An Evaluation of the Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes Using the Semi-Circular Bending Method and Digital Image Correlation
Abstract
1. Introduction
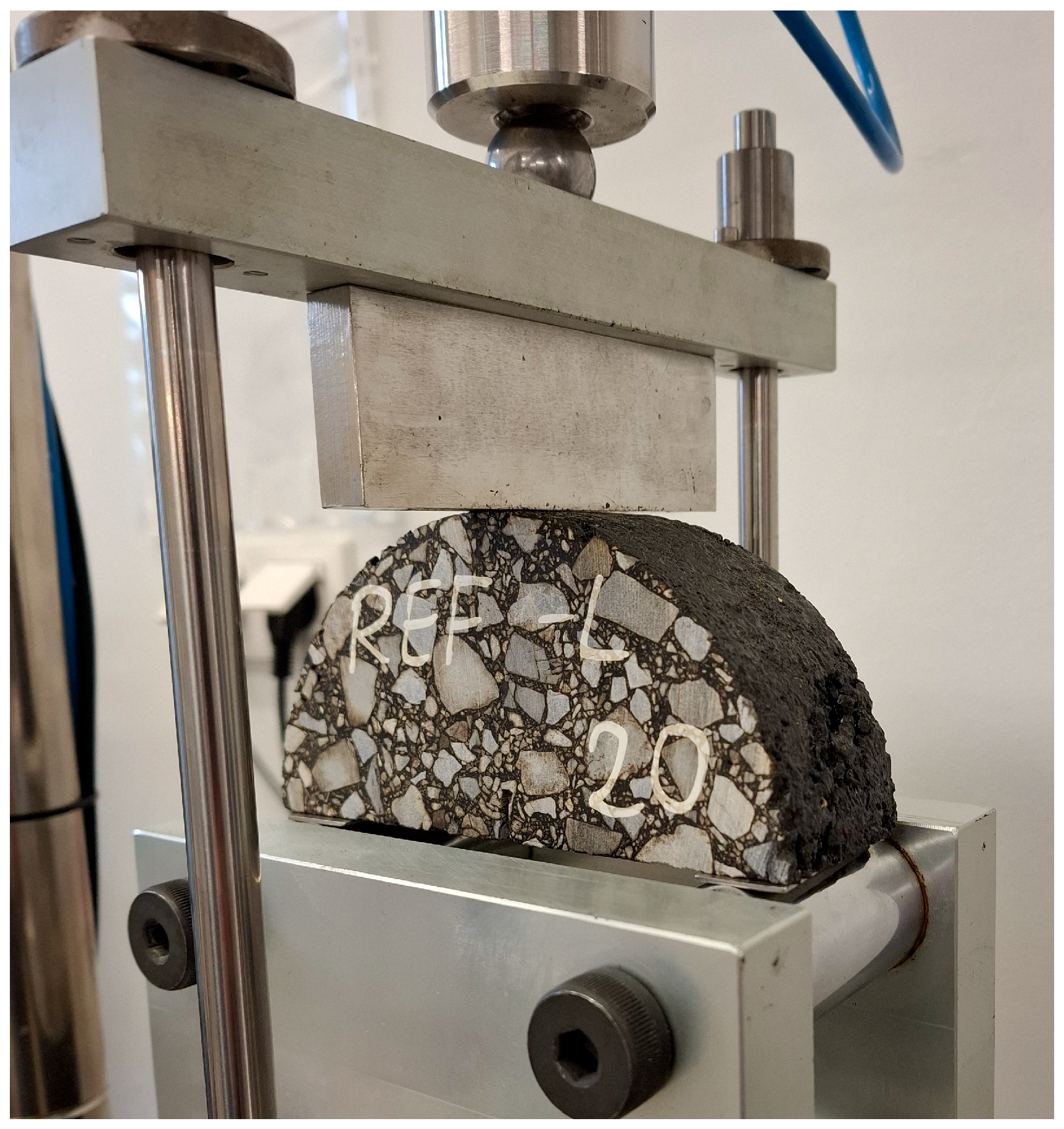
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Laboratory Results
3.2. Numerical Results
