Impact of Farm Biogas Plant Auxiliary Equipment on Electrical Power Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Agricultural Biogas Plants Studied
2.2. Analyzed Parameters of Electricity Quality
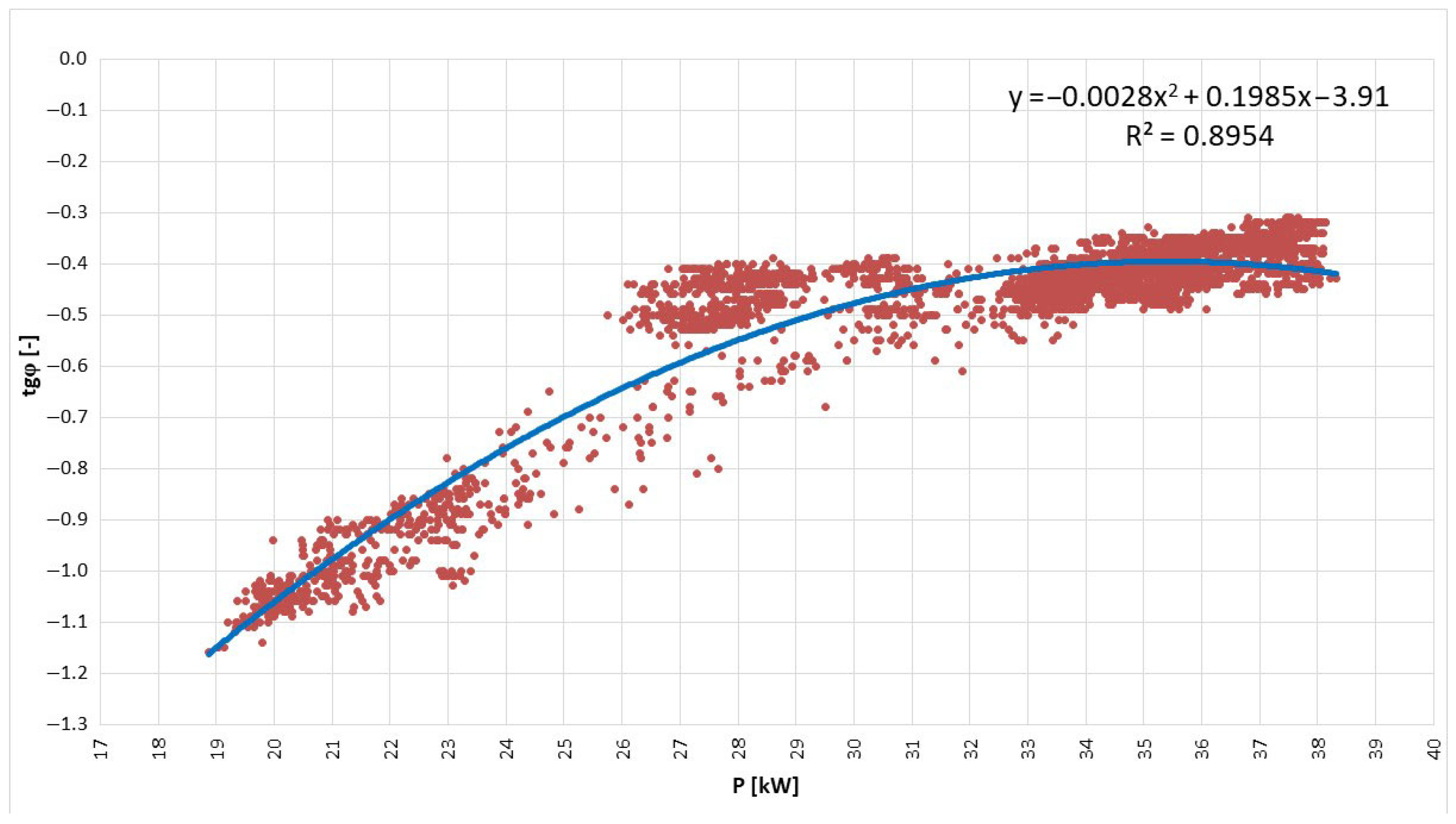
- The power factor (tg φ) should range from 0 to 0.4 and be inductive, calculated from the following relationship:where Q-reactive power is represented by [var], and P-active power is [W].
