Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Limestone-Derived Porous Rod Hierarchical Ca-based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Rod Ca–Metal–Organic Framework
2.2. Characterization
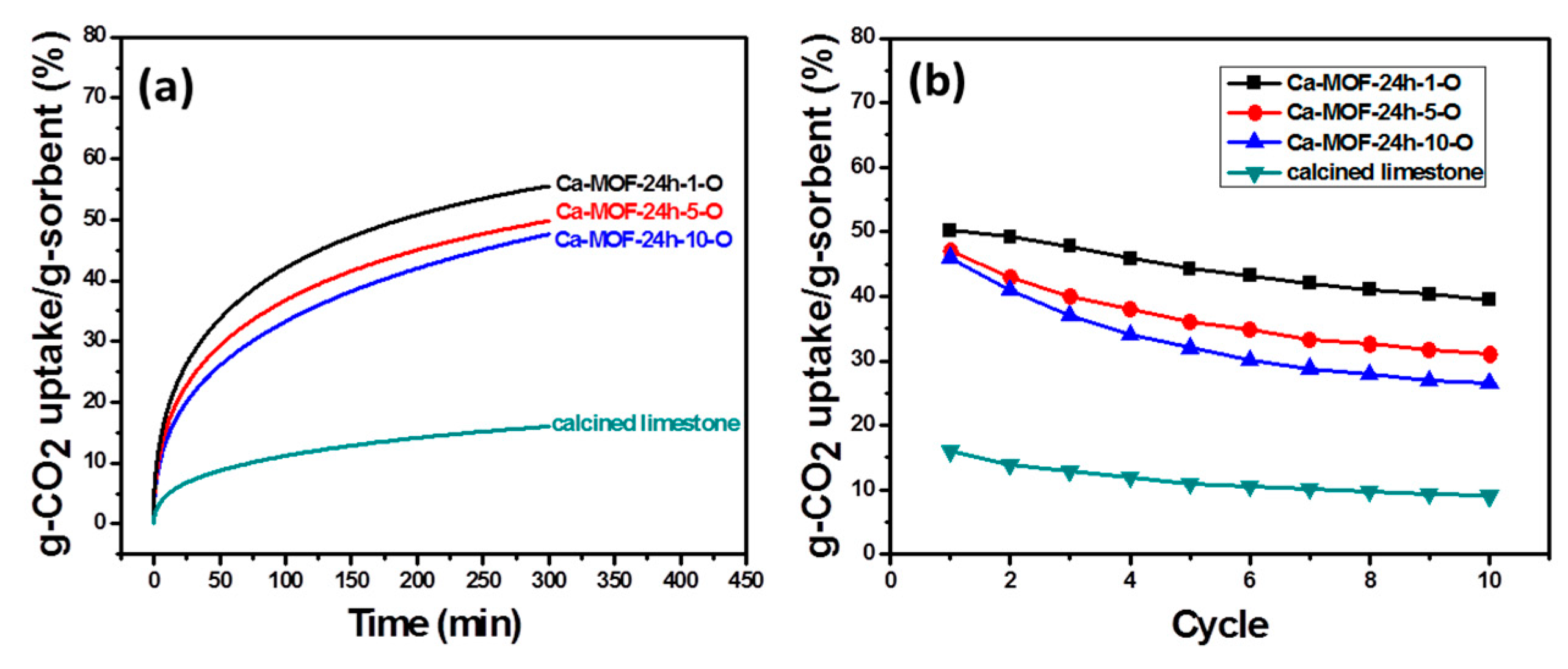
2.3. CO2 Adsorption Analysis
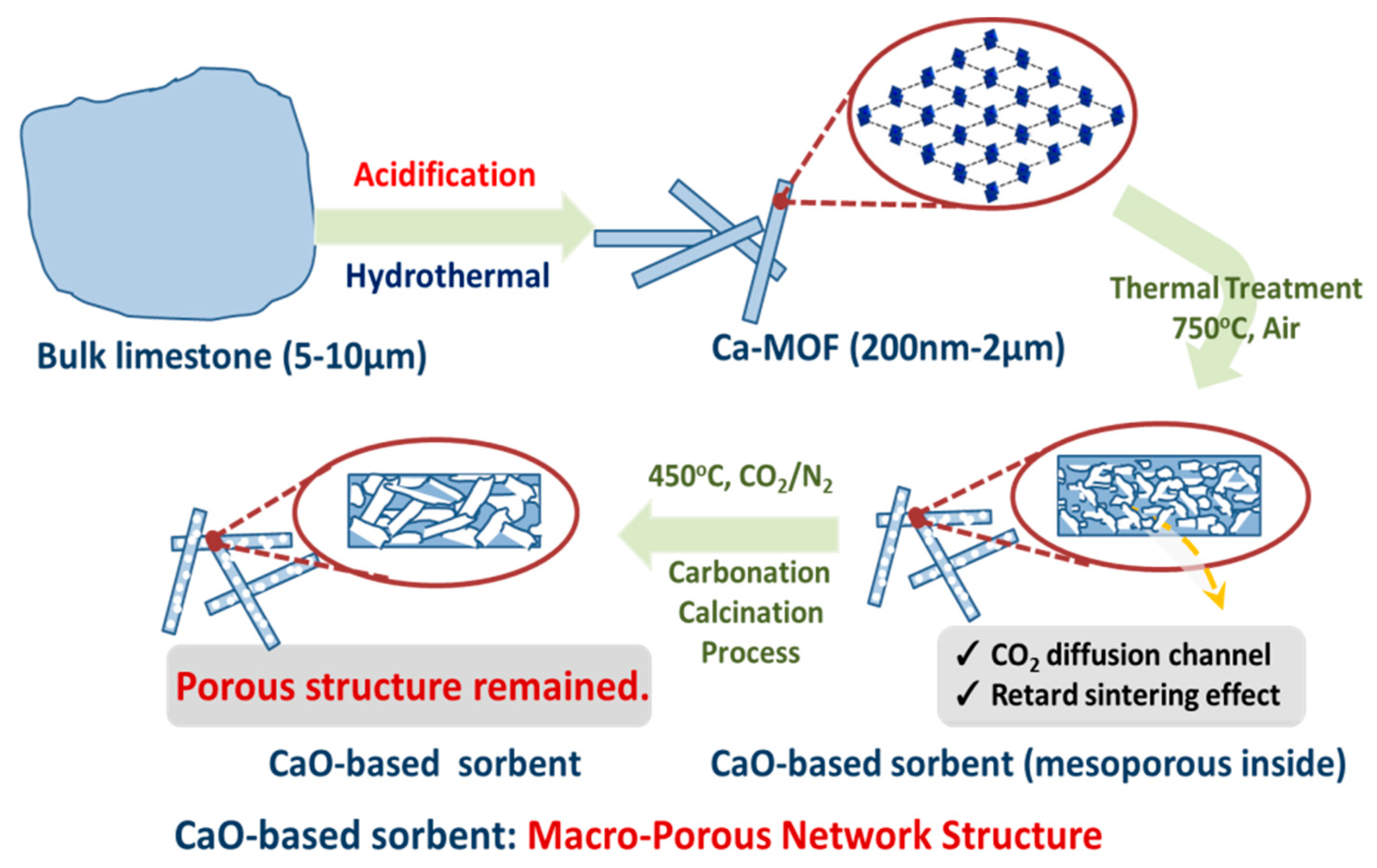
3. Results and Discussion
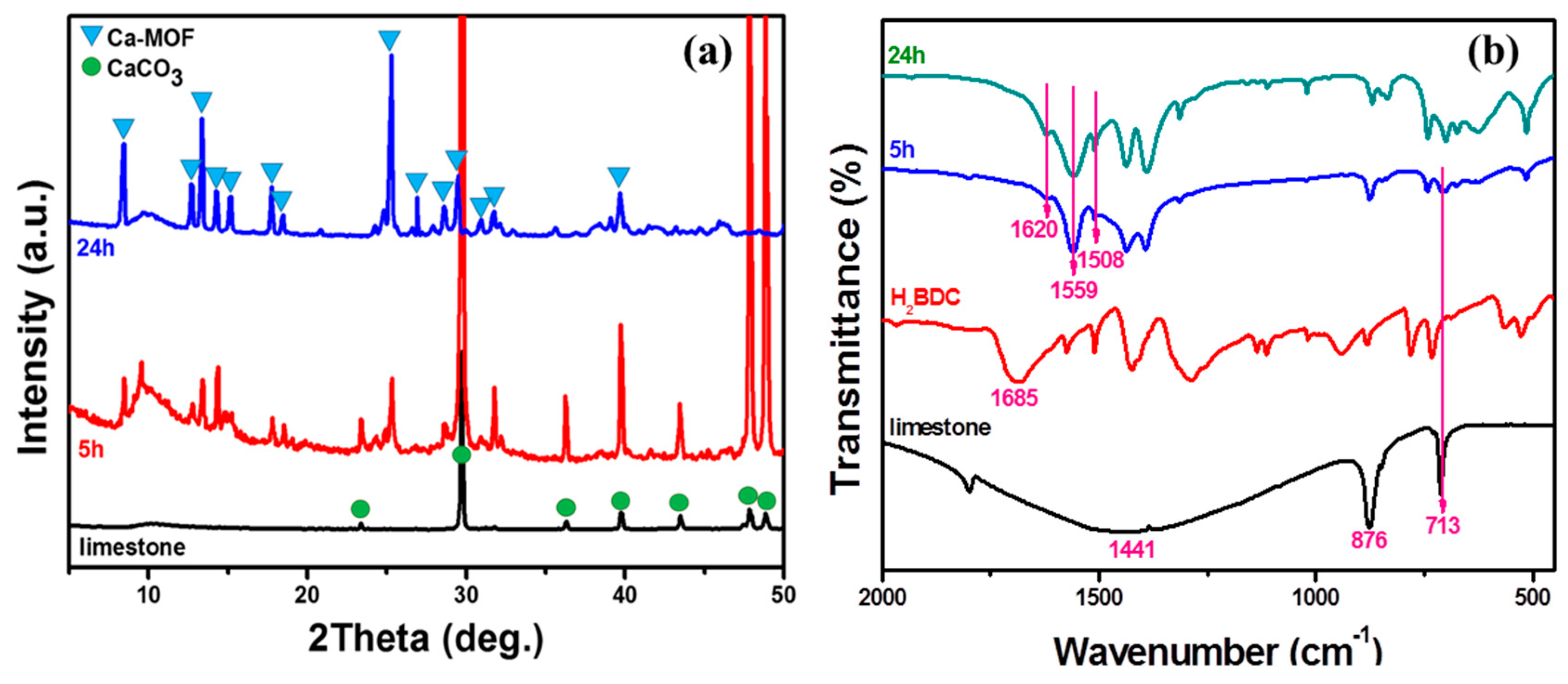
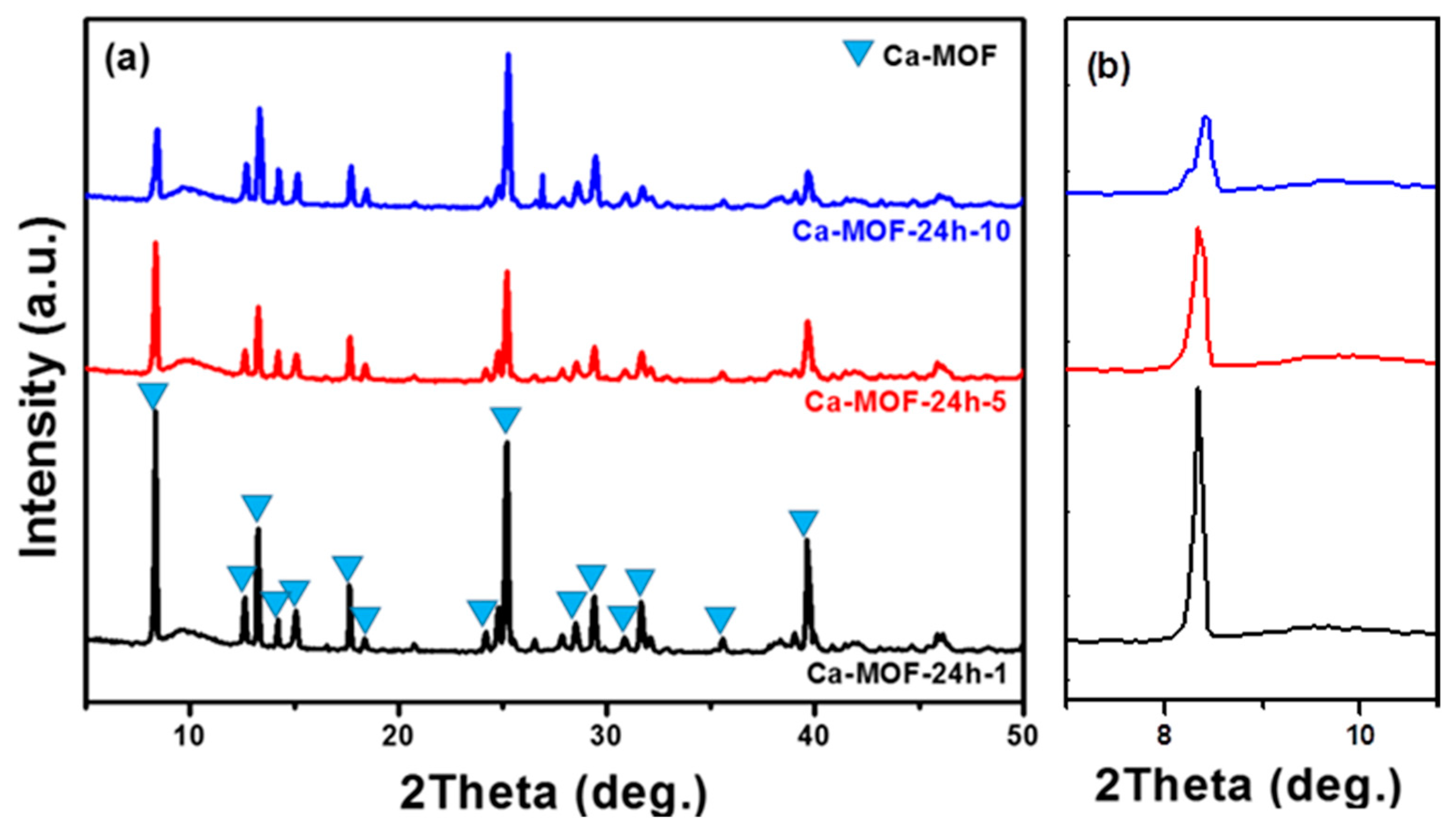
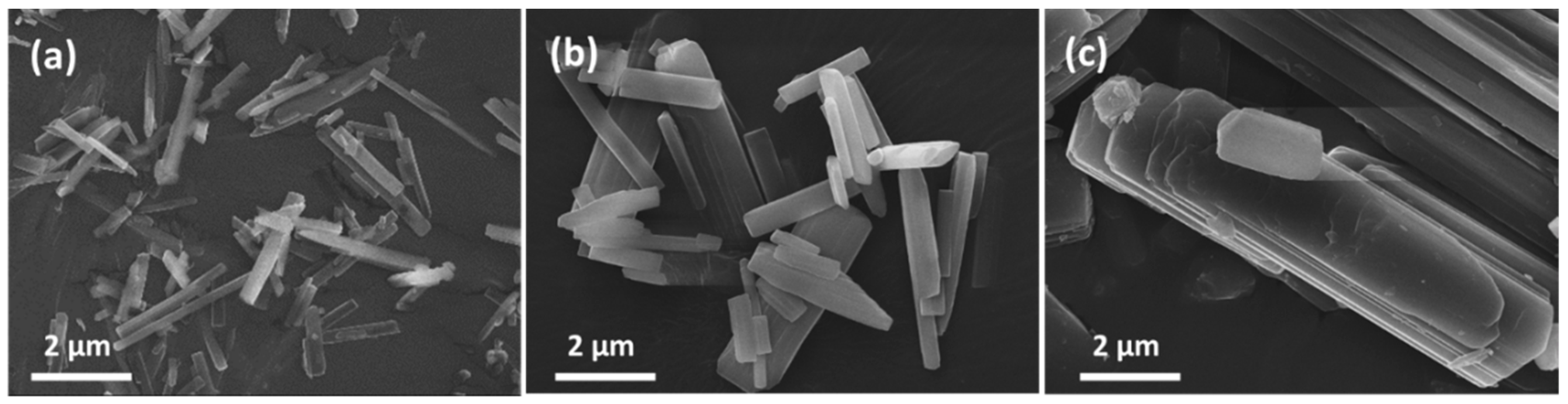
3.1. Characterizations and Properties of Limestone and Ca-MOF
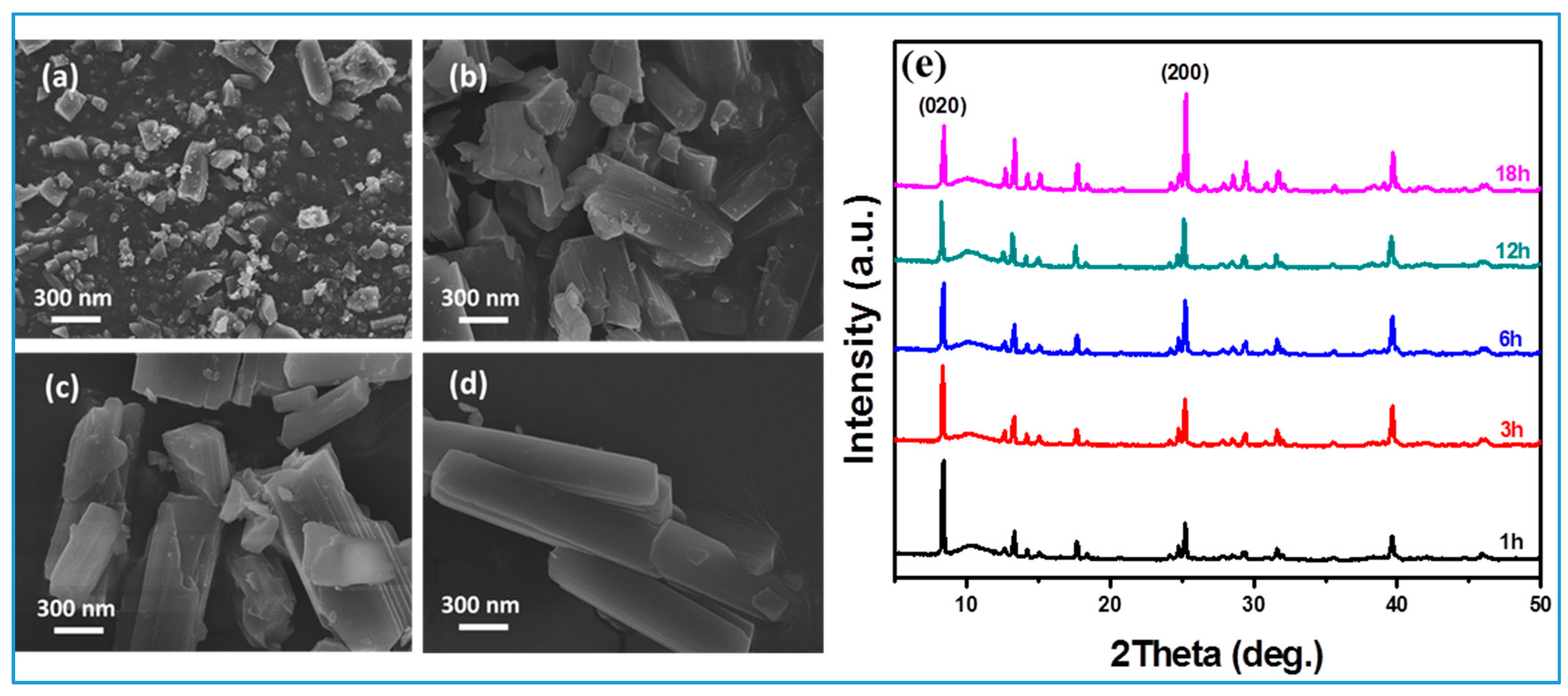
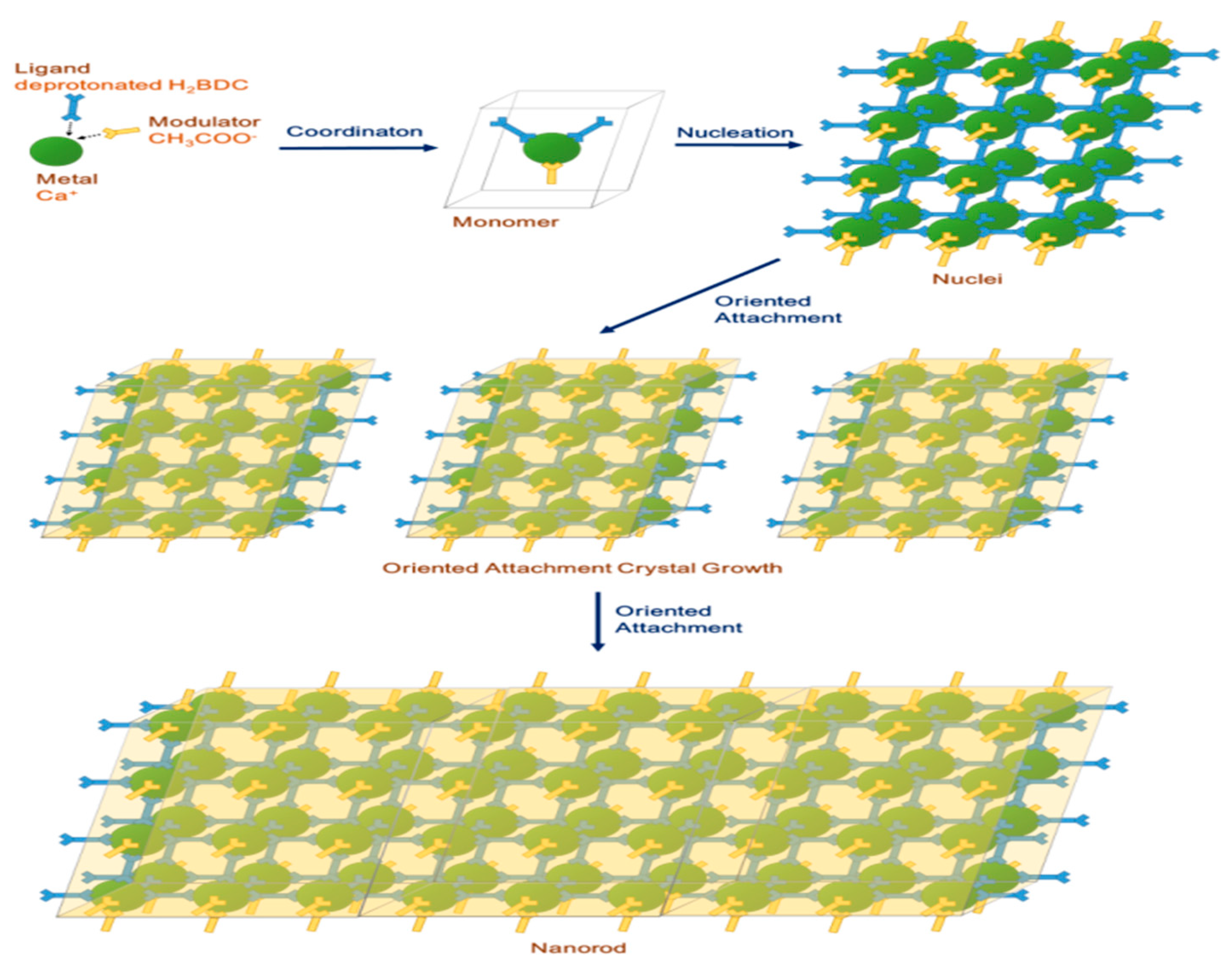
3.2. Formation Mechanism and Crystal Growth of Rod Ca-MOF
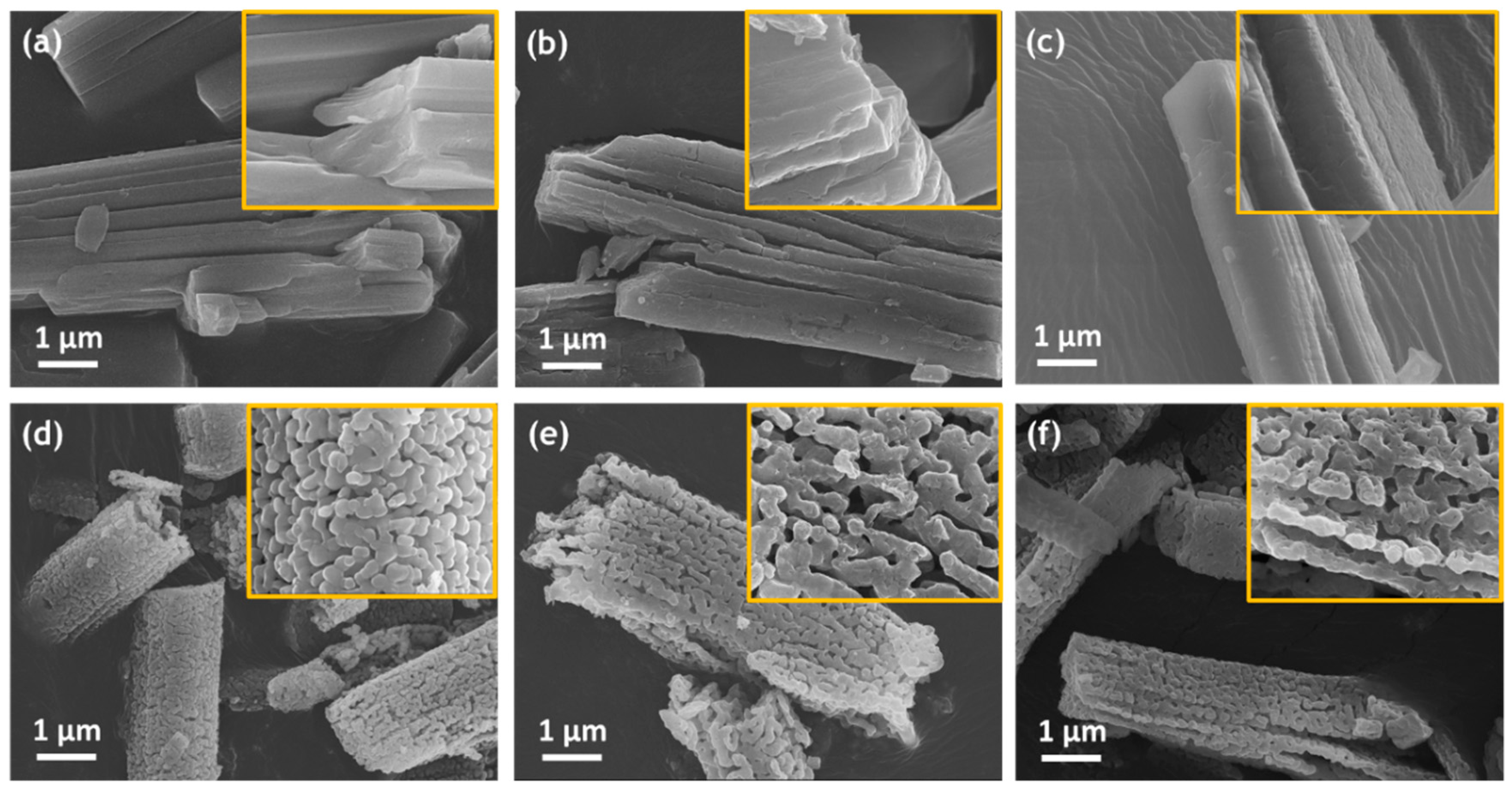
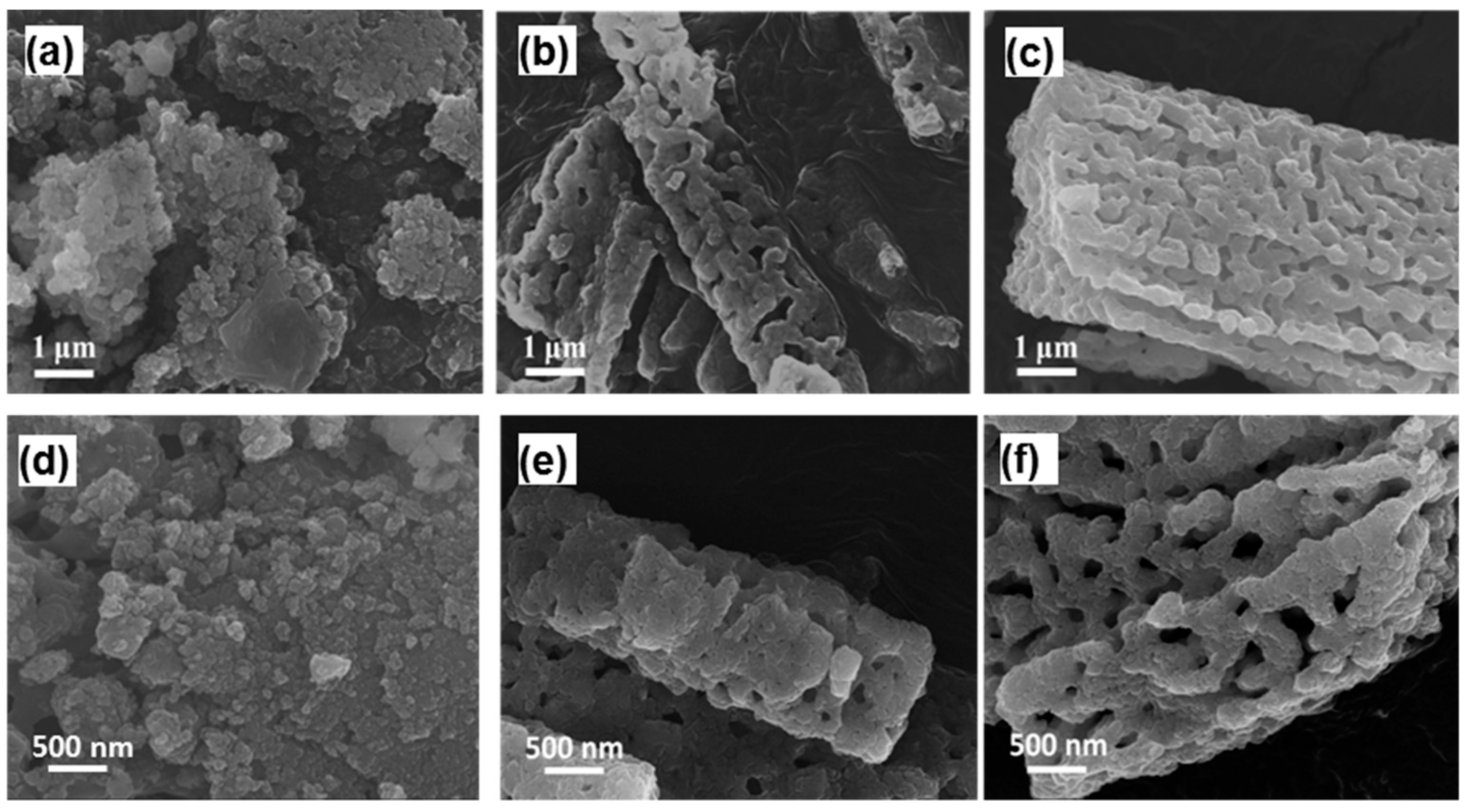
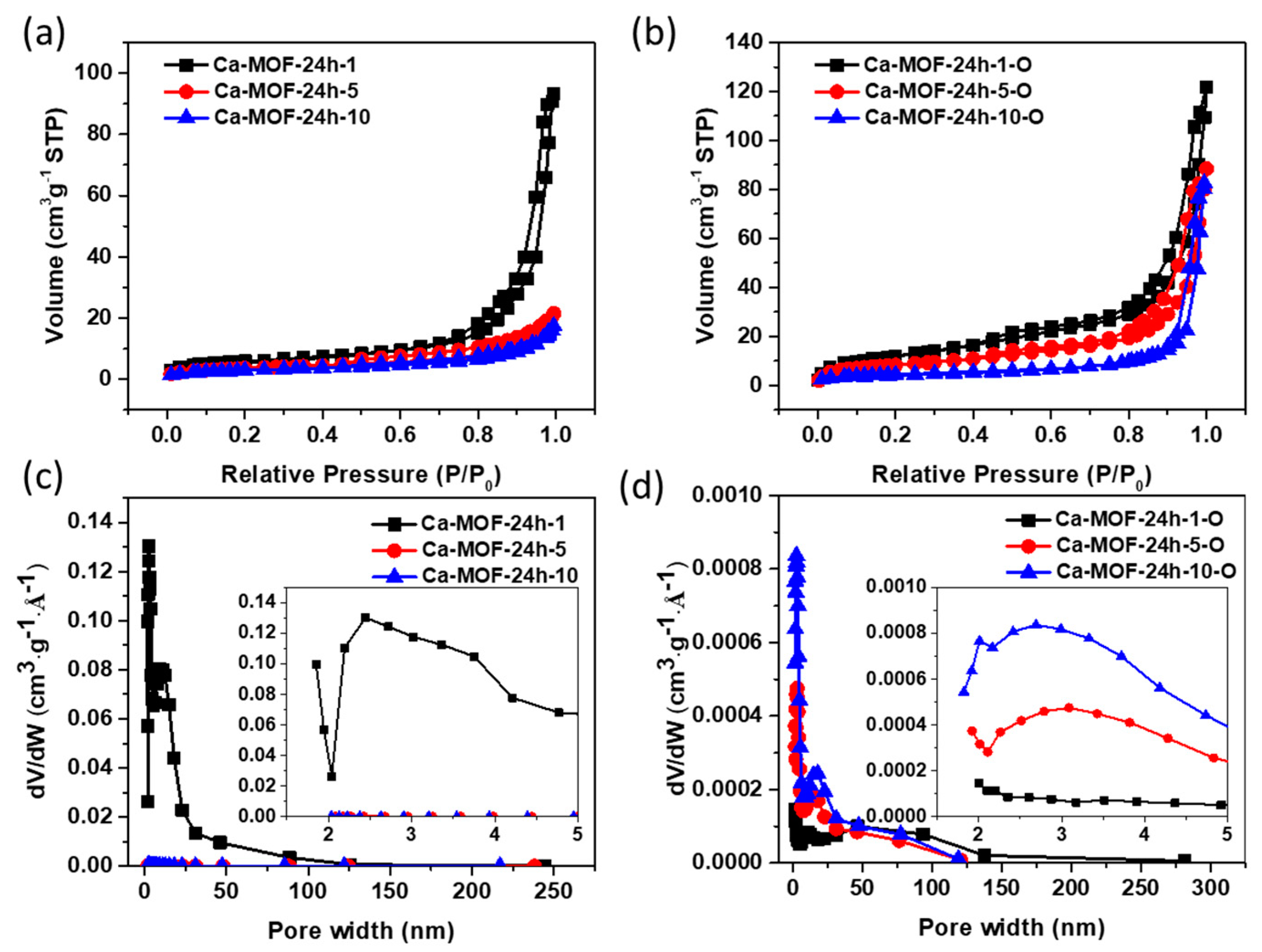
3.3. Characterizations of Rod Ca-MOF Structures Synthesized with Different Acetic Acid Concentrations
3.4. Pore Formation of Rod Ca-MOF Network
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kierzkowska, A.M.; Pacciani, R.; Müller, C.R. CaO-Based CO2 Sorbents: From Fundamentals to the Development of New, Highly Effective Materials. