Abstract
The current work was aimed at developing a new conditioning method of spent electrolyte-radioactive waste (RW) generated during the pyrochemical reprocessing of mixed nitride uranium-plutonium spent nuclear fuel. Magnesium potassium phosphate (MPP) compound samples were synthesized under solidification of the electrolyte surrogate solution in a LiCl-KCl-CsCl system. The phase composition and structure of obtained compounds were studied by XRD and SEM-EDS methods. It was found that the compounds possessed a high compressive strength of 17–26 MPa. Hydrolytic stability of the compounds was evaluated in accordance with the long semi-dynamic test GOST R 52126-2003 and with the static PCT test. The 137Cs content in the leached solutions was determined by gamma-ray spectrometry, and other compound components were determined by ICP–AES and ICP–MS methods. The differential leaching rate of Cs at 25 °C from monolithic samples on the 91st day of samples contact with water was 5–11 × 10−5 g/(cm2·day) (GOST R 52126-2003), and was 4–29 × 10−7 g/(cm2∙day) on the 7th day at 90 °C from crushed samples (PCT). The thermal stability of the compound at 180 °C and 450 °C was shown. The characteristics of the obtained MPP compound correspond to the current regulatory requirements for materials for RW conditioning.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, Russia is focused on the closure of the nuclear fuel cycle, which can be realized in a system that combines both thermal and fast neutron reactors. New types of fast neutron reactors and new types of fuel, including methods for recycling of spent nuclear fuel (SNF), are being developed. For example, combined pyrochemical and hydrometallurgical technology (PH-process) was proposed for the recycling of mixed nitride uranium-plutonium SNF (MNUP SNF) of lead-cooled BREST-OD-300 reactor. This technology allows recycling of MNUP SNF with a short exposure time and provides a high degree of purification of fissile materials. The anodic dissolution of (U,Pu)N in the melt of alkali metal chlorides and the cathodic deposition of fissile materials using a liquid cadmium cathode are the main processes in the pyrochemical recycling of MNUP SNF [1]. Various systems are used as electrolytes, including NaCl–2CsCl, NaCl–KCl, LiCl–4.53NaCl–4.88KCl–0.66CsCl, 3LiCl–2KCl and others. Spent electrolytes are classified as radioactive waste (RW), therefore their conversion to stable forms is required [2].
Scientists of different countries proposed numerous matrix materials for the immobilization of chloride waste, for example, orthophosphates of langbeinite structure [2], apatite [3,4], chlorapatites [3], chlorspodiosite [3], iron phosphate glass [4], monazite [4], tellurite glass [5], iron phosphate ceramic [6], SAP (SiO2-Al2O3-P2O5) [7], U-SAP (SiO2-Al2O3-B2O3-Fe2O3-P2O5) followed by vitrification in silicate or phosphate glass [8], sodalite (Na6(Li,K)2[(AlO2)6(SiO2)6]Cl2) [3,7,9,10], sodalite/glass [3,9], wadalite (Ca6Al5Si2O16Cl3) [9], calcium chlorosilicate (Ca3SiO4Cl2) [9], Ca-chloroapatite [11], Sr-chloroapatite [12] matrices and borosilicate glass [12]. Glass is the only matrix for solidification of high-level RW (HLW), brought to industrial use in Russia (phosphate glass), UK, Germany, France, USA, China and other countries (borosilicate glass). However, the vitrification method is not considered ideal for immobilizing the volatile radionuclides, because the vitrification process operates at high temperature (phosphate glass at (900÷1050) °C [13] and borosilicate glass at ~1150 °C [6]), which can lead to volatilization of cesium isotopes (CsCl volatility is above 750 °C [3]). Currently, the problem of spent electrolyte management hasn’t yet been solved, although various approaches and materials are being developed, as shown above in the literature. For that matter, the search for new matrices for reliable immobilization of Cs is an important task.
The magnesium potassium phosphate (MPP) matrix MgKPO4 × 6H2O is an effective mineral-like material, which contributes to retardation of highly toxic radionuclides, that makes it suitable for immobilization of RW of different activity levels [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Such a matrix is obtained by the reaction of magnesium oxide (MgO) with potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) in an aqueous solution at room temperature and it is an analog of the natural mineral K-struvite [23].
The aim of the current research consisted of the synthesis and study of the composition, structure, and physical and chemical properties of the MPP compound after conditioning of the spent electrolyte surrogate of pyrochemical reprocessing of MNUP SNF.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Procedures
Like previous work [17] the experiments were carried out in a glove box (Pererabotka, Dzerzhinsk, Nizhny Novgorod region, Russia) at ambient atmospheric conditions and chemicals used in it were of no less than chemically pure grade.
The synthesis of the MPP matrix was carried out according to the procedure previously described in the manuscript [24], by solidification of aqueous solutions of CsCl (salinity—540 g/L) and LiCl-KCl-CsCl with a ratio of 41.6%-52.9%-5.5% (as a surrogate of spent electrolyte, according to the manuscript [10]). The samples were prepared at the MgO: H2O:KH2PO4 weight ratio of 1:2:3. For preparing samples of MPP compounds, we used MgO (Rushim LLC, Moscow, Russia) precalcined at 1300 °C for 3 h (specific surface area was 6.6 m2/g) and KH2PO4 (Chimmed LLC, Moscow, Russia) crushed to a particle size of 0.15–0.25 mm. Compounds containing up to 15 wt% CsCl and up to 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl were obtained. The samples of the MPP compound obtained by solidification of LiCl-KCl-CsCl aqueous solutions and containing 28.6 wt% zeolite (hereinafter the samples are named MPPZ) were also synthesized. The natural zeolite of the Sokyrnytsya deposit, Transcarpathian region (ZEO-MAX LLC, Ramenskoye, Moscow region, Russia) with a particle size of 0.07–0.16 mm and a specific surface area of 17.5 m2/g was used for preliminary cesium binding and for increasing the mechanical strength of the MPP compound just as in the previous work [25], where its mineral composition was also determined.
To study the hydrolytic stability of the compound, samples were also prepared by solidification of LiCl-KCl-CsCl solution containing 137Cs with a specific activity of 1.0 × 107 Bq/L.
Cubic samples of the MPP compound with dimensions of 2 cm × 2 cm × 2 cm were prepared as required by [26]. It was decided to keep the samples for at least 15 days at ambient atmospheric conditions in accordance with previous studies [17,25].
2.2. Methods
The phase composition of the obtained MPP compound samples was identified by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method (Ultima-IV, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). The XRD data were interpreted using the Jade 6.5 program package (MDI, Livermore, CA, USA) with PDF-2 powder database. The microstructure of the samples was investigated by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a microscope Vega 3 (Tescan, Brno, Czech Republic), the electron probe microanalysis of the samples was performed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) using an analyzer X-ACT (Oxford Inst., High Wycombe, UK).
The compressive strength of the MPP compounds was determined using a test machine Cybertronic 500/50 kN (Testing Bluhm & Feuerherdt GmbH, Germany) [26] and a laboratory test press PRG-1-50 (VNIR, Moscow, Russia). The resistance of the samples to thermal cycles was determined in a MK-53 climate chamber (Binder, Tuttlingen, Germany). The samples were previously immersed in water for water saturation and then placed in a chamber, where they were kept for 30 cycles of successive freeze-thawing in the temperature range from –40 °C to +40 °C.
