Analysis of Eye and Head Coordination in a Visual Peripheral Recognition Task
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Participants
Apparatus
Visual targets
Procedure
Signal pre-processing
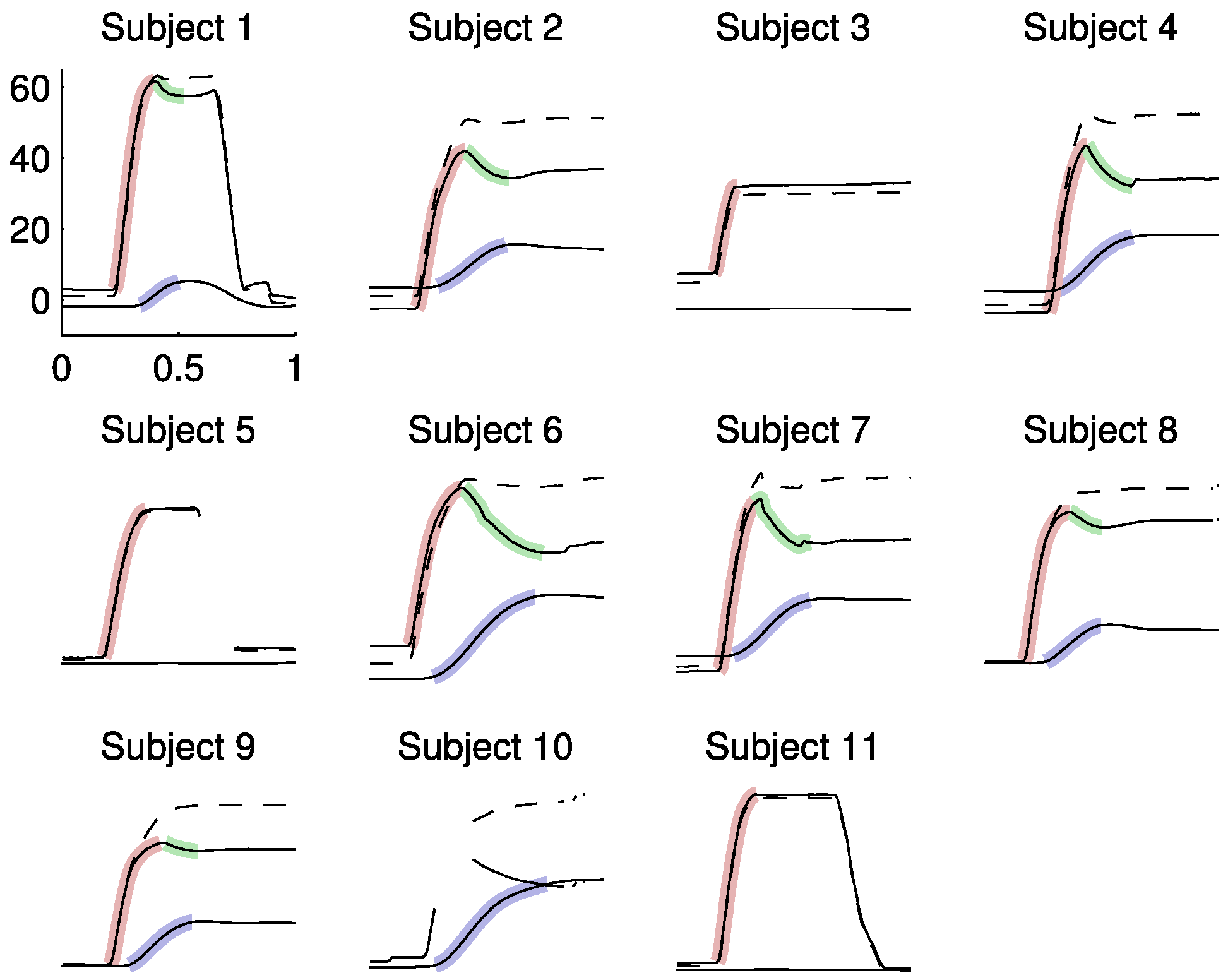
Identification of parameters
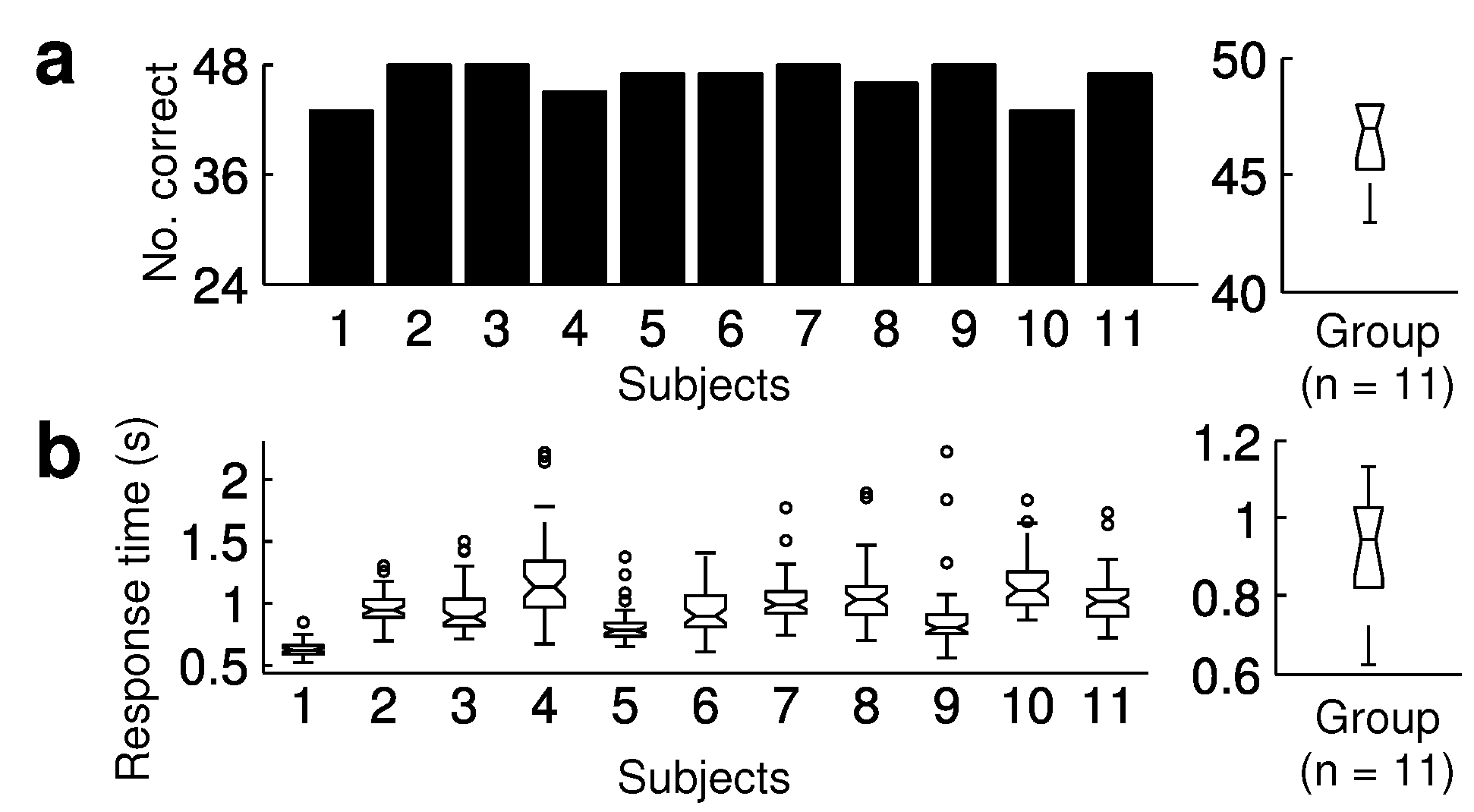
Results
Discussion
Acknowledgements
Appendix A How to use EHCA
References
- Altorfer, A., S. Jossen, O. Würmle, M. L. Käsermann, K. Foppa, and H. Zimmermann. 2000. Measurement and meaning of head movements in everyday face-to-face communicative interaction. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments & Computers 32, 1: 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, G. R. 1979. Vestibulo-ocular function during coordinated head and eye movements to acquire visual targets. Journal of Physiology 287: 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartz, A. E. 1966. Eye and head movements in peripheral vision: nature of compensatory eye movements. Science 152, 729: 1644–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W., R. rgens, J. Kassubek, D. Ecker, B. Kramer, and B. Landwehrmeyer. 2009. Eye-head coordination in moderately affected huntington’s disease patients: do head movements facilitate gaze shifts? Experimental Brain Research 192, 1: 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzi, E. 1979. Strategies of eye-head coordination. Progress in Brain Research 50: 795–803. [Google Scholar]
- Bizzi, E., R. E. Kalil, and V. Tagliasco. 1971. Eye-head coordination in monkeys: evidence for centrally patterned organization. Science 173, 3995: 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braff, D. L. 1993. Information processing and attention dysfunctions in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 19, 2: 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecala, A. L., and E. G. Freedman. 2008. Amplitude changes in response to target displacements during human eye-head movements. Vision Research 48, 2: 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. L., and M. M. G. Walton. 2005. Head movement evoked by electrical stimulation in the supplementary eye field of the rhesus monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology 94, 6: 4502–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corneil, B. D., and D. P. Munoz. 1999. Human eye-head gaze shifts in a distractor task. ii. reduced threshold for initiation of early head movements. Journal of Neurophysiology 82, 3: 1406–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J. D., M. Z. Ceylan, E. M. Klier, and D. Guitton. 