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Feng, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.G.; Barry, J.; Da Costa, J.C.D. Synthesis of Sintering-Resistant Sorbents for CO2 Capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chang, K.-P.; Yu, C.-T.; Chiang, P.-C.; Wang, C.-F. Development of high-temperature CO2 sorbents made of CaO-based mesoporous silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, N.; Wu, Q.; Bian, G.; Zheng, C. Development and Performance of CaO/La2O3 Sorbents during Calcium Looping Cycles for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11778–11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. Enhancement of attrition resistance and cyclic CO2 capture of calcium-based sorbent pellets. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 116, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, F.N.; Manović, V.; Wu, Y.; Macchi, A.; Anthony, E. Pelletized CaO-based sorbents treated with organic acids for enhanced CO2 capture in Ca-looping cycles. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 17, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, D.; Mahinpey, N. Highly Active CaO-Based Sorbents for CO2 Capture Using the Precipitation Method: Preparation and Characterization of the Sorbent Powder. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 4567–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Marín, M.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Nieto-Sánchez, A.; Garcia, S.; Pevida, C.; Suero, S.R. Influence of morphology, porosity and crystal structure of CaCO3 precursors on the CO2 capture performance of CaO-derived sorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Alfonsín, C.; Chambel, A.; Fernandes, A.; Dias, A.P.S.; Pinheiro, C.I.; Ribeiro, M.F. Investigation of a stable synthetic sol–gel CaO sorbent for CO2 capture. Fuel 2012, 94, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jeboori, M.J.; Nguyen, M.; Dean, C.; Fennell, P. Improvement of Limestone-Based CO2 Sorbents for Ca Looping by HBr and Other Mineral Acids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, F.N.; Manović, V.; Wu, Y.; Macchi, A.; Anthony, E. Post-combustion CO2 capture by formic