Exploring the Pharmacological Landscape of Undaria pinnatifida: Insights into Neuroprotective Actions and Bioactive Constituents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. U. pinnatifida Compounds and Applications
2.1. U. pinnatifida Polysaccharides
2.1.1. Fucoidan (Figure 1)
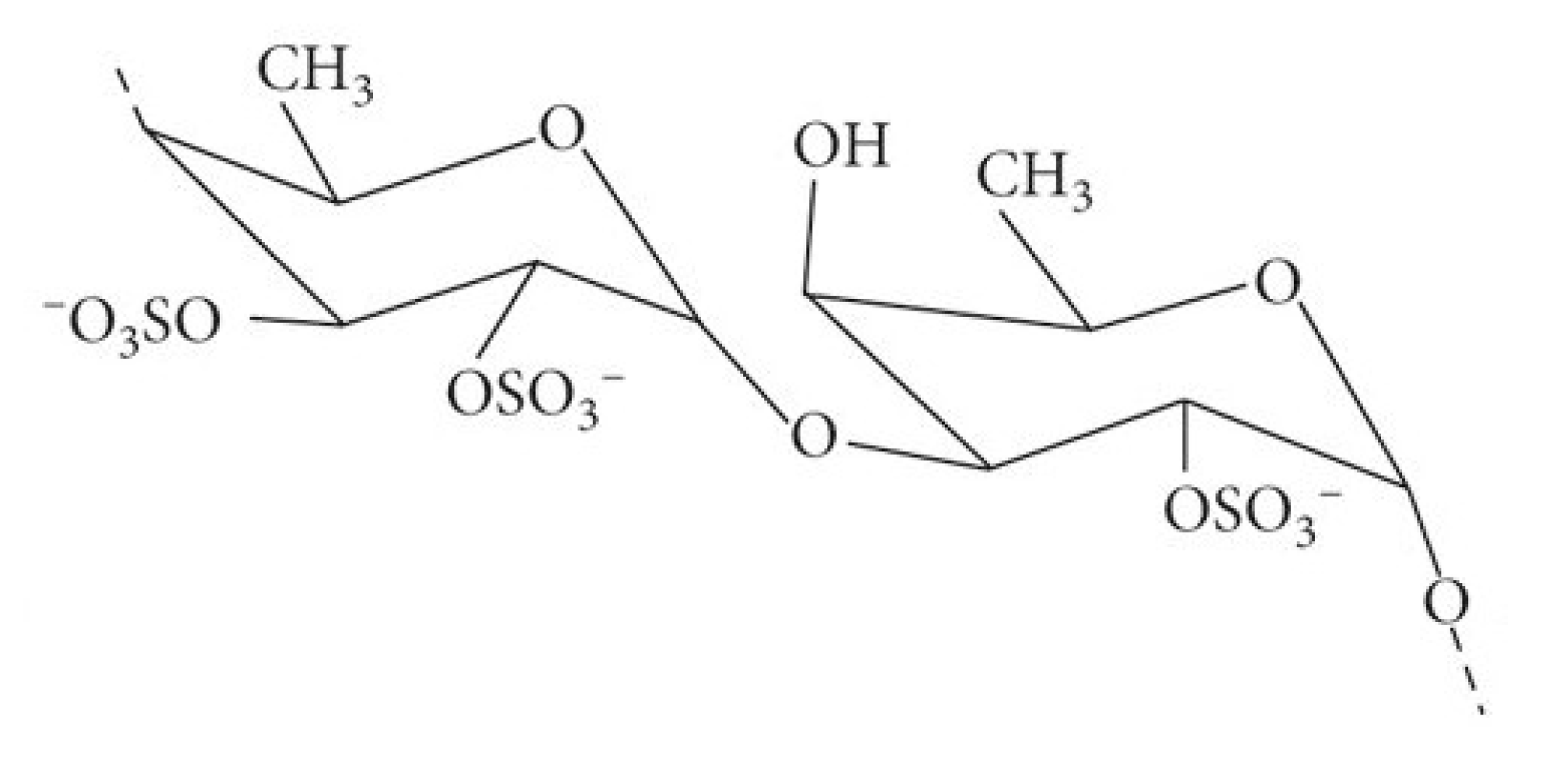
2.1.2. Alginates (Figure 3)
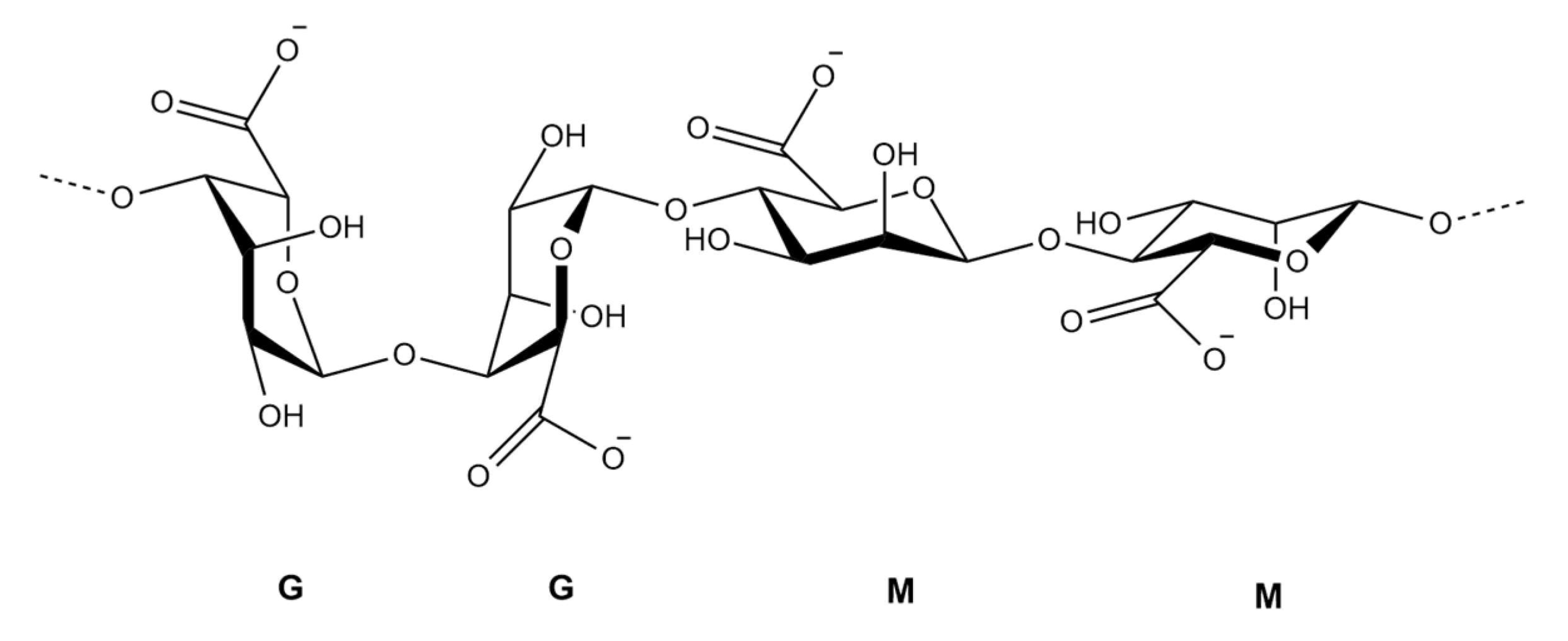
2.2. Pharmacological Activities of U. pinnatifida Polysaccharides
2.2.1. Anti-Angiogenic Activity
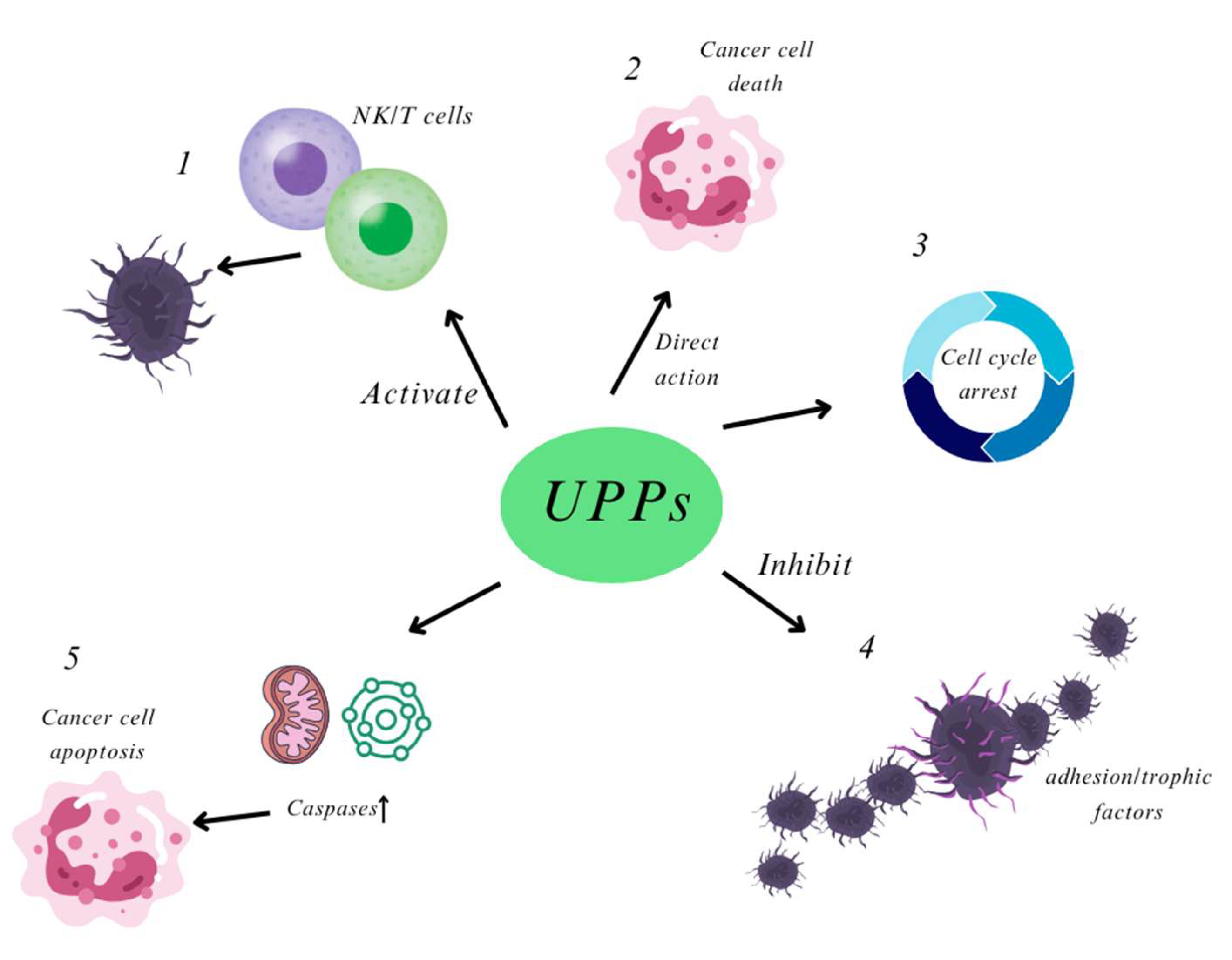
2.2.2. Anti-Tumor Activity
2.2.3. Antihypertension
2.2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.2.6. Immunomodulatory Activity
2.2.7. Antiviral and Antibacterial Activity
2.2.8. Anticoagulating and Antithrombotic Activities
2.2.9. Renoprotective Activities
2.3. U. pinnatifida Non-Polysaccharide Compounds and Their Pharmacological Applications
2.3.1. Fucoxanthin
2.3.2. Fucoesterols
2.3.3. Phenolic Compounds—Flavonoids and Phlorotannins
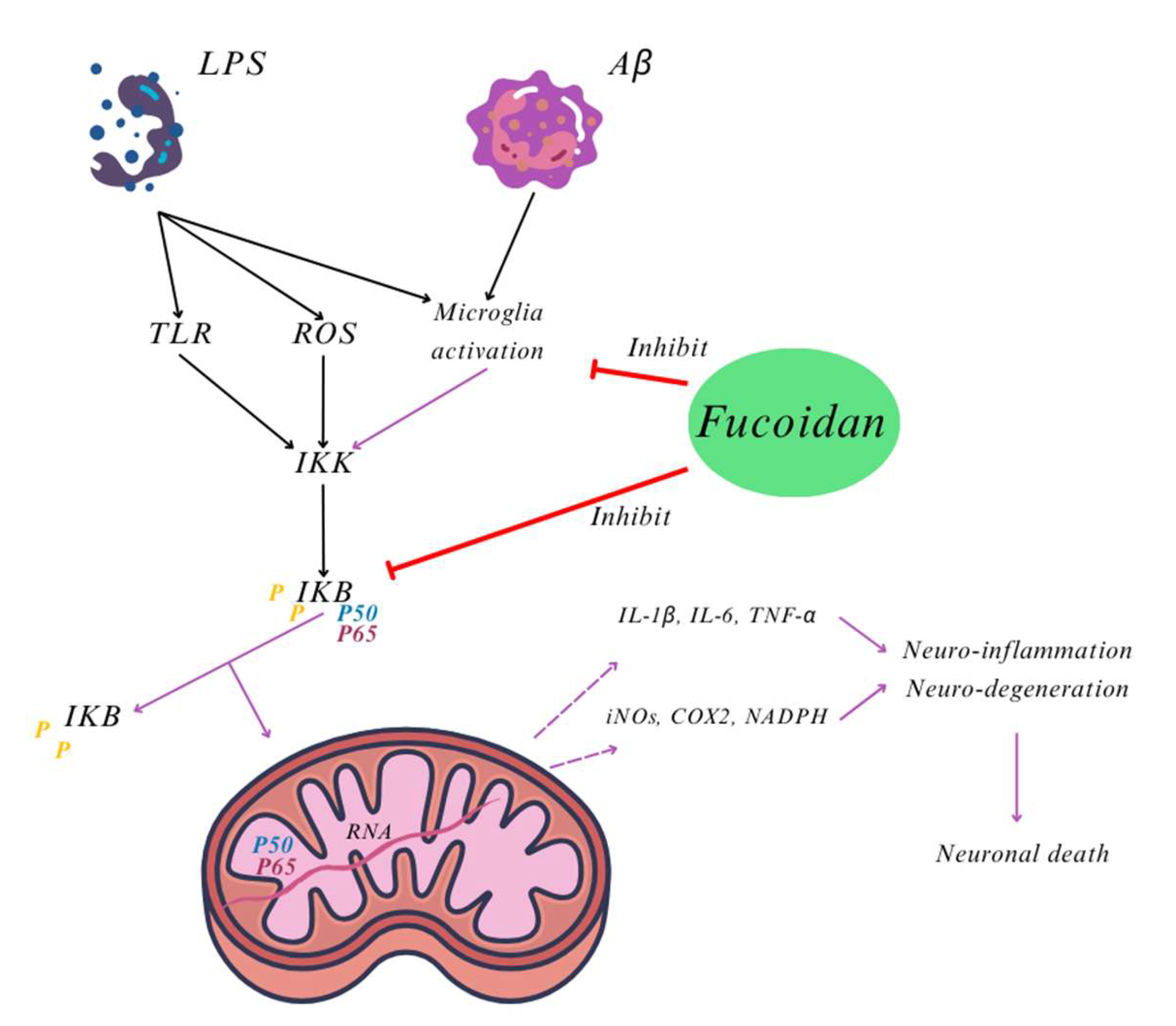
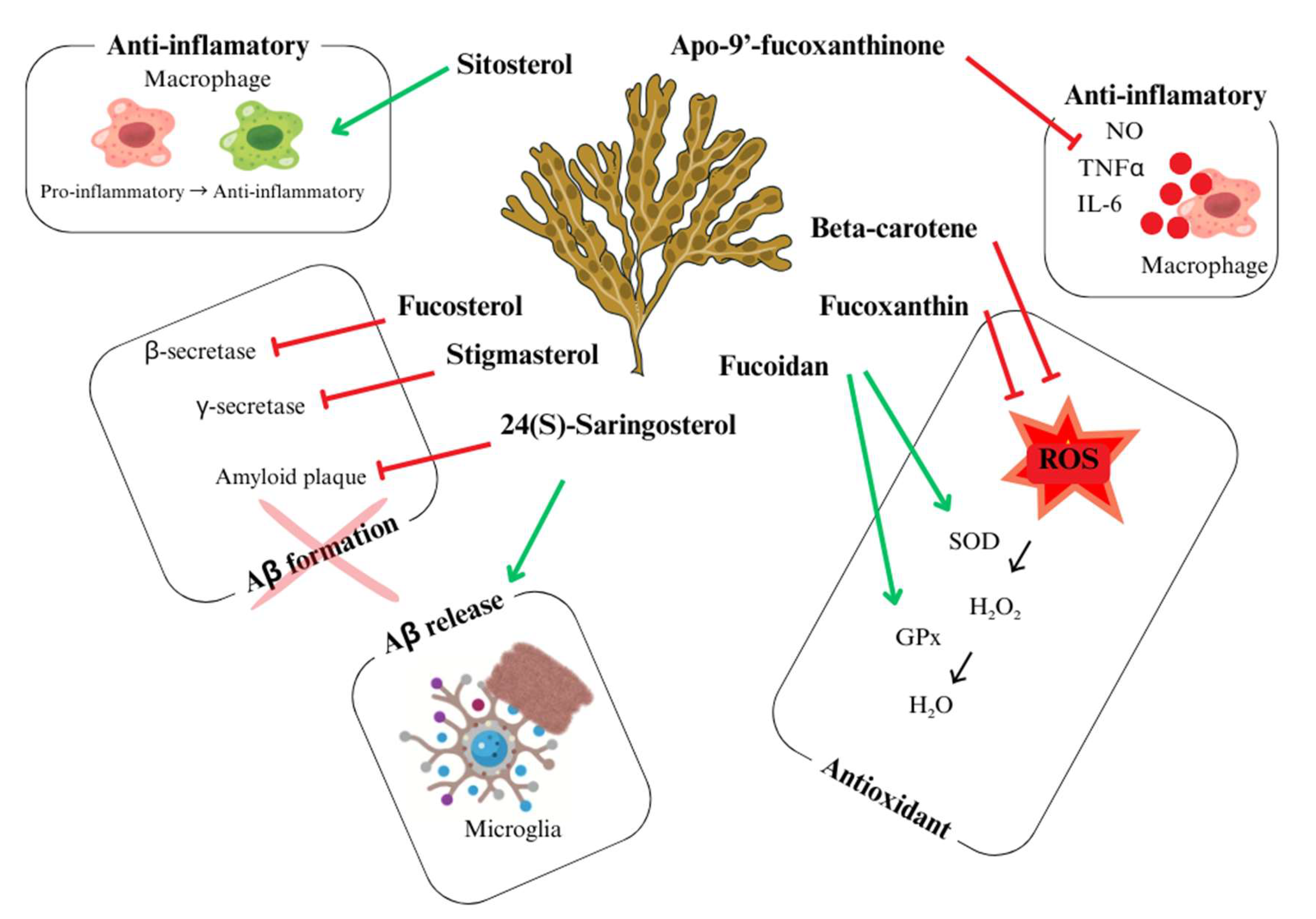
3. Focus on the Neuroprotective Actions of U. pinnatifida: Mechanisms and Key Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Undaria pinnatifida. Available online: https://fish-commercial-names.ec.europa.eu/fish-names/species/undaria-pinnatifida_pt (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Rubal, M.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, J.; Carreira-Flores, D.; Gomes, P.T.; Veiga, P. Current Distribution of the Invasive Kelp Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar, 1873 Along Artificial and Natural Habitats in North Portugal-Impacts and Mitigation Initiatives. Plants 2025, 14, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Luan, F.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Recent research advances in polysaccharides from Undaria pinnatifida: Isolation, structures, bioactivities, and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.A.; Becherucci, M.E. Study of the potential use of the invasive marine algae Undaria pinnatifida in the preliminary development of a functional textile. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 51, 8127S–8141S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M.; Nishitani, Y.; Tanoue, T.; Matoba, Y.; Ojima, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Kanazawa, K. Quantification and localization of fucoidan in Laminaria japonica using a novel antibody. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, S.; Yu, Y.; White, W.L.; Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Lu, J. Fucoidan Extracted from Undaria pinnatifida: Source for Nutraceuticals/Functional Foods. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Penas, E.; Rico, D.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Portillo, M.P.; Macarulla, M.T.; de Luis, D.A.; Miranda, J. Potential Usefulness of a Wakame/Carob Functional Snack for the Treatment of Several Aspects of Metabolic Syndrome: From In Vitro to In Vivo Studies. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, M.C.; Millán, R.; Miguez, M.I. Nutritional value of the marine algae wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and nori (Porphyra purpurea) as food supplements. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 25, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ryu, B. Bioactivities of the edible brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida: A review. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, J.S.; Park, N.G.; Lee, H.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Hong, Y.K. Anti-edema effects of brown seaweed (Undaria pinnatifida) extract on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced mouse ear inflammation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Dash, R.; Haque, M.N.; Mohibbullah, M.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Alam, M.; Moon, I.S. Neuroprotective potentials of marine algae and their bioactive metabolites: Pharmacological insights and therapeutic advances. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, M.; Tong, Y.; Xia, Z.; Tong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; et al. A review of volatile compounds in edible macroalgae. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Boland, W. The oxylipin chemistry of attraction and defense in brown algae and diatoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Xu, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Advances in Food Aroma Analysis: Extraction, Separation, and Quantification Techniques. Foods 2025, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liu, J.H.; Xu, N.G.; Liang, Z.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Xu, S.J.; Fu, W.B. Effects of acupuncture treatment on depression insomnia: A study protocol of a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hou, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, D.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Analysis of the medication rules of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) in treating liver cancer and potential TCMs exploration. