Abstract
Engineering disturbances are increasing in permafrost regions of northeastern China, where soil microorganisms play essential roles in biogeochemical cycling and are highly sensitive to linear infrastructure disturbances. However, limited research has addressed how microbial communities respond to different post-engineering-disturbance recovery stages. This study investigated the impacts of the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipelines (CRCOPs) on soil microbial communities in a typical boreal forest permafrost zone of the Da Xing’anling Mountains. Soil samples were collected from undisturbed forest (the control, CK); short-term disturbed sites associated with Pipeline II, which was constructed in 2018 (SD); and long-term disturbed sites associated with Pipeline I, which was constructed in 2011 (LD). Pipeline engineering disturbances significantly increased soil clay content and pH while reducing soil water content (SWC), soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) (p < 0.05). No significant differences in these soil properties were observed between SD and LD. Bacterial diversity increased significantly, whereas fungal diversity significantly decreased following pipeline disturbances (p < 0.05). The beta diversity of both bacterial and fungal communities differed significantly among the three disturbance types. At the phylum level, pipeline disturbance increased the relative abundances of Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, Ascomycota, and Mortierellomycota while reducing those of Bacteroidota and Basidiomycota. These shifts were associated with disturbance-induced changes in soil properties. Microbial co-occurrence networks in SD exhibited greater complexity and connectivity than those in CK and LD, suggesting intensified biotic interactions and active ecological reassembly during the early recovery phase. These findings suggest that pipeline disturbance could drive soil microbial systems into a new stable state that is difficult to restore over the long term, highlighting the profound impacts of linear infrastructure on microbial ecological functions in cold regions. This study provides a scientific basis for ecological restoration and biodiversity conservation in permafrost-affected areas.
1. Introduction
Permafrost is a critical component of the cryosphere [1], characterized by its high sensitivity to both climatic variations and anthropogenic disturbances [2]. In China, the Da and Xiao Xing’anling Mountains in the northeast constitute the country’s second largest permafrost area and the only high-latitude permafrost region [3]. The distinct forest–wetland ecosystem in this area plays a vital role in global carbon dynamics. To meet growing energy demands, various infrastructure projects have been launched to explore, extract, store, and transport the abundant oil and gas resources in permafrost zones [4]. The China–Russia Crude Oil Pipelines (CRCOPs), the country’s first long-distance oil pipelines traversing permafrost terrain, have profound implications for energy security, economic growth, and ecological balance [5]. The pipeline system consists of two parallel routes: CRCOP I, which has been operational since 2011, and CRCOP II, operational since 2018 [6]. The pipelines span a total length of 953 km within China, with 441 km running through the ecologically sensitive permafrost regions in the Da Xing’anling Mountains, northeastern China [7]. Permafrost conditions along these pipelines are characterized by high ice content, low thermal and hydrological characteristics, structural instability, and pronounced susceptibility to climate change and anthropogenic disturbances [5,8].
The CRCOPs project involves large-scale construction, extensive geographical coverage, prolonged construction periods, and substantial environmental impacts [9]. Pipelines in permafrost zones are typically installed underground at depths of 1.6 and 2 m [10]. In addition, in the process of pipeline construction, it is necessary to remove the surface coverings above the active layer on a large scale, such as vegetation and organic matter layer [5]. Furthermore, soil excavated from the foundation pit is difficult to layer and backfill properly; thus, topsoil and subsoil are mixed. This process changes the content and distribution of soil organic matter [11], thereby exerting considerable impacts on the local ecological environment and ecosystem diversity [12]. During operation, the continuous transport of heated oil gradually increases the temperature of surrounding soils, accelerating permafrost degradation, promoting soil carbon loss, and consequently affecting regional carbon cycling process primarily mediated by soil microorganisms [13]. Microbial communities, which are central to material cycling in permafrost ecosystems, play a vital role in regulating energy flow and nutrient transformations [14]. Previous studies have emphasized that microbial recovery from various disturbances is critical for maintaining ecosystem stability and functionality [15], highlighting the importance of microbial research in assessing the ecological consequences of engineering activities. Despite substantial progress in understanding the ecological consequences of infrastructure development in cold environments, significant knowledge gaps remain concerning microbial community responses to pipeline engineering disturbances.
Previous studies have confirmed the marked ecological impacts of pipeline installation and operation on cold-region ecosystems [16]. Pipeline construction and operation accelerate permafrost thaw, alter soil thermal and hydrological regimes, and modify vegetation, thereby reducing soil nutrient levels, significantly altering soil physicochemical properties, and subsequently influencing soil microbial diversity and community structures [17,18,19]. Specifically, pipeline construction has been reported to reduce microbial diversity and abundance, reshaping microbial communities in surrounding soils [17,20]. During the operation phase, the rise in temperature and thawing of permafrost have expanded the space for the survival and reproduction of microorganisms in the active soil layer, significantly enhanced the microbial activity, increased the diversity of bacteria and fungi, and altered the composition of the microbial community [21,22,23,24], thus affecting the environmental recovery around the pipeline. However, mechanisms regulating microbial diversity and community composition vary substantially depending on the type and intensity of anthropogenic disturbance [25]. For example, soil microbial communities undergo pronounced changes under adverse conditions created by infrastructure projects in cold regions [26]. Long-distance water diversion projects have been shown to significantly reduce microbial species abundance, increase bacterial biomass, decrease fungal biomass, and weaken microbial network stability [27]. Similarly, highway construction in the Canadian permafrost region has resulted in vegetation degradation and altered soil physicochemical properties, leading to notable shifts in microbial community structure and diversity [28]. Oil pipeline construction in permafrost zones has also been found to significantly alter microbial diversity and community composition across soil depths [29]. Notably, the recovery period following engineering disturbances plays a crucial role in the succession of microbial communities. With increasing recovery time, the complexity of bacterial networks tends to increase while community diversity decreases; in contrast, fungal network complexity initially decreases and later increases, accompanied by a progressive increase in community diversity [30]. Although the relationships between soil physicochemical parameters (e.g., temperature, pH, nutrients) and microbial communities are well documented [31], several limitations remain. First, there is limited understanding of long-term ecological effects of linear thermal disturbances, such as those caused by pipelines, in permafrost regions. Second, few studies have investigated microbial community dynamics over extended recovery periods following infrastructure development. Addressing these gaps constitutes a critical scientific challenge for microbial ecology in the Da Xing’anling permafrost region, particularly under the accelerating pressures of climate warming. Therefore, this study aims to investigate soil ecological dynamics in the Da Xing’anling Mountains using microbial ecological approaches.
