Carbon Micro-Alloying Promotes Creep Flow via Enhanced Structural Heterogeneity in Fe-Based Amorphous Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Sample Preparation, Structural and Dynamic Characterization
2.2. Nanoindentation Tests
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy Measurements
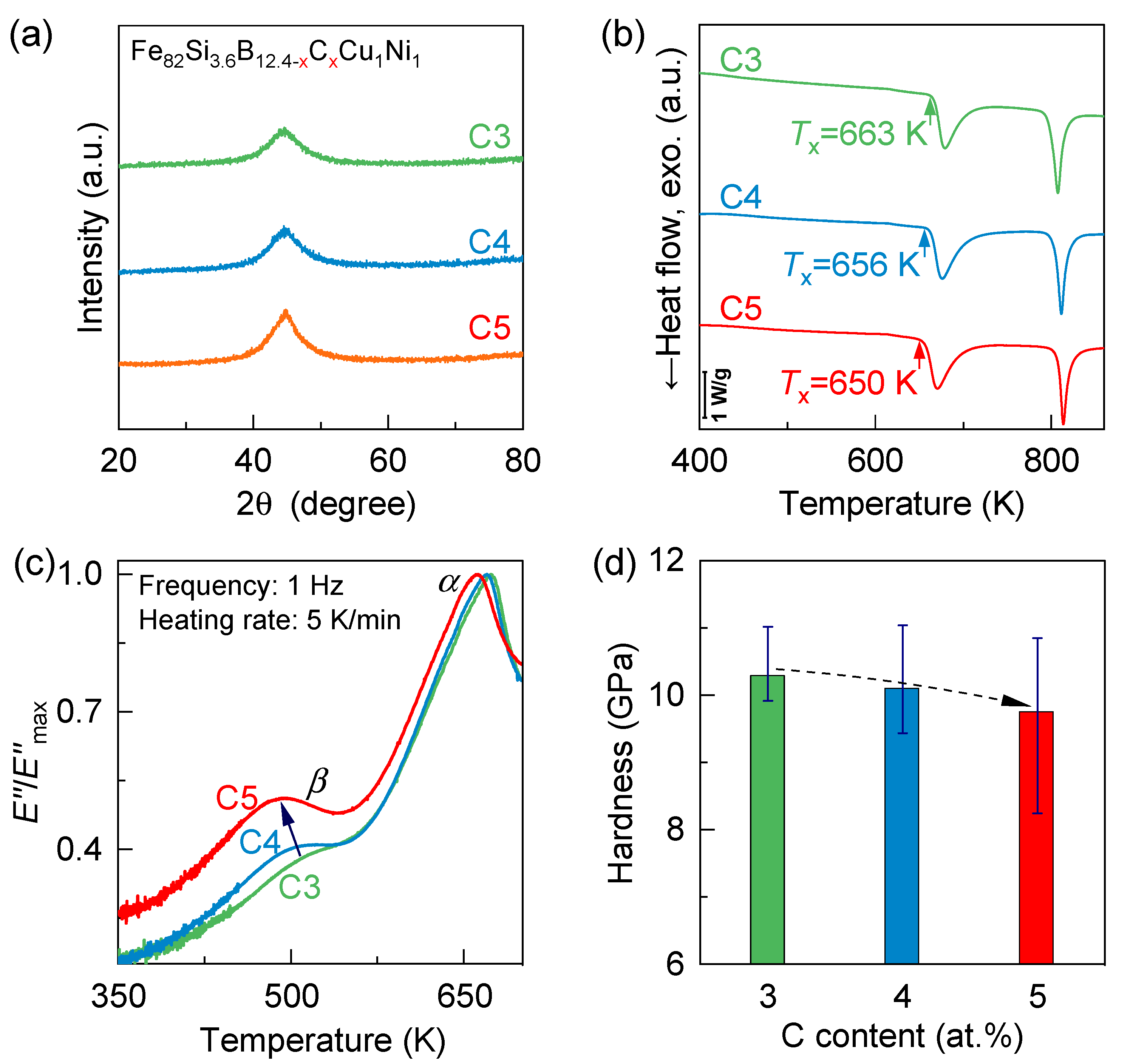
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Typical Physical Parameters
3.2. Nanoindentation Creep
3.3. Mapping the Viscoelastic Heterogeneity
3.4. Physical Origins of Micro-Alloying in Promoting Plastic Flow
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiao, J.; Wang, Q.; Pelletier, J.; Kato, H.; Casalini, R.; Crespo, D.; Pineda, E.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y. Structural heterogeneities and mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 250–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H. Dynamic relaxations and relaxation-property relationships in metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.J.; Huo, J.T.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y. Designing advanced amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys by controlling the energy state. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2311406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Yao, Y.; Pelletier, J.-M.; Keer, L. Understanding of micro-alloying on plasticity in Cu46Zr47−xAl7Dyx (0 ≤ x ≤ 8) bulk metallic glasses under compression: Based on mechanical relaxations and theoretical analysis. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 82, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.C.; Kelly, J.P.; Novitskaya, E.; Eliasson, V.; Hodge, A.M.; Graeve, O.A. Mechanical properties of an Fe-Based SAM2× 5-630 metallic glass matrix composite with tungsten particle additions. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.; Ivanov, Y.P.; Chuvilin, A.; Schöberl, T.; Stoica, M.; Zhang, Z.; Eckert, J. Origin of large plasticity and multiscale effects in iron-based metallic glasses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Roles of minor additions in formation and properties of bulk metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 540–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qu, Y.; Hu, L.; Qi, L.; Qu, F.; He, S.; Liu, X. Effect of Yttrium Doping on Glass-Forming Ability, Thermal Stability, and Corrosion Resistance of Zr50.7Cu28Ni9Al12.3 Bulk Metallic Glass. Metals 2023, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Hua, N.; Huang, L.; Zhang, T. Ternary Fe–P–C bulk metallic glass with good soft-magnetic and mechanical properties. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Feng, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; An, Q.; Ning, H.; Zhou, G.; Peng, Y. Effect of Fe-C alloy additions on properties of Cu-Zr-Ti metallic glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 798, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.-W.; Tan, J.; Cai, A.-H.; Yong, L.; Hong, W.; Qi, A.; Li, P.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Qing, Y. Fe–C micro-alloying effect on properties of Zr53Al11. 6Ni11. 7Cu23. 7 bulk metallic glass. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 2750–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, B.A.; Bai, H.Y.; Wang, W.H. Evolution of hidden localized flow during glass-to-liquid transition in metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Atomistic free-volume zones and inelastic deformation of metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balal, A.; Bian, X.; Han, D.; Huang, B.; Liao, S.; Li, N.; Ali, S.; Jia, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, G. The role of cryogenic treatment in the relaxation behavior of the elastically rejuvenated metallic glasses. Int. J. Plast. 2025, 189, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Zhao, D.; Kim, J.; Şopu, D.; Wang, G.; Pippan, R.; Eckert, J. Controlling the distribution of structural heterogeneities in severely deformed metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 752, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Inoue, A.; Sakurai, T.; Chen, M.W. Experimental characterization of shear transformation zones for plastic flow of bulk metallic glasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14769–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, G.; Wang, R.J.; Zhao, D.Q.; Pan, M.X.; Wang, W.H. Super plastic bulk metallic glasses at room temperature. Science 2007, 315, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Sun, B.A.; Wen, P.; Bai, H.Y.; Kong, Q.P.; Wang, W.H. Crossover from stochastic activation to cooperative motions of shear transformation zones in metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 081904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.