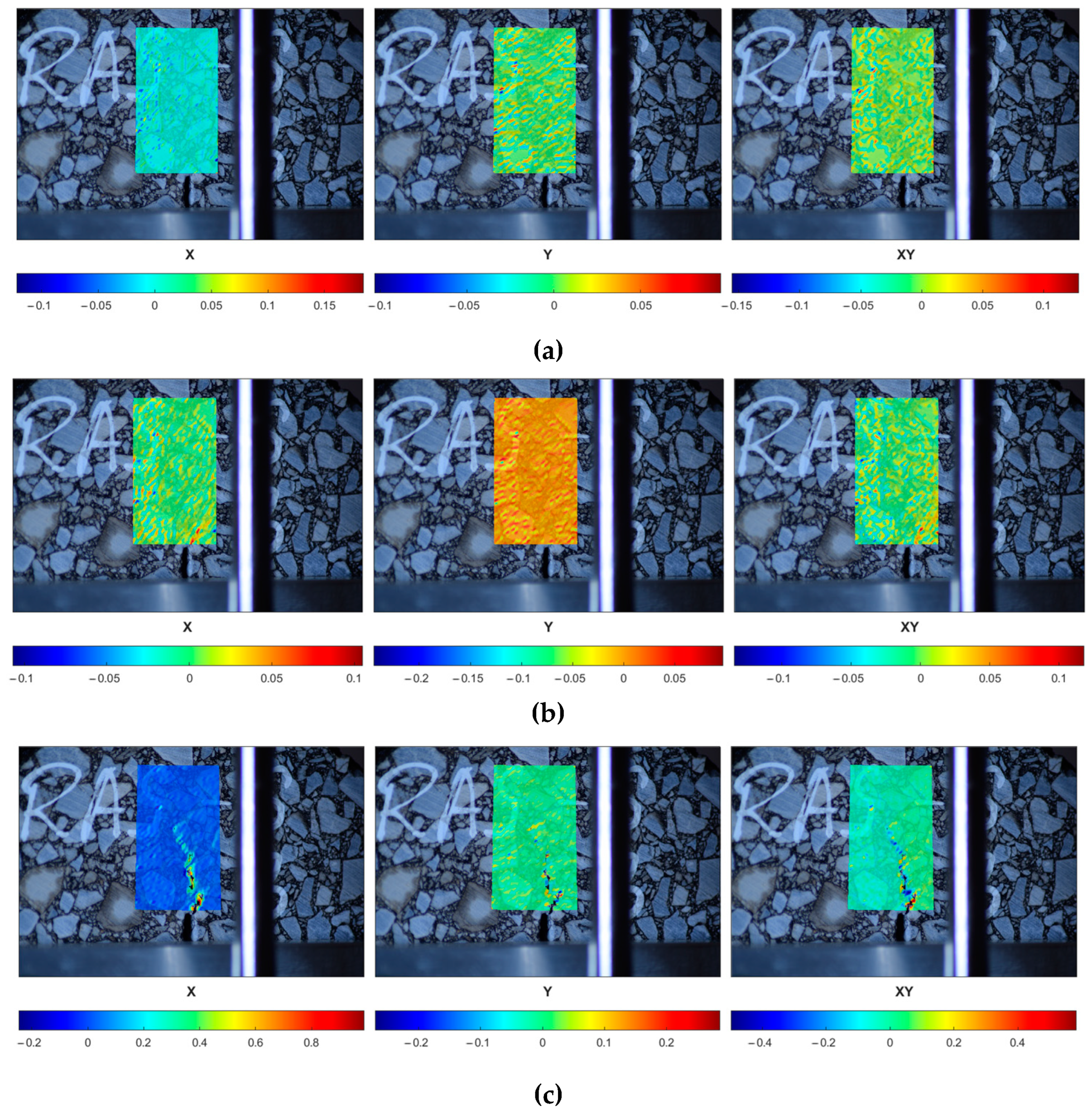
3.2.1. Digital Image Correlation
3.2.2. Image Processing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
- In this study, the application of a civil engineering waste product (RASs) was analyzed, which is in line with current trends based on sustainability.