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 3, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-Y.; Hao, R.-W.; Lan, Q.-Y.; Liang, J.-Q.; Du, Z.-C.; Lu, B.-D.; Deng, J.-G.; Hou, X.-T. Analysis of varieties and characteristics of marine Chinese medicines recorded in Compendium of Materia Medica. Zhongcaoyao 2020, 51, 4338–4347. [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto, M.; Kuda, T.; Eda, M.; Yamakawa, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B. Protective Effects of Mekabu Aqueous Solution Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum Sanriku-SU7 on Human Enterocyte-Like HT-29-luc Cells and DSS-Induced Murine IBD Model. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingson, J.A.; Falshaw, R.; Furneaux, R.; Thompson, K. Structure and antiviral activity of the galactofucan sulfates extracted from Undaria pinnatifida (Phaeophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2006, 18, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishchuk, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. The fucoidans from brown algae of Far-Eastern seas: Anti-tumor activity and structure-function relationship. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, H.; Zong, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula: Preparation, structural features and biological activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Suzuki, K.; Miyai, S.; Ohtsuki, K. Characterization of meFucoidan as a selective inhibitor for secretory phospholipase A2-IIA and the phosphorylation of meFucoidan-binding proteins by A-kinase in vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Lahaye, M.; Bonnet, C.; Mabeau, S.; Barry, J.L. In vitro fermentation by human faecal bacteria of total and purified dietary fibres from brown seaweeds. Br. J. Nutr. 1996, 75, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togari, N.; Ogawa, N.; Sakata, T. Poor fermentability of “mekabu” (sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida) alginic acid in batch culture using pig cecal bacteria. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1995, 41, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.; Dragar, C.; Elliot, K.; Fitton, J.; Godwin, J.; Thompson, K. GFS, a preparation of Tasmanian Undaria pinnatifida is associated with healing and inhibition of reactivation of Herpes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2002, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, S. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Undaria pinnitafida in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Yoon, K.Y.; Lee, B.Y. Low molecular weight fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses inflammation by promoting the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T. Suppression of Th2 immune responses by mekabu fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 137, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Metastasis in Mouse Hepatocarcinoma. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3514–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.J.; Jeun, J.; Houng, S.J.; Jun, H.J.; Kweon, D.K.; Lee, S.J. Toxicological evaluation of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida in vitro and in vivo. Phytother. Res. PTR 2010, 24, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadekaru, T.; Toyama, H.; Yasumoto, T. Safety Evaluation of Fucoxanthin purified from Undaria pinnatifida. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2008, 55, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteau, O.; Mulloy, B. Sulfated fucans, fresh perspectives: Structures, functions, and biological properties of sulfated fucans and an overview of enzymes active toward this class of polysaccharide. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 29R–40R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.T.; Bremmell, K.E.; Krasowska, M.; Stringer, D.N.; Thierry, B.; Beattie, D.A. Tuning polyelectrolyte multilayer structure by exploiting natural variation in fucoidan chemistry. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Jin, G.H.; Yeo, M.G.; Jang, C.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.H. Fabrication of electrospun biocomposites comprising polycaprolactone/fucoidan for tissue regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Herath, K.; Yang, H.W.; Choi, C.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Fucoidans to Treat Inflammatory Diseases: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaraja, M.; Anantha Krishnan, D.; Edwin Hillary, V.; William Raja, T.R.; Mathew, P.; Ravikumar, S.; Gabriel Paulraj, M.; Ignacimuthu, S. Fucoidan serves a neuroprotective effect in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2020, 12, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Tarafdar, A.; Badgujar, P.C.; El-Sohaimy, S. Seaweed as a Source of Natural Antioxidants: Therapeutic Activity and Food Applications. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 5753391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairinisa, M.A.; Latarissa, I.R.; Athaya, N.S.; Charlie, V.; Musyaffa, H.A.; Prasedya, E.S.; Puspitasari, I.M. Potential Application of Marine Algae and Their Bioactive Metabolites in Brain Disease Treatment: Pharmacognosy and Pharmacology Insights for Therapeutic Advances. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of alginates and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArtain, P.; Gill, C.I.; Brooks, M.; Campbell, R.; Rowland, I.R. Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, A.R.; Macierzanka, A.; Aarak, K.; Rigby, N.M.; Parker, R.; Channell, G.A.; Harding, S.E.; Bajka, B.H. Sodium alginate decreases the permeability of intestinal mucus. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idota, Y.; Kogure, Y.; Kato, T.; Ogawa, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Kakinuma, C.; Yano, K.; Arakawa, H.; Miyajima, C.; Kasahara, F.; et al. Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Calcium Alginate in Rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukaife, H.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Alfatama, M. Alginate Nanoformulation: Influence of Process and Selected Variables. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Quinnell, S.P.; Lanzi, A.M.; Vegas, A.J. Alginate-Based Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as a Drug Codelivery Platform. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 7495–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibe, Y.; Kreidieh, M.; El Hajj, H.; Khalifeh, I.; Mukherji, D.; Temraz, S.; Shamseddine, A. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-angiogenic Therapies in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogli, S.; Porta, C.; Del Re, M.; Crucitta, S.; Gianfilippo, G.; Danesi, R.; Rini, B.I.; Schmidinger, M. Optimizing treatment of renal cell carcinoma with VEGFR-TKIs: A comparison of clinical pharmacology and drug-drug interactions of anti-angiogenic drugs. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 84, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Chang, A.K.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Zou, X. Fucoidan extract derived from Undaria pinnatifida inhibits angiogenesis by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2012, 19, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, L.N.; Garcia, D.O.; Harris, R.B.; Oren, E.; Roe, D.J.; Jacobs, E.T. Adherence to Diet and Physical Activity Cancer Prevention