Laser-Induced Liquid-Phase Boron Doping of 4H-SiC
Abstract
1. Introduction
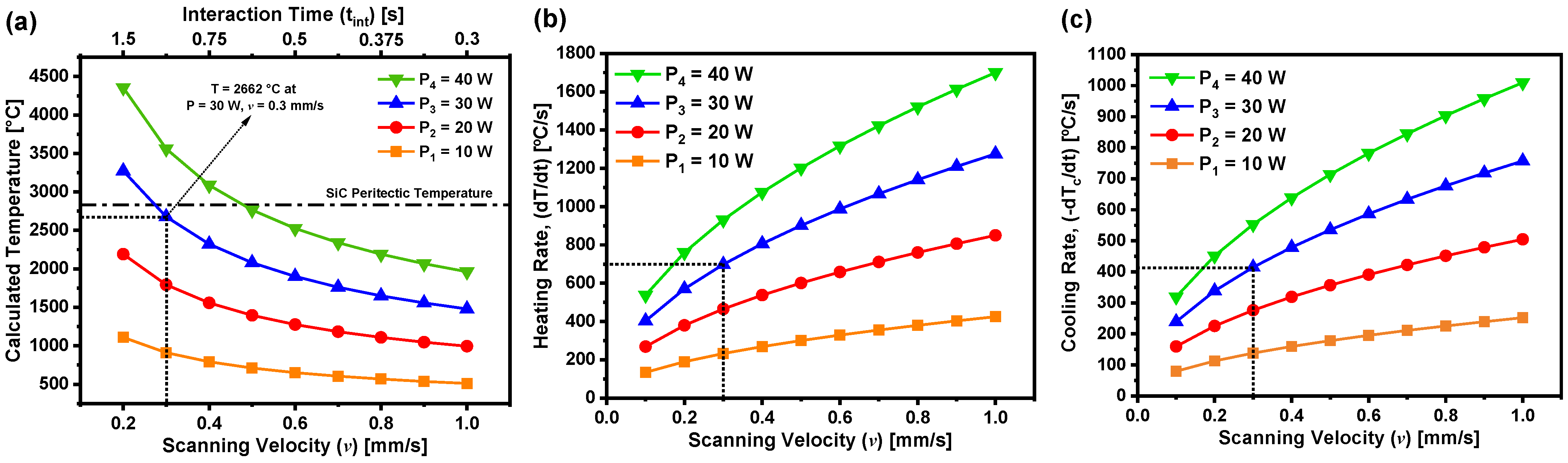
2. Process Parameters Selection
3. Experimental Procedure
3.1. SiC Substrate Cleaning Procedure and Preparation of Dopant Solution
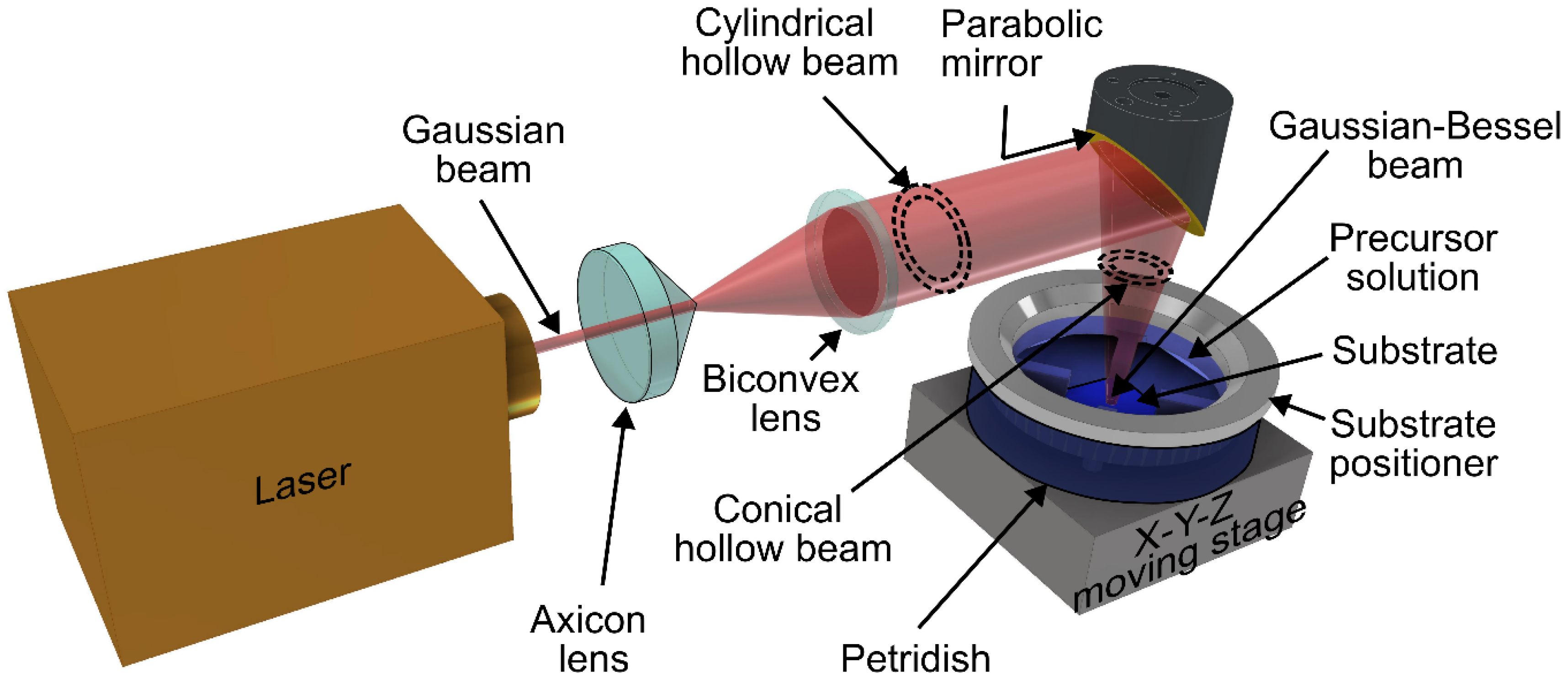
3.2. Optical Setup for Laser Doping
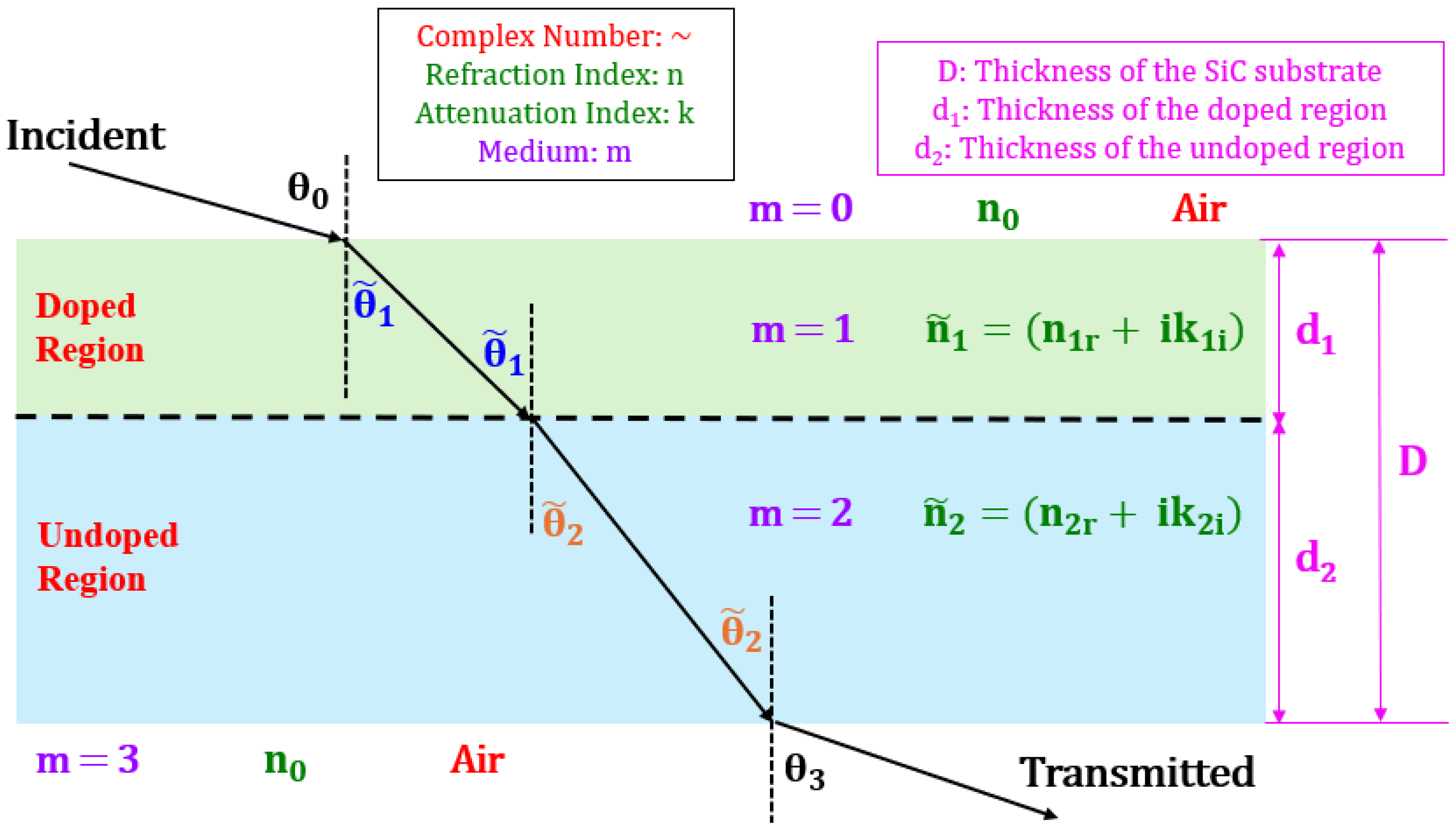
4. Absorption Models for the Determination of Refraction and Attenuation Indices Pre- and Post-Laser Doping
4.1. Single-Layer Absorption Model for Determining and for the Undoped SiC Region
4.2. Multi-Layer Absorption Model for Determining and for the Doped SiC Region
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Raman Spectra Analysis
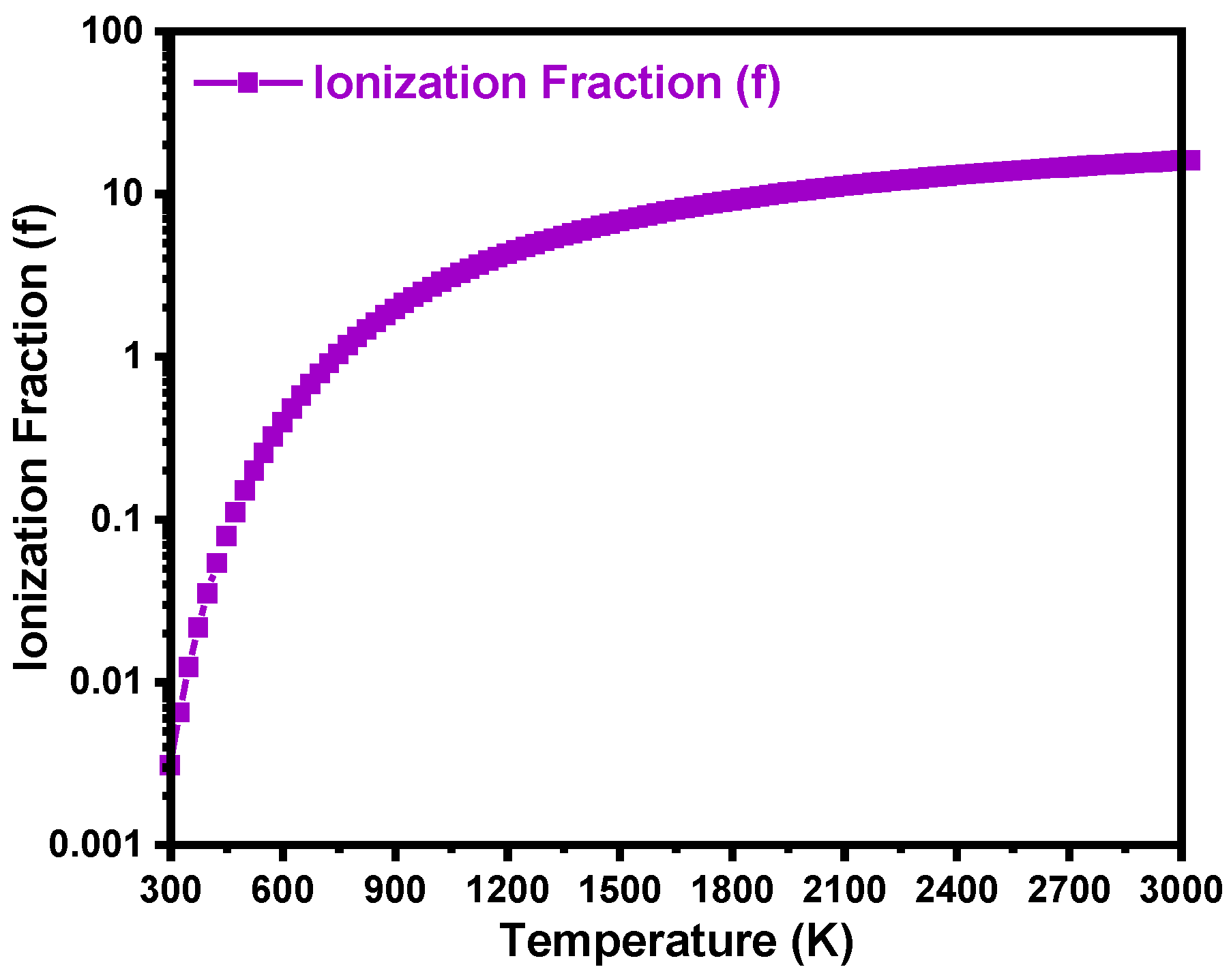
5.2. Temperature-Dependent Resistivity and Ionization Energy of Boron in 4H-SiC
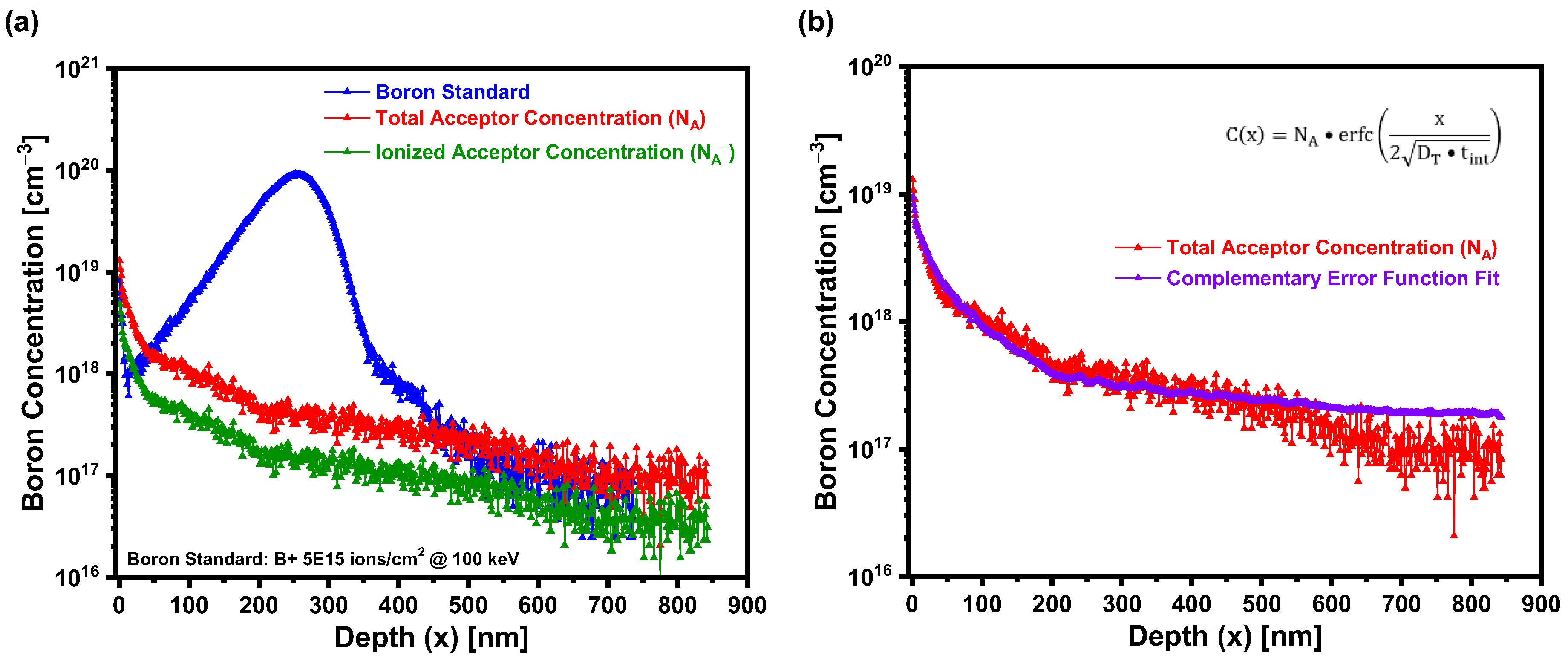
5.3. Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Analysis
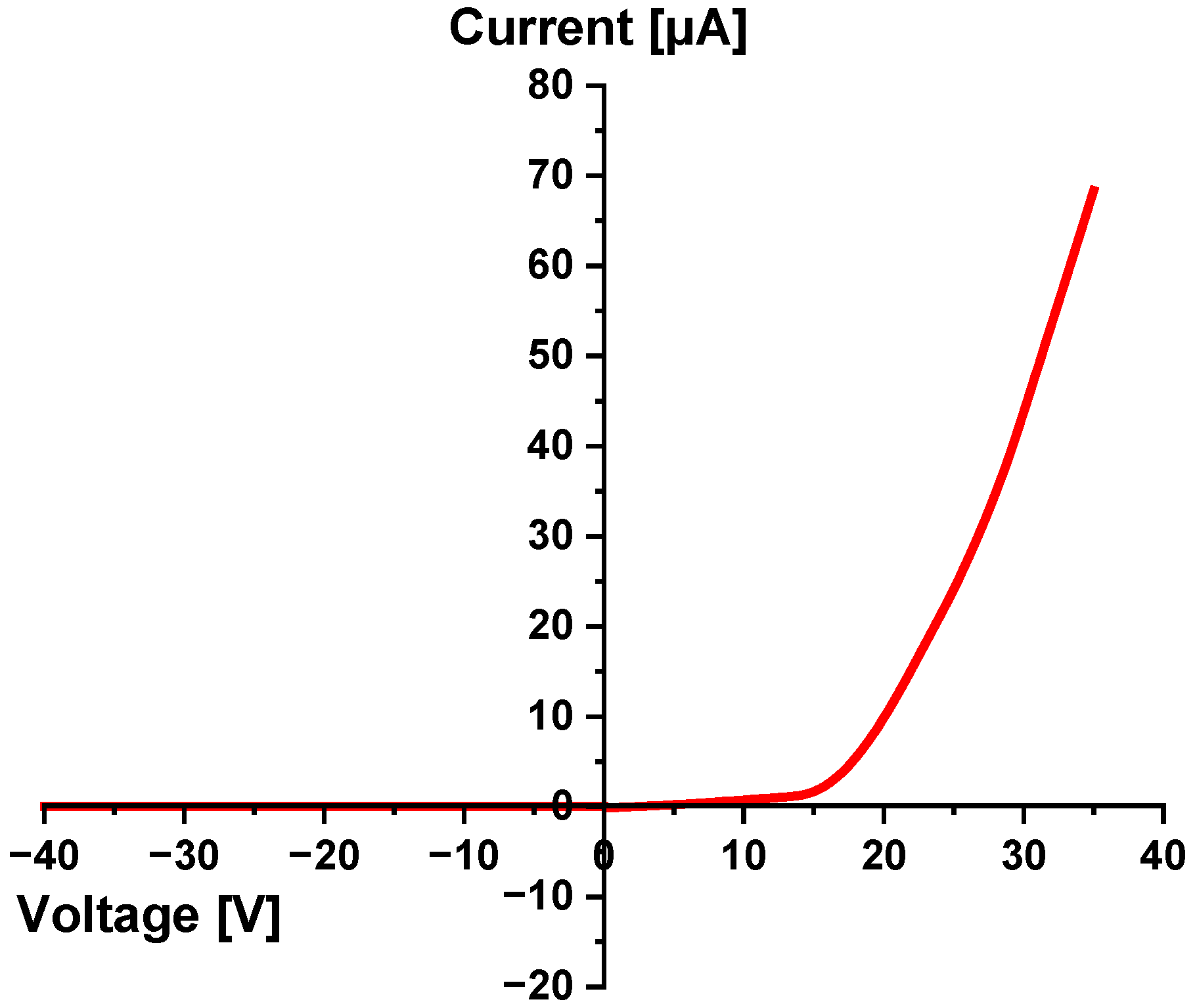
5.4. Current–Voltage Characteristics of the Laser-Fabricated p–n Junction
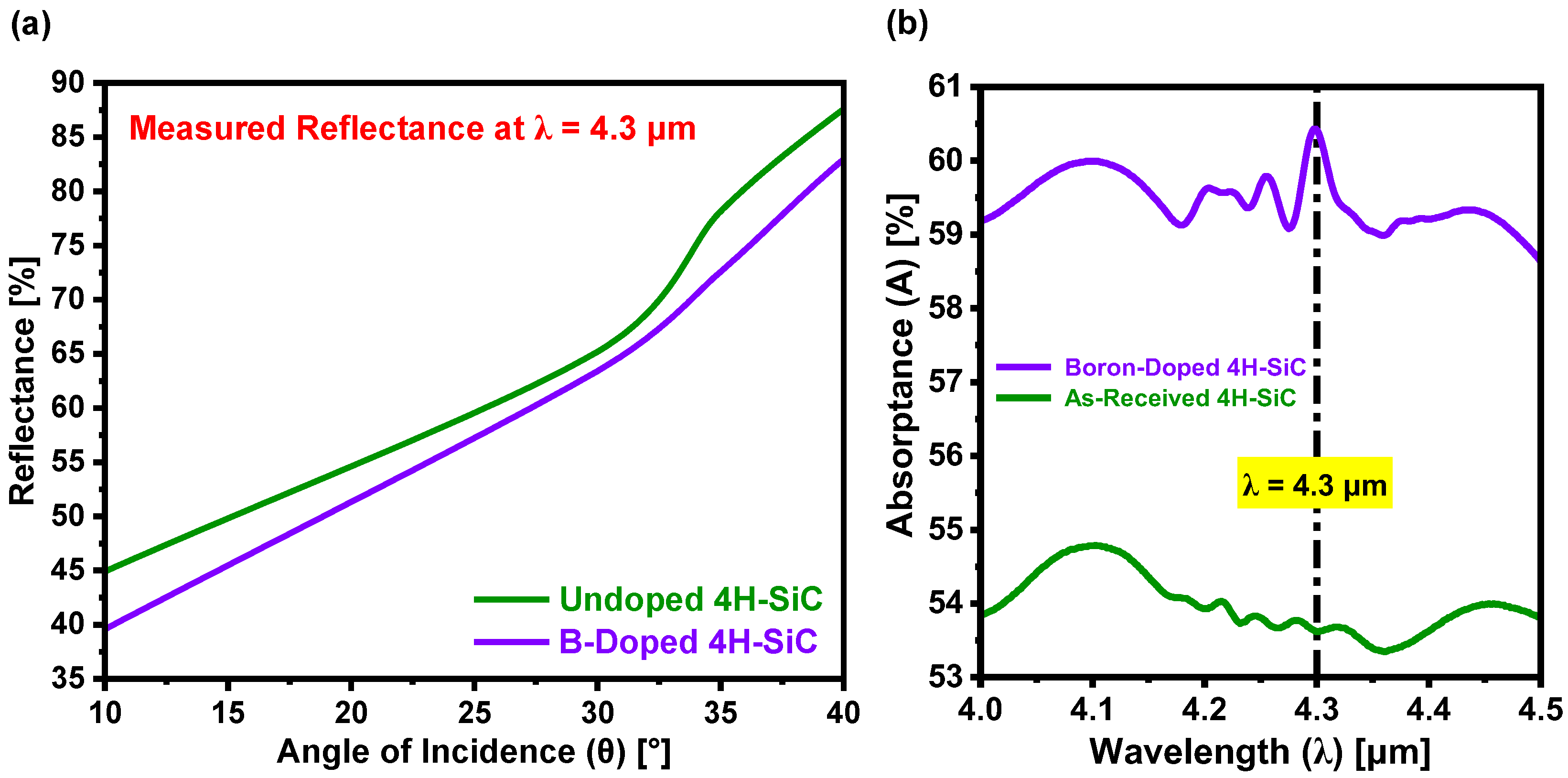
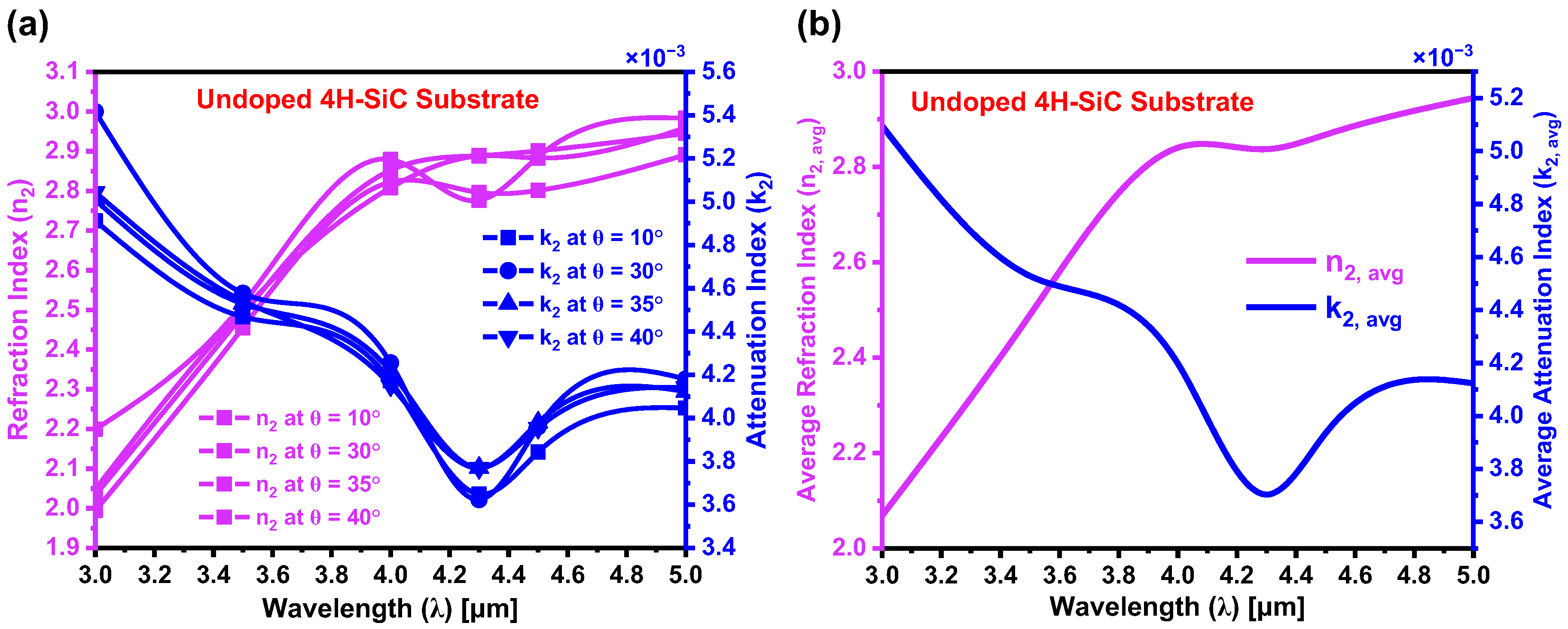
5.5. Determination of Refraction and Attenuation Indices Pre- and Post-Laser Doping
5.6. Determination of Dielectric Constant to Study Anomalous Dispersion in SiC