- RAS mixtures subjected to long-term aging stiffened significantly and, therefore, became much more susceptible to cracking compared to the reference one. To solve the above-mentioned problem, optimization of the type and amount of rejuvenator is planned in the future.
- SCB test parameters determined in accordance with the European standards [45], i.e., KIC and JC, do not allow for a proper assessment of AC mixtures.
- Correct differentiation between the mixture composition was achieved using energy parameters, i.e., total strain energy (Wf) and fracture energy (Gf), but in the case of aging conditions, evaluation based on them is not appropriate, which is consistent with the conclusions of the work conducted by Jiang et al. [49].
- The post-peak load indexes, i.e., FI and TI, turned out to be the most sensitive to the aging conditions of the mixtures; however, due to the relatively large dispersion of the results (COV is about 30%), they may be less conclusive in terms of assessing the statistical significance of differences between the tested series, especially for a small series of samples.
- The best sensitivity in terms of differentiating the tested mixtures was observed for the CRI parameter, the advantage of which is the relatively small scatter of the obtained results (COV is about 10%).
- The image processing techniques presented in the paper can be used for the enhancement of laboratory experiments due to the possibility of a more detailed description of analyzed phenomena. Further research efforts will reconstruct a fully tridimensional specimen microstructure and apply cohesive zone elements to model the fracture phenomena numerically.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| AC | Asphalt concrete |
| BCI | Balanced cracking index |
| COV | Coefficient of variation |
| CRI | Cracking resistance index |
| CUT | Cracow University of Technology |
| CZM | Cohesive zone model |
| DIC | Digital image correlation |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| FI | Flexibility index |
| MWAS | Manufacture waste asphalt shingles |
| RASs | Reclaimed asphalt shingles |
| REF | Reference mixture |
| SCB | Semi-circular bending |
| SM | Secant modulus |
| TOASs | Tear-off asphalt shingles |
| TI | Toughness index |
| ZNCC | Zero-mean normalized cross-correlation |
References
- Pouranian, M.R.; Shishehbor, M. Sustainability Assessment of Green Asphalt Mixtures: A Review. Environments 2019, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Cheng, X.; Luo, X.; Hu, Y. Maximizing the circularity of asphalt pavements by improving the RAP content in recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Haider, S.; Pasquini, E. Circular Economy for Transport Infrastructure: An Overview of the Sustainable Use of Recycled Asphalt Shingles in Asphalt Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, G.; Stroup-Gardiner, M.; Epps, J. Roofing Waste in Asphalt Paving Mixtures—Economic Consideration; Report No. 6-331-709-1; Center for Construction Materials Research, University of Nevada-Reno: Reno, NV, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Foxlow, J.J.; Daniel, J.S.; Swamy, A.K. RAP or RAS? The differences in performance of HMA containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and reclaimed asphalt shingles. J. Assoc. Asph. Paving Technol. 2011, 80, 347–376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Li, H.; Hu, S.; Button, J.W.; Epps, J.A. Characterization and Best Use of Recycled Asphalt Shingles in Hot-Mix Asphalt; Report No. FHWA/TX-13/0-6614-2; Texas A&M Transportation Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; 107p. [Google Scholar]
- Darnell, J.; Bell, C.A. Performance Based Selection of RAP/RAS in Asphalt Mixtures; Report No. FHWA/OR-RD-16-08; Oregon Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; 107p. [Google Scholar]
- West, R.; Leiva, F.; Julian, G.; Taylor, A.; Brown, E.; Willis, J.R. Using Recycled Asphalt Shingles with Warm Mix Asphalt Technologies; NCHRP Research Report 890; TRB: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; 208p. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, H.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Kanaan, A. Laboratory Evaluation of High Asphalt Binder Replacement with Recycled Asphalt Shingles (RAS) for a Low N-Design Asphalt Mixture; Report No. FHWA-ICT-12-018; Illinois Center for Transportation and University of Illinois at Urban-Champaign: Urban-Champaign, IL, USA, 2012; 32p. [Google Scholar]