Guidelines and Cancer Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Iizuka, M.; Nakano, T. The role of NK cells in antitumor activity of dietary fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls (Mekabu). Planta Med. 2006, 72, 1415–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T. Antitumor activity and immune response of Mekabu fucoidan extracted from Sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. In Vivo 2003, 17, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Teng, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Trangle, S.S.; Li, Y.; White, W.L.; Li, J.; Ying, T.; Kong, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J. Investigation of Different Molecular Weight Fucoidan Fractions Derived from New Zealand Undaria pinnatifida in Combination with GroA Therapy in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, H.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y. Effect of polysaccharide from Undaria pinnatifida on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of breast cancer cell MCF7. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishchuk, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds Saccharina japonica and Undaria pinnatifida: Isolation, structural characteristics, and antitumor activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Hui, Z.H.; Pang ZunTing, P.Z.; Han ChunChao, H.C. Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame): A seaweed with pharmacological properties. Sci. Int. 2014, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobiński, M.; Okła, K.; Bednarek, W.; Wawruszak, A.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; García-Sanz, P.; Wertel, I.; Kotarski, J. The effect of fucoidan, a potential new, natural, anti-neoplastic agent on uterine sarcomas and carcinosarcoma cell lines: ENITEC collaborative study. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovet, L.; Samer, C.; Daali, Y. Preclinical Evaluation of Safety of Fucoidan Extracts from Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus for Use in Cancer Treatment. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419876325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corban, M.; Ambrose, M.; Pagnon, J.; Stringer, D.; Karpiniec, S.; Park, A.; Eri, R.; Fitton, J.H.; Gueven, N. Pathway Analysis of Fucoidan Activity Using a Yeast Gene Deletion Library Screen. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakano, T.; Muramoto, K.; Kahara, T.; Funayama, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Nakano, T. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and their antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6245–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Sang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, H.; Yin, S. Fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida prevents vascular dysfunction through PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent mechanisms in the l-NAME-induced hypertensive rat model. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, W.S.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, K.; Byun, E.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Ahn, D.H. Characterization of Undaria pinnatifida Root Enzymatic Extracts Using Crude Enzyme from Shewanella oneidensis PKA 1008 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.R.; Majid, M.; Haq, I.U.; Khan, M.R.; Kim, S.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-arthritic, antioxidant efficacy of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, A.; Sook, C.E.; Lee, B.Y.; Jee, Y. The Role of Fucoidans Isolated from the Sporophylls of Undaria pinnatifida against Particulate-Matter-Induced Allergic Airway Inflammation: Evidence of the Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses. Molecules 2020, 25, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.N.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, M.C.; Kang, J.Y.; Park, N.G.; Fujii, H.; Hong, Y.K. Isolation of two anti-inflammatory and one pro-inflammatory polyunsaturated fatty acids from the brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6984–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Xie, J. The water-soluble non-starch polysaccharides from natural resources against excessive oxidative stress: A potential health-promoting effect and its mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, W.; Hamid, N.; Liu, T.; Lu, J.; White, W.L. Fucoidan from New Zealand Undaria pinnatifida: Monthly variations and determination of antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.S.; Kim, I.D.; Kwon, R.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, J.S.; Ha, B.J. The effects of fucoidan extracts on CCl(4)-induced liver injury. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyuki, T.; Hamamoto, H.; Ishii, K.; Urai, M.; Kataoka, K.; Takeda, T.; Shibata, S.; Sekimizu, K. Evaluation of innate immune stimulating activity of polysaccharides using a silkworm (Bombyx mori) muscle contraction assay. Drug Discov. Ther. 2012, 6, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Zou, X.