Situated at the sensitive southern edge of the Eurasian permafrost region, the forest-wetland ecosystems of the northern Da Xing’anling Mountains play a critical role in regional carbon sequestration. However, disturbances caused by the CRCOPs have reduced the stability of the local permafrost. To investigate how varying durations of CRCOP disturbance impact microbial community characteristics within the active layer soil of permafrost in the Da Xing’anling Mountains, this study focused on soils affected by pipeline construction. The objectives were to analyze differences in the effects of pre- and postdisturbance durations on soil microbial diversity, community composition, and network structure; quantify the correlations between soil physicochemical factors and microbial community characteristics; and identify key driving factors. Based on this, the following hypotheses are proposed: (1) pipeline engineering interference significantly changes the physical and chemical properties of soil; (2) there are strategic differences in the effects of pipeline interference duration on bacterial and fungal diversity; (3) there are stage differences in the driving force of soil physical and chemical factors on microbial communities. Through high-throughput sequencing, physical and chemical analysis, and network ecology methods, this study constructed a framework of “interference duration–microbial response–environmental driving”. The results will improve our understanding of the response of cold region ecosystems to linear engineering facilities, provide a basis for biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration strategies, and contribute to global carbon cycle research. Given the central role of soil microorganisms in regulating biogeochemical processes, particularly carbon cycling, this research provides critical insights into the contributions of cold-region ecosystems to global climate regulation. Moreover, the results have practical implications for ecological restoration, biodiversity protection, and sustainable management of permafrost-affected regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The study area is located in the Walagan region of Heilongjiang Province, China (52°35′76″ N, 124°32′96″ E), at elevations ranging from 460 to 480 m (Figure 1A). The region experiences a cold temperate continental monsoon climate, characterized by long cold, and dry winters, and short, wet summers. The monthly mean temperature remains below 0 °C for approximately seven months of the year, with a mean annual temperature of around −2.4 °C. Vegetation in the surrounding boreal forest is primarily composed of Larix gmelinii and Betula platyphylla Suk. Within the pipeline corridor, the vegetation is dominated by herbaceous species and low shrubs. Dominant herbaceous plants include Deyeuxia angustifolia, Equisetum hyemale, and Carex rhynchophysa, while prevalent shrub species comprise Betula fruticosa, Salix viminalis, and Vaccinium uliginosum. The dominant soil types in the region are brown coniferous forest soil, marsh soil, and peat soil. Pit surveys and high-density electrical resistivity measurements indicated the presence of extensive and continuous permafrost. However, the permafrost in areas adjacent to the pipelines has undergone notable degradation [5]. Because of its geographic and ecological characteristics, this region is highly sensitive to climate change and anthropogenic disturbances. It represents a critical ecological zone that plays a vital role in maintaining environmental stability in the cold regions of Northeast China.
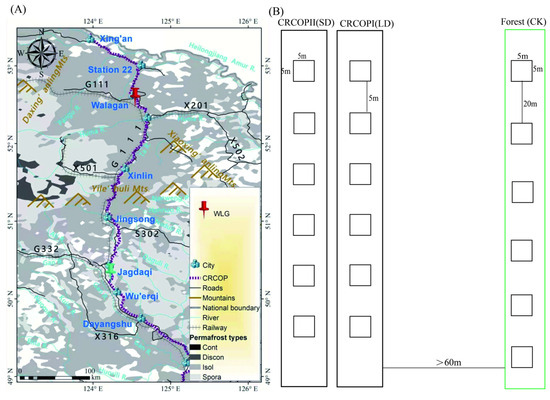
Figure 1.
Geographical location (A) and plot setting (B) map of the study area.
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
According to field surveys, permafrost occurred approximately 50 cm below the ground surface at the study site. Therefore, active layer soil (0–40 cm) in the Walagan (WLG) permafrost region of the Da Xing’anling Mountains was selected for analysis, and soil sampling was conducted between July and September 2022. Given that the thermal influence of pipeline operation extends up to 60 m horizontally [9], an undisturbed reference transect was established at a distance of more than 60 m from the pipeline. Three transects were designated for this study: (1) within the operational zone of CRCOP I (disturbed for 11 years, long-term disturbance, LD), (2) within the operational zone of CRCOP II (disturbed for 4 years, short-term disturbance, SD), and (3) within an undisturbed forest area (control, CK). Each transect included six sampling plots (5 × 5 m2), resulting in a total of 18 plots (Figure 1B). Within each plot, soil was collected using a five-point sampling method. At each plot, four soil layers were sampled: 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, 20–30 cm, and 30–40 cm. For each layer, samples from the five subsampling points were thoroughly homogenized to produce one composite sample per depth. Thus, each plot yielded four composite soil samples, resulting in a total of 72 samples across all plots. All samples were passed through a 2 mm mesh to remove plant debris, sealed in sterile containers, and transported to the laboratory under cooled conditions. Each sample was subsequently divided into two portions: one was air-dried at room temperature for physicochemical analysis, and the other, stored at −20 °C for microbial analysis [22].
2.3. Laboratory Analysis and Determination
Soil texture was analyzed using the hydrometer method to quantify sand, silt, and clay fractions. Soil water content (SWC) was measured by the drying method. First, the total weight of the wet soil was measured, and the total weight of the dry soil was measured after drying. The mass water content was calculated by the formula: SWC (%) = (wet soil weight − dry soil weight)/dry soil weight × 100. Soil pH was measured using a pH meter after extraction with deionized water (soil–deionized water = 1:2.5). A soil CN elemental analyzer was used to determine the soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) was determined with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer through the molybdenum antimony colorimetric method [32].
2.4. Soil Microbial DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
The soil samples were preserved on dry ice and submitted to Beijing Nuohe Zhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China for analysis of microbial communities using high-throughput sequencing via the Illumina NovaSeq system. Genomic DNA was extracted from soil utilizing a magnetic bead-based protocol with the TianGen soil genomic DNA extraction kit (TianGen, Beijing, China). The bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 region) was targeted with primers 515F/806R, whereas fungal ITS regions were amplified using ITS5-1737F/ITS2-2043R primers. Subsequently, PCR products meeting quality standards were purified using magnetic beads and assessed for concentration using 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The TianGen universal DNA purification gel recovery kit (TianGen, Beijing, China) was employed to isolate target DNA fragments. DNA quality was verified through electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel, and both purity and concentration were measured. DNA was adjusted to a final concentration of 1 ng/μL using sterile distilled water. Library preparation followed the NEB Next® Ultra™ II FS DNA PCR-free Library Prep Kit protocol (New England Biolabs, USA), with subsequent quantification of libraries performed via Qubit fluorometry and qPCR methods. Quantified libraries were pooled and sequenced on Illumina Nova 6000 platform, according to effective library concentration and data amountrequired. Raw sequencing reads were sorted according to barcodes and primer sequences, which were then trimmed, after which paired-end reads underwent merging via the FLASH software (v1.2.11) to produce raw tags. Quality filtering of raw tags was executed using fastp (v0.23.1) to eliminate low-quality sequences, resulting in clean tags. Effective tags were obtained after chimera sequences were identified and discarded through comparisons with established reference databases. The DADA2 module within the QIIME2 software (v2022.2) was then applied to denoise effective tags, remove residual low-quality reads, and generate amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) and their corresponding feature tables. ASV data normalization was performed to facilitate inter-sample comparisons, enabling downstream microbial community structure and diversity analyses.