- McGraw, J.; Zofka, A.; Krivit, D.; Schroer, J.; Olson, R.; Marasteanu, M. Recycled asphalt shingles in hot mix asphalt. In Asphalt Paving Technology: Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists-Proceedings of the Technical Sessions; Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists: Reno, NV, USA, 2007; Volume 76, pp. 235–274. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaan, A.I. Impact of Recycled Asphalt Shingles on Asphalt Concrete Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Urban-Champaign, Urban-Champaign, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.; Johnson, G.; Dai, S.; Linell, D.; McGraw, J.; Watson, M. Incorporation of Recycled Asphalt Shingles in Hot-Mixed Asphalt Pavement Mixtures; Report No. MN/RC 2010-08; Minnesota Department of Transportation: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2010; 83p. [Google Scholar]
- Koehl, K. Impact of recycling agents on the design of asphalt mixtures containing roofing shingles. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual IHEEP Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 September–2 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alvergue, A.; Elseifi, M.; Mohammad, L.N.; Cooper, S.B., Jr.; Cooper, S., III. Laboratory evaluation of asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt shingle prepared using wet process. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S1), 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseifi, M.A.; Mohammad, L.N.; Ying, H.; Cooper, S., III. Modeling and evaluation of the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures using the semicircular bending test at intermediate temperatures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2012, 13 (Suppl. S1), 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, K.; Daniel, J.S.; Foxlow, J.; Gray, K. An evaluation of reclaimed asphalt shingles in hot mix asphalt by varying sources and quantity of reclaimed asphalt shingles. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2014, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, P. Effect of reclaimed asphalt shingles addition on asphalt concrete dynamic modulus master curves. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2021, 67, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Mohammad, L.N.; Elseifi, M.A. Characterization of fracture properties of asphalt mixtures as measured by semicircular bend test and indirect tension test. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2296, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Lambros, J.; El-Khatib, A.; Singhvi, P.; Doll, B. Development of the fracture-based flexibility index for asphalt concrete cracking potential using modified semi-circle bending test parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S. Evaluate the Fracture and Fatigue Resistance of Hot Mix Asphalt Containing High Percentage Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) Materials at Low and Intermediate Temperatures. Ph.D. Dissertation, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2014; 121 p. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, T.; Ling, C.; Chaturabong, P.; Bahia, H. Evaluation of analysis methods of the semi-circular bend (SCB) test results for measuring cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, H.; Hanz, A.; Teymourpour, P.; Swiertz, D.; Ling, C.; Chaturabong, T.; Mandal, T.; Varma, R.; Lyngdal, E.; Hanz, A. Analysis and Feasibility of Asphalt Pavement Performance-Based Specifications for WisDOT; Report No. 0092-15-04; University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2016; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Lambros, J.; El-Khatib, A.; Singhvi, P.; Khan, T.; Rivera, J.; Doll, B. Testing Protocols to Ensure Performance of High Asphalt Binder Replacement Mixes Using RAP and RAS; Report No. FHWA-ICT-15-017; Illinois Centre for Transportation: Rantoul, IL, USA, 2015; 80p. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaquist, R.; Paye, B.; Johnson, C. Application of intermediate temperature semi-circular bending (SCB) test results to design mixtures with improved load associated cracking resistance. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18 (Suppl. S4), 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Lambros, J. Development of the Illinois Flexibility Index Test; Transportation Research Circular; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 31–50. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kong, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F. Study on the influence factors of fatigue properties of large-stone asphalt mixtures based on semi-circular bending tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Zheng, W. Evaluation of the significance of different mix design variables on asphalt mixtures’ cracking performance measured by laboratory performance tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Use of Semi-Circular Bend Test to Characterize Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete with Virgin and Recycled Materials. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2019; 188p. [Google Scholar]
