A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Livestock Manure
3. Environmental Impact of Livestock Manure Generation
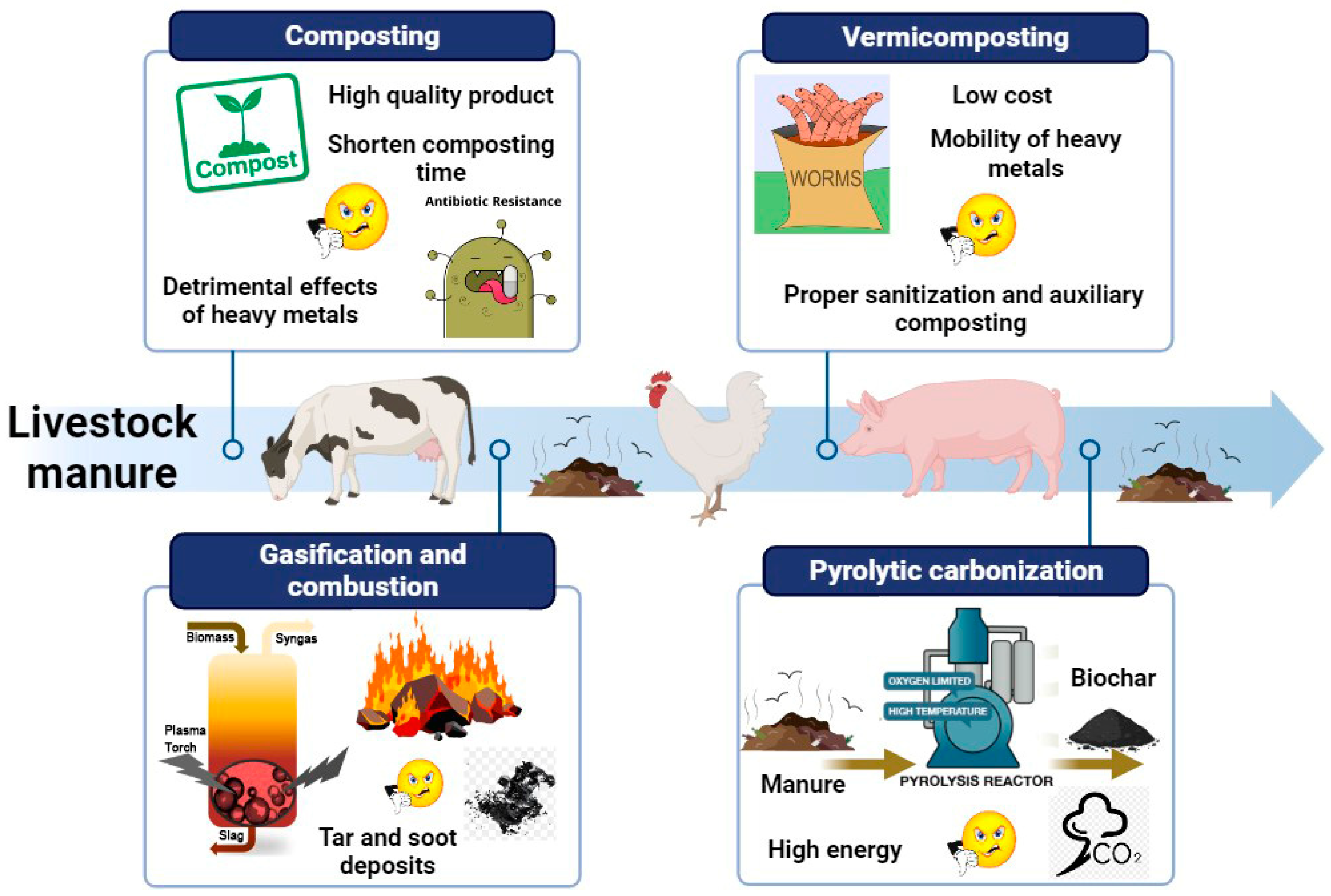
4. Global Livestock Manure Management Practices
4.1. Composting
4.2. Vermicomposting
4.3. Gasification and Combustion
4.4. Pyrolytic Carbonization
4.5. Pros and Cons of Global Livestock Manure Management Practices
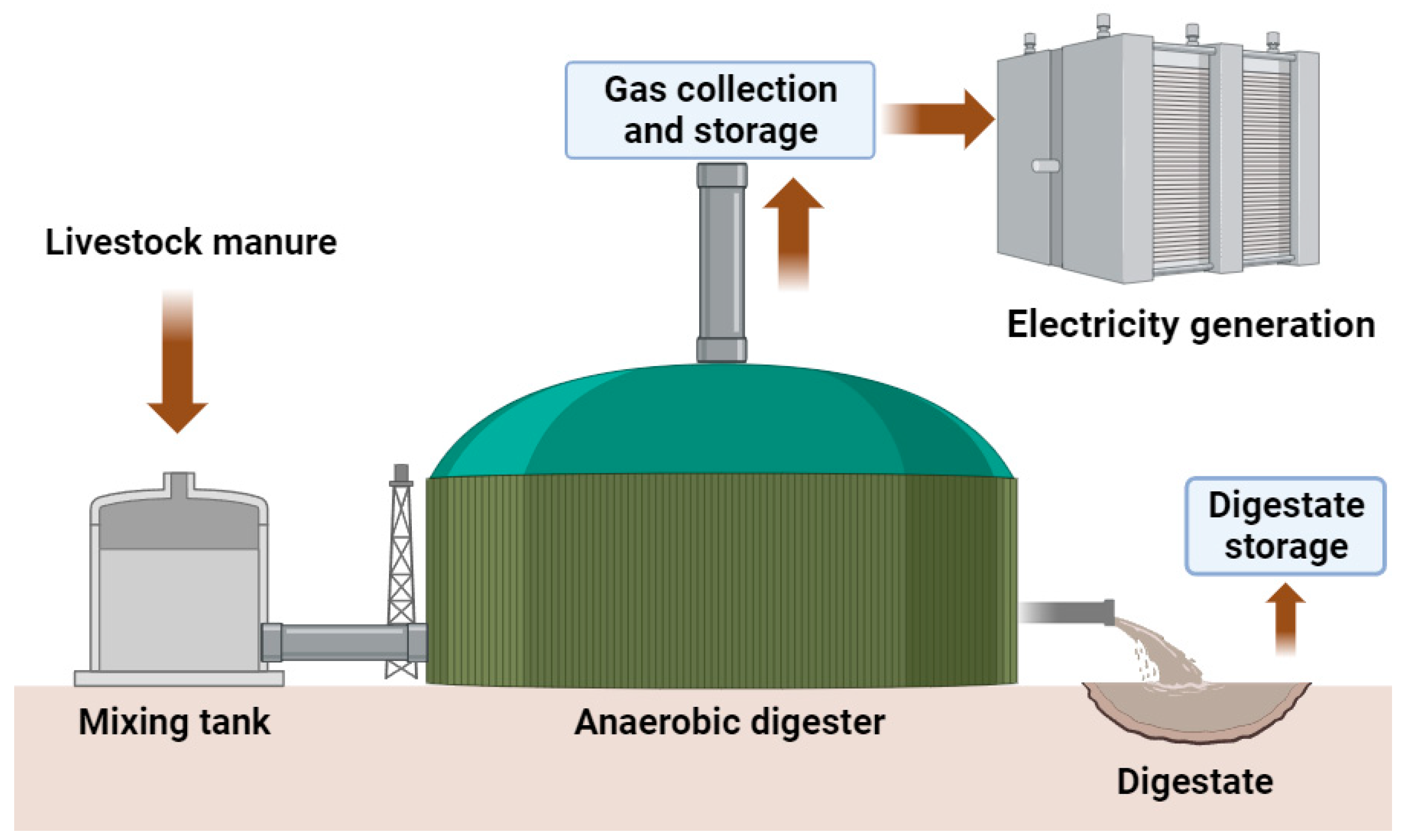
5. Anaerobic Digestion of Livestock Manures
- Sugar and Amino Acid Fermentation
- Long-Chain Fatty Acids Anaerobic Oxidation
- Acetogenesis
- Acetoclastic Methanogenesis
- Hydrogenotrophic Methanogenesis
6. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures and Its Synergistic Effects
7. Progress, Challenges, and Future Direction
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Haque, M.A.; Kabir, A.; Hashem, M.A.; Azad, M.A.K.; Bhuiyan, M.; Rahman, M. Efficacy of Biogas Production from Different Types of Livestock Manures. Int. J. Smart Grid 2021, 5, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zou, D.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Xiao, Z. Review on fate and bioavailability of heavy metals during anaerobic digestion and composting of animal manure. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasińska, A.; Grosser, A.; Meers, E. Possibilities and Limitations of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Animal Manure—A Critical Review. Energies 2023, 16, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, F.E. Soil Organic Matter and Its Role in Crop Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Hulse, J.H. Sustainable Development at Risk: Ignoring the Past; IDRC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J.; Sharpley, A.; Stewart, B.; Smith, S. Environmental impact of animal manure management in the southern plains. In Proceedings of the International Summer Meeting, Spokane, WA, USA, 20–23 June 1993. Paper No. 934011. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; McCarl, B.; Fei, C. Climate change and livestock production: A literature review. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, V.; Bowman, G.; Haubensak, M.; Baier, U.; Thees, O. Valorization of an untapped resource: Energy and greenhouse gas emissions benefits of converting manure to biogas through anaerobic digestion. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.Y. Feasibility of thermal hydrolysis pretreatment to reduce hydraulic retention time of anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufaner, F.; Avşar, Y. Effects of co-substrate on biogas production from cattle manure: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperatou, A.; Rasmussen, N.B.; Gavala, H.N.; Skiadas, I.V. Improving the anaerobic digestion of swine manure through an optimized ammonia treatment: Process performance, digestate and techno-economic aspects. Energies 2021, 14, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; McAdam, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Longhurst, P. Ammonia inhibition and toxicity in anaerobic digestion: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, M.M.; Sapci, Z.; Linjordet, R.; Schnürer, A.; Morken, J. Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and steam-exploded Salix with recirculation of liquid digestate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 136, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenien, F.; Namba, Y.; Kosseva, M.R.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Enhancement of methane production from co-digestion of chicken manure with agricultural wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanthong, K.; Kadam, R.; Kim, T.; Park, J. Synergetic effects of anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and algae on biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Oh, K.; Lee, B.; Pak, D.; Cha, J.; Park, J. Characteristics of biogas production from organic wastes mixed at optimal ratios in an anaerobic co-digestion reactor. Energies 2021, 14, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Kang, S.; Kim, K.; Park, J. Shockwave pre-treatment enhances the physicochemical availability and anaerobic mono-and co-digestion of highly concentrated algae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.K.; Fdez-Güelfo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.; Garcia, L.R.; Ng, W.J. Anaerobic co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW): Progress and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 380–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ndegwa, P.; Harrison, J.H.; Chen, Y. Methane yields during anaerobic co-digestion of animal manure with other feedstocks: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shober, A.L.; Maguire, R.O. Manure management. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FAO Livestock Systems. Available online: https://www.fao.org/livestock-systems/global-distributions/en/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Scarlat, N.; Fahl, F.; Dallemand, J.-F.; Monforti, F.; Motola, V. A spatial analysis of biogas potential from manure in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgutis, L.; Slepetiene, A.; Volungevicius, J.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K. Biogas production from chicken manure at different organic loading rates in a mesophilic full scale anaerobic digestion plant. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 141, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental sustainability assessment of pig manure mono-and co-digestion and dynamic land application of the digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Fuentes, J.; Capobianco, A.; Barbušová, J.; Hutňan, M. Manure from our agricultural animals: A quantitative and qualitative analysis focused on biogas production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Livestock and Environment Statistics: Manure and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Available online: https://www.fao.org/food-agriculture-statistics/data-release/data-release-detail/fr/c/1329440/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Sandars, D.; Audsley, E.; Canete, C.; Cumby, T.; Scotford, I.; Williams, A. Environmental benefits of livestock manure management practices and technology by life cycle assessment. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 84, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, C. Treatment of cattle manure by anaerobic co-digestion with food waste and pig manure: Methane yield and synergistic effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, D.-Y.; Harvey, J.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Improving biomethanation of chicken manure by co-digestion with ethanol plant effluent. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daramy, M.A.; Kawada, R.; Oba, S. Alterations of the chemical compositions, surface functionalities, and nitrogen structures of cage layer chicken manure by carbonization to improve nitrogen bioavailability in soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelster, D.E.; Gisore, B.; Goopy, J.; Korir, D.; Koske, J.; Rufino, M.C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from cattle excreta on an East African grassland. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, A.; Eraky, M.; Osman, A.I.; Ai, P.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, F.; Rooney, D.W. Bioenergy production from chicken manure: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2707–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Emissions from Livestock and Manure Management; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, A.; Liao, P.H.; Lo, K.V.; Harada, S. Optimization of radiofrequency-oxidation treatment of dairy manure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliver, D.O. Disinfection of animal manures, food safety and policy. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5392–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Ye, J.; Liang, J.; Nabi, M.; Zhou, Z.; Tao, X.; Chen, N.; Sun, K. Biological nutrient removal and recovery from solid and liquid livestock manure: Recent advance and perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Goyette, B.; Raghavan, V.; Bhaskar, A.; Rajagopal, R. Nutrient recovery via struvite production from livestock manure-digestate streams: Towards closed loop bio-economy. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; He, Z. Pelletizing animal manures for on-and off-farm use. Anim. Manure Prod. Charact. Environ. Concerns Manag. 2020, 67, 323–344. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnevisan, B.; Duan, N.; Tsapekos, P.; Awasthi, M.K.; Liu, Z.; Mohammadi, A.; Angelidaki, I.; Tsang, D.C.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J. A critical review on livestock manure biorefinery technologies: Sustainability, challenges, and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Febrisiantosa, A. Improvement of nitrogen balance (land budget) in South Korea in terms of livestock manure: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012011. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, R.; Khanthong, K.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Occurrence, fate, and implications of heavy metals during anaerobic digestion: A review. Energies 2022, 15, 8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S. Microbial transformation of nitrogen during composting. In Microbiology of Composting; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, R.; Gibbs, P.; Burchett, S.; Misselbrook, T. Effect of turning regime and seasonal weather conditions on nitrogen and phosphorus losses during aerobic composting of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Awasthi, M.K.