Abstract
This study investigated the combustion performance of pig manure, straw, and coal at various blending ratios using thermogravimetric analysis. The synergistic effect of coal and pig manure at various ratios was analyzed, and kinetic analysis was performed using the Coats–Redfern method. The results showed that the overall combustion performance and stability of the blended fuel improved as the blending ratio of pig manure and straw increased. Increasing the ratio of pig manure reduced the ignition temperature of blended fuel from 696 K to 675 K. Additionally, the combustion of pig manure and coal exhibited a significant synergistic effect, strongest at a 5% blending ratio. For combustion reactions with conversion rates between 0.2 and 0.8, the activation energy required was 75.82 kJ mol−1 for a 10% pig manure blending ratio and 44.33 kJ mol⁻1 for a 30% blending ratio. These results demonstrate that lower activation energies suggest that the combustion reaction is more likely to proceed. The activation energy of straw was higher than that of pig manure at all blending ratios. These findings suggest that pig manure burns more easily when blended with coal than straw.
1. Introduction
Coal is a significant source of energy on a global scale, particularly in China, where its use is pervasive. It is also a crucial fuel for power plants [1]. However, carbon dioxide emissions from burning coal and other fossil fuels are substantial and account for between 33 and 40 percent of global anthropogenic carbon emissions [2,3,4]. The largest source of carbon dioxide is coal utilization, and coal resources are limited by rising costs [5,6], at the same time, pollutants are diverse. Fossil resources, such as coal, remain the mainstay of energy production, despite the ongoing shift toward renewable and carbon-neutral energy sources [6]. While biomass resources are widely available and generate fewer pollutants, blending coal with biomass is conducive to the better utilization of biomass resources, reducing pollutant emissions and resource waste [7].
Livestock and poultry wastes are available to waste resources rich in organic matter, and N, P, and K. Their efficient resource utilization plays an important role in environmental protection and resource utilization [8]. In the case of modern pig breeding development, pig manure treatment is a key environmental protection technology, otherwise, it will cause environmental pollution. On the one hand, through the scientific treatment of fertilizer fermenter, pig manure can be added to high-quality organic fertilizer; on the other hand, pig manure can be employed as a type of combustion energy since it is easy to mold, has good molding qualities, and performs well during burning [9]. The magnitude of pigs raised in China is enormous, as is the magnitude of heat that can be generated from pig manure [10]. Biomass is a viable energy source that is characterized by its carbon neutrality, cost effectiveness, and reproducibility [11,12,13]. The utilization of biomass has also increased in recent years [14]. Coal and biomass can be burned together to maximize the use of biomass resources. The volatile components are burned extremely vigorously during the co-combustion process, and the biomass charcoal produced after pyrolysis is characterized by good reactivity and easy combustion.
Prayoga et al. [15] investigated the kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of samples of coal mixture and oil palm biomass. The thermogravimetric differential thermal analysis was performed at heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20 K min−1, respectively, with six samples comprising mixtures with varying coal, palm, and oil palm biomass ratios. Luo et al. [16] and Shuo et al. [17] investigated the kinetic characteristics of individual and coupled combustion of corncob biomass and low calorific value coal (coal slurry and gangue). They also examined the combustion characteristics of low-calorific-value coal. To investigate the combustion characteristics of coal in combination with eucalyptus (EU) and its blends, thermogravimetric analysis was utilized. The results showed that adding biomass improved coal’s combined combustion performance, outperforming coal’s combustion performance when burned alone. The coupled combustion of biomass and coal exhibited distinct responses, with different biomass–coal mixtures potentially promoting or inhibiting coal combustion. Guo et al. [18] looked at the co-pyrolysis and co-combustion characteristics of straw and low-rank coal, as well as their kinetic behavior. Thus, they came to the conclusion that as coal coke and carbonized straw co-combust, there are both antagonistic and synergistic effects, with the synergistic impact predominating. Based on the kinetics of conversion techniques like Kissinger–Akahira–Sunnose (KAS) and Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO), Sahu et al. [19] employed thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) to conduct a thorough kinetic and thermodynamic study of chickpea stems (CSs) at four distinct heating rates during thermal deterioration and disintegration. Different techniques were used to determine activation energies and kinetic parameters. Ma et al. [5] and Liu et al. [20] investigated the co-combustion behavior and gaseous pollutant emissions of moso bamboo (MB) and coal slurry (CS) mixtures in O, and the kinetic parameters of cattle manure mixed with corn stover, and calculated the activation energies by using four different kinetic methods to classify the combustion process of the samples into different phases. Zuo et al. [21] investigated the combustion properties of anthracite powder and municipal solid waste (MSW) mixtures using thermogravimetric analysis. The volumetric model (VM), unresponsive core model (URCM), and random pore model (RPM) were used by the researchers to assess the combustion reaction of pulverized MSW. Dorokhov et al. [6] examined the combustion kinetic parameters and thermal decomposition properties of composite fuels made of lignite, sawdust, coal refinery waste, and spent motor oil. They used thermogravimetric analysis to examine how the qualities of the different components affected the mixes’ overall thermal oxidation properties. While previous studies [5,15,16,17,18,20] have investigated the co-combustion properties of plants and coal, the combustion of cattle manure is the main study among farm solid wastes. The utilization of pig manure as a solid waste has been demonstrated to exert an effect on the environment [22]. Furthermore, the combustion of coal has been shown to generate pollution. The simultaneous combustion of pig manure and coal has been shown to both utilize the heat of pig manure and reduce the emission of pollutants. A paucity of studies has been dedicated to the combustion characteristics of coal, pig manure, and other plant materials. Pig manure, as a good combustion energy source, is not only abundant, but also has good combustion performance. Understanding the combustion performance of coal, pig manure, and straw is essential to further research their co-combustion properties. Nevertheless, research examining the co-combustion characteristics of pig manure, straw, and coal is severely limited, especially in terms of their co-combustion kinetics and synergistic effects. Thus, a theoretical foundation and useful insights into the combustion of the three combinations can be obtained by examining the co-combustion ratios and combustion processes of coal, straw, and pig manure.
This study examined the co-combustion properties of coal, straw, and pig manure using thermogravimetric analysis. Coats–Redfern kinetic analysis was utilized to examine the synergistic effect of the three fuels under various blending conditions, and it was investigated how the blending ratio affected the co-combustion process. The study’s findings can be used to optimize the proportion of coal, straw, and pig manure that is blended.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
The study’s sources of biomass (straw and pig manure) and coal were Yantai Longyuan Power Technology Co., Ltd, Yantai, China. In advance of the experiment, biomass and coal were both pulverized. Understanding the composition of coal and biomass as well as the mixtures, is essential to study their blended combustion characteristics. As illustrated in Table 1, the calorific value and the results of proximate and ultimate analyses of coal, straw, pig manure, and their mixtures at different blending ratios are presented. Biomass was measured using the national standards GB/T 28731-2012 [23] for proximate analysis and GB/T 28734-2012 [24] for ultimate analysis. The proximate and ultimate analysis of coal are measured using the national standards of GB/T 212-2008 [25] and GB/T 30733-2014 [26], respectively. The calorific value analysis of biomass and coal was measured using the automatic oxygen bomb calorimetry of GB/T 30727-2014 [27] and GB/T213-2008 [28], respectively. Table 2 presents the ash composition analysis of coal, straw, pig manure, and their mixtures at varying blending ratios. As illustrated in Table 2, the ash compositions of biomass and pig manure are more similar to each other than to coal.