-C.; Zhao, Y.; Yoo, B.-G.; Kim, Y.-J.; Suh, J.-Y.; Ramamurty, U.; Jang, J.-I. Estimation of the shear transformation zone size in a bulk metallic glass through statistical analysis of the first pop-in stresses during spherical nanoindentation. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M. Relating activation of shear transformation zones to β relaxations in metallic glasses. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 220201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Lyu, G.; Pineda, E.; Pelletier, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, J. Deciphering non-elastic deformation in amorphous alloy: Simultaneous aging-induced ordering and rejuvenation-induced disordering. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 175, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Pineda, E.; Song, K.; Qiao, J. Unraveling the microstructural heterogeneity and plasticity of Zr50Cu40Al10 bulk metallic glass by nanoindentation. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 154, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhao, R.; Li, F.C.; Luo, P.; Li, M.Z.; Bai, H.Y. Liquid-like atoms in dense-packed solid glasses. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, J. Unusual fast secondary relaxation in metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-B.; Richert, R.; Samwer, K. Structural rearrangements governing Johari-Goldstein relaxations in metallic glasses. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y.; Samwer, K. The β-relaxation in metallic glasses. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 429–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Nguyen, H.K.; Song, S.X.; Aji, D.P.B.; Hirata, A.; Wang, H.; Nakajima, K.; Chen, M.W. Intrinsic correlation between β-relaxation and spatial heterogeneity in a metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, J.S.; Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L.; Samwer, K. Anelastic to plastic transition in metallic glass-forming liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 135502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Chen, M.; Egami, T. Stress-temperature scaling for steady-state flow in metallic glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 205701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Perepezko, J.H. Mapping the viscoelastic heterogeneity at the nanoscale in metallic glasses by static force spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7558–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Nakajima, K.; Zhang, W.; Hirata, A.; Nishi, T.; Inoue, A.; Chen, M.W. Characterization of nanoscale mechanical heterogeneity in a metallic glass by dynamic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Song, S.; Reddy, K.M.; Hirata, A.; Chen, M. Spatial heterogeneity as the structure feature for structure–property relationship of metallic glasses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, B.; Ya, B.; Zhang, X. Study on soft magnetic properties of Finemet-type nanocrystalline alloys with Mo substituting for Nb. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 2017, 214, 1700074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ramanujan, R. The effect of niobium alloying additions on the crystallization of a Fe–Si–B–Nb alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2005, 403, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illeková, E.L. FINEMET-type nanocrystallization kinetics. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 387, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, L.; Wang, W.; Bai, H. Tensile plasticity in metallic glasses with pronounced β relaxations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 015504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hirata, A.; Liu, P.; Song, S.; Tian, Y.; Han, J.