- Zieliński, P. The use of the semi-circular bending method to assess the intermediate-temperature fracture toughness of asphalt concrete mixes with reclaimed asphalt shingles. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseer, F.; Yin, F.; Arambula-Mercado, E.; Martin, A.E.; Daniel, J.S.; Salari, S. Development of an index to evaluate the cracking potential of asphalt mixtures using the semi-circular bending test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Ma, J.; Hesp, S. Another look at the semi-circular bend test for the performance ranking of hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 395, 132367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidifard, H.; Jahangiri, B.; Rath, P.; Buttlar, W.G. Development of a balanced cracking index for asphalt mixtures tested in semi-circular bending with load-LLD measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 173, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslett, K.E. Evaluation of Cracking Indices for Asphalt Mixtures Using SCB Tests at Different Temperatures and Loading Rates. Honours Theses and Capstones, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nsemgiyumva, G.; Kim, Y.-R.; You, T. Development of Semicircular Bend (SCB) Test Method for Performance Testing of Nebraska Asphalt Mixtures; Report No. SPR-P1(15) MPMC07; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2015; 60p. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, H.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Barber, E.; Okte, E.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S. Evaluation of I-FIT Results and Machine Variability Using MNRoad Test Track Mixtures; Report No. FHWA-ICT-17-012; Illinois Centre for Transportation: Rantoul, IL, USA, 2017; 59p. [Google Scholar]
- Szydłowski, C.; Smakosz, Ł.; Stienss, M.; Górski, J. Monte Carlo simulations of the fracture resistance degradation of asphalt concrete subjected to environmental factors. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2023, LXIX, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, M.; Tekieli, M.; Zieliński, P.; Strzępek, M. DIC-Enhanced Identification of Bodner–Partom Model Parameters for Bitumen Binder. Materials 2023, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12697-3; Bituminous Mixtures—Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt—Part 3: Bitumen Recovery: Rotary Evaporator. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2019.
- Generalna Dyrekcja Dróg Krajowych i Autostrad. Nawierzchnie Asfaltowe na Drogach Krajowych, WT-2 Część I, Mieszanki Mineralno-Asfaltowe, Wymagania techniczne; [Bituminous pavements on national roads, WT-2 part I, Mineral-asphalt mixtures, Technical requirements]; GDDKiA: Warsaw, Poland, 2014; 52p. [Google Scholar]
- Elwardany, M.; Rad, F.Y.; Castorena, C.; Kim, Y. Evaluation of asphalt mixture laboratory long-term aging methods for performance testing and prediction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18 (Suppl. S1), 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Castorena, C.; Elwardany, M.; Rad, F.Y.; Underwood, S.; Gundla, A.; Gudipudi, P.; Farrar, M.J.; Glaser, R.R. Long-term Aging of Asphalt Mixtures for Performance Testing and Prediction; NCHRP Research Report 871; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; 127p. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelsaad, A.; White, G. & Jamshidi, A State of the Art Review of Ageing of Bituminous Binders and Asphalt Mixtures: Ageing Simulation Techniques, Ageing Inhibitors and the Relationship between Simulated Ageing and Field Ageing. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 12697-31; Bituminous Mixtures. Test Methods. Specimen Preparation by Gyratory Compactor. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2019.
- A Manugistics Inc. Product. Computer Program Statgraphics Plus v. 5.1; A Manugistics Inc.: Rockville, MD USA, 2000; No. 537672031051732. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN 12697-44; Bituminous Mixtures. Test Methods. Crack Propagation by Semi-Circular Bending Test. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2019.
