Eye Movement Patterns in Solving Science Ordering Problems
Abstract
Introduction
Eye-tracking and Problem-solving
Eye Movement Measures
Purpose of Study
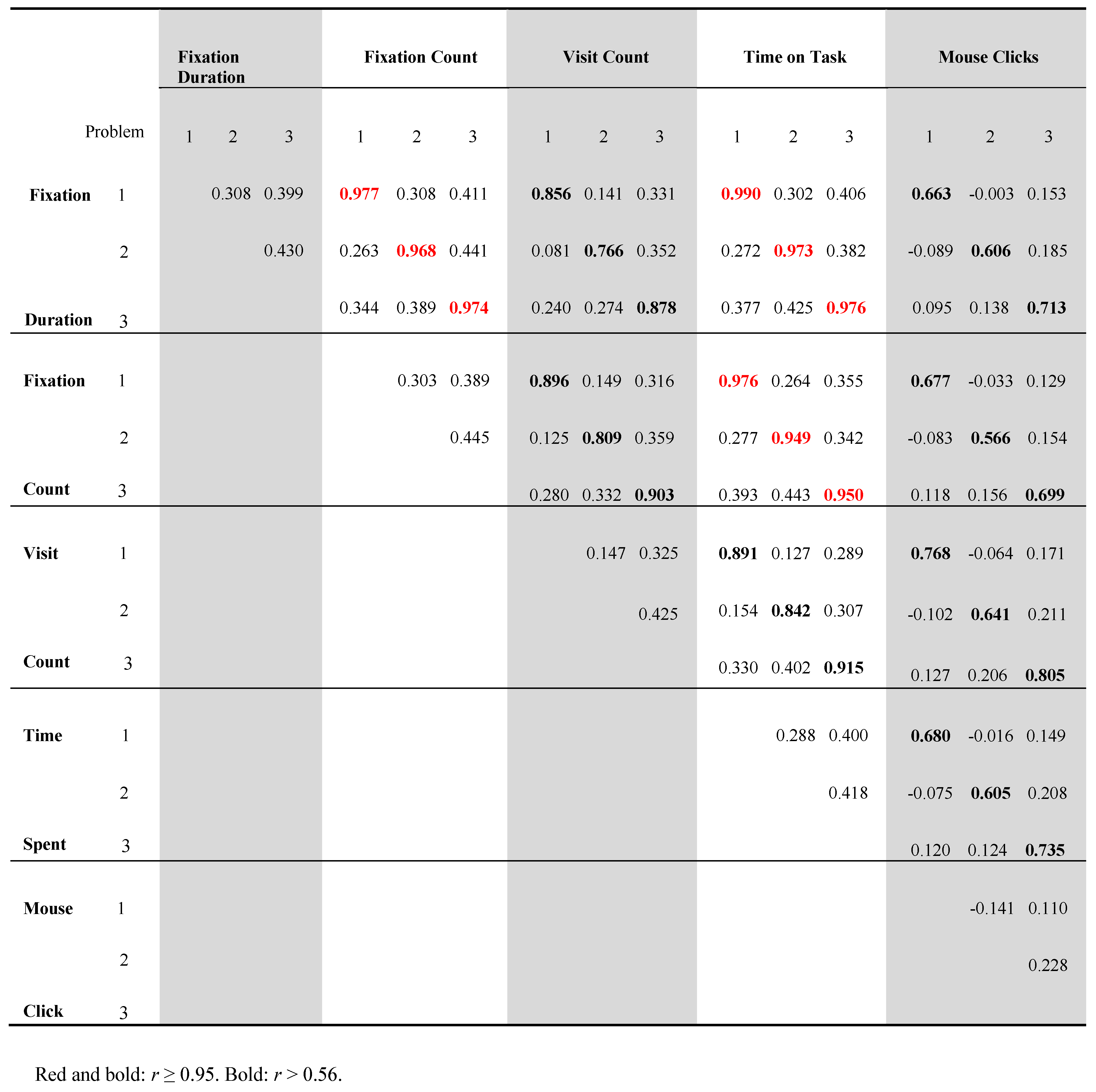
- What are the correlations between fixation duration, fixation count, visit count, time on task and number of mouse clicks?
- What are the relationships between student performance and the above factors?
- What are the differences in scanpath patterns between students who solved the problems correctly and incorrectly?
