Target Eccentricity and Form Influences Disparity Vergence Eye Movements Responses: A Temporal and Dynamic Analysis
Abstract
Introduction
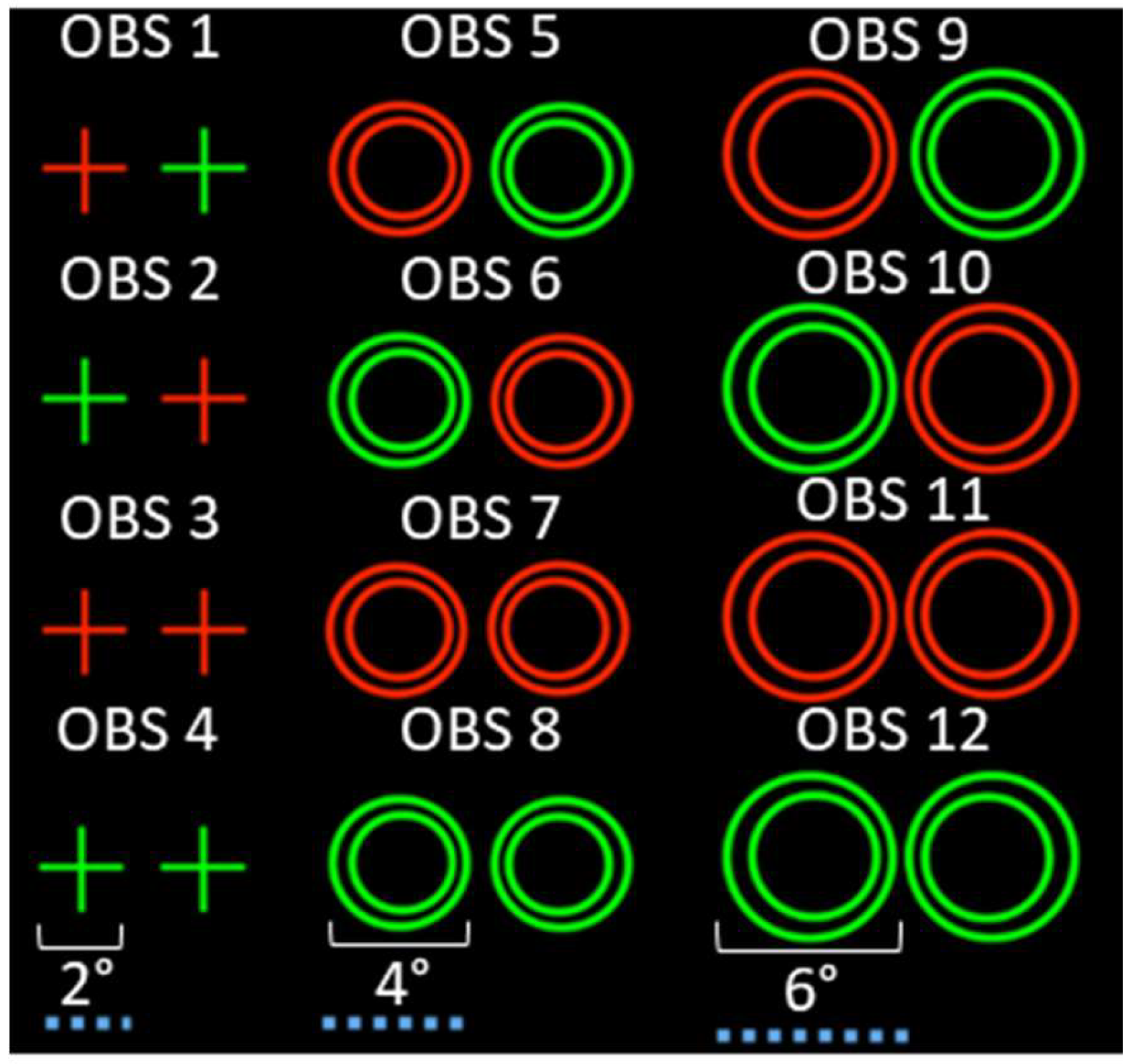
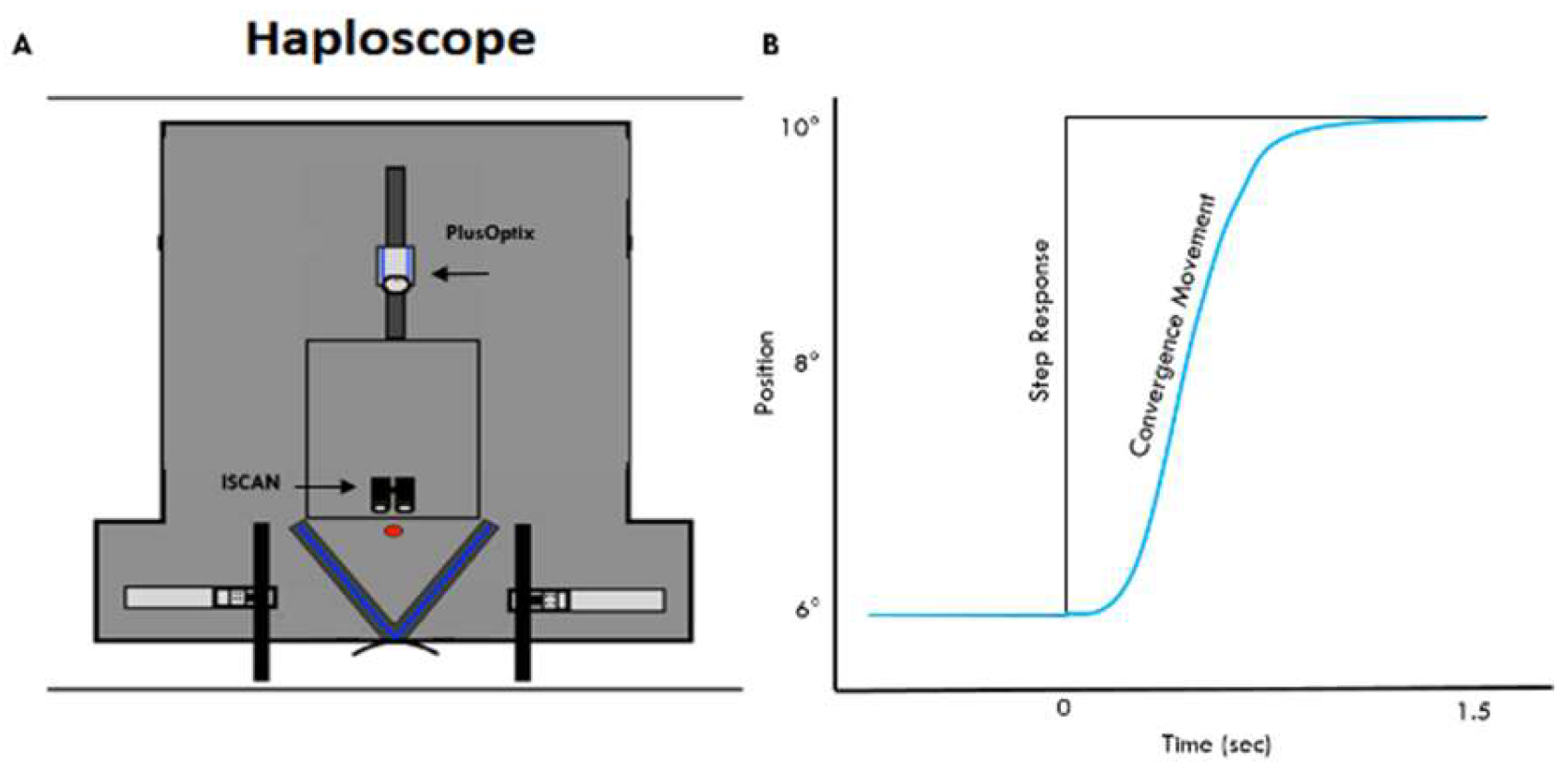
Methods
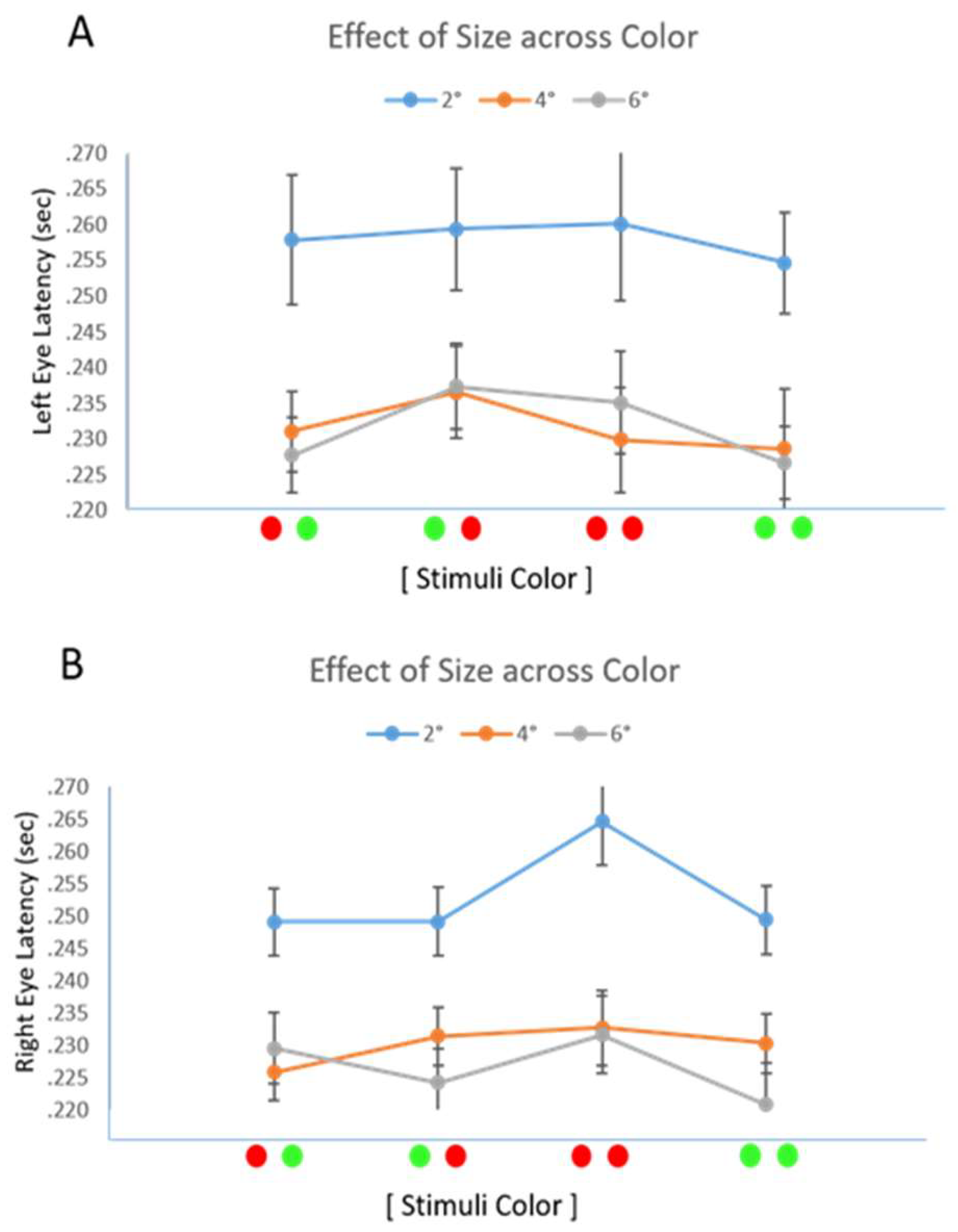
