Abstract
Given the growing number of residential photovoltaic installations and the challenges of self-consumption, accurate short-term PV production forecasting can become a key tool in supporting energy management. This issue is particularly significant in systems without energy storage, where excess production is fed back into the grid, reducing the profitability of prosumer investments. This paper presents an approach to forecasting short-term energy production in residential photovoltaic installations, based on real meteorological data and the use of machine learning methods. The analysis is based on measurement data from a functioning PV installation and a local weather station. This study compares three models: classical linear regression, Random Forest and the XGBoost algorithm. The method of data preparation, the model training process and the assessment of their effectiveness based on real energy production measurements are presented. This paper also includes a practical calculation example and an analysis of selected days in order to compare the forecast results with the actual production. Of the three models compared, the highest accuracy was achieved for XGBoost, with an MAE = 1.25 kWh, RMSE = 1.93 kWh, and coefficient of determination R2 = 0.94. Compared to linear regression, this means a 66% reduction in MAE and a 41% reduction in the Random Forest model, confirming the practical usefulness of this method in a real-world environment. The proposed approach can be used in energy management systems in residential buildings, without the need to use energy storage, and can support the development of a more conscious use of energy resources on a local scale.
1. Introduction
The growing electricity consumption in the residential sector, combined with dynamic climate change and increasingly volatile energy prices, is resulting in an increased interest in decentralized renewable energy sources [1,2,3,4]. In particular, photovoltaics (PV) has become a key element of the energy transformation both in Europe and around the world [5,6,7]. Thanks to the decreasing costs of PV modules, the introduction of prosumer solutions and regulations supporting the development of renewable energy sources, PV systems on residential roofs have become widely available and increasingly installed by end users [8,9]. However, with the popularization of home PV installations, new challenges have emerged [10,11,12,13,14]. One of the main problems is low self-consumption, i.e., a low share of the electricity produced “on site” in relation to the total production. In systems without energy storage, especially in countries such as Poland, a significant part of the electricity produced during the day goes to the power grid because household members are away from home during high generation hours [15]. In the net billing model, in which the value of energy sold to the grid is lower than the value of energy drawn from the grid, low self-consumption leads directly to a decrease in the profitability of investment in a PV installation [16,17,18,19].
To counteract this, energy management strategies in households are becoming increasingly important, in particular, those based on the optimization of PV energy use in real time. A key element of such strategies is the ability to forecast energy production for the next days or even hours [20,21,22,23,24]. Information about the expected generation allows for the conscious planning of the operation of energy-intensive devices such as heat pumps, washing machines, dishwashers or electric vehicle chargers. In more advanced cases, it can also be the basis for the operation of building automation (smart home systems) and for managing the charging and discharging of energy storage devices.
In the scientific literature, the development of methods for forecasting PV energy production is very intensive. Both deterministic, statistical and artificial intelligence-based methods are used [25,26,27,28,29]. Models based on meteorological data, such as linear regression models, decision trees, Random Forests, neural networks or gradient boosting algorithms (including XGBoost), allow for the prediction of energy production based on current or forecasted weather conditions. The advantage of these approaches is the possibility of taking into account nonlinear dependencies between input variables and the value of energy yield. Additionally, these algorithms cope well with a large number of variables and are resistant to outliers and missing data.
Of particular interest in the context of home systems are short-term (day-ahead) forecasts, i.e., forecasting energy production for one day ahead. They are relatively accurate and with a properly selected model can achieve relative errors of several percent, which, from a practical point of view, is sufficient for controlling loads in a household. Such forecasts can be used manually (by the user) as well as automatically in energy management systems (EMSs).
This paper attempts to develop and assess the accuracy of short-term predictive models based on real meteorological data and energy production data from a specific, identified PV installation with a capacity of 38.25 kWp, located in Rzeszow. The input data include daily measurements of solar radiation, air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and total precipitation, while the output data are recorded values of daily electricity production from the PV installation. These data were collected and organized over a period of more than two years, which provides a solid basis for training machine learning models.
Thise paper uses and compares three forecasting approaches: classical linear regression as a basic model, Random Forest and the XGBoost model as a more advanced method based on machine learning. The analysis includes an assessment of the quality of prediction based on MAE (mean absolute error), RMSE (root mean square error) and MAPE (mean absolute percentage error) indicators. In addition, a detailed calculation example was developed from real data (reference day), showing how the model works and comparing the predicted value with the actual one. A tabular summary of forecast results for randomly selected days was also prepared to enable the full verification of the models’ effectiveness.
In addition to the analysis of the accuracy of forecasts, this paper also presents their application to the optimization of self-consumption in the household. For this purpose, energy management scenarios for the user were developed, depending on the expected PV energy production, and the benefits resulting from consciously shifting electricity consumption to hours of high production were analyzed.
This article is based exclusively on actual measurements. This is crucial for the practical value of the presented results. Actual measurement data, although often noisier, better reflect the operating conditions of the installation and take into account local microclimatic phenomena, which have a significant impact on the energy yield from PV.
Although Random Forest and XGBoost models are widely used in forecasting energy production from PV installations, many publications focus on large systems or simulated data, limiting their usefulness in real-world prosumer environments. Many studies do not develop proprietary predictive models but utilize off-the-shelf forecasts from commercial weather APIs, simplifying the analysis but limiting control over prediction quality. Furthermore, the issues of short-term production forecasting, hourly variability analysis, and forecast integration with an energy management system and storage are rarely combined in a single approach. This paper presents a coherent solution in which accurate hourly forecasts based on real-world meteorological and production data from a 38.25 kWp installation are used to control the energy consumption profile via a simple, implementable storage management algorithm. The integration of these elements—PV production modeling, prosumer context, real-world data, and an algorithm supporting self-consumption—addresses a significant gap in the literature and has direct practical applications.
The presented analysis is a contribution to the developing field of energy management in single-family buildings with RES. It can also be extended to the needs of housing communities, public buildings or commercial systems. In addition, the presented approach can be the basis for implementing intelligent distributed energy management systems within the concept of an active prosumer or a so-called virtual power plant.
The aim of this article is therefore not only to analyze the accuracy of short-term PV production forecasts based on real data but also to show the potential of integrating such forecasts with energy management systems to increase local energy consumption and improve the energy efficiency of households. Additionally, this work shows that artificial intelligence tools such as XGBoost can also be successfully used in small installations and provide real support in everyday energy management.
As part of the conducted research, three research hypotheses were formulated to assess the effectiveness of selected machine learning methods in forecasting short-term energy production from PV installations and their potential impact on improving self-consumption in home systems:
The use of advanced machine learning methods such as XGBoost significantly improves the accuracy of short-term forecasts of energy production from PV installations compared to classic regression models.
Including real meteorological data (e.g., temperature, radiation, humidity, wind) in the model training process leads to higher forecast precision, especially in variable cloud cover conditions.
Accurate short-term forecasts of PV energy production enable an increase in the level of self-consumption of electricity in households without the need to use energy storage.
2. Literature Review
Forecasting energy production from photovoltaic (PV) installations plays an important role in energy system management, especially in the context of the growing share of renewable energy sources in the energy mix [30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Accurate forecasts enable the better planning of energy system operation, load management and the optimization of self-consumption. In the scientific literature, the development of PV energy production forecasting methods is very intensive, including deterministic, statistical and artificial intelligence-based methods [37,38,39,40,41].
PV energy production forecasting methods can be broadly divided into three main categories:
- Physical methods: They are based on modeling the physical processes occurring in the atmosphere and in the PV installations themselves. They use data from numerical weather prediction (NWP) models and information on the technical characteristics of PV systems.
- Statistical methods: They are based on the analysis of historical energy production data and meteorological conditions. They use various statistical techniques, such as regression models, autoregressive (AR) models, moving average (MA) models and their combinations (ARMA and ARIMA).
- Hybrid methods: They combine elements of physical and statistical methods, often integrating data from NWP models with machine learning techniques to improve the accuracy of forecasts.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in data-driven methods, especially using machine learning techniques that can model complex and nonlinear relationships between input variables and PV energy production.
The short-term forecasting of PV energy production, covering time horizons from a few minutes to several days, is particularly important for grid operators, energy suppliers and prosumers. Accurate forecasts in this area enable the better planning of energy systems, load management and the optimization of self-consumption.
Traditional statistical methods such as ARIMA models have been widely used in the past to forecast PV energy production [42]. However, their effectiveness is limited in the case of highly variable and nonlinear data, which is characteristic of solar energy production.
In response to these challenges, machine learning methods are increasingly being used, which can better capture complex patterns in the data and adapt to changing conditions. Machine learning can take into account the complex relationships between meteorological variables and energy generation, enabling the creation of precise, adaptive and weather-resistant predictive models that outperform traditional statistical methods in terms of accuracy and application flexibility. Machine learning (ML) offers a wide range of techniques that have been used in PV energy production forecasting. The most commonly used include the following [43,44,45,46,47,48,49]:
- Linear and multiple regression: Simple models that can be effective for data with linear dependencies.
- Decision trees and Random Forests: Tree-based models that can model nonlinear dependencies and are resistant to overfitting.
- Gradient Boosting Machines (GBMs), including XGBoost: Advanced ensemble models that iteratively improve the errors of previous models, achieving high forecast accuracy.
- Neural networks (ANN, CNN, RNN, LSTM, and GRU): Models inspired by the structure of the human brain, capable of modeling complex temporal and spatial dependencies.
For example, Xiang et al. (2024) proposed a hybrid TCN-ECANet-GRU model combining convolutional networks with a channel attention mechanism and GRUs, which demonstrated high accuracy in forecasting PV power production under different seasonal conditions [50]. Other studies, such as Hossain and Mahmood (2020), demonstrated the effectiveness of LSTM networks in forecasting short-term PV power production, especially under variable weather conditions [51]. It is also worth noting that hybrid methods combining different machine learning techniques often achieve better results than single models. For example, Bai et al. (2021) proposed a model based on ConvLSTM and kernel density estimation (KDE), which enables the probabilistic forecasting of PV power production with high accuracy [52].
Despite significant progress in the field of PV energy production forecasting, there are still challenges that require further research:
- Data quality and availability—The accuracy of forecasts is highly dependent on the quality of input data, such as solar radiation, temperature, or wind speed measurements. Missing or poor data quality can significantly reduce the performance of models.
- Weather variability—Sudden changes in weather, such as cloud or precipitation, can significantly affect PV energy production, which poses a challenge for forecasting models.
- Integration with energy management systems—To be useful in practice, forecasts must be integrated with building energy management systems, which requires appropriate interfaces and communication protocols.
- The consideration of forecast uncertainty—Many current models provide point forecasts without uncertainty information, which may be insufficient for decision-making in energy systems.
In response to these challenges, an increasing amount of research is focused on developing probabilistic methods that provide not only point forecasts but also confidence intervals, allowing for better risk management.