Thermal stability of the MPP compounds, obtained after solidification of LiCl-KCl-CsCl aqueous solutions, was investigated in accordance with the current requirements [27] for solidified HLW. For this purpose, the samples were kept at 180 °C, 10 h and at 450 °C, 4 h (hereinafter named MPPZ_180 and MPPZ_450, respectively) in a muffle furnace (SNOL 30/1300, AB UMEGA GROUP, Utena, Lithuania), as in previous work [25].
The hydrolytic stability of the MPP compounds was determined in accordance with the semi-dynamic standard GOST R 52126-2003 at 25 ± 3 °C [28] and the international static PCT test (Method A) at 90 ± 2 °С [29]. In accordance with GOST R 52126-2003, before leaching monolithic cubic samples (2 cm × 2 cm × 2 cm) of the compound were immersed in ethanol for 5–7 s to clean them from mechanical impurities, then the samples were dried in air for 30 min. Bidistilled water (pH 6.6 ± 0.1, volume 200 mL) was used as a leaching agent with its periodic replacement after 1, 3, 7, 10, etc. days, the total test duration was 90–91 days. PCT-A leaching test was carried out on 0.07–0.16 mm powders that were obtained by crushing and sieving the samples. Compound powders were washed in bidistilled water and ethanol. Conditions PCT-A: test duration was 7 days ± 2%, leaching agent was bidistilled water (pH 6.6 ± 0.1), leachate volume, mL/sample weight, g was 10 ± 0.5 mL/g. Leaching was carried out in an electrical drying oven 2В-151 (Medlabortehnika, Odessa, Ukraine) in a tightly closed PTFE container. The leached solution was decanted and the content of the matrix components in the solution after leaching was determined by ICP–AES и ICP–MS (iCAP-6500 Duo and X Series2, respectively, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The 137Cs content in the solution was determined by gamma-ray spectrometry on a spectrometer with a high-purity germanium detector GC 1020 (Canberra Ind, USA).
The leaching rate LR, [g/(cm2·day)], of the components was calculated by Equation (1).
where с – element concentration in solution after leaching, g/L; V–the volume of leaching agent, L; S–the sample surface, cm2; f–element content in matrix, g/g; t–leaching time, days (for calculating the differential leaching rate t - duration of the n-th leaching period between shifts of contact solution). The sample surface (S) was the open geometric surface area of the monolithic samples for GOST R 52126-2003 test, and the surface of the crushed samples was calculated by BET method for PCT test. The specific surface area (SBET) of the compound powders sieved to 0.07–0.16 mm was measured using a Quadrasorb SI/Kr analyzer (Quantachrome Instruments, Boynton Beach, FL, USA); nitrogen with a purity of 99.999% was served as an adsorbate. The calculation was carried out by BET multiple-point isotherm in the range of P/P0 0.05 to 0.30. A more detailed description of the technique for evaluation of specific surface area is given in [30]. The Density Functional Theory (DFT) method was used to calculate the volume and average pore size, and the T-method Halsey was used to calculate the micropore volume and surface area of the micropore powder.
To assess the leaching mechanism of cesium from the compounds, a de Groot–van der Sloot model [31] was used; in this case, the results of calculating the slope of a linear relationship of log (Bi) on log (t) were used [20,32].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the MPP Compound Containing Chloride
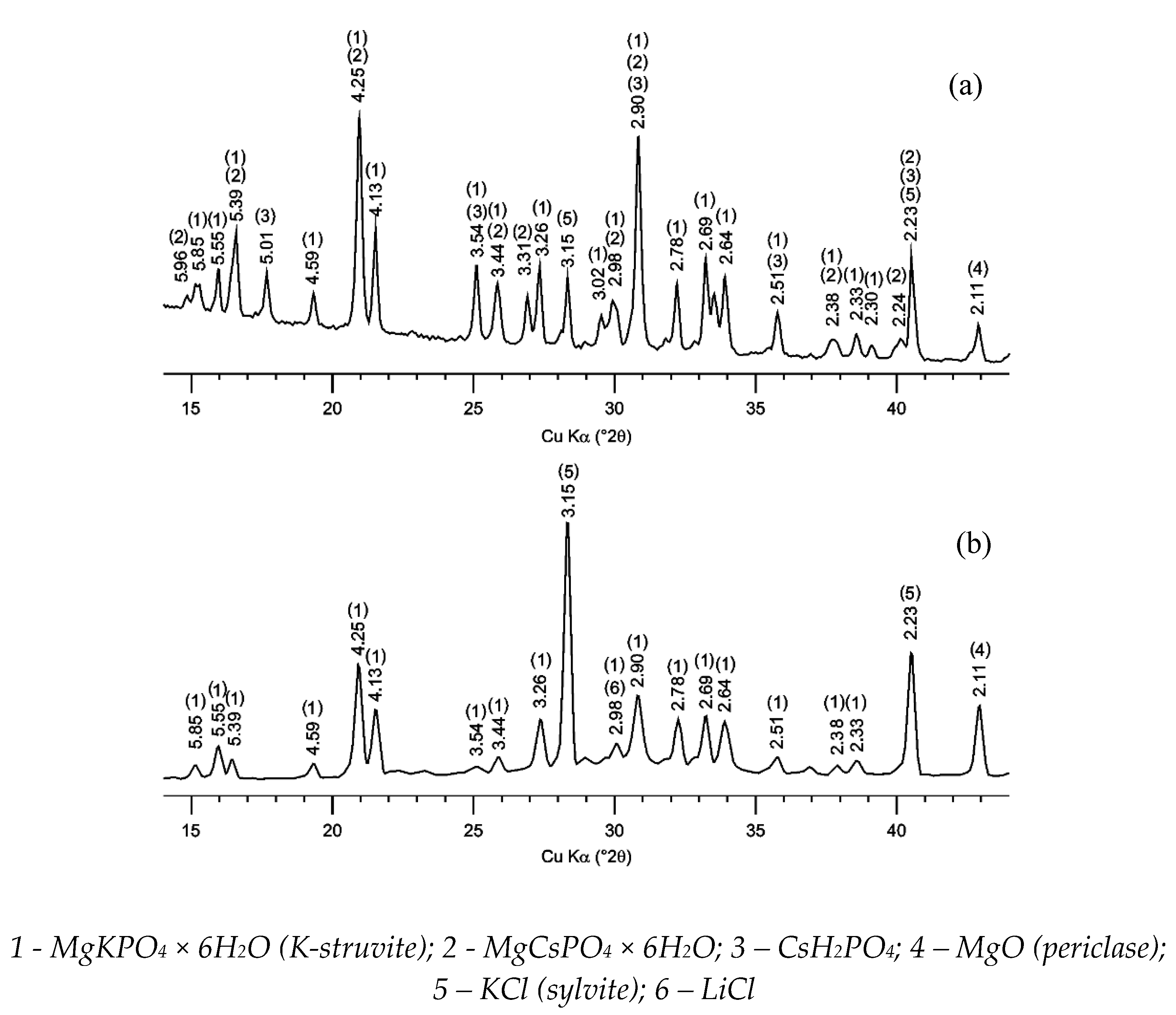
The obtained X-ray diffraction patterns of the compound samples after solidification of solutions of CsCl and spent electrolyte surrogate LiCl-KCl-CsCl are shown in Figure 1. It was shown that MgKPO4 × 6H2O an analog of K-struvite was the main crystalline phase of the studied compound samples. It was noted that the KCl phase is contained in compound and obviously formation of this phase occurs due to the replacement of potassium ions by cesium ones in the matrix structure (MgCsPO4 × 6H2O) and in initial potassium dihydrogen phosphate (CsH2PO4) in the case of solidification of CsCl solution (Figure 1a). The salts of KCl and LiCl were contained in the compound obtained in the case of solidification of the electrolyte surrogate (Figure 1b), and the salt of CsCl wasn’t found due to its low content in the compound (less than 1 wt%).