2.5. Data Analysis
Data collation was performed in Excel 2010, while statistical analyses and data visualization were conducted using SPSS 27 and R 4.3.1. Because of the non-normal distribution of soil physicochemical properties and microbial alpha (α) diversity (including richness and Shannon index), significance testing was performed using the Scheirer–Ray–Hare test, a nonparametric two-way ANOVA alternative, to assess the effects of disturbance type and soil depth. Post hoc comparisons were conducted to evaluate intergroup differences. In addition, since there was no significant difference between the soil layers of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, 20–30 cm, and 30–40 cm (p > 0.05), the four soil layers were repeated and merged in each transect in the subsequent analysis, and the impacts of pipeline disturbance on the soil and microbial community were focused on. Microbial α-diversity was assessed using QIIME based on ASV-level taxonomic assignments. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) based on a Bray–Curtis distance matrix was conducted using the “vegan” package (v2.6-8) in R to visualize the similarities among bacterial and fungal communities [25]. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance ordinations (PERMANOVA, 999 permutations) was applied to test for significant differences in community composition among disturbance groups.
Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the relationship between soil physical and chemical factors and microbial diversity and community composition at the phylum level. ASV-level microbial co-occurrence networks were constructed by selecting only ASVs with relative abundance > 0.01%. Pairwise Spearman correlations among ASVs were computed using the “igraph” package (v2.1.2), excluding self-loops and correlations below thresholds (|r| < 0.7, p > 0.01) [33]. Network visualizations were executed in Gephi 0.10.0, and topological metrics were calculated to characterize microbial interaction patterns under different disturbance conditions.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Pipeline Engineering Disturbances on Soil Physicochemical Properties
Compared with CK, SD and LD exhibited significantly lower SWC, SOC, TN, and TP, but higher clay content and pH; no significant differences were observed in silt and sand contents (p < 0.05) (Table 1). Specifically, SWC decreased by 85.06% and 79.05%, SOC by 225.17 g·kg−1 and 251.15 g·kg−1, TN by 11.84 g·kg−1 and 13.14 g·kg−1, and TP by 0.54 g·kg−1 and 0.57 g·kg−1, respectively (p < 0.05), while clay content increased by 119.47% and 125.66%, and pH by 0.55 and 0.46, in SD and LD, respectively (p < 0.05). No significant differences in any of these soil physicochemical properties were detected between SD and LD.

Table 1.
Differences in soil physicochemical properties under different pipeline disturbance conditions.
3.2. Effects of Pipeline Engineering Disturbances on Diversity and Composition of Bacterial and Fungal Communities
This analysis identified a total of 35,298 bacterial ASVs and 12,225 fungal ASVs. Soil bacterial and alpha diversity (richness and Shannon index) exhibited opposite responses to pipeline engineering disturbances (Figure 2). Bacterial diversity significantly increased, while fungal diversity decreased, in both SD and LD compared with CK (p < 0.05). However, no significant differences were observed between SD and LD (p > 0.05) (Figure 2). The NMDS and ANOSIM analyses revealed significant differences in the soil bacterial and fungal community structure between among different pipeline engineering disturbances (p = 0.001) (Figure 3).
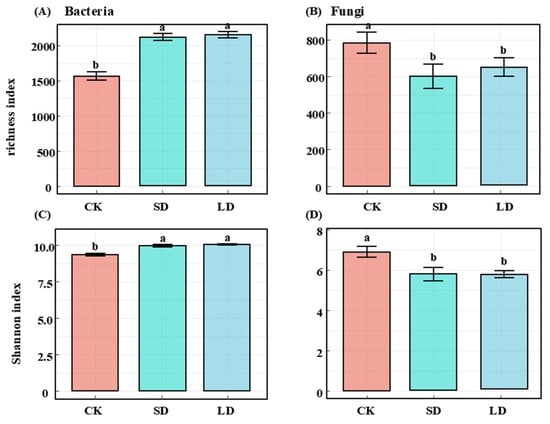
Figure 2.
Changes in α-diversity of bacteria (A,C) and fungi (B,D) under different pipeline disturbance conditions. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). CK: control; SD: short-term disturbance; LD: long-term disturbance.
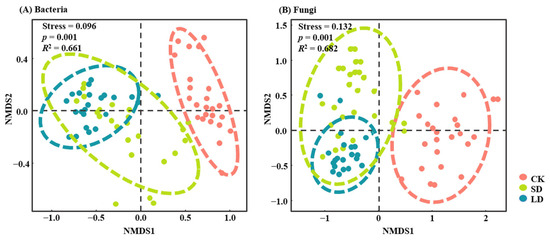
Figure 3.
NMDS analysis of bacterial (A) and fungal (B) communities under different pipeline engineering disturbances. Stress represents the stress value; p denotes significance; R2 indicates explanatory power. CK: control; SD: short-term disturbance; LD: long-term disturbance.
Dominant bacterial phyla (relative abundance ≥ 10%) [34] were Proteobacteria (36%), Acidobacteriota (22.6%), Actinobacteriota (12.9%), and Bacteroidota (10%), accounting for approximately 82% of total abundance. Compared with CK, the relative abundances of Proteobacteria after the disturbances in the SD and LD increased by 4.4% and 8.3%, respectively; the relative abundances of Acidobacteriota increased by 0.1% and 3.5%, respectively; and the relative abundances of Actinobacteriota increased by 3.8% and 1.7%, respectively, while the relative abundances of Bacteroidota decreased by 1.6% and 2.6%, respectively (Figure 4A). For fungi, the dominant phyla were Ascomycota (44.3%), Basidiomycota (30.3%), and Mortierellomycota (18.5%), representing approximately 93% of te total abundance. Compared with CK, the relative abundances of Ascomycota after the disturbances in SD and LD increased by 1.3% and 3.2%, respectively, and the relative abundances of Mortierellomycota increased by 3% and 21.5%, respectively, while the relative abundances of Basidiomycota decreased by 1.4% and 2%, respectively. It is worth noting that Basidiomycota was dominant in CK, but Ascomycota became the dominant phylum in SD and LD (Figure 4B).