3. Methodology
3.1. Characteristics of the Analyzed Photovoltaic Installation
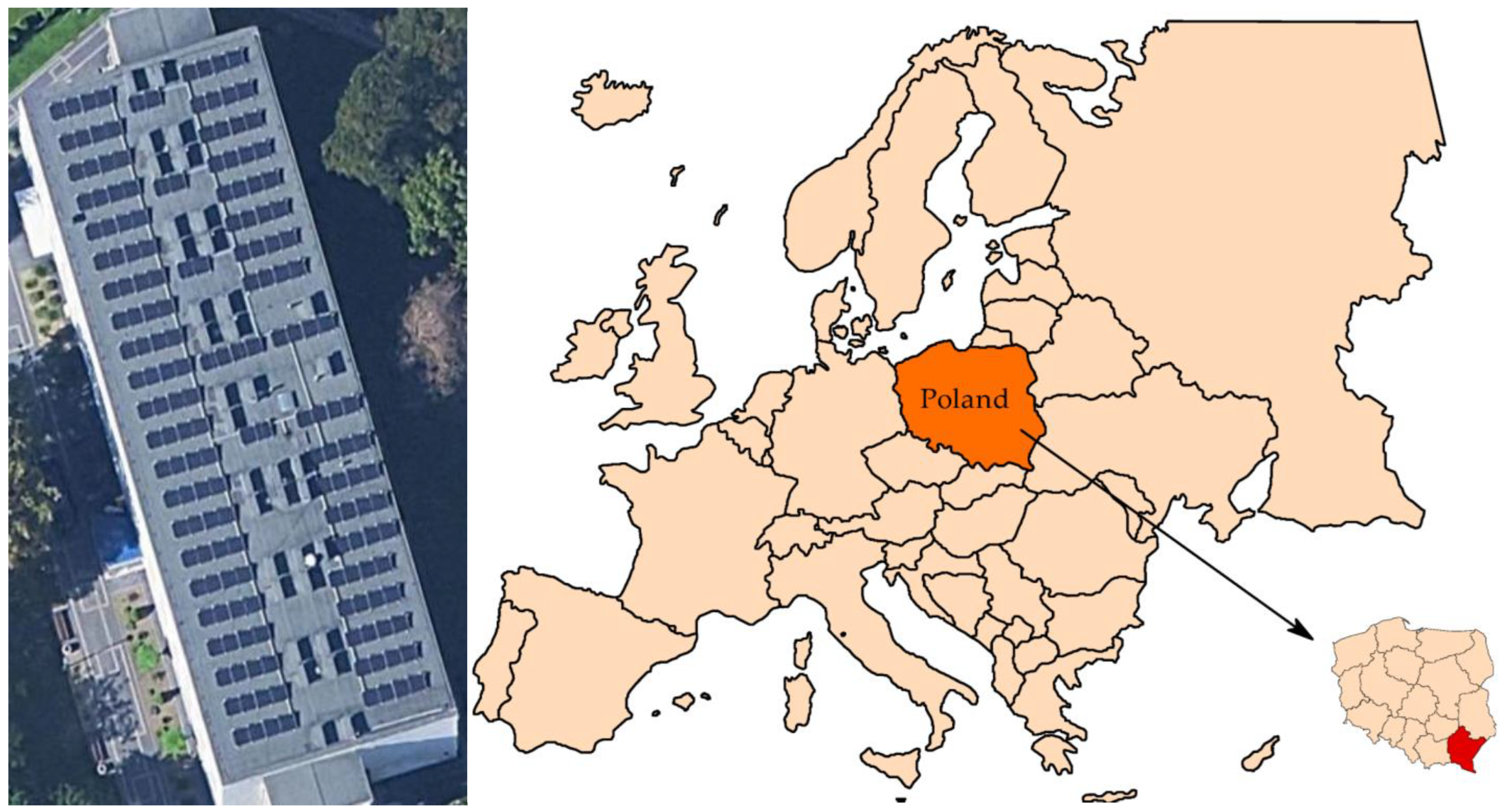
The analyzed photovoltaic installation was installed on a flat roof of the building and has a total installed power of 38.25 kWp (Figure 1). The system consists of 85 photovoltaic modules, each of which has a nominal power of 450 W. These modules are made in monocrystalline technology, which ensures high efficiency in converting solar energy into electrical energy with a limited mounting surface.
Figure 1.
The satellite image and location of the analyzed photovoltaic installation.
A 40 kW inverter is responsible for converting direct current (DC) generated by the panels to alternating current (AC), which allows the monitoring and optimization of the installation in real time. The modules were installed on a ballast structure adapted to a flat roof, without the need to interfere with the roof covering, which minimizes the risk of damage to the building insulation.
The installation is also equipped with a complete set of AC/DC protections and surge protection systems, in accordance with applicable safety standards. Production data from the system are obtained from the inverter and compared with meteorological data from a measuring station located in the immediate vicinity of the installation, which allows for a detailed analysis of the impact of weather conditions on energy yield. The installation is not equipped with an energy storage, which makes it a particularly interesting case for analyzing the possibilities of improving self-consumption based on short-term production forecasts.
3.2. Meteorological Data
In order to develop and validate the forecasting models, actual meteorological data and production data obtained from the photovoltaic installation described in the previous point were used. The set of meteorological data comes from a local measuring station located in the immediate vicinity of the analyzed PV installation. The following input variables were taken into account:
- Average daily solar radiation intensity [kWh/m2];
- Average daily air temperature [°C];
- Average relative humidity [%];
- Average wind speed [km/h];
- Daily precipitation total [mm].
Meteorological data were available in 5 min intervals and were averaged to an hourly level. Continuous values such as air temperature, dew point, relative humidity, wind speed and gusts, atmospheric pressure and solar radiation were averaged. In the case of precipitation or other accumulative variables, the summation or calculation of increments in a given hour was used. This method of data processing ensures the consistency of the model input features and eliminates interference resulting from differences in time resolution between measurements and forecasts.
3.3. Division of the Day into Time Zones in Forecasting Photovoltaic Energy Production
In the presented study, actual electricity production was forecasted on an hourly basis, rather than daily or 24-hourly. This means that a separate value of energy generation from the photovoltaic installation was predicted for each full hour of the day. This approach allows for a detailed representation of production variability throughout the day and allows for the direct use of forecasts in modern energy management systems that operate with high temporal resolution. Importantly, no hourly aggregation of forecasts derived from daily data was performed—each hour was an independent forecast point trained on actual input data. The hourly resolution was consciously adopted both during the input data preparation and during the definition of the dependent variable to maintain consistency with meteorological forecasts and enable an analysis of prediction accuracy across the 24 h cycle. Electricity production was measured in 5 min intervals. For modeling purposes, the data were transformed into an hourly form by summing the differences in cumulative energy within each full hour. This approach ensures consistency with the time system of meteorological forecasts and allows for an accurate representation of the actual energy generation profile.
The advantage of the hourly approach is the possibility of the direct use of the results in practical operational applications. Forecasts of hourly energy production can support various applications, including energy storage charging control, inverter optimization, electric vehicle charging, and the scheduling of low-priority loads. Additionally, a detailed analysis of the forecast errors on an hourly basis allows for the identification of hours with an increased risk of prediction error, e.g., resulting from variable cloud cover or sudden weather changes. Hourly modeling also facilitates the implementation of forecasts in automation and control systems, where forecasts with high time resolution are required.
3.4. Models Used in the Analysis
In this study, three regression models were used to forecast daily energy production from a photovoltaic installation: classical linear regression, Random Forest and the XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting) algorithm. The choice of these three approaches results from the desire to compare the effectiveness of a simple, well-interpretable model with an advanced ensemble learning method that can capture complex, nonlinear relationships between meteorological variables and energy yield. Both models were trained on a data set consisting of real weather variables and their corresponding energy production values on a given day. The linear regression model was included in the analysis as a benchmark for more complex algorithms that learn nonlinear relationships, such as Random Forest and XGBoost. Its role in the study is not limited to a comparative function; it allows us to assess whether the use of advanced machine learning methods yields significant benefits in terms of forecast accuracy. Due to its simplicity and transparency, linear regression also serves an interpretive function, enabling an understanding of the fundamental relationships between input variables and the forecasted value of PV production. There are many other models used as benchmarks in time series forecasting in the scientific literature, including ARIMA, models based on support vector machines (SVR), and LSTM neural networks. In this paper, we deliberately refrain from expanding the spectrum of analyzed algorithms in favor of focusing on a qualitative assessment of models based solely on real-world data and their potential application in prosumer settings. Instead of expanding the list of models, we opted for an in-depth analysis of selected, representative approaches. This strategy allowed for a better grasp of the differences between a simple linear approach and models capable of modeling complex, nonlinear interactions and for obtaining clear application conclusions.
3.4.1. Linear Regression
Linear regression is one of the simplest prediction models, assuming a linear relationship between input variables (meteorological) and the forecasted value of the dependent variable (energy production):
where —forecasted electricity production, —intercept of the regression model, —regression coefficient for variable , —the value of the i-th meteorological variable (e.g., solar irradiance, temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind), and n—the number of input features.
This model was chosen as a baseline due to its interpretability and low computational complexity.
3.4.2. Random Forest
Random Forest is a predictive algorithm based on the ensemble method, using a set of decision trees to predict continuous values. In this model, each decision tree is trained on a random subsample of data (the so-called bootstrap) and on a random subset of input features, which ensures model diversity and reduces prediction variance.
The construction of the decision tree is based on the CART algorithm (Classification and Regression Trees), in which a partition is selected at each node that minimizes the mean square error (MSE). In the case of regression, the prediction of the entire forest is calculated as the average of the predictions of individual trees, according to the following formula:
where B is the number of trees in the forest, and is a single tree prediction for sample x.
Random Forest, due to its structure, enables the modeling of nonlinear dependencies between features, detecting interactions, and is resistant to overfitting, which makes it an attractive tool in forecasting PV energy production under variable weather conditions.
For the Random Forest model, hyperparameter tuning was performed using the GridSearchCV grid search method and five-fold cross-validation. Although this algorithm is considered robust to overfitting, its performance depends largely on the proper setting of parameters controlling the model’s structure and randomness. The following hyperparameters were tested for optimization:
- The number of decision trees in the model; a larger number increases prediction stability but increases training time.
- The maximum depth of the tree; lower values limit model complexity and prevent overfitting.
- The minimum number of samples required to split a node; this affects the tree branching method.
- The minimum number of samples assigned to each leaf; higher values promote generalization.
- The number of features considered in each split; this regulates randomness and reduces interdependence between trees.
The set of test values for each hyperparameter was selected based on preliminary experiments with local data. The final configuration was a compromise between accuracy and model generalization ability, with minimizing the RMSE as the primary evaluation criterion.
In the case of the Random Forest model, which has a built-in validation mechanism in the form of out-of-BAG (OOB) samples, the possibility of its use was considered to assess the effectiveness of predictions. OOB consists of using observations that were not used to create a specific tree, which allows you to estimate the error without the need for an additional validation harvest. However, due to the desire to maintain methodological cohesion between compared models and enabling the use of gridsearchcV in the process of tuning hyperparameters, it was ultimately decided to divide the data: 70% training, 15% validation and 15% test. This approach allowed a direct comparison of results with the XGBOOST model while maintaining uniform experimental conditions. The data were split in time order (time-based splitting), which prevents information leakage and enables a realistic evaluation of the model in the context of time series prediction.
3.4.3. XGBoost
In this study, one of the prediction models used was XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting), which belongs to the group of ensemble algorithms and is based on the gradient boosting methodology. XGBoost is distinguished by its high prediction efficiency, the ability to model nonlinear dependencies, and flexibility in adjusting parameters, which makes it one of the most commonly used algorithms in data competitions and predictive analyses.
XGBoost works on the principle of iteratively building many decision trees, each of which corrects the errors made by its predecessors. Instead of building all trees in parallel, as in classic bagging algorithms (e.g., Random Forest), XGBoost learns sequentially, minimizing a specific loss function, most often the mean square error (MSE). The algorithm also uses regularization mechanisms that penalize overly complex trees and thus prevent overfitting. Each tree is built to maximize the improvement in the prediction of the entire model while controlling complexity.