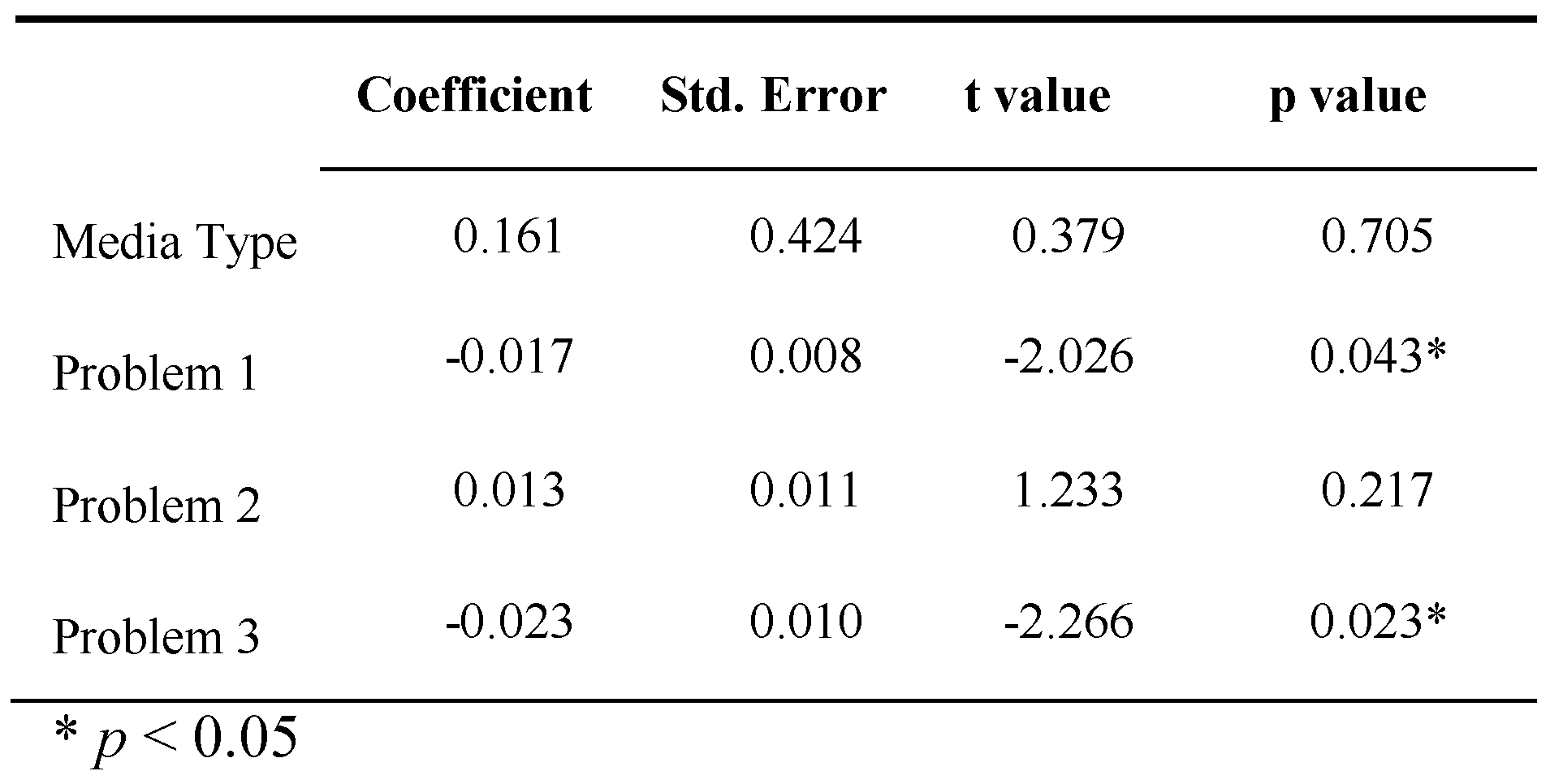
- How does media type affect whether students solve the problems correctly or incorrectly?
