Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
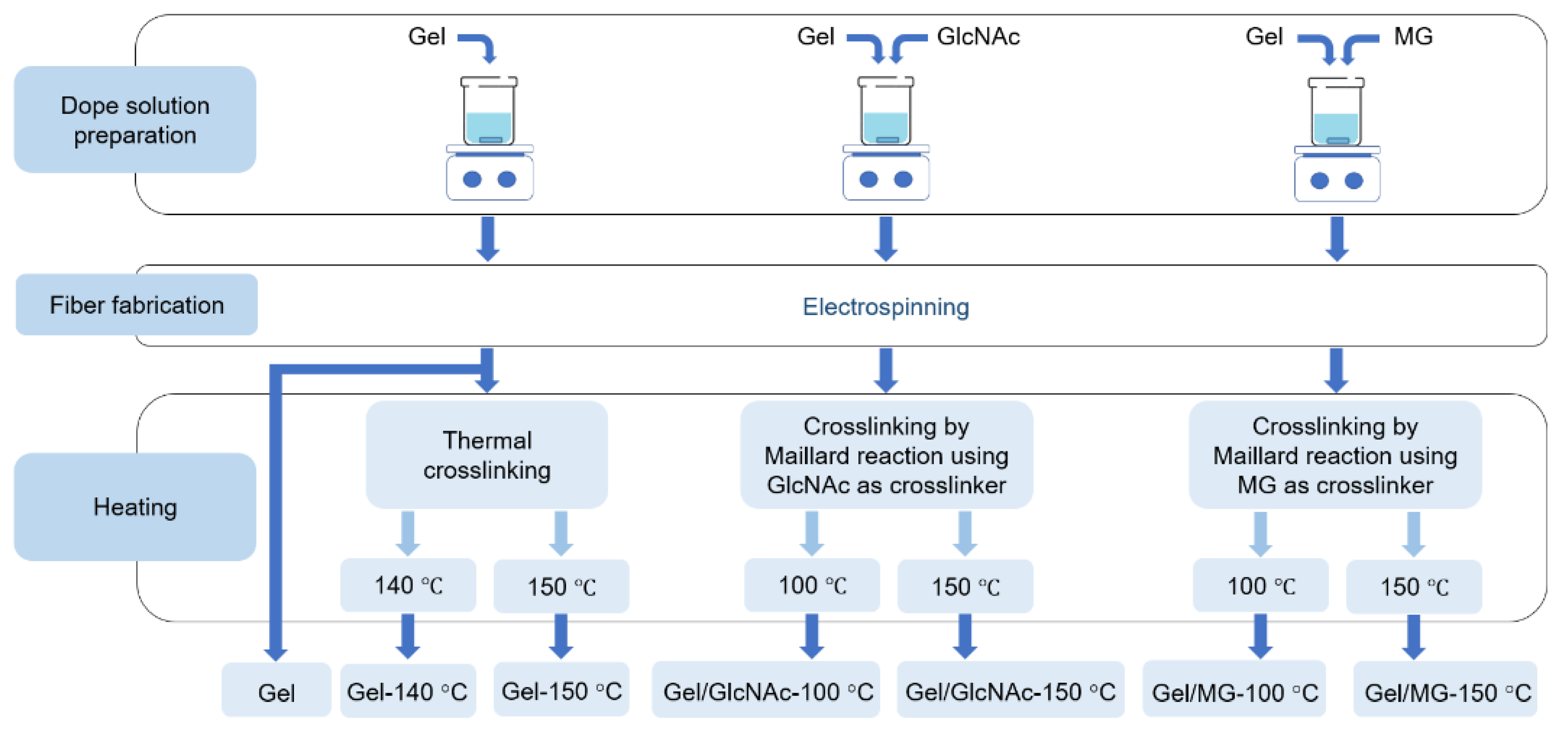
2.2. Preparation of Gel Solution
2.3. Preparation of Gel/GlcNAc Solution and Gel/MG Solution
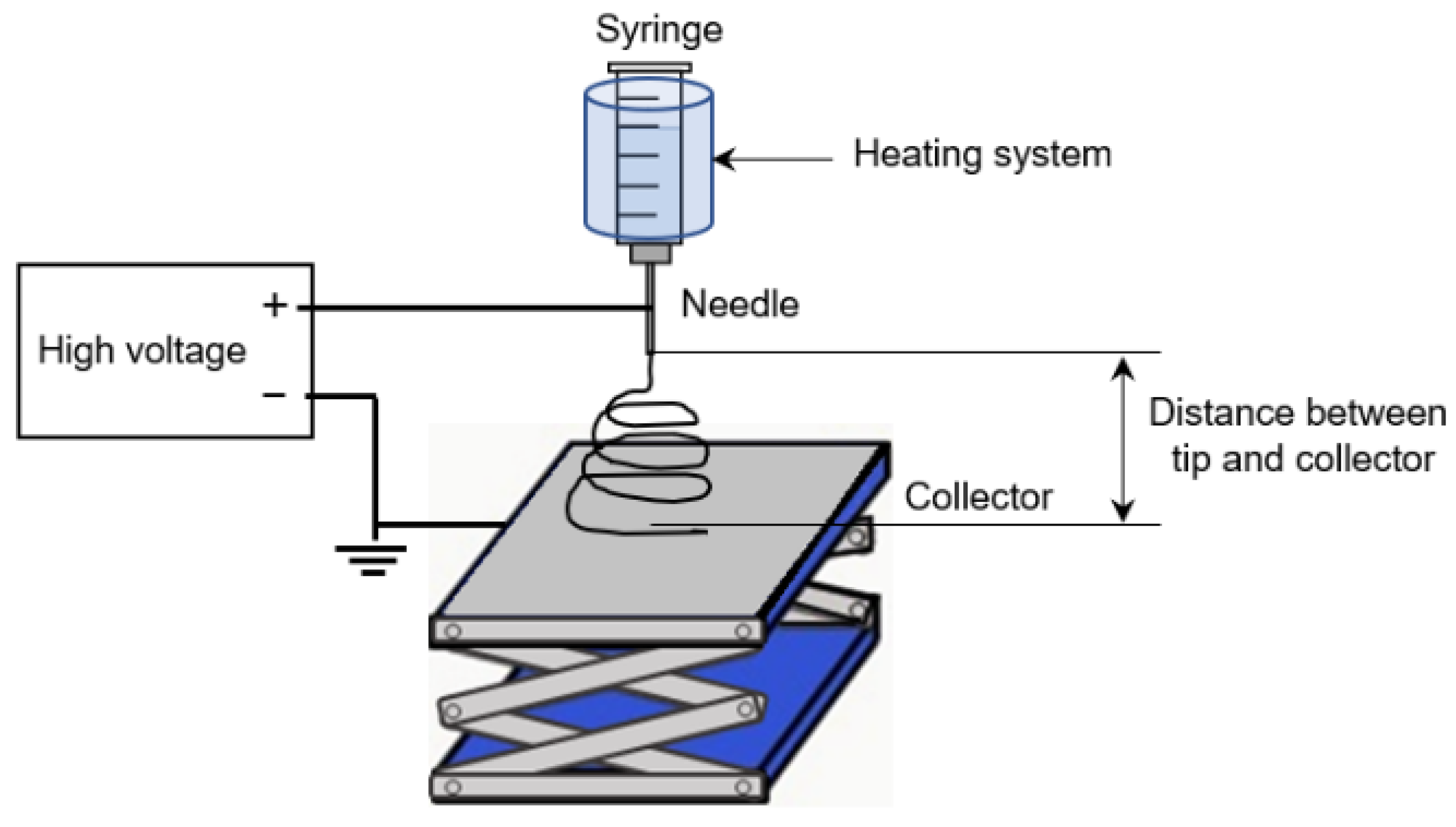
2.4. Preparation of Nonwoven Gel Nanofibers by Electrospinning Technique
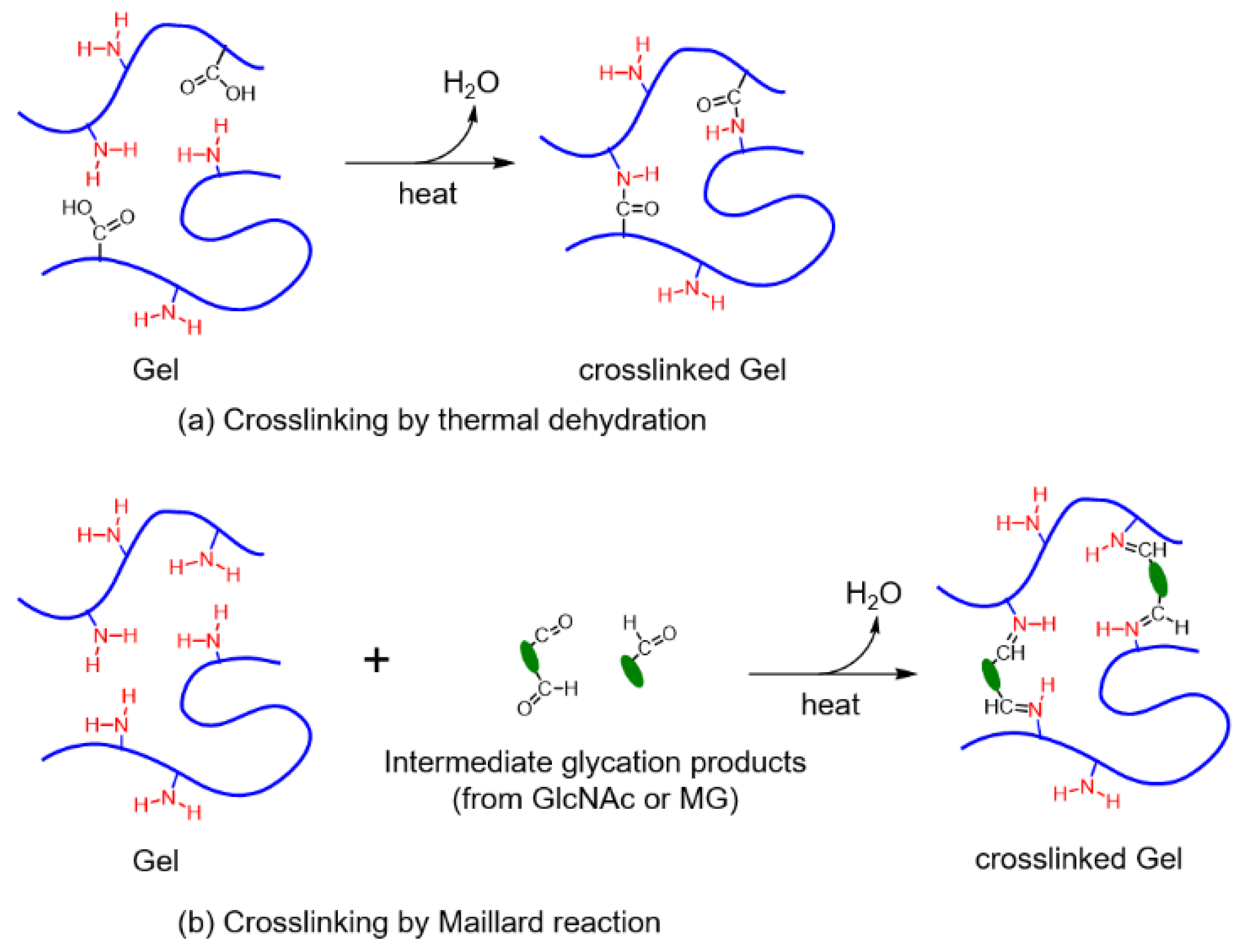
2.5. Crosslinking by Thermal Dehydration
2.6. Crosslinking by the Maillard Reaction
2.7. Morphology of Nanofibers
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Measurement
2.9. Tensile Properties of Nanofibers
2.10. PBS Solution-Resistance Test
2.11. Cell Culture
3. Results and Discussion
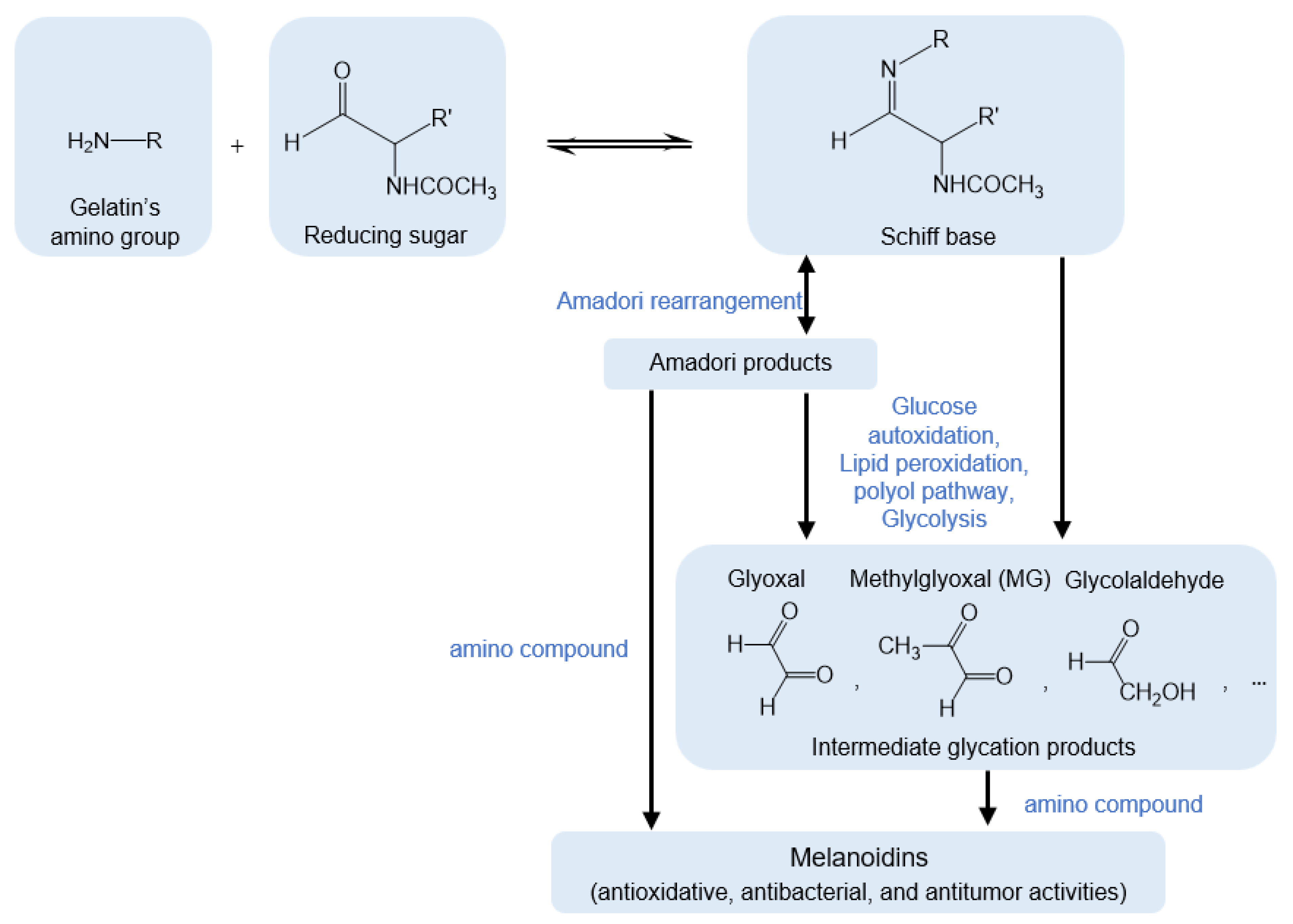
3.1. Maillard Reaction Mechanism of Gel by GlcNAc and MG
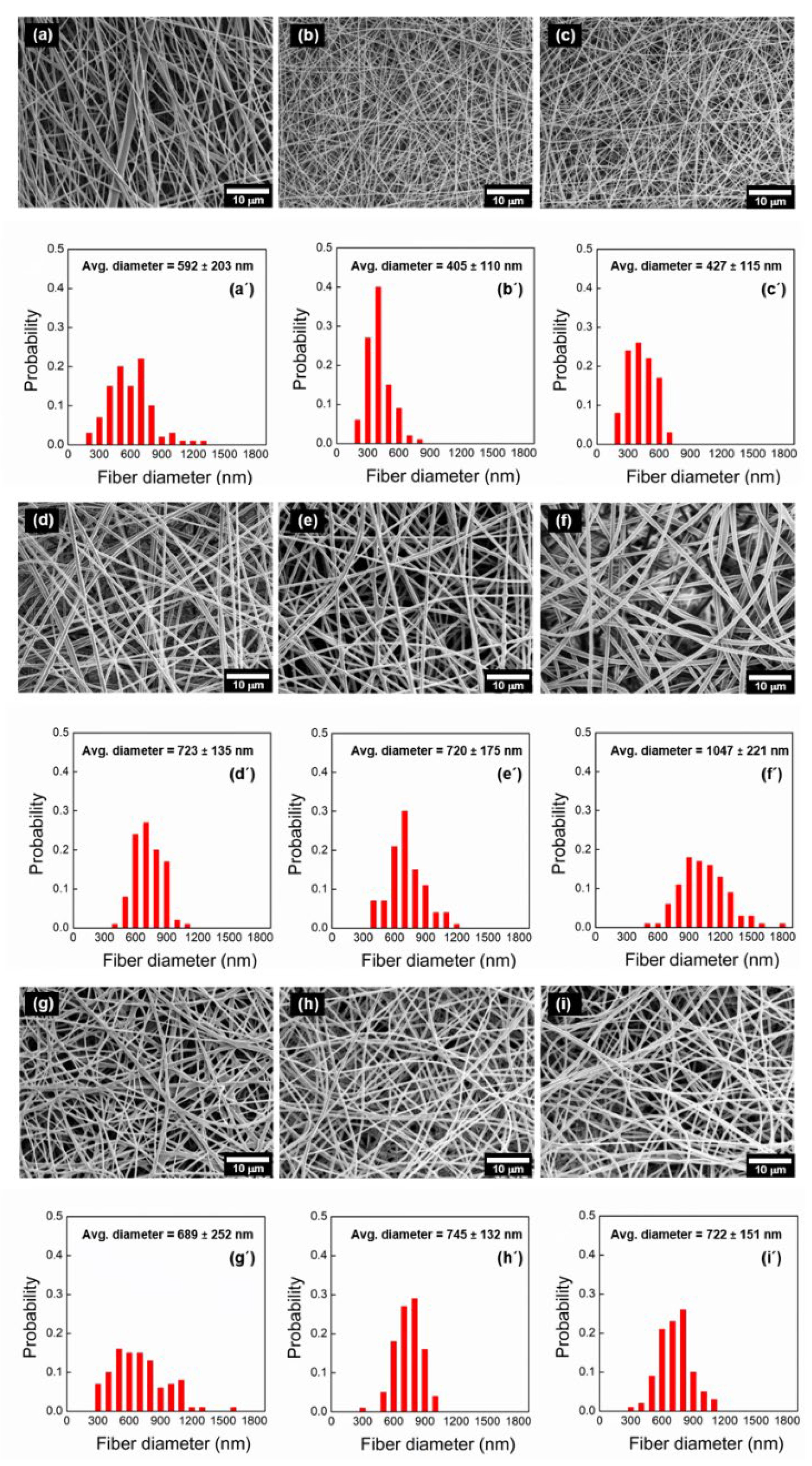
3.2. Morphological Observation
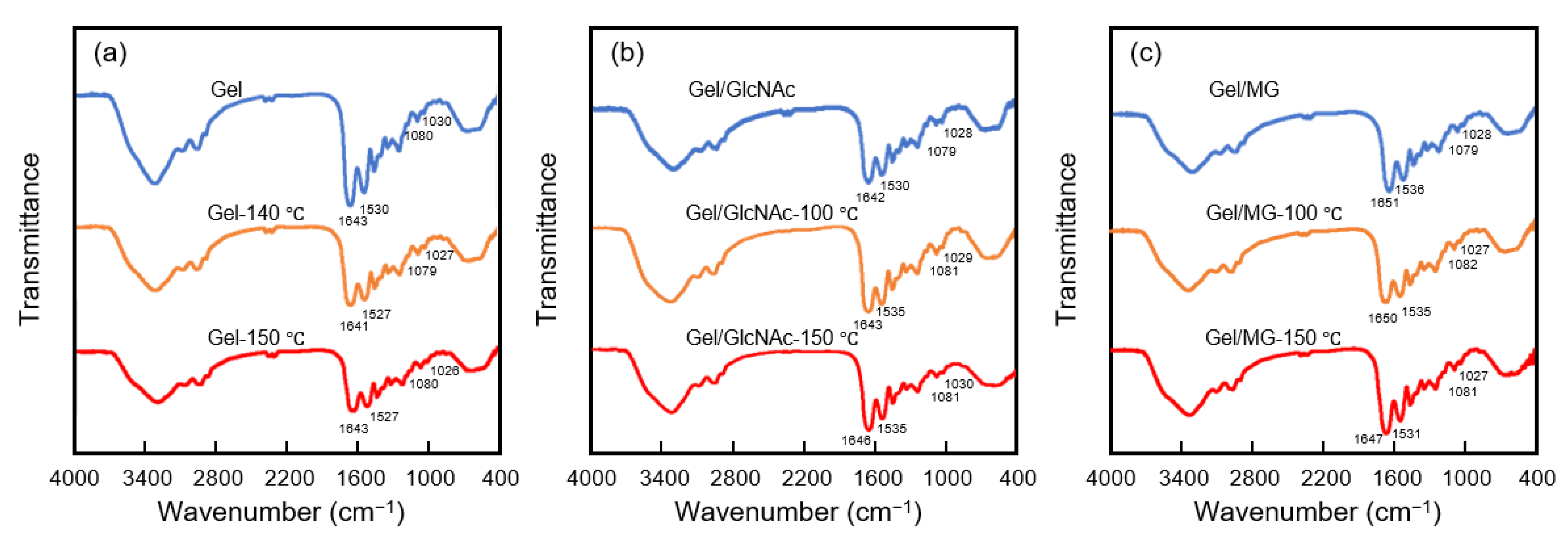
3.3. Characterization by FTIR Analysis
3.4. Mechanical Properties
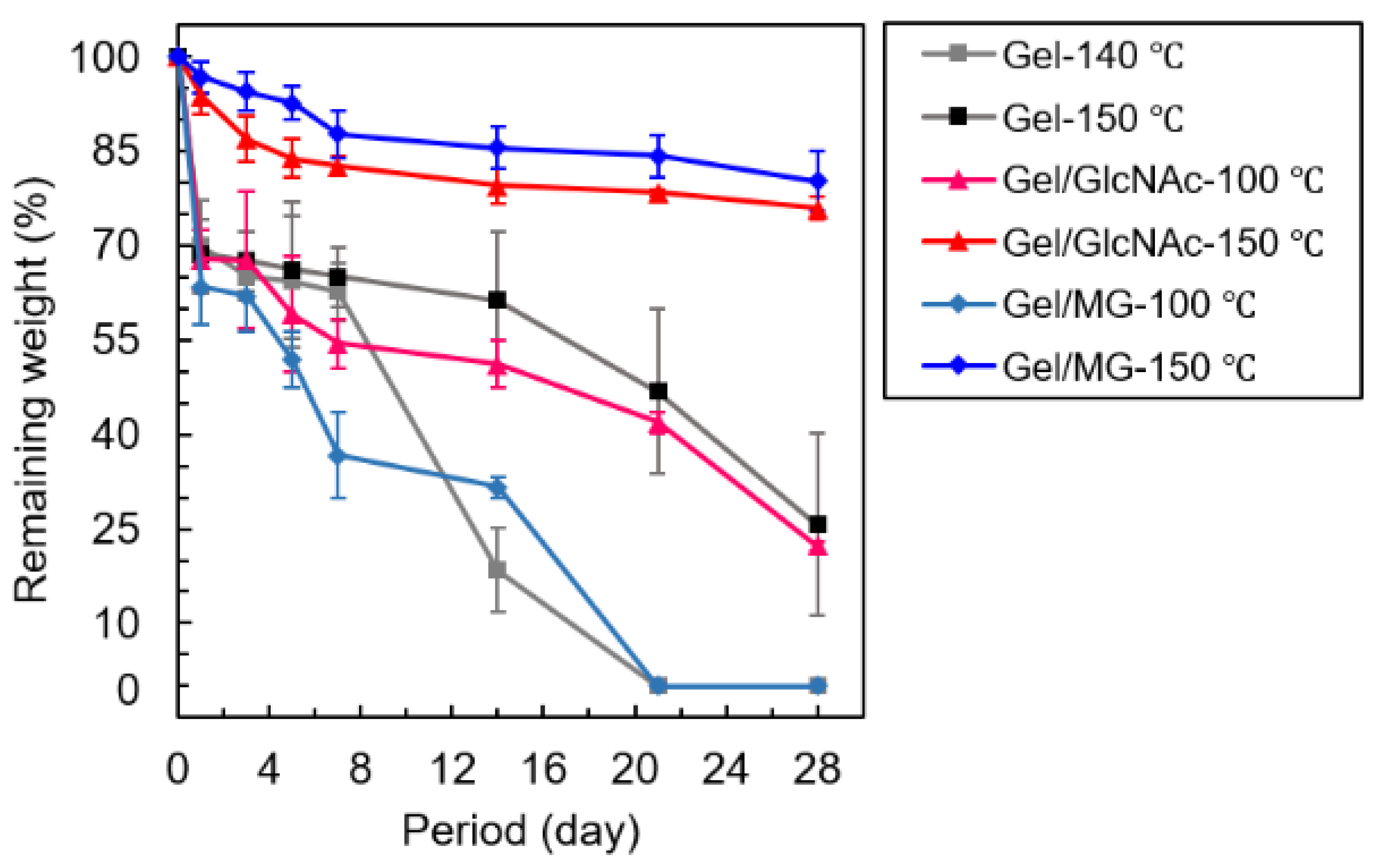
3.5. PBS Solution Resistance
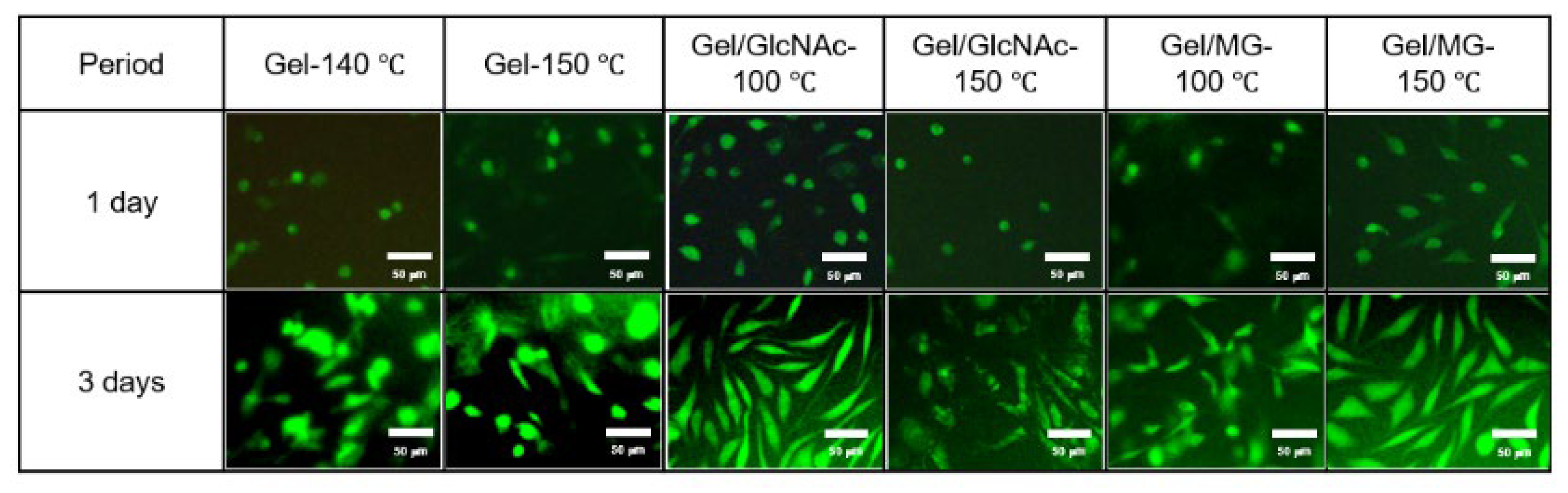
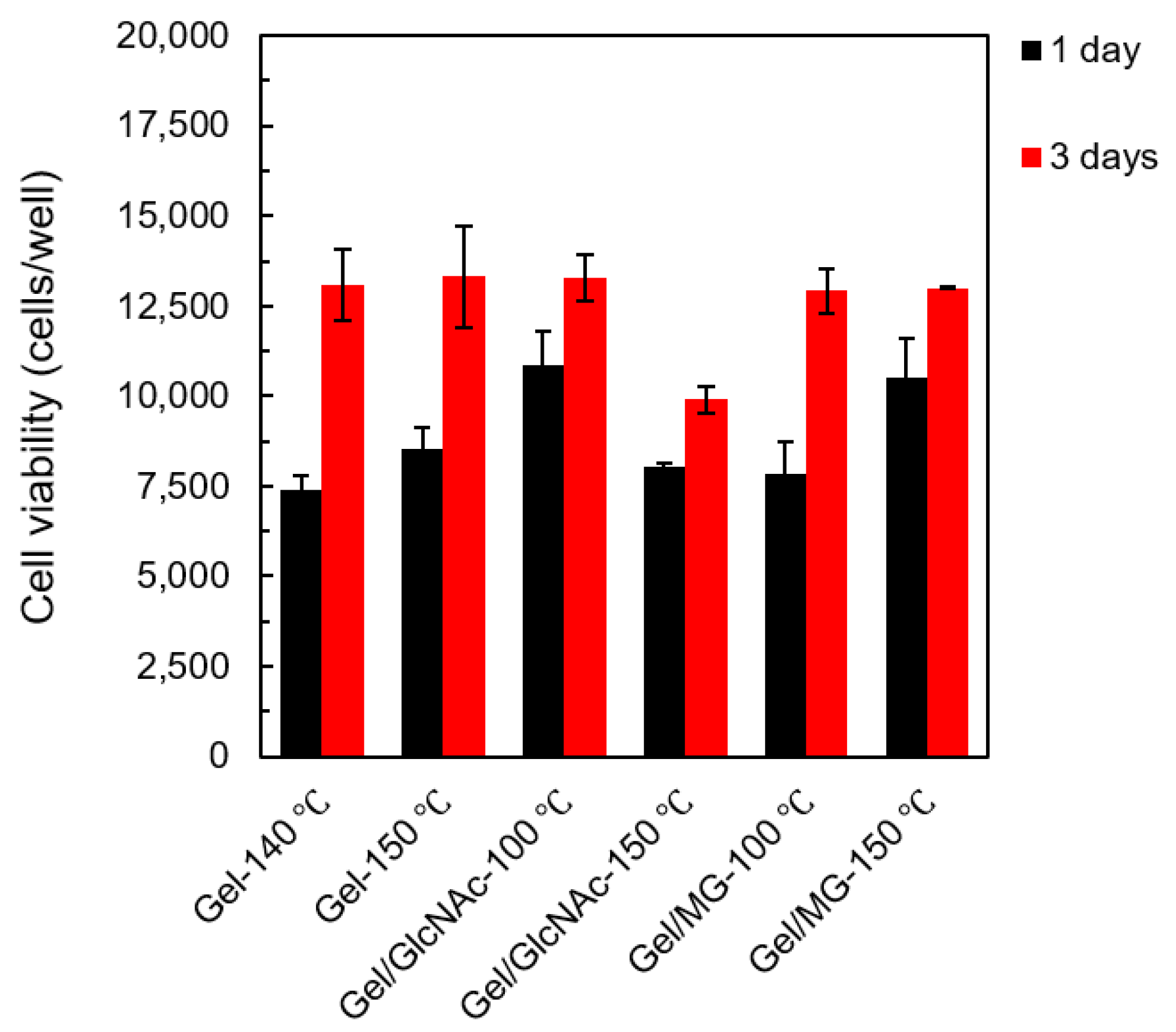