The prediction model in XGBoost can be written formally as
where —the predicted value of the dependent variable for observation i, —the output of the k-th decision tree for input vector , k—the total number of trees in the model, and —space of all possible decision trees (e.g., regression trees of limited depth).
Training the model involves minimizing the loss function with regularization:
where —loss function (e.g., squared error: ) and —regularization term penalizing the complexity of tree . For example,
where T—number of leaves in the tree, —weight of leaf j, and γ and λ—hyperparameters controlling the strength of regularization.
Compared to classical regression models, XGBoost offers the following advantages:
- The ability to automatically model interactions between input features.
- Flexibility in adjusting loss and cost functions.
- Handling data with missing and non-numeric variables (after appropriate encoding).
- High computational efficiency thanks to implementation using memory optimization and support for parallel computations.
In the context of forecasting energy production from photovoltaic installations, XGBoost allows for the effective use of meteorological data, which are often characterized by high variability and the occurrence of nonlinear dependencies. Due to this complexity and the high sensitivity of the model to configuration, special attention was paid to the selection of hyperparameters, which significantly impact the accuracy and stability of predictions. Hyperparameters are settings defined before the training process begins and—unlike parameters learned from the data—are not directly modified by the algorithm. Their appropriate selection can significantly impact model performance, error reduction, and generalization ability. This study employed the XGBoost algorithm with hyperparameter optimization performed using grid search (GridSearchCV) and five-fold cross validation. This method allows for the systematic testing of various combinations of hyperparameter values and selecting those that lead to the best results for a given data set. The goal was to minimize the RMSE while maintaining the model’s generalization ability. The following hyperparameters were tuned:
- The number of decision trees built by the model; a larger number can increase prediction accuracy but also involves a higher computational cost and the risk of overfitting.
- The maximum depth of each tree; lower values limit the model’s complexity, helping to avoid overfitting.
- The learning rate, which controls the impact of newly added trees on the final result; lower values require more iterations but increase learning stability.
- The minimum sum of weights assigned to leaf samples; higher values limit the creation of very specific rules and improve the model’s generality.
- The fraction of data samples used to build each tree; lower values increase randomness and reduce the risk of overfitting.
- The fraction of features randomly selected for tree construction; reducing this value reduces the correlation between trees.
- The minimum value of the cost function reduction required to perform a split; this parameter controls the degree of the regularization of the tree structure.
The set of values tested for each parameter was based both on the results of previous studies on photovoltaic production forecasting and preliminary experiments performed on the analyzed local data. The final configuration was chosen as a compromise between accuracy (low error) and generalization capability, which refers to the model’s ability to correctly predict outcomes not only for the training data but also for new, previously unknown observations. In the context of PV production forecasting, generalization is particularly important because input data (e.g., meteorological conditions) change over time and are not repeatable, requiring the model to be resistant to overfitting to the specifics of the training set and maintain good predictive performance in real-world conditions.
To ensure an objective and reliable assessment of the XGBoost model’s prediction quality, the entire data set was divided into three independent parts: 70% of the observations were used for model training, 15% for validation during the hyperparameter optimization process, and the remaining 15% for the final test. This three-way split is a proven practice in machine learning, particularly for regression tasks, where achieving not only low training error but also, above all, the model’s ability to generalize to previously unknown data is crucial. The validation set played a key role in the parameter tuning process using GridSearchCV—it was used to select the most effective combinations of model settings, minimizing prediction error and reducing the risk of overfitting. The test set, completely separated from the training and validation processes, served as an independent source for assessing the final model quality. The division of data into training, validation, and test sets took into account the chronological order of observations, eliminating the risk of look-ahead bias—a situation in which the model could unwittingly use information from the future relative to the forecast time. By maintaining the natural temporal order, the adopted data division method faithfully reflects the actual operational scenario of forecast use, where decisions are made solely based on historical data. This approach ensures a reliable assessment of model effectiveness in the context of their potential application in real-world energy management systems.
In this study, XGBoost was trained using an input set including weather data from the previous day, and its goal was to predict the total PV energy production for the next day. Linear regression was used as a reference point, which allows for an objective assessment of the performance of a more advanced model in the context of practical applications.
3.5. Methods for Assessing the Effectiveness of Models
To objectively evaluate the effectiveness of the applied prediction models, four standard regression metrics were used: mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The choice of these metrics results from their common use in the scientific literature and their complementary nature—each of the metrics describes a different aspect of forecast quality. MAE and RMSE measure the absolute deviation of forecasts from actual values, with RMSE penalizing larger errors more strongly. MAPE expresses the relative error in percentage form, which facilitates the interpretation of results regardless of the scale of the data. In turn, the R2 coefficient allows for us to assess the extent to which the data variability is explained by the model. The combined use of these metrics allows for a comprehensive assessment of forecast accuracy and a comparison of the effectiveness of different modeling approaches.
MAE was calculated using the following formula:
where n—the total number of observations, —the actual value of photovoltaic energy production for observation I, and —the predicted value for observation i.
RMSE was designated as follows:
MAPE was calculated on the basis of the following formula:
The determination factor R2 was defined as
where the mean of all actual values.
4. Forecast Results for Analyzed Models
In order to assess the effectiveness of predictive models, a detailed comparative analysis was carried out including three approaches: linear regression, Random Forest and XGBBOOST. All models were taught using the input data set containing both historical information on electricity production and meteorological forecasts for the next day, which allows their practical application in real energy management systems. To illustrate the behavior of models in typical operational conditions, Table 1 presents the results of the forecast for 10 randomly selected days, which are characterized by a diverse level of energy production and atmospheric variability. For each day, real values were combined and the corresponding hourly forecasts generated by each of the three models. Table 1 also contains total daytime production—both real and forecast—which allows you to assess accuracy in daily terms, relevant from the point of view of energy balance management.

Table 1.
Hourly true and forecast electricity production for selected 10 days.
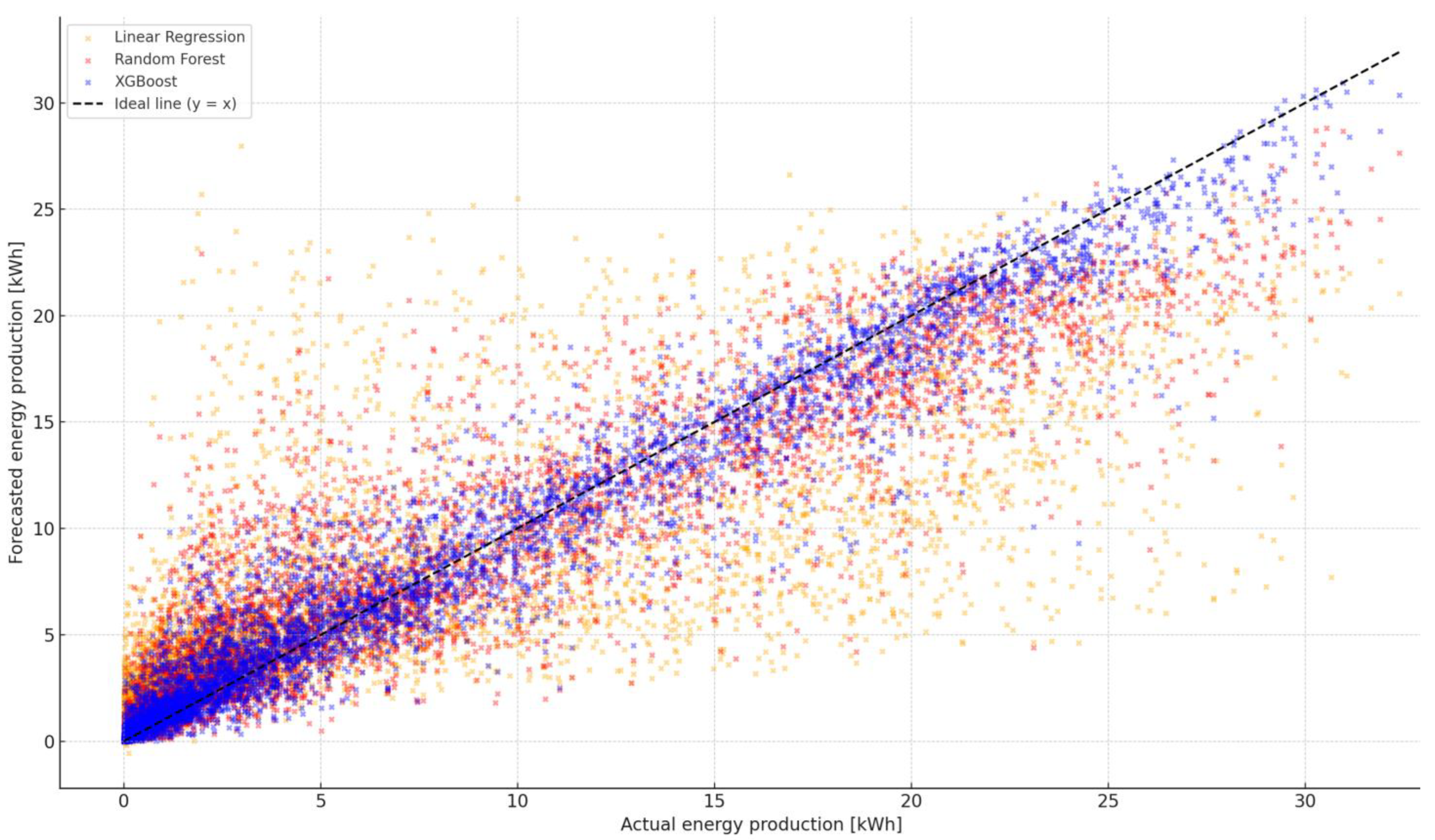
To compare the quality of predictions obtained from the regression models used for the entire period, as seen in the graph (Figure 2), the relationship between the forecast and real electricity production from the PV installation is presented. The chart combined values obtained from the three models, linear regression, Random Forest and XGBOOS, relative to the actual values of the hour generation.
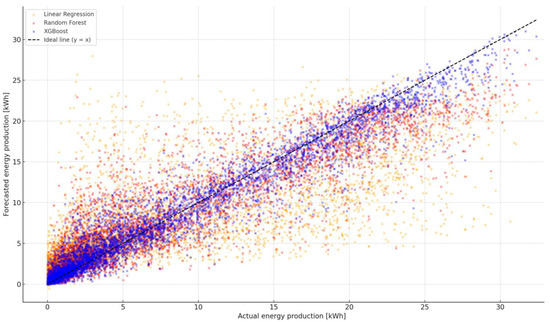
Figure 2.
Comparison of forecast and real PV production for XGBOOST models, Random Forest and linear regression.
In order to compare the effectiveness of predictive models, standard error records were calculated: average absolute error (Mae), an element of medium-rate error (RMSE), average percentage absolute error (map) and the determination factor (R2). Table 2 presents a list of these indicators for the three analyzed models: linear regression, Random Forest and XGBOOST. All values were determined on the basis of data from hours when the actual production of electricity was higher 0 KWh.

Table 2.
Error metrics for three predictive models.
The analysis of the obtained error metrics clearly indicates the diverse effectiveness of the predictive models considered. Among the three compared approaches—linear regression, Random Forest and XGBoost—the highest quality of the mapping of real photovoltaic energy production was achieved using the XGBoost model. This is evidenced by the lowest values of all key error indicators: Mae, RMSE and MAPE. In addition, the R2 determination factor of 0.94 confirms the very high compliance of the model with real values while maintaining generalization capacity.