Table 1.
Proximate and ultimate analysis and calorific value of biomass and raw coal.

Table 2.
Analysis of the ash composition of raw coal, pig manure, and biomass, and different blending ratios of raw coal, pig manure, and biomass.
2.2. Thermogravimetric Experiment
In this study, thermogravimetric testing was used to examine the co-combustion properties of biomass and coal. The instrument used for the thermogravimetric measurements was the Labsys Evo Simultaneous Thermal Analyzer, which is manufactured by Setaram Instruments Company in Lyon, France. The device was able to measure TG and DSC at temperatures ranging from ambient temperature to 1873 K. The gas flow rate was set to 0.67 mL s−1 after placing the experimental sample weighing 3.50 ± 0.10 mg during the experiment. The atmosphere was set to 79% N2 and 21% O2. The exper-imental system was blown at room temperature for 300 s and waited for stabilization. Subsequently, at a rate of 0.17 K s−1, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 1473 K. Thereafter, it was sustained at this temperature for 1800 s before the cooling process.
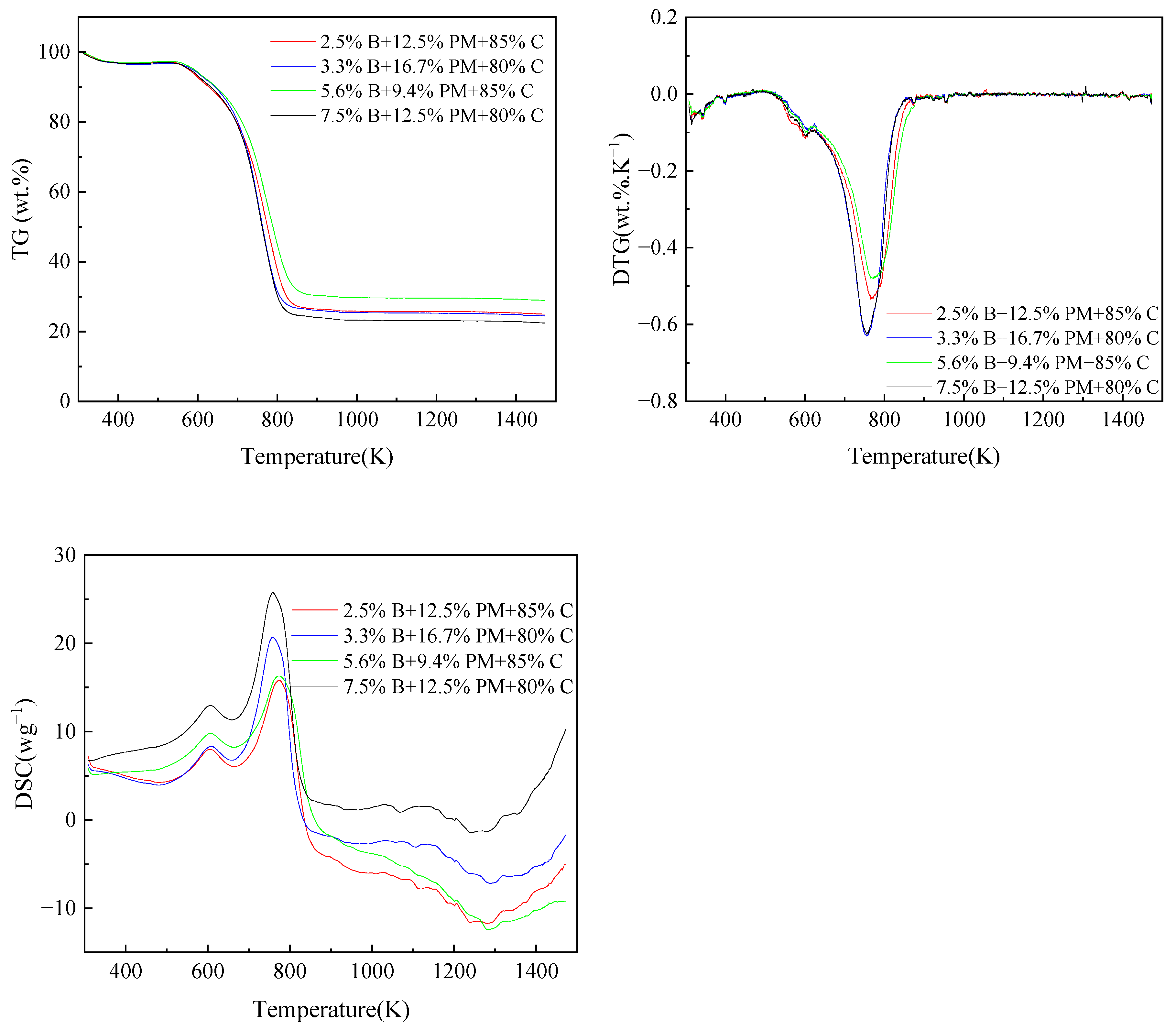
Pig manure and coal were blended in the following proportions: 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 30%, and 100%. Coal and straw were blended at percentages of 100%, 15%, 20%, and 0%, respectively. The blending ratios of straw, pig manure and coal were 0.025 B + 0.125 PM+ 0.85 C, 0.033 B + 0.167 PM + 0.8 C, 0.056 B + 0.094 PM+ 0.85 C and 0.075 B + 0.125 PM + 0.8 C (B stands for biomass straw, PM stands for pig manure, C stands for coal). The thermogravimetric data required for the experiment were measured using an analyzer. Before the initiation of the experiments, blank calibration experiments were established. It is crucial to remember that every experiment was carried out at least three times to guarantee the accuracy of the findings.
2.3. Analytical Method
The two main characteristics of fuel combustion characteristics are ignition temperature and burnout temperature. Ignition temperature and burnout temperature are the two primary fuel combustion properties. In this work, the ignition temperature and burnout temperature are solved using the tangent approach. At the start and finish of weight reduction, two horizontal tangent lines are created, and the peak point of the DTG curve that corresponds to the TG curve’s point is used to build a tangent line. The temperature designated as Ti, which occurs at the point of intersection between the tangent line and the horizontal line at the inception of weight loss, is referred to as the ignition temperature. Similarly, the temperature Tb, which is the point at which the tangent line and the horizontal line connect when weight loss stops, is known as the burnout temperature [29,30]. The stable combustion characteristics index Dw shows how stable the fuel’s combustion is and how easy it is to ignite. In the pre-combustion phase, the flammability index Ci indicates the fuel’s reactivity, and higher values indicate greater flammability. The overall igniting and combustion performance of the fuel is indicated by the comprehensive combustion characteristics index S. It has been shown that an increase in the value translates into an improvement in the fuel’s overall combustion performance [31,32,33].
