Effect of Bias Voltage on Mechanical Properties of HiPIMS/RFMS Cosputtered Zr–Si–N Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
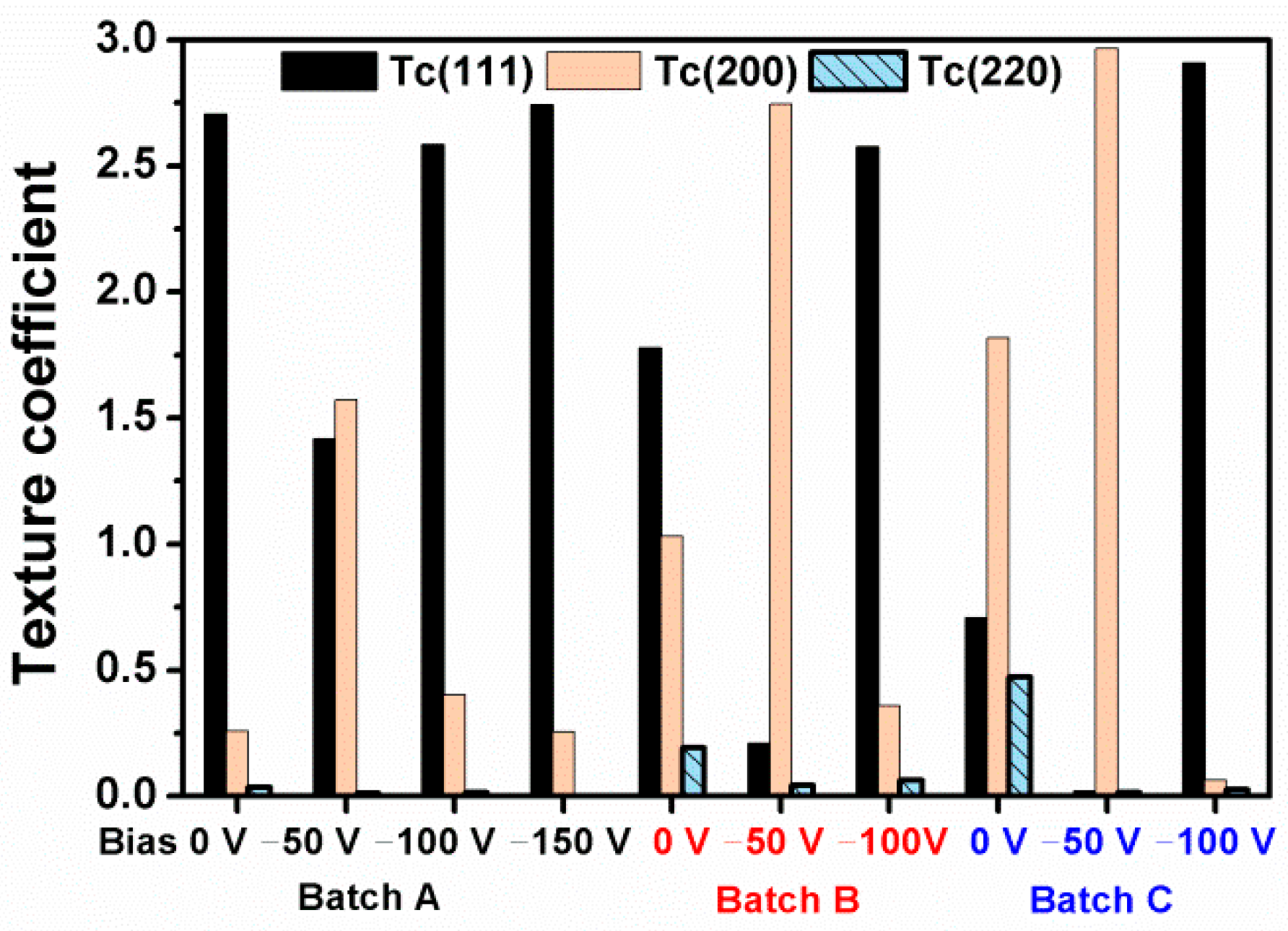
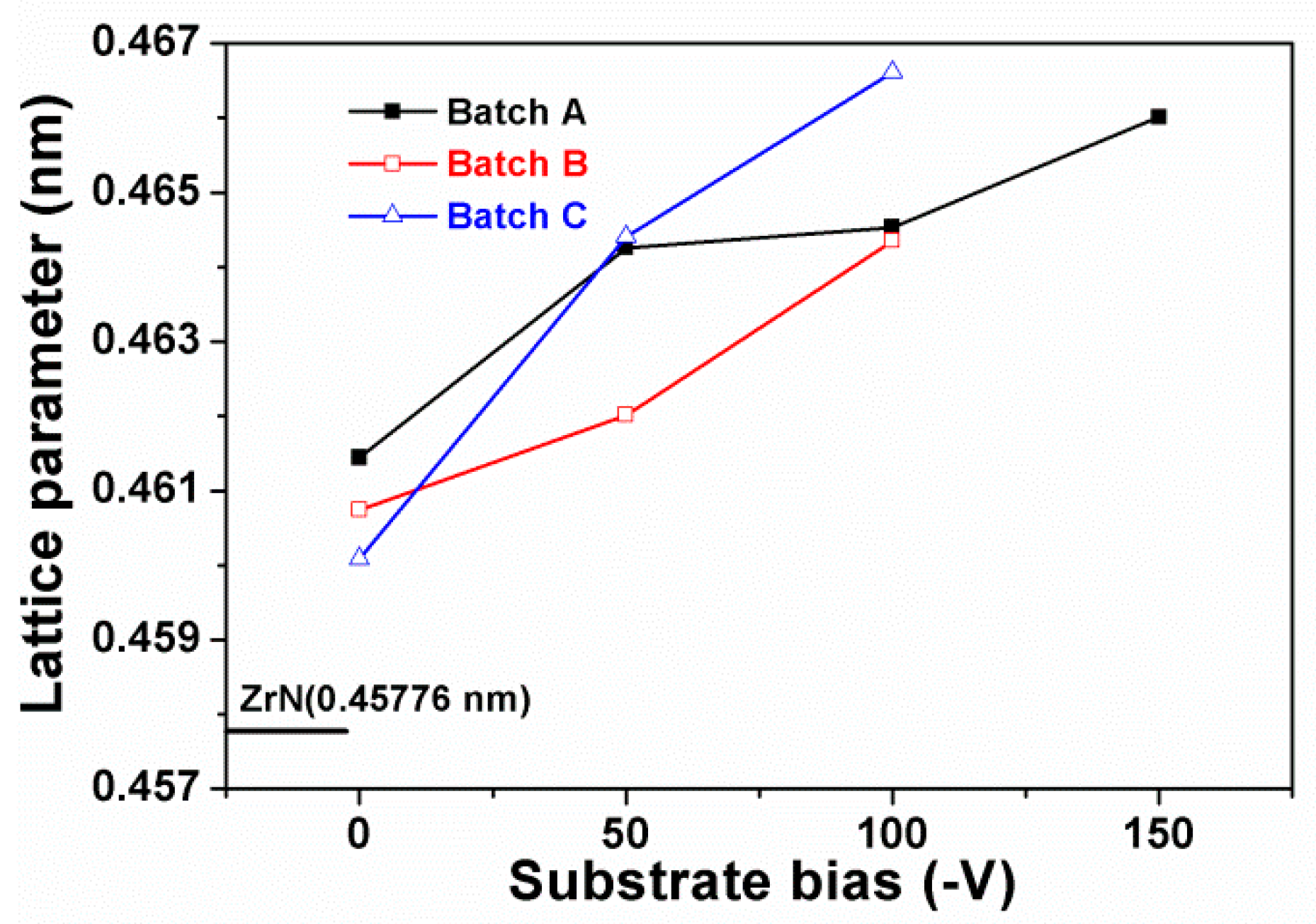
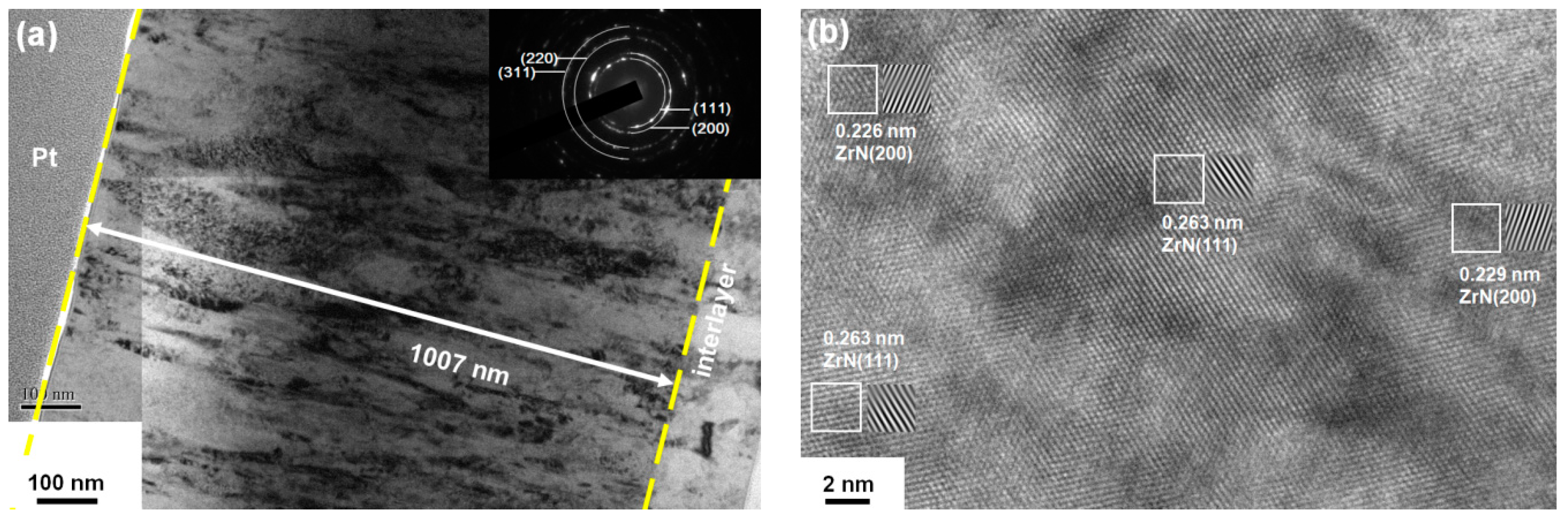
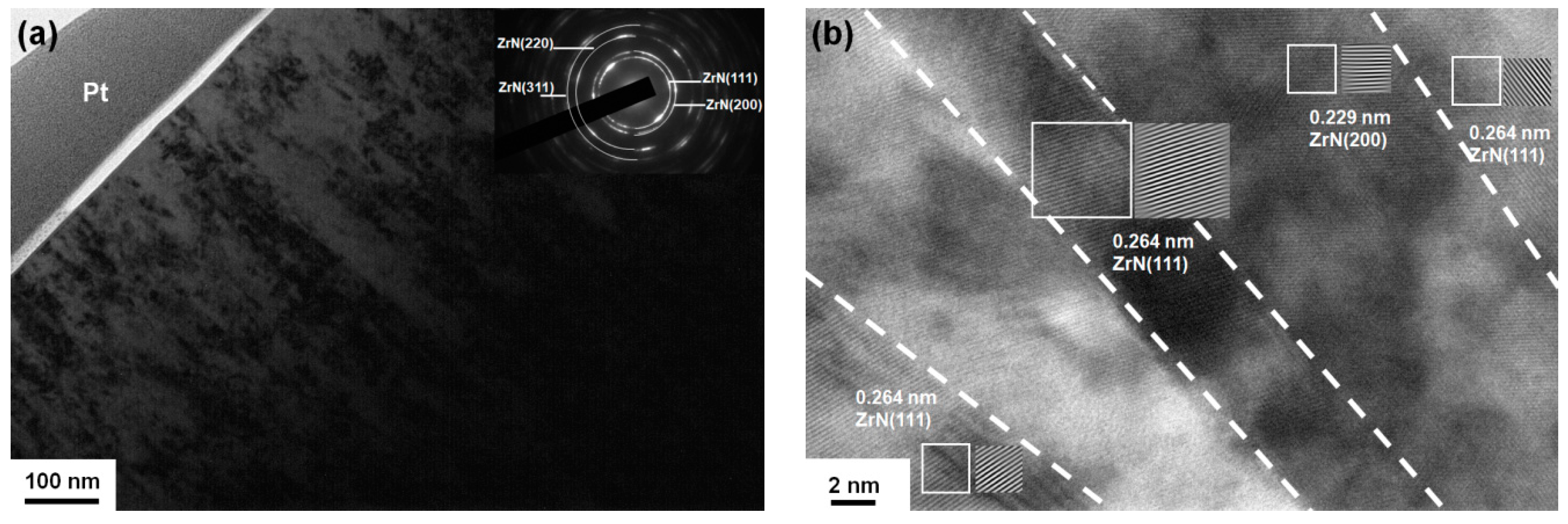
3.1. Chemical Compositions and Phases
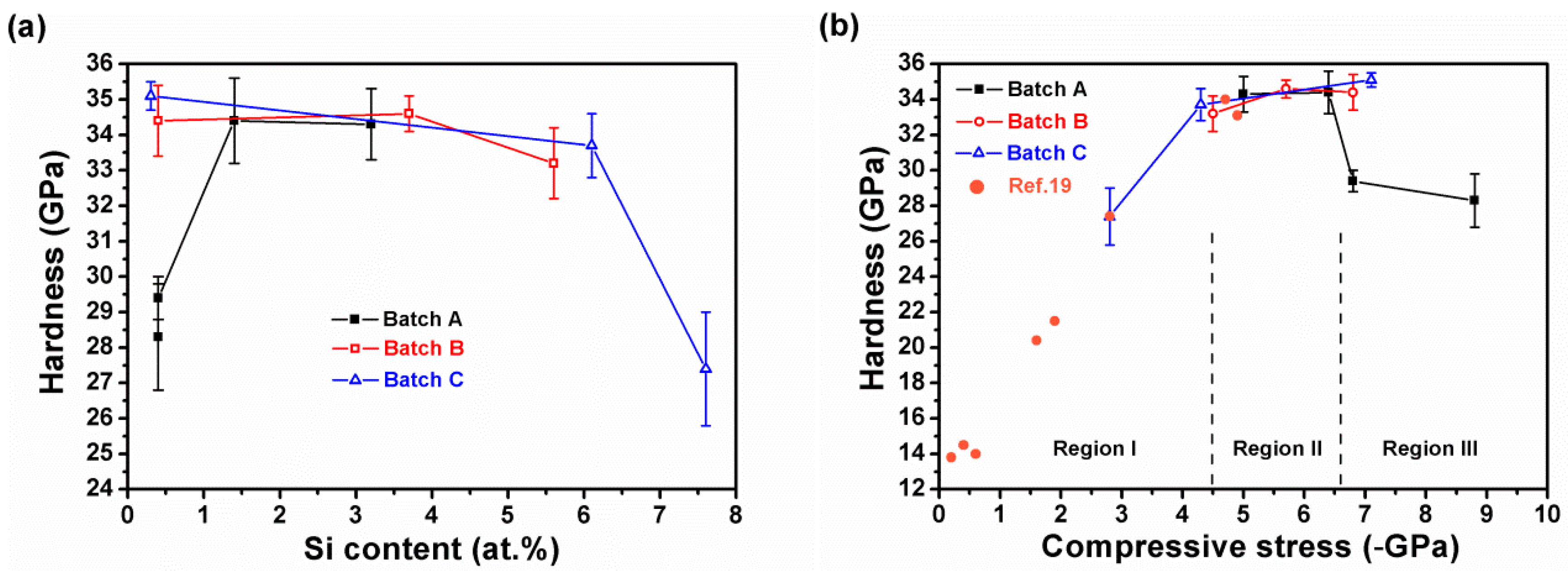
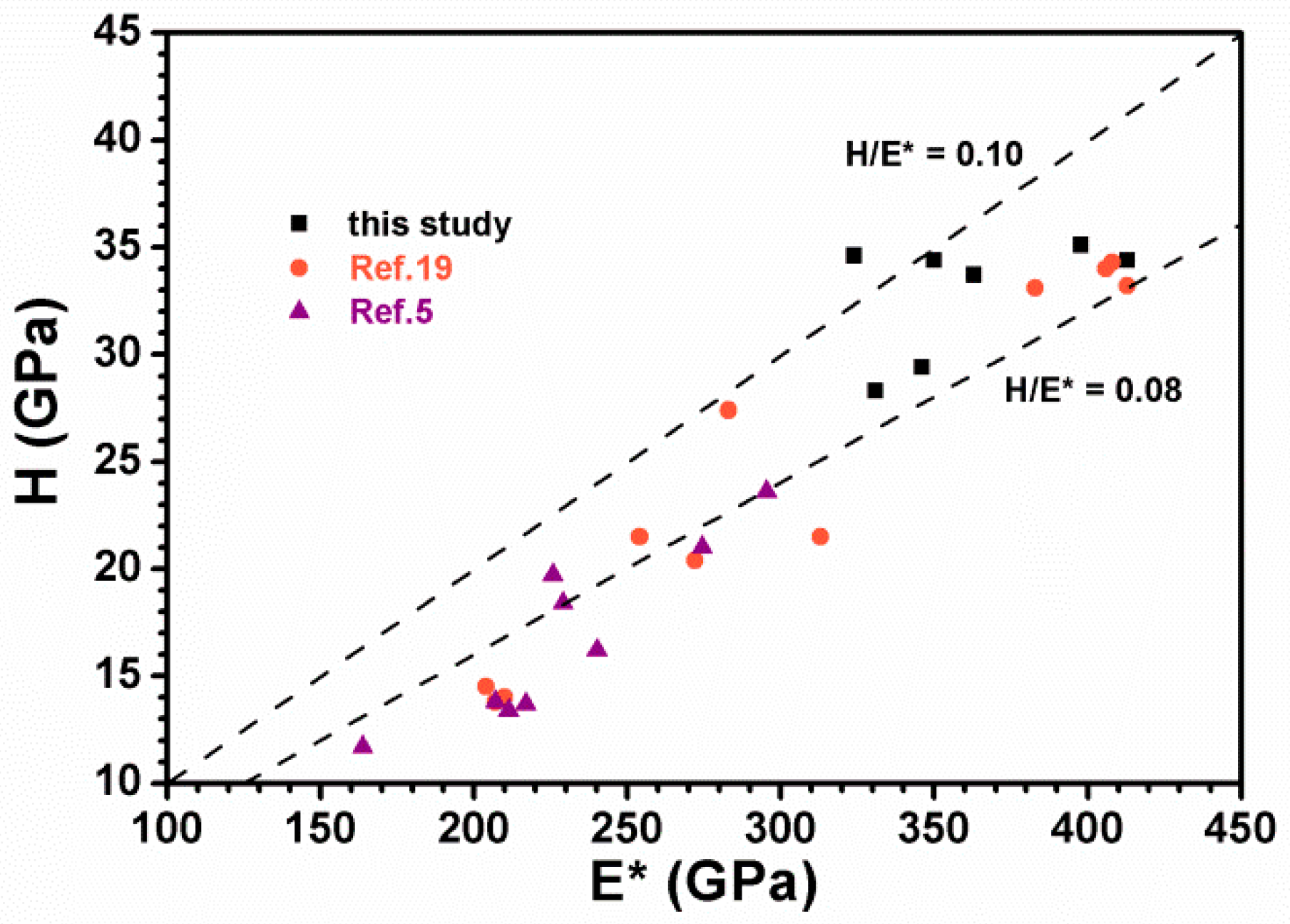
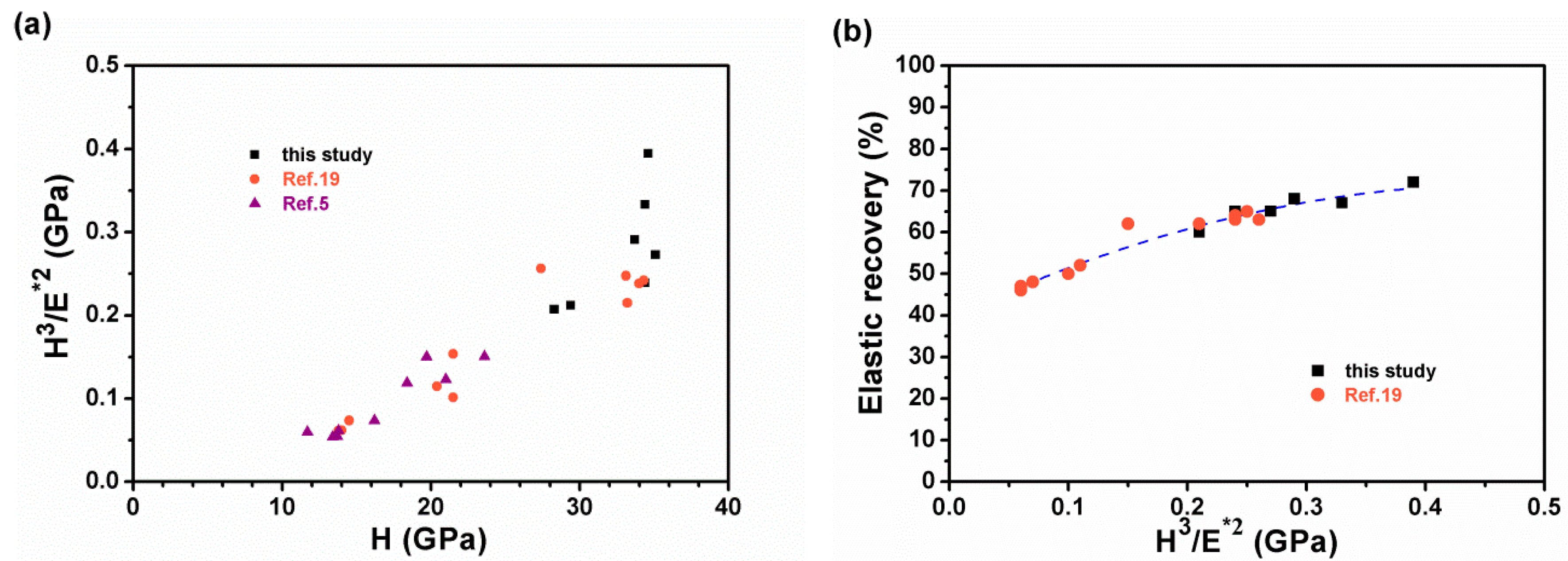
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mae, T.; Nose, M.; Zhou, M.; Nagae, T.; Shimamura, K. The effects of Si addition on the structure and mechanical properties of ZrN thin films deposited by an r.f. reactive sputtering method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.J.; Bendavid, A.; Cairney, J.M.; Hoffman, M. Nanocomposite Ti–Si–N, Zr–Si–N, Ti–Al–Si–N, Ti–Al–V–Si–N thin film coatings deposited by vacuum arc deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Influence of silicon on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Zr–Si–N composite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Jang, J.; Zhang, T.; Kim, J.H.; Park, I.W.; Kim, K.H. Effect of Si addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological properties of Zr–Si–N nanocomposite coatings deposited by a hybrid coating system. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.I.; Chang, S.C.; Chang, L.C. Oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of Zr–Si–N coatings with cyclic gradient concentration. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 320, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.I.; Chang, S.C.; Liu, B.L. Bonding characteristics and chemical inertness of Zr–Si–N coatings with a high Si content in glass molding. Coatings 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veprek, S.; Niederhofer, A.; Moto, K.; Bolom, T.; Männling, H.