The Random Forest model obtained indirect results—better than linear regression but clearly weaker than in the case of the XGBoost algorithm. Although obtained error records indicate a relatively good matching of the model to data, its effectiveness is limited by the lack of an iterative mechanism of error correction. Despite the ability to reproduce non-linear dependencies and natural resistance to overtraining, Random Forest is not able to fully capture local irregularities occurring in production data, which translates into higher error values compared to the XGBoost model.
The lowest results were obtained for linear regression. The high relative error and low error of determination indicate that this model is not adapted to the characteristics of the phenomenon, which is variable in time and non-linear energy production from PV installations. Limitations result from its assumption with a fixed, linear relationship between the input variables and the model’s response, which is insufficient in the context of data of high complexity and meteorological variability.
In the context of practical applications, a particularly important indicator of the quality assessment of predictive models is the average percentage absolute error (MAPE), which allows a relative interpretation of the accuracy of forecasts, regardless of the scale of production. The map value allows you to assess whether the model meets the accuracy requirements set by operational applications, such as auto-consumption forecasting, balancing the PV system operation or managing excess energy sent to the network. In the analysis carried out in this study, only the XGBoost model reached the level of relative error, which can be considered sufficient from the point of view of precise short-term forecasting. Random Forest showed moderate effectiveness, while linear regression reached the values of maps exceeding the permissible boundaries used in prognostic analyzes. It should be noted that in the literature on the subject, approximate interpretation intervals of MAPE values are presented, used as a reference point in the assessment of the quality of forecasts, but they should be treated as general guidelines depending on the specific application and the field. In the case of analyzed models, linear regression does not meet the accuracy criteria required for operational applications, while XGBoost not only ensures the stability of prediction but also sufficient precision for practical use in renewable energy systems.
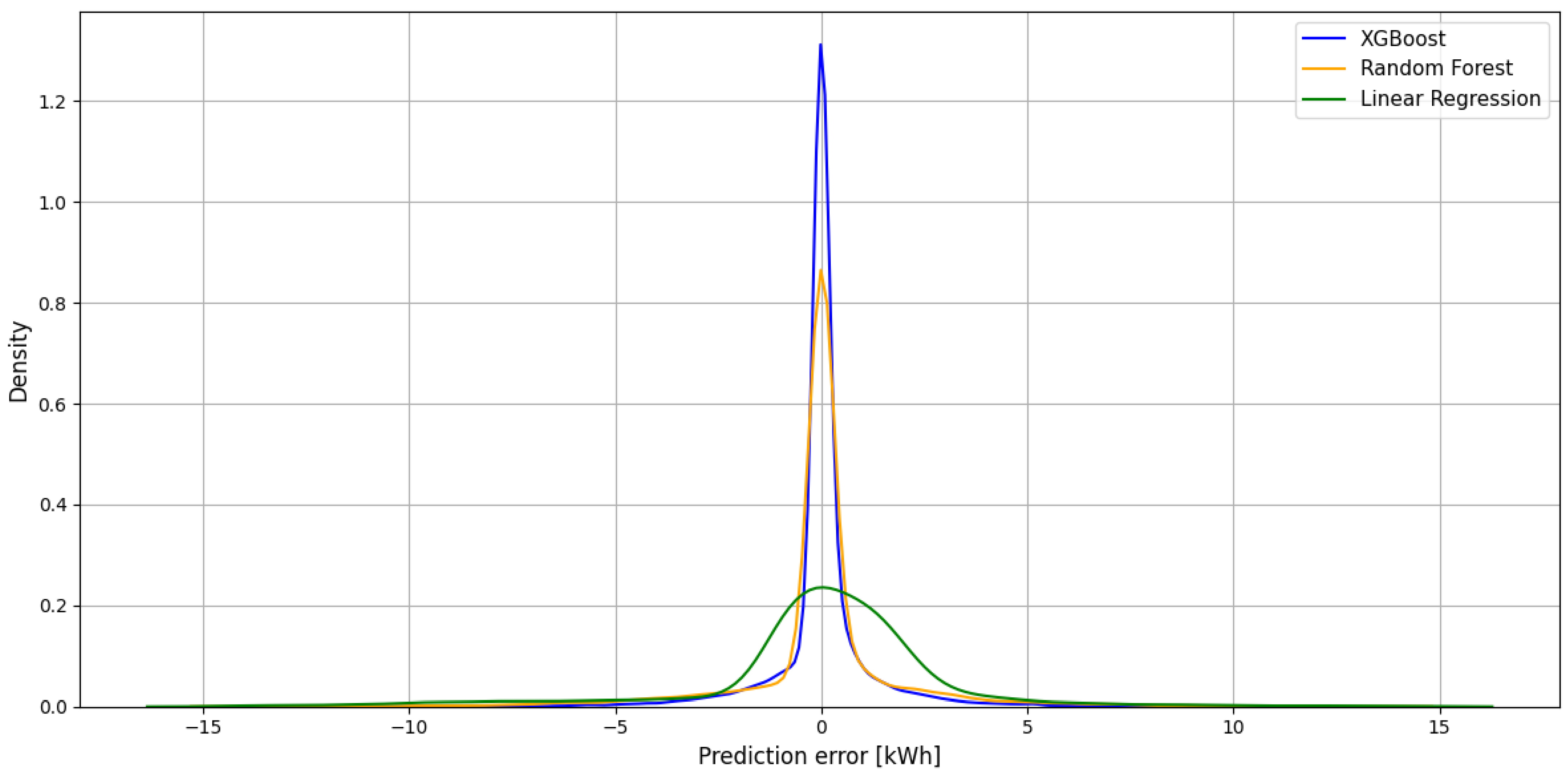
In order to better illustrate the decomposition of prediction errors for individual models, Figure 3 shows a chart of error density function. This approach allows you to assess not only the average error value, but also its dispersion and frequency of specific values, which complements the analysis presented in Table 2.
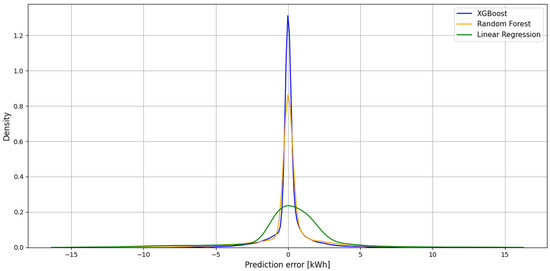
Figure 3.
Distribution of error density for XGBoost, Random Forest and linear regression.
According to the density chart analysis, the XGBoost model is clearly characterized by a narrower and higher peak around zero, which indicates a low rate of errors and their concentration in a small range of values. This means that this model not only reaches the lowest medium errors but also maintains a high stability of prediction. In the case of Random Forest and linear regression models, a wider spread of errors is observed, which translates into lower density function.
However, in order to understand precisely under what conditions the models achieve the highest predictive accuracy, it is necessary to analyze their behavior at different times of the day, starting from the key midday zone. The midday zone is a key period from the point of view of the total energy generation in photovoltaic systems. In this time period, PV panels usually reach their maximum instantaneous power, and the production profile shows the greatest stability, assuming no dynamic changes in cloud cover. For this reason, the accuracy of forecasts in this part of the day has significant practical significance—errors made during the peak can significantly affect the daily energy balance of the facility and the efficiency of local energy management. An analysis of the model results for this time range showed a clear advantage of the XGBoost model over the other methods. This model was characterized not only by low values of absolute prediction errors (MAEs) but also relatively low root mean square errors (RMSEs), which indicates good forecast stability without large outliers. The key advantage of XGBoost in this respect was its ability to adaptively map the generation curve—including taking into account delicate nonlinearities related to the irradiance curve and the temperature effect of PV modules. The Random Forest model performed moderately, with more conservative predictions and a tendency to smooth out extreme values. As a result, the model often underestimated peak production values, as confirmed by comparisons of actual and forecast daily curves. Although the Random Forest was able to respond relatively well to stable weather conditions, its performance was limited at maximum generation levels, which can be attributed to the model structure based on the aggregation of simple decision trees, without an iterative error correction mechanism. Linear regression showed the poorest fit in this time frame. The model was unable to capture the nonlinear nature of production during peak hours, resulting in a systematic underestimation of actual values. In the case of sunny days, this led to significant prediction errors, especially at high irradiance and low atmospheric variability. The model’s inability to account for saturation effects in inverter operation and for kinks in the production curve during transient conditions (e.g., temporary cloud cover) further highlighted its limitations. In summary, during the afternoon hours—crucial from the perspective of maximum PV production—the XGBoost model showed the highest accuracy and stability of prediction. The remaining models, in particular linear regression, did not meet the accuracy requirements necessary for the operational use of forecasts in this range of the day.
The morning hours, especially from sunrise to late morning, are characterized by a high level of forecast uncertainty resulting from two key factors: the dynamically changing angle of solar radiation and high susceptibility to local weather conditions, such as fog, dew, low stratified clouds or point obscurations. Energy production in these hours is relatively low and its growth can be rapid—which poses a significant challenge for predictive models. The analysis shows that compared to the southern zone, the accuracy of forecasts in the morning hours deteriorates noticeably in all models. The XGBoost model again coped best with this zone, which—thanks to the iterative amplification mechanism and the ability to take into account subtle dependencies between input variables—showed the greatest ability to capture early signs of the start of production. Although the errors were higher compared to those observed during peak hours, the forecasts were still relatively stable and there were no significant overestimations. The Random Forest model showed moderate prediction quality in the morning hours, but its limitation was a tendency towards a delayed detection of the onset of production. As a result, forecasts in the first hours often underestimated the real production values, especially in the case of clear mornings. This model managed relatively well with stable production growth but had difficulty adapting to abrupt changes resulting from, for example, the sudden disappearance of morning cloud cover. Linear regression also proved to be the least effective during this part of the day. Its forecasts showed significant inertia and often completely omitted the onset of production, which resulted not only in underestimation, but even in the lack of model response to the first increases in generation. Due to its simplified assumptions, this model was unable to respond appropriately to rapid changes in radiation intensity and their nonlinear effect on the output power of the installation. In a practical context, underestimations in the morning hours can lead to errors in the strategies for starting up receivers or initiating the charging of energy storage devices. Therefore, a precise forecast in this zone is no less important than in the afternoon hours. In this respect, XGBoost remains the only model analyzed that offers sufficient responsiveness and adaptability for operational applications.
The afternoon hours are the last phase of the daily cycle of energy production in photovoltaic installations. They are characterized by a gradual decrease in the intensity of solar radiation, a growing zenith angle and a significant influence of atmospheric conditions, which often change dynamically in the second half of the day. An increase in cloudiness, the appearance of convective clouds or local storms can significantly affect the actual production, making this time band one of the most demanding prediction areas. The analysis of the prediction results indicates that the accuracy of the models in the afternoon hours is varied, both in terms of the size of errors and their direction. The XGBoost model—similarly to the previous zones—achieved the best fit to the actual production. Although the prediction accuracy was no longer as high as in the afternoon hours, the model still showed relatively low errors and a limited number of overestimations. It performed particularly well on stable weather days, in which the production decline curve had a predictable, monotonic course. In deteriorating weather conditions, it also showed good flexibility, making it a useful tool for predicting the PV generation during twilight hours. The Random Forest model revealed its structural limitations during this part of the day. During the hours when the production curve started to decline, the model tended to show a delayed rate of decline. This often led to overestimations, especially during the rapid decay of radiation—e.g., due to the appearance of heavy cloud cover at the end of the day. This can be explained by the nature of RF ensemble models, which are based on the average results of many trees—thus limiting their ability to accurately represent sudden changes in the trend. In turn, the linear regression in the afternoon hours continued the error pattern also observed in other time zones. Its forecasts were characterized by strong inertia and low sensitivity to the variability of conditions. The model most often overestimated production values after 16:00, not taking into account the clear rate of generation decline. As a result, the predictions were less and less consistent with reality, which reduced their utility value at the end of the day, when the accuracy of the predictions can affect, for example, decisions regarding the discharge of energy storage or the preparation of systems for the night. To sum up, the afternoon hours are particularly demanding for prediction models due to the complexity and variability of factors influencing PV production. Of the analyzed methods, only XGBoost maintained a relatively high quality of predictions, demonstrating resistance to random phenomena and rapidly changing weather conditions. The Random Forest and linear regression models were not able to respond appropriately to changes occurring at the end of the day, which significantly reduced their usefulness in this time period.
