Therapeutic Advances of Rare ALK Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
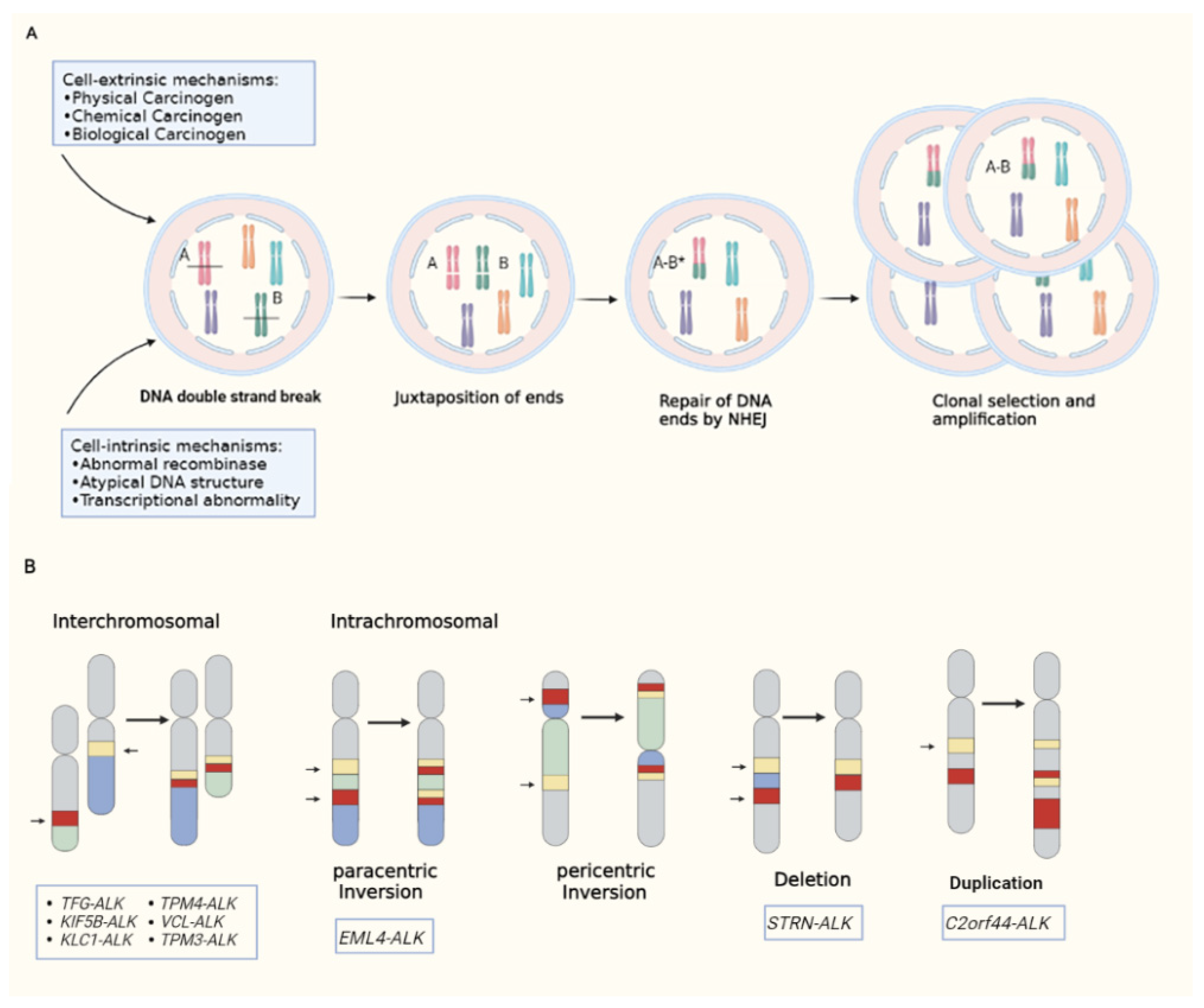
2. The Biology of ALK Fusion Kinases
3. Detection Methods for ALK Rearrangements
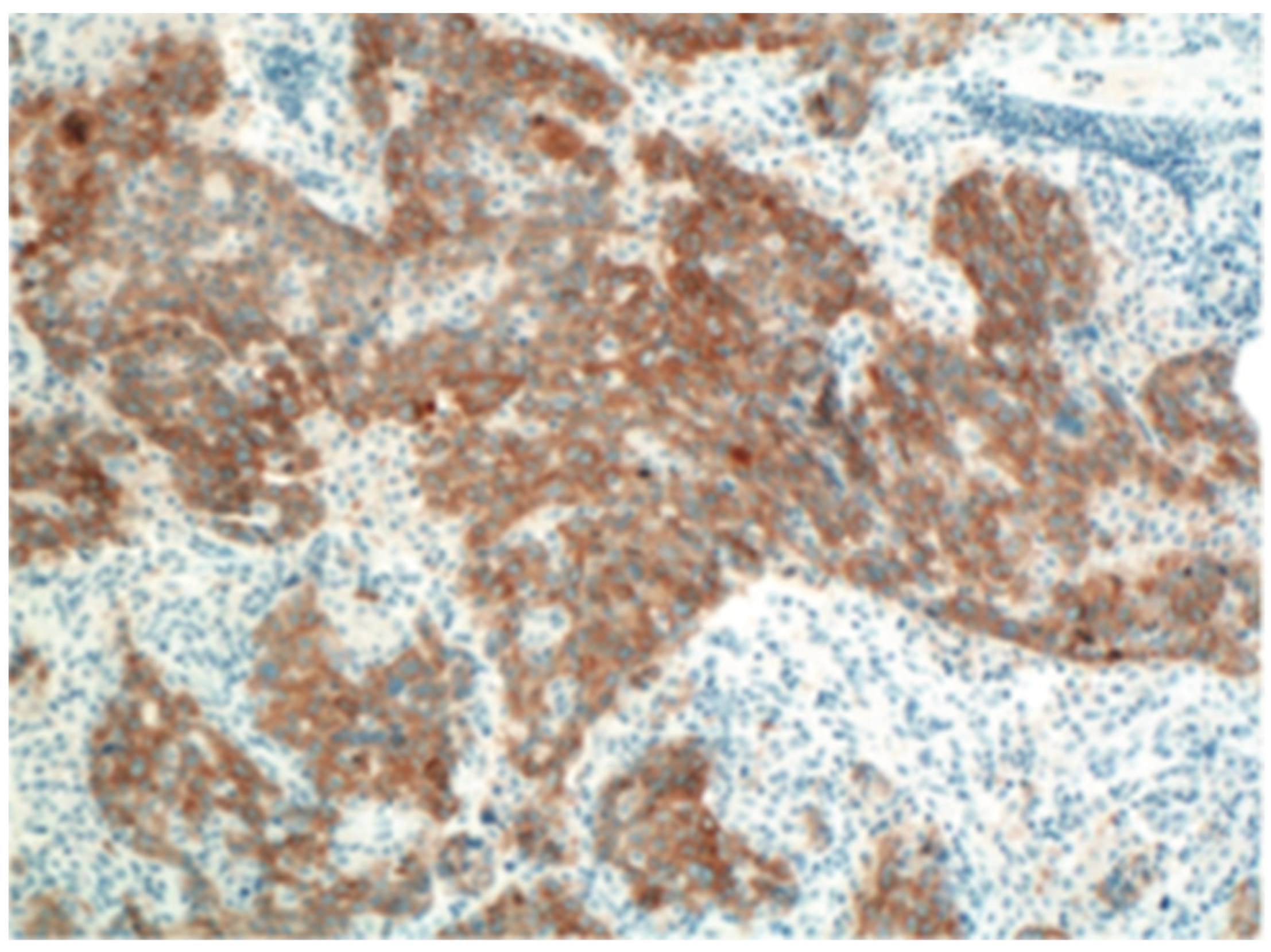
3.1. Immuno-Histochemistry
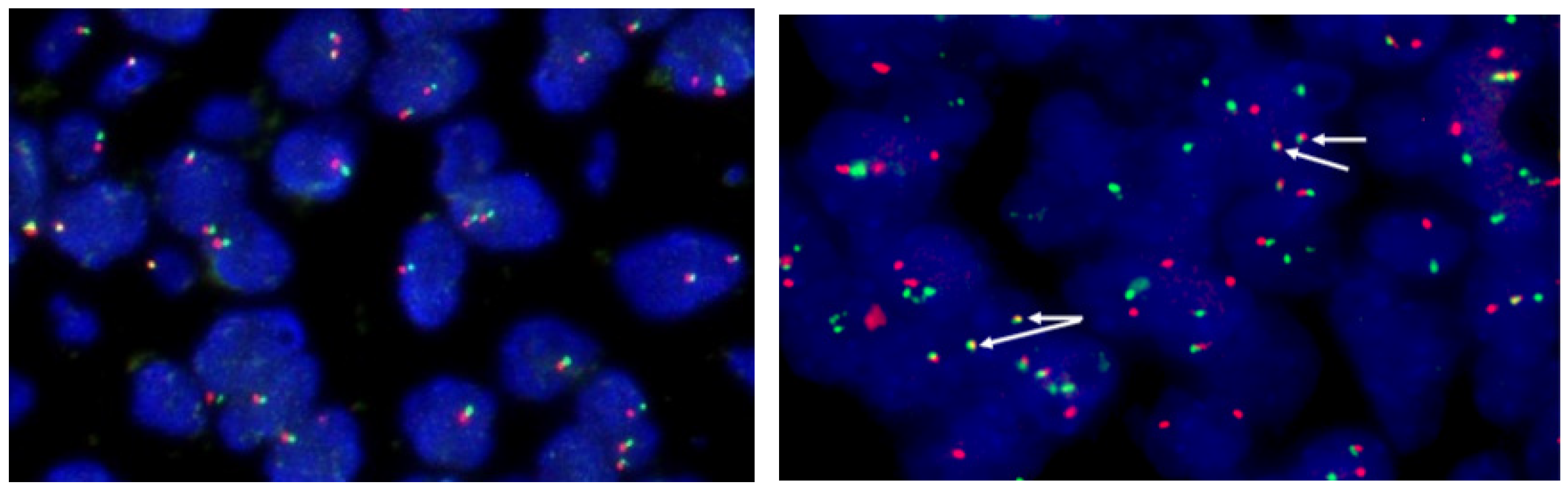
3.2. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization
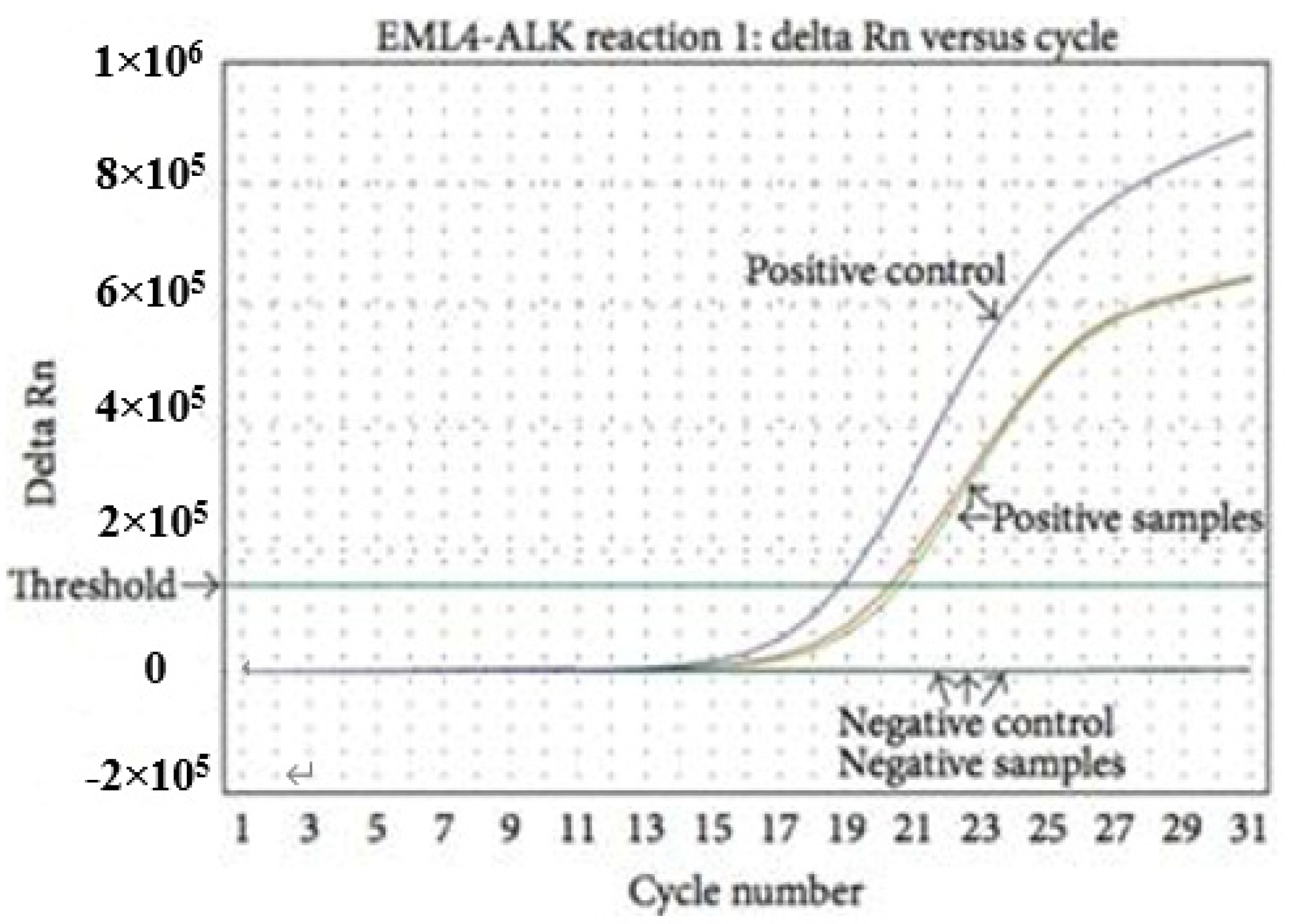
3.3. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
3.4. Next-Generation Sequencing
4. Rare ALK Fusions and Therapeutic Advances
4.1. STRN-ALK
4.2. KIF5B-ALK
4.3. HIP1-ALK
4.4. Other Rare ALK Fusions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducray, S.P.; Natarajan, K.; Garland, G.D.; Turner, S.D.; Egger, G. The Transcriptional Roles of ALK Fusion Proteins in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Pan, P.; Sun, H.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, T. Drug Discovery Targeting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10927–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfstetter, G.; Pfeifer, K.; Backman, M.; Masudi, T.A.; Mendoza-García, P.; Chen, S.; Sonnenberg, H.; Sukumar, S.K.; Uçkun, E.; Varshney, G.K.; et al. Identification of the Wallenda JNKKK as an Alk suppressor reveals increased competitiveness of Alk-expressing cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçkun, E.; Wolfstetter, G.; Anthonydhason, V.; Sukumar, S.K.; Umapathy, G.; Molander, L.; Fuchs, J.; Palmer, R.H. In vivo Profiling of the Alk Proximitome in the Developing Drosophila Brain. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.F.; Tai, Y.H.; Gao, H.J. ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, G.E.; Kuo, A.; Powers, C.; Bowden, E.T.; Sale, E.B.; Riegel, A.T.; Wellstein, A. Midkine binds to anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and acts as a growth factor for different cell types. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35990–35998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.B.; Lax, I.; Reshetnyak, A.; Ligon, G.F.; Lillquist, J.S.; Natoli, E.J., Jr.; Shi, X.; Folta-Stogniew, E.; Gunel, M.; Alvarado, D.; et al. Heparin is an activating ligand of the orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ALK. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, J.; Ju, H.M.; Song, J.Y.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R.; Choi, J. A Polytherapy Strategy Using Vincristine and ALK Inhibitors to Sensitise EML4-ALK-Positive NSCLC. Cancers 2022, 14, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Fu, X.; Liang, Y.; Chai, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; He, Y.; Kong, G.; Lian, J.; et al. ALKAL1 gene silencing prevents colorectal cancer progression via suppressing Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Suda, K.; Wiens, J.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2016, 388, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Felip, E.; Blackhall, F.H.; Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Mekhail, T.; Paolini, J.; et al. Intracranial Efficacy of Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From PROFILE 1014. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagitani, N.; Uchibori, K.; Koike, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Kitazono, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Horiike, A.; Ohyanagi, F.; Tambo, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; et al. Drug resistance mechanisms in Japanese anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical responses based on the resistant mechanisms. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Leung, E.L.; Wong, S.K.; Tin, V.P.; Sihoe, A.D.; Cheng, L.C.; Au, J.S.; Chung, L.P.; Wong, M.P. A novel KIF5B-ALK variant in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, J.A.; Taviaux, S.; Béganton, B.; Godreuil, S.; Audran, P.; Grand, D.; Clermont, E.; Serre, I.; Szablewski, V.; Coopman, P.; et al. Detection of known and novel ALK fusion transcripts in lung cancer patients using next-generation sequencing approaches. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ning, R.; Yu, Q. STRN-ALK Fusion in Lung Adenocarcinoma with Excellent Response Upon Alectinib Treatment: A Case Report and Literature Review. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 12515–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zeng, D.; Xie, F.; Yu, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, K.; Shao, Y.W.; Lu, H.; Jiang, J. Rare GCC2-ALK fusion G13:A20 detected by next generation sequencing in non-small cell lung cancer patients and treatment response. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Kim, R.N.; Song, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Oh, E.; Lira, M.E.; Mao, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Han, J.; Kim, J.; et al. HIP1-ALK, a novel fusion protein identified in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, A.F.; Zanon, M.F.; Carloni, A.C.; de Paula, F.E.; Morini, M.A.; Ferreira-Neto, M.; Soares, I.C.; Miziara, J.E.; de Marchi, P.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; et al. Detection of ALK fusion transcripts in FFPE lung cancer samples by NanoString technology. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Shi, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, L.; Ren, D.; Song, Z.; Huang, C.; et al. A Case of Simultaneously Diagnosed Lung Adenocarcinoma and Endobronchial Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor with Two Distinct Types of ALK Translocation. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK Inhibitor-Naive Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC: Final Results of Phase 3 ALTA-1L Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tang, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. A novel HIP1-ALK fusion variant in lung adenocarcinoma showing resistance to Crizotinib. Lung Cancer 2021, 151, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Noe, J.; Nowicka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cheema, P.; Pavlakis, N.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Updated Efficacy and Safety Data and Impact of the EML4-ALK Fusion Variant on the Efficacy of Alectinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, K.; Shao, Y.; Ying, J. Potential Unreliability of Uncommon ALK, ROS1, and RET Genomic Breakpoints in Predicting the Efficacy of Targeted Therapy in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, P.J.; Lupski, J.R.; Rosenberg, S.M.; Ira, G. Mechanisms of change in gene copy number. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S.F.; Nussenzweig, A. End-joining, translocations and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Togashi, Y.; Soda, M.; Hatano, S.; Inamura, K.; Takada, S.; Ueno, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y.; et al. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemps, P.G.; Picarsic, J.; Durham, B.H.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.; van den Bos, C.; van de Wetering, M.D.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; van Laar, J.A.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; et al. ALK-positive histiocytosis: A new clinicopathologic spectrum highlighting neurologic involvement and responses to ALK inhibition. Blood 2022, 139, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalo, D.; Manchado, E.; Concepcion, C.P.; Bonetti, C.; Vidigal, J.A.; Han, Y.C.; Ogrodowski, P.; Crippa, A.; Rekhtman, N.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. In vivo engineering of oncogenic chromosomal rearrangements with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Nature 2014, 516, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, L.M.; Barila, G.; Liu, P.; Evdokimova, V.N.; Trivedi, S.; Panebianco, F.; Gandhi, M.; Carty, S.E.; Hodak, S.P.; Luo, J.; et al. Identification of the transforming STRN-ALK fusion as a potential therapeutic target in the aggressive forms of thyroid cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4233–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, D.; Capelletti, M.; Yelensky, R.; Otto, G.; Parker, A.; Jarosz, M.; Curran, J.A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Bloom, T.; Brennan, K.W.; et al. Identification of new ALK and RET gene fusions from colorectal and lung cancer biopsies. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Hsu, P.P.; Awad, M.M.; Engelman, J.A. Tyrosine kinase gene rearrangements in epithelial malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, H.; Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Adachi, J.; Takemoto, A.; Kutkowska, J.; Maruyama, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Oh-Hara, T.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Gilteritinib overcomes lorlatinib resistance in ALK-rearranged cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.W.; O’Regan, L.; Roth, D.; Montgomery, J.M.; Straube, A.