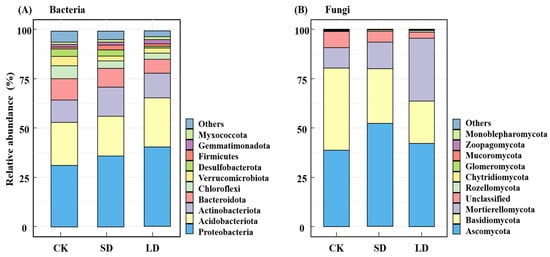
Figure 4.
Composition of bacterial (A) and fungal (B) communities at the phylum level under different pipeline engineering disturbance conditions. CK: control; SD: short-term disturbance; LD: long-term disturbance.
3.3. Co-Occurrence Networks of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities Under Pipeline Engineering Disturbances
Based on Spearman correlations at the ASV level, co-occurrence networks of bacterial and fungal communities were constructed before and after pipeline engineering disturbances, and corresponding topological attributes were calculated. The overall network structures of both bacterial and fungal communities differed significantly across disturbance levels (Figure 5). In bacterial networks, with increasing disturbance duration, the proportion of positive correlations decreased from 88.76% (CK) to 68.27% (LD), while negative correlations increased from 11.24% to 31.13%. In contrast, fungal networks exhibited a fluctuating pattern: the proportion of positive correlations decreased from 92.67% in CK to 77.08% in SD but increased to 89.17% in LD. In all treatments, bacterial and fungal networks were predominantly composed of positive correlations. Additionally, the numbers of nodes, edges, average degree, and graph density for both bacterial and fungal communities were highest in SD compared with CK and LD. Conversely, average path length was lowest in SD (Table 2).
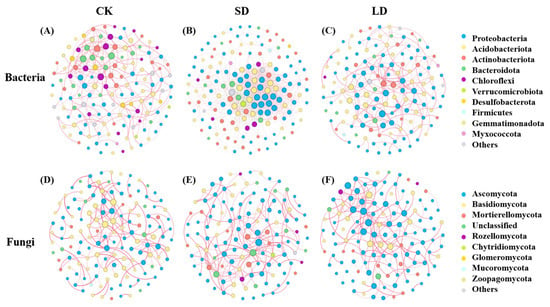
Figure 5.
Co-occurrence networks of bacterial (A–C) and fungal (D–F) communities under pipeline engineering disturbance. CK: control; SD: short-term disturbance; LD: long-term disturbance.

Table 2.
Topological properties of bacterial and fungal co-occurrence networks under pipeline engineering disturbance.
3.4. Relationship Between Soil Microbial Communities and Soil Physicochemical Properties
Significant correlations were identified between soil physicochemical factors and microbial diversity, as well as dominant phyla abundances. The results of correlation analysis between environmental factors and bacterial and fungal diversity showed that bacterial richness and Shannon index correlated positively with soil clay content and pH but negatively with soil SWC, SOC, TN, and TP. In contrast, fungal communities showed inverse relationships (p < 0.05) (Table 3). Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota showed significant positive correlations with soil clay content. Additionally, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteriota were positively associated with soil pH, whereas Proteobacteria and Acidobacteriota were negatively correlated with soil SWC, TN, and TP. Meanwhile, Bacteroidota was positively associated with SWC and TN and negatively associated with clay content (p < 0.01). In the fungal community, Asomycota was significantly positively correlated with soil pH and negatively correlated with sand content. Basidiomycota was significantly negatively correlated with soil clay content and pH but significantly positively correlated with soil SWC, SOC, TN, and TP. Mortierellomycota was significantly negatively correlated with soil silt content, SWC, TN, and TP (p < 0.001) and positively correlated with clay content (p < 0.05) (Figure 6).

Table 3.
Correlations between α-diversity of soil bacterial and fungal communities and soil physicochemical properties.
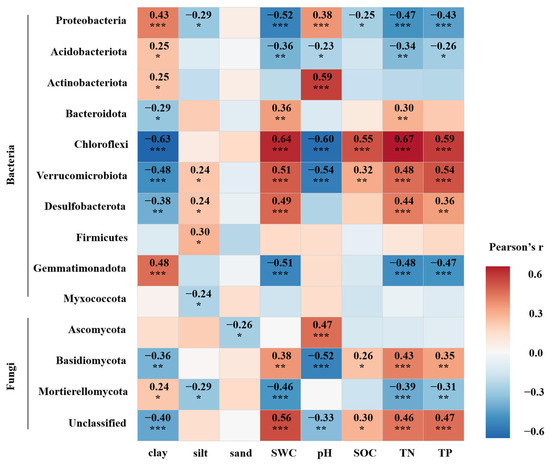
Figure 6.
Correlation analysis between relative abundances of major bacterial and fungal communities at the phylum level and soil physicochemical properties. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. r is the correlation coefficient.
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties Due to Pipeline Engineering Disturbance
This study found that CRCOP engineering disturbances significantly decreased SWC, SOC, TN, and TP while significantly increasing clay content and pH (p < 0.05). These findings are consistent with the general ecological impacts of linear engineering disturbances but reflect distinct mechanisms under permafrost conditions [35,36]. Pipeline engineering disturbances affect soil structure and nutrient cycling through multiple pathways [17]. The undisturbed area was dominated by Larix gmelinii, with dense vegetation cover and abundant litter input contributing to the formation of a thick humus layer and promoting soil organic matter accumulation. Litter decomposition improves soil physical properties by increasing porosity, reducing bulk density, and enhancing water retention [37,38]. By contrast, pipeline construction imposed multiple disturbances on soil physical and chemical properties. First, vegetation removal reduced evapotranspiration buffering and increases direct solar exposure, which accelerated surface evaporation and led to a significant decline in SWC [38]. Second, the absence of proper stratified excavation, storage, and backfilling of topsoil and subsoil during pipeline construction resulted in the mixing of organic-rich surface horizons with nutrient-poor mineral layers. This process diluted surface nutrient concentration and exposed previously protected organic matter to oxygen, thereby enhancing microbial decomposition and accelerating the loss of SOC, TN, and TP [17,19,36]. In addition to these effects, soil compaction caused by heavy machinery, along with the residual presence of alkaline construction materials such as cement, contributed to decreased soil porosity and increased pH [39,40]. These results are consistent with earlier studies reporting increased pH and reduced organic matter in pipeline-affected soils [38,40,41,42].