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M. Correlation between local structure order and spatial heterogeneity in a metallic glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 215501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Song, L.; Xu, W.; Huo, J.; Wang, J.-Q.; Li, R.-W. The evolution of relaxation modes during isothermal annealing and its influence on properties of Fe-based metallic glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 509, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Maaß, R. Elastic fluctuations and structural heterogeneities in metallic glasses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Fujita, T.; Aji, D.P.B.; Matsuura, M.; Chen, M.W. Structural origins of Johari-Goldstein relaxation in a metallic glass. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, D.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Fan, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Substantially enhanced plasticity of bulk metallic glasses by densifying local atomic packing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.A.; Yu, H.B.; Jiao, W.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wang, W.H. Plasticity of ductile metallic glasses: A self-organized critical state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 035501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, S.; Trost, C.O.W.; Kreiml, P.; Cordill, M.J. Accurate measurement of thin film mechanical properties using nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.; Crawford, B. Measuring substrate-independent modulus of thin films. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Nix, W.D. Effects of the substrate on the determination of thin film mechanical properties by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Kiener, V.; Durst, K. Advanced nanoindentation testing for studying strain-rate sensitivity and activation volume. JOM 2017, 69, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yu, H.-B. Fundamental links between shear transformation, β relaxation, and string-like motion in metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Kardani, A.; Liu, M.; Lin, Z.; Bagherifard, S. Exploring the bonding mechanism in cold spray deposition of engineered graphene nanoplates-Ni nanocomposite powder. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 191, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Sheng, H.W.; Li, M.Z. Effect of pressure on β relaxation in La60Ni15Al25 metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 125108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-B.; Wang, W.-H.; Samwer, K. The β relaxation in metallic glasses: An overview. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, T.; Fan, W.; Mao, Y. Effect of cooling rate on the order degree, residual stress, and room temperature mechanical properties of Fe-6.5wt.%Si alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 571, 170550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Tkatch, V.; I Limanovskii, A.; Denisenko, S.N.; Rassolov, S.G. The effect of the melt-spinning processing parameters on the rate of cooling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 323, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, D.; Teng, S.; Lv, J.; Su, X.; Tong, Y.; Xiang, M.; Song, L.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, J.; et al. Carbon Micro-Alloying Promotes Creep Flow via Enhanced Structural Heterogeneity in Fe-Based Amorphous Alloys. Materials 2025, 18, 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194637
Cao D, Teng S, Lv J, Su X, Tong Y, Xiang M, Song L, Gao M, Zhang Y, Huo J, et al. Carbon Micro-Alloying Promotes Creep Flow via Enhanced Structural Heterogeneity in Fe-Based Amorphous Alloys. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194637
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Deyu, Sishi Teng, Jiajie Lv, Xin Su, Yu Tong, Mingliang Xiang, Lijian Song, Meng Gao, Yan Zhang, Juntao Huo, and et al. 2025. "Carbon Micro-Alloying Promotes Creep Flow via Enhanced Structural Heterogeneity in Fe-Based Amorphous Alloys" Materials 18, no. 19: 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194637
APA StyleCao, D., Teng, S., Lv, J., Su, X., Tong, Y., Xiang, M., Song, L., Gao, M., Zhang, Y., Huo, J., & Wang, J. (2025). Carbon Micro-Alloying Promotes Creep Flow via Enhanced Structural Heterogeneity in Fe-Based Amorphous Alloys. Materials, 18(19), 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194637