In order to assess the statistical significance of the differences between the accuracy of the prediction of individual models, the T-Student test for subsidiaries was carried out. The analysis was based on the hourly MAE values for each model, which allowed the comparison of the effectiveness of their operation in the actual working conditions of the solar system. The test results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
T-Student test results for comparison of accuracy of forecasts of individual models.
The analysis covered three pairs of models: linear regression–Random Forest, Random Forest–XGBoost and linear regression–XGBoost. In all cases, very low p (<0.001) values were obtained, which indicates statistically significant differences between compared models. The value of the t-test depends not only on the difference in average errors but also on the variability of these differences. Therefore, despite the fact that the MAE difference between Random Forest and XGBoost models was smaller than between linear regression and Random Forest, the lower standard deviation in the first pair resulted in a higher value of the t-test. The obtained results are consistent with previous analyses contained in this article—they confirm that the XGBoost model achieves the lowest values of forecast errors, and the differences between models are not only noticeable but also statistically important. The T-Student test is therefore complemented and formal confirmation is provided regarding the advantage of nonlinear models over classic linear regression in the context of forecasting short-term energy production from PV installations.
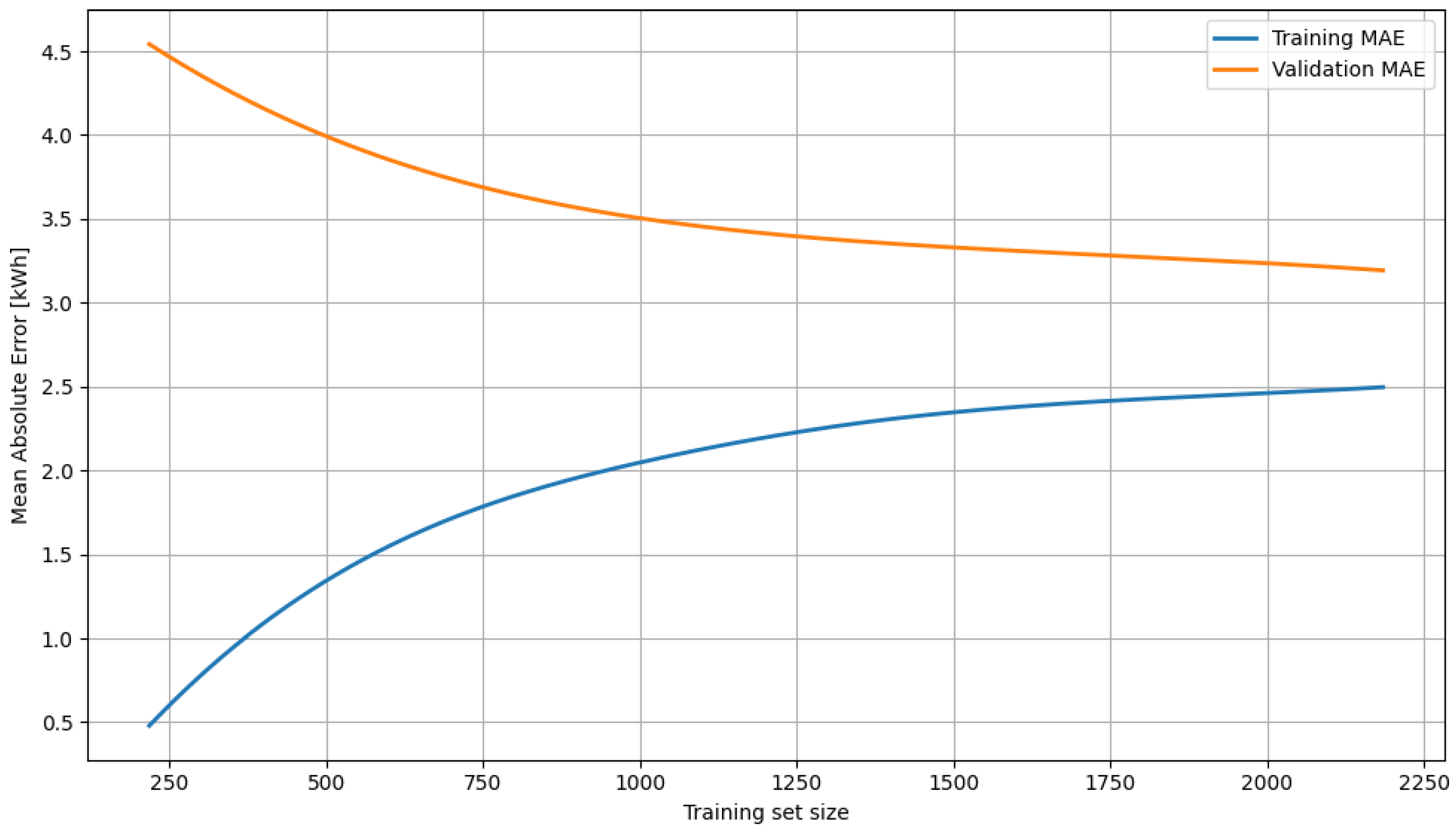
To better illustrate the behavior of the XGBoost model during the training process, a learning curve analysis was performed (Figure 4). This method allows us to assess how the prediction error changes depending on the number of training examples, both for the training and validation sets. The analysis was performed exclusively for the XGBoost model, as it achieved the best MAE and RMSE results among all tested algorithms. Furthermore, XGBoost, being a gradient-based algorithm, is more susceptible to overfitting when the training sets are small, making learning curve analysis particularly important for assessing its stability and generalization ability.
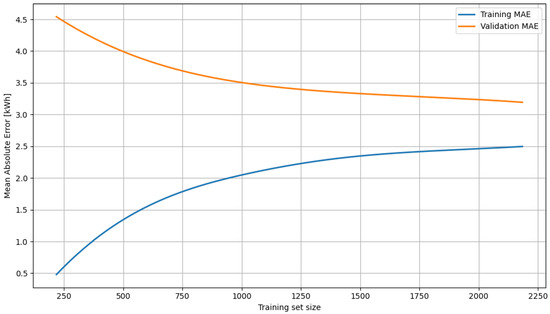
Figure 4.
XGBoost model learning curve.
As the graph shows, the MAE curve for the training set gradually increases, while for the validation set, it systematically decreases until it stabilizes. Both curves exhibit a similar tendency to converge, which is a positive sign and indicates the absence of significant overfitting or underfitting. Although the gap between training and validation error does not disappear completely, it remains within acceptable limits—in particular, the gap does not widen with larger samples. The shape of the validation curve suggests that further increases in data yield diminishing returns (the effect of diminishing returns). Nevertheless, the lack of sudden fluctuations and the relatively narrow uncertainty range confirm the model’s stability and readiness for practical application. This curve also confirms that, in the case of XGBoost, appropriate regularization and hyperparameter selection allowed for a satisfactory compromise between fit and generalization.
5. The Proposed Approach to Energy Management Using Short-Term Forecasts and Storage in the Building
5.1. Algorithm Structure
In the presented approach, energy storage management is formulated as a mathematical optimization problem, replacing the classic heuristic approach based on rigid decision rules. Instead of local, short-term decisions (e.g., “charge the battery when there is a PV surplus”), the proposed algorithm determines a globally optimal battery charging and discharging schedule within a given time horizon (e.g., 24 h), taking into account variable system operating conditions and physical constraints. This formalization of the problem allows for a more informed balancing of gains and losses throughout the entire forecast period. The objective function considers not only the energy balance but also the cost associated with battery degradation. The flow of each unit of energy through the battery (both during charging and discharging) causes its wear, which in the long term translates into a decrease in capacity and the need to replace the device. This cost is included as an additional component of the objective function, representing a “penalty” for the charge/discharge cycle, allowing for more efficient storage operation—the system avoids energy-inefficient operations that could shorten battery life while providing minimal energy gain. Additionally, the model takes into account actual energy losses associated with the charging and discharging cycle. Unlike simplified models that assume 100% efficiency, this algorithm assumes an actual round-trip efficiency of 90%, with the possibility of further limiting the allowable state-of-charge (SOC) range as efficiency deteriorates. This prevents the algorithm from repeatedly “shoveling” energy through the battery, thus reducing system losses. Another element that improves planning quality is robustness to forecast uncertainty. To this end, a Model Predictive Control (MPC) strategy with a sliding time horizon is employed. In practice, this means that the schedule determined based on forecasts is implemented only for a short time period (e.g., the next hour), after which—based on the updated data—the entire optimization problem is recalculated for the remaining period. This approach allows us to dynamically adapt the system’s operation to actual conditions, increasing resilience to forecast errors. Moreover, the algorithm can incorporate additional safety margins, such as limiting the battery’s depth of discharge during unstable weather conditions, to maintain energy reserves. A significant extension of the proposed solution is the use of a consumer energy consumption forecast. Previously, many studies assumed known or constant demand, simplifying the model but reducing its realism. This approach introduces a short-term demand forecasting module (STLF), which can be based on an independent model, such as XGBoost, an LSTM network, or classical regression methods. Knowledge of the trajectories of both the projected PV production and the consumer’s demand is crucial for the proper planning of the energy storage system’s operation—it enables an accurate prediction of moments of energy surplus and deficit and effective compensation. Incorporating a consumption forecast—even as an external module—significantly increases the algorithm’s effectiveness and usability in real-world operating conditions.
The above improvements are captured in a formal decision-making model. We formulate the energy management problem as a discrete-time optimization problem. The horizon considered in the model is one day (24 h, although it can easily be extended to a week), divided into equal time steps (e.g., h, corresponding to the resolution of available forecasts).
The main decision variable at each step t is the battery power , delivered or consumed during a given time interval. It can be modeled in two ways: (1) as a single variable taking positive values during discharging (when the battery delivers power to the load or the grid) and negative values during charging (when it draws energy from the PV surplus or the grid) or (2) by two non-negative variables, for the charging power and for the delivered power, with the additional condition that only one of them can be non-zero at a given step (the battery cannot charge and discharge simultaneously). For clarity, the second approach will be adopted. Then, the algorithm’s decisions at time t are represented by and . The system state variable is the battery state of charge (state of charge) at the beginning of each time interval t. This state is updated from step to step depending on the charging/discharging decisions made.
The optimization criterion is to minimize the total cost of energy storage operation and grid energy consumption over a given time horizon (day). The total cost consists of the following components:
- Grid energy cost—The fee for energy drawn from the grid reduced by any potential revenue from selling surplus energy to the grid. We assume a known tariff structure: denotes the purchase price of 1 kWh from the grid in period t (e.g., hourly rate, day/night tariff), while is the selling (purchasing) price of energy to the grid in the event of surplus energy (e.g., feed-in tariff). Let denote the power/energy imported from the grid in period t and denote the power exported to the grid. Then, the net cost of purchasing energy from the grid during a 24 h period iswhere t is the number of time intervals (e.g., T = 24 for a day). Minimizing is equivalent to maximizing the self-consumption of energy from one’s own PV; each kilowatt-hour consumed on-site instead of drawn from the grid reduces this cost.
