Research on Voltage Compensation Methods and Optimization Algorithm for Insulated Core Transformer High-Voltage Power Supply
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Compensation Methods
2.1. Turns Compensation Method
2.2. Dummy Primary Winding Compensation Method (DPWC)
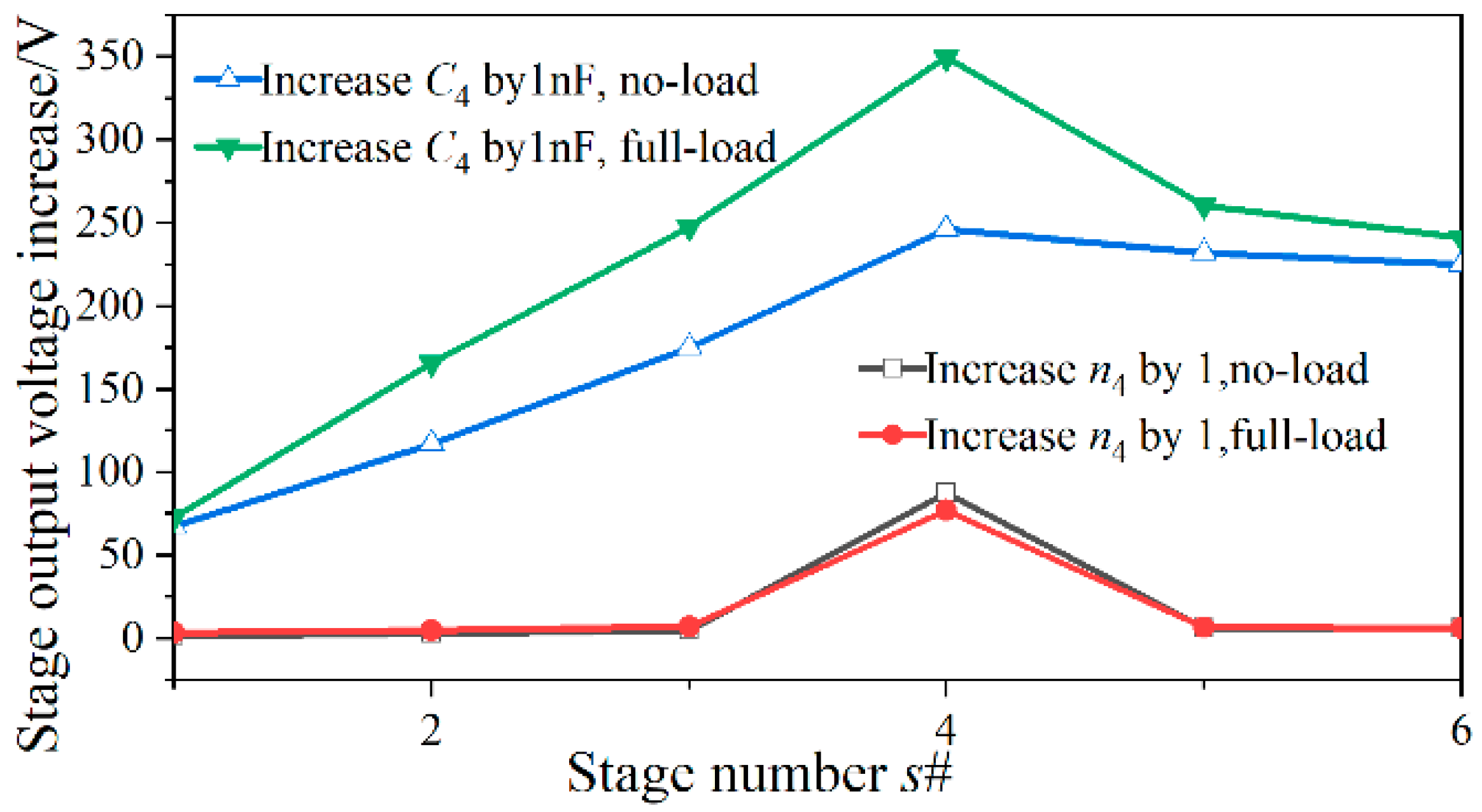
2.3. Capacitor Compensation Method
