Classification of Tree Species in Poland Using CNNs Tabular-to-Pseudo Image Approach Based on Sentinel-2 Annual Seasonality Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Preprocessing
2.2. Method
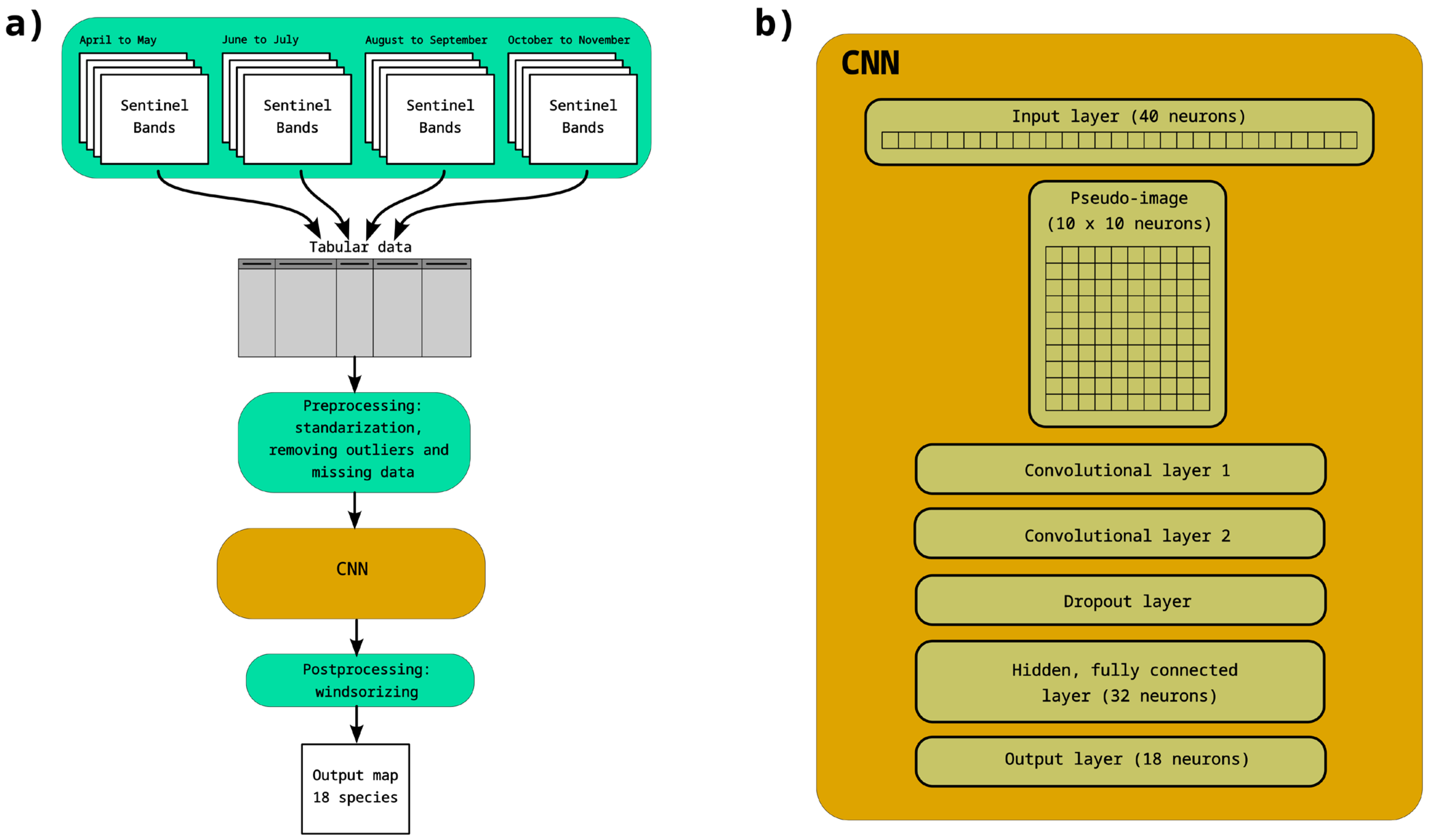
2.2.1. CNN Topology
2.2.2. Post-Processing
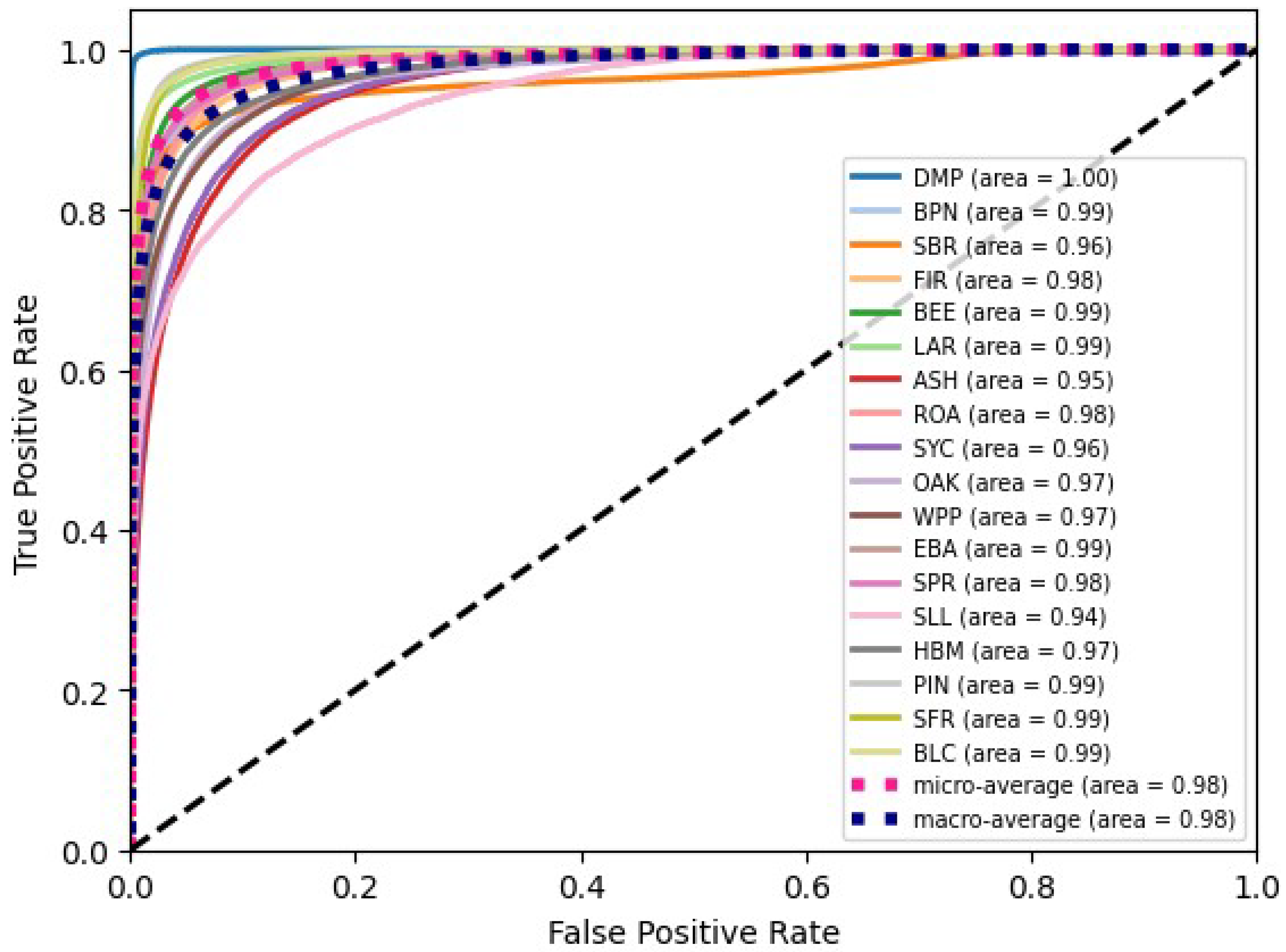
2.2.3. Model Quality Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CA | Classification Accuracy |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CK | Cohen Kappa Index |
| DBH | Diameter at Breast Height |
| FC-Viz | Feature Clustering-Visualization |
| FDB | Forest Data Bank |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| NCTD | Novel Algorithm for Convolving Tabular Data |
| RELU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| RF | Random Forest |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristics |
| SCA | Species Classification Accuracy |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TabPFN | Tabular Prior Fitted Network |
References
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Margules, C.R.; Botkin, D.B. Indicators of Biodiversity for Ecologically Sustainable Forest Management. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Hall, R.J.; Coops, N.C.; Franklin, S.E. High Spatial Resolution Remotely Sensed Data for Ecosystem Characterization. Bioscience 2004, 54, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, G.J.; Hall, R.J.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, G.A.; Franklin, S.E.; Stenhouse, G.B.; Kobliuk, T.; LeDrew, E.F. Remote Sensing and Forest Inventory for Wildlife Habitat Assessment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Stereńczak, K.; Modzelewska, A.; Lefsky, M.; Waser, L.T.; Straub, C.; Ghosh, A. Review of Studies on Tree Species Classification from Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisong, E. Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-4842-4469-2. [Google Scholar]