This study also found no significant differences in soil physicochemical properties between SD (4 years of disturbance) and LD (11 years of disturbance) sites (p > 0.05). This implies that, following disturbance, soil systems in permafrost region may rapidly shift to a new physicochemical equilibrium within four years, without clear evidence of recovery even after more than a decade. These findings differ from those of Shi et al. [43], who reported that soil physicochemical properties recovered within 6 years after the pipeline construction was completed. The results presented here indicate that pipeline infrastructure may exert persistent thermal and structural effects on soil carbon dynamics in permafrost regions. Therefore, the ecological consequences of such disturbances likely extend well beyond the immediate physical impacts of construction, underscoring the need for long-term monitoring and sustained research efforts.
4.2. Microbial Community Responses and Underlying Mechanisms
Engineering construction substantially alters soil nutrient conditions, reshaping the original soil microenvironment and leading to changes in the composition and diversity of the soil microbial community [44]. Previous studies have generally reported that engineering disturbances tend to reduce the diversity of both bacterial and fungal communities [23,45]. However, our results revealed a contrasting pattern under pipeline disturbance: bacterial diversity increased while fungal diversity declined. This divergence warrants a discussion of the underlying mechanisms. Correlation analysis indicated that bacterial diversity was significantly positively correlated with soil clay content and pH, consistently with findings by Terrat et al. [46]. Soil clay provides greater microbial habitat heterogeneity and nutrient retention capacity [47], while increased pH can reduce environmental stress, improve nutrient availability, and broaden the spectrum of suitable ecological niches [48]. Consequently, soils with higher clay and pH levels may foster a more diverse bacterial community. Conversely, bacterial diversity showed significant negative correlations with SWC, SOC, TN, and TP. This appears inconsistent with the general expectation that higher moisture and nutrient levels promote microbial diversity in stable ecosystems [49,50]. We propose that this discrepancy arises from the unique conditions characterizing the ‘disturbance-recovery’ stage following pipeline construction. The topsoil stripping and subsoil mixing during pipeline construction may inhibit the original dominant bacterial population [5,11], thus creating a vacant niche in the spatial and resource dimensions in the subsequent restoration stage, resulting in the destruction of the competitive balance. This niche release may promote the colonization and proliferation of subordinate or exogenous opportunistic bacteria previously inhibited by dominant populations, thereby driving the observed increase in bacterial diversity. This disturbance-mediated niche release effect aligns with findings by Zhao et al. [51], who reported significant increases in bacterial α-diversity during ecological restoration. In contrast, fungal diversity exhibited positive correlations with SWC, SOC, TN, and TP and negative correlations with clay content and pH. These associations are consistent with prior research on environmental determinants of fungal communities [52,53,54]. Given that pipeline disturbance significantly reduced SWC and nutrient levels (SOC, TN, TP) while increasing clay content and pH, the observed decline in fungal diversity likely reflected nutrient limitation and altered habitat suitability for many fungal taxa. From an ecosystem stability perspective, the increased bacterial diversity may enhance system resilience and adaptability to environmental fluctuations [55]. However, the concurrent decline in fungal diversity could weaken key aspects of ecological stability, particularly by impairing the pathways and efficiency of organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling, processes where fungi play pivotal roles [56]. Therefore, although pipeline disturbance may transiently elevate bacterial diversity through niche release mechanisms, the overall functional stability of the soil microbial community is likely compromised due to the significant loss of fungal diversity and its associated functions.
The results of this study show that the relative abundances of the dominant bacterial and fungal phyla in the soil shifted following pipeline engineering disturbance. In the bacterial community, the relative abundances of Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota increased following pipeline engineering disturbance, whereas Bacteroidota decreased. These phyla responded differentially to environmental variables. Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota showed significant positive correlation with soil clay content. Additionally, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteriota were positively associated with soil pH, whereas Proteobacteria and Acidobacteriota were negatively correlated with soil SWC, TN, and TP. These patterns are consistent with previous studies [32,57,58,59]. Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria are known for their high environmental adaptability, maintaining metabolic activity and proliferation under harsh conditions such as high temperatures and nutrient-poor environments. In contrast, Acidobacteria are typically adapted to more acidic soils [60,61]. During crude oil pipeline construction and operation, the thermal diffusion from crude oil transport can raise surrounding soil temperatures, concurrently increasing clay content and pH while reducing SWC and nutrient availability. These conditions may select for phyla such as Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota, which exhibit physiological plasticity and stress tolerance, leading to their increased relative abundances [17]. Conversely, Bacteroidota was significantly positively correlated with SWC and TN, which aligns with findings from Zhao et al. [62], who reported similar relationships in rhizosphere soils of wild morels. The decline in water and nutrient content following disturbance likely contributed to the reduction in Bacteroidota, a group functionally associated with the degradation of complex organic substrates [63]. A decline in its abundance may inhibit organic matter decomposition, reduce nutrient availability for plants, and impair the efficiency of carbon and nitrogen cycling in the soil ecosystem. In the fungal community, Ascomycota replaced Basidiomycota as the dominant phylum following disturbance, accompanied by an increase in the relative abundance of Mortierellomycota. Ascomycota showed a significant positive correlation with soil pH, while Basidiomycota was more closely associated with soil moisture and organic carbon (SOC) and nutrient (TN and TP) content [64]. The increase in pH and decline in moisture and nutrients likely suppressed the functional capacity of Basidiomycota, particularly their ability to degrade complex compounds such as lignin [63], while favoring Ascomycota, which are efficient decomposers of labile carbon. These findings are consistent with those of Wang et al. [65], suggesting that pipeline-induced changes in soil chemistry can restructure fungal functional roles—accelerating labile carbon turnover while retarding lignin decomposition. This shift may extend the residence time of organic carbon in soil and reduce its conversion to inorganic forms. Furthermore, Mortierellomycota was negatively correlated with soil SWC, TN, and TP, consistently with the findings of Wu et al. [66], indicating that nutrient depletion and altered soil conditions from pipeline disturbance may have facilitated its proliferation under stress conditions. Collectively, these findings suggest that pipeline construction imposes a compound disturbance mechanism consisting of both physical mixing and chemical stress. This disturbance alters soil texture and chemical properties, thereby reshaping microbial ecological niches in permafrost soils.