- Peak cost (optional)—If a given system is subject to peak power charges (so-called demand charges, calculated, for example, based on the highest power consumption from the grid within a day or month), term can be added to the objective function, depending on the maximum value of in the horizon. The algorithm could then penalize peak consumption by implementing a peak-shaving function.
- Cyclic battery degradation cost—According to the assumptions, at each time step, a fee is charged for battery use, proportional to the amount of energy flowing through the battery. The simplest implementation is to assume a constant cost factor (expressed in [PLN/kWh]) and multiply it by the energy converted by the battery. If, by converted energy, we mean the sum of energy input to and output from the battery, then for step t, it is:
- The total cost of battery consumption over the horizon is therefore:where is a constant determined based on the estimated battery cycle cost, e.g., if the purchase cost of a battery of a given capacity is X and the lifetime is Y full cycles, then
This defined component of the objective function penalizes excessive cycling—the algorithm will minimize it, which indicates a preference for saving batteries. It is worth adding that in more advanced models, may not be constant but depend on the current battery state or the DOD (depth of discharge) cycle depth. For the purposes of this model, however, a simplified, linear dependence of the cost on the transferred energy is assumed. The final objective function of the algorithm is the sum of the above components (ignoring the possible if peak charges are not taken into account). Formally, the optimization problem can be written as
This criterion means minimizing the total daily energy cost borne by the user, taking into account battery “amortization” (costs of its consumption) and, optionally, penalties for peak consumption.
The optimization model must meet a number of constraints resulting from the physics and logic of the system:
- Microgrid power balance: At each time step, the principle of energy conservation applies—all demand must be met by available PV generation, battery operation, or import from the grid. Excess energy (when PV production exceeds the load and the battery cannot absorb any more) is exported to the grid. We model this using the following balance equation:where is the power generated by photovoltaics, and is the consumer’s demand in period t. This means that the sum of power from local sources (PV and battery in discharge mode) and any import from the grid must equal the sum of power absorbed by local loads (load and battery in charging mode) and any output to the grid. The following can be hypothesized.
- If exceeds (there is an energy surplus in the microgrid), the excess can be used to charge battery or, in the case of a full battery, exported ( will be positive, and ).
- However, if is less than (there is an energy deficit), the missing power must be drawn from the grid (with ) or—if possible—the battery can cover the deficit (by appropriately increasing the output power by ). In practice, the optimization algorithm will decide whether it is more profitable to use the stored energy or import the missing energy from the grid, taking into account tariffs and future needs.
- Battery power limitations: The charging and discharging rates are limited by the device capabilities (inverter power and battery efficiency). We introduce the maximum allowable charging power, , and the maximum discharging power, . The decision variables must satisfy
- Concurrent charging and discharging constraint: In the case of the separate modeling of and , it must be ensured that the battery is not charged and discharged simultaneously at a given moment. Formally, it is possible to introduce binary variables and and impose the conditions and . In practice, however, such restrictions are usually unnecessary—the optimal solution does not assume simultaneous charging and discharging anyway because this would only lead to energy losses (no gain from immediate energy exchange). Therefore, to simplify the model, binary decision variables defining the energy storage operating mode are omitted—it is sufficient to assume that the optimal solution always has or (except in the idle situation, when ).
- State-of-charge constraints: The battery’s state of charge SOC(t) (expressed as a percentage or fraction of its maximum capacity) must remain within an acceptable range, typicallywhere (of the order of 10–20%) prevents the battery from completely discharging, and (e.g., 90–95%) leaves a buffer and avoids extremely high state-of-charge conditions, which reduce battery efficiency and accelerate degradation. Furthermore, the dynamic change in the SOC is described by the battery state-of-charge equation. For the assumed variables and ,where is the nominal battery capacity (expressed in kWh corresponding to 100% SOC), while and are the charge and discharge efficiencies (for simplicity, we treat them as constants, e.g., ). The above equation ensures that for positive , the state of charge increases, and for positive , it decreases. The model can optionally also take into account the slow self-discharge of the battery or a reduction in available capacity with progressive degradation (e.g., a decrease in in the long run), but on a daily scale, these effects are negligible.
- Final condition: An additional requirement is often imposed on the battery state at the end of the horizon (e.g., the end of the day)—to leave a certain minimum charge level for the start of the next cycle (especially before a period without PV production, e.g., at night). If this is important, a constraint is added:where is the state of charge at the end of the day (for T = 24, if t = 1 represents the beginning of the first hour, t=24 represents the end of the last hour of the day). This condition prevents the storage from being completely discharged at the end of the optimized period—this allows the plan to preserve energy reserves for the beginning of the next day or another critical moment.
The above model is essentially a linear programming (LP) or mixed-integer programming (MILP) problem, depending on whether we introduce discrete binary variables for the operating mode or peak cost. In this form, all equations and inequalities are linear with respect to the decision variables, and the objective function is a sum of linear elements. This means that standard optimization solvers (e.g., CPLEX, Gurobi, or open-source CBC/GLPK via libraries like PuLP or Pyomo in Python (version 3.10.12)) can be successfully used to determine the optimal solution. Due to the small scale of the problem (24 periods, several dozen continuous variables, and possibly 24 binary variables if we include the operating mode in each step), the computations are very fast—finding the optimum takes a fraction of a second on a standard computer.
Alternatively, the problem can be treated as a dynamic optimization problem and solved using dynamic programming (DP). In DP, the state would be SOC(t) (the charge levels would need to be discretized, e.g., every 1% of capacity), and the action would be the choice of charge/discharge power at a given step. Using Bellman recursion, one can iteratively, step by step, determine the minimum cost from a given state to the end of the horizon. DP methods are very well suited for battery optimization problems, allowing for the natural inclusion of nonlinearities (e.g., if we wanted to more accurately model degradation dependent on cycle depth or efficiency dependent on current/SOC). The disadvantage of DP is the potential increase in computational time with higher state resolution, but at a daily scale and moderate discretization (e.g., 100 SOC levels), this can still be calculated in less than a minute. Furthermore, DP guarantees finding the global optimum (for the discretized problem) and can generate so-called control policy—i.e., the cost function depending on the state—which enables flexible online control (the agent can make decisions on the fly depending on the current SOC, using a previously calculated strategy).
The proposed algorithm, despite its increased complexity compared to simpler rules, is fully feasible in practice. It contains all the elements necessary for implementation in a PV + BESS micro-installation control system. The practical implementation is as follows:
- Forecast module—The first step requires obtaining forecasts of basic values for the following day. As intended, a daily PV generation forecast model is used (e.g., the previously implemented XGBoost model, trained on solar irradiance and generation data). A load forecast module is added to this—e.g., a similar machine learning model trained on consumer energy consumption data, or in the absence of historical data, an approximate typical profile is used (e.g., an average consumption pattern is assumed throughout the day). The output of the forecast module is two 24 h vectors (for subsequent hours of the day), for t = 1…24 and for t = 1…24, representing the projected PV generation and consumer demand.
- Formulating and solving the optimization problem—Given the predictive data, the algorithm formulates the problem described in the previous sections in mathematical form. In practice, this can be implemented, for example, in Python using a library like PuLP/Pyomo or a solver interface (Gurobi, CPLEX, etc.). One must declare the decision variables , add the described constraints (power balance, battery constraints, updating SOC, etc.), and define the objective function to minimize. This is relatively simple in code—for example, in PuLP, one can use a loop over t to generate iterative constraints. The model prepared this way is passed to the linear/MILP solver, which calculates the solution—which, as mentioned, takes a fraction of a second. Alternatively, you can implement the dynamic programming described above: for example, create a cost table DP[time][SOC] and, also in a loop (from t = 1…24), calculate the minimum cost of achieving a given state, based on the costs from the previous step. This second method requires slightly more code and prior discretization of the SOC, but it is also feasible and can serve as an independent validation of the optimization result.
- Once the algorithm is implemented, it can be used in a real energy management system in model predictive control (MPC) mode. A key element is the forecast module, based on a trained XGBoost model, which predicts PV production and—in conjunction with the load model—the customer’s demand for the next 24 h. Based on these forecasts, the algorithm determines the optimal battery operation plan. The algorithm runs cyclically—for example, once a day and hourly. Once a day, for example, in the evening, when the forecasts for the following day are known, the battery charging and discharging plan for the entire 24 h is calculated. Then, during the day, the algorithm updates this plan hourly using new data and a shortened optimization horizon. After each hour, actual data and new forecasts (also updated by XGBoost) are known. Based on these data, the algorithm re-solves the decision problem and adapts the system’s operation to current conditions. Thanks to the short computation time, such an implementation is possible in real time. In practice, many SCADA systems operate in a similar manner, regularly refreshing decisions at predetermined intervals, for example, hourly.
5.2. Proposed Indicators for Assessing the Performance of the Decision Algorithm
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed energy management algorithm in the PV-BESS system, a new set of evaluation metrics was developed. These metrics consider not only technical and economic aspects but also operational aspects, such as the stability of decision-making and the risk of overloading system resources. Unlike traditional evaluation methods, which focus primarily on self-consumption or energy costs, the proposed metrics also consider important practical phenomena, such as battery degradation, operating strategy variability, and demand mismatch. These metrics were designed to evaluate the performance of a predictive–corrective (MPC) algorithm operating on real-world data. They allow not only for a detailed analysis of the algorithm’s performance under various conditions but also for a comparison with reference approaches (e.g., rule-based approaches) and the identification of its limitations. This work proposes five new quantitative metrics that enable a comprehensive assessment of the algorithm’s performance in terms of efficiency, stability, and operational security:
- RCD (Reduction in Cycling Degradation)—This indicator indicates the extent to which the algorithm limits battery wear, which translates into longer battery life. The higher the RCD, the fewer cycles the battery uses compared to the reference strategy.
- where is the number of full battery cycles (charge/discharge) in the analyzed period for the algorithm and is the number of complete cycles in the reference strategy (e.g., without optimization).
- DER (Dynamic Energy Response)—This determines the intensity and variability of battery operation, meaning how rapidly power changes over time. A high DER can indicate operation with significant fluctuations, which can impact the durability of the converters and the entire system.
- where is the battery power (positive means charging and negative means discharging) at time t, is the maximum permissible battery power, and T is the number of time steps (e.g., hours).
- RSLs (Relative System Losses)—This indicator indicates how much of the energy produced was not used locally or was lost due to system limitations. A value close to 0 indicates high energy efficiency.
- where means unused energy (e.g., excess production exported to the grid without local consumption) and means całkowita energia wyprodukowana przez PV w analizowanym okresie.
- CES (Correction Efficiency Score)—measures the consistency between the algorithm’s plan and the actual energy storage operation, which is especially important when forecasts are subject to error. A high CES indicates that the algorithm is effectively compensating for forecast uncertainty.
- where indicates the actual battery charge state at time t, indicates the state planned by the algorithm at time t, and is the nominal battery capacity.
- SCD (Stability of Cost Decisions)—This measures the variability of operating costs over time, which is of direct importance to the end user—predictable bills make it easier to manage the budget and assess profitability.
- where is the cost of purchasing energy on day d, is the average daily cost in the analyzed period, and D is the number of days.