- Immitzer, M.; Atzberger, C.; Koukal, T. Tree Species Classification with Random Forest Using Very High Spatial Resolution 8-Band WorldView-2 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2661–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Lindberg, E.; Reese, H. Tree Species Classification with Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiola, T.M.; Fantinel, R.A.; Dos Santos, F.D.; De Bastos, F.; Schuh, M.S.; Fernandes, P.; Simões, B.A.; Pereira, R.S. Use of Machine Learning Algorithms in the Classification of Forest Species. Anuário Inst. Geociências 2023, 46, 50490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Szwagrzyk, E.; Tiede, D.; Sudmanns, M.; Kozak, J. Map of Forest Tree Species for Poland Based on Sentinel-2 Data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2024, 16, 2877–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Support Vector Machines for Tree Species Identification Using LiDAR-Derived Structure and Intensity Variables. Geocarto Int. 2013, 28, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deur, M.; Gašparović, M.; Balenović, I. Tree Species Classification in Mixed Deciduous Forests Using Very High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery and Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballanti, L.; Blesius, L.; Hines, E.; Kruse, B. Tree Species Classification Using Hyperspectral Imagery: A Comparison of Two Classifiers. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubin, N.A.; Nadarajoo, E.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Hamedianfar, A. Young and Mature Oil Palm Tree Detection and Counting Using Convolutional Neural Network Deep Learning Method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7500–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep Learning in Environmental Remote Sensing: Achievements and Challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.; Li, Q.; Jing, L. CNN-Based Individual Tree Species Classification Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Airborne LiDAR Data. Forests 2021, 12, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Neuwirth, M.; Böck, S.; Brenner, H.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. Optimal Input Features for Tree Species Classification in Central Europe Based on Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimannejad, L.; Ullah, S.; Abedi, R.; Dees, M.; Koch, B. Evaluating the Potential of Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Irs Satellite Images in Tree