3.6. Cell Culture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kchaou, H.; Benbettaieb, N.; Jridi, M.; Nasri, M.; Debeaufort, F. Influence of Maillard reaction and temperature on functional, structure and bioactive properties of fish gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kchaou, H.; Benbettaïeb, N.; Jridi, M.; Abdelhedi, O.; Karbowiak, T.; Brachais, C.; Leonard, M.; Debeaufort, F.; Nasri, M. Enhancement of structural, functional and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin films using Maillard reactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.M.; Ko, L.Y.; Huang, T.J. Effect of pore size on ECM secretion and cell growth in gelatin scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalumon, K.T.; Deepthi, S.; Anupama, M.S.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R.; Chennazhi, K.P. Fabrication of poly (L-lactic acid)/gelatin composite tubular scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nano/micro scale poly(L-lactic acid) aligned fibers and their potential in neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darshan, T.G.; Chen, C.; Kuo, C.; Shalumon, K.T.; Chien, Y.; Kao, H.; Chen, J. Development of high resilience spiral wound suture-embedded gelatin/PCL/heparin nanofiber membrane scaffolds for tendon tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Onyeri, S.; Siewe, M.; Moshfeghian, A.; Madihally, S.V. In vitro characterization of chitosan–gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7616–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, H.; Kashiki, T.; Nwe, N.; Jayakumar, R.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Preparation of biodegradable chitin/gelatin membranes with GlcNAc for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, L.J.D.; Wever, O.D.; Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Vanderleyden, E.; Dubruel, P.; Vos, F.D.; Vervaet, C.; Remona, J.P.; Geest, B.G.D. Engineered 3D microporous gelatin scaffolds to study cell migration. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3512–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Chong, M.S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, Y.M. Study of gelatin-containing artificial skin V: Fabrication of gelatin scaffolds using a salt-leaching method. Biomaterials 2006, 26, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.; Hung, S.; Lai, J.; Wang, D.; Hsieh, H. Electrospun chitosan–gelatin–polyvinyl alcohol hybrid nanofibrous mats: Production and characterization. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, M.; Williams, G.R.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, L. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers loaded with vitamins A and E as antibacterial wound dressing materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.G.; Mousa, H.M.; Blaudez, F.; Abd El-sadek, M.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Abdel-Jaber, G.T.; Abdal-hay, A.; Ivanovski, S. Dual nanofiber scaffolds composed of polyurethane- gelatin/nylon 6- gelatin for bone tissue engineering. Colloids. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 597, 124817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuno, K.; Wang, J.; Suzuki, K.; Nakahata, M.; Sakai, S. Gelatin-based electrospun fibers insolubilized by horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed cross-linking for biomedical applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 21254–21259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.Y.; Chang, N.Y.; Li, C.; Chan, V.; Hsieh, J.H.; Tsai, Y.; Lin, T. Fabrication of gelatin nanofibers by electrospinning—Mixture of gelatin and polyvinyl alcohol. Polymers 2022, 14, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y. Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, V.Y.; Tul’chinskii, V.M. A study of gelatin by IR spectroscopy. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1982, 18, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Study on wettability, mechanical property and biocompatibility of electrospun gelatin/zein nanofibers cross-linked by glucose. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.K.; Park, J.; Yun, H.; Jeon, K.; Kang, D. Effect of crosslinkable sugar molecules on the physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ames, J.M.; Smith, R.D.; Baynes, J.W.; Metz, T.O. A perspective on the Maillard reaction and the analysis of protein glycation by mass spectrometry: Probing the pathogenesis of chronic disease. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Maté, J.I.; Prabakar, S.; Brimble, M.; Naffa, R. Analysis of advanced glycation end products in ribose-, glucose- and lactose-crosslinked gelatin to correlate the physical changes induced by Maillard reaction in films. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siimon, K.; Siimon, H.; Järvekülg, M. Mechanical characterization of electrospun gelatin scaffolds cross-linked by glucose. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuike, T.; Chaochai, T.; Okubo, T.; Mori, T.; Tamura, H. Fabrication of nonwoven fabrics consisting of gelatin nanofiberscross-linked by glutaraldehyde or N-acetyl-d-glucosamine by aqueous method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowotny, K.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Grune, T. Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, D.; Boulestin, H.; Campbell, F.M.; Williams, L.M. The role of dietary advanced glycation end products in metabolic dysfunction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 1900934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of gelatin nanofiber prepared from gelatin–formic acid solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.S.; Yoon, K.; Ki, C.S.; Kim, H.J.; Bae, D.G.; Lee, K.H.; Park, Y.H.; Um, I.C. Effect of degumming condition on the solution properties and electrospinnablity of regenerated silk solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siimon, K.; Reemann, P.; Põder, A.; Pook, M.; Kangur, T.; Kingo, K.; Jaks, V.; Mäeorg, U.; Järvekülg, M. Effect of glucose content on thermally cross-linked fibrous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Chu, H.; Kuo, T.; Hwang, M.; Wang, C. Preparation and surface activities of modified gelatin–glucose conjugates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 408, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, M. Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, S. Development of fish gelatin-chitooligosaccharide conjugates through the Maillard reaction for the encapsulation of curcumin. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şen, Ö.; Culha, M. Boron nitride nanotubes included thermally cross-linked gelatin–glucose scaffolds show improved properties. Colloids. Surf. B 2016, 138, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Saquing, C.D.; Harding, J.R.; Khan, S.A. In situ cross-linking of electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

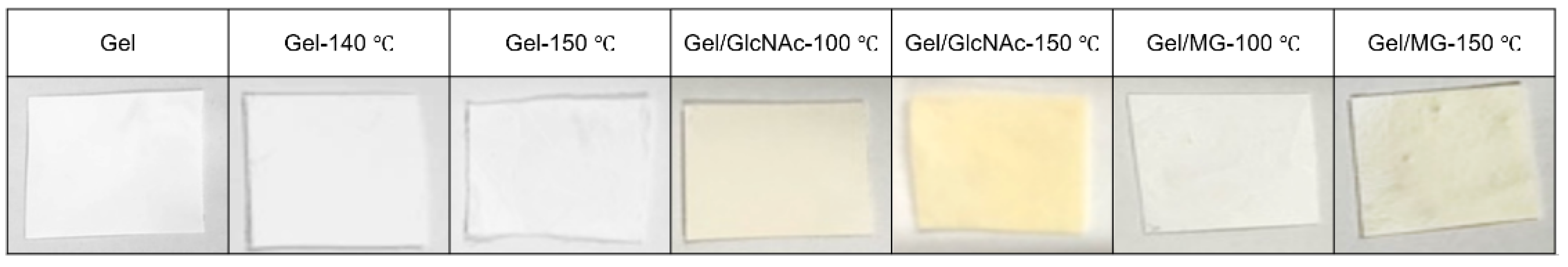

| Sample Name | Dope Solution | Heat Treatment Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Gel | Gel | – |
| Gel-140 °C | Gel | 140 °C for 1 d |
| Gel-150 °C | Gel | 150 °C for 1 d |
| Gel/GlcNAc | Gel/GlcNAc | – |
| Gel/GlcNAc-100 °C | Gel/GlcNAc | 100 °C for 2 d |
| Gel/GlcNAc-150 °C | Gel/GlcNAc | 150 °C for 2 d |
| Gel/MG | Gel/MG | – |
| Gel/MG-100 °C | Gel/MG | 100 °C for 1 d |
| Gel/MG-150 °C | Gel/MG | 150 °C for 1 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dechojarassri, D.; Kaneshige, R.; Tamura, H.; Furuike, T. Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions. Materials 2023, 16, 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114078
Dechojarassri D, Kaneshige R, Tamura H, Furuike T. Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions. Materials. 2023; 16(11):4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114078
Chicago/Turabian StyleDechojarassri, Duangkamol, Ryota Kaneshige, Hiroshi Tamura, and Tetsuya Furuike. 2023. "Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions" Materials 16, no. 11: 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114078
APA StyleDechojarassri, D., Kaneshige, R., Tamura, H., & Furuike, T. (2023). Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions. Materials, 16(11), 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114078