DTGmax denotes the maximum burning speed (%·s−1), while DTGmean indicates the average burning speed (%·s−1). The purpose of the total weight loss (ΔTG) is to examine the synergistic effect of burning blended fuel while also examining the synergistic effect induced by different fuel ratios. To find ΔTG, Equations (4) and (5) were utilized [31,34,35,36]:
In the context of the mixture, the symbols for biomass and coal contents are (%) and (%), respectively. The weight loss of coal and biomass is represented by and . Conversely, the estimated and calculated weight loss rates are denoted by and , respectively.
The energy required for intermolecular reactions is represented by the activation energy (E). The ease with which a reaction can proceed is reflected by the activation energy E. The greater the activation energy, the less likely the reaction will proceed. In intermolecular collisions, the effective frequency is represented by the pre-exponential factor (A), and it might affect a reaction’s pace. A more thorough evaluation of blended fuel combustion processes is possible by combining E and A.
The blended fuel combustion process is non-homogeneous, so the degree to which the reaction proceeds is expressed in terms of the rate of conversion (α) [37]. The Arrhenius equation defined by k(T) can be seen in Equation (7) [38]. A stabilized rate of temperature increase (β = dT/dt) is used to apply Equation (8). The following are the expressions for the rate of the reaction process and the formulas for calculating E and A:
Given the absence of an analytical solution, the equation is solved using the Coats–Redfern method [39]; this has the following solution:
A straight line can be obtained by graphing the calculated data into Equation (9), and thus E and A can be obtained by solving according to the slope as well as the intercept, and the combustion reaction mechanism is modeled by the following equation [40]:
In this particular instance, the number of reaction levels, designated as n, is set at 1.
Consequently, g can be written as
Graphing the situation gives you E as well as A for the corresponding situation.
, , and can be calculated from the kinetic data in the following equations [41]:
where KB is the Boltzmann constant, equal to 1.381 × 10−23 m2 kg/s−2 K−1. Tm is the maximum temperature at which maximum decomposition occurs. h is the Prandtl constant, equal to 6.626 × 10−34 m2 kg/s, and R is the universal gas constant, equal to 0.008314 kJ/mol K. The maximum temperature at which maximum decomposition occurs is the temperature at which maximum decomposition occurs.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Combustion Characteristics of Different Materials