acid-modified CaO-based sorbents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 16, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Porous Spherical CaO-based Sorbents via PSS-Assisted Fast Precipitation for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18072–18077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.Q.; Li, W.; Liu, B.-C.; Li, R.-X. Synthesis, characterization, and high temperature CO2 capture of new CaO based hollow sphere sorbents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyjoo, Y.; Merigot, K.; Lamonier, J.-F.; Pareek, V.K.; Tade, M.; Liu, J. Synthesis of CaCO3@C yolk–shell particles for CO2 adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24872–24876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Wu, U.-T.; Lin, H.-P. Cyclic performance of CaCO3@mSiO2 for CO2 capture in a calcium looping cycle. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8252–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Pontiga, F.; Soria-Hoyo, C.; Quintanilla, M.; Moreno, H.; Duran, F.J.; Espin, M. Improving the gas–solids contact efficiency in a fluidized bed of CO2 adsorbent fine particles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiga, F.; Valverde, J.M.; Moreno, H.; Duran-Olivencia, F. Dry gas–solid carbonation in fluidized beds of Ca(OH)2 and nanosilica/Ca(OH)2 at ambient temperature and low CO2 pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Anthony, E. On the Decay Behavior of the CO2 Absorption Capacity of CaO-Based Sorbents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, F.N.; Manović, V.; Macchi, A.; Anthony, M.A.; Anthony, E. Assessment of limestone treatment with organic acids for CO2 capture in Ca-looping cycles. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 116, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Calcium-looping for thermochemical energy storage in concentrating solar power applications: Evaluation of the effect of acoustic perturbation on the fluidized bed carbonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. CO2 Capture by Temperature Swing Adsorption: Working Capacity as Affected by Temperature and CO2 Partial Pressure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 3593–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-R.; Kuppler, R.J.; Zhou, H.