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R. Microtubule association of EML proteins and the EML4-ALK variant 3 oncoprotein require an N-terminal trimerization domain. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medves, S.; Noël, L.A.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Albu, R.I.; Schoemans, H.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Demoulin, J.B. Multiple oligomerization domains of KANK1-PDGFRβ are required for JAK2-independent hematopoietic cell proliferation and signaling via STAT5 and ERK. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Medves, S.; Demoulin, J.B. Tyrosine kinase gene fusions in cancer: Translating mechanisms into targeted therapies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, N.; Sasaki, T.; Okumura, S.; Minami, Y.; Chiba, S.; Ohsaki, Y. Monomerization of ALK Fusion Proteins as a Therapeutic Strategy in ALK-Rearranged Non-small Cell Lung Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, T.; Lee, W.; Obenauf, A.C.; Ran, L.; Murali, R.; Zhang, Q.F.; Wong, E.W.; Hu, W.; Scott, S.N.; Shah, R.H.; et al. Alternative transcription initiation leads to expression of a novel ALK isoform in cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuckmann, J.M.; Balke-Want, H.; Malchers, F.; Peifer, M.; Sos, M.L.; Koker, M.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Pao, W.; et al. Differential protein stability and ALK inhibitor sensitivity of EML4-ALK fusion variants. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4682–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Oya, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, J.; Horio, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Sakao, Y.; Hida, T.; Yatabe, Y. Differential Crizotinib Response Duration Among ALK Fusion Variants in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino-Kenudson, M.; Chirieac, L.R.; Law, K.; Hornick, J.L.; Lindeman, N.; Mark, E.J.; Cohen, D.W.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; et al. A novel, highly sensitive antibody allows for the routine detection of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas by standard immunohistochemistry. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Chuang, J.C.; Berry, G.J.; Wakelee, H.A. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Testing: IHC vs. FISH vs. NGS. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.C.; Kim, H.K.; Shin, B.K. Clinicopathological features and diagnostic methods of ALK fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer in Korea. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kulig, K.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, Y.K.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Immunohistochemical screening for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutz, J.C.; Craddock, K.J.; Torlakovic, E.; Brandao, G.; Carter, R.F.; Bigras, G.; Deschenes, J.; Izevbaye, I.; Xu, Z.; Greer, W.; et al. Canadian anaplastic lymphoma kinase study: A model for multicenter standardization and optimization of ALK testing in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Medeiros, L.J. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) for Detecting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Rearrangement in Lung Cancer: Clinically Relevant Technical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Chang, H.; Cha, Y.J.; Liang, S.; Tai, Y.C.; Li, G.; Pestova, E.; Policht, F.; Perez, T.; Soo, R.A.; et al. Validation of ALK/ROS1 Dual Break Apart FISH Probe probe in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixidó, C.; Karachaliou, N.; Peg, V.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Rosell, R. Concordance of IHC, FISH and RT-PCR for EML4-ALK rearrangements. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, C.; Spitaleri, G.; Catania, C.; Barberis, M.; Noberasco, C.; Santarpia, M.; Delmonte, A.; Toffalorio, F.; Conforti, F.; De Pas, T.M. Targeting ALK in patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer: Biology, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 89, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hout, D.R.; Schweitzer, B.L.; Lawrence, K.; Morris, S.W.; Tucker, T.; Mazzola, R.; Skelton, R.; McMahon, F.; Handshoe, J.; Lesperance, M.; et al. Performance of a RT-PCR Assay in Comparison to FISH and Immunohistochemistry for the Detection of ALK in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. Mechanistic insight into ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in human cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachaliou, N.; Rosell, R. Optimal detection of ALK rearranged lung adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Xing, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. Effect of multiple cycles of freeze-thawing on the RNA quality of lung cancer tissues. Cell Tissue Bank. 2017, 18, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. A Screening Method for the ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeke, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Vallee, A.; Allegra, M.; Mazieres, J.; Fayada, J.; Rajamani, J.; Lee, M.; Ordinario, E.; Tiotiu, A.; et al. Detection of ALK fusion transcripts in plasma of non-small cell lung cancer patients using a novel RT-PCR based assay. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, T.; Tachihara, M.; Nagano, T.; Kobayashi, K. Review of Therapeutic Strategies for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, I.J.; Mittempergher, L.; Davidson, N.M.; Bosma, A.; Willems, S.M.; Horlings, H.M.; de Rink, I.; Greger, L.; Hooijer, G.K.; Peters, D.; et al. Identification of recurrent FGFR3 fusion genes in lung cancer through kinome-centred RNA sequencing. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.Y.; Yao, J.H.; Zhou, Y.C.; Xu, L.J.; Zhao, F.Y.; Yang, Y. High STRN Expression Promotes HCC Invasion and Migration but Not Cell Proliferation or Apoptosis through Facilitating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6152925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérot, G.; Soubeyran, I.; Ribeiro, A.; Bonhomme, B.; Savagner, F.; Boutet-Bouzamondo, N.; Hostein, I.; Bonichon, F.; Godbert, Y.; Chibon, F. Identification of a recurrent STRN/ALK fusion in thyroid carcinomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusano, H.; Togashi, Y.; Akiba, J.; Moriya, F.; Baba, K.; Matsuzaki, N.; Yuba, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kanamaru, H.; Kuroda, N.; et al. Two Cases of Renal Cell Carcinoma Harboring a Novel STRN-ALK Fusion Gene. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakirevich, E.; Resnick, M.B.; Mangray, S.; Wheeler, M.; Jackson, C.L.; Lombardo, K.A.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.M.; Gill, A.J.; Wang, K.; et al. Oncogenic ALK Fusion in Rare and Aggressive Subtype of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma as a Potential Therapeutic Target. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3831–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Masuda, S.; Iida, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S. Case Report of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with STRN-ALK Translocation: A Nonresponder to Alectinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e202–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Q. Coexistence of a secondary STRN-ALK, EML4-ALK double-fusion variant in a lung adenocarcinoma patient with EGFR mutation: A case report. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2021, 32, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, F.; Nikitski, A.V.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Kaya, C.; Yip, L.; Condello, V.; Wald, A.I.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Chiosea, S.I. Characterization of thyroid cancer driven by known and novel ALK fusions. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasota, J.; Chłopek, M.; Wasąg, B.; Kowalik, A.; Christiansen, J.; Lamoureux, J.; Kuźniacka, A.; Felisiak-Gołąbek, A.; Liu, Y.; Reyes, T.A.R.; et al. Colorectal Adenocarcinomas Harboring ALK Fusion Genes: A Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetic Study of 12 Cases and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, P.; Li, W. Case Report: Identification of Two Rare Fusions, PDK1-ALK and STRN-ALK, That Coexist in a Lung Adenocarcinoma Patient and the Response to Alectinib. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 722843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, M.; Sarvadevabatla, N.; Iwata, S.; Ge, Y.; Sukari, A.; Klosowski, C.; Yanagihara, R. STRN-ALK, A Novel In-Frame Fusion With Response to Alectinib. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Sakashita, T.; Yanagitani, N.; Ninomiya, H.; Horiike, A.; Friboulet, L.; Gainor, J.F.; Motoi, N.; Dobashi, A.; Sakata, S.; et al. P-glycoprotein Mediates Ceritinib Resistance in Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-rearranged Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. EBioMedicine 2016, 3, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; An, Z.; Tang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. Mixed responses to first-line alectinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients with rare ALK gene fusions: A case series and literature review. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9476–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Yoda, S.; Lennerz, J.K.; Langenbucher, A.; Lin, J.J.; Rooney, M.M.; Prutisto-Chang, K.; Oh, A.; Adams, N.A.; Yeap, B.Y.; et al. MET Alterations Are a Recurring and Actionable Resistance Mechanism in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.; Grenda, A.; Terlecka, P.; Błach, J.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Kucharczyk, T.; Chmielewska, I.; Kieszko, R.; Jarosz, B.; Gil, M.; et al. Crizotinib efficacy in advanced non-squamous NSCLC patients with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Otterson, G.A.; Clark, J.W.; Ignatius Ou, S.H.; Weiss, J.; Ades, S.; Shapiro, G.I.; Socinski, M.A.; Murphy, D.A.; Conte, U.; et al. Crizotinib in Patients With MET-Amplified NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N. Responder of Gefitinib Plus Crizotinib in Osimertinib Failure EGFR-mutant NSCLC-Resistant With Newly Identified STRN-ALK by Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e143–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, S.K.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.M.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wu, Q. A Rare STRN-ALK Fusion in Lung Adenocarcinoma Identified Using Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling Exhibits Excellent Response to Crizotinib. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2017, 1, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Marques, A.; Martin, M.; Katrukha, E.A.; Grigoriev, I.; Peeters, C.A.; Liu, Q.; Hooikaas, P.J.; Yao, Y.; Solianova, V.; Smal, I.; et al. Concerted action of kinesins KIF5B and KIF13B promotes efficient secretory vesicle transport to microtubule plus ends. eLife 2020, 9, 61302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.; Tian, P.; Li, W. A rare KIF5B-ALK fusion variant in a lung adenocarcinoma patient who responded to crizotinib and acquired the ALK L1196M mutation after resistance: A case report. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 8352–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Chiang, C.L.; Hung, J.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Su, W.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Wei, Y.F.; Lee, K.Y.; Tseng, Y.H.; Su, J.; et al. Resistance profiles of anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter study using targeted next-generation sequencing. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Ku, B.M.; Olsen, S.; Park, S.; Lefterova, M.; Odegaard, J.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Longitudinal monitoring by next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in ALK rearranged NSCLC patients treated with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2944–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, D.; Ceccon, M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Mologni, L. Activity of second-generation ALK inhibitors against crizotinib-resistant mutants in an NPM-ALK model compared to EML4-ALK. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordi, P.; Tiseo, M.; Rofi, E.; Petrini, I.; Restante, G.; Danesi, R.; Del Re, M. Detection of ALK and KRAS Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA of Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC With Disease Progression During Crizotinib Treatment. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W. Mutation L1196M-induced conformational changes and the drug resistant mechanism of anaplastic lymphoma kinase studied by free energy perturbation and umbrella sampling. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2017, 19, 30239–30248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, A. Alectinib: A novel second generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor for overcoming clinically-acquired resistance. Acta Pharm. Sinica. B 2015, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, I.; Ehrlich, M.; Ashery, U. The Sla2p/HIP1/HIP1R family: Similar structure, similar function in endocytosis? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Jan, Y.H.; Su, C.Y.; Yao, Y.C.; Cheng, H.C.; Hsu, T.I.; Wang, P.S.; Su, W.P.; Yang, C.J.; et al. Huntingtin-Interacting Protein-1 Is an Early-Stage Prognostic Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Suppresses Metastasis via Akt-mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalchman, M.A.; Koide, H.B.; McCutcheon, K.; Graham, R.K.; Nichol, K.; Nishiyama, K.; Kazemi-Esfarjani, P.; Lynn, F.C.; Wellington, C.; Metzler, M.; et al. HIP1, a human homologue of S. cerevisiae Sla2p, interacts with membrane-associated huntingtin in the brain. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, H. Non-solid oncogenes in solid tumors: EML4-ALK fusion genes in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Tang, Y.; Lizaso, A.; Ye, J.; Shao, L.; Li, Y. Unique molecular features and clinical outcomes in young patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring ALK fusion genes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.H.; Klempner, S.J.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Azada, M.; Schrock, A.B.; Ali, S.M.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.J.; Miller, V.A. Identification of a novel HIP1-ALK fusion variant in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and discovery of ALK I1171 (I1171N/S) mutations in two ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients with resistance to Alectinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, P.; Guan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Grenda, A.; Christopoulos, P.; Denis, M.G.; Guo, Q. High efficacy of alectinib in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma with 2 rare ALK fusion sites: A case report. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.S.; Wang, X.; Vedell, P.T.; Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Ellison, D.W.; Evans, J.M.; Johnson, S.H.; Yang, P.; Sukov, W.R.; et al. Custom Gene Capture and Next-Generation Sequencing to Resolve Discordant ALK Status by FISH and IHC in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Q.; Lira, M.; Xu, Q.; Sun, H.; Qian, M.; Sheng, W.; Ozeck, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. HIP1-ALK, a novel ALK fusion variant that responds to crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couëtoux du Tertre, M.; Marques, M.; Tremblay, L.; Bouchard, N.; Diaconescu, R.; Blais, N.; Couture, C.; Pelsser, V.; Wang, H.; Higenell, V.; et al. Analysis of the Genomic Landscape in ALK+ NSCLC Patients Identifies Novel Aberrations Associated with Clinical Outcomes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Deng, Q.M.; Peng, K.C.; Li, P.; Zhu, B.T.; Wang, P.; Chu, X.P.; Zhong, W.Z.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, W.X.; et al. Clinicopathological features and resistance mechanisms in HIP1-ALK-rearranged lung cancer: A multicenter study. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2022, 61, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, C.; Yin, X. NCOA1-ALK: A novel ALK rearrangement in one lung adenocarcinoma patient responding to crizotinib treatment. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Gan, J.; Hong, S.; Lu, F.; Zhang, L. MPRIP-ALK, a Novel ALK Rearrangement That Responds to ALK Inhibition in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e148–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Capelletti, M.; Le, A.T.; Kako, S.; Butaney, M.; Ercan, D.; Mahale, S.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Pilling, A.B.; et al. Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, N.; Cerami, E.; Schalm, S.; Kim, J.L.; Lengauer, C. The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, N.; Schwaab, J.; Metzgeroth, G.; Jawhar, M.; Haferlach, C.; Göhring, G.; Schlegelberger, B.; Dietz, C.T.; Schnittger, S.; Lotfi, S.; et al. Fusion of PDGFRB to MPRIP, CPSF6, and GOLGB1 in three patients with eosinophilia-associated myeloproliferative neoplasms. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2015, 54, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.F.; Wang, W.X.; Xu, C.W.; Huang, L.C.; Li, X.F.; Lan, G.; Zhai, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.C.; Du, K.Q.; Lei, L.; et al. A novel SOS1-ALK fusion variant in a patient with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma and a remarkable response to crizotinib. Lung Cancer 2020, 142, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillig, R.C.; Sautier, B.; Schroeder, J.; Moosmayer, D.; Hilpmann, A.; Stegmann, C.M.; Werbeck, N.D.; Briem, H.; Boemer, U.; Weiske, J.; et al. Discovery of potent SOS1 inhibitors that block RAS activation via disruption of the RAS-SOS1 interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerboth, S.; Frittoli, E.; Palamidessi, A.; Baltanas, F.C.; Salek, M.; Rappsilber, J.; Giuliani, C.; Troglio, F.; Rolland, Y.; Pruneri, G.; et al. Phosphorylation of SOS1 on tyrosine 1196 promotes its RAC GEF activity and contributes to BCR-ABL leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q. Coexistence of a novel CCNY-ALK and ATIC-ALK double-fusion in one patient with ALK-positive NSCLC and response to crizotinib: A case report. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2494–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Zou, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, N.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Novel NLRC4-ALK and EML4-ALK double fusion mutations in a lung adenocarcinoma patient: A case report. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gu, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Kong, J. Coexistence of a Novel PRKCB-ALK, EML4-ALK Double-Fusion in a Lung Adenocarcinoma Patient and Response to Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e266–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.D.; Jiao, X.D.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Zang, Y.S. Identification of a Novel EML4-ALK, BCL11A-ALK Double-Fusion Variant in Lung Adenocarcinoma Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Response to Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e115–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ren, G.; Liang, X. A Novel EML6-ALK FBXO11-ALK Double Fusion Variant in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Response to Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, e234–e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, F.; Lu, Y. Reporting on Two Novel Fusions, DYSF-ALK and ITGAV-ALK, Coexisting in One Patient with Adenocarcinoma of Lung, Sensitive to Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, e43–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Liu, Z.; Mu, J.; Gai, F.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L. Concomitant novel ALK-SSH2, EML4-ALK and ARID2-ALK, EML4-ALK double-fusion variants and confer sensitivity to crizotinib in two lung adenocarcinoma patients, respectively. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Shi, J.; Yao, M.; Jin, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Jiang, D. A rare double ALK fusion variant EML4-ALK and CDK15-ALK in lung adenocarcinoma and response to crizotinib: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e22631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, Q.; Pu, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, W.; Zhu, D.; Xu, F. Case Report: A Novel Non-Reciprocal ALK Fusion: ALK-GCA and EML4-ALK Were Identified in Lung Adenocarcinoma, Which May Respond to Alectinib Adjuvant-Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 782682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.; Bartlett, C.H.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Cui, J.; Iafrate, A.J. Crizotinib for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A success story to usher in the second decade of molecular targeted therapy in oncology. Oncol. 2012, 17, 1351–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ban, Y.; Qin, H.; Tai, Y. CMTR1-ALK: An ALK fusion in a patient with no response to ALK inhibitor crizotinib. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ref | Year | Accompanying Mutations | ALK-TKIs | Treatment | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yang, Y. et al. [76] | 2017 | MYC amplification; TP53 (R181C) | Crizotinib | Third line | CR > 6 m |
| 2 | Zhou, C. et al. [75] | 2019 | EGFR (19DEL) | Crizotinib +Gefitinib | Third line | PR > 6 m |
| 3 | Nakanshi, Y. et al. [64] | 2017 | ABCB1 mRNA overexpression | Alectinib | First line | PD < 3 m |
| 4 | Su, C. et al. [18] | 2020 | GRM8 (E508K); SETD2 (E1553K) | Alectinib | First line | PR > 19 m |
| 5 | Nagasaka, M. et al. [69] | 2020 | TP53 (L43fs);MYC amplification | Alectinib | First line | PR > 6 m |
| 6 | Zeng, H. et al. [68] | 2020 | PDK1-ALK (P7: A20); TP53 | Alectinib | First line | PR > 7 m |
| 7 | Li, M. et al. [71] | 2021 | MET amplification | Alectinib Crizotinib | First line Second line | PD: 3 m PFS > 11 m |
| Ref | Year | Variants | ALK-TKIs | Treatment | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Takeuchi, K. et al. [29] | 2009 | (K24:A19) | Not treated with ALK-TKIs | – | – |