-D.; Nesladek, P.; Dollinger, G.; Bergmaier, A. Composition, nanostructure and origin of the ultrahardness in nc-TiN/a-Si3N4/a- and nc-TiSi2 nanocomposites with HV = 80 to ≥ 105 GPa. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 133–134, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diserens, M.; Patscheider, J.; Lévy, F. Mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of nanocomposite TiN–SiNx physical-vapor-deposited thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 120–121, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkahoul, M.; Sandu, C.S.; Tabet, N.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M.; Karimi, A.; Lévy, F. Effect of Si incorporation on the properties of niobium nitride films deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188–189, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, C.S.; Benkahoul, M.; Sanjinés, R.; Lévy, F. Model for the evolution of Nb–Si–N thin films as a function of Si content relating the nanostructure to electrical and mechanical properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2897–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, C.S.; Sanjinés, R.; Benkahoul, M.; Medjani, F.; Lévy, F. Formation of composite ternary nitride thin films by magnetron sputtering co-deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, V.; Macák, K.; Schneider, J.M.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. A novel pulsed magnetron sputter technique utilizing very high target power densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1990, 122, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, U.; Lattemann, M.; Bohlmark, J.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Gudmundsson, J.T. Ionized physical vapor deposition (IPVD): A review of technology and applications. Thin Solid Films 2006, 513, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, J.T.; Brenning, N.; Lundin, D.; Helmersson, U. High power impulse magnetron sputtering discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2012, 30, 030801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purandare, Y.P.