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z. Combining biochar, zeolite and wood vinegar for composting of pig manure: The effect on greenhouse gas emission and nitrogen conservation. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Duan, Y.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z. Effect of biochar and bacterial inoculum additions on cow dung composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chadwick, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Luo, W.; Du, L.; He, S.; Peng, S. Effects of aeration rate on maturity and gaseous emissions during sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Garg, V. Vermicomposting of waste: A zero-waste approach for waste management. In Sustainable Resource Recovery and Zero Waste Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hanc, A.; Enev, V.; Hrebeckova, T.; Klucakova, M.; Pekar, M. Characterization of humic acids in a continuous-feeding vermicomposting system with horse manure. Waste Manag. 2019, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Xing, M.; Yang, J. Speciation and transformation of heavy metals during vermicomposting of animal manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, A.; Mamphweli, S.; Reddy, P.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, O. Pre-processing of sugarcane bagasse for gasification in a downdraft biomass gasifier system: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 775–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalólio, F.S.; da Silva, J.N.; de Oliveira, A.C.C.; Tinôco, I.d.F.F.; Barbosa, R.C.; de Oliveira Resende, M.; Albino, L.F.T.; Coelho, S.T. Poultry litter as biomass energy: A review and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Pandey, D.S.; Haynes-Parry, M.; Briggs, C.; Manuel, H.L.C.; Umapathi, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Panigrahi, S.; Goel, M. Sustainable valorisation of animal manures via thermochemical conversion technologies: An inclusive review on recent trends. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 553–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradian, F.; Pettersson, A.; Svärd, S.H.; Richards, T. Co-combustion of animal waste in a commercial waste-to-energy BFB boiler. Energies 2013, 6, 6170–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Jensen, A.D.; Jensen, P.A. Retention of organic elements during solid fuel pyrolysis with emphasis on the peculiar behavior of nitrogen. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, L.; Yao, Y.; Sun, G.; Guo, X. Anaerobic digestion of swine manure using aqueous pyrolysis liquid as an additive. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Shahzad, S.M.; Chatterjee, N.; Arif, M.S.; Farooq, T.H.; Altaf, M.M.; Tufail, M.A.; Dar, A.A.; Mehmood, T. Nitrous oxide emission from agricultural soils: Application of animal manure or biochar? A global meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, Y.K.; Barkat, A.; CUI, X.-Q.; Ying, F.; PAN, F.-S.; Lin, T.; YANG, X.-E. Cow manure and cow manure-derived biochar application as a soil amendment for reducing cadmium availability and accumulation by Brassica chinensis L. in acidic red soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Impraim, R.; Coates, T.; Flesch, T.; Trouve, R.; van Grinsven, H.; Cao, Y.; Hill, J.; Chen, D. Lignite effects on NH3, N2O, CO2 and CH4 emissions during composting of manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Park, J.; Shin, W.; Kim, B.; Byun, B.; Jun, H. Maximizing biogas production by pretreatment and by optimizing the mixture ratio of co-digestion with organic wastes. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 24, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Ekama, G.A.; Brdjanovic, D. Biological Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.M. Anaerobic Co-Digestion: Design of Substrate Mixtures and the Impacts on Process Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Batstone, D.; Keller, J.; Angelidaki, I.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Pavlostathis, S.; Rozzi, A.; Sanders, W.; Siegrist, H.; Vavilin, V. Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 (ADM1), IWA Task Group for Mathematical Modelling of Anaerobic Digestion Processes; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Karki, R.; Chuenchart, W.; Surendra, K.; Shrestha, S.; Raskin, L.; Sung, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic co-digestion: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chae, C.; Kim, H.