1999. Three-dimensional eye-head coordination during gaze saccades in the primate. Journal of Neurophysiology 81, 4: 1760–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchowski, A. T. 2007. Eye tracking methods: Theory and practice. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- user, W., F. Schumann, J. Vockeroth, K. Bartl, M. Cerf, J. Harel, and et al. 2009. Distinct roles for eye and head movements in selecting salient image parts during natural exploration. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1164: 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, J., K. Fukushima, N. Morita, and I. Yamashita. 1990. Disturbances in the control of saccadic eye movement and eye-head coordination in schizophrenics. Journal of Vestibular Research 1, 2: 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J. H. 1992. Head movement propensity. Experimental Brain Research 92, 1: 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, H. H., and A. J. Van Opstal. 1997. Human eye-head coordination in two dimensions under different sensorimotor conditions. Experimental Brain Research 114, 3: 542–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H. C., J. M. Gibson, W. H. Zangemeister, and C. Kennard. 1990. The effect of treatment on eye-head coordination in parkinson’s disease. Journal of Vestibular Research 1, 2: 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, M. M. J., J. Goumans, and J. van der Steen. 2006. Recording three-dimensional eye movements: scleral search coils versus video oculography. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 47, 1: 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klier, E. M., H. Wang, and J. D. Crawford. 2001. The superior colliculus encodes gaze commands in retinal coordinates. Nature Neuroscience 4, 6: 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M. F., and P. McLeod. 2000. From eye movements to actions: how batsmen hit the ball. Nature Neuroscience 3, 12: 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteon, J. A., A. G. Constantin, H. Wang, J. MartinezTrujillo, and J. D. Crawford. 2010. Electrical stimulation of the frontal eye fields in the head-free macaque evokes kinematically normal 3d gaze shifts. Journal of Neurophysiology 104, 6: 3462–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, M., and W. H. Zangemeister. 2003. The effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation over the cerebellum on the synkinesis of coordinated eye and head movements. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 213, 1-2: 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuechterlein, K. H., and M. E. Dawson. 1984. Information processing and attentional functioning in the developmental course of schizophrenic disorders. Schizophrenia Bulletin 10, 2: 160–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, B. S., R. M. Smith, and J. S. Stahl. 2004. The influence of future gaze orientation upon eye-head coupling during saccades. Experimental Brain Research 155, 1: 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oommen, B. S., and J. S. Stahl. 2005. Amplitudes of head movements during putative eye-only saccades. Brain Research 1065, 1-2: 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirce, J. W. 2008. Generating stimuli for neuroscience using PsychoPy. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 2: 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J. O., A. F. Fuchs, L. Ling, Y. Iwamoto, and S. Votaw. 1997. Gain adaptation of eye and head movement components of simian gaze shifts. Journal of Neurophysiology 78, 5: 2817–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Populin, L. C., and A. Z. Rajala. 2011. Target modality determines eye-head coordination in nonhuman primates: implications for gaze control. Journal of Neurophysiology 106, 4: 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Proudlock, F. A., and I. Gottlob. 2007. Physiology and pathology of eye-head coordination. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 26, 5: 486–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J. L., R. Lencer, J. R. Bishop, S. Keedy, and J. A. Sweeney. 2008. Pharmacological treatment effects on eye movement control. Brain and Cognition 68, 3: 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A., J. Churan, D. E. Guitton, and C. C. Pack. 2011. Perceptual compression of visual space during eye-head. gaze shifts. Journal of Vision 11, 12: 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, D. D., and J. H. Goldberg. 2000. Identifying fixations and saccades in eye-tracking protocols. In Proceedings of the 2000 symposium on eye tracking research & applications. New York, NY, USA, ACM: pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, S. 2011. EHCA: Eye-head coordination analyzer for the MATLAB programming language. Available online: http://sourceforge.net/projects/ehca/.