Species Classification of Hyrcanian Forest of Iran Using Random Forest. J. Sustain. For. 2019, 38, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionova, S.; Trekin, A.; Ignatiev, V.; Oseledets, I. Tree Species Mapping on Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery with Weakly Supervised Classification and Object-Wise Sampling. Forests 2021, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, A.; Mukharamova, S.; Yermolaev, O.; Shaykhutdinova, G. Automated Recognition of Tree Species Composition of Forest Communities Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlswede, S.; Schulz, C.; Gava, C.; Helber, P.; Bischke, B.; Förster, M.; Arias, F.; Hees, J.; Demir, B.; Kleinschmit, B. TreeSatAI Benchmark Archive: A Multi-Sensor, Multi-Label Dataset for Tree Species Classification in Remote Sensing. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2023, 15, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.H.; Valdez, M.; Chen, C.-F. Forest tree species distribution mapping using landsat satellite imagery and topographic variables with the maximum entropy method in mongolia. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieva, O.; Brovkina, O.; Saidov, A. An Original Method for Tree Species Classification Using Multitemporal Multispectral and Hyperspectral Satellite Data. Silva Fenn. 2020, 54, 10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad Turlej, C.; Ozdogan, M.; Radeloff, V.C. Mapping Forest Types over Large Areas with Landsat Imagery Partially Affected by Clouds and SLC Gaps. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S. A Comparative Analysis of High Spatial Resolution IKONOS and WorldView-2 Imagery for Mapping Urban Tree Species. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeren, D.; Fauvel, M.; Josipović, V.; Lopes, M.; Planque, C.; Willm, J.; Dejoux, J.-F. Tree Species Classification in Temperate Forests Using Formosat-2 Satellite Image Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Ørka, H.O.; Ene, L.T.