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, I. Investigation to Enhance Solid Fuel Quality in Torrefaction of Cow Manure. Energies 2023, 16, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougias, P.G.; Angelidaki, I. Biogas and its opportunities—A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Mohd Ghazi, T.I.; Omar, R. Anaerobic digestion technology in livestock manure treatment for biogas production: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehhaghi, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M.; Panahi, H.K.S.; Nizami, A.-S. A state-of-the-art review on the application of nanomaterials for enhancing biogas production. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillero, L.; Solera, R.; Perez, M. Improvement of the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by co-digestion with wine vinasse and poultry manure: Effect of different hydraulic retention times. Fuel 2022, 321, 124104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, M.; Castellucci, S.; Moneti, M. Biogas production from poultry manure and cheese whey wastewater under mesophilic conditions in batch reactor. Energy Procedia 2015, 82, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Khan, A.; Xiong, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X. A critical review on the interaction of substrate nutrient balance and microbial community structure and function in anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Nikolausz, M.; Zhang, J.; Riya, S.; Terada, A.; Hosomi, M. Variation of the microbial community in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of pig manure mixed with different ratios of rice straw. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 122, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure and corn stover in batch and continuously stirred tank reactor (CSTR). Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Harun, R.M.; Mohd Ghazi, T.; Wan Azlina, W.; Idris, A.; Yunus, R. Anaerobic treatment of cattle manure for biogas production. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of American Institute of Chemical Engineers, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 16–21 November 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- MarañóN, E.; Castrillón, L.; Vázquez, I.; Sastre, H. The influence of hydraulic residence time on the treatment of cattle manure in UASB reactors. Waste Manag. Res. 2001, 19, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahring, B.K.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Mladenovska, Z. Effect of temperature increase from 55 to 65 C on performance and microbial population dynamics of an anaerobic reactor treating cattle manure. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harikishan, S.; Sung, S. Cattle waste treatment and Class A biosolid production using temperature-phased anaerobic digester. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andara, A.R.G.; Esteban, J.L. Kinetic study of the anaerobic digestion of the solid fraction of piggery slurries. Biomass Bioenergy 1999, 17, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, K.; Jang, A.; Yim, S.; Kim, I.S. The effects of digestion temperature and temperature shock on the biogas yields from the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, D.I.; Masse, L.; Croteau, F. The effect of temperature fluctuations on psychrophilic anaerobic sequencing batch reactors treating swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Gamiz, M.; Almeida, M.; Ruiz, A. Pilot project of biogas production from pig manure and urine mixture at ambient temperature in Ventanilla (Lima, Peru). Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujoczek, G.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Sparling, R.; Cenkowski, S. High solid anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 76, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atuanya, E.I.; Aigbirior, M. Mesophilic biomethanation and treatment of poultry waste-water using pilot scale UASB reactor. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 77, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenien, F.; Fujiwara, W.; Namba, Y.; Kosseva, M.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Improved methane fermentation of chicken manure via ammonia removal by biogas recycle. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6368–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherzadeh, M.J.; Karimi, K. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1621–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, M.-Q.; Borja, V.