Methodology
Participants
Apparatus
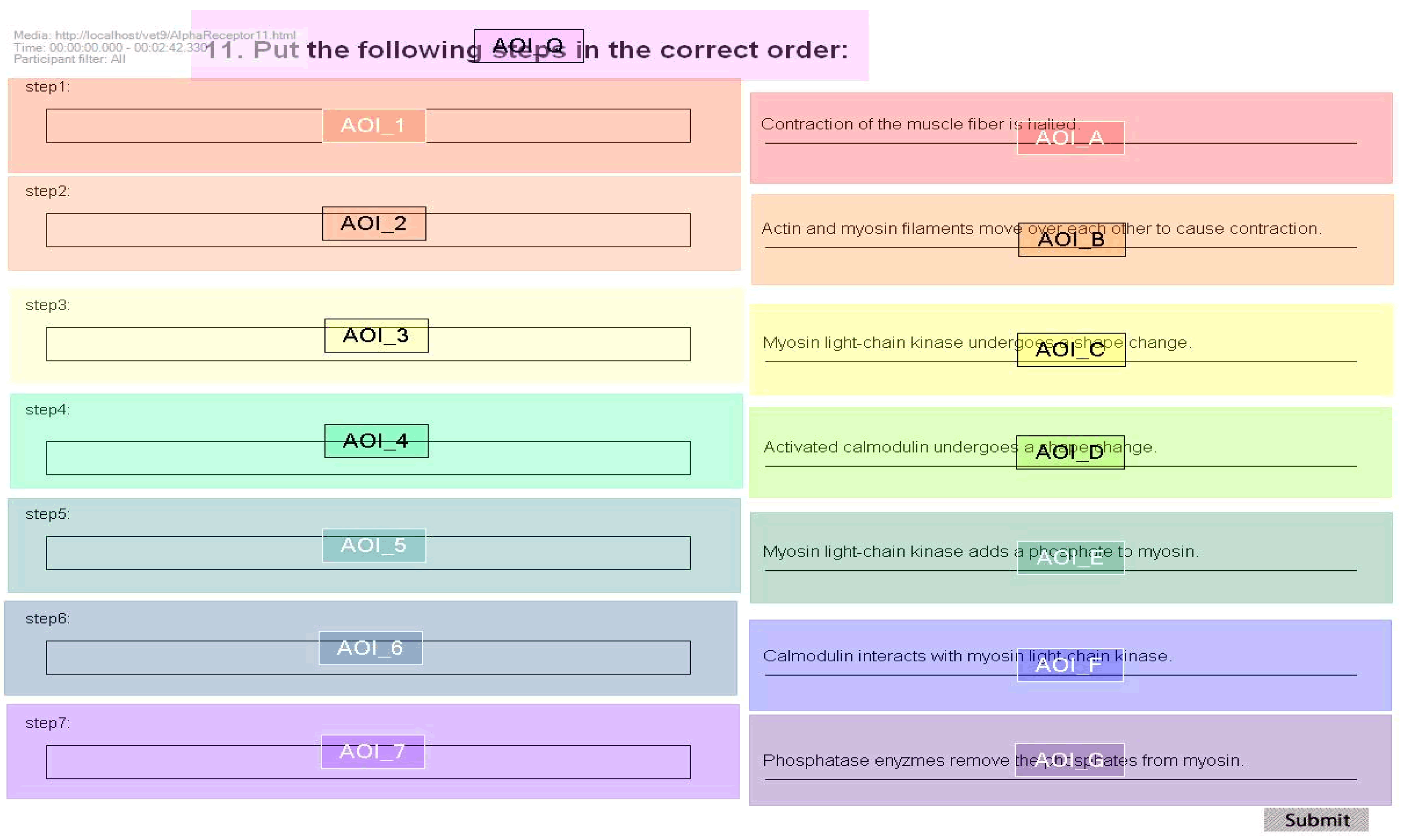
Materials
Procedure
Data Analysis
Results
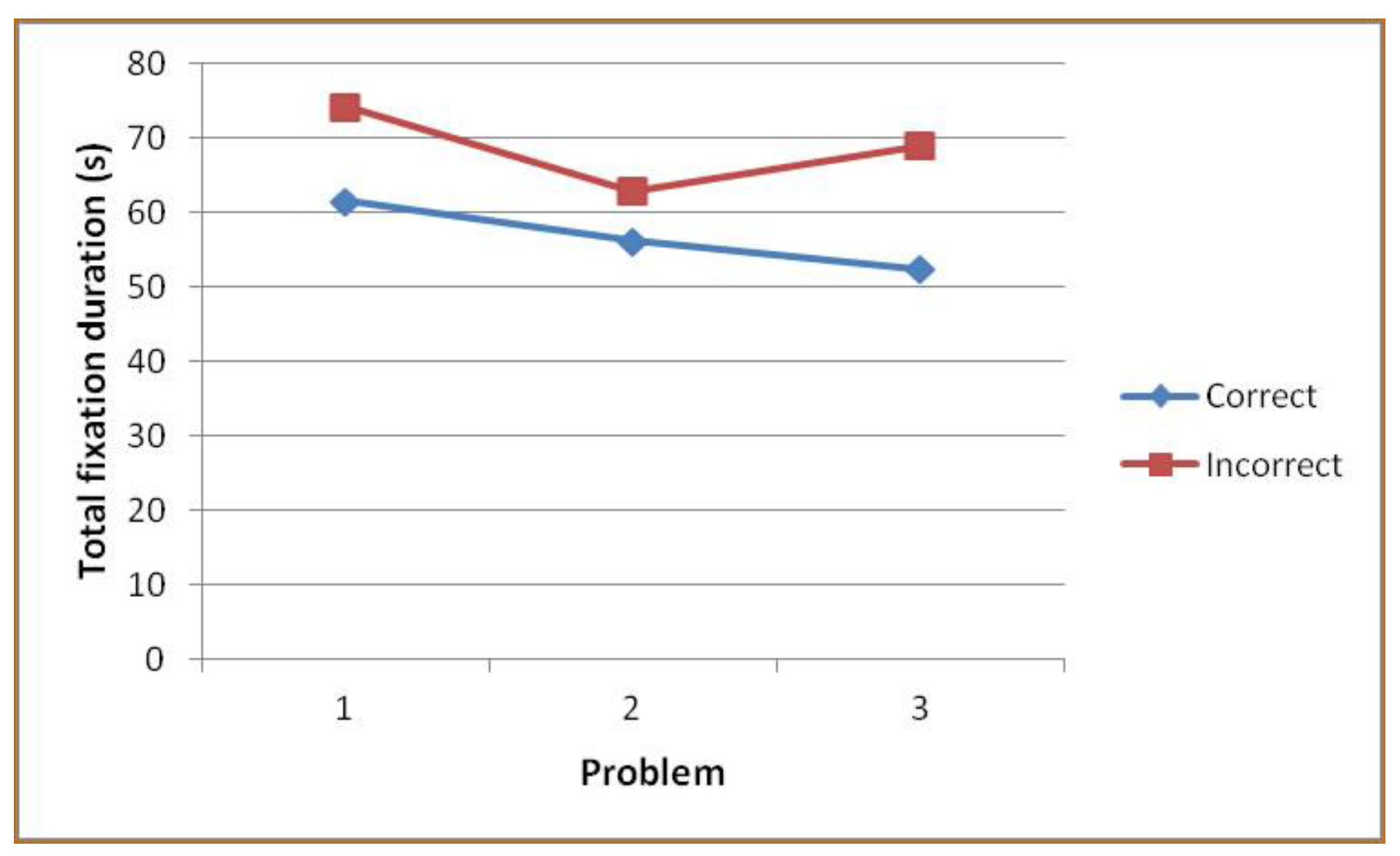
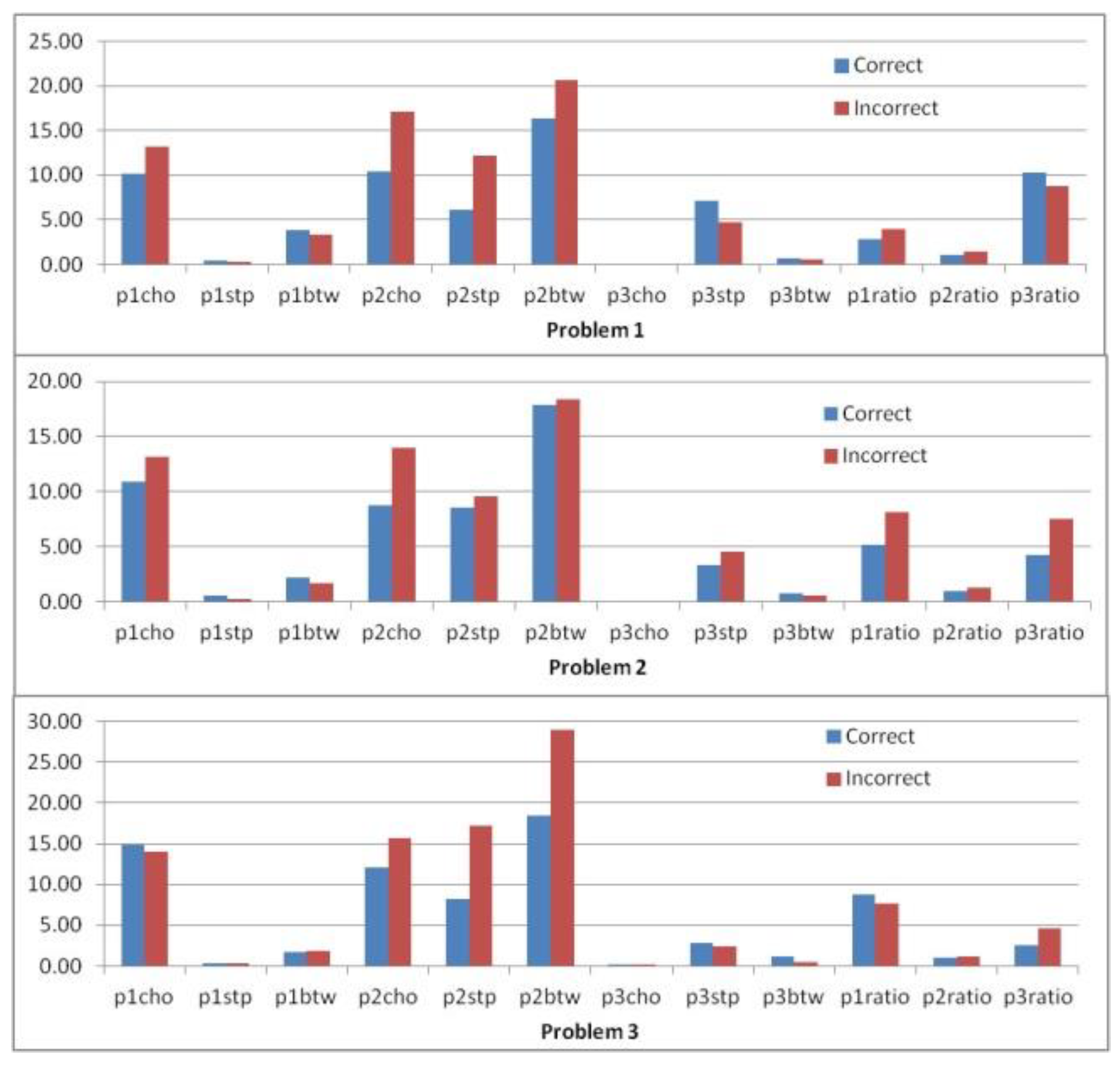
Problems
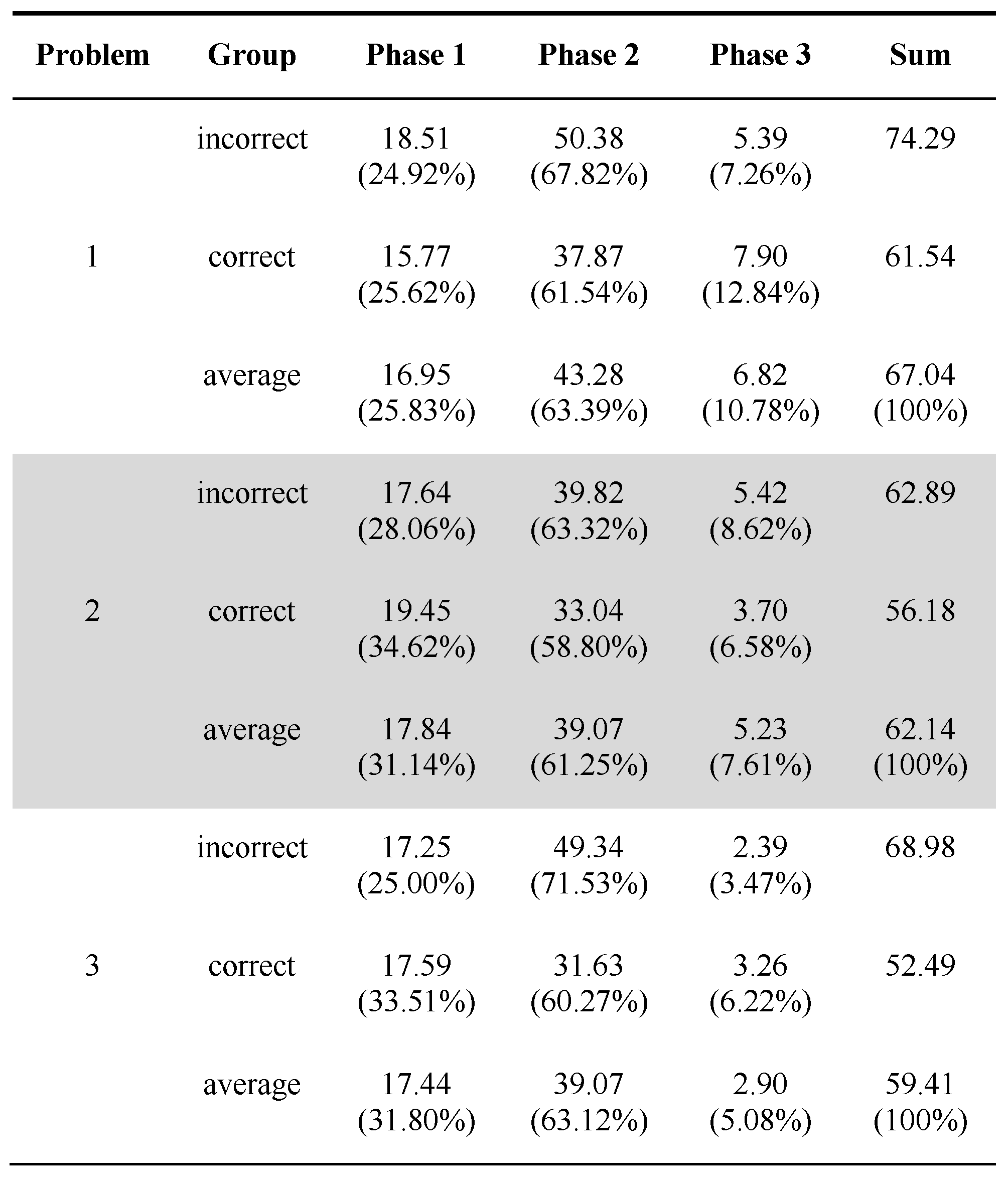
Phases
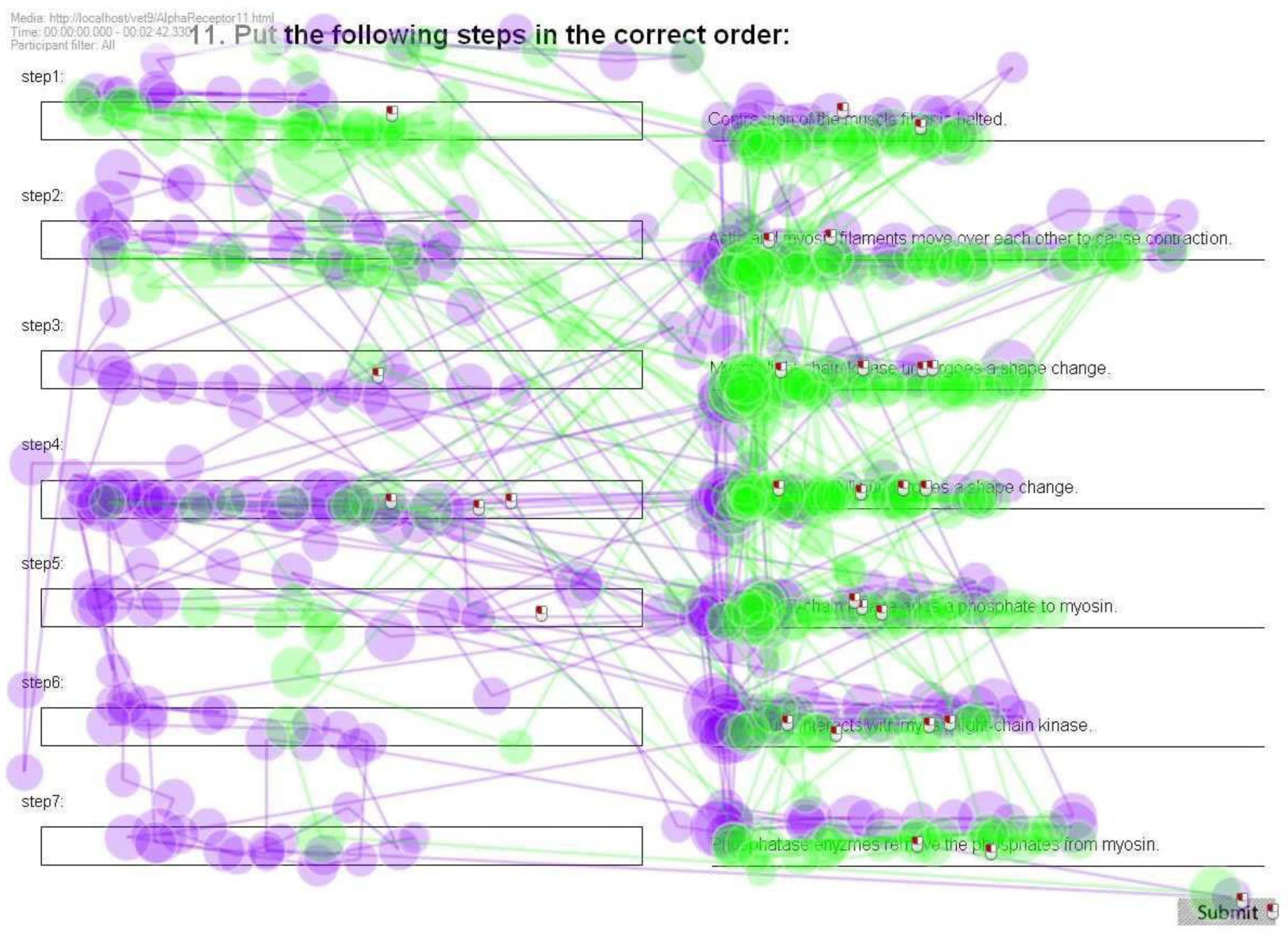
Scanpath patterns
Discussion
Limitations and Future Work
Conclusions
Appendix
 |
References
- Aldahmash, A. H., and M. R. Abraham. 2009. Kinetic versus static visuals for facilitating college students’ understanding of organic reaction mechanisms in chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education 86: 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarik, R., S. Eivazi, and H. Vrzakova. 2013. A Computational Approach for Prediction of Problem-Solving Behavior Using Support Vector Machines and Eye-Tracking Data. In Eye Gaze in Intelligent User Interfaces. Springer London: pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, M. F., W. C. Carter, L. M. Cowgill, D. J. Hurley, S. J. Lewis, J. N. MacLeod, and T. P. Robertson. 2005. Using 3D animations to teach intracellular signal transduction mechanisms: taking the arrows out of cells. Journal of veterinary medical education 32, 1: 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M. T. 1997. Quantifying qualitative analyses of verbal data: A practical guide. The journal of the learning sciences 6, 3: 271–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. 