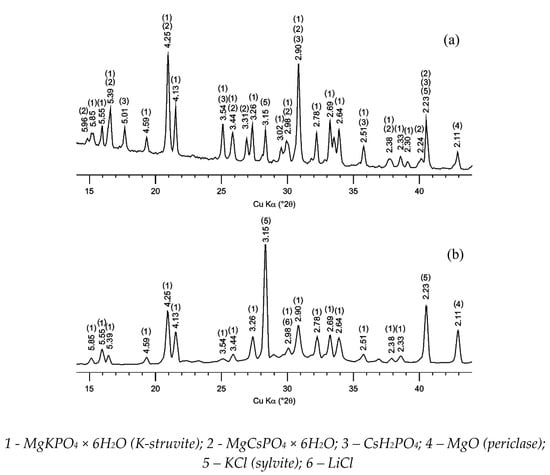
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction patterns of a compound containing (a) CsCl and (b) LiCl-KCl-CsCl.
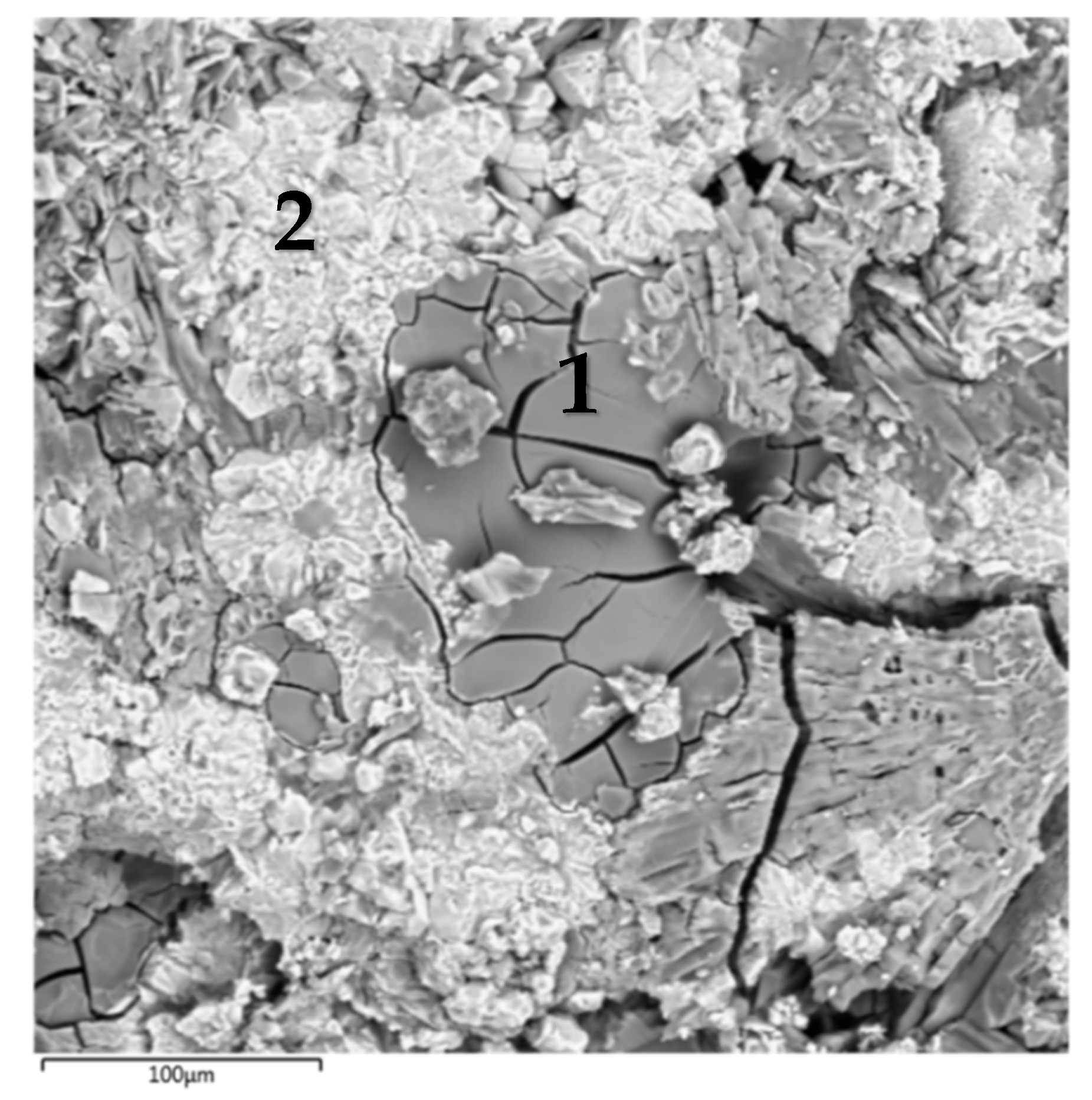
The SEM micrograph of the surface of the MPP compound containing CsCl is shown in Figure 2, and the average EDS results of the found phases are presented in Table 1. The major phases of the MPP compound (e.g., Phase #1, Figure 2, Table 1) includes Mg, P, K, and Cs. The composition of this phase can be represented in general form (Mg,K,Cs)PO4 × nH2O, where Cs content is 0.3–0.6 at% (Table 1). In this case, there were separate particles of a phase containing phosphorus and cesium up to 38 at%, that confirmed the formation of the CsH2PO4 phase (it is shown in Figure 1a), and there were separate particles of cesium orthophosphate Cs3PO4 (on the example of particles in Phase #2, Figure 2, Table 1) in compound, as we showed in earlier work [24].