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E. Tree Crown Delineation and Tree Species Classification in Boreal Forests Using Hyperspectral and ALS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Dobrinić, D.; Pilaš, I. Mapping of Allergenic Tree Species in Highly Urbanized Area Using Planetscope Imagery—A Case Study of Zagreb, Croatia. Forest 2023, 14, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyn, C.; Lejeune, P.; Michez, A.; Latte, N. Mapping Tree Species Proportions from Satellite Imagery Using Spectral–Spatial Deep Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionova, S.; Trekin, A.; Ignatiev, V.; Oseledets, I. Neural-Based Hierarchical Approach for Detailed Dominant Forest Species Classification by Multispectral Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, F.; Morin, D.; Planells, M.; Vincent-Barbaroux, C. Tree Species Classification at the Pixel Level Using Deep Learning and Multispectral Time Series in an Imbalanced Context. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Owari, T.; Tsuyuki, S.; Hiroshima, T.; Hong, D. Combined Gated Graph Convolution Neural Networks with Multi-Modal Geospatial Data for Forest Type Classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Li, F.; Feng, F.; Zhao, Y. An Innovative Lightweight 1D-CNN Model for Efficient Monitoring of Large-Scale Forest Composition: A Case Study of Heilongjiang Province, China. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2271246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in Vegetation Remote Sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Abelenda, F.J.; Chushig-Muzo, D.; Peiro-Corbacho, P.; Gómez-Martínez, V.; Wägner, A.M.; Granja, C.; Soguero-Ruiz, C. Transfer Learning for a Tabular-to-Image Approach: A Case Study for Cardiovascular Disease Prediction. J. Biomed. Inform. 2025, 165, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, L.M.; da Silva Neto, S.R.; Endo, P.T. A Comparative Analysis of Converters of Tabular Data Into Image for the Classification of Arboviruses Using Convolutional Neural Networks. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Sentinel Data, 2018–2021. Retrieved from Google Earth Engine, Processed by ESA. Available online: https://browser.dataspace.copernicus.eu (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Sharma, A.; Vans, E.; Shigemizu, D.; Boroevich, K.A.; Tsunoda, T. DeepInsight: A Methodology to Transform a Non-Image Data to an Image