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, G. An Uncooled Mid-Wave Infrared Detector Based on Optical Response of Laser-Doped Silicon Carbide. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, K.; Ikeda, A.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Phosphorus doping into 4H-SiC by irradiation of excimer laser in phosphoric solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 06GF02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Salama, I.A.; Quick, N.R.; Kar, A. Effects of different laser sources and doping methods used to dope silicon carbide. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, E.M.; Rao, M.V.; Holland, O.W.; Chi, P.H.; Jones, K.A.; Derenge, M.A.; Vispute, R.D.; Venkatesan, T. Al, B, and Ga ion-implantation doping of SiC. J. Electron. Mater. 2000, 29, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, T.; Cooper, J.A. Appendix C: Major physical properties of common SiC polytypes. In Fundamentals of Silicon Carbide Technology: Growth, Characterization, Devices, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2014; pp. 521–524. [Google Scholar]
- Järrendahl, K.; Davis, R.F. Materials properties and characterization of SiC. In Semiconductors and Semimetals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 52, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, T. SiC material properties. In Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Power Devices; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Capan, I. Electrically active defects in 3C, 4H, and 6H silicon carbide polytypes: A review. Crystals 2025, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.; Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Defects as qubits in 3C- and 4H-SiC. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 045208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, K.N.; Peppas, G.D.; Fetsis, T.T.; Tegopoulos, S.N.; Charalampakos, V.P.; Kyritsis, A.; Yiotis, A.G.; Gonos, I.F.; Pyrgioti, E.C. Dielectric and thermal response of TiO2 and SiC natural ester based nanofluids for use in power transformers. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 79222–79236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; McGarrity, M.; Kim, J.H.; Zhao, F. Silicon carbide-based DNA sensing technologies. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Han, H.; Zhang, P. A review of SiC sensor applications in high-temperature and radiation extreme environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bet, S. Laser Enhanced Doping for Silicon Carbide White Light Emitting Diodes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, A.; Nishi, K.