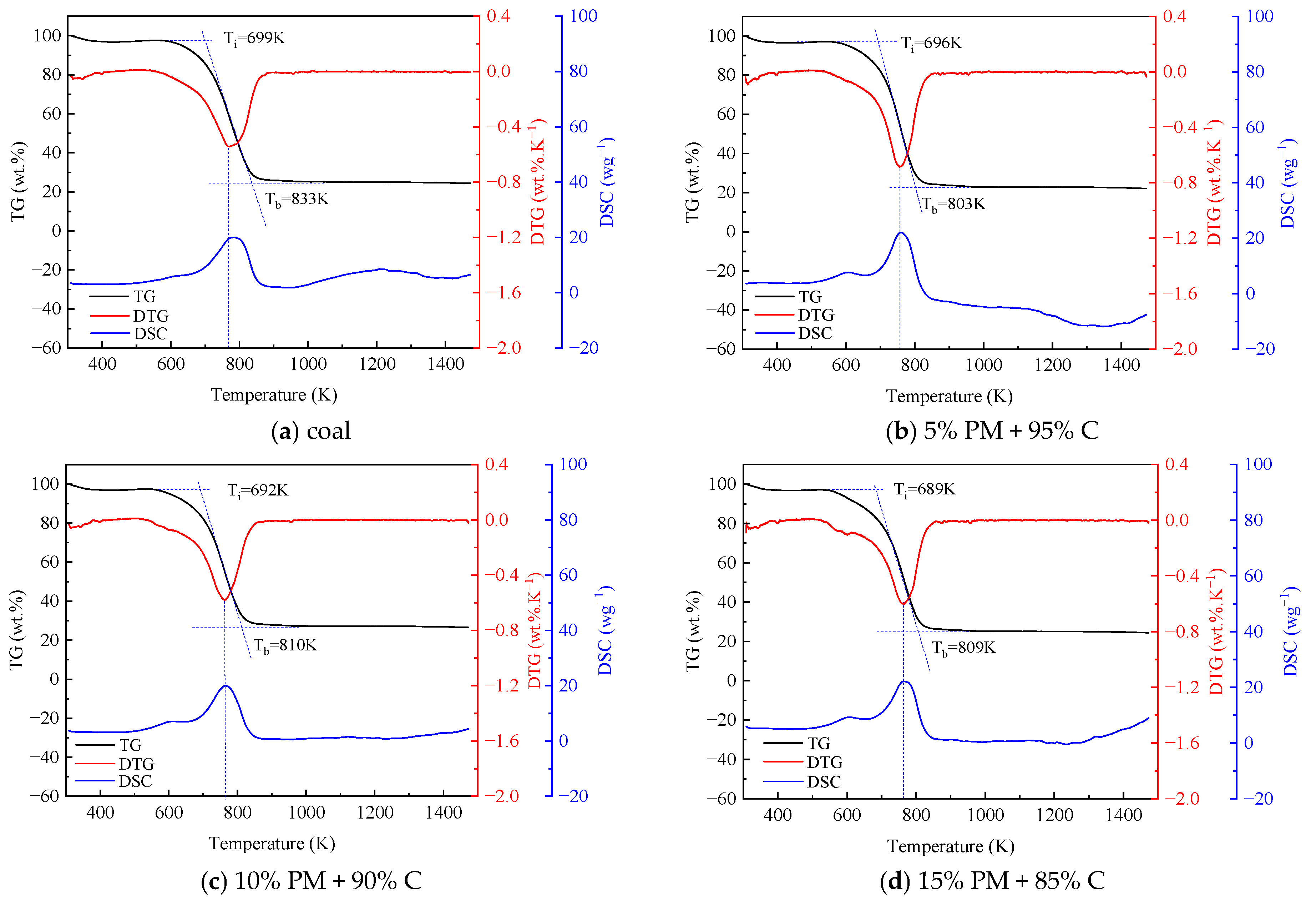
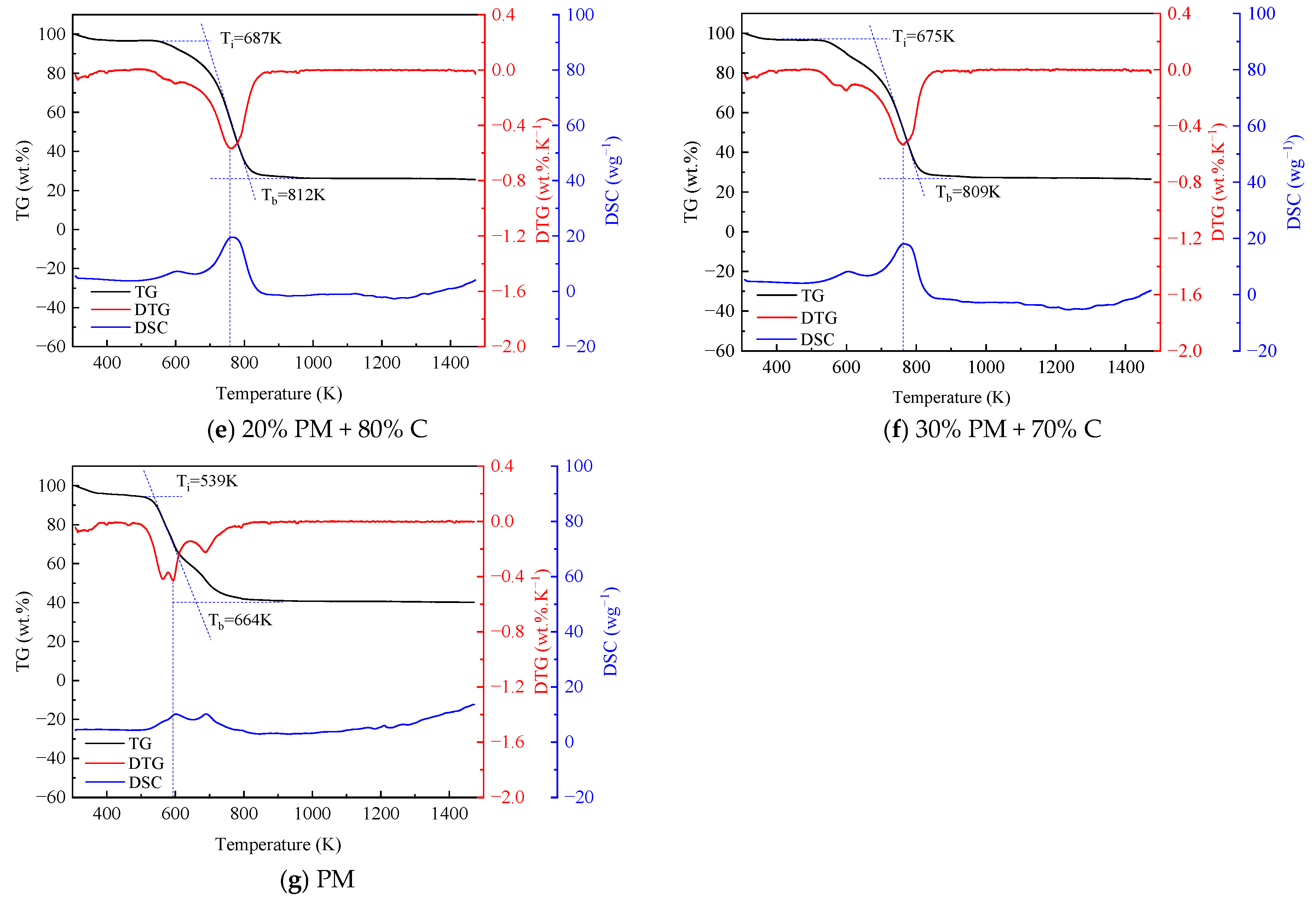
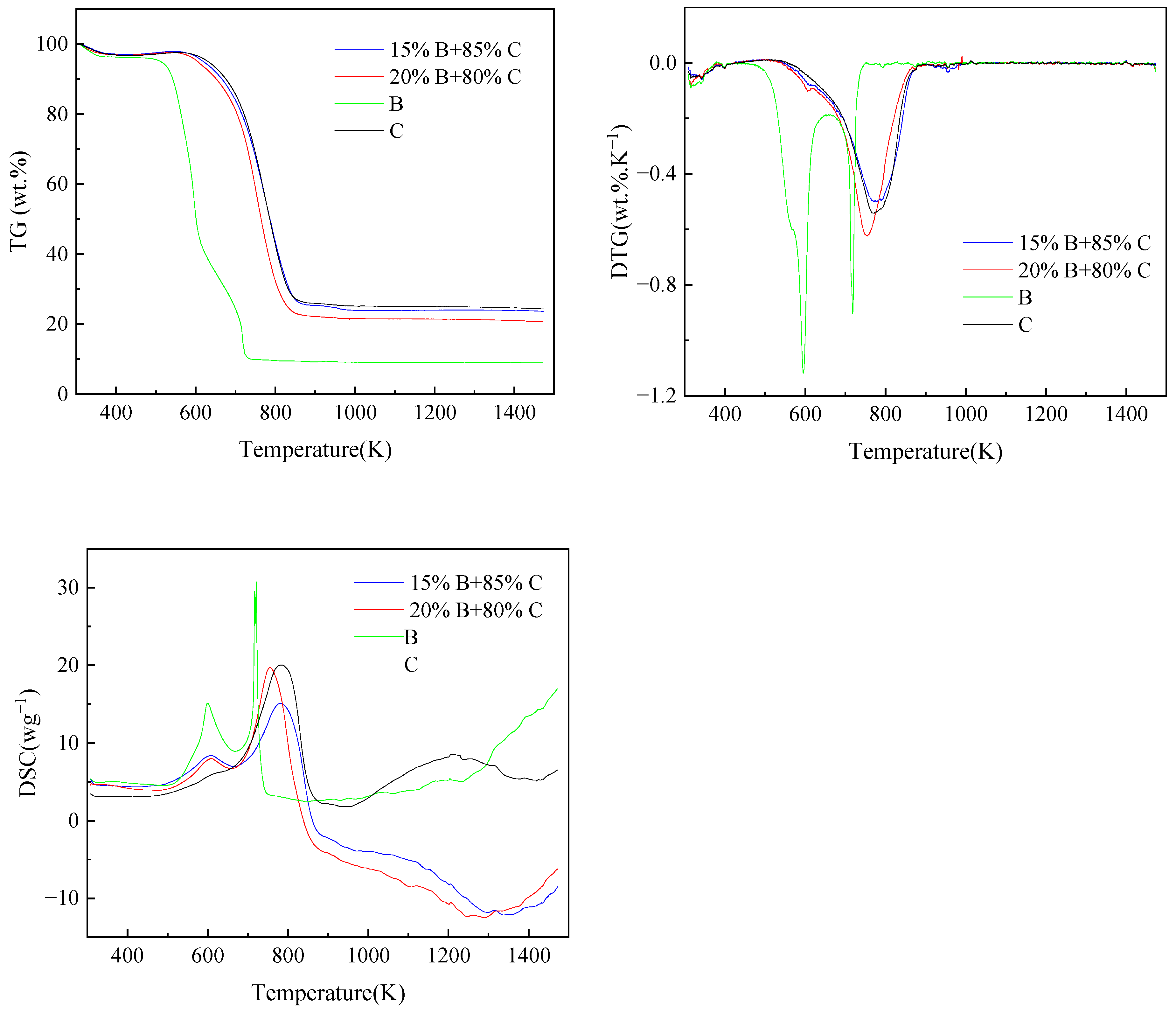
Figure 1 illustrates the TG-DTG-DSC plots formed by the blended combustion of pig manure and coal at different mixing ratios. The TG, DTG, and DSC plots of coal and straw combined and burned at various blending ratios are shown in Figure 2. Pig manure, straw, and coal burned at various blending ratios are depicted in Figure 3 as TG, DTG, and DSC plots. Table 3 displays the combustion performance indicators for several samples. From the Table 3, it can be seen that the ignition temperature of pig manure is in general agreement with the ignition temperature in the literature [9]. When coal and pig manure are combined, it is evident from the study of Figure 1 and Table 3 that the ignition temperature advances noticeably as the ratio of pig manure increases, and the burnout temperature also shows a fluctuating trend with the increase of the ratio. Concurrently, the steady combustion characteristic index Dw is larger than that of coal, but it displays a trend of progressive decline as the proportion rises. In a similar vein, Figure 2 illustrates that the ignition and burnout temperatures exhibit the same pattern when coal and straw are mixed. Figure 3 illustrates that when coal, pig manure, and straw are blended, the ignition temperature advances somewhat when the blending ratio of pig manure rises, provided that the coal blending ratio remains constant. This phenomenon suggests that the incorporation of biomass facilitates the initiation of combustion, yet it concomitantly diminishes the stability of the combustion process. Biomass is easier to ignite than coal, but increasing the ratio of pig manure in the fuel mixture results in slightly earlier ignition. The reason for this is that biomass’s high volatile matter, H, and O concentration causes it to emit more volatile matter more quickly during combustion, which encourages igniting [42,43]. A comparison of the flammability index of straw, pig manure, and coal shows that the flammability index Ci of pig manure is lower than that of straw, and the flammability index Ci fluctuates as the amount of biomass grows. Nevertheless, it is more than that of coal, suggesting that a higher biomass blending ratio generally improves the combustibility of blended fuels made of coal and biomass. It is evident that the index S, which is used to comprehensively measure combustion characteristics, fluctuates in response to an increase in the biomass blending ratio.