- Tekieli, M.; Santis, S.d.; Felice, G.d.; Kwiecień, A.; Roscini, F. Application of digital image correlation to composite reinforcements testing. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 670–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, M.; Jaworska, I.; Tekieli, M. 2D Digital Reconstruction of Asphalt Concrete Microstructure for Numerical Modeling Purposes. Materials 2022, 15, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdideh, M.; Ghasemi, A. A Comparison of Various Statistical and Geostatistical Methods in Estimating the Geomechanical Properties of Reservoir Rocks. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, H.; Bahia, H.U. Factors controlling pre- and post-peak behavior of asphalt mixtures containing RAP in the SCB test. Mater. Struct. 2022, 55, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Sieve Size [mm] | Grading Curve | Bitumen Properties |
|---|---|---|
| 5.6 | 100 | |
| 4.0 | 83.8 | |
| 2.0 | 72.0 | |
| 0.5 | 56.4 | |
| 0.125 | 46.8 | |
| 0.063 | 40.8 | |
| Bitumen amount [%] | 34.1 | |
| Penetration [0.1 mm] | 17 | |
| Softening Point [°C] | 102.8 |
| O.N. | Components | Participation in AC [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | RAS | ||
| 1 | Limestone filler | 4.3 | 3.34 |
| 2 | Sand 0/2 | 9.56 | 9.54 |
| 3 | Dolomite 0/4 | 26.77 | 24.99 |
| 4 | Dolomite 4/8 | 15.77 | 15.74 |
| 5 | Dolomite 8/16 | 39.2 | 39.1 |
| 6 | RAS | - | 4.0 |
| 7 | Paving bitumen 50/70 | 4.4 | 3.3 |
| Sieve Size [mm] | Grading Curve | |
|---|---|---|
| REF | RAS | |
| 22.4 | 100 | 100 |
| 16.0 | 98.2 | 98.2 |
| 11.2 | 78.4 | 78.4 |
| 8.0 | 58.2 | 58.2 |
| 5.6 | 47.5 | 47.6 |
| 4.0 | 42.7 | 42.3 |
| 2.0 | 31.9 | 31.8 |
| 0.5 | 14.2 | 14.5 |
| 0.125 | 7.3 | 7.5 |
| 0.063 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| Bitumen recovered [%] | 4.41 | 4.56 |
| Bitumen Results | Fresh Bitumen 50/70 | REF-S | REF-L | RAS-S | RAS-L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration [0.1 mm] | 61 | 28 | 23 | 24 | 16 |
| R&B [°C] | 49.2 | 62.2 | 65.9 | 66.9 | 80.8 |
| Mixture Designation | Reclaimed Asphalt Additive | Aging Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| REF_S | (-) | Short-term (S) |
| RAS_S | (RAS) | Short-term (S) |
| REF_L | (-) | Long-term (L) |
| RAS_L | (RAS) | Long-term (L) |
| Mixture Type | Notch Depth [mm] | Pmax [kN] | ΔPmax [mm] | Δmdp [mm] | SM [N/mm] | U [N*mm] | dU/da [N] | JC [N/mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF_S | 10 | 3.00 | 1.13 | 1.65 | 2.68 | 1760 | −56.29 | 1.10 |
| 22 | 2.00 | 0.93 | 1.53 | 2.18 | 974 | |||
| 34 | 1.23 | 0.80 | 1.40 | 1.58 | 510 | |||
| RAS_S | 10 | 3.41 | 0.96 | 1.27 | 3.60 | 1512 | −42.88 | 0.83 |
| 22 | 2.22 | 0.71 | 1.07 | 3.15 | 783 | |||
| 34 | 1.43 | 0.72 | 1.04 | 2.07 | 414 | |||
| REF_L | 10 | 3.78 | 0.98 | 1.37 | 3.95 | 1924 | −61.20 | 1.19 |
| 22 | 2.65 | 0.77 | 1.15 | 3.45 | 1023 | |||
| 34 | 1.53 | 0.60 | 1.02 | 2.53 | 474 | |||
| RAS_L | 10 | 4.30 | 0.83 | 0.97 | 5.23 | 1597 | −52.42 | 1.00 |
| 22 | 2.96 | 0.64 | 0.80 | 4.64 | 835 | |||
| 34 | 1.72 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 3.41 | 363 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | −0.92 * | −0.97 * | −0.49 |
| REF_S—REF_L | −1.27 * | −1.27 * | −0.96 * |
| REF_S—RAS_L | −2.55 * | −2.46 * | −1.83 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | −0.35 | −0.29 | −0.47 |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | −1.63 * | −1.48 * | −1.34 * |
| REF_L—RAS_L | −1.28 * | −1.18 * | −0.88 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 0.64 | 0.42 | 0.55 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | 1.56 * | −1.01 * | −1.75 * |
