N., Alismaeili, Z., & Al Raisi, J. J. (2025). Wilson’s Disease in Oman: A National Cohort Study of Clinical Spectrum, Diagnostic Delay, and Long-Term Outcomes. Clinics and Practice, 15(8), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15080144