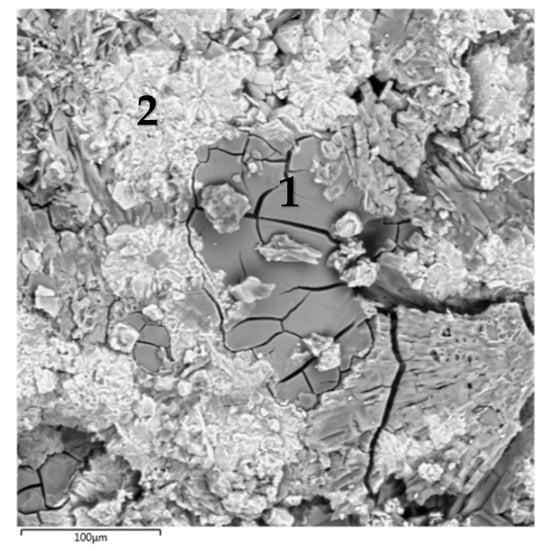
Figure 2.
SEM image of the compound containing CsCl.

Table 1.
Average data of elemental composition of the compound containing CsCl.
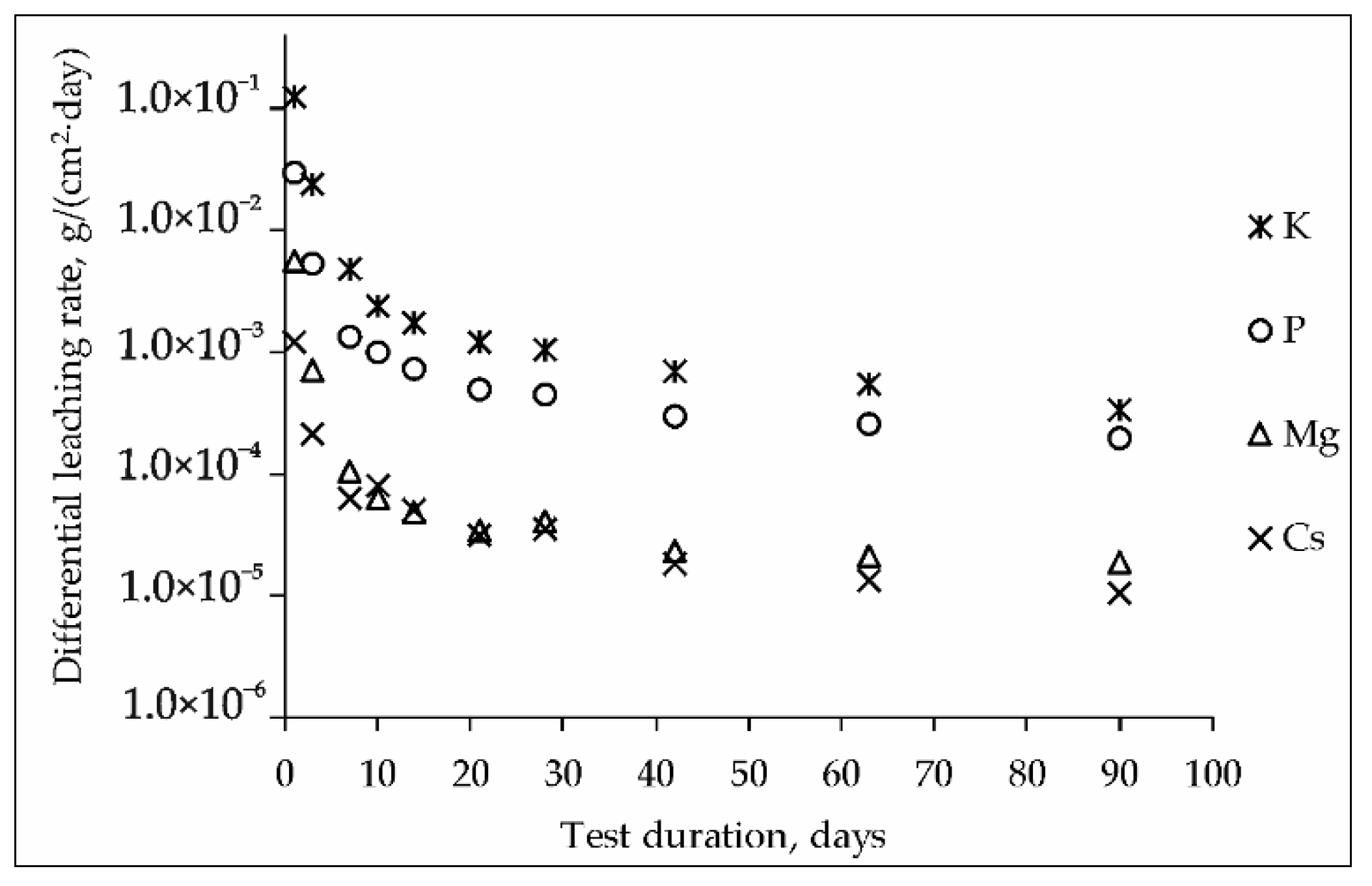
The kinetic curves of the leaching rate of elements from the MPP compound containing CsCl are shown in Figure 3. The blank MPP matrix was also used as a reference sample in the research. It was found that the addition of a significant amount of CsCl (15 wt%) did not affect the hydrolytic stability of the compound to the leaching of the structure-forming components of the matrix. The differential leaching rate on the 90th day test, g/(cm2∙day) was 1.8 × 10−5 for Mg, 3.3 × 10−4 for K and 1.9 × 10−4 for P.
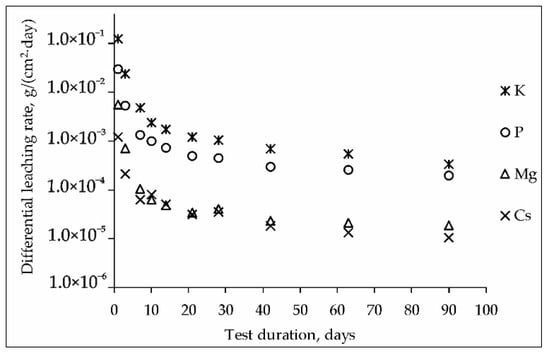
Figure 3.
Kinetic curves of the leaching rate of elements from the MPP compound containing CsCl (test GOST R 52126-2003).
It was shown (Figure 3), that the differential leaching rate of cesium from the compound during the 90-day test was reduced to 1.0 × 10−5 g/(cm2·day), which was significantly below the requirements [27] for a cement compound (not above 1.0 × 10−3 g/(cm2·day)) and corresponded to the requirements of a glass-like compound application for HLW immobilization in Russia (1.0 × 10−5 g/(cm2∙day)). Cesium leaching (integral leaching degree –0.56 wt%) probably due to the dissolution of the readily soluble phases CsH2PO4 (Figure 1) and Cs3PO4 (Table 1).
It was found that the compressive strength of compounds containing solutions of CsCl and LiCl-KCl-CsCl was 10.0 ± 0.5 and 9.1 ± 0.4 МPa, respectively, according to requirements [27]. Samples containing CsCl were resistant to 30 thermal cycles from −40 °C to +40 °C: the compressive strength was 9.6 ± 0.3 MPa. At the same time, it was noted that under heating to 450 °C of the compound, the samples practically lost their compressive strength. Earlier in [25] it was established, that the addition of about 29 wt% zeolite to the composition of the MPP compound led to a significant increase in both mechanical strength and thermal stability of samples. To study the effect of zeolite on the efficiency of immobilization of spent electrolyte, compound samples obtained during solidification of LiCl-KCl-CsCl solution and contained 28.6 wt% zeolite were used.