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Hovsepian, P.E. Structure and properties of ZrN coatings deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering technology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2011, 29, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiasarian, A.P.; Münz, W.-D.; Hultman, L.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. High power pulsed magnetron sputtered CrNx films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Lu, J.; Jensen, J.; Bolz, S.; Kölker, W.; Schiffers, C.; Lemmer, O.; Greene, J.E.; Hultman, L. A review of metal-ion-flux-controlled growth of metastable TiAlN by HIPIMS/DCMS co-sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Chang, C.Y.; You, Y.W. Ta–Zr–N thin films fabricated through HIPIMS/RFMS co-sputtering. Coatings 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.I. Mechanical properties of Zr–Si–N films fabricated through HiPIMS/RFMS co-sputtering. Coatings 2018, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Lou, B.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, J.W. Mechanical property evaluation of ZrSiN films deposited by a hybrid superimposed high power impulse- medium frequency sputtering and RF sputtering system. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundgren, J.-E.; Johansson, B.-O.; Hentzell, H.T.G.; Karlsson, S.-E. Mechanisms of reactive sputtering of titanium nitride and titanium carbide III: Influence of substrate bias on composition and structure. Thin Solid Films 1983, 105, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Hultman, L.; Helmersson, U.; Sundgren, J.-E.; Greene, J.E. Microstructure modification of TiN by ion bombardment during reactive sputter deposition. Thin Solid Films 1989, 169, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Ahn, H.J. Effect of the substrate bias voltage on the crystallographic orientation of reactively sputtered AlN thin films. Thin Solid Films 1994, 251, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Bias effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of magnetron sputtered nanocrystalline titanium carbide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5419–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, F.; Rebouta, L.; Goudeau, P.; Girardeau, T.; Pacaud, J.; Riviére, J.P.; Traverse, A. Structural transitions in hard Si-based TiN coatings: The effect of bias voltage and temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 146–147, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.T.; Yang, B.; Guo, L.P.; Fu, D.J. Effect of bias voltage on the structure and hardness of Ti–Si–N composite coatings synthesized by cathodic arc assisted middle-frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 473, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J.; Kunc, F.; Zeman, H.; Poláková, H. Relationships between hardness, Young’s modulus and elastic recovery in hard nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 154, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, G.C.A.M.; Abdalla, M.M.; van Keulen, F.; Pujada, B.R.; van Venrooy, B. Celebrating the 100th anniversary of the Stoney equation for film stress: Developments from polycrystalline steel strips to single crystal silicon wafers. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, 3rd ed.; VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sandu, C.S.; Cusnir, N.; Oezer, D.; Sanjinés, R.; Patscheider, J. Influence of bias voltage on the microstructure and physical properties of magnetron sputtered Zr–Si–N nanocomposite thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Tien, S.K.; Kuo, Y.C. The effects of pulse frequency