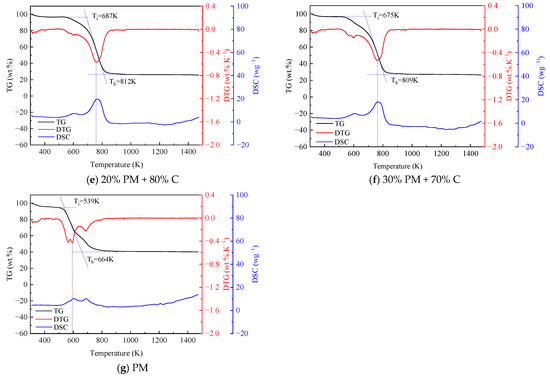
Figure 1.
TG, DTG, and DSC curves for blended fuels of pig manure and coal (PM stands for pig manure, C stands for coal).

Figure 2.
TG, DTG, and DSC curves for blended fuels of straw and coal (B stands for biomass straw, C stands for coal).
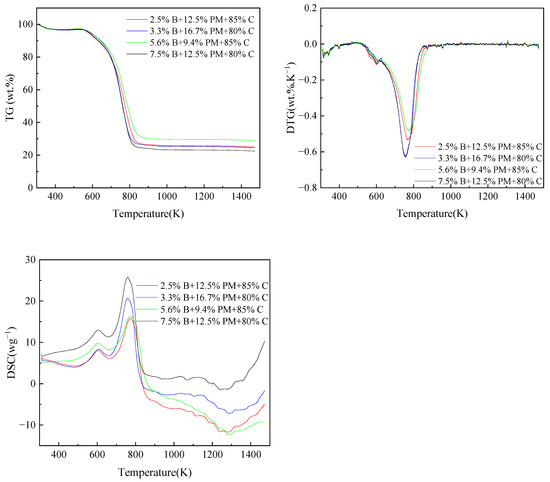
Figure 3.
TG, DTG, and DSC curves of blended fuel with pig manure, straw, and coal (B stands for biomass straw, PM stands for pig manure, C stands for coal).

Table 3.
Combustion characteristic parameters of the samples.
3.2. Influence of Biomass Ratios
As the blending ratio of pig manure increases, it is clear from the TG curves in Figure 1 that the TG curves shift more and more into the low-temperature region, and the absolute value of the slope of the curve also shows an increasing trend, which suggests that the addition of pig manure makes it easier to ignite the blended fuels, and combustion is more likely to be carried out. This is because processed pig manure has a loose surface with many pores, which has more interaction with air and a lower packing density than coal, and because pig manure has a significantly higher volatile content than coal, which makes it easier to burn, and the ability of adsorption of oxygen on the surface of the particles at the active sites is enhanced. The combustion of straw has the same pattern and traits as pig manure, as seen in Figure 2. The TG curves in Figure 3 reflect that the blending ratio of pig manure affects the quickness of catching fire, but the change is very small when the difference in coal content is not large.
The inclusion of pig manure can speed up the coal combustion process, as shown in Figure 1, which also shows a tendency for the DTG curves to move to the low-temperature zone as the ratio of blending increases. In addition, the degree of advancement gets more noticeable as the biomass blending ratio rises. This is because biomass has a larger volatile content, which improves its ignition and combustion properties. In Figure 1, the combined coal and pig manure samples do not exhibit more noticeable weight loss peaks in the 323–403 K temperature range. This is because both pig manure and coal are in a drier state, and there is no obvious water loss. In addition, in the temperature range from 683 to 853 K, there is a combustion weight loss peak for both raw coal and blended fuels with a lower ratio of pig manure, and the concentrated combustion of volatiles and fixed carbon could be seen from the DTG curve. The blended fuel with a higher ratio of pig manure has two obvious weight loss stages. The initial stage, which primarily entails the precipitation and combustion of volatiles, transpires within the temperature range of 513 K to 653 K. At these temperatures, the DTG values of coal and blended fuels are minimal, ranging from 0.05 to 0.15 wt.%·K−1. Conversely, the DTG values for pig manure attained 0.4 wt.%·K−1. The second stage, which occurs at a temperature range of 713 K to 853 K, is primarily characterized by the combustion of fixed carbon. The DTG values focus on the range of 0.53 to 0.68 wt.%·K−1 [44,45]. The fact that the fixed carbon combustion peak in pig manure emerged sooner is particularly noteworthy. This might be because there is enough oxygen present, which encourages pig manure to burn completely. The blended sample of straw and coal in Figure 2 has a weight loss peak at 573–623 K, which is a water loss peak. But among them, mainly the water loss peak of straw is more obvious. The obvious weight loss stage in the straw and coal blended fuel is between 723 and 823 K, which is not much different from the pig manure and coal blended fuel. Similarly, the DTG curves of the three fuel blends in Figure 3 have the same trend with little difference.