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Phosphorus doping of 4H SiC by liquid immersion excimer laser irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 052104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, G.; Bougdid, Y.; Sugrim, C.J.; Kumar, R.; Kar, A. Laser doping of n-type 4H-SiC with boron using solution precursor for mid-wave infrared optical properties. J. Laser Appl. 2024, 36, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marui, D.; Ikeda, A.; Nishi, K.; Ikenoue, H.; Asano, T. Aluminum doping of 4H-SiC by irradiation of excimer laser in aluminum chloride solution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 06JF03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkby, J.W.; Moro, F.; Perego, M.; Taglietti, F.; Lidorikis, E.; Kalfagiannis, N.; Koutsogeorgis, D.C.; Fanciulli, M. Fabrication of nitrogen-hyperdoped silicon by high-pressure gas immersion excimer laser doping. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, N.R. Novel techniques in synthesis and processing of advanced materials. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Novel Techniques in Synthesis and Processing of Advanced Materials, Rosemont, IL, USA, 2–6 October 1994; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Quick, N.R.; Matson, R.J. Characterization of a ceramic electrical conductor synthesized by a laser conversion process. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 12–16 December 1994; STS Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Incropera, F.P.; Dewitt, D.P.; Bergman, T.L.; Lavine, A.S. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bougdid, Y.; Chenard, F.; Sugrim, J.; Kumar, R.; Kar, A. CO2 laser-assisted sintering of TiO2 nanoparticles for transparent films. J. Laser Appl. 2023, 35, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuck, R.; Fogarassy, E.; Muller, J.C.; Hodeau, M.; Wattiaux, A.; Siffert, P. Laser-induced diffusion by irradiation of silicon dipped into an organic solution of the dopant. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1981, 38, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. Optics; Pearson Education India: Chennai, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, J.R.; Mengüç, M.P.; Daun, K.; Siegel, R. Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, S.; Harima, H. Raman investigation of SiC polytypes. Phys. Status Solidi B 1997, 202, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Shen, L. Effects of doping on the vibrational and electronic properties of 4H-SiC: A Raman and theoretical study. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 165703. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.M.; Li, Y.; Ng, K.K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Vivona, M.; Greco, G.; Giannazzo, F. Selective doping in silicon carbide power devices. Materials 2021, 14, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troffer, T.; Schadt, M.; Frank, T.; Itoh, H.; Pensl, G.; Heindl, J.; Strunk, H.P.; Maier, M. Doping of SiC by implantation of boron and aluminum. Phys. Status Solidi A 1997, 162, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, R.F. Semiconductor Device Fundamentals; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.F. Principles of Materials Science and Engineering, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kubiak, A.; Rogowski, J. Boron and aluminum diffusion into 4H–SiC substrates. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Quick, N.R.; Kar, A. Laser endotaxy and PIN diode fabrication of silicon carbide. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2005, 911, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Quick, N.R.; Kar, A. Laser endotaxy in silicon carbide and PIN diode fabrication. J. Laser Appl. 2008, 20, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S. 4H-Silicon Carbide p-n Diode for Harsh Environment Sensing Applications. Master’s Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R. Reliability and performance limitations in SiC power devices. Microelectron. Reliab. 2004, 44, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.K. Simulation and Electrical Evaluation of 4H-SiC Junction Field Effect Transistors and Junction Barrier Schottky Diodes with Buried Grids. Ph.D. Thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Racka, K.; Avdonin, A.; Sochacki, M.; Tymicki, E.; Grasza, K.; Jakieła, R.; Surma, B.; Dobrowolski, W. Magnetic, optical and electrical characterization of SiC doped with scandium during the PVT growth. J. Cryst. Growth 2015, 413, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugrim, J.C.; Kulkarni, G.; Bougdid, Y.; Heylman, K.; Kumar, R.; Kar, A.; Sundaram, K. Numerical investigation of laser doping parameters for semi-insulating 4H-SiC substrate. J. Laser Appl. 2024, 36, 022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, J.; Kar, A. Theory and Application of Laser Chemical Vapor Deposition; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cherroret, N.; Chakravarty, A.; Kar, A. Temperature-dependent refractive index of semiconductors. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