1988. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- De Corte, E., L. Verschaffel, and A. Pauwels. 1990. Influence of the semantic structure of word problems on second graders’ eye movements. Journal of Educational Psychology 82, 2: 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S., S. O’Brien, and M. Carl. 2010. Eye tracking as an MT evaluation technique. Machine translation 24, 1: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C. F., J. Elith, S. Bacher, C. Buchmann, G. Carl, G. Carré, and T. Münkemüller. 2013. Collinearity: a review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 36, 1: 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, S., and R. Bednarik. 2011. Predicting problem-solving behavior and performance levels from visual attention data. In Proc. Workshop on Eye Gaze in Intelligent Human Machine Interaction at IUI. pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Epelboim, J., and P. Suppes. 2001. A model of eye movements and visual working memory during problem solving in geometry. Vision Research 41, 12: 1561–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R. M., and J. P. Thibaut. Using eye-tracking to predict children’s success or failure on analogy tasks. In Livre/Conférence Proceedings of the Thirty-Sixth Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society. Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society. pp. 2222–2227.
- Feusner, M., and B. Lukoff. 2008. Testing for statistically significant differences between groups of scan patterns. In Proceedings of the 2008 symposium on Eye tracking research & applications. ACM, March, pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, E. R., and M. J. Spivey. 2003. Eye movements and problem solving guiding attention guides thought. Psychological Science 14, 5: 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H. J., P. Lemaire, and S. Dufau. 2007. Eye movement correlates of younger and older adults’ strategies for complex addition. Acta psychologica 125, 3: 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Greene, M. R., T. Liu, and J. M. Wolfe. 2012. Reconsidering Yarbus: A failure to predict observers’ task from eye movement patterns. Vision research 62: 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, M., R. E. Mayer, and C. E. Green. 1992. Comprehension of arithmetic word problems: Evidence from students’ eye fixations. Journal of Educational Psychology 84, 1: 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzum, M., K. D. Hansen, and H. H. Andersen. 