The initial peak occurs between 573 and 663 K when analyzing the DSC curves in Figure 1, which primarily indicates the release and combustion of the fuel’s volatile components. Between 673 and 823 K, the second peak is significantly greater than the first. This stage is primarily characterized by the fuel’s fixed carbon burning, and the peak is higher because of the higher exothermic amount of fixed carbon. The exothermic time of pig manure is significantly faster than that of the other blended fuels, with combustion of the basic volatile components and fixed carbon almost complete at approximately 602–689.8 K. Pure coal exhibits the slowest exothermic time, and the combustion of fixed carbon peaks at approximately 783.2 K. This phenomenon is because pig manure has a high volatile matter and O content, which makes it easier to ignite and burn, however, pig manure has a smaller and less exothermic comparable calorific value. Therefore, pig manure has a lower peak value than the other combined fuels. It is evident in the fixed carbon combustion stage that the sample with 15% blending ratio of pig manure has the highest exothermic value, which can reach 22.1 wg−1, which is more than twice as much as the exothermic value of pig manure (10.2 wg−1). A comparison of the two peaks for pig manure shows that the peak in the volatile fraction combustion phase is slightly smaller than the peak in the fixed carbon combustion phase, which suggests that the volatile fraction in pig manure is not sufficiently combusted. Straw’s volatile combustion stage is significantly greater than the fixed carbon combustion stage, according to an analysis of the DSC curve in Figure 2, but the same exothermic time is advanced. Analysis of the DSC curve of the three substances’ blended combustion in Figure 3 shows that when the coal blending ratio is the same, the lower the ratio of pig manure. Both the fixed carbon combustion stage and the volatile combustion stage will see an increase in exothermic amounts. This is partly because the calorific value of pig manure is lower than that of straw, and partly because the volatile combustion stage of straw is sufficiently long and the amount of heat released is also large. The stable combustion characteristic index fluctuates erratically, but the mixed fuels’ overall combustion performance is improved. In general, when the blend’s biomass ratio rises, blended fuels made of coal and biomass often have lower ignition and burnout temperatures. According to these results, the blended fuels were simpler to ignite when the biomass was added.
3.3. The Synergistic Effect of Blended Fuel
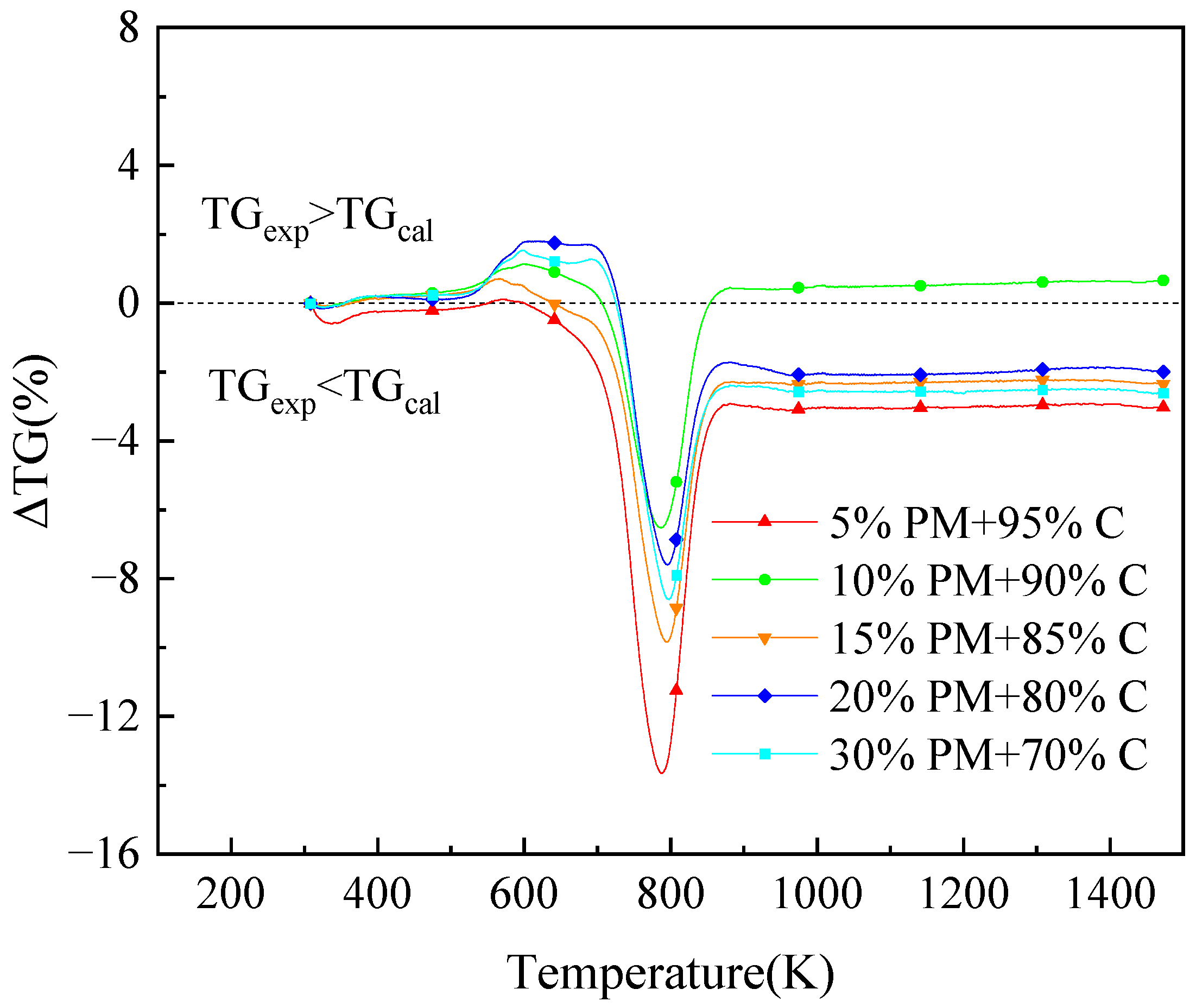
The ΔTG graphs for various coal and pig manure blending percentages are displayed in Figure 4. ΔTG is equal to zero only at the first 309.7 K, indicating that the blending of coal and pig manure is not simply a linear superposition, but rather has an interactive effect. In the previously mentioned calculations. As demonstrated in Figure 4, the residual combustion mass is less than the computed value when there are ΔTG values below zero. This indicates that the actual blended combustion losses are higher than the theoretical losses. This further suggests that when the ΔTG is less than zero, the mixture of burning of coal and pig manure has a synergistic effect rather than being a straightforward linear combination.

Figure 4.
The ΔTG curves of blended fuels of pig manure and coal at different blending ratios.
As seen, 800 K and 596 K are the corresponding locations of the ΔTG peaks for both fuels for most combination ratios. The site of the last peak is not far from these figures. The burning of fixed carbon is the main reason for the peak at about 800 K. Combined with the analysis of the ash composition in Table 2, it is known that alkali and alkaline earth metals are present in the organisms, and alkali metals have a great influence on biomass combustion, as they interact with the components of the mixture during the reaction process, thus showing different combustion states [46,47]. During this period, the addition of pig manure makes it easier to burn the fixed carbon in the mixture. Similar to this, when the amount of pig manure blended is 5%, it has a facilitating influence on the release of volatile components from the mixture during the volatile combustion stage, but other ratios has an inhibitory effect. The burning of fixed carbon is intensive and quick at 683 to 800 K, and the absolute value of ΔTG rises. After that, the absolute value ΔTG shows a decreasing trend, but ΔTG is still less than 0 and in synergistic effect. Figure 4 shows that the ΔTG difference is greatest when the blending ratio of pig manure is 5%. This indicates that the synergistic combustion is at its strongest at this blending ratio. Synergistic effects do not increase with increasing blending ratios, but have different synergistic effects at different ratios. The synergistic impact is at its worst at a blending ratio of 10%. Most of the fuels at the blending ratio remain in the synergistic combustion scenario as the temperature rises above 877 K, as seen in Figure 4.