This study reveals the dynamic effects of pipeline engineering disturbances on the complexity and stability of soil microbial co-occurrence networks. In the SD stage, bacterial and fungal networks exhibited significantly increased numbers of nodes and edges, higher average degree, greater graph density, and reduced average path length compared with CK, collectively indicating a more complex and tightly connected network structure. These changes suggest that, during the early stages of ecological recovery, microorganisms respond to environmental heterogeneity by intensifying interspecific interactions. Although positive correlations remained dominant, an increase in negative correlations indicated intensified competition. This pattern reflects the postdisturbance adjustment phase, where microbial communities are characterized by active colonization, competitive–symbiotic interactions, and high sensitivity to environmental changes [67], consistently with the findings of Shade et al. [68]. In the LD stage, the network complexity gradually converged toward that of CK, indicating that with the advancement of ecological succession, microorganisms tend to establish a simplified yet stable community structure through adaptive processes. This transition may indicate that the ecosystem is entering a metastable equilibrium state, characterized by reduced functional redundancy but enhanced resistance to external disturbances [69,70]. Notably, compared with the SD stage, the proportion of positive correlations in the fungal network increased during long-term disturbance LD, whereas it continued to decline in the bacterial network. This divergence indicates distinct recovery trajectories among microbial groups, suggesting that ecosystem restoration is not a simple, linear process and that different microbial taxa exhibit differential responses to prolonged disturbance. Overall, the elevated network complexity observed in the SD stage may support short-term functional stability via dense positive interactions but also implies greater structural vulnerability. In contrast, the reduced complexity observed in LD appears to enhance system robustness against secondary disturbances. These findings are consistent with the conclusions of Chen et al. [71], who proposed that while high network complexity may contribute to functional redundancy, moderate structural simplification can improve ecosystem resistance and promote long-term stability.
4.3. Implications for Ecological Restoration and Management in Permafrost Regions
This study reveals the multidimensional effects of engineering disturbances on the microbial communities of permafrost ecosystems and provides important insights into the mechanisms of ecosystem restoration in cold regions. Coordinated changes in soil physicochemical properties and microbial characteristics directly regulate nutrient cycling and carbon sequestration in permafrost ecosystems [72]. From the perspective of soil nutrient cycling, the synergistic interactions between soil physicochemical properties and microbial functional attributes are essential in maintaining nutrient balance [73]. In terms of soil structure restoration and stability, microbial diversity and stability play crucial roles in preserving soil structure, preventing erosion and degradation, and providing a favorable environment for plant root development [74]. During the SD stage, the highly complex microbial network increased ecosystem vulnerability, lowering resistance to external disturbances and elevating the risk of instability under continued perturbation. In contrast, the LD stage was characterized by a simpler but more stable microbial community structure. Nevertheless, full ecological function recovery may require an extended period, as it depends not only on structural stabilization but on the re-establishment of functional linkages among microbial taxa and the restoration of synergistic interactions with other ecosystem components (e.g., plants and soil abiotic properties) [75,76]. Pipeline-induced microbial shifts can significantly influence the long-term carbon sequestration capacity of permafrost ecosystems.
Despite the above findings, this study compared only the two time points of 4 years (SD) and 11 years (LD) after disturbance and lacked continuous monitoring data across longer time scales, so there was still a lack of sufficient understanding of the long-term ecological trajectory of microbial communities. In addition, the study did not involve depth analysis of the soil’s vertical profile, and the analysis of the comprehensive mechanisms of complex environmental variables such as permafrost warming was insufficient. Future research needs to include dynamic monitoring of longer time series, combined with multidimensional environmental variables such as soil vertical profile microbial distribution characteristics, frozen soil temperature field changes, and vegetation succession, to systematically analyze the long-term succession rules and key driving factors of microbial communities. This will deepen the understanding of the dynamics of microbial communities and their regulatory mechanisms under pipeline interference in the permafrost region of the Da Xing’anling Mountains and provide more solid scientific support for the assessment of ecosystem resilience in cold regions.
Based on this study and current ecological theory, several recommendations are proposed to guide ecological restoration in cold-region engineering projects: (1) implement stratified excavation and backfilling during pipeline construction to minimize soil compaction, preserve the vertical integrity of soil horizons, and reduce disruption to microbial habitats; (2) establish long-term, multidimensional monitoring systems following disturbance to evaluate recovery trajectories across microbial, physicochemical, and vegetation components, thereby enabling adaptive management; (3) identify and cultivate key functional microbial taxa with beneficial roles in nutrient cycling, organic matter decomposition, or stress tolerance, and consider their targeted reintroduction to accelerate soil microbial reassembly and ecosystem recovery; (4) construct synthetic microbial consortia with complementary ecological functions, promoting functional redundancy and cooperative interactions, to enhance soil multifunctionality, system resilience, and long-term stability under ongoing climatic and anthropogenic stress. Collectively, these strategies may provide a robust theoretical and operational framework for restoring permafrost-affected ecosystems disturbed by linear engineering infrastructure.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study examined the impacts of the CRCOPs project on soil physicochemical properties and microbial community characteristics in the upper active layer (0–40 cm) of the permafrost region in the Da Xing’anling Mountains. The results indicated that pipeline engineering disturbances significantly increased bacterial diversity while decreasing fungal diversity. The pronounced shifts in the relative abundances of dominant microbial taxa were closely associated with variations in environmental factors. Notably, although there were no significant differences in soil properties and microbial diversity between the long-term disturbance (LD, in operation since 2011) and short-term disturbance (SD, in operation since 2018), the microbial community in the SD exhibited a more complex co-occurrence network. Moreover, the network structure in the LD gradually approached that of CK, highlighting the resilience and adaptive capacity of soil microbial communities in response to engineering disturbances. This dynamic reflects a two-phase microbial adaptation mechanism: initial functional compensation via network complexity (SD) followed by structural resilience through network simplification (LD). Through the synergistic effect of the soil physical and chemical screening–microbial strategy differentiation–community assembly process, pipeline engineering disturbance drives the microbial community in the active layer of frozen soil to a new steady state of “simplified function but stable structure”. The core mechanisms include niche release from microhabitats and the differential response of bacterial and fungal communities to the selection strategy of disturbance duration. This study comprehensively evaluated the ecological impact of pipeline engineering on soil microbial dynamics in permafrost environments. The findings offer critical baseline data for biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration planning in the Da Xing’anling permafrost region and contribute valuable insights for the sustainable management of infrastructure development in cold-region ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y. and H.J.; data curation, Z.L., W.W. and S.H.; formal analysis, Y.S.; funding acquisition, X.Y., X.J. and H.J.; investigation, Z.L., W.W. and S.H.; methodology, X.J.; project administration, H.J.; writing—original draft, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, X.Y., Y.S. and X.