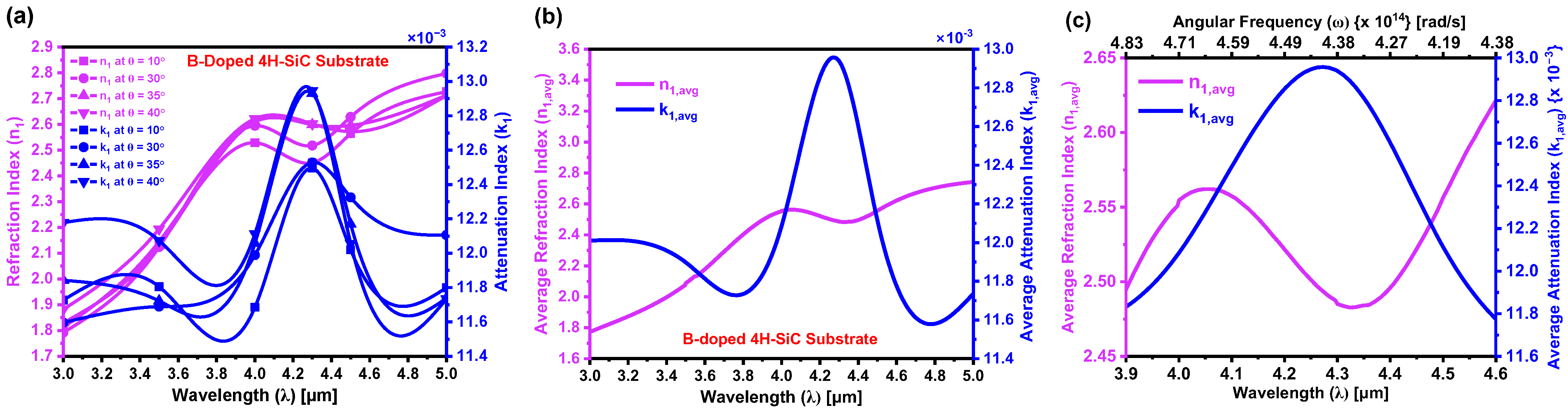
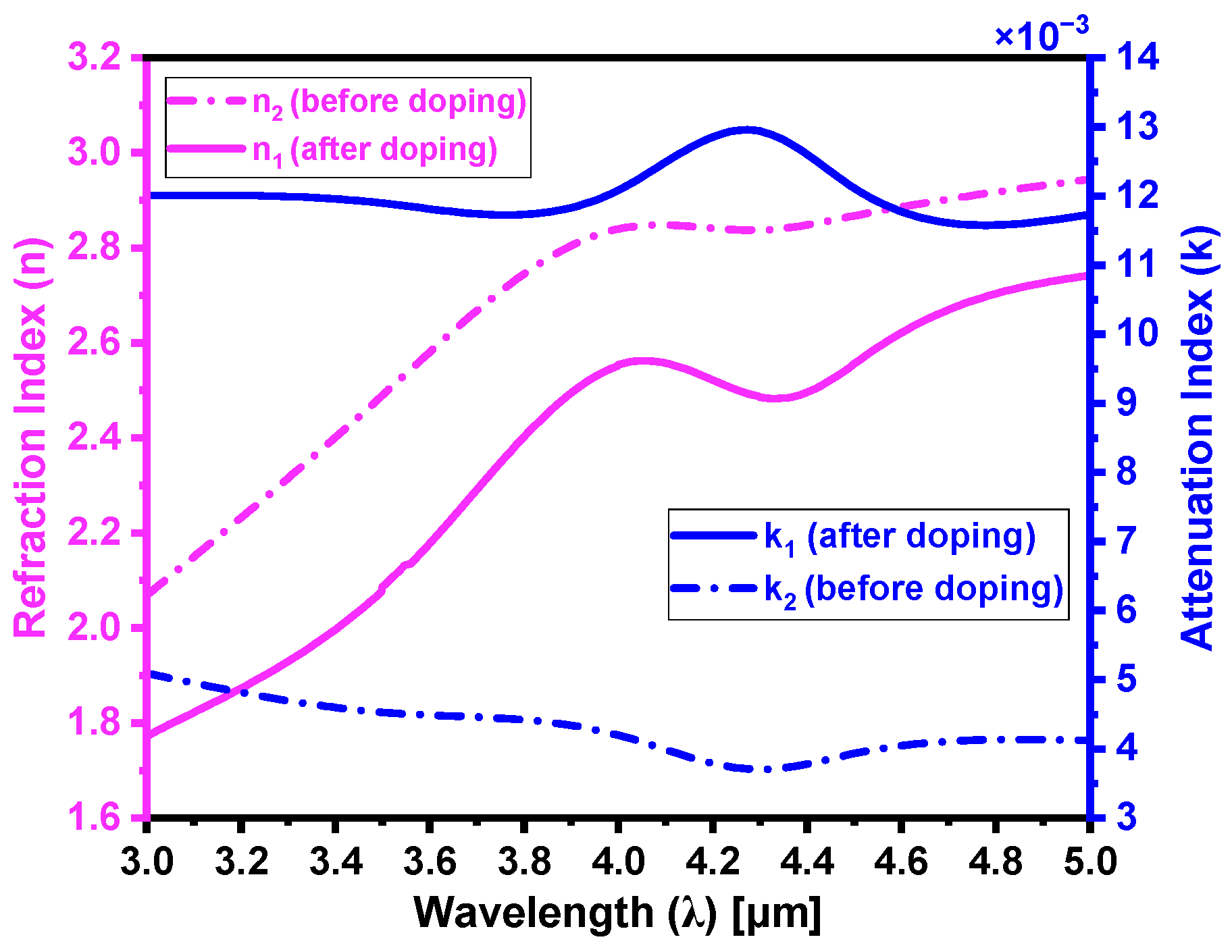

| Fresnel’s Method | Absorption Models [Current Study] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength (λ) | Parameter | As-Received | Boron-Doped | Δ | As-Received | Boron-Doped | Δ |
| n | |||||||
| k | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulkarni, G.; Bougdid, Y.; Sugrim, C.; Kumar, R.; Kar, A. Laser-Induced Liquid-Phase Boron Doping of 4H-SiC. Materials 2025, 18, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122758
Kulkarni G, Bougdid Y, Sugrim C, Kumar R, Kar A. Laser-Induced Liquid-Phase Boron Doping of 4H-SiC. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122758
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulkarni, Gunjan, Yahya Bougdid, Chandraika (John) Sugrim, Ranganathan Kumar, and Aravinda Kar. 2025. "Laser-Induced Liquid-Phase Boron Doping of 4H-SiC" Materials 18, no. 12: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122758
APA StyleKulkarni, G., Bougdid, Y., Sugrim, C., Kumar, R., & Kar, A. (2025). Laser-Induced Liquid-Phase Boron Doping of 4H-SiC. Materials, 18(12), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122758