3.4. Kinetic Analysis
The two fuels’ E and A values fluctuate depending on the blending ratio, as seen in Table 4. Activation energy calculations were performed at conversion rates between 0.2 and 0.8, so the activation energy here represents the activation energy required for combustion reactions with combustion conversion rates between 0.2 and 0.8. When pig manure is blended with coal, most blended fuels have a decreasing activation energy, and as the blending ratio rises, the activation energy steadily drops. The corresponding thermodynamic parameter values can be derived from the peaks of the DTG curves. ΔH is used to denote the measure of the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complexes. The smaller the difference, the more easily combustion can occur. Furthermore, greater values of E compared to ΔH indicate more favorable combustion. It is evident that as the magnitude of ΔG decreases, the energy demands for sustaining the reaction decrease concomitantly [48]. Table 5 demonstrates the correlation between mixing ratio and both ΔH and activation energy, with analogous outcomes observed for the other parameters.

Table 4.
Kinetic parameters of blended fuels.

Table 5.
Thermodynamic parameters of blended fuels.
The activation energy of most of the blended fuels decreases when the ratio of pig manure blending is 15% and the activation energy is 64.98 KJ mol−1. When combining 30% pig manure, the activation energy drops to 44.33 KJ mol−1. The ratio of combining pig manure clearly has a substantial effect on the activation energy, and it significantly affects how well the combined fuels burn. Comparing the blended fuel with straw blended at 15% with the blended fuel with pig manure blended at 15%, it is evident that with a 15% straw blending ratio, the activation energy is 70.38 KJ mol−1, greater than 64.98 KJ mol−1. As shown, blending pig manure has a greater activation energy benefit than blending straw.
4. Conclusions
Biomass combustion typically results in the production of excess ash. Furthermore, the accumulation of manure has the potential to contaminate the environment. The combustion of a mixture of pig manure and coal has been demonstrated to utilize the heat from the former, while concomitantly reducing pollutants and lowering the ash content of the product. In this study, the combustion performance of coal, pig manure, and straw at varying mixing ratios was examined using thermogravimetric analysis. The synergistic effect of coal and hog manure at varying mixing ratios was also analyzed, as were the kinetics. The results of the study are enumerated below:
- (1)
- The entire fuel mixture’s combustion performance can be enhanced by adding pig manure and straw, and this performance will also improve when the blending ratio is increased. When pig manure is blended with coal, the increase in the ratio of pig manure blended makes the ignition temperature decrease from 696 K to 675 K, and the ignition performance is improved, and the same straw has the same effect. Similarly, the addition of biomass also improves the stability of combustion.
- (2)
- The synergistic effect can be seen in the blending of pig manure and coal, and the synergistic effect of adding pig manure is very obvious. The strongest synergistic combustion is exhibited at a blending ratio of 5%, yet the synergistic effect does not increase with increasing ratio but rather demonstrates a fluctuating trend. It is noteworthy that the majority of the blended fuels continue to exhibit a synergistic effect even at temperatures exceeding 913 K.
- (3)
- At 10% and 30% pig manure ratios, respectively, the activation energy was 75.82 KJ mol−1 and 44.33 KJ mol−1, which shows that the activation energy was reduced and it was easier for the reaction to take place. The activation energy of straw blended at 15% and 20% was 70.38 KJ mol−1 and 78.40 KJ mol−1, respectively, whereas pig manure blended at 15% and 20% had an activation energy that was less than 70 KJ mol−1 at the same blending ratio, which indicates that pig manure blended with coal at this ratio is more reactive than that of straw blended. It can be inferred that a 15% blending ratio of pig manure to coal can result in improved combustion outcomes when combined with other indicators such as the activation energy and combustion characteristic index.
Author Contributions
C.S.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft. Y.Z. (Yan Zhang): Investigation, Data curation, Methodology, Writing—original draft. G.L.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. D.W.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review and editing. J.Z.: Investigation, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. K.Y.: Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft. X.W.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. Q.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing—review and editing. X.D.: Data curation, Writing—review and editing. Y.Z. (Yong Zhang): Investigation, Writing—review and editing. J.M.: Data curation, Writing—original draft. L.D.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work acknowledges financial support from the project “Research on the comprehensive utilization technology of coal-fired power station coupled with farming-type solid waste of Guoneng Sanhe Power Generation Co., Ltd.” (HT/YTLY-DZ-JF). The authors also thank the staff at the Instrument Analysis Center of Xi’an Jiaotong University for their assistance with the sample analysis.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this study received funding from Sanhe Power Generation Co., Ltd. Authors Chengzhe Shen, Yan Zhang, Gengsheng Liu, Dongxu Wang, Jinbao Zhang, Kai Yang, Xintong Wen, Quan Sun and Xuejun Douwas employed by the Sanhe Power Generation Co., Ltd. Author Yong Zhang Yantai Longyuan Power Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| A | Pre-exponential factor | R2 | Goodness of fit |
| Aar | Ash content as received basis | S | Comprehensive combustion characteristics index |
| B | Biomass | St, ar | Sulfur element as received basis |
| C | Coal | Tb | Burnout temperature |
| Car | Carbon element as received basis | Ti | Ignition temperature |
| Ci | Flammability index | Net calorific value as received basis | |
| Stable Combustion Characteristic Index | R | Universal gas constant | |
| DTGmax | Maximum burning speed | Change of entropy | |
| DTGmean | Average burning speed | Weight loss of biomass | |
| E | Activation energy | Calculated rates of weight loss | |
| FCar * | Fixed carbon as received basis | Weight loss of coal | |
| Gibbs Free Energy | Experimental rates of weight loss | ||
| h | Planck constant | ΔTG | Total weight loss |
| Har | Hydrogen element as received basis | Tm | Maximum temperature |
| change of enthalpy | Var | Volatile as received basis | |
| kB | Boltzmann constant | α | Conversion rate |
| Mar | Moisture as received basis | β | Steady rate of temperature rise |
| Nar | Nitrogen element as received basis | Contents of biomass | |
| Oar | Oxygen element as received basis | Contents of coal | |
| PM | Pig manure |
References
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Wu, K.; Luo, S.; Fan, W. Progress and Prospect of Research on the Reaction Mechanism of Oxyfuel Combustion of Pulverized Coal. Clean Coal Technol. 2025, 31, 80–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, X.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Oxy-fuel combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of lignite coal from thermo-gravimetric data. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 553, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroshnichenko, D.; Zhylina, M.; Shmeltser, E. Modern Use of Biochar in Various Technologies and Industries. A Review. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2024, 18, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ning, H.; Zang, Z.; Ma, P.; Hu, X.; Xing, X. Co-combustion characteristics and kinetic analyses of coal slime and moso bamboo blends under oxy-fuel conditions. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorokhov, V.; Kuznetsov, G.; Paushkina, K.; Strizhak, P. Kinetics of thermal oxidation of coals, industrial wastes, and their mixtures. Powder Technol. 2025, 454, 120712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, X. Experimental study on the soot emission characteristics of biomass during pressurized pyrolysis. Clean Coal Technol. 2024, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Shang, T. Comparison of thermal efficiency and content of harmful gas released between honeycomb cattle manure and several conventional fuels. China Cattle Sci. 2024, 50, 25–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wen, L.; Xue, L.; Jiang, Z. Analysis of direct combustion characteristics of pig manure based on thermogravimetry. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Huang, G.; Yang, Z.; Han, L. Compositional characteristics and energy potential of Chinese animal manure by type and as a whole. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Song, Z.; Bi, H.; Jiang, C.; Sun, H.; Qiu, Z.; He, L.; Lin, Q. The effect of cellulose on the combustion characteristics of coal slime: TG-FTIR, principal component analysis, and 2D-COS. Fuel 2023, 333, 126310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, T.Y.A.; Fahmy, Y.; Mobarak, F.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Abou-Zeid, R.E. Biomass pyrolysis: Past, present, and future. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, M.; Lyu, D.; Nazari, M.; Shah, A.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Biomass for a sustainable bioeconomy: An overview of world biomass production and utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pstrowska, K.; Łużny, R.; Fałtynowicz, H.; Jaroszewska, K.; Postawa, K.; Pyshyev, S.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Unlocking Sustainability: A Comprehensive Review of Up-Recycling Biomass Waste into Biochar for Environmental Solutions. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2024, 18, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayoga, M.Z.E.; Putra, H.P.; Adelia, N.; Luktyansyah, I.M.; Ifanda, I.; Prismantoko, A.; Darmawan, A.; Hartono, J.; Wirawan, S.S.; Aziz, M.; et al. Co-combustion performance of oil palm biomass with coal: Thermodynamics and kinetics analyses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 2873–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Z. Kinetic characterization of coupled low calorific value coal/biomass combustion based on thermogravimetric analysis. Coal Technol. 2025, 44, 228–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, C.; He, L.; Li, B.; Peng, G.; Ma, X. Co-combustion characteristics, interaction and kinetic analysis of multiple coal and eucalyptus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, M.; He, H.; Song, F.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, J.; Lu, S.; Sang, S.; Wu, J. Co-pyrolysis and co-combustion characteristics of low-rank coal and waste biomass: Insights into interactions, kinetics and synergistic effects. J. Energy Inst. 2025, 118, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Gangil, S. Thermo-kinetic analysis of pyrolysis of chickpea stalk using thermogravimetric analysis and artificial neural network. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 198, 107860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Luo, H.; Ren, S. Characterization and kinetic analysis of combustion of cow manure mixed with corn stover. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2024, 45, 635–642. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q. Study of Mixed Combustion Behavior of Pulverized Municipal Solid Waste and Anthracite Coal. Processes 2024, 12, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhong, Z. Optimization of the co-combustion of coal and composite biomass pellets. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 28731-2012; Proximate analysis of solid biofuels. State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration (SACMA), Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 28734-2012; Determination of Carbon and Hydrogen in Solid Biofuels. Administration of the People’s Republic of China for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 212-2008; Proximate Analysis of Coal. State General Administration of the People’s Republic of China for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 30733-2014; Determination of Total Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen Content in Coal―Instrumental Method. Testing and Research Branch of the General Research Institute of Coal Science (GRIC),Shenhua Trading Group Limited, Changsha Kaiyuan Instrument Co.: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 30727-2014; Determination of Calorific Value in Solid Biofuels. Administration of the People’s Republic of China for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- GB/T213-2008; Determination of Calorific Value of Coal. Administration of the People’s Republic of China for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W.; Sun, J.; Chang, K.; Kuo, J.; Xie, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, S.; et al. Co-combustion thermal conversion characteristics of textile dyeing sludge and pomelo peel using TGA and artificial neural networks. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Singh, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S. A thermogravimetric assessment of the tri-combustion process for coal, biomass and polyethylene. Fuel 2021, 287, 119355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G. Combustion Characteristics and Kinetic Analysis of Biomass Pellet Fuel Using Thermogravimetric Analysis. Processes 2021, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wen, S.; Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Kuo, J.; Lu, X.; Sun, S.; Chang, K.; Buyukada, M.; Evrendilek, F. Comparative thermogravimetric analyses of co-combustion of textile dyeing sludge and sugarcane bagasse in carbon dioxide/oxygen and nitrogen/oxygen atmospheres: Thermal conversion characteristics, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Liang, W.X.; Qin, H.; Wang, Q. Synergy in co-combustion of oil shale semi-coke with torrefied cornstalk. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Reinmöller, M.; Meyer, B. Effect of inherent mineral matter on the co-pyrolysis of highly reactive brown coal and wheat straw. Fuel 2019, 239, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Huang, X.; Ren, J.; Deng, L.; Da, Y. Thermogravimetric Assessment and Differential Thermal Analysis of Blended Fuels of Coal, Biomass and Oil Sludge. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.A.D.; de Morais, L.C. Kinetic parameters of red pepper waste as biomass to solid biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Li, Z.; Meng, W. Research on coal combustion catalysts for cement kiln via comprehensive evaluation method based on combustion characteristics. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 50, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.W.; Redfern, J.P. Kinetic Parameters from Thermogravimetric Data. Nature 1964, 201, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.a.; Che, D. Experimental study on interaction and kinetic characteristics during combustion of blended coals. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Tariq, R.; Hameed, Z.; Ali, I.; Naqvi, M.; Chen, W.H.; Ceylan, S.; Rashid, H.; Ahmad, J.; Taqvi, S.A.; et al. Pyrolysis of high ash sewage sludge: Kinetics and thermodynamic analysis using Coats-Redfern method. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, K.S.; Libra, J.A.; Bae, S.; Berge, N.D.; Flora, J.R.V.; Pecenka, R. Combustion Behavior of Animal-Manure-Based Hydrochar and Pyrochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mohanty, K. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behavior of waste sawdust biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, K.K.; Prabhansu, S.; Kumar, K.M.; Kumar, P.A.; Chatterjee, P.K. A comparative study on pyrolysis characteristics of bituminous coal and low-rank coal using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharara, M.A.; Sadaka, S.S.; Costello, T.A.; VanDevender, K.; Carrier, J.; Popp, M.; Thoma, G.; Djioleu, A. Combustion kinetics of swine manure and algal solids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lopez, M.; Pedrosa-Castro, G.J.; Valverde, J.L.; Sanchez-Silva, L. Kinetic analysis of manure pyrolysis and combustion processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, L. Thermodynamics and synergistic effects on the co-combustion of coal and biomass blends. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 7749–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, D.; Mahanta, P.; Moholkar, V.S. Synergistic Effects in Gasification of Coal/Biomass Blends: Analysis and Review. In Coal and Biomass Gasification: Recent Advances and Future Challenges; De, S., Agarwal, A.K., Moholkar, V.S., Thallada, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, R. Combustion Characterization and Kinetic Analysis of Mixed Sludge and Lignite Combustion. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 6912–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).