2.4. Full-Parameter Compensation Method
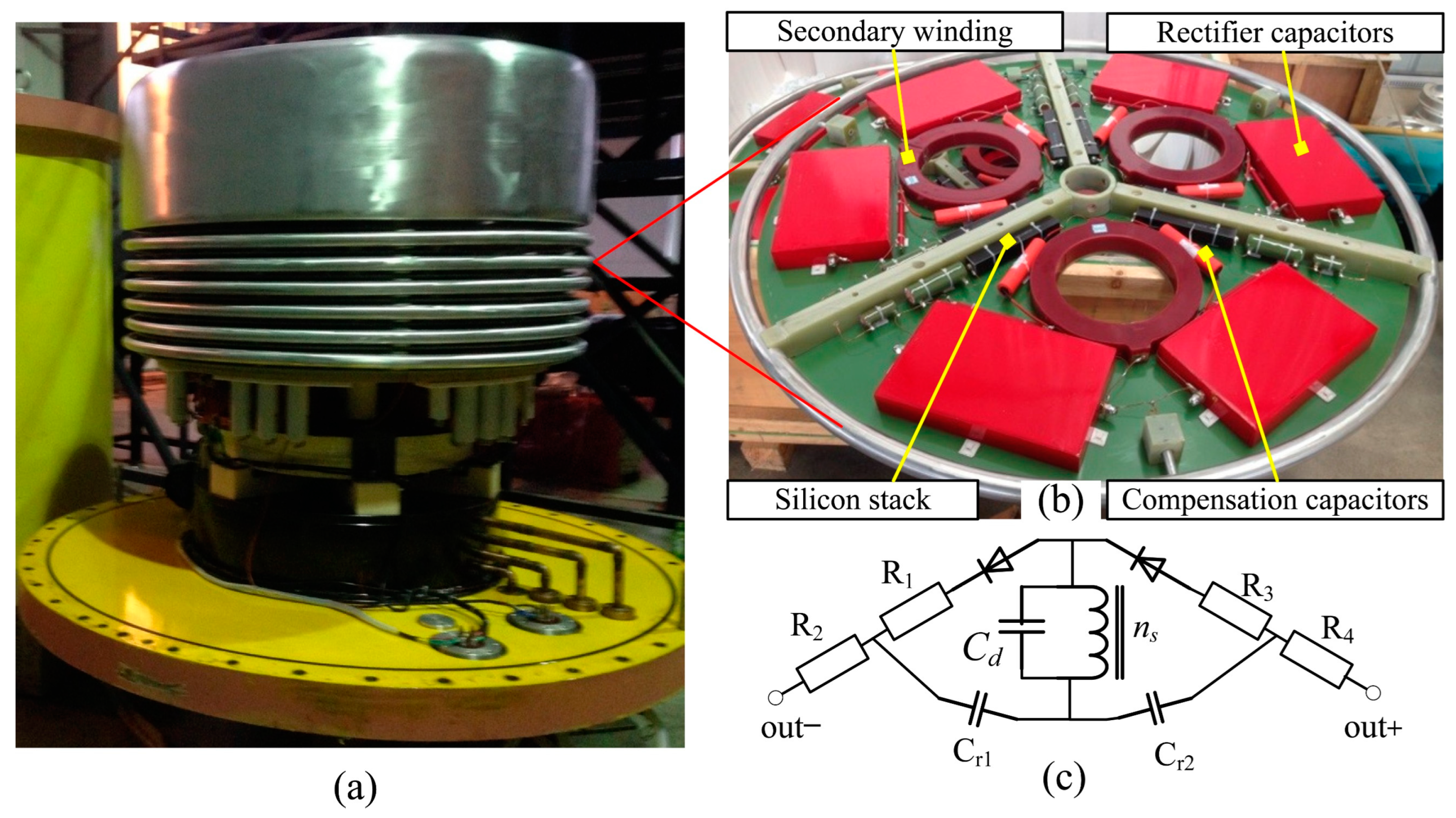
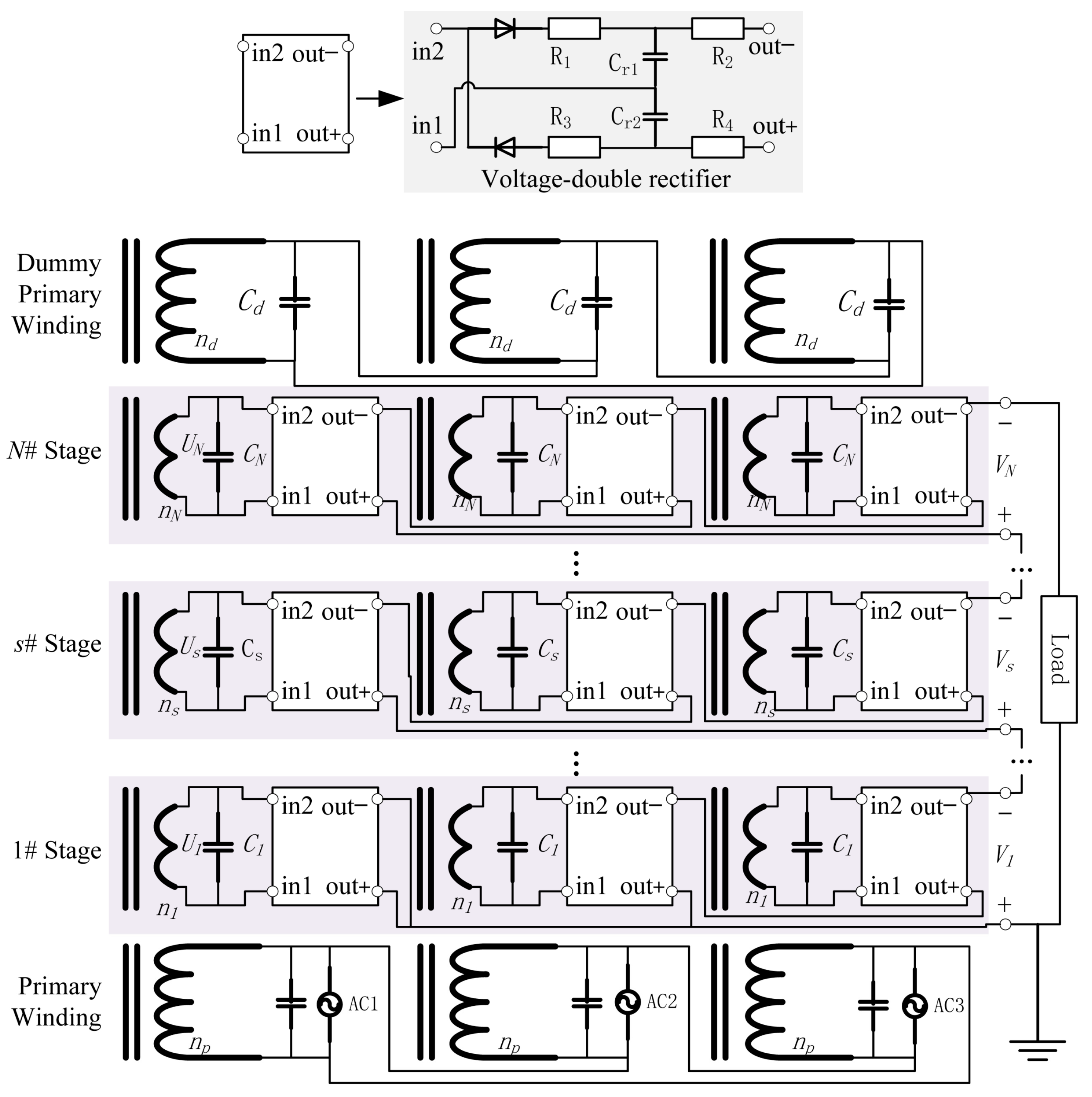
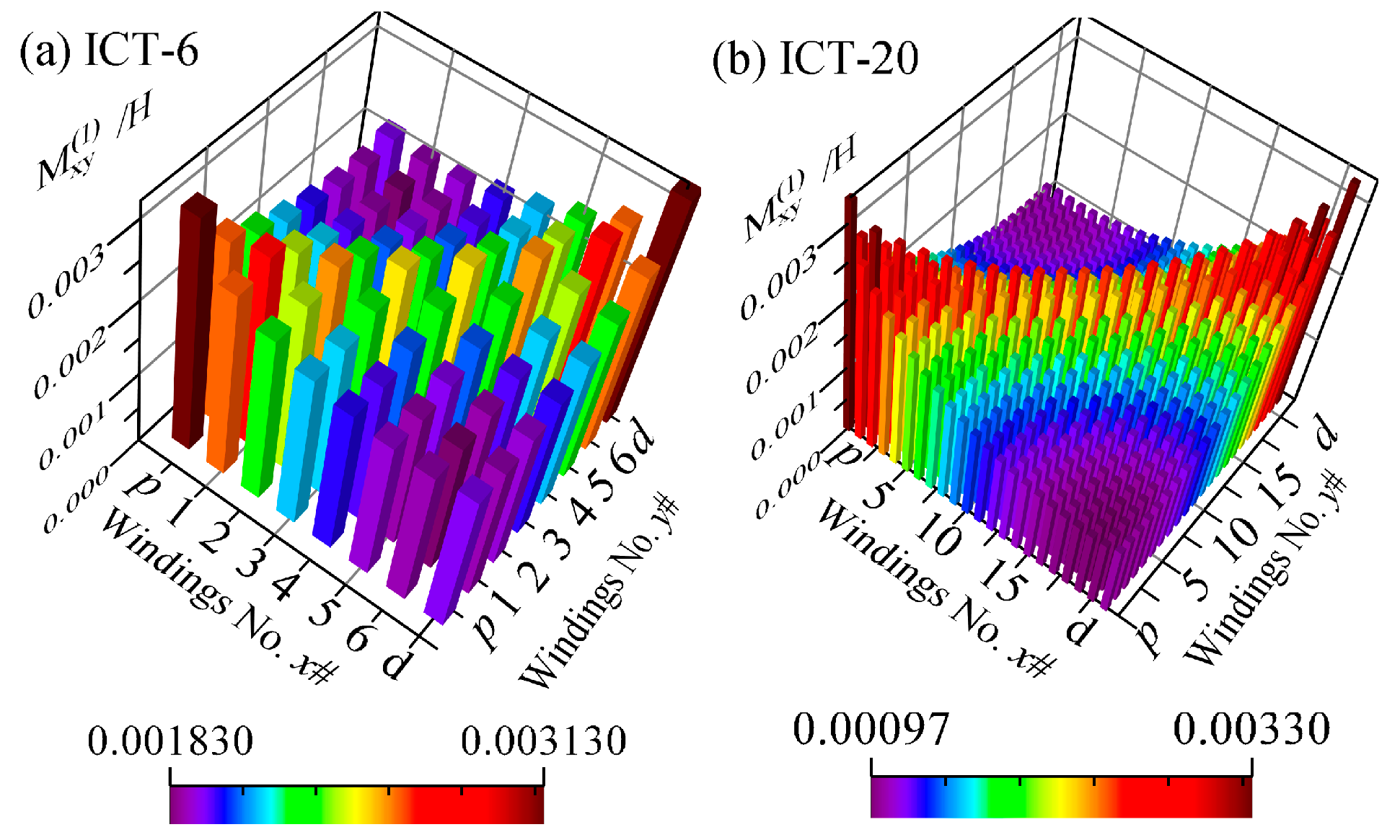
3. Unified Circuit Model and Simulation Method
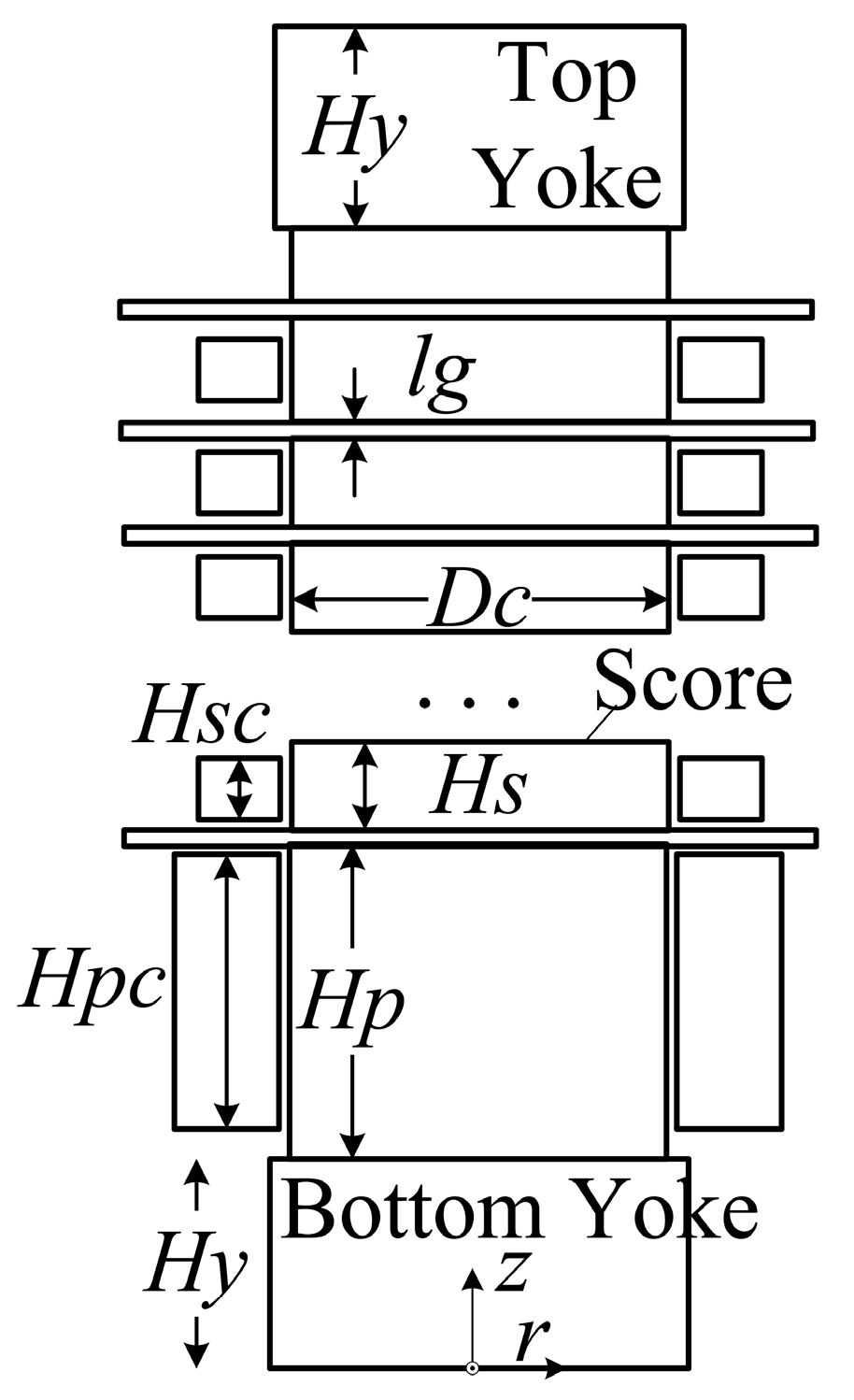
4. Parameters of ICT for Two Energy Levels
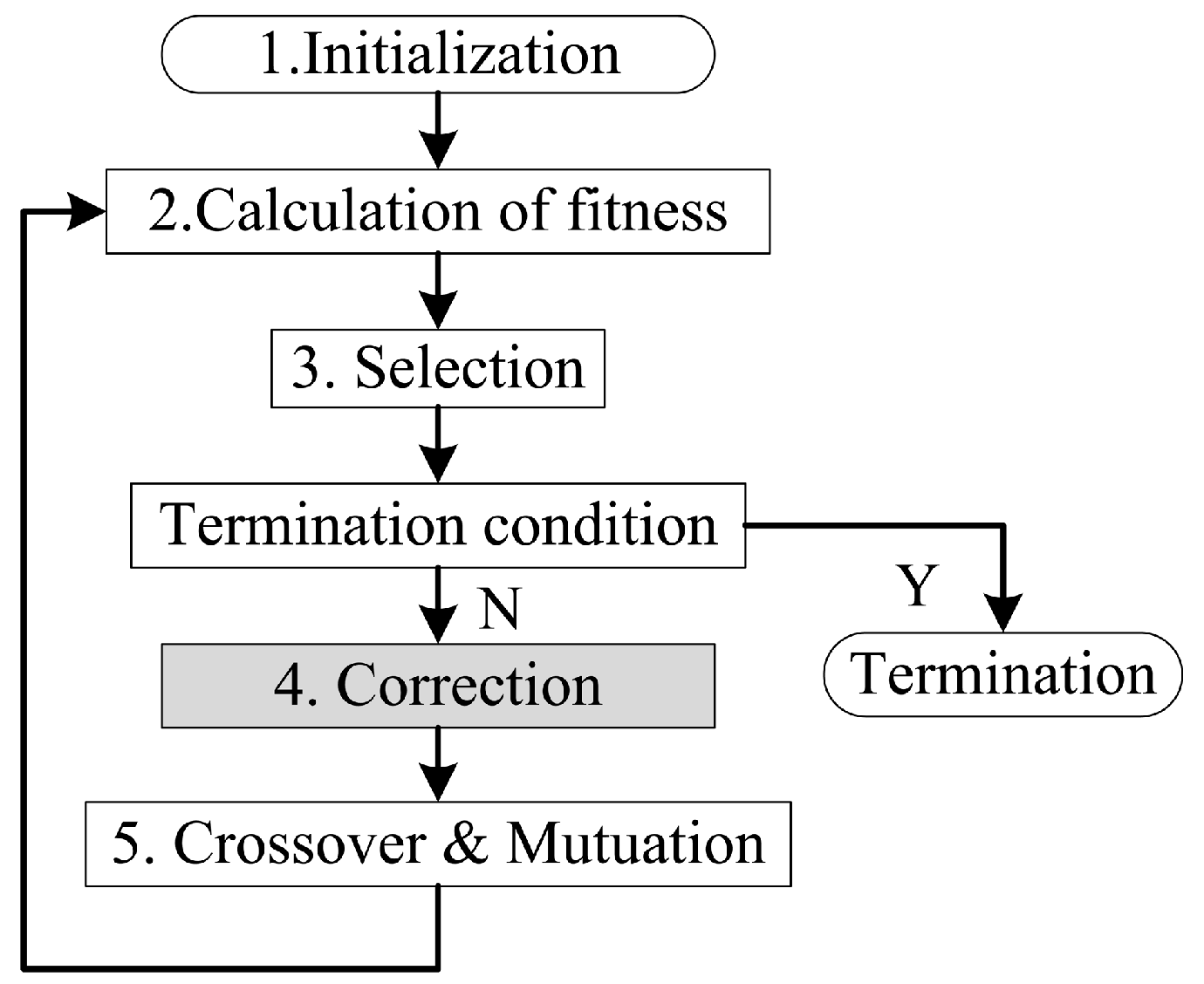
5. Optimization Algorithm
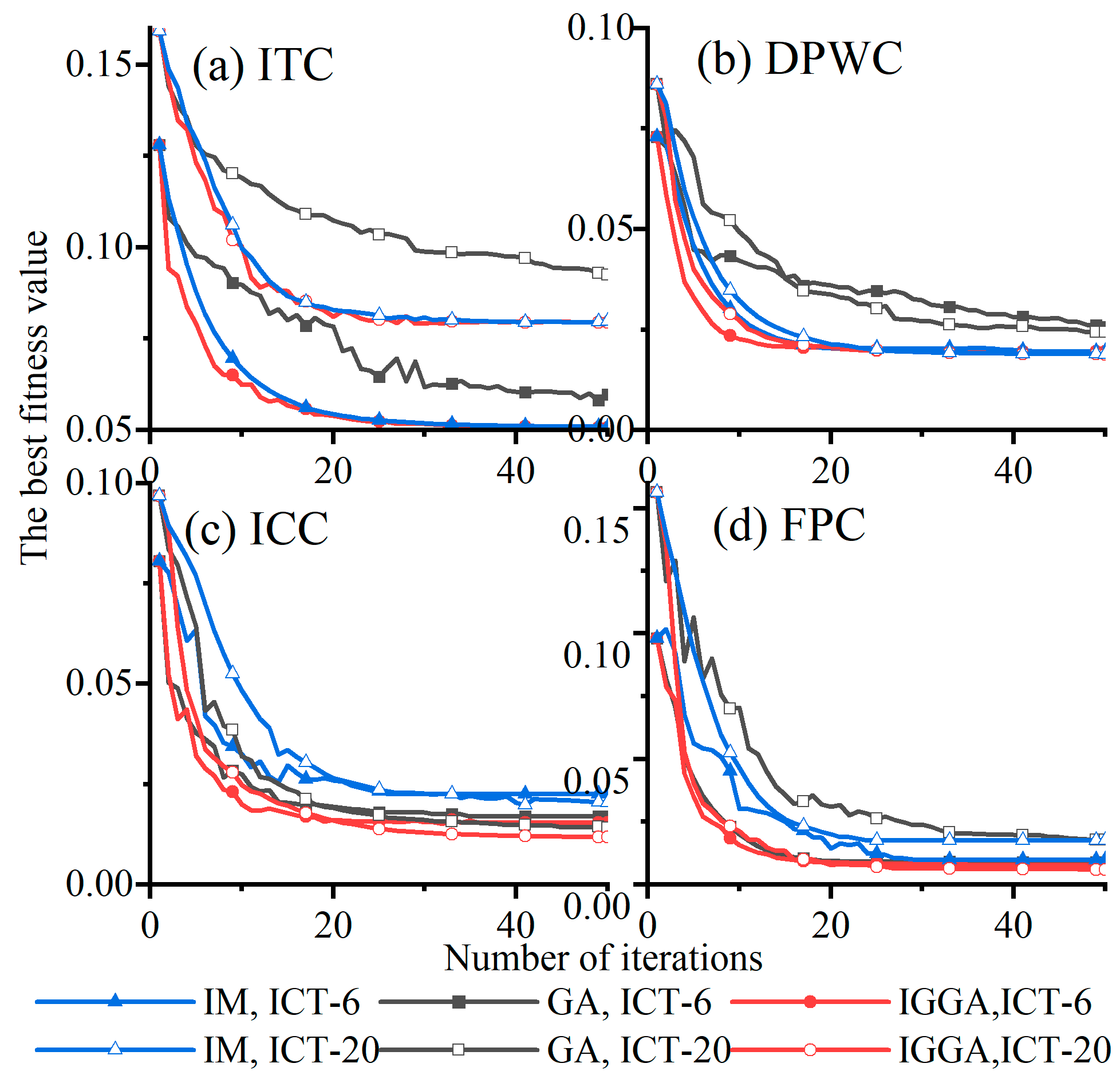