3.2. Characterization of MPP Compound Containing LiCl-KCl-CsCl and Zeolite
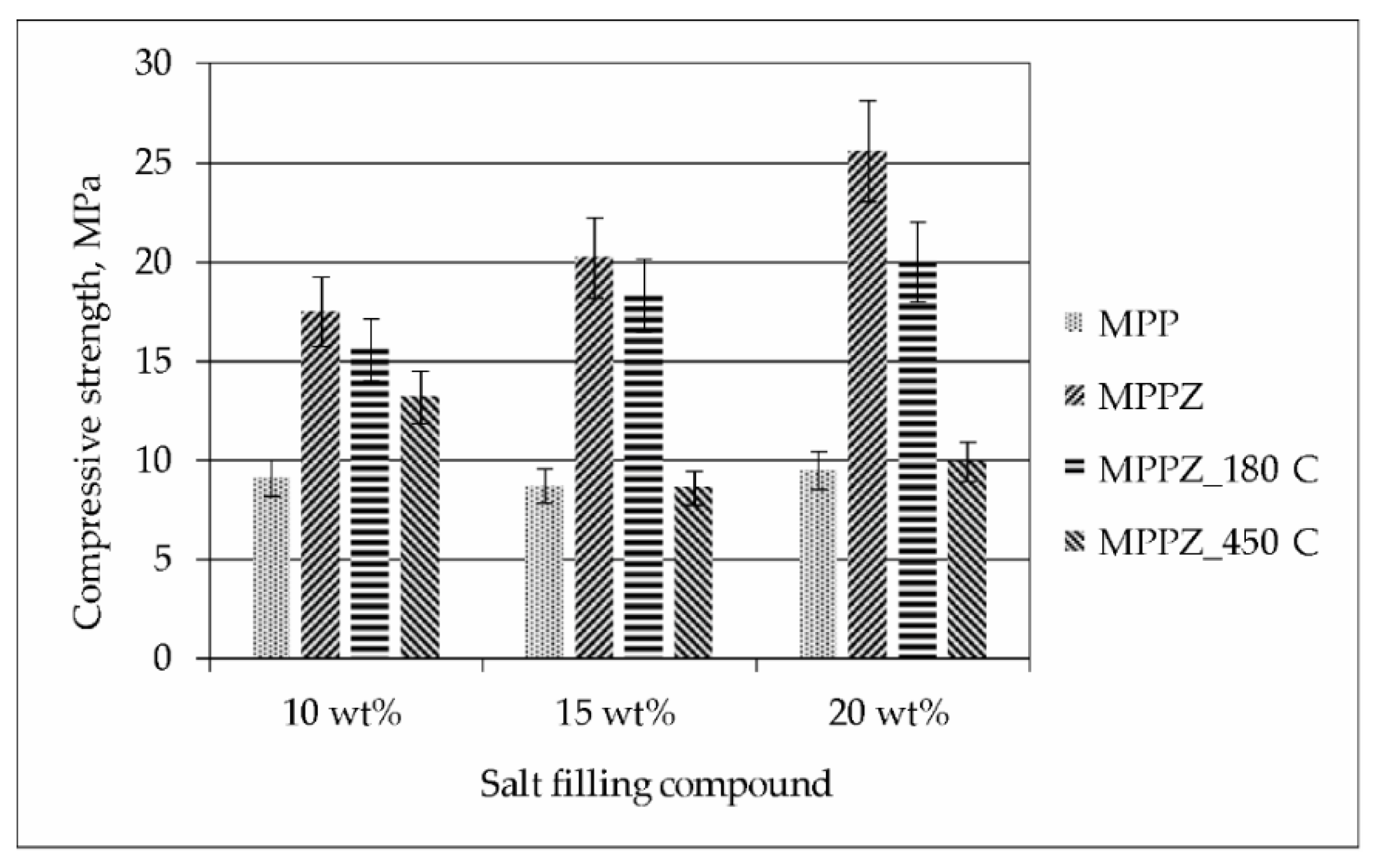
The data on the compressive strength of the MPP compound containing LiCl-KCl-CsCl solution and 28.6 wt% zeolite is shown in Figure 4. It was found that the compressive strength of the compound increases 1.9–2.7 times with the addition of 28.6 wt% zeolite. The compressive strength of the samples was 17–26 MPa, and after heat treatment at 180 °С and 450 °C it was 16–20 and 9–13 MPa, respectively. It was pointed, that an increase of the content of LiCl-KCl-CsCl from 10 to 20 wt% in the compound not only did not reduce the compressive strength of the compound, but on the other hand, there was a tendency to increase it (Figure 4).
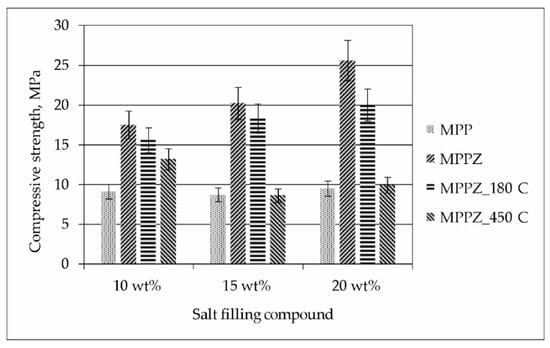
Figure 4.
Compressive strength of the MPP compound containing LiCl-KCl-CsCl and 28.6 wt% zeolite.