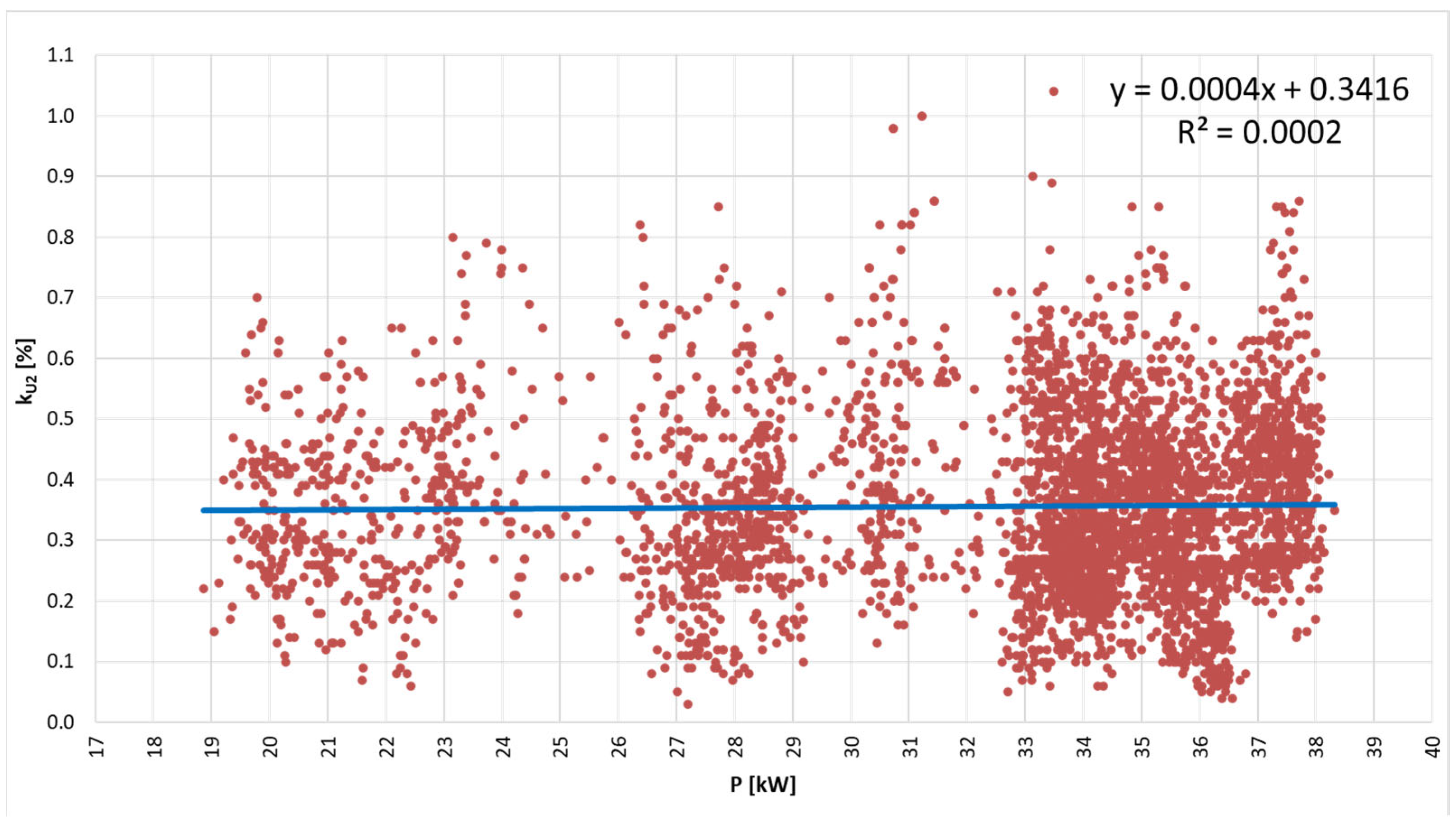
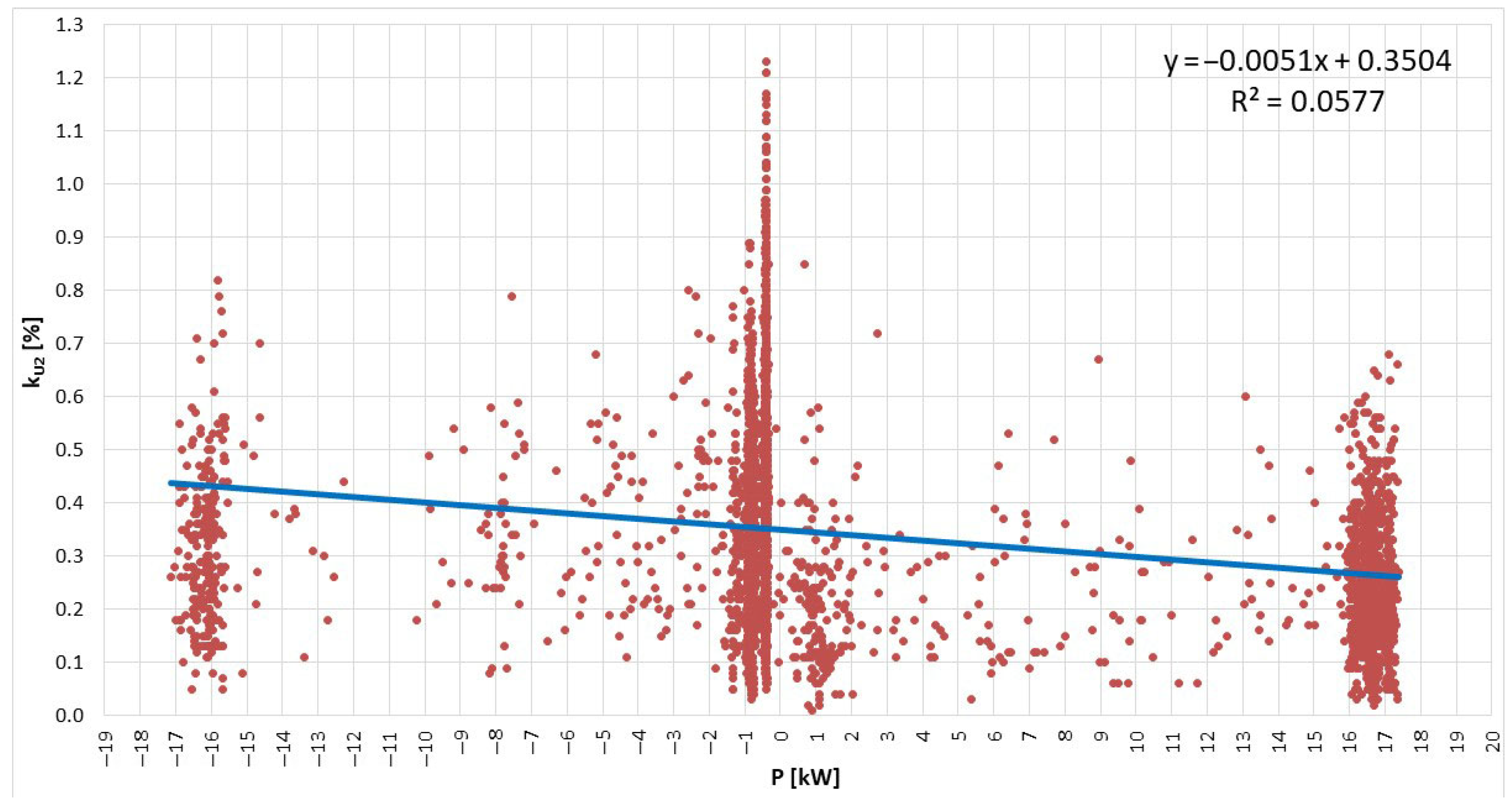
- Voltage asymmetry. The inequality of voltage values between successive phase voltages is described by the voltage asymmetry factor (it should not exceed 2%) [39]:where U1 is the composite value of the symmetrical components of the compatible voltage order [V], and U2 is the composite value of the symmetrical components of the opposite voltage order [V].