and substrate bias to the mechanical properties of CrN coatings deposited by pulsed DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2006, 494, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ke, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, A. Influence of substrate negative bias on structure and properties of TiN coatings prepared by hybrid HIPIMS method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.I.; Kao, H.L. Mechanical properties and oxidation behavior of ZrNx thin films fabricated through high-power impulse magnetron sputtering deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2016, 34, 02D107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.B.; Sun, P.; Zhu, F.P.; Wang, Z.C.; Peng, D.L.; Wu, C.H. The inverse Hall–Petch effect in nanocrystalline ZrN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3692–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. On the significance of the H/E ratio in wear control: A nanocomposite coating approach to optimised tribological behavior. Wear 2000, 246, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Wu, F.B. Fabrication and tribological behavior of sputtering TaN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Beresnev, V.M.; Bondar, O.V.; Postolnyi, B.O.; Zaleski, K.; Coy, E.; Jurga, S.; Lisovenko, M.O.; Konarski, P.; Rebouta, L.; et al. Superhard CrN/MoN coatings with multilayer architecture. Mater. Des. 2018, 153, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J. Hard nanocomposite coatings: Thermal stability, oxidation resistance and toughness. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 207, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, T.Y.; Pharr, G.M.; Oliver, W.C.; Bhatia, C.S.; White, R.L.; Anders, S.; Anders, A.; Brown, I.G. Nanoindentation and nanoscratching of hard carbon coatings for magnetic disks. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1995, 383, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Diyatmika, W.; Lou, B.S.; Lu, Y.C.; Duh, J.G.; Lee, J.W. Influences of target poisoning on the mechanical properties of TiCrBN thin films grown by a superimposed high power impulse and medium-frequency magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Neto, P.C.; Freitas, F.G.R.; Fernandez, D.A.R.; Carvalho, R.G.; Felix, L.C.; Terto, A.R.; Hubler, R.; Mendes, F.M.T.; Silva Junior, A.H.; Tentardini, E.K. Investigation of microstructure and properties of magnetron sputtered Zr-Si-N thin films with different Si content. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 353, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J.; Daniel, R.; Zeman, P.; Takai, O. Structure and properties of magnetron sputtered Zr–Si–N films with a high (≥ 25 at.%) Si content. Thin Solid Films 2005, 478, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
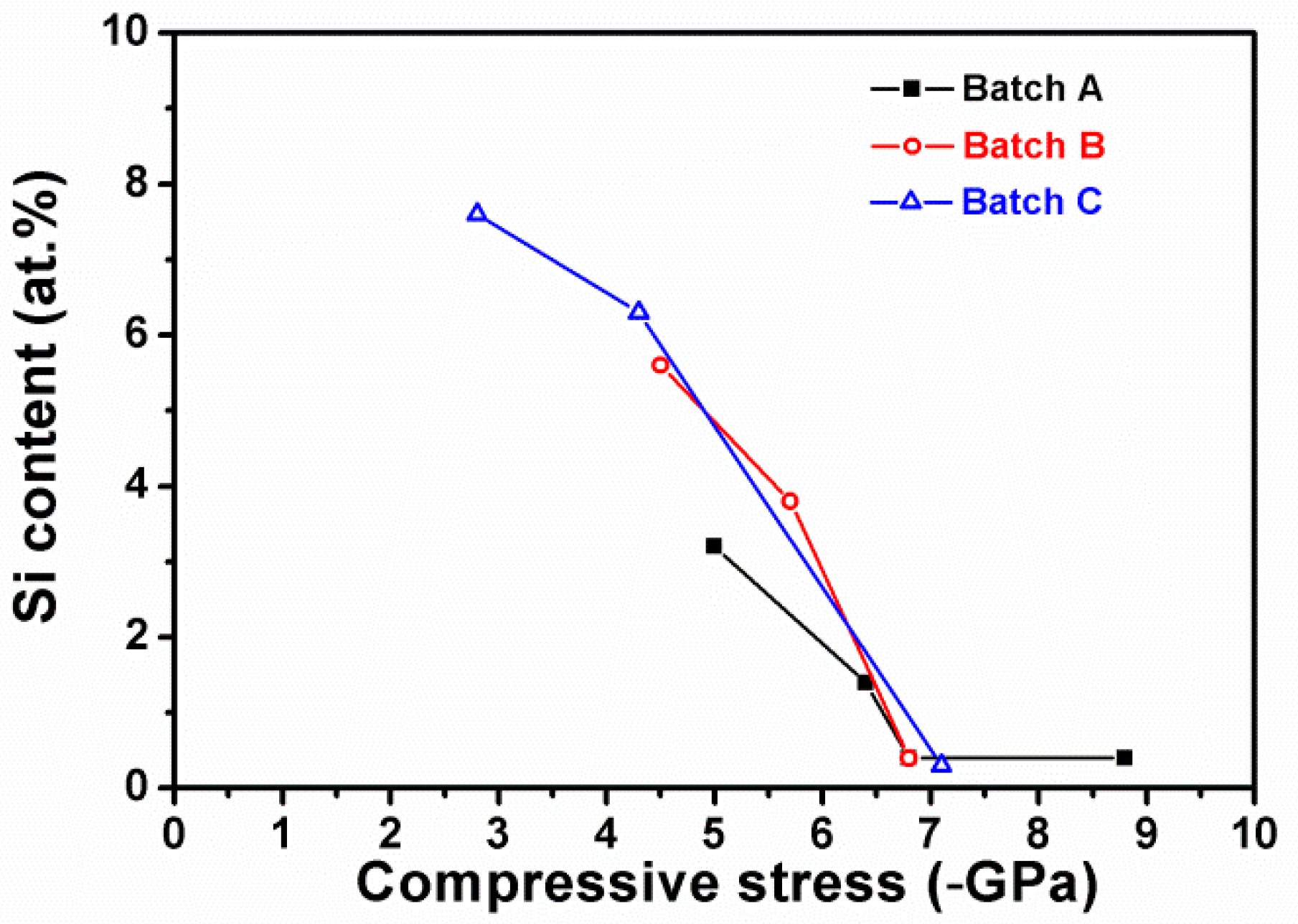
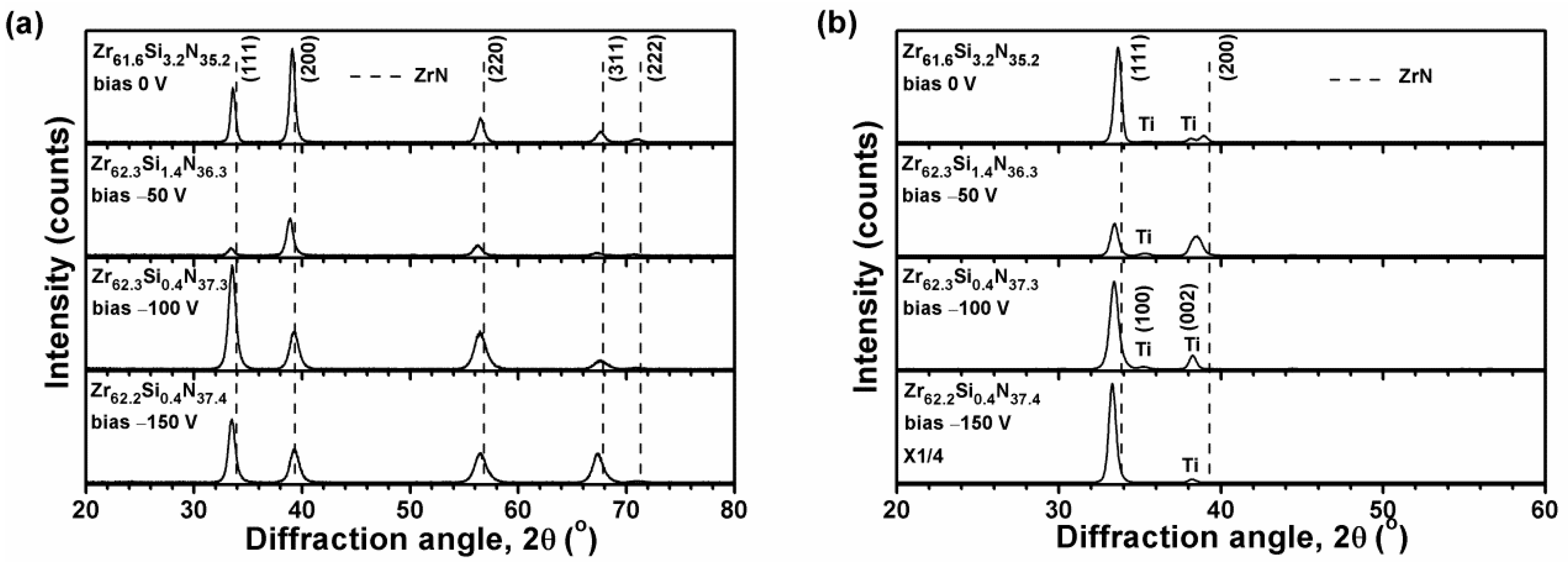
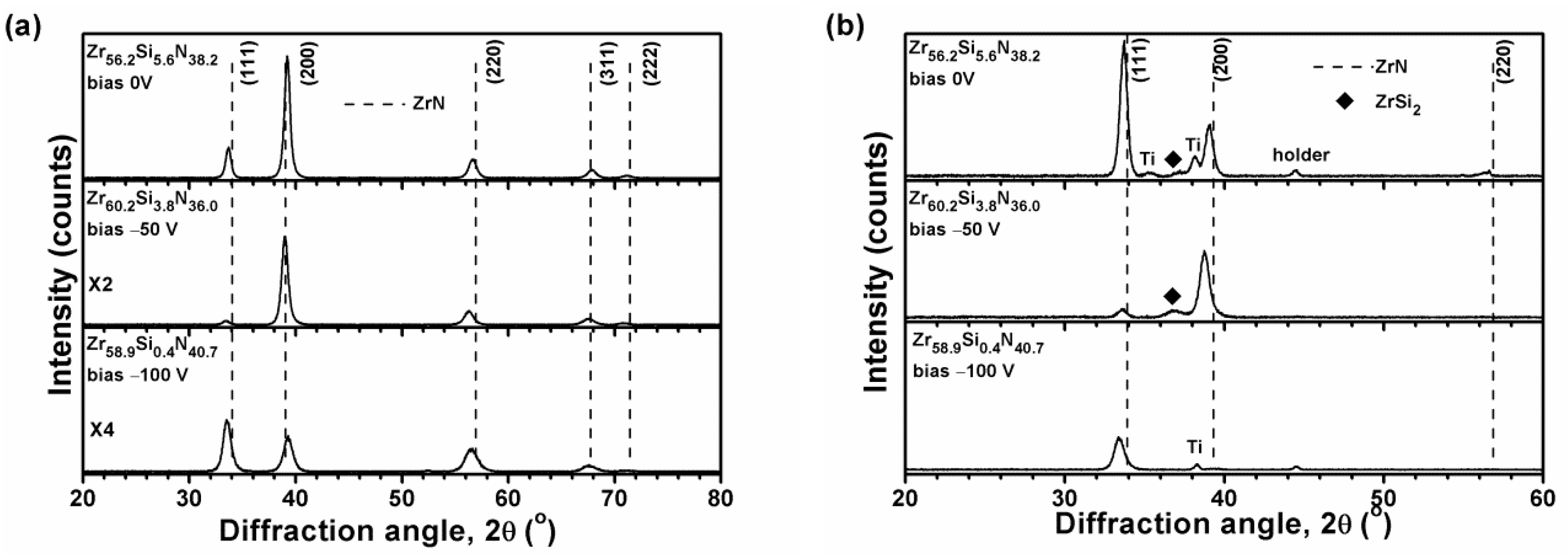
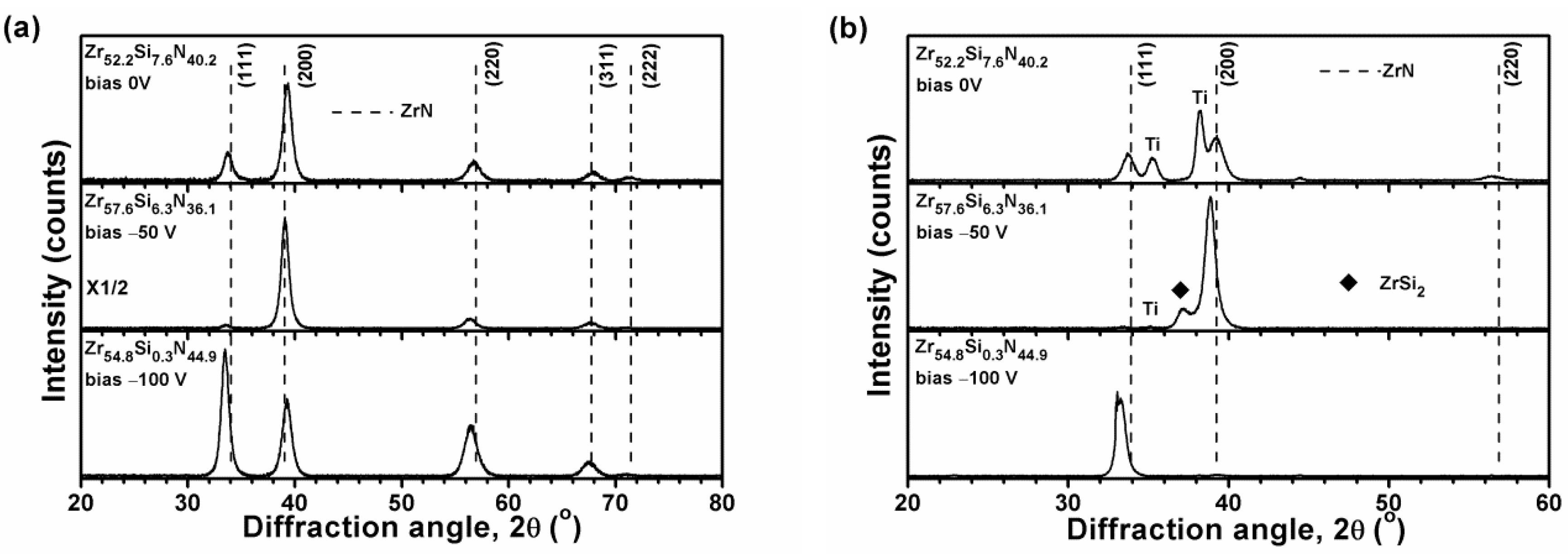
| Sample | Bias | Chemical Composition (at.%) | Time | T 1 | Ra 2 | Stress | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−V) | Zr | Si | N | O | (min) | (nm) | (nm) | (GPa) | |
| Batch A, PSi = 30 W | |||||||||
| Zr61.6Si3.2N35.2 | 0 | 61.0 ± 0.4 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 34.9 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 270 | 932 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | −5.0 ± 0.4 |
| Zr62.3Si1.4N36.3 | 50 | 62.2 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 36.2 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 300 | 1007 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | −6.4 ± 0.6 |
| Zr62.3Si0.4N37.3 | 100 | 62.3 ± 2.1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 37.3 ± 2.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 300 | 966 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | −6.8 ± 0.3 |