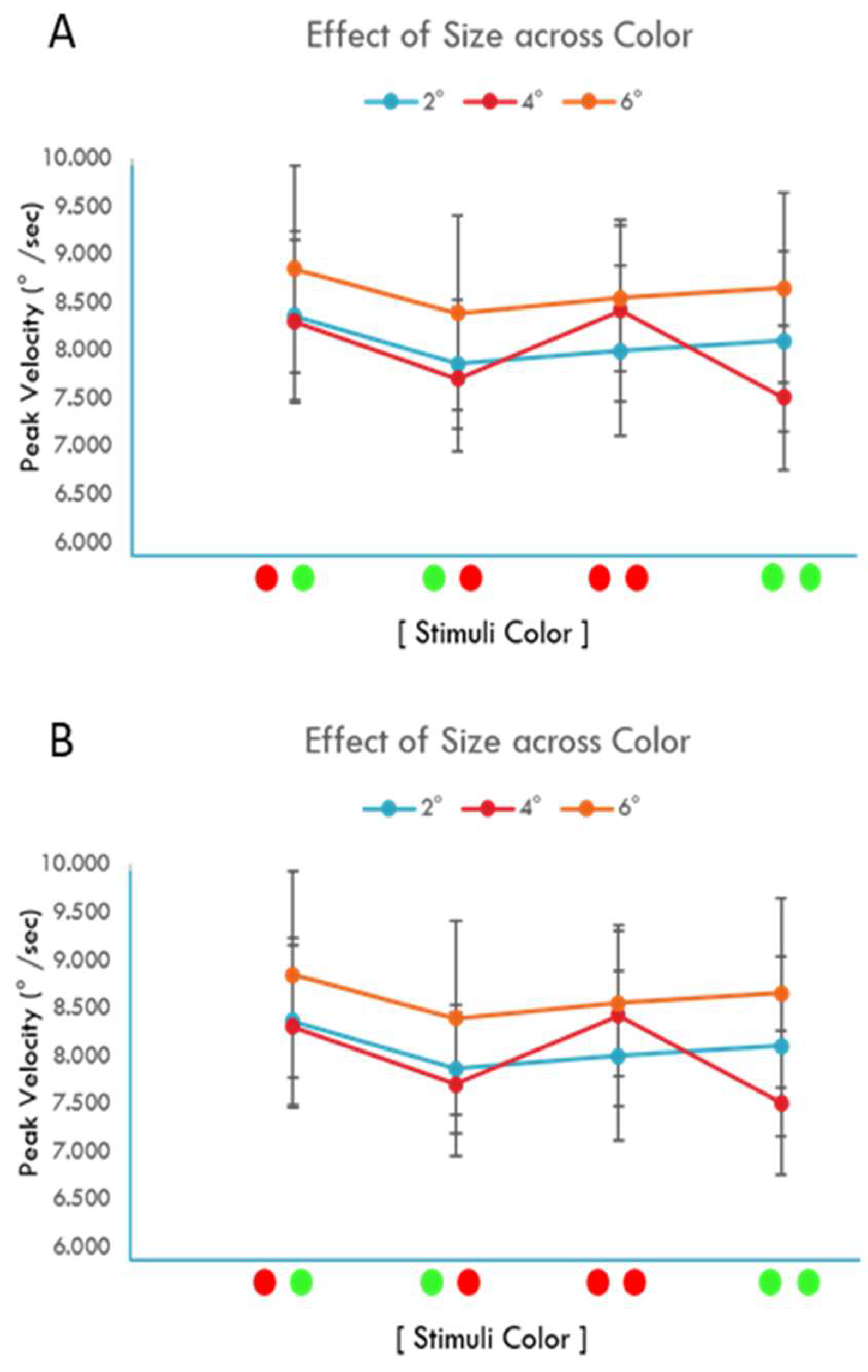
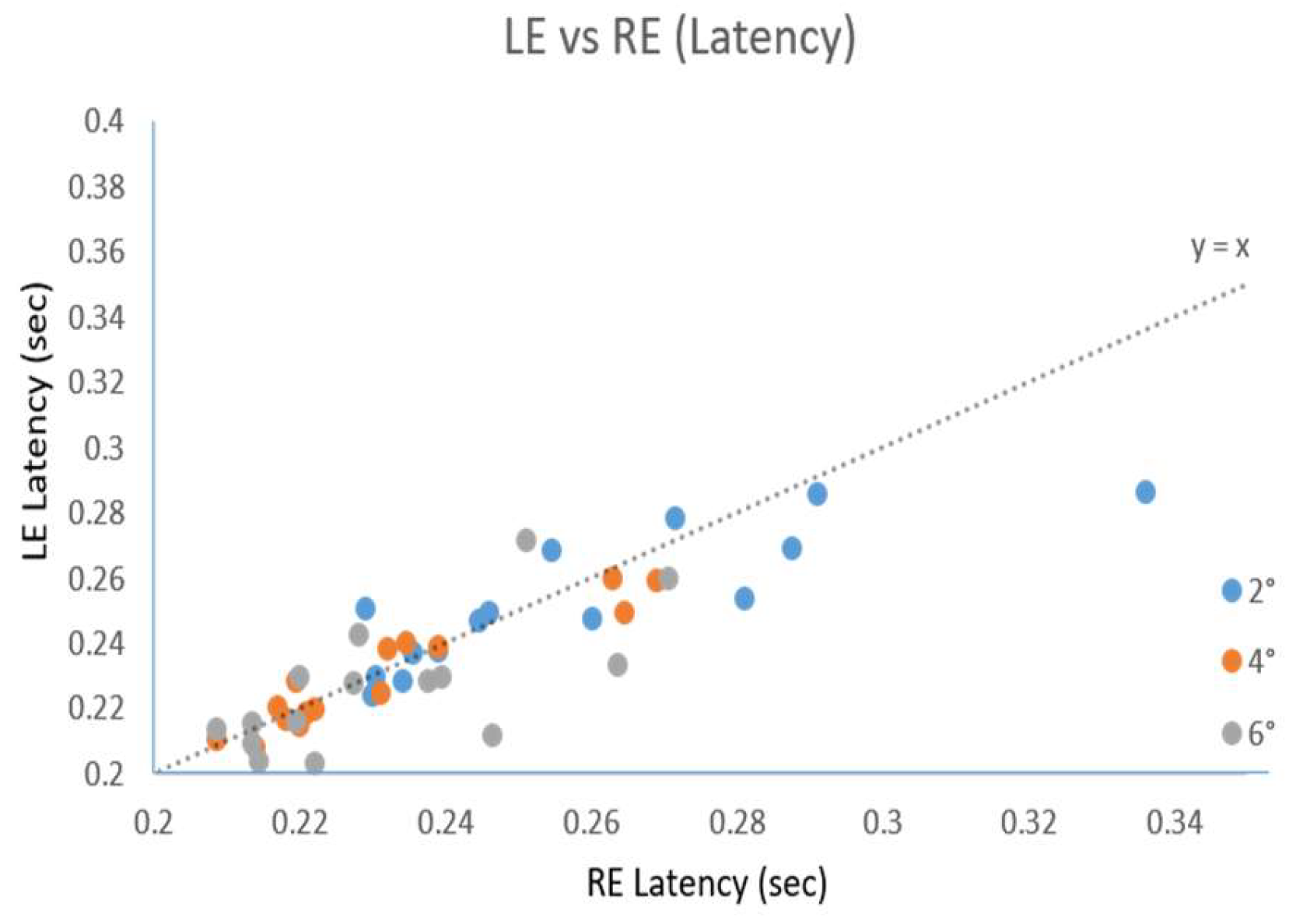
Results
Discussion
Ethics and Conflict of Interest
Acknowledgments
References
- Iskander, J.; Hossny, M.; Nahavandi, S. Using biomechanics to investigate the effect of VR on eye vergence system. Appl Ergon. 2019, 81, 102883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sitzmann, V.; Serrano, A.; Pavel, A.; Agrawala, M.; Gutierrez, D.; Masia, B.; et al. Saliency in VR: How Do People Explore Virtual Environments? IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2018, 24, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallari, B.; Spaeth, E.K.; Goh, H.; Boyd, B.S. Virtual reality as an analgesic for acute and chronic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2053–2085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eijlers, R.; Dierckx, B.; Staals, L.M.; Berghmans, J.M.; van der Schroeff, M.P.; Strabbing, E.M.; et al. Virtual reality exposure before elective day care surgery to reduce anxiety and pain in children: A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2019.