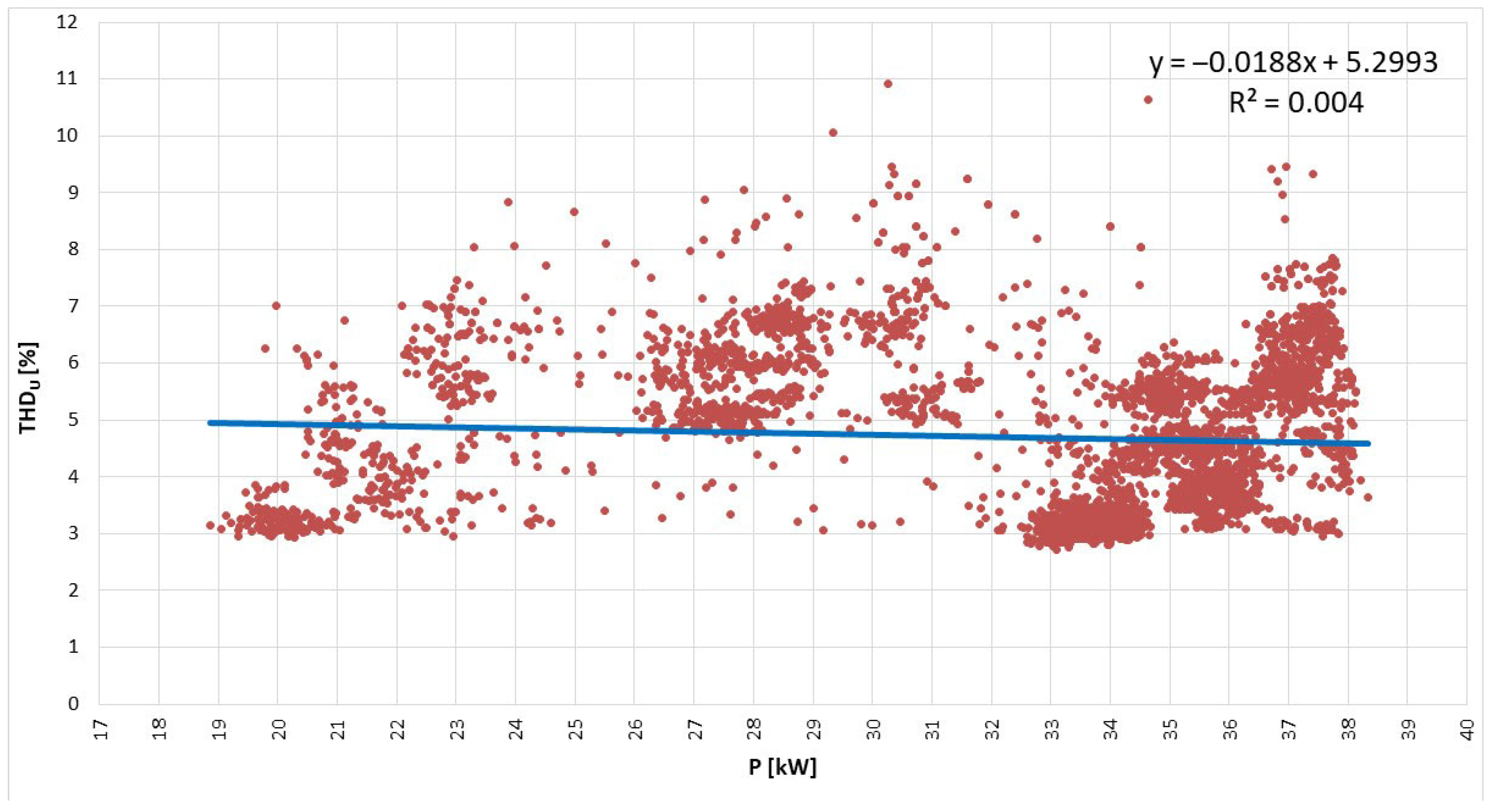
- Voltage distortion of voltage and current waveforms, defined by the total harmonic distortion factor (THDU in low-voltage networks should not exceed 8%), is described as the percentage ratio of the rms value of the higher voltage harmonics to the rms value of the fundamental harmonic [40]:where Uh is the rms voltage for the h-th harmonic [V], U1 is the rms voltage for the first harmonic [V], and h is the harmonic order.
- The distortion of the current waveform is defined by the total harmonic distortion factor (THDI in low-voltage networks is not normalized), which defines the percentage ratio of the rms value of the higher harmonics of the current to the rms value of the fundamental harmonic [40]:where Ih is the rms value of current for the h-th harmonic [A], I1 is the rms value of the current for the first harmonic [A], and h is the harmonic order.
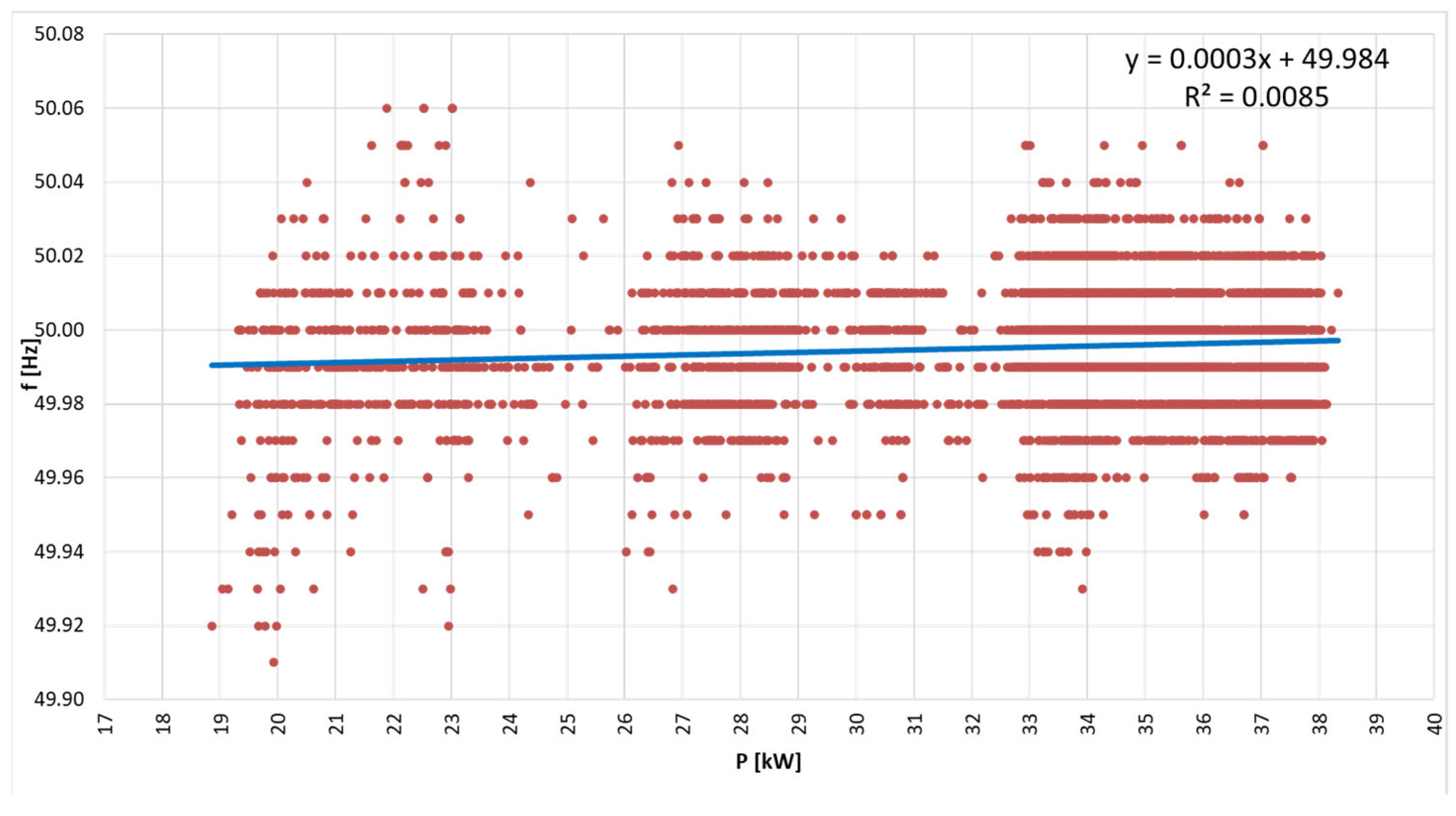
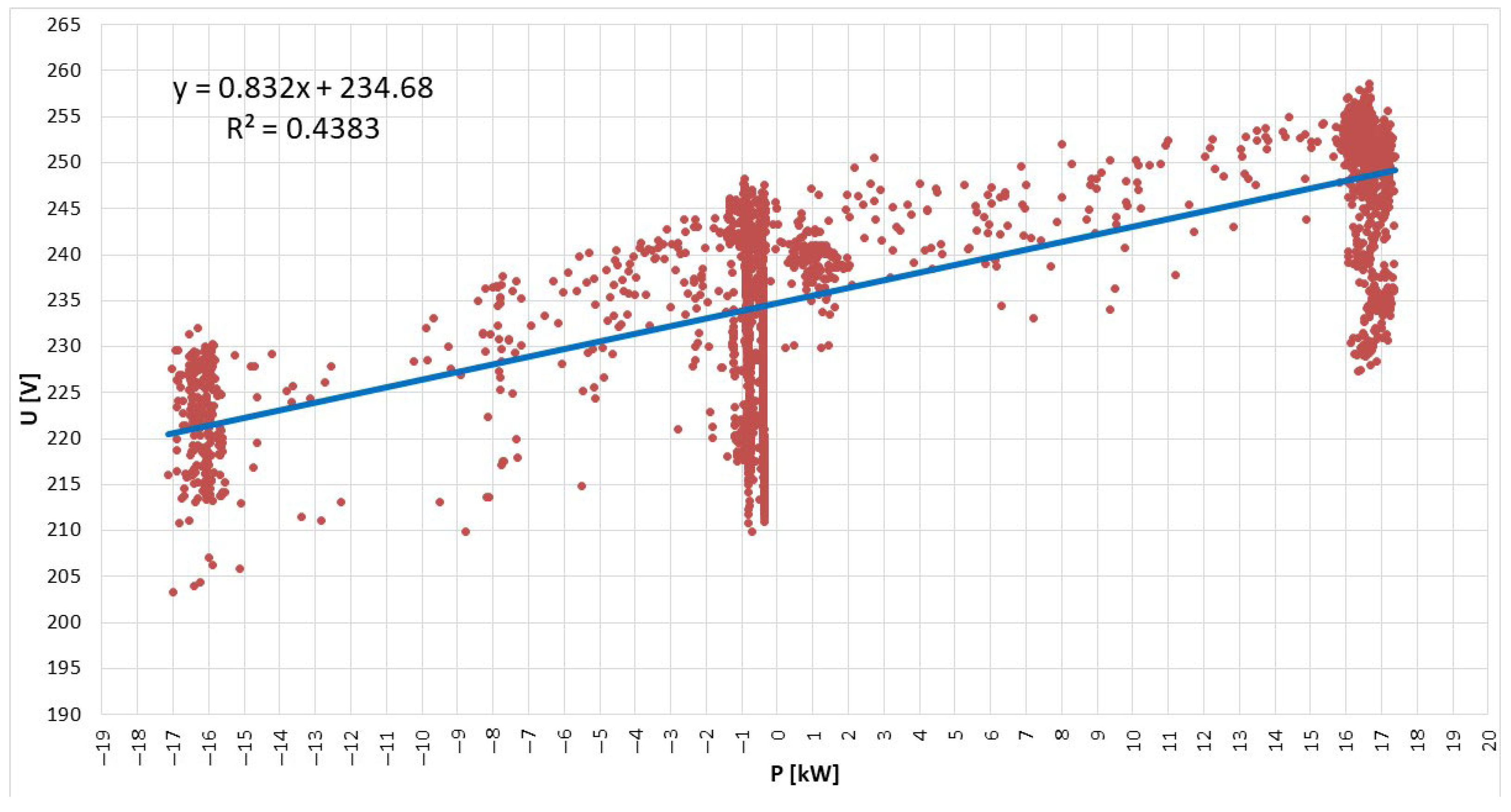
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Hafeez, M.; Ullah, S.; Sohail, M.T. How does natural resource depletion affect energy security risk? New insights from major energy-consuming countries. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 54, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Sustainable Energy Transition for Renewable and Low-Carbon Grid Electricity Generation and Supply. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 743114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, M.; Lyu, D.; Nazari, M.; Shah, A.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Biomass for a sustainable bioeconomy: An overview of world biomass production and utilisation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baasch, S. Energy transition with biomass residues and waste: Regional-scale potential and conflicts. A case study from North Hesse, Germany. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2021, 23, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Le, C.F.; Lam, S.S.; Chee, C.S.C.; Ooi, M.S.L.; Show, P.L. Sustainable utilisation of biowaste compost for renewable energy and soil amendments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, M.F.D.; Andiappan, V.; Lee, J.-Y.; Tan, R.R. Increasing the reliability of bioenergy parks utilising agricultural waste feedstock under demand uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, M.; Komorowska, M.; Atilgan, A.; Abduvasikov, A. Labelling the Carbon Footprint as a Strategic Element of Enviro-mental Assessment of Agricultural Systems. Agric. Eng. 2024, 28, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derehajło, S.; Tymińska, M.; Skibko, Z.; Borusiewicz, A.; Romaniuk, W.; Kuboń, M.; Olech, E.; Koszel, M. Heavy Metal Content in Substrates in Agricultural Biogas Plants. Agric. Eng. 2023, 27, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, Y.; Masron, T.A.; Azman, N.H.N. Biofuels, environmental sustainability, and food security: A review of 51 countries. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 68, 101549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M. Possibility of utilising agriculture biomass as a renewable and sustainable future energy source. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08905. Available online: https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(22)00193-1#au1 (accessed on 5 March 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Pant, M.; Pant, G.; Kumar, G. Second-Generation Biofuels: Concepts, Applications, and Challenges. In Microbial Applications for Environmental Sustainability; Karnwal, A., Mohammad Said Al-Tawaha, A.R., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Xue, S.; Liu, L.; Lvy, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, G. Coupling biochar with anaerobic digestion in a circular economy perspective: A promising way to promote sustainable energy, environment, and agriculture development in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymińska, M.; Skibko, Z.; Borusiewicz, A. The Effect of Agricultural Biogas Plants on the Quality of Farm Energy Supply. Energies 2023, 16, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadirli, G.; Pilarska, A.A.; Dach, J.; Pilarski, K.; Kolasa-Więcek, A.; Borowiak, K. Fundamentals, Operation and Global Prospects for the Development of Biogas Plants-A Review. Energies 2024, 17, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzodinma, E.O.U.; Ofoefule, A.U.; Eze, J.I.; Onwuka, N.D. Optimum Mesophilic Temperature of Biogas Production from Blends of Agro-Based Wastes. Trends Appl. Sci. Res. 2007, 2, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of Temperature on Biogas Production Efficiency and Microbial Community in a Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion System. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyjak-Wojciechowska, M. Proper Mixing Is a Challenge, Now Environment. 2 April 2024. Available online: https://www.teraz-srodowisko.pl/publikacje/biogaz-biometan-insight-Polska-2024/teraz-srodowisko-publikacja-biogaz-biometan-insight-Polska-2024.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Grzybek, A. Biogas Plants as an Opportunity for Agriculture for the Environment; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development: Warsaw, Poland, 2013; p. 37. ISBN 978-83-937363-0-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmer, A.; Naegele, H.-J.; Sondermann, J. How Efficient are Agitators in Biogas Digesters? Determination of the Efficiency of Submersible Motor Mixers and Incline Agitators by Measuring Nutrient Distribution in Full-Scale Agricultural Biogas Digesters. Energies 2013, 6, 6255–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowin, K. Technological Solutions for a ‘Universal’ Biogas Plant. Czysta Energia, no. 3. 2017. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-f1a6da9b-a6a8-4750-a7a6-2a3e11d3ff3a (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Skibko, Z.; Borusiewicz, A.; Romaniuk, W.; Pietruszynska, M.; Milewska, A.; Marczuk, A. Voltage Problems on Farms with Agricultural Biogas Plants-A Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatter, P. The Engineering Hydrodynamics of Viscoplastic Suspensions. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboń, M.; Skibko, Z.; Borusiewicz, A.; Romaniuk, W.; St. Gajda, J.; Kłosowska, O.; Wasąg, Z. Influence of the Parameters of an Agricultural Biogas Plant on the Amount of Power Generated. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Adelard, L. Advances in Computational Fluid Dynamics modelling of anaerobic digestion process for renewable energy production: A review. Waste Biomass Valoriz 2023, 14, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Nowak, M.; Bojarski, W. Anaerobic Digestion and Composting as Methods of Bio-Waste Management. Agric. Eng. Sciendo 2023, 27, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Sisani, F.; Norouzi, O.; Mersky, R.L. The effectiveness of anaerobic digestion of bio-waste in replacing primary energies: An EU28 case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Szamosi, Z.; Siménfalvi, Z. State of the art on mixing in an anaerobic digester: A review. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroot, P.G.; McMahon, K.D.; Mackie, R.I.; Raskin, L. Anaerobic codigestion of municipal solid waste and biosolids under various mixing conditions-I. digester performance. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaparaju, P.; Buendiaa, I.; Ellegaardb, L.; Angelidakiaa, I. Effects of mixing on methane production during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of manure: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindmark, J.; Thorin, E.; Fdhila, R.B.; Dahlquista, E. Effects of mixing on the result of anaerobic digestion: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Bastide, A.; Adelard, L. Advances in Computational Fluid Dynamics modeling of anaerobic digestion process for renewable energy production: A review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 6, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, P.; Escudero-González, J.; Martínez, T.M.; Montañana, V.F.; Gualtieri, C. Application of CFD methods to an anaerobic digester: The case of Ontinyent WWTP, Valencia, Spain. J. Eng. Water Process 2015, 7, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesvikar, M.S.; Al-Dahhan, M. Flow pattern visualisation in a mimic anaerobic digester using CFD. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Chen, S. CFD simulation of non-Newtonian fluid flow in anaerobic digesters. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 99, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillet, H.; Bastide, A.; Adelard, L. CFD Simulations in Mechanically Stirred Tank and Flow Field Analysis: Application to the Wastewater (Sugarcane Vinasse) Anaerobic Digestion; Promising Techniques for Wastewater Treatment and Water Quality, Assessment; Moujdin, I.A., Summers, J.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 93926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, B.; Jeremiah, M.; Oludolapo, O. Biogas Treatment and Upgrading Techniques. In Proceedings of the 4th Asia Pacific International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 12–14 September 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 50160:2010; Supply Voltage Parameters for Public Distribution Networks. EU: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2010.