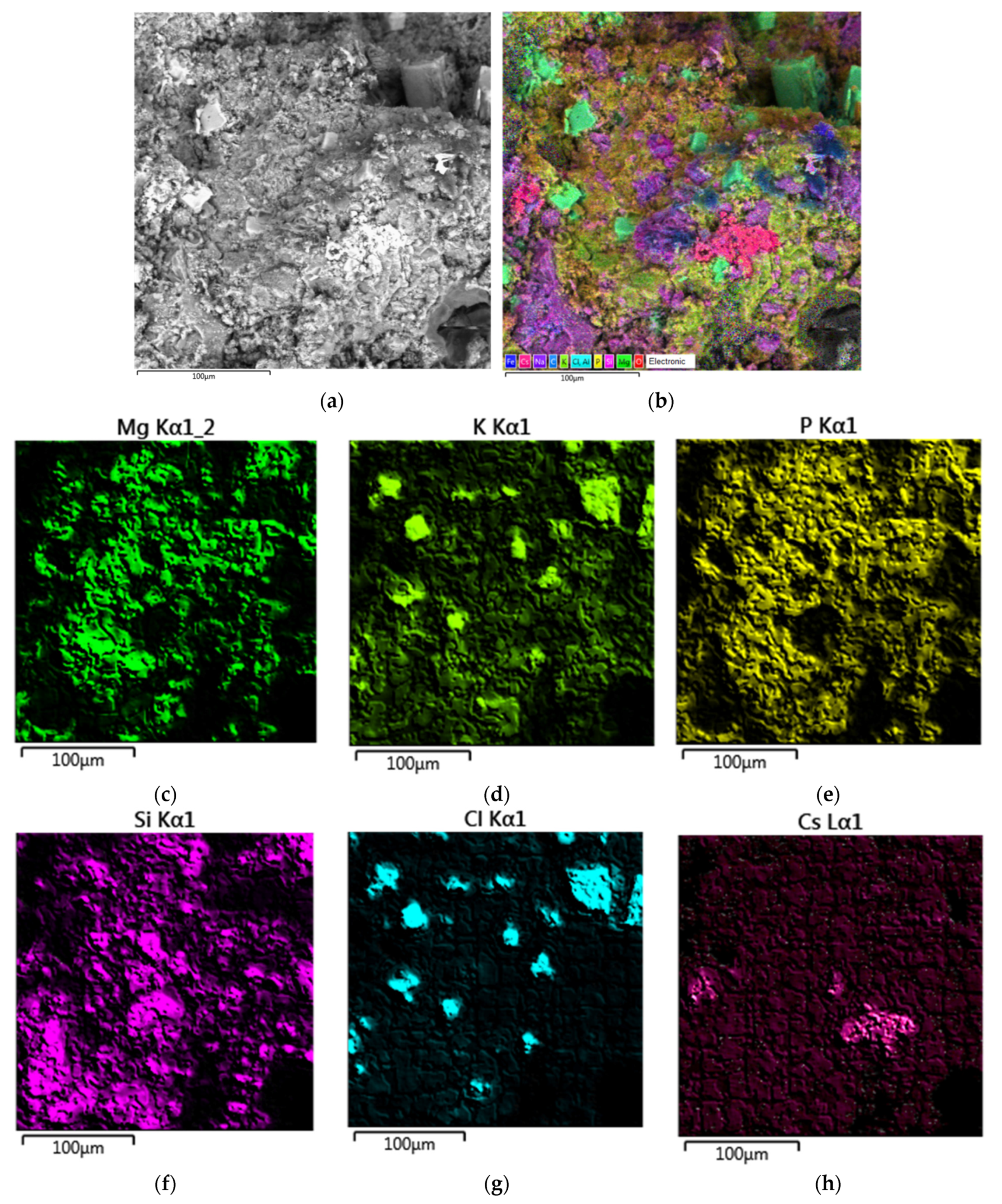
SEM micrograph of the surface and X-ray elemental mapping of major elements of the MPPZ compound containing 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl and 28.6 wt% zeolite are shown in Figure 5. It is apparent that the distribution of Mg, P, the main amount of K, and also Si was similar, that corresponded to a mixture of the main matrix phase MgKPO4 × 6H2O with zeolite. The heterogeneity of the distribution of Cl and partially K was observed, that corresponded to strongly-pronounced separate phase of KCl of a cubic form (Figure 5a,b). The distribution of Cs corresponded to the phase distribution of the matrix and zeolite, and also separate particles enriched in cesium, that were similar to the data of the compound research with CsCl (Section 3.1).
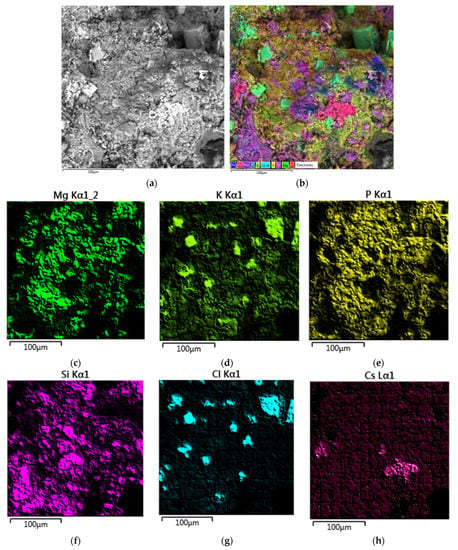
Figure 5.
Scanning electron microscope images (a) and elemental mapping of major elements (b–h) of the MPPZ compound containing 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl and 28.6 wt% zeolite.
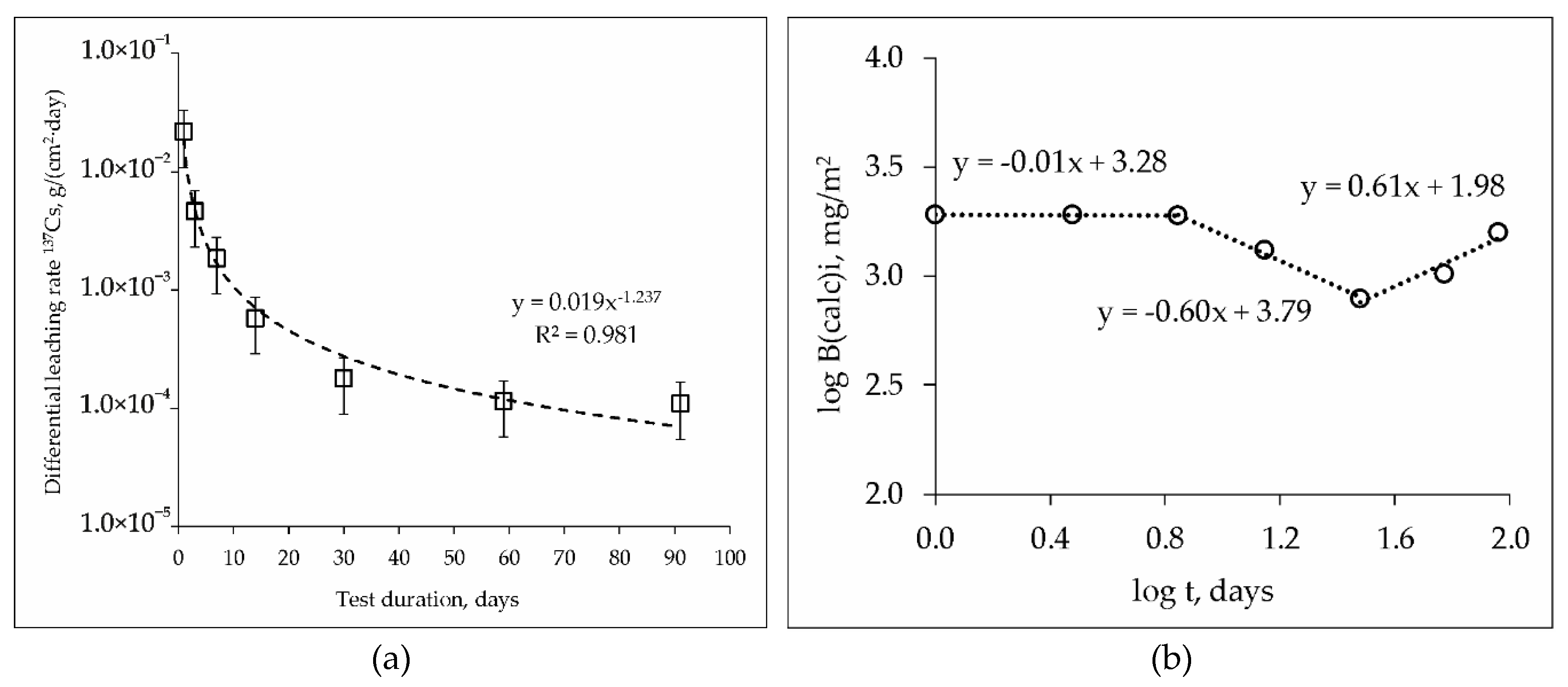
During study of hydrolytic stability of the MPPZ compound in accordance with GOST R 52126-2003 it was established, that the kinetic curves of the leaching rate of 137Cs possess a similar nature for the samples studied, both containing 10 or 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl, and after their heat treatment. The data on differential leaching rate in the case of the sample with 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl is represented in Figure 6a. The differential leaching rate of 137Cs from all samples under study on the 91st day of contact of the samples with water was 5–11 × 10−5 g/(cm2·day). The heat treatment (450 °С) of the compounds did not lead to a significant change in rate, which was 7–11 × 10−5 g/(cm2·day).