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2024YFF0809102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42101119 and 42201139).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fan, X.W.; Lin, Z.J.; Gao, Z.Y.; Meng, X.L.; Niu, F.J.; Luo, J.; Yin, G.A.; Zhou, F.J.; Lan, A.Y. Cryostructures and ground ice content in ice-rich permafrost area of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau with Computed Tomography Scanning. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Jin, H.J.; Marchenko, S.S.; Romanovsky, V.E. Difference between near-surface air, land surface and ground surface temperatures and their influences on the frozen ground on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geoderma 2018, 312, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, D.; Song, D.; Liu, L. Vertical distribution of bacterial community diversity in the Greater Khingan Mountain permafrost region. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Li, G.Y.; Cao, Y.P.; Chen, D.; Wu, G.; Du, Q.S.; Wang, F.; Alexander, F.; Che, F.Q.; Zhang, Z.R.; et al. Permafrost thawing caused by the China-Russia Crude oil pipeline based on multi-type data and its impacts on geomorphological reshaping and water erosion. Catena 2024, 242, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Cao, Y.P.; Ma, W.; Jin, X.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Yu, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Mu, Y.H.; Jin, H.J. Permafrost engineering problem along China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline and mitigative measure. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, G.; Ma, W.; Wu, Q.; Serban, M.; Vera, S.; Alexandr, F.; Jiang, N.; Wang, B. Pipeline–permafrost interaction monitoring system along the China–Russia crude oil pipeline. Eng. Geol. 2019, 254, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.J.; Hao, J.; Chang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.H.; Qi, J.; Lü, L.; Wang, S. Zonation and assessment of frozen-ground conditions for engineering geology along the China–Russia crude oil pipeline route from Mo’he to Daqing, Northeastern China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 64, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.T.; Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Cao, Y.P.; Wu, G.; Mu, Y.H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Assessment of freeze–thaw hazards and water features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in permafrost regions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Jin, X.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Jin, H.J.; Tang, L.; Li, X.Y.; He, R.X.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.J.; Zhang, S.F. Investigation of permafrost engineering geological environment with electrical resistivity tomography: A case study along the China-Russia crude oil pipelines. Eng. Geol. 2021, 291, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Mu, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.W.; Mao, Y.C. Permafrost thawing along the China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline and countermeasures: A case study in Jiagedaqi, Northeast China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 155, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.R.; Doherty, J.M. The legacy of pipeline installation on the soil and vegetation of southeast Wisconsin wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 39, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Cai, T.J.; Ge, S.S.; Liu, J.X.; Qu, C.Y.; Sun, X.X. Effects of Mohe-Daqing oil pipeline project construction on typical forest ecosystems in Daxing’an. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2015, 37, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Xue, K.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, T.; Kang, S.C.; Rui, J.P.; Thies, J.E.; et al. Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025321118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Sun, Q.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Review on the Study of Soil Microorganisms in Wetland Ecosystems. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2013, 19, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Griffiths, B.S.; Langenheder, S. Microbial community resilience across ecosystems and multiple disturbances. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00026-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.F.; Wang, G.P.; Zou, Y.C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.M.; Lu, X.G. Effects of Pipeline Construction on Wetland Ecosystems: Russia–China Oil Pipeline Project (Mohe-Daqing Section). Ambio 2010, 39, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, W.H.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Effects of Natural Gas Pipeline Construction on Soil Nutrients and Bacteria Diversity in the Fragile Loess Region. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2018, 38, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.Y.; Jin, H.J.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.R.; Yang, S.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, H.W.; He, R.X.; et al. Shrubification along pipeline corridors in permafrost regions. Forests 2022, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Shi, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.D. Potential effects of large linear pipeline construction on soil and vegetation in ecologically fragile regions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8037–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Mi, S.F.; Peng, X.W.; Han, Y.J. The mutual influence between corrosion and the surrounding soil microbial communities of buried petroleum pipelines. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18930–18940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.K.; Kong, W.D.; Liang, C.; Zhang, T.Q.; Jia, H.Z.; Dong, X.B. Permafrost thawing exhibits a greater influence on bacterial richness and community structure than permafrost age in Arctic permafrost soils. Cryosphere 2020, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, R.A.; Jones, R.M.; Douglas, T.A.; Doherty, S.J.; Messan, X.K.; Foley, K.L.; Perkins, E.J.; Thurston, A.K.; Garcia-Reyero, N. Not all permafrost microbiomes are created equal: Influence of permafrost thaw on the soil microbiome in a laboratory incubation study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Mon, C.; Stierli, B.; Plötze, M.; Frey, B. Fast and persistent responses of alpine permafrost microbial communities to in situ warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messan, K.S.; Jones, R.M.; Doherty, S.J.; Foley, K.; Douglas, T.A.; Barbato, R.A. The role of changing temperature in microbial metabolic processes during permafrost thaw. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.T.; Sun, J.F.; He, T.X.; Hu, B.Q. Effects of long-term human disturbances on soil microbial diversity and community structure in a karst grassland ecosystem of northwestern Guangxi, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, M.G.; Scrano, L.; Mang, S.M.; Scalese, B.E.; Bufo, S.A.; Modley, L.A.; Buongarzone, E.; Salzano, G. Changes in the Bacterial Community Composition of Cultivated Soil after Digging up Operations for Laying a Pipeline. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, X.Z.; Lyu, Y.; Sun, W.L. Differential impacts of water diversion and environmental factors on bacterial, archaeal, and fungal communities in the eastern route of the South-to-North water diversion project. Environ. Int. 2025, 195, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, E.A.; Lantz, T.C. Persistent Changes to Ecosystems following Winter Road Construction and Abandonment in an Area of Discontinuous Permafrost, Nahanni National Park Reserve, Northwest Territories, Canada. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2017, 49, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Z.; Wen, X.; Jin, H.J.; Wu, Q.B. Pyrosequencing Investigation into the Bacterial Community in Permafrost Soils along the China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline (CRCOPs). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, S.; Avera, B.N.; Strahm, B.D.; Badgley, B.D. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities Show Distinct Recovery Patterns during Forest Ecosystem Restoration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00966-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, D.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Man, H.R.; Wu, X.W.; Li, M.; Zang, S.Y. Organic Carbon Mineralization and Bacterial Community of Active Layer Soils Response to Short-Term Warming in the Great Hing’an Mountains of Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 802213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Li, M.S.; Liu, X.L.; Yin, W.P.; Li, G.F.; Mu, L.Q.; Cui, X.Y.; Cheng, Z.C. Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity of Typical Permafrost in Greater Khingan Mountains. Microbiol. China. 