- Stahl, J. S. 1999. Amplitude of human head movements associated with horizontal saccades. Experimental Brain Research 126, 1: 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, N. 2006. A PC parallel port button box provides millisecond response time accuracy under Linux. Behavior Research Methods 38, 1: 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumser, Z. C., B. S. Oommen, I. S. Kofman, and J. S. Stahl. 2008. Idiosyncratic variations in eye-head coupling observed in the laboratory also manifest during spontaneous behavior in a natural setting. Experimental Brain Research 191, 4: 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, D., B. Glenn, and T. Vilis. 1995. Eye-head coordination during large gaze shifts. Journal of Neurophysiology 73, 2: 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, J. N., and M. A. Frens. 2002. Recording eye movements with video-oculography and scleral search coils: a direct comparison of two methods. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 114, 2: 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, G., and E. Foxlin. 2002. Motion tracking: no silver bullet, but a respectable arsenal. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 22, 6: 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambarbieri, D., R. Schmid, M. Versino, and G. Beltrami. 1997. Eye-head coordination toward auditory and visual targets in humans. Journal of Vestibular Research 7, 2-3: 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2012 by the authors. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Schwab, S.; Würmle, O.; Altorfer, A. Analysis of Eye and Head Coordination in a Visual Peripheral Recognition Task. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2012, 5, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.5.2.3
Schwab S, Würmle O, Altorfer A. Analysis of Eye and Head Coordination in a Visual Peripheral Recognition Task. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2012; 5(2):1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.5.2.3
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwab, Simon, Othmar Würmle, and Andreas Altorfer. 2012. "Analysis of Eye and Head Coordination in a Visual Peripheral Recognition Task" Journal of Eye Movement Research 5, no. 2: 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.5.2.3
APA StyleSchwab, S., Würmle, O., & Altorfer, A. (2012). Analysis of Eye and Head Coordination in a Visual Peripheral Recognition Task. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 5(2), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.5.2.3