2009. Scrutinising usability evaluation: does thinking aloud affect behaviour and mental workload? Behaviour & Information Technology 28, 2: 165–181. [Google Scholar]
- Holmqvist, K., M. Nyström, R. Andersson, R. Dewhurst, H. Jarodzka, and J. Van de Weijer. 2011. Eye tracking: A comprehensive guide to methods and measures. Oxford University Press: Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y. M., S. Lee, R. Mallipeddi, H. W. Kwak, and M. Lee. 2011. Recognition of human’s implicit intention based on an eyeball movement pattern analysis. In Neural Information Processing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, January, pp. 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Just, M. A., and P. A. Carpenter. 1984. Using eye fixations to study reading compre hension. Edited by D. E. Kieras and M. A. Just. In New Methods in Reading Comprehension Research. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, pp. 151–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kanan, C., N. A. Ray, D. N. Bseiso, J. H. Hsiao, and G. W. Cottrell. 2014. Predicting an observer’s task using multi-fixation pattern analysis. In Proceedings of the symposium on eye tracking research and applications. ACM, March, pp. 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, J., E. Hefer, and G. Matthew. 2014. Attention distribution and cognitive load in a subtitled academic lecture: L1 vs. L2. Journal of Eye Movement Research 7, 5: 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenshtein, V. I. 1966. Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions, and reversals. Soviet physics doklady 10, 8: 707–710. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, R. E., J. H. Larkin, and J. B. Kadane. 1984. A cognitive analysis of mathematical problem-solving ability. Edited by R. J. Sternberg. In Advances in the psychology of human intelligence. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, Vol. 2, pp. 231–273. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, D., and P. C. H. Cheng. 2001. Graph-based reasoning: From task analysis to cognitive explanation. In Proceedings of the twenty-third annual conference of the cognitive science society. pp. 762–767. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, A., and L. J. Ball. 2006. Eye tracking in HCI and usability research. Encyclopedia of human computer interaction 1: 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. 2015. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. URL http://www.R-project.org/.