6. Comparison of Optimization Results
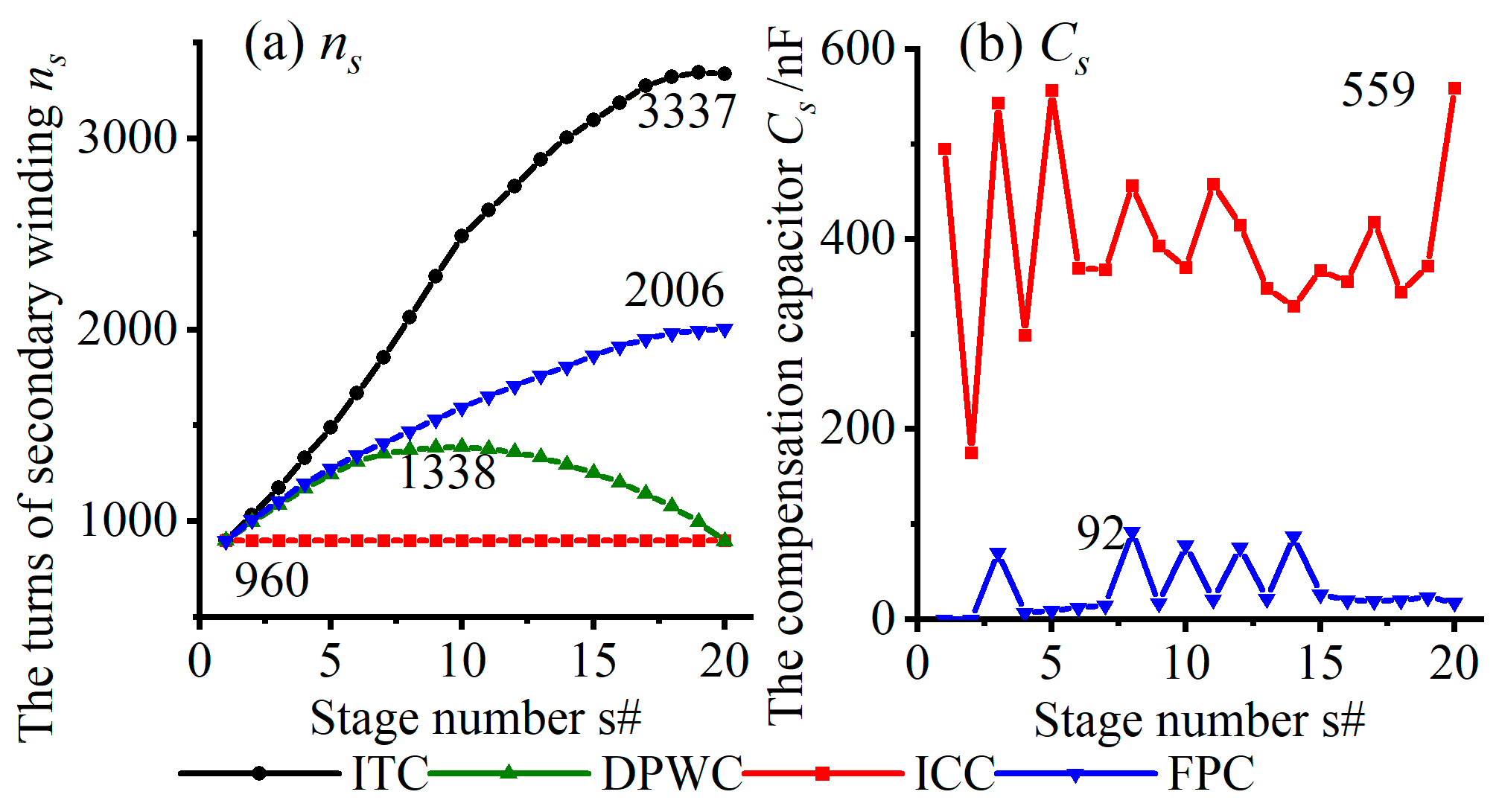
6.1. Optimal Compensation Parameters
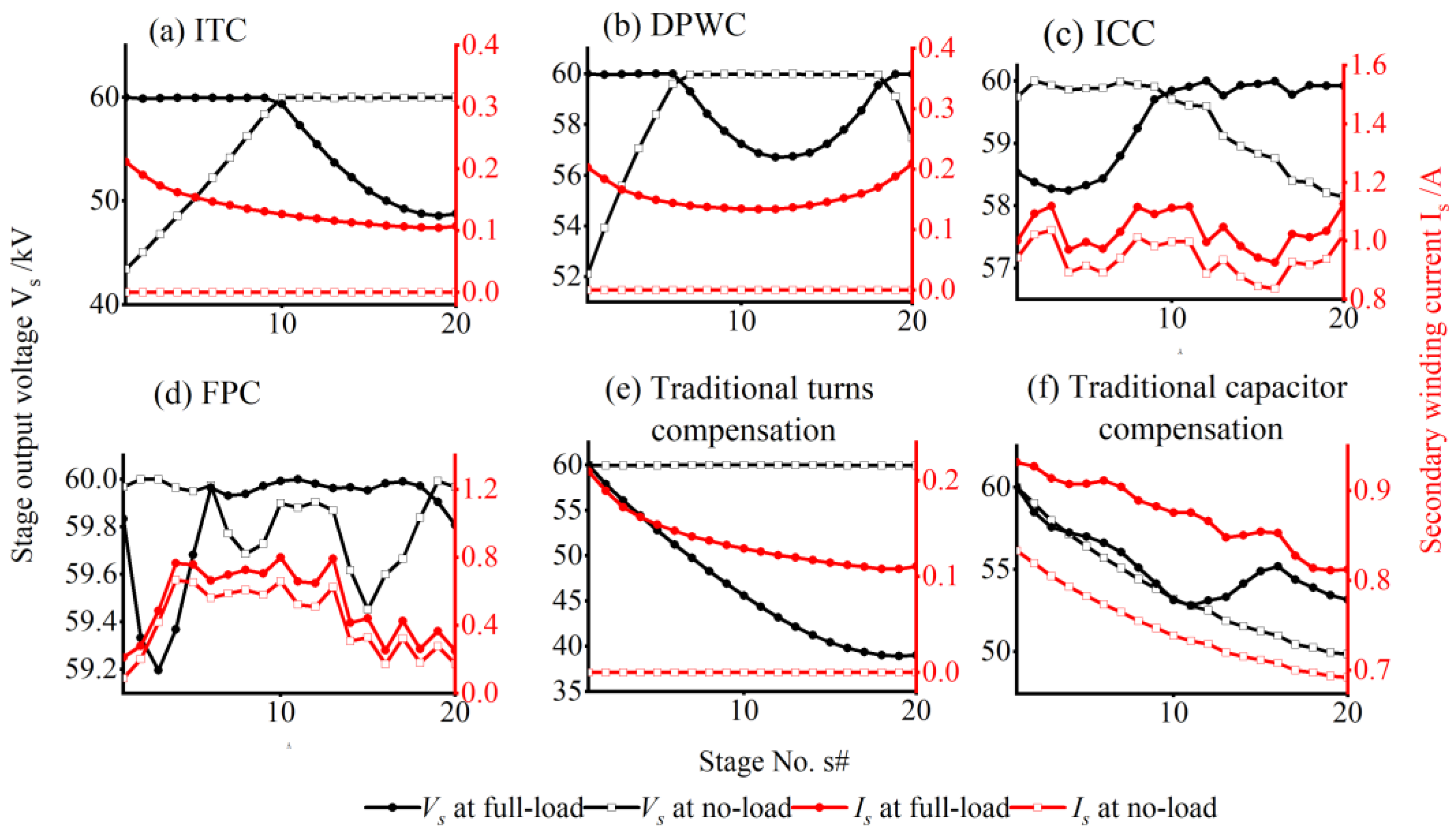
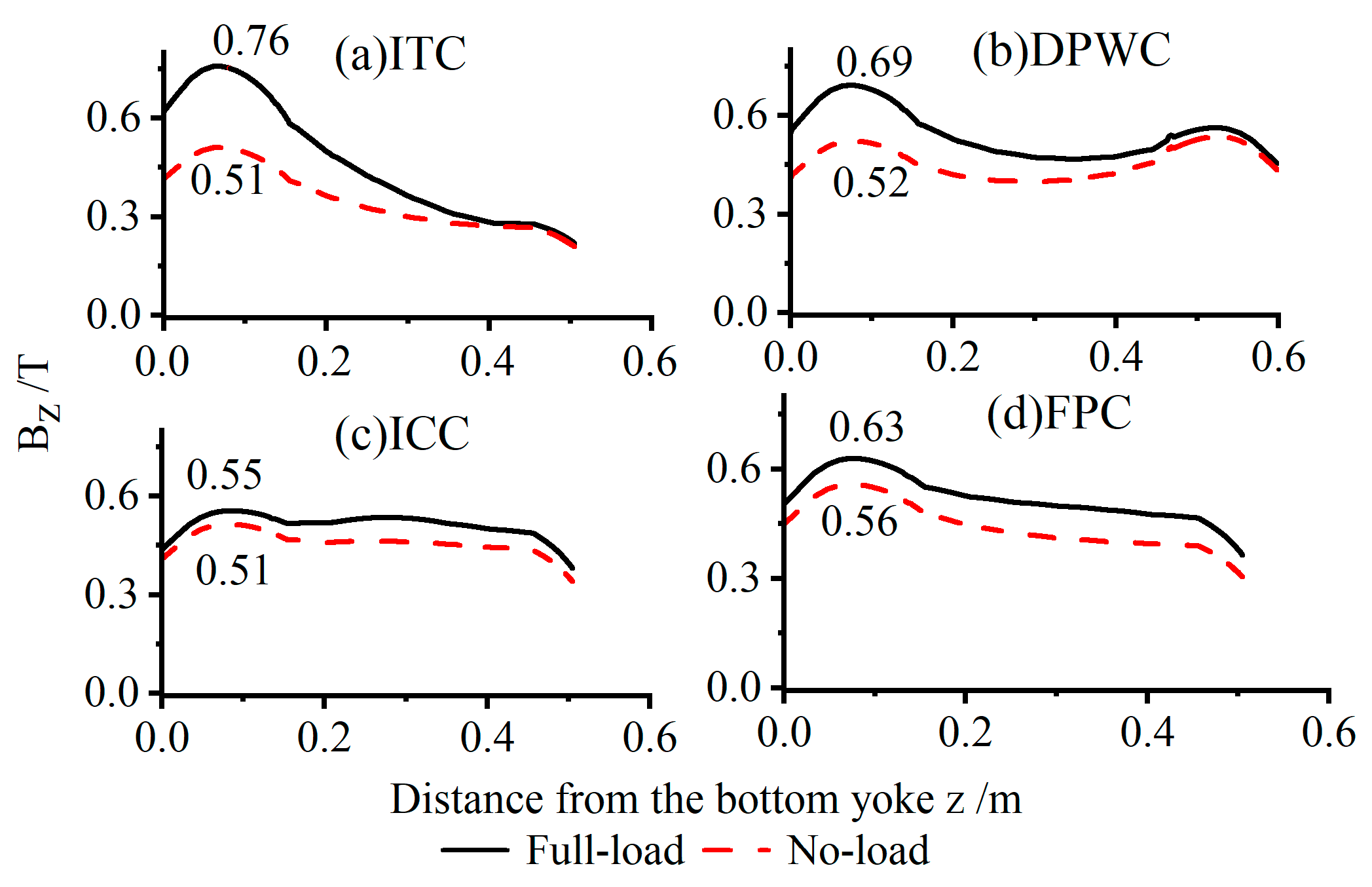
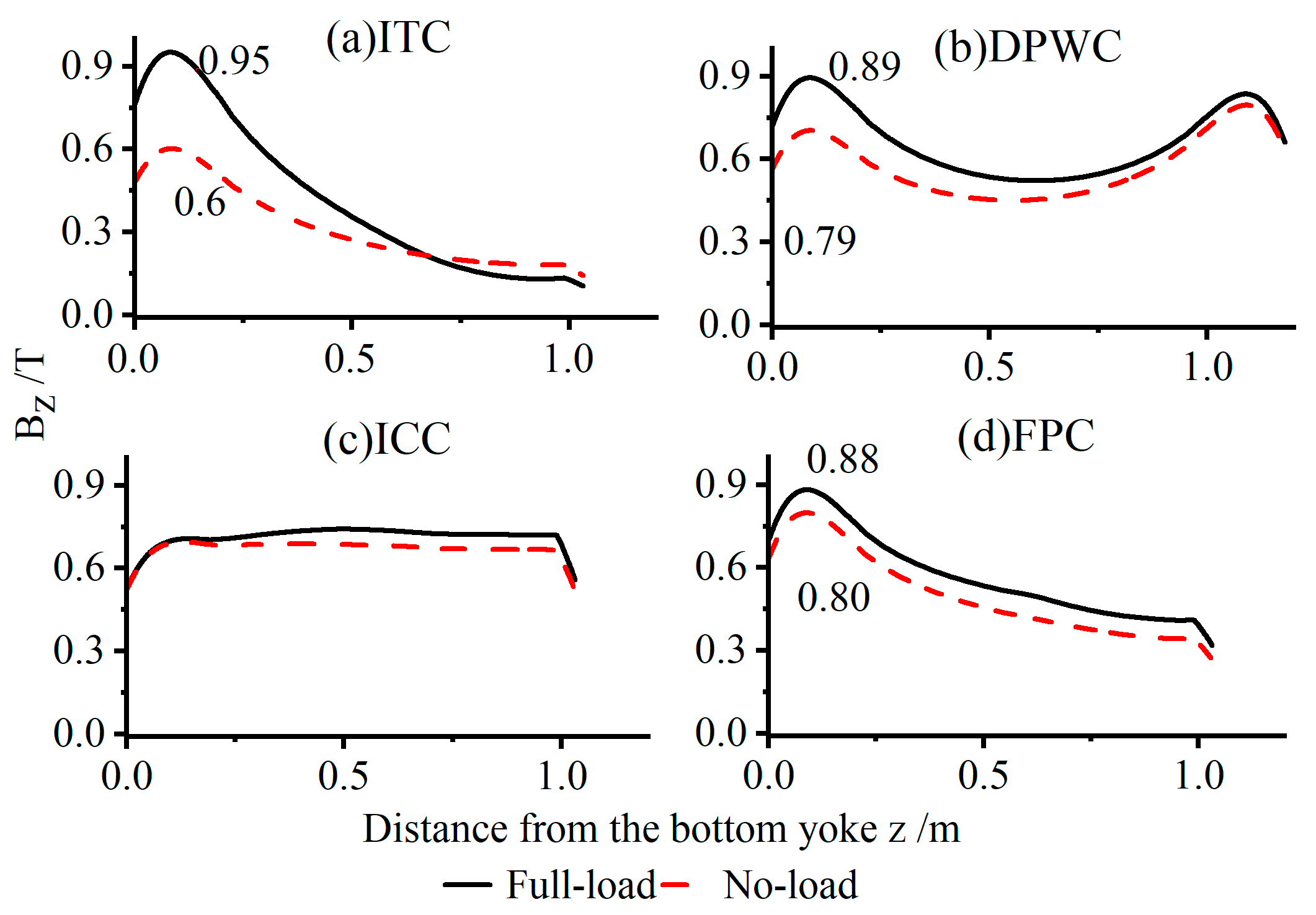
6.2. Optimized ICT Performance
6.3. Recommendations on the Selection of Compensation Methods
- (1)
- The ITC does not require compensation capacitors; it only needs windings of different turns, resulting in a simple engineering implementation. However, this method exhibits poor voltage uniformity (ICT-20: 7.7%) and SL (ICT-20: 36.43%). These values indicate the high internal resistance of the power supply and limited load capacity, resulting in a low output voltage and small output current. Therefore, the method is recommended for an ICT with a lower voltage level and smaller output current.
- (2)
- The DPWC increases the complexity of engineering implementation more than the ITC by adding a set of DPWs and also increases the overall height of the device. Moreover, the axial magnetic field distribution is more uniform, and the peak value is smaller. Yet, it can slightly decrease δ and SL. Hence, it is recommended to use the DPWC in situations requiring a higher ICT output voltage and larger output current (greater than the ITC).
- (3)
- The characteristic of the ICC is that all the secondary windings have the same number of turns, and only different values of compensating capacitors need to be paralleled, making it relatively easy to implement. After undergoing this method, the winding current Is becomes larger, the magnetic field peak becomes smaller and distributed more evenly, with a low load regulation rate and robust load-carrying capacity. Therefore, it is recommended to use the ICC method in situations requiring a higher output current (greater than 200 mA). This method is applicable to ICTs of all voltage levels.