for Convolution Neural Network Architecture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Brettin, T.; Xia, F.; Partin, A.; Shukla, M.; Yoo, H.; Evrard, Y.A.; Doroshow, J.H.; Stevens, R.L. Converting Tabular Data into Images for Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TMP. 2nd Place Solution—With 1D-CNN (Private LB: 0.01601), Kaggle. 2021. Available online: https://Www.Kaggle.Com/c/Lish-Moa/Discussion/202256 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Xi, Y.; Ren, C.; Tian, Q.; Ren, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z. Exploitation of Time Series Sentinel-2 Data and Different Machine Learning Algorithms for Detailed Tree Species Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7589–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-Hub. Sentinel2-Cloud-Detector. Available online: https://Github.Com/Sentinel-Hub/Sentinel2-Cloud-Detector (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I. Handbook of Mathematical Functions: With Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Keras. Available online: https://Github.com/Fchollet/Keras (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- O’Malley, T.; Bursztein, E.; Long, J.; Chollet, F.; Jin, H.; Invernizzi, L. Keras Tuner. 2019. Available online: https://Github.Com/Keras-Team/Keras-Tuner (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Lundberg, S.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07874. [Google Scholar]
- Štrumbelj, E.; Kononenko, I. Explaining Prediction Models and Individual Predictions with Feature Contributions. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2014, 41, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
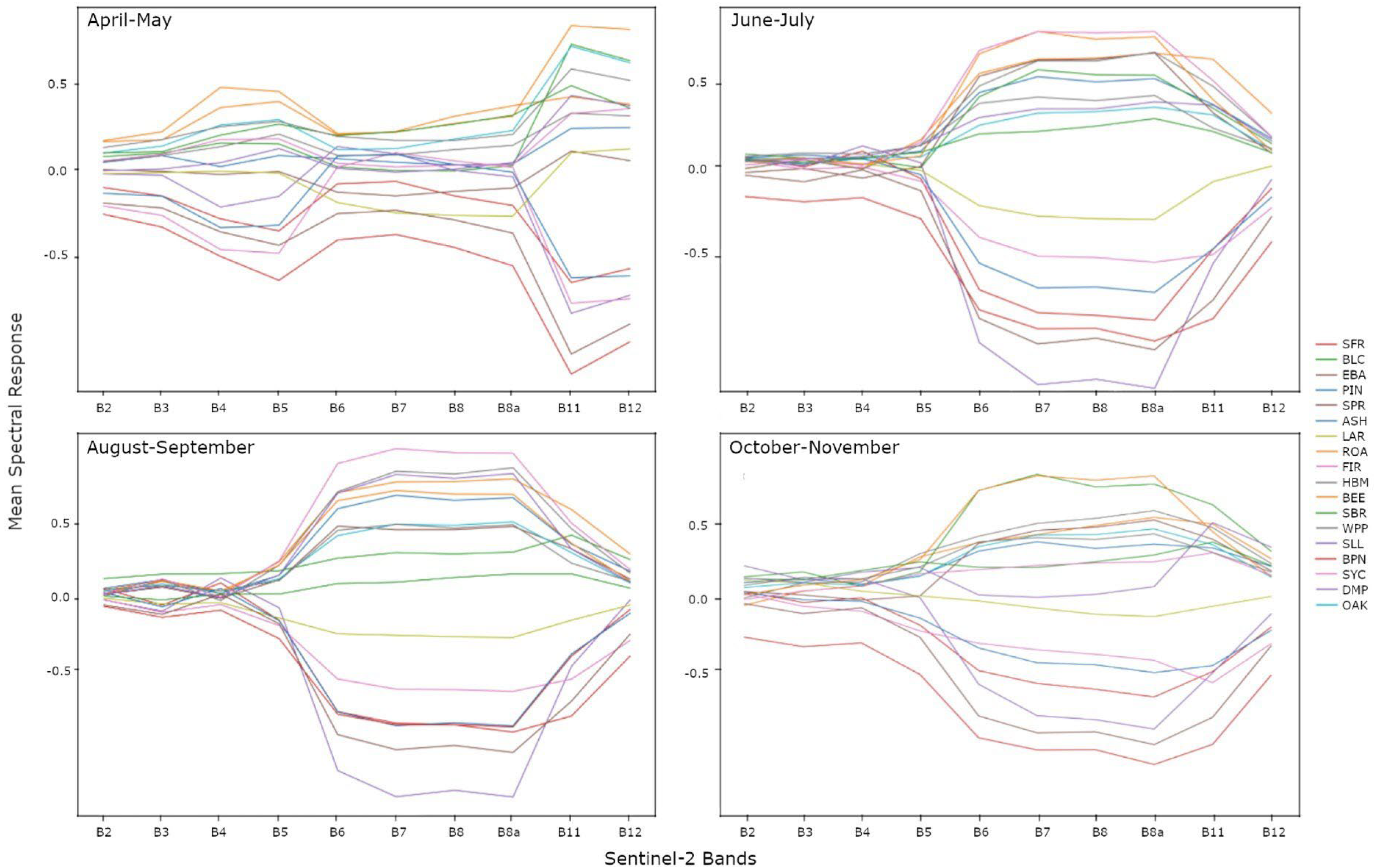
- Papes, M.; Tupayachi, R.; Martinez, P.; Peterson, A.T.; Asner, G.P.; Powell, G.V.N. Seasonal Variation in Spectral Signatures of Five Genera of Rainforest Trees. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.A.; Milton, E.J. Seasonal Variations in the Spectral Reflectance of Deciduous Tree Canopies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, E.; Awaya, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Matsumura, N. Seasonal Patterns of Canopy Structure, Biochemistry and Spectral Reflectance in a Broad-Leaved Deciduous Fagus Crenata Canopy. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 167, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, C.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Yu, B. Impacts of Leaf Age on Canopy Spectral Signature Variation in Evergreen Chinese Fir Forests. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A.; Clark, D.B. Climate-Induced Annual Variation in Canopy Tree Growth in a Costa Rican Tropical Rain Forest. J. Ecol. 1994, 82, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, G.; Sarris, D. Identifying the Full Spectrum of Climatic Signals Controlling a Tree Species’ Growth and Adaptation to Climate Change. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, D.; Müller, A.; Behnke, S. Evaluation of Pooling Operations in Convolutional Architectures for Object Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6354, pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C. Stop Explaining Black Box Machine Learning Models for High Stakes Decisions and Use Interpretable Models Instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.G.; Lee, S.-I. Consistent Individualized Feature Attribution for Tree Ensembles. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03888. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, C.; Förster, M.; Kleinschmit, B. Testing the Red Edge Channel for Improving Land-Use Classifications Based on High-Resolution Multi-Spectral Satellite Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5583–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Remote Sensing of Leaf Water Content in the near Infrared. Remote Sens. Environ. 1980, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, W.W.; Kun, J.J.; ShunLin, L.L. Assessment of Sentinel-2 MSI Spectral Band Reflectances for Estimating Fractional Vegetation Cover. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.; Karnieli, A.; Bonfil, D.J.; Cohen, Y.; Alchanatis, V. SWIR-Based Spectral Indices for Assessing Nitrogen Content in Potato Fields. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2010, 31, 5127–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Merzlyak, M.N. Use of a Green Channel in Remote Sensing of Global Vegetation from EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenizy, H.A.; Berri, J. Transforming Tabular Data into Images via Enhanced Spatial Relationships for CNN Processing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damri, A.; Last, M.; Cohen, N. Towards Efficient Image-Based Representation of Tabular Data. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 1023–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
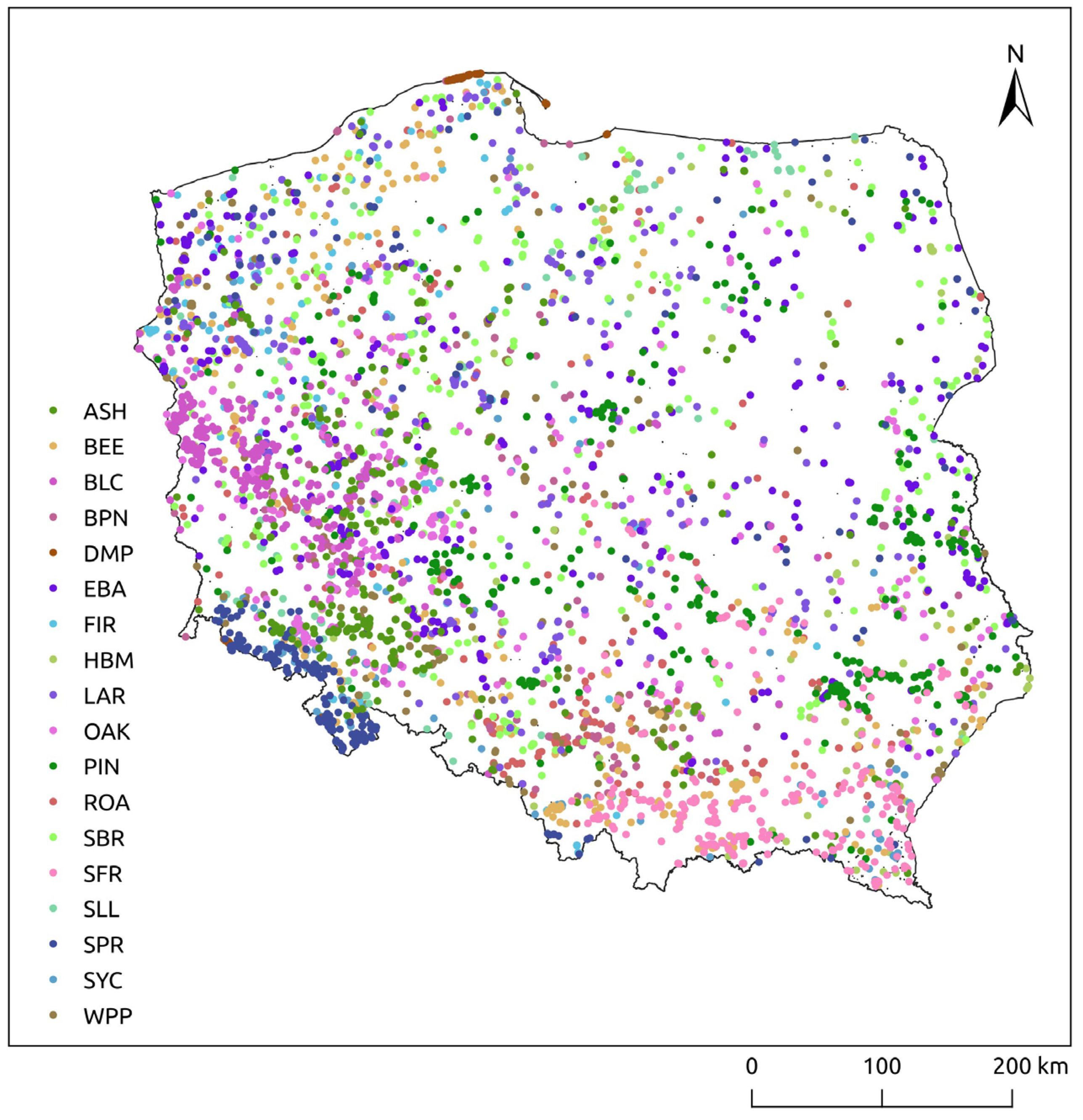

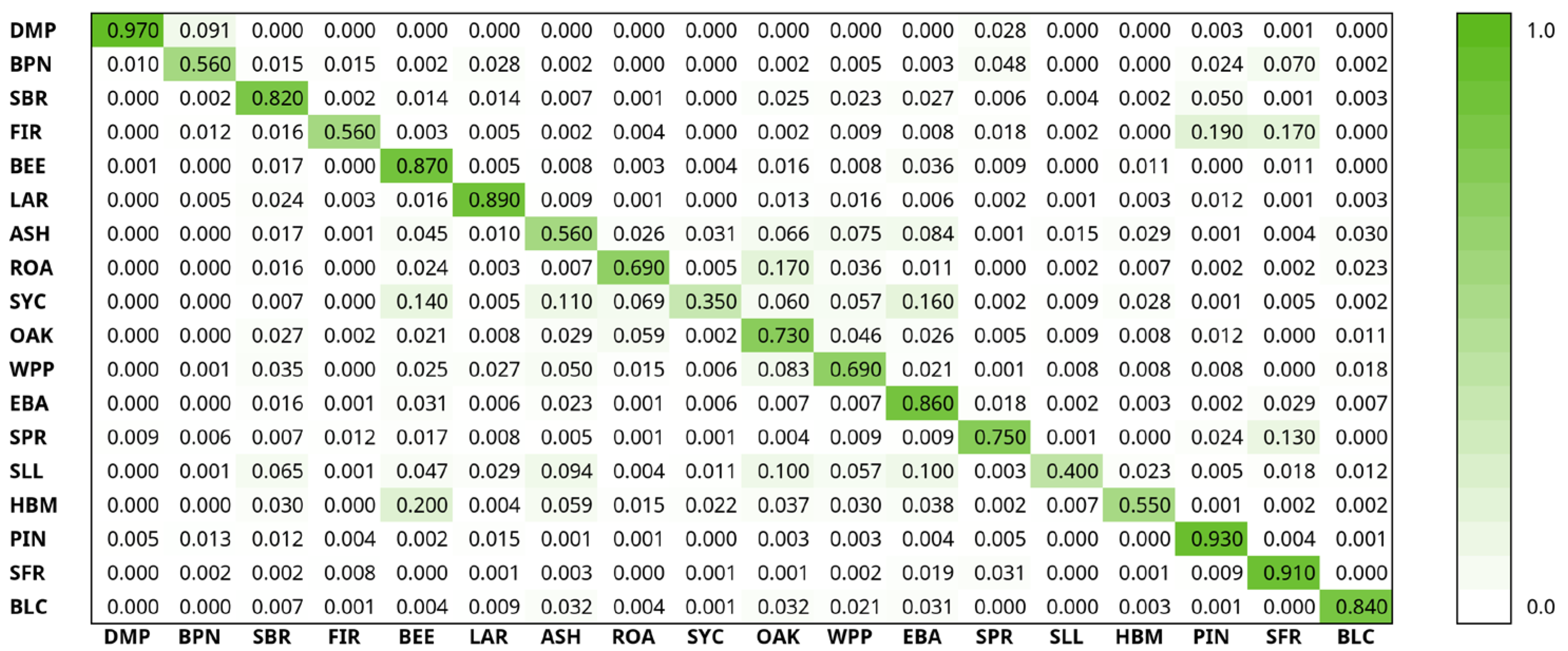
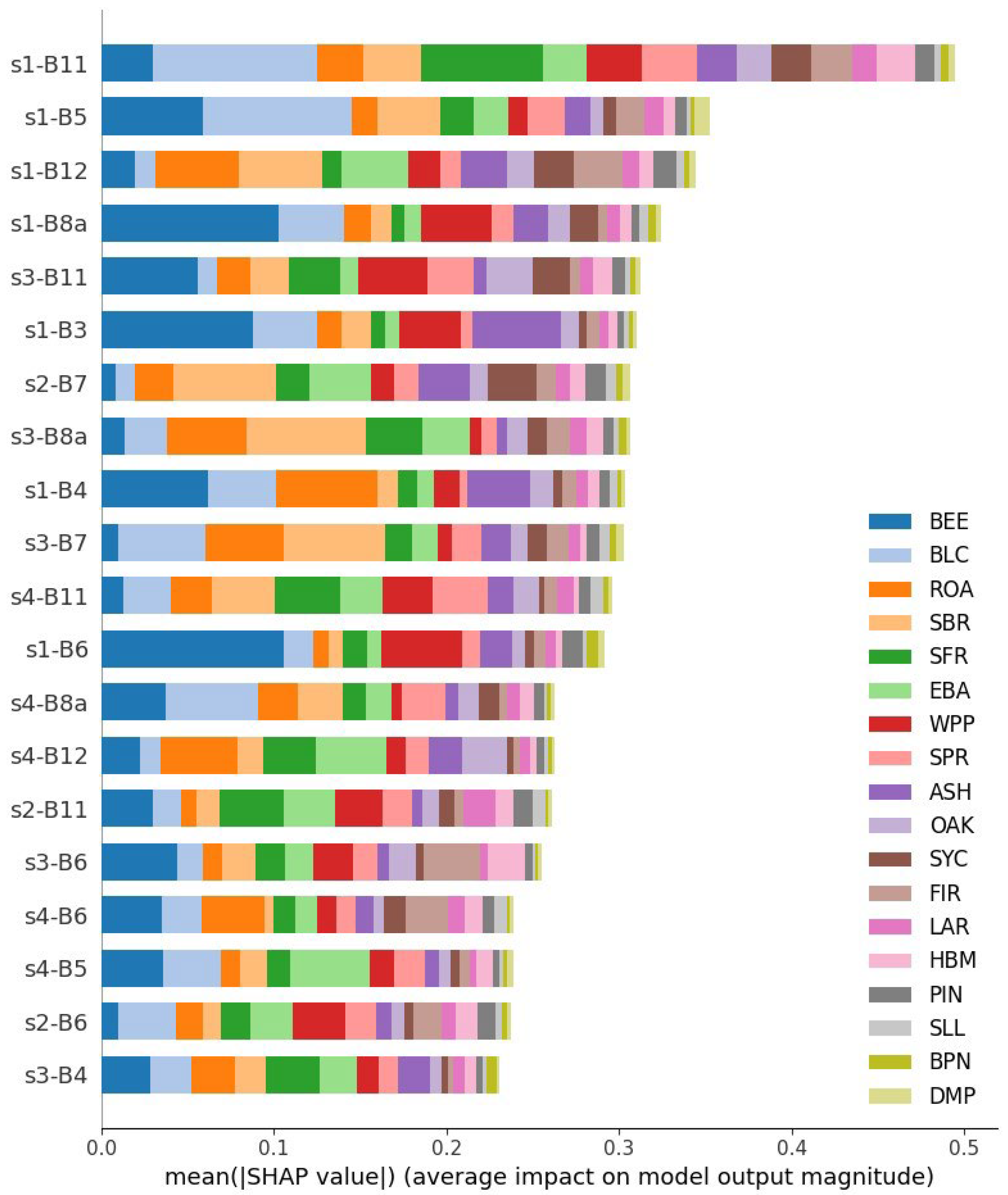
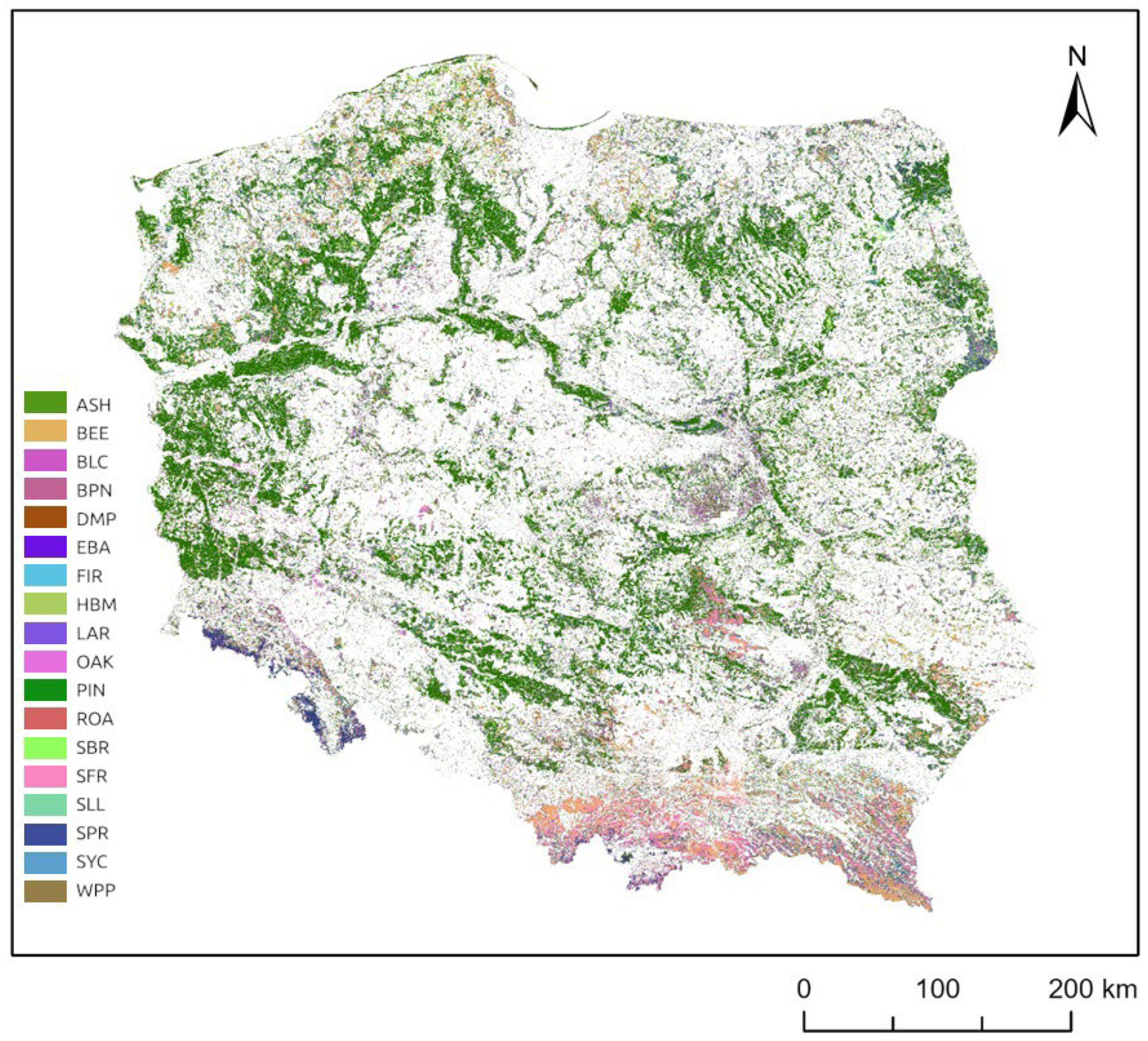
| Abbreviation | Latin Name | Popular Name | Cells Sampled | Number of Stands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASH | Fraxinus excelsior L. | European ash | 196,470 | 336 |
| BEE | Fagus sylvatica L. | European beech | 458,448 | 315 |
| BLC | Robinia pseudoacacia L. | Black locust | 167,099 | 351 |
| BPN | Pinus nigra Arn. | Black pine | 65,240 | 161 |
| DMP | Pinus mugo Turra | Dwarf mountain pine | 117,172 | 127 |
| EBA | Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. | European black alder | 506,234 | 520 |
| FIR | Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco | Douglas fir | 71,295 | 178 |
| HBM | Carpinus betulus L. | European Hornbeam | 86,110 | 176 |
| LAR | Larix decidua Mill. | European larch | 331,760 | 300 |
| OAK | Quercus undefined | Oak undefined | 398,095 | 360 |
| PIN | Pinus sylvestris L. | Scots pine | 436,300 | 355 |
| ROA | Quercus rubra L. | northern red oak | 162,934 | 278 |
| SBR | Betula pendula Roth | Silver birch | 332,170 | 355 |
| SFR | Abies alba Mill. | Silver Fir | 506,935 | 303 |
| SLL | Tilia cordata Mill. | Small-leaved linden | 57,385 | 127 |
| SPR | Picea abies (L.) H.Karst | European spruce | 231,753 | 269 |
| SYC | Acer pseudoplatanus L. | Sycamore maple | 50,063 | 163 |
| WPP | Populus alba L. | White poplar | 292,989 | 584 |
| Species | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASH | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 37,356 |
| BEE | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 80,108 |
| BLC | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 32,165 |