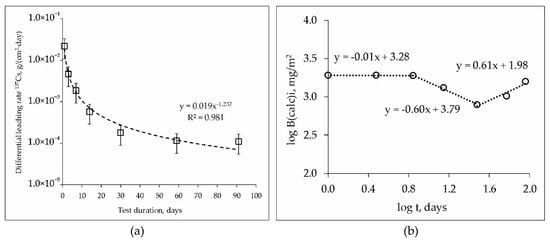
Figure 6.
Kinetic curve of the leaching rate (a) and logarithmic dependence of the release (b) of 137Cs from the MPPZ compound containing 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl and 28.6 wt% zeolite.
It is known from the literature that different values of the equation coefficient of the linear relationship of log (Bi) on log (t) correspond to different leaching mechanisms: >0.65–surface dissolution; 0.35–0.65–diffusion transport; <0.35–surface wash off (or a depletion if it is found in the middle or at the end of the test) [32]. Based on the results of applying the model [31] in the case of the sample with 20 wt% LiCl-KCl-CsCl (Figure 6b), it was found that the cesium leaching mechanisms change during the test time. At the first 7 days of compound contact with water the coefficient of the equation of the linear dependence of log (Bi) on log (t) was −0.01, which corresponded to surface wash off, and up to a 30 days–subsequent surface depletion (−0.60). Subsequent contact of the compound with water for up to 91 days (and obviously further) leads to changes in the mechanism of Cs leaching, and the release of Cs occurs due to diffusion from the inner layers of the compound (0.61). Two possible reasons of the observed behavior of cesium during the leaching from the compounds may be suggested. First, cesium leaching occurs from the surface layer of the compound in the first 30 days, and a slightly soluble protective matrix layer is formed as a result. Subsequent cesium leaching from 30 to 91 days occurs due to diffusion from the inner layers of the compound. Second, cesium leaching occurs due to the dissolution of the readily soluble phases CsH2PO4 and Cs3PO4 in the first 30 days, and then due to diffusion of cesium from the phase of the composition (Mg, K, Cs)PO4 × nH2O, which is the target phase of the matrix with a high physico-chemical stability. The formation of neoformed phases containing cesium as a result of leaching of the MPP compound in bidistilled water seems to be low-probability.
The data on specific surface area of the powders of the crushed compounds used in the PCT test are given in Table 2. It was shown that heat treatment of samples leads to a decrease in their specific surface area, that is due to the removal of bound water from the structure of the obtained matrix (Mg,K,Cs)PO4 × nH2O. At the same time, micropores were not detected both before and after heat treatment, but after heat treatment the number of macropores (50–80 nm) increased significantly in accordance with the IUPAC classification [33], which were almost absent in the initial sample, and the average pore size decreased from 5.48 to 4.89 nm after holding the sample at 450 °C (Table 2).

Table 2.
Specific surface of the crushed samples for determine hydrolytic stability in accordance with the PCT test.
The data on leaching rate of compound components are represented in Table 3. It was shown that the compound had high hydrolytic stability also at 90 ± 2 °C. Leaching rate of Cs was less than 1.9 × 10−6 g/(cm2∙day), which corresponded to the leaching rate of cesium from high-temperature matrices with almost the same load of waste. For example, it was shown in [7], that normalized release of cesium (g/m2) after 7 days leaching test at 90 ± 2 °C from SAP based samples (in the system SiO2-Al2O3-P2O5), mixed with glass frit or borosilicate glass and containing 23.33 wt% an electrolyte surrogate of pyrochemical reprocessing of SNF, was 0.0395 or (0.811–1.36), that corresponded to a normalized release rate of Cs - 5.6 × 10−7 or (1.2–1.9) × 10−5 g/(cm2∙day), respectively.

Table 3.
Hydrolytic stability of the MPP compound samples containing LiCl-KCl-CsCl and zeolite in accordance with the PCT test.
4. Conclusions
The possibility of solidification of the spent electrolyte surrogate LiCl-KCl-CsCl (up to 20 wt%) in the MPP matrix was shown. The characteristics (compressive strength, resistance to thermal cycles of freezing and thawing, thermal stability, hydrolytic stability) of the obtained MPP compound correspond to the current regulatory requirements for materials for RW conditioning in Russia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.K. and S.E.V.; methodology, S.A.K.; validation, S.A.K., E.A.T. and S.E.V.; formal analysis, S.A.K., K.Y.B. and S.E.V.; investigation, S.A.K. and K.Y.B.; resources, E.A.T. and S.E.V.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.K.; writing—review and editing, S.E.V.; visualization, E.A.T. and S.E.V.; supervision, S.E.V.; project administration, S.E.V.; funding acquisition, S.E.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Synthesis of the MPP compound samples and further study of their composition, structure, mechanical and thermal stability is due to a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 16-13-10539). The hydrolytic stability of the compounds was determined in the framework of GEOKHI RAS state assignment (0137-2019-0022).