-M. Pretreatment of animal manure biomass to improve biogas production: A review. Energies 2020, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.; Sun, C. Comparison of anaerobic digestion characteristics and kinetics of four livestock manures with different substrate concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, C. Biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of durian shell with chicken, dairy, and pig manures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 198, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millati, R.; Wikandari, R.; Ariyanto, T.; Putri, R.U.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Pretreatment technologies for anaerobic digestion of lignocelluloses and toxic feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Methods for increasing the biogas potential from the recalcitrant organic matter contained in manure. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.R.; Banjara, S.P.; Choi, O.K.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.W. Pretreatment of agricultural biomass for anaerobic digestion: Current state and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, R.; Poulsen, T.G.; Nizami, A.-S.; Murphy, J.D.; Kiely, G. Effect of thermal, chemical and thermo-chemical pre-treatments to enhance methane production. Energy 2010, 35, 4556–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ni, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Yan, X.; Leng, X.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Pretreatment of swine manure containing β-lactam antibiotics with whole-cell biocatalyst to improve biogas production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.S.; Sutaryo, S.; Ward, A.J.; Møller, H.B. Effects of high-temperature isochoric pre-treatment on the methane yields of cattle, pig and chicken manure. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Barbosa, S.; Alves, M.; Sousa, D. Thermochemical pre-and biological co-treatments to improve hydrolysis and methane production from poultry litter. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J.; Romero-Güiza, M.; Fonoll, X.; Peces, M.; Astals, S. A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010 and 2013. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dębowski, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Nowicka, A.; Rokicka, M.; Szwarc, K. Cavitation-based pretreatment strategies to enhance biogas production in a small-scale agricultural biogas plant. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2019, 49, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuenchart, W.; Logan, M.; Leelayouthayotin, C.; Visvanathan, C. Enhancement of food waste thermophilic anaerobic digestion through synergistic effect with chicken manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 136, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qin, K.; Ding, J.; Xue, M.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q. Optimization of the co-digestion of sewage sludge, maize straw and cow manure: Microbial responses and effect of fractional organic characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bian, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, F.; Ye, F.; Jin, T.; Pan, M.; Chen, T.; Yan, J. Thermal-alkali and enzymes for efficient biomethane production from co-digestion of corn straw and cattle manure. Bioresources 2019, 14, 5422–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; Yang, G. Process performance and methane production optimizing of anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure and corn straw. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agayev, E.; Ugurlu, A. Biogas production from co-digestion of horse manure and waste sewage sludge. TechConnect Briefs 2011, 3, 657–660. [Google Scholar]
- Astals, S.; Nolla-Ardèvol, V.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and crude glycerol at mesophilic conditions: Biogas and digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanpracha, N.; Annachhatre, A.P. Anaerobic co-digestion of cyanide containing cassava pulp with pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Paranhos, A.G.; Adarme, O.F.H.; Barreto, G.F.; de Queiroz Silva, S.; de Aquino, S.F. Methane production by co-digestion of poultry manure and lignocellulosic biomass: Kinetic and energy assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122588. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre, G.; Gómez, M.; Pascual, A.; Ruiz, B. Anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure with rice straw: Economic & energy feasibility. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Bicho, P.; Wu, Q. Effect of steam explosion treatment on characteristics of wheat straw. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Saifullah Lar, J.; He, Y.; Zhu, B. Anaerobic codigestion of kitchen waste with cattle manure for biogas production. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtomäki, A.; Huttunen, S.; Rintala, J. Laboratory investigations on co-digestion of energy crops and crop residues with cow manure for methane production: Effect of crop to manure ratio. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 51, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, C.; Muñoz, N.; Fernández, J.; Rico, J.L. High-load anaerobic co-digestion of cheese whey and liquid fraction of dairy manure in a one-stage UASB process: Limits in co-substrates ratio and organic loading rate. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Fernández, C.; Gómez, X.; Morán, A. Anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure with energy crop residues. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-Y.; Zhong, C. Effects of feed to inoculum ratio, co-digestion, and pretreatment on biogas production from anaerobic digestion of cotton stalk. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudi, K.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Romero-García, L.I. Semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of sugar beet byproduct and pig manure: Effect of the organic loading rate (OLR) on process performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, A.; Molaey, R.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Sahinkaya, E.; Çalli, B. Biogas production from chicken manure: Co-digestion with spent poppy straw. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahunsi, S.; Osueke, C.; Olayanju, T.; Lawal, A. Co-digestion of Theobroma cacao (Cocoa) pod husk and poultry manure for energy generation: Effects of pretreatment methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 283, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; Han, X. Optimizing feeding composition and carbon–nitrogen ratios for improved methane yield during anaerobic co-digestion of dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.-H.; Wu, G.; Zhan, X. Impact of total solids content on anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste: Insights into shifting of the methanogenic pathway. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennehy, C.; Lawlor, P.; McCabe, M.; Cormican, P.; Sheahan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Gardiner, G. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste; effects on digestate biosafety, dewaterability, and microbial community dynamics. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yi, J. High-solid anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and cattle manure: The effects of volatile solid ratio and pH. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-S.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, B.-S.; Lee, E.Y. Comparison of microbial communities in swine manure at various temperatures and storage times. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Bai, S.; Zhao, X. Recognition of core microbial communities contributing to complex organic components degradation during dry anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbayram, E.G.; Ince, O.; Ince, B.; Harms, H.; Kleinsteuber, S. Comparison of rumen and manure microbiomes and implications for the inoculation of anaerobic digesters. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupper, T.; Bürge, D.; Bachmann, H.J.; Güsewell, S.; Mayer, J. Heavy metals in source-separated compost and digestates. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, S.; Lucas, J., Jr.; Santos, D.; Costa, M. Anaerobic co-digestion of sweet potato and dairy cattle manure: A technical and economic evaluation for energy and biofertilizer production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataki, S.; Hazarika, S.; Baruah, D. Assessment of by-products of bioenergy systems (anaerobic digestion and gasification) as potential crop nutrient. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.-G.; Chen, Q.-L.; Hu, H.-W.; He, J.-Z. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes during high-solid anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure with lignite. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Tuo, X.; Guo, A.; Qiu, L. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during anaerobic co-digestion of Chinese medicinal herbal residues and swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Norli, I.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Yhaya, M.F. Impacts of trace element supplementation on the performance of anaerobic digestion process: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, J.H.; Labatut, R.A.; Lodge, J.S.; Williamson, A.A.; Trabold, T.A. Anaerobic co-digestion of commercial food waste and dairy manure: Characterizing biochemical parameters and synergistic effects. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Energy production from different organic wastes by anaerobic co-digestion: Maximizing methane yield versus maximizing synergistic effect. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, C.A.; Moset, V.; Wahid, R.; Møller, H.B. The efficiency of shredded and briquetted wheat straw in anaerobic co-digestion with dairy cattle manure. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 139, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Saikawa, A.; Tarukawa, K.; Qi, G.; Pan, Z.; Yamashiro, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Ihara, I.; Nishida, T.; Umetsu, K. Anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure, meat and bone meal, and crude glycerol under mesophilic conditions: Synergistic effect and kinetic studies. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 40, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhou, M.; Pan, X.; Li, C.; Lv, N.; Wang, T.; Cai, G.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhu, G. Simultaneous biogas and biogas slurry production from co-digestion of pig manure and corn straw: Performance optimization and microbial community shift. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, S.; Mi, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X. Effects of feedstock ratio and organic loading rate on the anaerobic mesophilic co-digestion of rice straw and cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Umar, M.; Ding, W.; Mehryar, E.; Zhao, C. Methane enhancement through co-digestion of chicken manure and oxidative cleaved wheat straw: Stability performance and kinetic modeling perspectives. Energy 2017, 141, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.; Cui, S.; Yu, Q.; Ma, R. Anaerobic co-digestion of animal manures with corn stover or apple pulp for enhanced biogas production. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.B.; Sørensen, P.; Olesen, J.E.; Petersen, S.O.; Nyord, T.; Sommer, S.G. Agricultural biogas production—Climate and environmental impacts. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.N.I.; Wahid, Z.A. Achievements and perspectives of anaerobic co-digestion: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Ren, G. Anaerobic co-digestion of animal manure and wheat straw for optimized biogas production by the addition of magnetite and zeolite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 97, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Attia, Y.; Abdel-Hadi, M.; Hassan, H.; Badr, Y. Effects of Co and Ni nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 141, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parawira, W. Enzyme research and applications in biotechnological intensification of biogas production. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahunsi, S.; Oranusi, S.; Efeovbokhan, V. Pretreatment optimization, process control, mass and energy balances and economics of anaerobic co-digestion of Arachis hypogaea (Peanut) hull and poultry manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naran, E.; Toor, U.A.; Kim, D.-J. Effect of pretreatment and anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and waste activated sludge on stabilization and methane production. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, E.; Antonopoulou, G.; Lyberatos, G.; Gavala, H.N.; Skiadas, I.V. Continuous anaerobic digestion of swine manure: ADM1-based modelling and effect of addition of swine manure fibers pretreated with aqueous ammonia soaking. Appl. Energy 2016, 172, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, B.; Tian, D.; Jun, H. Bioelectrochemical enhancement of methane production from highly concentrated food waste in a combined anaerobic digester and microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muha, I.; Zielonka, S.; Lemmer, A.; Schönberg, M.; Linke, B.; Grillo, A.; Wittum, G. Do two-phase biogas plants separate anaerobic digestion phases?—A mathematical model for the distribution of anaerobic digestion phases among reactor stages. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.-F.; Xu, X.-H.; Dai, M.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Guo, R.-B. Hydrogen and methane production from vinasse using two-stage anaerobic digestion. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.-C. A bench scale study of fermentative hydrogen and methane production from food waste in integrated two-stage process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Cattle Manure | Pig Manure | Chicken Manure |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS (g/kg) | 200–310 | 50–70.6 | 132–171 |
| VS(g/kg) | 150–235.3 | 45–56.5 | 55–75 |
| TSS (g/kg) | 250–280 | 46–58.5 | NA |
| VSS (g/kg) | 190–230 | 34–46.8 | NA |
| pH | 7.0–8.0 | 7.0–7.6 | 6.9–7.4 |
| TCOD (g/kg) | 290.8 | 134.5 | 87–130 |
| SCOD(g/kg) | 22.5 | 39.4 | 32–97 |
| TVFAs (g COD/kg) | 1.5 | 22.3 | 10–50 |
| TN (g/kg) | 9.1 | 6.1 | 4 |