- Regulation of the Minister of Economy of 4 May 2007 on Detailed Conditions for the Operation of the Electric Power System (in Polisch). JoL. 2007 No 93 Item 623. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20070930623 (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Robak, S.; Pawlicki, A.; Pawlicki, B. The analysis of the voltage and current asymmetry in the power transmission lines. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2014, 90, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kosicki, Ł.; Typańska, D. The research of current and voltage distortions generated by luminaries with the light emmiting diodes. Electr. Eng. 2017, 92, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Song, K.; Zhang, T.; Lian, Z.; Li, H.; Jin, D.; Wang, R. Solving Power Supply Stability Issues in Remote Agricultural Areas Based on an Improved Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control Method. Agriculture 2025, 15, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiangebeni Lusimbakio, K.; Boketsu Lokanga, T.; Sedi Nzakuna, P.; Paciello, V.; Nzuru Nsekere, J.-P.; Tshimanga Tshipata, O. Evaluation of the Impact of Photovoltaic Solar Power Plant Integration into the Grid: A Case Study of the Western Transmission Network in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Energies 2025, 18, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertkov, M.; Backhaus, S.; Turtisyn, K.; Chernyak, V.; Lebedev, V. Voltage Collapse and ODE Approach to Power Flows: Analysis of a Feeder Line with Static Disorder in Consumption/Production. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1106.5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatsevskiy, K.V.; Antonov, A.I.; Gonenko, T.V.; Khatsevskiy, V.F. The voltage asymmetry in electrical networks with single-phase load. In Proceedings of the 2017 Dynamics of Systems, Mechanisms and Machines (Dynamics), Omsk, Russia, 14–16 November 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodapanah, M.; Zobaa, A.F.; Abbod, M. Estimating power factor of induction motors at any