- Tarassoli, S.P. Artificial intelligence, regenerative surgery, robotics? What is realistic for the future of surgery? Ann Med Surg. 2019, 41, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, T.; Guo, S. A fast and stable vascular deformation scheme for interventional surgery training system. Biomed Eng Online. 2016, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, I.T.; Kirchhoff, P.; Chen, D.C. Blended Learning Methods for Surgical Education. Surg Technol Int. 2018, 33, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yaramothu, C.; Greenspan, L.D.; Scheiman, M.; Alvarez, T.L. Vergence Endurance Test: A pilot study for a concussion biomarker. J Neurotrauma [Internet] 2019. [cited 2019 Mar 20];neu.2018.6075. [Google Scholar]
- Yaramothu, C.; d’Antonio-Bertagnolli, J.V.; Santos, E.M.; Crincoli, P.C.; Rajah, J.V.; Scheiman, M.; et al. Proceedings #37: Virtual Eye Rotation Vision Exercises (VERVE): A Virtual Reality Vision Therapy Platform with Eye Tracking. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, e107–e108. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Semmlow, J.L.; Yuan, W.; Munoz, P. Disparity vergence double responses processed by internal error. Vision Res. 2000, 40, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M.; Talasan, H.; Mitchell, G.L.; Alvarez, T.L. Objective Assessment of Vergence after Treatment of Concussion-Related CI: A Pilot Study. Optom Vis Sci. 2016.
- Yaramothu, C.; Santos, E.M.; Alvarez, T.L. Effects of visual distractors on vergence eye movements. J Vis [Internet]. 2018, [cited 2019 Mar 20]. 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Erkelens, C.J.; Collewijn, H. Eye movements and stereopsis during dichoptic viewing of moving random-dot stereograms. Vision Res. 1985, 25, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Horng, J.L.; Semmlow, J.L.; Hung, G.K.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Dynamic asymmetries in disparity convergence eye movements. Vision Res [Internet]. 1998, [cited 2019 Jun 20]. 38, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Semmlow, J.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Alvarez, T.L.; Pedrono, C. Saccadic Behavior during the Response to Pure Vergence Stimuli I: General Properties. J Eye Mov Res. 2007, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Lee, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Semmlow, J.L.; Alvarez, T.L. Behaviors, models, and clinical applications of vergence eye movements. J Med Biol Eng. 2010, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.H.; Alvarez, T.L. The frequency of horizontal saccades in near and far symmetrical disparity vergence. Vision Res. 2012, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Kim, E.H. Analysis of Saccades and Peak Velocity to Symmetrical Convergence Stimuli: Binocularly Normal Controls Compared to Convergence Insufficiency Patients. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Internet]. 2013, [cited 2018 Mar 14]. 54, 4122. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, E.M.; Yaramothu, C.; Alvarez, T.L. Comparison of symmetrical prism adaptation to asymmetrical prism adaptation in those with normal binocular vision. Vision Res. 2018, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkelens, I.M.; Bobier, W.R. Asymmetries between convergence and divergence reveal tonic vergence is dependent upon phasic vergence function. J Vis. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Semmlow, J.L.; Pedrono, C. Divergence eye movements are dependent on initial stimulus position. Vision Res [Internet]. 2005, [cited 2015 Jan 20]. 45, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erkelens, I.M.; Bobier, W.R. Adaptation of reflexive fusional vergence is directionally biased. Vision Res. 2018, 149, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Wick, B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision: Heterophoric, Accommodative, and Eye Movement Disorders [Internet], 4th ed.; Shaw, R., Ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2014; [cited 2018 Mar 14]; 722p. [Google Scholar]