| 2 | Wong, D.W. et al. [16] | 2011 | (K15:A20) | Not treated with ALK-TKIs | – | – |
| 3 | Zeng, H. et al. [78] | 2021 | (K20:A20) | Crizotinib Ceritinib | First line Second line | PFS: 11 m PFS > 9 m |
| Ref | Year | Variants | ALK-TKIs | Treatment | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fang, D.D. et al. [93] | 2014 | (H28:A20) | Not treated with ALK-TKIs | – | PDX is sensitive to crizotinib |
| 2 | Hong, M., et al. [20] | 2014 | (H21:A20) | Crizotinib | First line | PFS > 15 m |
| 3 | Ou, S.H., et al. [90] | 2014 | (H30:A20) | Crizotinib Alectinib | First line Second line | PD PFS > 12 m |
| 4 | Jang, J. S, et al. [92] | 2016 | (H19:A20) | Not treated with ALK-TKIs | – | Not reported |
| 5 | Couetoux, D. T. M, et al. [94] | 2019 | (H28:A20) | Crizotinib | First line | PR PFS:26.9 m |
| 6 | Tian, P, et al. [89] | 2020 | (H22:A21) | Crizotinib | First line | PR PFS: 7.0 m |
| 7 | Li, M, et al. [24] | 2021 | (H19:A20) | Crizotinib Alectinib | First line Second line | PD PFS > 9 m |
| 8 | Li Y, et al. [91] | 2022 | (H30:A20) | Alectinib | First line | PFS > 19 m |
| Ref | Rare ALK Fusion Types | Merge Mutations | ALK-TKIs | Treatment | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cao Q, et al. [96] | NCOA1–ALK | CDAK27Q, ERCC1N118N, DPYDI543V, MTHFRA222V,GSTP1I105V | Crizotinib | Third line | PFS > 18 m |
| 2 | Fang, W. et al. [97] | MPIP-ALK | Crizotinib | Second line | PFS > 11 m | |
| 3 | Tian, P. et al. [89] | CHRNA7-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 18 m | |
| 4 | Tian, P. et al. [89] | LOC349160-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 7 m | |
| 5 | Tian, P. et al. [89] | TACR1-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 15 m | |
| 6 | Tian, P. et al. [89] | CENPA-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 4 m | |
| 7 | Tian, P. et al. [89] | DYSF-ALK ITGAV-ALK | ALK p.Q1146P; MET p.M636V | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 23 m |
| 8 | Chen, H.F. et al. [101] | SOS1-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS > 6 m | |
| 9 | Li, M. et al. [71] | LMO7-ALK | NRG1 c.602A > T;TP53 | Alectinib Ensartinib | First line Second line | PD PFS > 18 m |
| Ref | Year | Double Fusion | ALK-TKIs | Treatment | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wu, X. et al. [104] | 2020 | CCNY-ALK ATIC-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PR > 6 m |
| 2 | Wu, X. et al. [105] | 2020 | NLRC4-ALK;EML4-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS > 10 m |
| 3 | Luo, J. et al. [106] | 2019 | PRKCB-ALK; EML4-ALK | Crizotinib Ceritinib | First line Second line | PFS: 6 m PFS > 2 m |
| 4 | Qin, B. et al. [107] | 2019 | BCL11A-ALK; EML4-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 13 m |
| 5 | Lin, H. et al. [108] | 2018 | FBXO11-ALK; EML6-ALK | Crizotinib | Second line | PFS > 11 m |
| 6 | Yin, J. et al. [109] | 2018 | DYSF-ALK; ITGAV-ALK | Crizotinib | Second line | PFS > 3 m |
| 7 | Tao, H. et al. [110] | 2022 | ALK-SSH2; EML4-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 9 m |
| 8 | Tao, H. et al. [110] | 2022 | ARID2-ALK; EML4-ALK | Crizotinib | First line | PFS: 12 m |
| 9 | Guo, J. et al. [111] | 2020 | CDK15-ALK; EML4-ALK | Crizotinib | Second line | PFS: 23 m |
| 10 | Zeng, H. et al. [68] | 2021 | PDK1-ALK; STRN-ALK | Alectinib | First line | PFS > 11 m |
| 11 | Zhai, X. et al. [112] | 2022 | ALK-GCA; EML4-ALK | Alectinib | First line | PFS > 20 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, T.; Liu, J.; Lu, K. Therapeutic Advances of Rare ALK Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7816-7831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100618
Xiang Y, Zhang S, Fang X, Jiang Y, Fang T, Liu J, Lu K. Therapeutic Advances of Rare ALK Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7816-7831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100618
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Yan, Shiyu Zhang, Xiaoxu Fang, Yingying Jiang, Tingwen Fang, Jinwen Liu, and Kaihua Lu. 2022. "Therapeutic Advances of Rare ALK Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7816-7831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100618
APA StyleXiang, Y., Zhang, S., Fang, X., Jiang, Y., Fang, T., Liu, J., & Lu, K. (2022). Therapeutic Advances of Rare ALK Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7816-7831. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100618