-C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.K.; Tallapragada, R.M.; Branton, A.; Nayak, G.; Latiyal, O.; Mishra, R.K.; Jana, S. Physicochemical Characterization of Biofield Energy Treated Calcium Carbonate Powder. Am. J. Health Res. 2015, 3, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, T.-Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Fu, H.; Wang, E. Metal–organic frameworks constructed from three kinds of new Fe-containing secondary building units. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 384, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-S.; Talapin, D.V.; Gaschler, W.; Murray, C.B. Designing PbSe Nanowires and Nanorings through Oriented Attachment of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7140–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederberger, M.; Cölfen, H. Oriented attachment and mesocrystals: Non-classical crystallization mechanisms based on nanoparticle assembly. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3271–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruoka, T.; Furukawa, S.; Takashima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Isoda, S.; Kitagawa, S. Nanoporous Nanorods Fabricated by Coordination Modulation and Oriented Attachment Growth. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4739–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mou, C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Deng, Q.; Li, J. Structure-Property of Metal Organic Frameworks Calcium Terephthalates Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 173, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Ca-MOF-24h-1 | Ca-MOF-24h-5 | Ca-MOF-24h-10 | Ca-MOF-24h-1-O | Ca-MOF-24h-5-O | Ca-MOF-24h-10-O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2g−1) | 21 | 13 | 11 | 48 | 30 | 15 |
| Smicro/SBET (%) | 14 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 14 |
| Smeso/macro/SBET (%) | 86 | 97 | 95 | 93 | 95 | 86 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, P.-H.; Hsu, H.-P.; Wu, S.-C.; Peng, C.-H. Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Limestone-Derived Porous Rod Hierarchical Ca-based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Capture. Materials 2020, 13, 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194297
Chang P-H, Hsu H-P, Wu S-C, Peng C-H. Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Limestone-Derived Porous Rod Hierarchical Ca-based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Capture. Materials. 2020; 13(19):4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194297
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Po-Hsueh, Hua-Pei Hsu, Szu-Chen Wu, and Cheng-Hsiung Peng. 2020. "Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Limestone-Derived Porous Rod Hierarchical Ca-based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Capture" Materials 13, no. 19: 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194297
APA StyleChang, P.-H., Hsu, H.-P., Wu, S.-C., & Peng, C.-H. (2020). Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Limestone-Derived Porous Rod Hierarchical Ca-based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Capture. Materials, 13(19), 4297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194297