5.3. An Analysis of the Implementation of the Algorithm for the Analyzed Building
To verify the effectiveness of the developed algorithm, simulations were conducted for actual electricity production and consumption data in a building equipped with a 38.25 kWp photovoltaic installation and a 50 kWh energy storage device. The aim of the simulations was to compare the efficiency of energy management between three scenarios: (A) a system using an energy storage device with an implemented decision-making algorithm; (B) a system with a storage device but without advanced control, based on a simple rule of charging in the event of excess PV and discharging in the event of deficiency; and (C) a baseline scenario in which the energy produced by the PV system was consumed directly or exported to the grid without the possibility of accumulation.
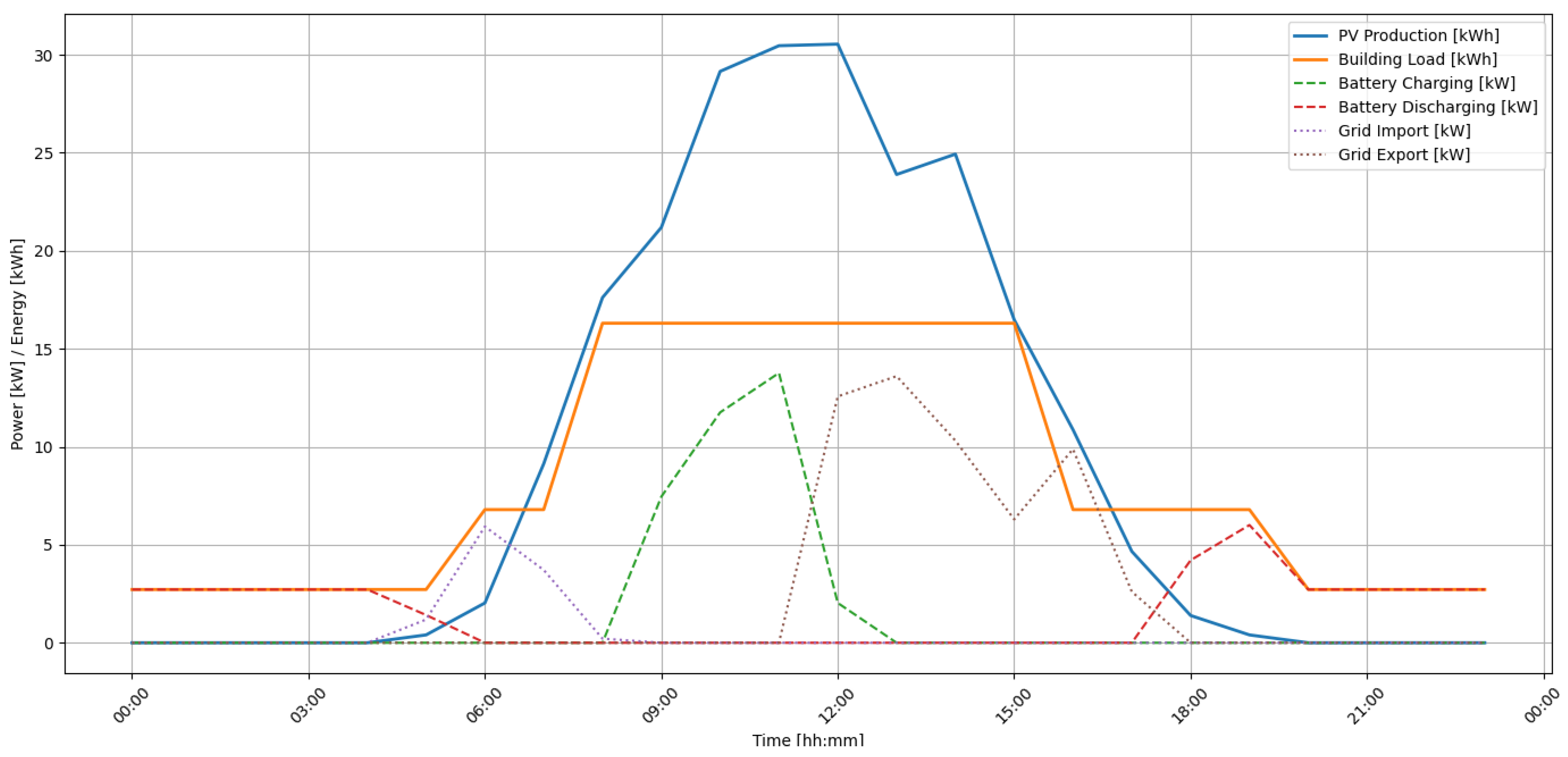
To illustrate the actual operation of the proposed energy management algorithm in a PV-BESS system, a graph for a typical day is presented in Figure 5. The graph shows hourly energy flows in the photovoltaic system with an energy storage system and the power grid. The graph includes six key signals: PV production, building demand, energy storage charging and discharging power, import from the grid, and export to the grid.
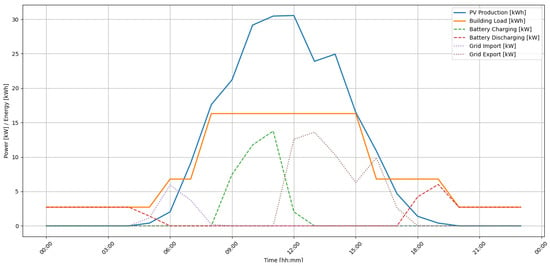
Figure 5.
The energy flow profile in the analyzed PV-BESS system.
An analysis of the graph indicates that energy production from the PV source begins around 6:00 AM, peaks between 11:00 AM and 1:00 PM, and then gradually declines. During peak production hours (between 9:00 AM and 12:00 PM), intensive battery charging is observed (the green dashed line), indicating the effective use of surplus energy for self-consumption in the future. After 6:00 PM, when production drops to zero, the battery enters discharging mode (the red dashed line), helping to meet the building’s evening demand. It is also worth noting the relatively low level of energy import from the grid (the purple dashed line), which occurs only during the morning hours, confirming the algorithm’s effectiveness in minimizing grid dependence. Energy export (the brown dashed line) occurs only after the battery is fully charged and the building’s current demand is met, indicating that self-consumption is prioritized. The whole thing illustrates the dynamic and adaptive operation of the algorithm, which strives to optimize both energy consumption and the use of available storage resources.
The results of the analysis of individual scenarios revealed significant differences in the structure of the energy balance and the economic potential of the system. In scenario A, 76% of the energy consumed in the building came from local sources (PV and battery), while energy import from the grid was limited to 24%. In scenario B, in the absence of prediction and optimization, the auto-consumption rate was lower at 64%, and the share of imported energy increased to 36%. In scenario C, where the lack of storage prevents the retention of surpluses, only 52% of demand was met locally, while 48% had to be purchased from the grid. At the same time, in scenario A, only 21% of the PV energy was exported, compared to 29% in scenario B, and 60% in the absence of storage. This means that the use of the algorithm not only reduced energy purchase costs but also allowed for more selective energy export to the grid, generating additional revenue. Taking into account both savings from self-consumption and revenues from energy export, variant A allows for the largest reduction in energy expenditure—by 39% compared to the baseline scenario (variant C) and by 21% compared to variant B. These results confirm the validity of using predictive energy management algorithms in PV-BESS systems, even with moderate storage capacity, as an effective tool for increasing energy efficiency and investment profitability.
To quantitatively evaluate the performance of the developed MPC algorithm, five indicators were determined to characterize its impact on battery consumption, control quality, and the system’s energy and economic balance. The RCD (Reduction in Cycling Degradation) index value was 0.222, meaning that the number of full battery charge and discharge cycles was reduced by over 22% compared to the reference strategy. This effect indicates that the algorithm effectively limits the intensity of battery use, which can translate into longer battery life and reduced operating costs. In turn, the low level of charge and discharge power variability, reflected by the DER (Dynamic Energy Response) index of 0.23, confirms that the predictive strategy avoided abrupt transitions between operating modes, thereby improving inverter stability and reducing losses. The Relative System Loss (RSL) index reached 0.238, meaning that approximately 24% of the energy produced by the PV system was not consumed locally but fed into the grid—partially with financial benefits, but with limited self-consumption efficiency. The high Correction Efficiency Score (CES) of 0.984 indicates very good agreement between the planned and actual battery state of charge, confirming both the high quality of the forecast and the precision of the MPC algorithm. The final index, Stability of Cost Decisions (SCD), reached 0.34, suggesting a relatively stable and predictable energy cost profile. All these results demonstrate that the use of a predictive control algorithm contributes to the improved operational, energy, and economic efficiency of the PV-BESS system.
6. Conclusions
This article analyzes the use of machine learning models for the short-term forecasting of energy production in a photovoltaic system installed on a real facility. A detailed assessment of three predictive models—linear regression, Random Forest, and XGBoost—demonstrated a clear advantage of the XGBoost algorithm in terms of both accuracy and forecast stability. The XGBoost model achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.25 kWh, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.93 kWh, and a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.94. These values represent a significant improvement compared to Random Forest (MAE = 2.14 kWh, RMSE = 3.23 kWh, and R2 = 0.83) and linear regression (MAE = 3.65 kWh, RMSE = 5.14 kWh, and R2 = 0.58). This confirms that XGBoost better captures the nature of hourly fluctuations in energy generation, particularly during periods of intensive solar radiation. The consistently high R2 value, persisting above 0.9 for periods of non-zero production, further supports the applicability of this model in real operational environments. The applied assessment methodology was adapted to practical conditions—only periods in which the PV generation actually occur—which allowed us to eliminate interference resulting from night hours or periods of zero production. This approach reflects real engineering requirements in which the quality of prediction must be assessed from the point of view of its operational usefulness. The results also indicate that the quality of forecasts is clearly dependent on the time of day—the greatest accuracy was obtained in the afternoon hours, while the greatest relative errors were recorded in the morning and afternoon, which can be associated with greater variability of local weather conditions.
The analyzed models differed not only in accuracy but also resistance to forecasting errors with low energy production. The linear regression model, despite the simplicity of implementation, showed limited adaptability to non-linear relationships between meteorological variables and PV production, which resulted in very high map values, exceeding the operational acceptability thresholds. The Random Forest model achieved indirect results, but it clearly gave way to the XGBoost in terms of the precision of mapping extreme values and dynamics of production. XGBoost can be considered the most promising model due to its high accuracy and computational efficiency, which makes it a potential candidate for future integration into energy management systems.
As part of this work, a predictive energy management algorithm was developed for a PV-BESS system, which takes into account forecasted photovoltaic production when making decisions about charging and discharging the storage device. This solution allows for the conscious planning of energy flows in advance, instead of making local, momentary decisions. The tests demonstrated that the proposed algorithm effectively controls system operation, leading to reduced battery degradation, stabilized power consumption, and improved self-consumption rates. Compared to reference variants—both without the storage device and with simple rule-based control—the algorithm demonstrated improved operational properties. Thanks to its transparent structure and moderate complexity, it can be successfully implemented in real-world prosumer installations without the need for advanced SCADA systems. Despite the high effectiveness of the presented approach, pay attention to several potential restrictions. First of all, the quality of prediction strongly depends on the accuracy of the input data, in particular, meteorological forecasts. Secondly, the model does not include possible anomalies in the operation of PV installations, such as dynamic shading, equipment failures or the dirt of panels. Thirdly, the error records used, although widely accepted, do not always fully reflect the impact of the error of the forecast on real operational decisions, which can be important in commercial or system applications.
Therefore, future research should focus on expanding the scope of predictions with other significant variables, such as energy consumption forecast, variable dynamic tariffs or local network load forecasts. An interesting direction may also be the integration of predictive models with demand management systems and with algorithms for controlling energy resources in real time. It is also worth considering comparing the XGBoost approach with sequential models such as LSTM, which can better map the continuity and time dependencies characteristic of energy data.