- Sheard, C. Zones of Ocular Comfort. Am J Optom. 1930, 7, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Von Noorden, G.K.; Campos, E.C.; Louis, S.; Philadelphia, L.; Toronto, S. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility Theory and Management of Strabismus [Internet], 6th ed.; Lampert, R., Ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, 2002; [cited 2019 Jun 25]. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.H.; Vicci, V.R.; Han, S.J.; Alvarez, T.L. Sustained Fixation Induced Changes in Phoria and Convergence Peak Velocity. Miller JM, editor. PLoS One [Internet]. 2011, [cited 2018 Mar 14]. 6, e20883. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.H.; Vicci, V.R.; Granger-Donetti, B.; Alvarez, T.L. Short-term adaptations of the dynamic disparity vergence and phoria systems. Exp Brain Res. 2011, 212, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Kim, E.H.; Granger-Donetti, B. Adaptation to Progressive Additive Lenses: Potential Factors to Consider. Sci Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Semmlow, J.L.; Yuan, W.; Munoz, P. Comparison of disparity vergence system responses to predictable and non-predictable stimulations. Curr Psychol Cogn [Internet]. 2002, 21, 243–262. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Bhavsar, M.; Semmlow, J.L.; Bergen, M.T.; Pedrono, C. Short-term predictive changes in the dynamics of disparity vergence eye movements. J Vis. 2005, 5, 640–649. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Alkan, Y.; Gohel, S.; Douglas Ward, B.; Biswal, B.B. Functional anatomy of predictive vergence and saccade eye movements in humans: a functional MRI investigation. Vision Res [Internet]. 2010, [cited 2015 Jan 20]. 50, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.N.; Han, Y.H.; Garbutt, S.; Leigh, R.J. Properties of anticipatory vergence responses. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002, 43, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar]
- Gowdy, P.D.; Cicerone, C.M. The spatial arrangement of the L and M cones in the central fovea of the living human eye. Vision Res [Internet]. 1998, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 38, 2575–2589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krauskopf, J. Relative number of long- and middle-wavelength-sensitive cones in the human fovea. J Opt Soc Am A [Internet]. 2000, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 17, 510. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Chui, T.Y.P.; Zhong, Z.; Elsner, A.E.; Burns, S.A. Variation of Cone Photoreceptor Packing Density with Retinal Eccentricity and Age. Investig Opthalmology Vis Sci [Internet]. 2011, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 52, 7376. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.P.; Chung, J.K.; Greenstein, V.; Tsang, S.H.; Chang, S. A study of factors affecting the human cone photoreceptor density measured by adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Exp Eye Res [Internet]. 2013, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, M.; Serrao, S.; Lombardo, G. Technical Factors Influencing Cone Packing Density Estimates in Adaptive Optics Flood Illuminated Retinal Images. Biagini G, editor. PLoS One [Internet]. 2014, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 9, e107402. [Google Scholar]
- Genenfurtner, K.R.; Sharpe, L.T. Color Vision: From Genes to Perception [Internet], 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, 1999; [cited 2019 Jun 25]; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, H.; Singer, B.; Williams, D.R. Different sensations from cones with the same photopigment. J Vis [Internet]. 2005, [cited 2019 Jun 25]. 5, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Legge, G.E.; Parish, D.H.; Luebker, A.; Wurm, L.H. Psychophysics of reading XI Comparing color contrast and luminance contrast. J Opt Soc Am A. 1990, 7, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kotulak, J.C.; Schor, C.M. The dissociability of accommodation from vergence in the dark. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986, 27, 544–551. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Alvarez, T.L. VisualEyes: a modular software system for oculomotor experimentation. J Vis Exp. 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial (CITT) Study Group. The Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial: Design, Methods, and Baseline Data. Ophthalmic Epidemiol [Internet]. 2008, [cited 2018 Mar 14]. 15, 24–36.