| BPN | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 0.65 | 18,165 |
| DMP | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 35,749 |
| EBA | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 169,852 |
| FIR | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 17,040 |
| HBM | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 19,620 |
| LAR | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 57,875 |
| OAK | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 114,673 |
| PIN | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 112,260 |
| ROA | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 35,600 |
| SBR | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 82,715 |
| SFR | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 121,970 |
| SLL | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 7830 |
| SPR | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 57,179 |
| SYC | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 9918 |
| WPP | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.73 | 84,900 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikołajczyk, Ł.; Hawryło, P.; Netzel, P.; Talaga, J.; Zdunek, N.; Socha, J. Classification of Tree Species in Poland Using CNNs Tabular-to-Pseudo Image Approach Based on Sentinel-2 Annual Seasonality Data. Forests 2025, 16, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071039
Mikołajczyk Ł, Hawryło P, Netzel P, Talaga J, Zdunek N, Socha J. Classification of Tree Species in Poland Using CNNs Tabular-to-Pseudo Image Approach Based on Sentinel-2 Annual Seasonality Data. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikołajczyk, Łukasz, Paweł Hawryło, Paweł Netzel, Jakub Talaga, Nikodem Zdunek, and Jarosław Socha. 2025. "Classification of Tree Species in Poland Using CNNs Tabular-to-Pseudo Image Approach Based on Sentinel-2 Annual Seasonality Data" Forests 16, no. 7: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071039
APA StyleMikołajczyk, Ł., Hawryło, P., Netzel, P., Talaga, J., Zdunek, N., & Socha, J. (2025). Classification of Tree Species in Poland Using CNNs Tabular-to-Pseudo Image Approach Based on Sentinel-2 Annual Seasonality Data. Forests, 16(7), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071039