Acknowledgments
ICP-MS and ICP-AES analyzes was performed at the Laboratory of Methods for Investigation and Analysis of Substances and Materials, GEOKHI RAS (A.V. Zhilkina, I.N. Gromyak). The authors thank V.V. Krupskaya and I.A. Morozov (Lomonosov Moscow State University; Institute of Geology of Ore Deposits, Petrography, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Russian Academy of Sciences) for the opportunity provided to use Ultima-IV X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku) purchased within the framework of implementation of the Development Program of the Lomonosov Moscow State University. The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Shadrin, A.Y.; Dvoeglazov, K.N.; Maslennikov, A.G.; Kashcheev, V.A.; Tret’yakova, S.G.; Shmidt, O.V.; Vidanov, V.L.; Ustinov, O.A.; Volk, V.I.; Veselov, S.N.; et al. PH process as a technology for reprocessing mixed uranium-plutonium fuel from BREST-OD-300 reactor. Radiochemistry 2016, 58, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizin, A.A.; Tomilin, S.V.; Gnevashov, O.E.; Lukinykh, A.N.; Orlova, A.I. Orthophosphates of langbeinite structure for immobilization of alkali metal cations of salt wastes from pyrochemical processes. Radiochemistry 2012, 54, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.R.; Davis, J.; Olufson, K.; Chironi, I.; Karatchevtseva, I.; Farnan, I. Candidate waste forms for immobilisation of waste chloride salt from pyroprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 420, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.; Asuvathraman, R.; Raja Madhavan, R.; Jena, H.; Govindan Kutty, K.V.; Vasudeva Rao, P.R. Studies on Novel Matrices for High Level Waste from Fast Reactor Fuel Reprocessing. Energy Procedia 2011, 7, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Riley, B.J.; Kroll, J.O.; Peterson, J.A.; Pierce, D.A.; Ebert, W.L.; Williams, B.D.; Snyder Michelle, M.V.; Frank, S.M.; George, J.L.; Kruska, K. Assessment of lead tellurite glass for immobilizing electrochemical salt wastes from used nuclear fuel reprocessing. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 495, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Um, W.; Choung, S. Development of iron phosphate ceramic waste form to immobilize radioactive waste solution. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 452, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbo, F.; Da Ros, M.; Macerata, E.; Mariani, M.; Giola, M.; De Angelis, G.; Capone, M.; Fedeli, C. An experimental study on Sodalite and SAP matrices for immobilization of spent chloride salt waste. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 499, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, K.-R.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, I.-T.; Hur, J.M.; Lee, Y.-S. Treatment of radioactive waste salt by using synthetic silica-based phosphate composite for de-chlorination and solidification. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 493, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leturcq, G.; Grandjean, A.; Rigaud, D.; Perouty, P.; Charlot, M. Immobilization of fission products arising from pyrometallurgical reprocessing in chloride media. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 347, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepry, W.C.; Riley, B.J.; Crum, J.V.; Rodriguez, C.P.; Pierce, D.A. Solution-based approaches for making high-density sodalite waste forms to immobilize spent electrochemical salts. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 442, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, H.; Maji, B.K.; Asuvathraman, R.; Govindan Kutty, K.V. Synthesis and thermal characterization of glass bonded Ca-chloroapatite matrices for pyrochemical chloride waste immobilization. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, H.; Maji, B.K.; Asuvathraman, R.; Govindan Kutty, K.V. Effect of pyrochemical chloride waste loading on thermo-physical properties of borosilicate glass bonded Sr-chloroapatite composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 162, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poluektov, P.P.; Schmidt, O.V.; Kascheev, V.A.; Ojovan, M.I. Modelling aqueous corrosion of nuclear waste phosphate glass. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 484, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulyako, Y.M.; Slyunchev, O.M.; Rovny, S.I.; Myasoedov, B.F. Low-temperature immobilization of actinides and other components of high-level waste in magnesium potassium phosphate matrices. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 385, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulyako, Y.M.; Slyunchev, O.M.; Rovnyi, S.I.; Wagh, A.S.; Maloney, M.D.; Myasoedov, B.F. Magnesium potassium phosphate matrices for immobilization of high-level liquid wastes. Radiochemistry 2009, 51, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuropatenko, V.A. High level wastes immobilization in ceramic and hydrated phosphate matrix. East Eur. J. Phys. 2016, 3, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulikova, S.A.; Myasoedov, B.F. Magnesium Potassium Phosphate Compound for Immobilization of Radioactive Waste Containing Actinide and Rare Earth Elements. Materials 2018, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulikova, S.A.; Myasoedov, B.F. Hydrolytic and thermal stability of magnesium potassium phosphate compound for immobilization of high level waste. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 318, 2401–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulikova, S.A.; Myasoedov, B.F. Solidification of high level waste using magnesium potassium phosphate compound. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 51, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulikova, S.A.; Krupskaya, V.V.; Danilov, S.S.; Gromyak, I.N.; Myasoedov, B.F. Investigation of the leaching behavior of components of the magnesium potassium phosphate matrix after high salt radioactive waste immobilization. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 315, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayenko, S.Y.; Shkuropatenko, V.A.; Dikiy, N.P.; Tarasov, R.V.; Ulybkina, K.A.; Surkov, O.Y.; Litvinenko, L.M. Clinoptilolite with cesium immobilization to potassium magnesium phosphate matrix. East Eur. J. Phys. 2017, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wagh, A.S.; Sayenko, S.Y.; Shkuropatenko, V.A.; Tarasov, R.V.; Dykiy, M.P.; Svitlychniy, Y.O.; Virych, V.D.; Ulybkina, Е.А. Experimental study on cesium immobilization in struvite structures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, S.; Postl, W.; Bojar, H.-P.; Berlepsch, P.; Armbruster, T.; Raber, T.; Ettinger, K.; Walter, F. Struvite-(K), KMgPO4∙6H2O, the potassium equivalent of struvite—A new mineral. Eur. J. Mineral. 2008, 20, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, S.E.; Kulikova, S.A.; Krupskaya, V.V.; Myasoedov, B.F. Magnesium Potassium Phosphate Compound for Radioactive Waste Immobilization: Phase Composition, Structure, and Physicochemical and Hydrolytic Durability. Radiochemistry 2018, 60, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, S.A.; Vinokurov, S.E. The Influence of Zeolite (Sokyrnytsya Deposit) on the Physical and Chemical Resistance of a Magnesium Potassium Phosphate Compound for the Immobilization of High-Level Waste. Molecules 2019, 24, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KODEKX. Procedure for Measuring the Ultimate Strength of Cement Compounds Incorporating Radioactive Waste Using a Testing Cybertronic Testing Machine. 2013. Available online: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/437125221 (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Federal Norms and Rules in the Field of Atomic Energy Use. “Collection, Processing, Storage and Conditioning of Liquid Radioactive Waste. Safety Requirements” (NP-019-15); Rostekhnadzor: Moscow, Russia, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- GOST R 52126-2003. Radioactive Waste. Long Time Leach Testing of Solidified Radioactive Waste Forms; Gosstandart 305: Moscow, Russian, 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C1285-14. Standard Test Methods for Determining Chemical Durability of Nuclear, Hazardous, and Mixed Waste Glasses and Multiphase Glass Ceramics: The Product Consistency Test (PCT); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014; Available online: www.astm.org (accessed on 20 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Belousov, P.; Semenkova, A.; Egorova, T.; Romanchuk, A.; Zakusin, S.; Dorzhieva, O.; Tyupina, E.; Izosimova, Y.; Tolpeshta, I.; Chernov, M.; et al. Cesium Sorption and Desorption on Glauconite, Bentonite, Zeolite, and Diatomite. Minerals 2019, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, G.J.; van der Sloot, H.A. Determination of leaching characteristics of waste materials leading to environmental product certification. In Stabilization and Solidification of Hazardous, Radioactive and Mixed Wastes; Gilliam, T.M., Wiles, G., Eds.; ASTMSTP 1123; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; Volume 2, pp. 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras, J.; Buj, I.; Rovira, M.; de Pablo, J. Semi-dynamic leaching tests of nickel containing wastes stabilized/solidified with magnesium potassium phosphate cements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.H. Manual of Symbols and Terminology for Physicochemical Quantities and Units, Appendix II: Definitions, Terminology and Symbols in Colloid and Surface Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1972, 31, 577–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).