It is important to emphasize that all analyses were conducted based on data from a single, carefully monitored PV installation with a capacity of 38.25 kWp located in Rzeszow. While this limits the generalizability of the results to other locations, systems, or climatic conditions, it also ensures full control over the quality and consistency of the measurement data. This allowed for a detailed comparative analysis of the forecasting models in a realistic operating scenario. However, the authors recognize the need to expand the research to other installation types and locations in the future, which would allow for a more comprehensive assessment of the models’ effectiveness in various climatic and geographical conditions.
To sum up, this study confirms the effectiveness of selected machine learning models in the context of forecasting PV energy in real conditions. In particular, the XGBoost model is distinguished by its high-quality prediction and universality of applications, which makes it a useful tool in modern energy management strategies in buildings.
Author Contributions
P.-Methodology, P.K. and K.P.-U.; validation, P.K. and K.P.-U.; formal analysis, P.K. and K.P.-U.; investigation, P.K.; resources, P.K.; data curation, P.K.; writing—original draft preparation, P.K.; writing—review and editing, K.P.-U.; supervision, K.P.-U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Goop, J.; Nyholm, E.; Odenberger, M.; Johnsson, F. Impact of Electricity Market Feedback on Investments in Solar Photovoltaic and Battery Systems in Swedish Single-Family Dwellings. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparisi-Cerdá, I.; Ribó-Pérez, D.; García-Melón, M.; D’Este, P.; Poveda-Bautista, R. Drivers and Barriers to the Adoption of Decentralised Renewable Energy Technologies: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Energy 2024, 305, 132264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish kumar, S.; Pramila, V.; Rudhra, S.; Vinod, S.; Lakshmi, D. Enhancing Demand Response and Energy Management in Multi- Microgrid Systems with Renewable Energy Sources. Renew. Energy 2025, 253, 123490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igliński, B.; Pietrzak, M.B. Renewable and Sustainable Energy—Current State and Prospects. Energies 2025, 18, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, M.; Igliński, B.; Kujawski, W.; Iwański, P. Energy Transition in Poland—Assessment of the Renewable Energy Sector. Energies 2021, 14, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheba, K.; Bąk, I.; Pietrzak, M.B. Conditions of The Green Transformation. The Case of The European Union. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2022, 29, 438–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerzak, A.; Uddin, G.S.; Dutta, A.; Pietrzak, M.B.; Igliński, B. Energy Mix Management: A New Look at the Utilization of Renewable Sources from the Perspective of the Global Energy Transition. Equilibrium. Q. J. Econ. Econ. Policy 2024, 19, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kut, P.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B. Reliability-Oriented Design of a Solar-PV Deployments. Energies 2021, 14, 6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabczak, S.; Mateichyk, V.; Smieszek, M.; Nowak, K.; Kolomiiets, S. Evaluating the Energy Efficiency of Combining Heat Pumps and Photovoltaic Panels in Eco-Friendly Housing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, R.; Dong, Y.; Hou, J. Feasibility and Challenges of Quantum Dot Solar Cells in Urban Renewal Photovoltaic Buildings. Sol. Energy 2025, 298, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, C.V.; Ngagoum Ndalloka, Z.; Kośny, J. Transforming Urban Energy: Developments and Challenges in Photovoltaic Integration. Front. Sustain. Cities 2025, 7, 1584917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, A.K.; Neven-du Mont, S.; Nikitina, V.; Romer, P.; von Kutzleben, D.; Latif, N.A.; Forster, J.; Wellens, C.; Heinrich, M.; Neuhaus, D.H. Pushing the Boundaries: Challenges That Arise in Manufacturing and Designing Photovoltaic Modules for New Application Areas. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2025, 291, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, S.; Olabi, A.G.; Mahmoud, M. A Review of Solar Photovoltaic Technologies: Developments, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2025, 27, 101057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A.; Maghami, M.R. Harnessing Photovoltaic Innovation: Advancements, Challenges, and Strategic Pathways for Sustainable Global Development. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2025, 27, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.T.; Sepúlveda, F.J.; Fernández, A.; Arranz, J.I.; Montero, I. Analysis of Photovoltaic Self-Consumption as a Function of the Demand Profile in Detached Houses. Energy Build. 2024, 316, 114375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalcazar, P.; Andrade, C.; Guamán, W. Prosumer Policy Options in Developing Countries: A Comparative Analysis of Feed-in Tariffs, Net Metering, and Net Billing for Residential PV-Battery Systems. Polityka Energetyczna Energy Policy J. 2025, 28, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalcazar, P.; Kalka, M.; Kamiński, J. Transitioning from Net-Metering to Net-Billing: A Model-Based Analysis for Poland. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 72, 104073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, K.J. Profitability Analysis of a Prosumer Photovoltaic Installation in Light of Changing Electricity Billing Regulations in Poland. Energies 2024, 17, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, M.; d’Obyrn, J.; Sołowiej, P. Economic Analysis of Profitability of Using Energy Storage with Photovoltaic Installation in Conditions of Northeast Poland. Energies 2024, 17, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSharabi, K.; Bin Salamah, Y.; Aljalal, M.; Abdurraqeeb, A.M.; Alturki, F.A. Long-Term Forecasting of Solar Irradiation in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, Using Machine Learning Techniques. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz May, E.; Ricalde, L.J.; Atoche, E.J.R.; Bassam, A.; Sanchez, E.N. Forecast and Energy Management of a Microgrid with Renewable Energy Sources Using Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Systems, London, UK, 10–12 July 2018; Brito-Loeza, C., Espinosa-Romero, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gaamouche, R.; Chinnici, M.; Lahby, M.; Abakarim, Y.; Hasnaoui, A.E. Machine Learning Techniques for Renewable Energy Forecasting: A Comprehensive Review. In Computational Intelligence Techniques for Green Smart Cities; Lahby, M., Al-Fuqaha, A., Maleh, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 3–39. ISBN 978-3-030-96429-0. [Google Scholar]
- Voyant, C.; Notton, G.; Kalogirou, S.; Nivet, M.-L.; Paoli, C.; Motte, F.; Fouilloy, A. Machine Learning Methods for Solar Radiation Forecasting: A Review. Renew. Energy 2017, 105, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kleissl, J.; Gueymard, C.A.; Pedro, H.T.C.; Coimbra, C.F.M. History and Trends in Solar Irradiance and PV Power Forecasting: A Preliminary Assessment and Review Using Text Mining. Sol. Energy 2018, 168, 60–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Pagliantini, C. Forecasting Electricity Demand in Renewable-Integrated Systems: A Case Study from Italy Using Recurrent Neural Networks. Electricity 2025, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Su, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Zou, L.; Song, J. A Hybrid Framework for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using Shifted Windows Transformer-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction. Energies 2025, 18, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, Z.; He, D.; Chen, J. Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecasting Based on Secondary Data Decomposition and Hybrid Deep Learning Model. Energies 2025, 18, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Niu, G. Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using a Bi-LSTM Neural Network Optimized by Hybrid Algorithms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Hurtado, I.; Gómez-Sarduy, J.R.; García-Sánchez, Z.; Hernández-Herrera, H.; Silva-Ortega, J.I.; Reyes-Calvo, R. Advanced Multivariate Models Incorporating Non-Climatic Exogenous Variables for Very Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Electricity 2025, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, T.; Fu, H.; Liang, M.; Zhang, S. Robust Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Model Under Complex Meteorological Conditions. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; You, Z.; Jia, A. Research on Ultra-Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using Multimodal Data and Ensemble Learning. Energy 2025, 330, 136831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoortere, J.; Driesen, J.; Suykens, J.; Kazmi, H.S. SolNet: Open-Source Deep Learning Models for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting across the Globe. Int. J. Forecast. 2025, 41, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, L.; Su, T.; Pan, M. An Embedded Spatiotemporal Hybrid Model Integrating Multi-Graphs and Attention-Driven Fusion for Single- and Multi-Site Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 336, 119897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Yu, B.; Yu, Y. Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based on an Improved Zebra Optimization Algorithm—Stochastic Configuration Network. Sensors 2025, 25, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gai, M. PV-MLP: A Lightweight Patch-Based Multi-Layer Perceptron Network with Time–Frequency Domain Fusion for Accurate Long-Sequence Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Renew. Energy 2025, 251, 123277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Geng, H.; Zhang, H. Multi-Step Power Forecasting Method for Distributed Photovoltaic (PV) Stations Based on Multimodal Model. Sol. Energy 2025, 298, 113572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Cacho, A.; Sanchez-Barroso, G.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.; Garcia-Sanz-Calcedo, J. Long-Term Power Forecasting of Photovoltaic Plants Using Artificial Neural Networks. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, R.; Fulginei, F.R.; Quercio, M.; Mahrouch, A. Artificial Neural Networks for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting: A Review of Five Promising Models. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 90461–90485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaravel, G.; Kirthiga, S.; Shekaili, M.M.H.A.; Othmani, Q.H.S.A.A. A Solar Photovoltaic Performance Monitoring and Statistical Forecasting Model Using a Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Neural Network and Artificial Intelligence. Baghdad Sci. J. 2024, 21, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Lu, W.; Li, W.; Wang, S. Forecasting the Temperature of a Building-Integrated Photovoltaic Panel Equipped with Phase Change Material Using Artificial Neural Network. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 57, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H. Simulation and Forecasting of Power by Energy Harvesting Method in Photovoltaic Panels Using Artificial Neural Network. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 120017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapundzhi, F.; Chikalov, A.; Georgiev, S.; Georgiev, I. Predictive Modeling of Photovoltaic Energy Yield Using an ARIMA Approach. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardianto, F.; Ermatita, E.; Sofijan, A. Photovoltaic Fault Detection in Remote Areas Using Fuzzy-Based Multiple Linear Regression (FMLR). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2025, 16, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, Y.; Baquedano, W.; Loo, L. Profitability Prospects for Residential Photovoltaic Installations in Honduras under Foggy Conditions: A Machine Learning Approach to Photovoltaic Production Prediction Using Sarima and Linear Regression. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Latin American Conference on Computational Intelligence (LA-CCI), Bogota, Colombia, 13–15 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yan, B.; Chen, G. Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mountainous Area: Environmental Impacts Analysis Based on Random Forest Algorithm. Renew. Energy 2025, 254, 123670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Pan, G.; Liang, C.; Lin, B.; Yu, O. Research on Output Prediction Method of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Gradient-Boosting Decision Trees. Processes 2025, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Bello, D.; Vargas-Salgado, C.; Alcazar-Ortega, M.; Alfonso-Solar, D. Optimizing Photovoltaic Power Plant Forecasting with Dynamic Neural Network Structure Refinement. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Rural Distributed Photovoltaic Spatial Generation Forecasting Based on Graph Convolutional Neural Networks with Temporal-Spatial Correlation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Clean and Green Energy Solutions: ICCGE 2024 Proceedings, Harbin, China, 16 August 2024; Muyeen, S.M., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Zhou, G.; Yao, P.; Dong, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, D. Deep Multi-Attribute Spatial–Temporal Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network-Based Multivariable Spatial–Temporal Information Fusion for Short-Term Probabilistic Forecast of Multi-Site Photovoltaic Power. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 279, 127458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J. A Short-Term Forecasting Method for Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on the TCN-ECANet-GRU Hybrid Model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Mahmood, H. Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using an LSTM Neural Network and Synthetic Weather Forecast. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172524–172533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, D. Deep Attention ConvLSTM-Based Adaptive Fusion of Clear-Sky Physical Prior Knowledge and Multivariable Historical Information for Probabilistic Prediction of Photovoltaic Power. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).