| Zr62.2Si0.4N37.4 | 150 | 62.2 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 37.4 ± 0.7 | 0.0 ± 0.1 | 300 | 959 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | −8.8 ± 0.3 |
| Batch B, PSi = 40 W | |||||||||
| Zr56.2Si5.6N38.2 | 0 | 55.8 ± 0.2 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 37.9 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 230 | 847 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | −4.5 ± 0.6 |
| Zr60.2Si3.8N36.0 | 50 | 58.7 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 35.1 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 220 | 747 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | −5.7 ± 0.5 |
| Zr58.9Si0.4N40.7 | 100 | 58.0 ± 1.0 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 40.1 ± 1.0 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 300 | 1080 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | −6.8 ± 0.5 |
| Batch C, PSi = 50 W | |||||||||
| Zr52.2Si7.6N40.2 | 0 | 52.0 ± 1.1 | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 40.1 ± 1.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 210 | 831 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | −2.8 ± 0.1 |
| Zr57.6Si6.3N36.1 | 50 | 56.3 ± 1.9 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 35.3 ± 1.8 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 210 | 747 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | −4.3 ± 0.3 |
| Zr54.8Si0.3N44.9 | 100 | 54.0 ± 2.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 44.3 ± 2.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 265 | 981 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | −7.1 ± 0.3 |
| Sample | Bias | Stress | H1 | E*2 | H/E* | H3/E*2 | We3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−V) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (%) | ||
| Batch A, PSi = 30 W | |||||||