| TP (g/kg) | 1.0 | 1.8 | 8.1 |
| C (%) of dm | 38.8 | 46.4 | 30.92 |
| H (%) of dm | 4.9 | 5.9 | 3.89 |
| O (%) of dm | 29.3 | 34.5 | 32.08 |
| N (%) of dm | 1.6 | 2.1 | 7.74 |
| Alkalinity (g CaCO3/kg) | 32.7 | 13.8 | NA |
| Livestock Manure Management Practice | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Composting | Compost product, pathogen elimination, volume reduction, mobilizing soil nutrients, improves soil fertility. | GHG emissions (932 g kg−1 of CO2 and 0.4 g kg−1 of N2O), residue of heavy metals and antibiotics. |
| Vermicomposting | Vermicompost, soil enrichment, limited mobility of heavy metals. | Limitation in commercial application |
| Gasification and combustion | Syngas, processing versatility, heat, and power generation. | Low efficiency (50% for gasification and 45–55% for combustion). |
| Pyrolytic carbonization | Bio-oil and biochar. | High energy input. |
| Livestock Manure | Reactor Type | Temperature (°C) | OLR (kg VS m−3 day−1) | HRT (d) | Biogas Yield (m3 kg−1 VS) | CH4 Content (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Batch | 53 | NA | 17 | 0.159 | 65 | [74] |
| Cattle | UASB | 37 | 2.35 | 22.5 | 0.200 | 64 | [75] |
| Cattle | CSTR | 55 | 3 | 15 | NA | NA | [76] |
| Cattle | TPAD | 35 | 5.8 | 14 | NA | 60 | [77] |
| Pig | Stirred Batch | 35 | 12.39 | 0.9–3.6 | NA | 50 | [78] |
| Pig | Batch | 25 | NA | 20 | NA | 44 | [79] |
| Pig | ASBR | 20 | 1.1 | 15 | NA | 75 | [80] |
| Pig | Batch | 22.6 | NA | 80 | 0.207 | 22 | [81] |
| Pig | Batch | 35 | NA | 15 | NA | 70 | [82] |
| Chicken | Batch | 35 | NA | 33 | NA | 41 | [82] |
| Chicken | UASB | 34 | 2.9 | 13.2 | NA | NA | [83] |
| Chicken | Batch | 55 | NA | 10 | NA | 67 | [84] |
| Livestock Manure | Type of Pretreatment | CH4 (mL/g VS) | CH4 Enhancement (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Physical (maceration and pressurized at 100 atm. pressure | 276 | 20 | [90] |
| Chemical (peracetic acid) | 182.4 | 39 | [91] | |
| Biological (Incubation with B4 bacteria) | 300 | 30 | [90] | |
| Pig | Physiochemical (100 °C) for 1 h | 237.5 | 28 | [92] |
| Chemical, Ca (OH)2, 1 h (70 °C) | 345 | 72 | [92] | |
| Biological (cell biocatalyst) | 98.7 | 93.2 | [93] | |
| Chicken | Physiochemical (High pressure and temperature) | 518 | 54.6 | [94] |
| Chemical, Ca (OH)2, at 90 °C and 1.27 bar pressure | 137 | NA | [95] | |
| Biological (Clostridium saccharolyticum and Clostridium thermocellum as bioaccumulation strains) | 102 | 15 | [95] |
| Livestock Manure | Co-Substrate | Reactor Configuration | Biogas or CH4 Production Increase | Methane (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Wheat straw | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.460 m3/kg VSadd (+24.6%) | 53 (1.3%) | [97] |
| Food waste | CSTR | Sp. CH4 yield 0.6–0.8 m3/kg VSadd +88.6%) | 61.3–65.8 (+4.7%) | [98] | |
| Maize straw | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.534–0.614 m3/kg VSadd (39.8%) | 51.2–58.6 (+39.5%) | [99] | |
| Corn straw | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.290 m3/kg VSadd (+31.8%) | NA | [100] | |
| Pig | Corn straw | Batch | CH4 yield 220 (mL/g VSadd) At PM:CS-70:30 | [101] | |
| Sewage sludge | Batch | Biogas yield 410 mL/g VSadd at TS 2% | 65% at TS 2% | [102] | |
| Glycerol | CSTR | Biogas production 5.44–5.58 L/g VSadd | NA | [103] | |
| Cassava pulp | Semi-continuous reactor | Sp. Methane yield 380 mL/g VSadd | NA | [104] | |
| Chicken | Agricultural waste | 500 mL anaerobic vials | CH4 yield 695 mL/g VS | NA | [14] |
| Rice straw | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.123–270 m3/kg VSadd | NA | [105] | |
| Corn cob | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.131–0.291m3/kg VSadd | NA | [105] | |
| Sugar cane bagasse | Batch | Sp. CH4 yield 0.140–230 m3/kg VSadd | NA | [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadam, R.; Jo, S.; Lee, J.; Khanthong, K.; Jang, H.; Park, J. A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management. Energies 2024, 17, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030546
Kadam R, Jo S, Lee J, Khanthong K, Jang H, Park J. A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management. Energies. 2024; 17(3):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030546
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadam, Rahul, Sangyeol Jo, Jonghwa Lee, Kamonwan Khanthong, Heewon Jang, and Jungyu Park. 2024. "A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management" Energies 17, no. 3: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030546
APA StyleKadam, R., Jo, S., Lee, J., Khanthong, K., Jang, H., & Park, J. (2024). A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management. Energies, 17(3), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030546