- (4)
- The advantage of the FPC lies in its excellent nonuniformity and relatively good load regulation suitable for ICTs with various voltage levels. Furthermore, this method is particularly suitable on some occasions where the voltage level is very high, or where the voltage distribution is required to be very uniform due to the small insulation design margin.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- da Costa, J.P.d.C.; Assis, M.; Teodoro, V.; Rodrigues, A.; de Foggi, C.C.; San-Miguel, M.A.; do Carmo, J.P.P.; Andres, J.; Longo, E. Electron beam irradiation for the formation of thick Ag film on Ag3PO4. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21745–21753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Ahn, J.-W.; Kim, K.-H.; Son, Y.-S. Historic and futuristic review of electron beam technology for the treatment of SO2 and NOx in flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, W.A.P.; Duarte, C.L.; Machado, L.D.B.; Manzoli, J.E.; Geraldo, A.B.C.; Kodama, Y.; Silva, L.G.A.; Pino, E.S.; Somessari, E.S.; Silveira, C.G. Electron beam accelerators—Trends in radiation processing technology for industrial and environmental applications in Latin America and the Caribbean. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, R. Mechanisms of radiation damage in beam-sensitive specimens, for TEM accelerating voltages between 10 and 300 kV. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2012, 75, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandramoorthy, R.; Bernal, R.; Espinosa, H.D. Pushing the envelope of in situ transmission electron microscopy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4675–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machi, S. Trends for electron beam accelerator applications in industry. Rev. Accel. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.; Lewin, P.; Spong, M. An investigation into the suitability of insulated core transformer technology for an ultra high voltage power supply. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2019, 26, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.; Pilgrim, J.; Lewin, P.; Spong, M. An investigation into the next generation of high density, ultra high voltage, power supplies. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference (IPMHVC), Jackson, WY, USA, 3–7 June 2018; pp. 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, J.; Fan, M. Application of Particle Swarm Optimization in the Design of an ICT High-Voltage Power Supply with Dummy Primary Winding. Electronics 2021, 10, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Ma, D.; Hu, L.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Liu, J. An improved design procedure for a 10 kHz, 10 kW medium-frequency transformer considering insulation breakdown strength and structure optimization. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 3525–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De, G.R.J. High Voltage Electromagnetic Apparatus Having an Insulating Magnetic Core. U.S. Patent No. 3,187,208, 1 June 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Van De, G.R.J. High Voltage Electromagnetic Chargedparticle Accelerator Apparatus Having an Insulating Magnetic Core. U.S. Patent No. 3,323,069, 30 May 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Analysis of Output Voltage on a Planar Insulating Core Transformer. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2021, 23, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, J.D. Modular High Voltage Power Supply with Integral Flux Leakage Compensation. U.S. Patent No. 6,026,004, 15 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Yonghao, L.; Jianming, H.; Deming, L. Compensation of leakage flux on insulated core flat winding transformer. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2012, 24, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, K.; Qin, B.; Chen, D. A combined compensation method for the output voltage of an insulated core transformer power supply. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 063302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. A new compensation method for insulated core transformer power supply and its optimization using genetic algorithm. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 960, 163585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liang, X.; Yao, X.; Liao, W. Calculation of the composite short-circuit impedance and circulating current based on the equivalent single-turn inductance matrix. In Zhongguo Dianji Gongcheng Xuebao (Proceedings of the Chinese Society of Electrical Engineering); Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Jaraczewski, M.; Sobczyk, T. Leakage inductances of transformers at arbitrarily located windings. Energies 2020, 13, 6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhmeyer, U. KSI’s Cross Insulated Core Transformer Technology; AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, ML, USA, 2009; pp. 1099–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Aggarwal, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, F. Simulation model’s design of a new converter transformer based on multi-coil coupling. Diangong Jishu Xuebao/Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2010, 25, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Dujic, D.; Allmeling, J. Leakage flux modeling of medium-voltage phase-shift transformers for system-level simulations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 2635–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Javadi, M.S.; Catalão, J.P. Integrated generation-transmission expansion planning considering power system reliability and optimal maintenance activities. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 145, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, D.; Tanaka, K. Machine Learning-Based Estimation of COP and Multi-Objective Optimization of Operation Strategy for Heat Source Considering Electricity Cost and On-Site Consumption of Renewable Energy. Energies 2023, 16, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Kimiyaghalam, A.; Alhelou, H.H.; Javadi, M.S.; Ashouri, A.; Catalão, J.P. Transmission expansion planning considering power losses, expansion of substations and uncertainty in fuel price using discrete artificial bee colony algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135983–135995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, K. Thermal Network Modeling of High Frequency Insulated Core Transformers. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2022, 32, 0600805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Constraints | Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| ITC | nd = 0, Cd = 0, Cs = 0 | ns |
| DPWC | nd = np, Cd is from Equation (2), Cs = 0 | ns |
| ICC | nd = 0, Cd = 0, ns is from Equation (1) | Cs |
| FPC | nd = 0, Cd = 0 | Cs, ns |
| ICT-6 | ICT-20 | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 6 | 20 |
| Dc/mm | 178 | 250 |
| Score/mm2 | 2.3 × 104 | 4.9 × 104 |
| np, nd | 92 | 32 |
| lg/mm | 2 | 2 |
| Hs/mm | 45.6 | 38 |
| Hp/mm | 125 | 170 |
| Hsc/mm | 31.5 | 27.5 |
| Hpc/mm | 155 | 190 |
| Yoke diameter/mm | 660 | 960 |
| Hy/mm | 100 | 120 |
| ITC | DPW | ICC | FPC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICT-6 | δn | 4.32% | 1.64% | 1.53% | 0.52% |
| δl | 4.32% | 1.65% | 1.53% | 0.52% | |
| SL | 32.81% | 24.4% | 7.48% | 11.38% | |
| ICT-20 | δn | 7.74% | 2.20% | 1.30% | 0.51% |
| δl | 7.71% | 2.18% | 1.07% | 0.43% | |
| SL | 36.43% | 21.1% | 2.70% | 12.16% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Research on Voltage Compensation Methods and Optimization Algorithm for Insulated Core Transformer High-Voltage Power Supply. Energies 2024, 17, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030547
Yang L, Liu X, Yang J. Research on Voltage Compensation Methods and Optimization Algorithm for Insulated Core Transformer High-Voltage Power Supply. Energies. 2024; 17(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lei, Xialing Liu, and Jun Yang. 2024. "Research on Voltage Compensation Methods and Optimization Algorithm for Insulated Core Transformer High-Voltage Power Supply" Energies 17, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030547
APA StyleYang, L., Liu, X., & Yang, J. (2024). Research on Voltage Compensation Methods and Optimization Algorithm for Insulated Core Transformer High-Voltage Power Supply. Energies, 17(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030547