| Zr61.6Si3.2N35.2 | 0 | −5.0 ± 0.4 | 34.3 ± 1.0 | 408 ± 12 | 0.084 | 0.24 | 64 |
| Zr62.3Si1.4N36.3 | 50 | −6.4 ± 0.6 | 34.4 ± 1.2 | 350 ± 14 | 0.098 | 0.33 | 67 |
| Zr62.3Si0.4N37.3 | 100 | −6.8 ± 0.3 | 29.4 ± 0.6 | 346 ± 10 | 0.085 | 0.21 | 60 |
| Zr62.2Si0.4N37.4 | 150 | −8.8 ± 0.3 | 28.3 ± 1.5 | 331 ± 11 | 0.086 | 0.21 | 60 |
| Batch B, PSi = 40 W | |||||||
| Zr56.2Si5.6N38.2 | 0 | −4.5 ± 0.6 | 33.2 ± 1.0 | 413 ± 13 | 0.080 | 0.21 | 62 |
| Zr60.2Si3.8N36.0 | 50 | −5.7 ± 0.5 | 34.6 ± 0.5 | 324 ± 8 | 0.107 | 0.39 | 72 |
| Zr58.9Si0.4N40.7 | 100 | −6.8 ± 0.5 | 34.4 ± 1.0 | 413 ± 4 | 0.083 | 0.24 | 65 |
| Batch C, PSi = 50 W | |||||||
| Zr52.2Si7.6N40.2 | 0 | −2.8 ± 0.1 | 27.4 ± 1.6 | 283 ± 8 | 0.097 | 0.26 | 63 |
| Zr57.6Si6.3N36.1 | 50 | −4.3 ± 0.3 | 33.7 ± 0.9 | 363 ± 6 | 0.093 | 0.29 | 68 |
| Zr54.8Si0.3N44.9 | 100 | −7.1 ± 0.3 | 35.1 ± 0.4 | 398 ± 6 | 0.088 | 0.27 | 65 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-I.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Chang, L.-C.; Liu, Y.-H. Effect of Bias Voltage on Mechanical Properties of HiPIMS/RFMS Cosputtered Zr–Si–N Films. Materials 2019, 12, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172658
Chen Y-I, Zheng Y-Z, Chang L-C, Liu Y-H. Effect of Bias Voltage on Mechanical Properties of HiPIMS/RFMS Cosputtered Zr–Si–N Films. Materials. 2019; 12(17):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172658
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yung-I, Yu-Zhe Zheng, Li-Chun Chang, and Yu-Heng Liu. 2019. "Effect of Bias Voltage on Mechanical Properties of HiPIMS/RFMS Cosputtered Zr–Si–N Films" Materials 12, no. 17: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172658
APA StyleChen, Y.-I., Zheng, Y.-Z., Chang, L.-C., & Liu, Y.-H. (2019). Effect of Bias Voltage on Mechanical Properties of HiPIMS/RFMS Cosputtered Zr–Si–N Films. Materials, 12(17), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172658