loading conditions using support vector regression (SVR). Electr Eng. 2018, 100, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdElhafez, A.; Alruways, S.; Alsaif, Y.; Althobaiti, M.; AlOtaibi, A.; Alotaibi, N. Reactive Power Problem and Solutions: An Overview. J. Power Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alawasa, K.M.; Al-Badi, A.H. Investigation and Analysis of the Power Quality in an Academic Institution’s Electrical Distribution System. Energies 2024, 17, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.L.M.; Leal, A.F.R.; Almeida, G.O.d.; Tostes, M.E.d.L. Harmonic Effects Due to the High Penetration of Photovoltaic Generation into a Distribution System. Energies 2021, 14, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Unit | Biogas Plant No. | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| pH | - | 8 | 8.6 | 8.3 |
| dry matter | % | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| total nitrogen | % | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.46 |
| phosphorus | % P2O5 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.285 |
| phosphorus | % K2O | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.325 |
| calcium | % CaO | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| magnesium | % MgO | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.145 |
| total sulfur | % DM | 0.452 | 0.449 | 0.4505 |
| iron | g/kg DM | 1.036 | 0.975 | 1.0055 |
| manganese | g/kg DM | 0.467 | 0.401 | 0.434 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Internal combustion engine type | Otto WG1605 |
| Number of cylinders in an internal combustion engine | 4 |
| Internal combustion engine speed | 2700 rpm |
| Electrical efficiency of the internal combustion engine | 32% |
| Maximum temperature of flue gases | 110 °C |
| Generator type | Asynchronous 4P/IE2 |
| Rated active power of the generator | 20 kW |
| Nominal apparent generator power | 26 kVA |
| Rated unit voltage | 400 V |
| Rated unit current | 29 A |
| Rated frequency of the unit | 50 Hz |
| Rated power factor φ | 0.25 |