- Reindl, K.M., A.R. White, C. Johnson, B. Bender, B.M. Slator, and P. McLean. 2015. The virtual cell animation collection: Tools for teaching molecular and cellular biology. PLoS Biol 13, 4: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slykhuis, D. A., E. N. Wiebe, and L. A. Annetta. 2005. Eye-tracking students’ attention to PowerPoint photographs in a science education setting. Journal of Science Education and Technology 14, 5–6: 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieff, M., M. Hegarty, and G. Deslongchamps. 2011. Identifying Representational Competence with Multi-representational Displays. Cognition Instruct. 29, 1: 123−145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppes, P., M. Cohen, R. Laddaga, J. Anliker, and R. Floyd. 1983. A procedural theory of eye movements in doing arithmetic. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 27, 4: 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, R. H., J. F. Loehr, and F. J. Brigham. 2006. An exploration of the use of eye-gaze tracking to study problem-solving on standardized science assessments. International journal of research & method in education 29, 2: 185–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H., and N. Pienta. 2012. Eye-tracking study of complexity in gas law problems. Journal of Chemical Education 89, 8: 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H., J. Kirk, and N. J. Pienta. 2014. Investigating the Effect of Complexity Factors in Stoichiometry Problems Using Logistic Regression and Eye Tracking. Journal of Chemical Education 91, 7: 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H., J. J. Topczewski, A. M. Topczewski, and N. J. Pienta. 2012. Permutation test for groups of scanpaths using normalized Levenshtein distances and application in NMR questions. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. ACM, March, pp. 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Tobii. 2011. Tobii Studio 2.X User Manual. Stockholm, Sweden. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y. F., E. Viirre, C. Strychacz, B. Chase, and T. P. Jung. 2007. Task performance and eye activity: predicting behavior relating to cognitive workload. Aviation, space, and environmental medicine 78 Supplement 1: B176–B185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M. J., H. T. Hou, M. L. Lai, W. Y. Liu, and F. Y. Yang. 2012. Visual attention for solving multiple-choice science problem: An eye-tracking analysis. Computers & Education 58, 1: 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tversky, B., J. B. Morrison, and M. Betrancourt. 2002. Animation: can it facilitate? International journal of human-computer studies 57, 4: 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gog, T., F. Paas, and J. J. G. Van Merriënboer. 2005. Uncovering expertise-related differences in troubleshooting performance: Combining eye movement and concurrent verbal protocol data. Applied Cognitive Psychology 19: 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gog, T., H. Jarodzka, K. Scheiter, P. Gerjets, and F. Paas. 2009. Attention guidance during example study via the model’s eye movements. Computers in Human Behavior 25, 3: 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W. N., and B. D. Ripley. 2002. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed. Springer, New York. [Google Scholar]
- West, J. M., A. R. Haake, E. P. Rozanski, and K. S. Karn. 2006. eyePatterns: software for identifying patterns and similarities across fixation sequences. In Proceedings of the 2006 symposium on Eye tracking research & applications. ACM, March, pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, V. M., M. Hegarty, G. Deslongchamps, K. C. Williamson, III, and M. J. Shultz. 2013. Identifying student use of ball-and-stick images versus electrostatic potential map images via eye tracking. Journal of Chemical Education 90, 2: 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


 |
 |
 |
Copyright © 2016. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Day, E.; Kendhammer, L.; Moore, J.N.; Brown, S.A.; Pienta, N.J. Eye Movement Patterns in Solving Science Ordering Problems. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2016, 9, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.3.6
Tang H, Day E, Kendhammer L, Moore JN, Brown SA, Pienta NJ. Eye Movement Patterns in Solving Science Ordering Problems. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2016; 9(3):1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.3.6
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hui, Elizabeth Day, Lisa Kendhammer, James N. Moore, Scott A. Brown, and Norbert J. Pienta. 2016. "Eye Movement Patterns in Solving Science Ordering Problems" Journal of Eye Movement Research 9, no. 3: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.3.6
APA StyleTang, H., Day, E., Kendhammer, L., Moore, J. N., Brown, S. A., & Pienta, N. J. (2016). Eye Movement Patterns in Solving Science Ordering Problems. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 9(3), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.9.3.6