2020, 47, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan, S.F.M.; Ji, L.; Schädler, M.; Wu, Y.T.; Sansupa, C.; Tanunchai, B.; Buscot, F.; Purahong, W. Future climate conditions accelerate wheat straw decomposition alongside altered microbial community composition, assembly patterns, and interaction networks. ISME J. 2023, 17, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.H.; Zheng, Y.T.; Li, P.F.; Cui, J.X.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Gao, W.S. Organic management increases beneficial microorganisms and promotes the stability of microecological networks in tea plantation soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Cai, T.J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Effects of Mohe-Daqing Oil Pipeline Poroject on Soil Nutrientin the Areas Along the Line. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Niu, B.; Pei, Y.; Song, S.; Lei, T.Z.; Yun, H.B. Soil texture influences soil bacterial biomass in the permafrost-affected alpine desert of the Tibetan plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1007194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.L.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.G. Litter decomposition and nutrient release from monospecific and mixed litters: Comparisons of litter quality, fauna and decomposition site effects. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.Y.; Fu, D.X.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, X.G. Effects of Terrain on Soil Hydrological Characteristics of Alpine Grasslands. J. For. Environ. 2024, 44, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, T.; Culman, S.W. Pipeline installation effects on soils and plants: A review and quantitative synthesis. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2022, 5, e20312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, D.; Tucker, C.L.; Koehler, P.G. Influence of Portland cement amendment on soil pH and residual soil termiticide performance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Y.K.; Rice, W.A.; Arshad, M.A.; Millis, P.F. Effect of pipeline installation on crop yield and some biological properties of boreal soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 80, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, L.D. Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2504–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, L.D. The effects of pipeline construction disturbance on soil properties and restoration cycle. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.K.; Gao, Q.Z.; Liu, S.L.; Ganjurjav, H.; Wang, X.X.; Su, X.K.; Wu, X.Y. Soil bacterial and fungal diversity differently correlated with soil biochemistry in alpine grassland ecosystems in response to environmental changes. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 43077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.X.; Zhou, J.Q.; Sun, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Chen, T.; Li, R.; Wang, X. The variation trends of plant and soil fungi communities in alpine grassland along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrat, S.; Horrigue, W.; Dequietd, S.; Saby, N.; Lelièvre, M.; Nowak, V.; Tripied, J.; Régnier, T.; Jolivet, C.; Arrouays, D.; et al. Mapping and predictive variations of soil bacterial richness across France. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, F.M.; George, P.B.L.; Lebron, I.; Jones, D.L.; Creer, S.; Robinson, D.A. Soil textural heterogeneity impacts bacterial but not fungal diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, Q.Y.; Ji, N.N.; Zheng, Y.; Taylo, J.W.; Guo, L.D.; Gao, C. Bacterial genome size and gene functional diversity negatively correlate with taxonomic diversity along a pH gradient. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.H.; Hu, Y.M.; Bu, R.C. Vertical distribution patterns and drivers of soil bacterial communities across the continuous permafrost region of northeastern China. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, F.Y.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, P.; Yang, B.P.; Ding, R.X.; Nie, J.F.; Jia, Z.K. Effects of farmland mulching patterns on soil microbial diversity and community structure in dryland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Li, W.Y.; Huo, R.; Wu, C.B.; Di, Y.L.; Shi, K.; Zhou, S.L. Response mechanism of bacterial community and physicochemical factors evolution to ecological restoration in sediment and water dual medium of Baiyangdian Lake. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Lu, G.X.; Yan, H.L.; Wang, Y.C. Effects of the Transformation from Natural Alpine Grassland to Mixed Artificial Grassland on the Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.M.; Qu, M.J.; Shao, S.; Li, J.W. Soil fungal guilds as important integrators linking plant richness and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stocks in oasis–desert ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Rufty, T.; Shi, W. Soil microbial diversity and composition: Links to soil texture and associated properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Liu, B.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Lei, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cheng, B.H.; Zhou, T.; Peng, S.L. Effects of daytime and nighttime warming on soil microbial diversity. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Cheng, L.; Che, L.G.; Su, Y.Z.; Li, Y.L. Nutrients addition decreases soil fungal diversity and alters fungal guilds and co-occurrence networks in a semi - arid grassland in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Xiong, J.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Li, X.J.; Li, X.Y.; Liang, W.J.; Chu, H.Y. Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Saez, J.M.; Costa, J.S.D.; Colin, V.L.; Fuentes, M.S.; Cuozzo, S.A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A.; Amoroso, M.J. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing - based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Lu, D.X.; Jin, H.; Yang, A.L.; Qin, P.; Wei, J.Q.; Guo, R.; Zhang, W.Q. Relationship between the bacterial community and environmental factors in the rhizosphere soil of wild morels in Gansu. Microbiol. China. 2022, 49, 514–528. [Google Scholar]
- Naumoff, D.G.; Dedysh, S.N. Lateral gene transfer between the Bacteroidetes and Acidobacteria: The case of α-l-rhamnosidases. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3843–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.S.; Wang, S.S.; Fang, W.; Zheng, M.Q.; Jiang, B.H.; Shao, S.; Ma, X.M.; Xu, Q.F. Bamboo invasion surrounding forest increased soil pH, changed soil chemical nutrient and microbial community: A meta-analysis. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2024, 61, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, M.; Liu, Q.H.; Li, C.; Pang, X.Y. Fungal, but not bacterial, diversity and network complexity promote network stability during roadside slope restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.K.; Ji, S.; Qiu, X.X.; Du, S.B.; Xie, H.C. Structural characteristics of soil fungal communities at different altitudes on the southern slope of the Qilian Mountains. J. For. Environ. 2024, 44, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; DiLegge, M.J.; Minas, I.S.; Hamm, A.; Manter, D.; Vivanco, J.M. Soil sterilization leads to re-colonization of a healthier rhizosphere microbiome. Rhizosphere 2019, 12, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.; Peter, H.; Allison, S.D.; Baho, D.L.; Berga, M.; Bürgmann, H.; Huber, D.H.; Langenheder, S.; Lennon, J.T.; Martiny, J.B.H.; et al. Fundamentals of Microbial Community Resistance and Resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Martiny, J.B.H. Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105 (Suppl. 1), 11512–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan, E.; Neshat, S.A.; Wuertz, S. Disturbance and stability dynamics in microbial communities for environmental biotechnology applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2025, 93, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yan, H.; Di, S.S.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Gold, A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Mapping Pesticide-Induced Metabolic Alterations in Human Gut Bacteria. bioRxiv. 2024, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglese, C.N.; Christiansen, C.T.; Lamhonwah, D.; Moniz, K.; Montross, S.N.; Lamoureux, S.; Lafrenière, M.; Grogan, P.; Walker, V.K. Examination of soil microbial communities after permafrost thaw subsequent to an active layer detachment in the high Arctic. Arct. Antarct. Alpine Res. 2017, 49, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medriano, C.A.; Chan, A.; De Sotto, R.; Bae, S. Different types of land use influence soil physicochemical properties, the abundance of nitrifying bacteria, and microbial interactions in tropical urban soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardy, V.; Mathieu, O.; Lévêque, J.; Terrat, S.; Chabbi, A.; Lemanceau, P.; Ranjard, L.; Maron, P.-A. Stability of soil microbial structure and activity depends on microbial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Norton, D.A. Towards a conceptual framework for restoration ecology. Restor. Ecol. 1996, 4, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).