| Overall turbine efficiency | 97% |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
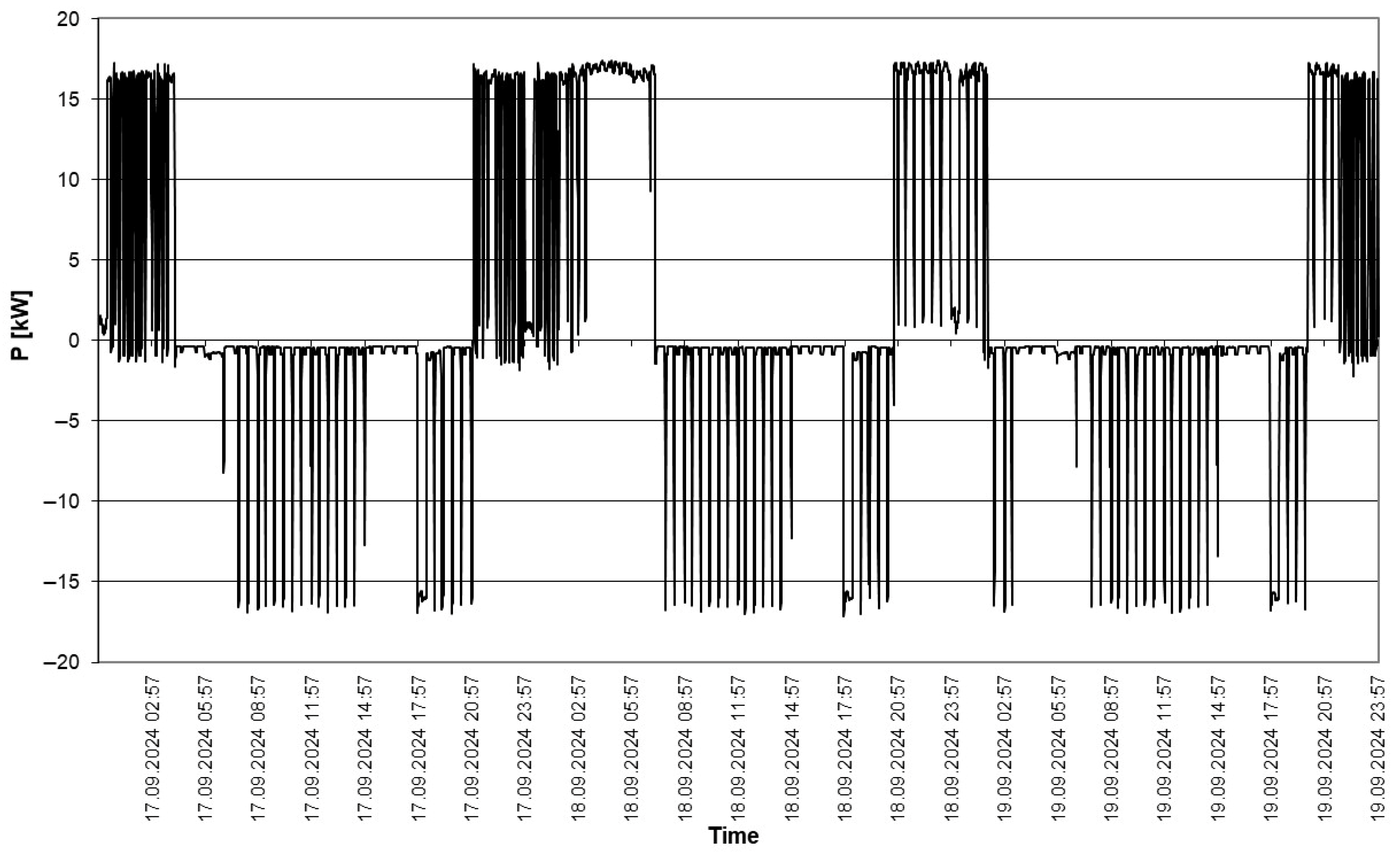
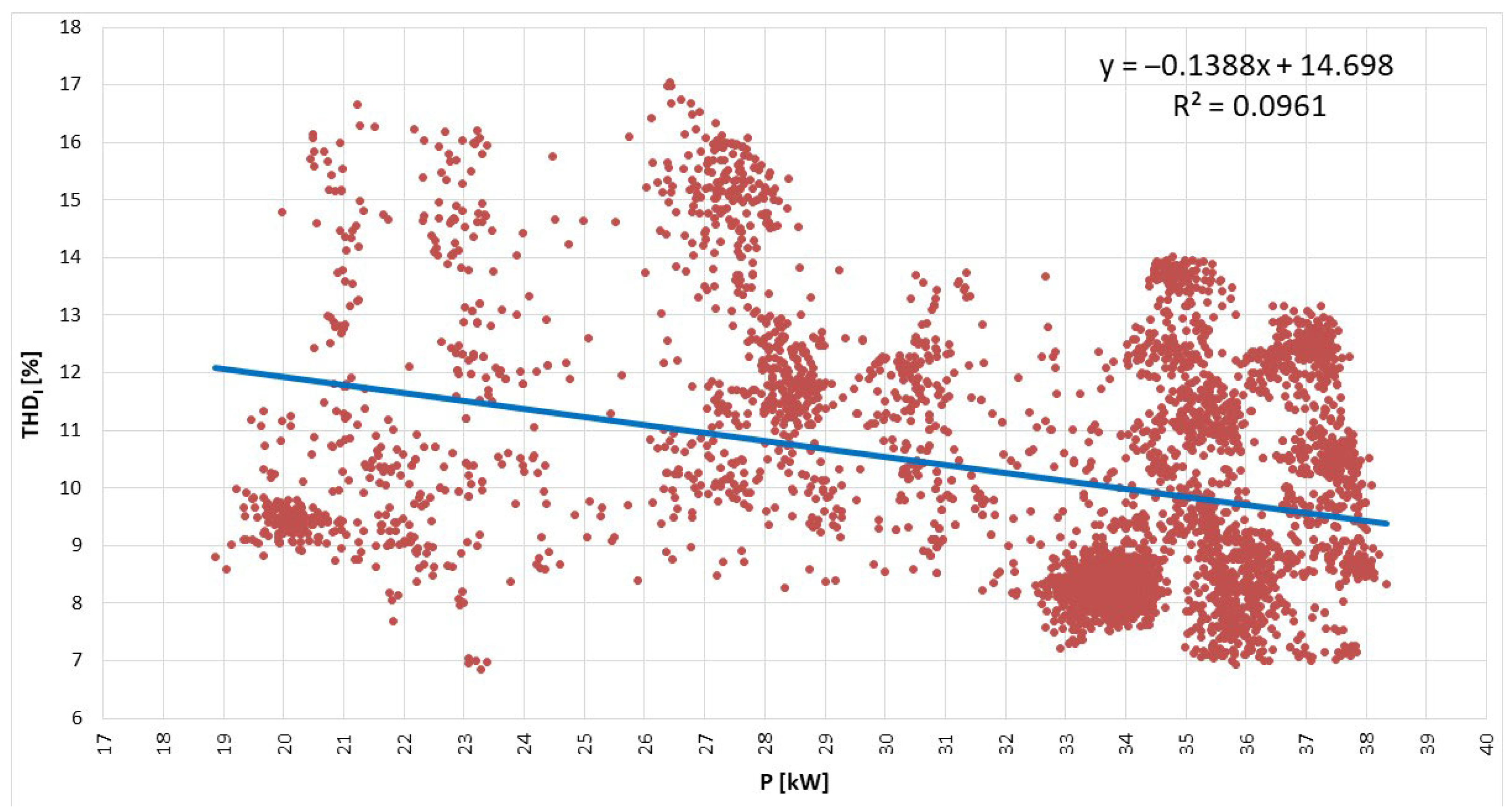
| Mean | 32.42995 | kW |
| Standard Error | 0.072423 | kW |
| Median | 33.97441 | kW |
| Mode | 28.38627 | kW |
| Standard Deviation | 4.760141 | kW |
| Sample Variance | 22.65894 | kW2 |
| Kurtosis | 0.48279 | - |
| Skewness | −1.1993 | - |
| Range | 19.46663 | kW |
| Minimum | 18.8621 | kW |
| Maximum | 38.32873 | kW |
| Confidence Level (95.0%) | 0.141986 | kW |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
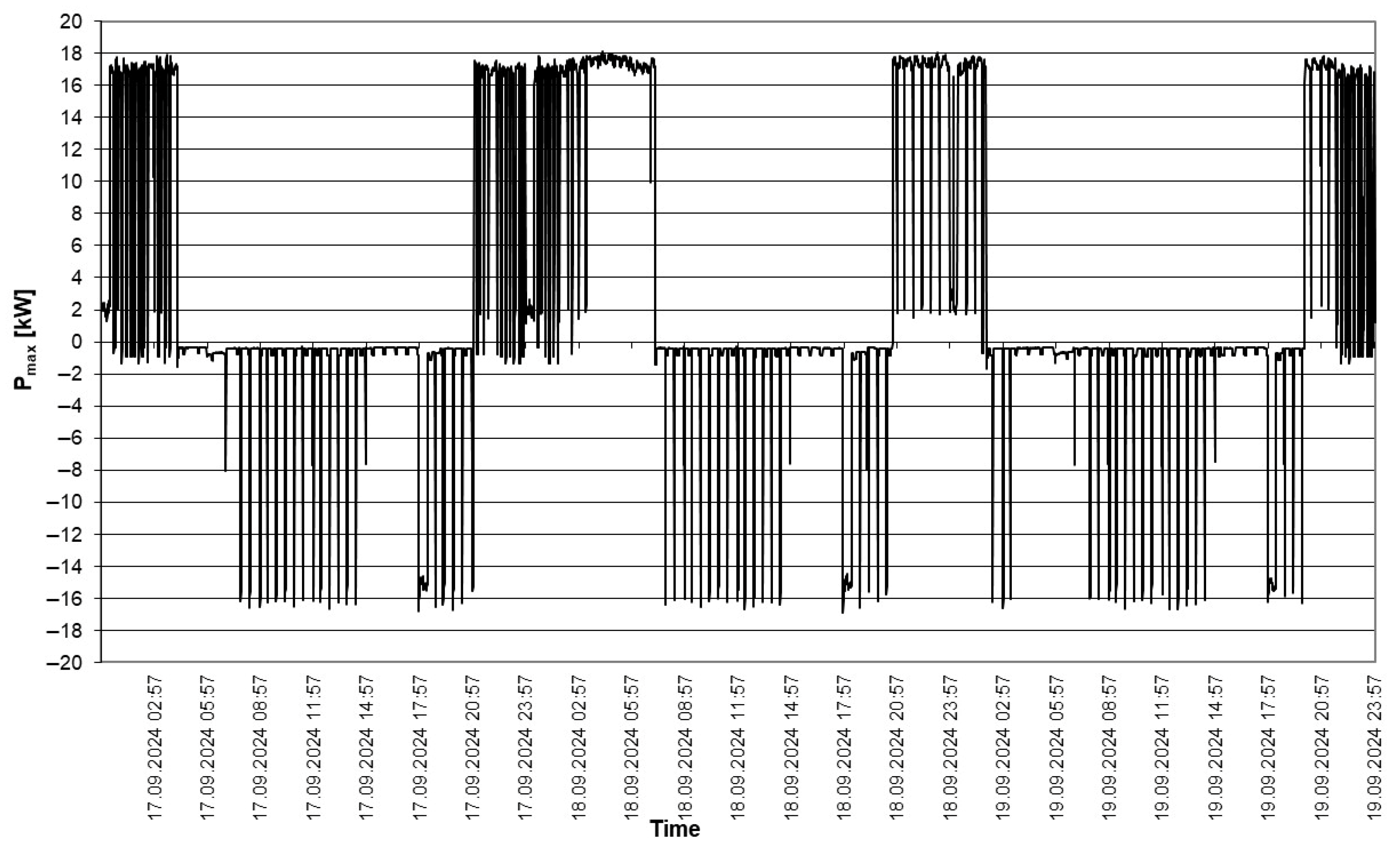
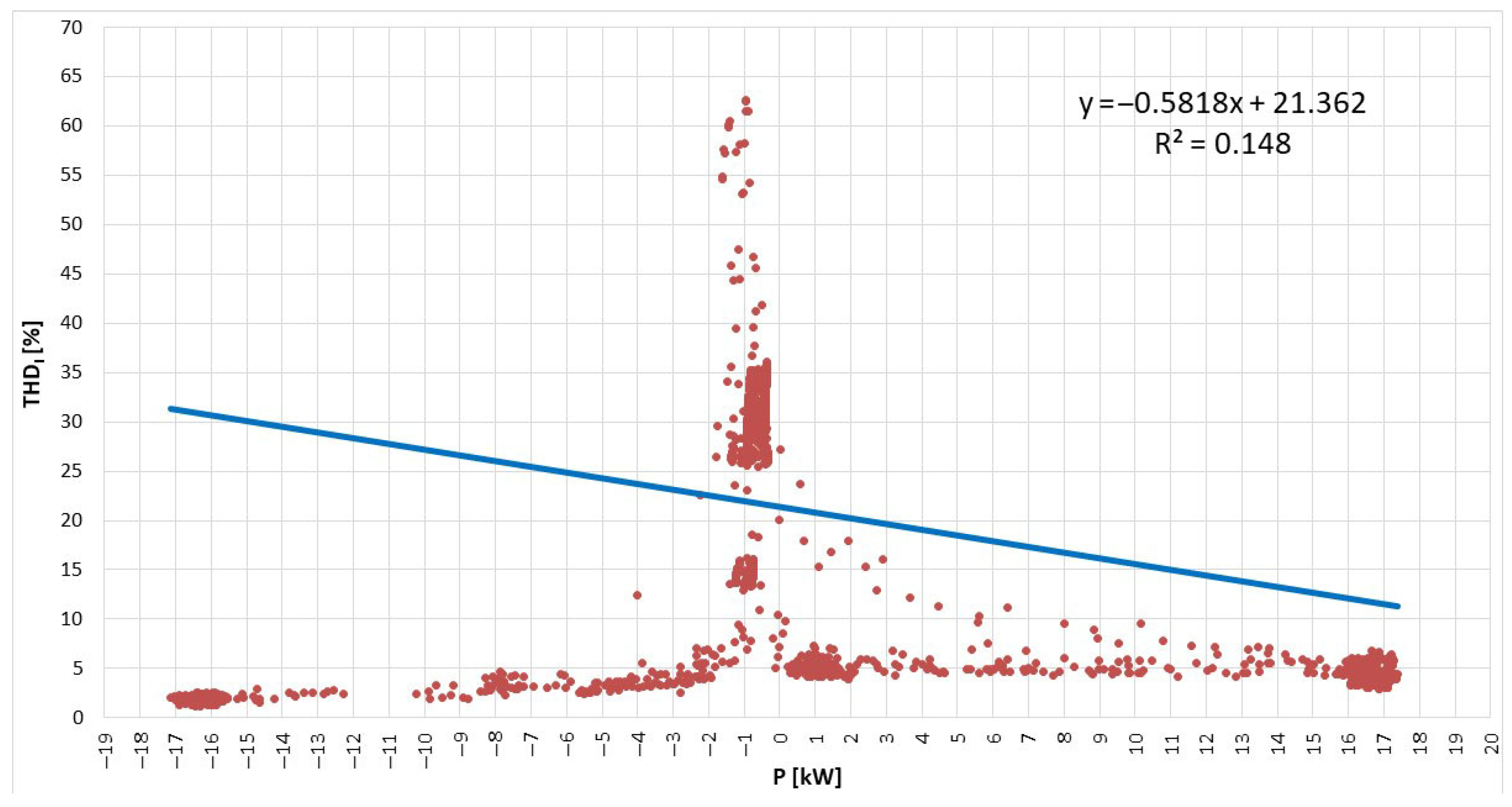
| Mean | 2.529704 | kW |
| Standard Error | 0.132715 | kW |
| Median | −0.41462 | kW |
| Mode | 16.6456 | kW |
| Standard Deviation | 8.72292 | kW |
| Sample Variance | 76.08933 | kW2 |
| Kurtosis | −0.08842 | - |
| Skewness | 0.32512 | - |
| Range | 34.513 | kW |
| Minimum | −17.1332 | kW |
| Maximum | 17.37978 | kW |
| Confidence Level (95.0%) | 0.26019 | kW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skibko, Z.; Borusiewicz, A.; Filipkowski, J.; Pisarek, Ł.; Kuboń, M. Impact of Farm Biogas Plant Auxiliary Equipment on Electrical Power Quality. Energies 2025, 18, 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143849
Skibko Z, Borusiewicz A, Filipkowski J, Pisarek Ł, Kuboń M. Impact of Farm Biogas Plant Auxiliary Equipment on Electrical Power Quality. Energies. 2025; 18(14):3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143849
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkibko, Zbigniew, Andrzej Borusiewicz, Jacek Filipkowski, Łukasz Pisarek, and Maciej Kuboń. 2025. "Impact of Farm Biogas Plant Auxiliary Equipment on Electrical Power Quality" Energies 18, no. 14: 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143849
APA StyleSkibko, Z., Borusiewicz, A., Filipkowski, J., Pisarek, Ł., & Kuboń, M. (2025). Impact of Farm Biogas Plant Auxiliary Equipment on Electrical Power Quality. Energies, 18(14), 3849. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143849