| REF_S—REF_L | −1.28 * | −3.40 * | −2.52 * |
| REF_S—RAS_L | −3.00 * | −5.07 * | −3.84 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | −2.84 * | −2.40 * | −0.77 |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | −4.56 * | −4.07 * | −2.09 * |
| REF_L—RAS_L | −1.73 * | −1.67 * | −1.32 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | −798 * | 585 * | 304 * |
| REF_S—REF_L | −192 | 55 | 70 |
| REF_S—RAS_L | 431 * | 831 * | 469 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | −989 * | −531 * | −234 * |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | 431 * | 246 | 165 |
| REF_L—RAS_L | 1420 * | 776 * | 399 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 364 | 266 | 167 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | −116 * | 144 * | 172 * |
| REF_S—REF_L | −59 * | 114 * | 116 * |
| REF_S—RAS_L | −82 * | 248 * | 280 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | 57 * | −29 | −56 * |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | 199 * | 104 * | 108 * |
| REF_L—RAS_L | 142 * | 133 * | 164 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 32 | 41 | 52 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | 1.54 * | 2.47 * | 2.92 * |
| REF_S—REF_L | 1.00 * | 2.29 * | 2.41 * |
| REF_S—RAS_L | 2.36 * | 3.61 * | 4.13 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | −0.54 * | −0.19 | −0.51 |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | 0.82 * | 1.13 * | 1.20 * |
| REF_L—RAS_L | 1.36 * | 1.32 * | 1.72 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 0.33 | 0.96 | 1.08 |
| Compared Mixtures | Difference for Notch Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 22 mm | 34 mm | |
| REF_S—RAS_S | 0.55 * | 0.45 * | 0.30 * |
| REF_S—REF_L | 0.21 * | 0.35 * | 0.17 * |
| REF_S—RAS_L | 0.84 * | 0.69 * | 0.40 * |
| RAS_S—REF_L | 0.21 * | −0.10 | 0.12 |
| RAS_S—RAS_L | 0.29 * | 0.24 * | 0.10 |
| REF_L—RAS_L | 0.63 * | 0.35 * | 0.23 * |
| Statistically significant limit | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.13 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Dolomite Young modulus | GPa | 38.16 |
| Dolomite Poisson ratio | - | 0.24 |
| Binder Young modulus | GPa | 0.89 |
| Binder Poisson ratio | - | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zieliński, P.; Klimczak, M.; Tekieli, M.; Strzępek, M. An Evaluation of the Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes Using the Semi-Circular Bending Method and Digital Image Correlation. Materials 2025, 18, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050967
Zieliński P, Klimczak M, Tekieli M, Strzępek M. An Evaluation of the Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes Using the Semi-Circular Bending Method and Digital Image Correlation. Materials. 2025; 18(5):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050967
Chicago/Turabian StyleZieliński, Piotr, Marek Klimczak, Marcin Tekieli, and Mateusz Strzępek. 2025. "An Evaluation of the Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes Using the Semi-Circular Bending Method and Digital Image Correlation" Materials 18, no. 5: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050967
APA StyleZieliński, P., Klimczak, M., Tekieli, M., & Strzępek, M. (2025). An Evaluation of the Fracture Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes Using the Semi-Circular Bending Method and Digital Image Correlation. Materials, 18(5), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050967