- Alvarez, T.L.; Vicci, V.R.; Alkan, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Gohel, S.; Barrett, A.M.; et al. Vision Therapy in Adults with Convergence Insufficiency: Clinical and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measures. Optom Vis Sci. 2010, 87, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.; Selenow, A.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Feldman, J.; Faverty, J.; Hokoda, S.C.; et al. Reduction of asthenopia in patients with convergence insufficiency after fusional vergence training. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1983, 60, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, R.; Ni, T.; Bowman, D.A.; Pinho, M. Design and evaluation of navigation techniques for multiscale virtual environments. In Proceedings - IEEE Virtual Reality; IEEE, 2006; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Noorlander, C.; Koenderink, J.J.; Den Olden, R.J.; Edens, B.W. Sensitivity to spatiotemporal colour contrast in the peripheral visual field. Vision Res [Internet]. 1983, [cited 2019 Jul 1]. 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.; Abramov, I. Color vision in the peripheral retina II Hue and saturation*. J Opt Soc Am [Internet]. 1977, [cited 2019 Jul 1]. 67, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, D.R.; Kertesz, A.E. Fusional Vergence Response to Local Peripheral Stimulation. J Opt Soc Am. 1983, 73, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.S.; Howard, I.P.; Fang, X. The stimulus integration area for horizontal vergence. Exp Brain Res. 2004, 156, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howard, I.P.; Fang, X.; Allison, R.S.; Zacher, J.E. Effects of stimulus size and eccentricity on horizontal and vertical vergence. Exp Brain Res. 2000, 130, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, S.B.; Reed, P.E.; Yang, J. The effect of target size and eccentricity on reflex disparity vergence. Vision Res. 1999, 39, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, G.K.; Semmlow, J.L.; Ciuffreda, K.J. A dual-mode dynamic model of the vergence eye movement system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1986, 33, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Semmlow, J.L.; Yuan, W. Closely spaced, fast dynamic movements in disparity vergence. J Neurophysiol. 1998, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Lee, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Semmlow, J.L.; Alvarez, T.L. Review: Behaviors, Models, and Clinical Applications of Vergence Eye Movements. J Med Biol Eng. 2010, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Alvarez, T.L. Quantitative assessment of divergence eye movements. J Vis. 2008, 8, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.E.; Porter, J.D.; Gamlin, P.D.; Tello, C.A. Neural control of vergence eye movements: neurons encoding vergence velocity. [Internet]. 1986, [cited 2019 Jul 1]. [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.E.; Gamlin, P.D.R. Neuronal circuitry controlling the near response. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995, 5, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamlin, P.D.R. Neural Mechanisms for the Control of Vergence Eye Movements. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002, 956, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, G.K.; Semmlow, J.L.; Sun, L.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Vergence control of central and peripheral disparities. Exp Neurol [Internet]. 1991, [cited 2015 Sep 1]. 113, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasan, H.; Scheiman, M.; Li, X.; Alvarez, T.L. Disparity vergence responses before versus after repetitive vergence therapy in binocularly normal controls. J Vis. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmlow, J.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Granger-Donetti, B.; Alvarez, T.L. Correction of Saccade-Induced Midline Errors in Responses to Pure Disparity Vergence Stimuli. J Eye Mov Res. 2008, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmlow, J.L.; Chen, J.; Granger, Y.F.; Donnetti, B.; Alvarez, T.L. Correction of Saccade-Induced Midline Errors in Responses to Pure Disparity Vergence Stimuli. J Eye Mov Res Semmlow. 2009, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschinski-Kruza, W. Dark vergence in relation to fixation disparity at different luminance and blur levels. Vision Res. 1994, 34, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschinski, W. Relation between static and dynamic aspects of vergence, estimated with a subjective test using flashed dichoptic nonius lines. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2004, 24, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Copyright © 2019. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Yaramothu, C.; Jaswal, R.S.; Alvarez, T.L. Target Eccentricity and Form Influences Disparity Vergence Eye Movements Responses: A Temporal and Dynamic Analysis. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2019, 12, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.4.7
Yaramothu C, Jaswal RS, Alvarez TL. Target Eccentricity and Form Influences Disparity Vergence Eye Movements Responses: A Temporal and Dynamic Analysis. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2019; 12(4):1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.4.7
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaramothu, Chang, Rajbir S. Jaswal, and Tara L. Alvarez. 2019. "Target Eccentricity and Form Influences Disparity Vergence Eye Movements Responses: A Temporal and Dynamic Analysis" Journal of Eye Movement Research 12, no. 4: 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.4.7
APA StyleYaramothu, C., Jaswal, R. S., & Alvarez, T. L. (2019). Target Eccentricity and Form Influences Disparity Vergence Eye Movements Responses: A Temporal and Dynamic Analysis. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 12(4), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.4.7