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Y.; You, L. Chemistry and immunostimulatory activity of a polysaccharide from Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Yu, B.; Han, Q.; Lu, J.; White, W.L.; Lai, Q.; Cai, N.; Luo, W.; Gu, L.; Li, S.; et al. Immune Activation of RAW264.7 Macrophages by Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan Extracted from New Zealand Undaria pinnatifida. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10721–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.O.; Yu, Q. Fucoidan delays apoptosis and induces pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human neutrophils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 73, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. The enhancing effect of fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida on immunoglobulin production by mouse spleen lymphocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q.; Jin, J.O. Fucoidan from Macrocystis pyrifera has powerful immune-modulatory effects compared to three other fucoidans. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Wang, S. Progress of Plant Medicine Derived Extracts and Alkaloids on Modulating Viral Infections and Inflammation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 1385–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, E.A.; Falshaw, R.; Carnachan, S.M.; Kern, E.R.; Prichard, M.N. Virucidal activity of polysaccharide extracts from four algal species against herpes simplex virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.D.; Dragar, C. Antiviral activity of Undaria pinnatifida against herpes simplex virus. Phytother. Res. PTR 2004, 18, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Novel antiviral fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida (Mekabu). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, E.G.; Verbrugghe, P.; Perkins, T.T.; Tay, C.Y. Fucoidans Disrupt Adherence of Helicobacter pylori to AGS Cells In Vitro. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2015, 2015, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Koo, Y.K.; Jung, M.K.; Moon, H.R.; Kim, S.M.; Synytsya, A.; Yun-Choi, H.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.K.; Park, Y.I. Anticoagulating activities of low-molecular weight fuco-oligosaccharides prepared by enzymatic digestion of fucoidan from the sporophyll of Korean Undaria pinnatifida. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.K.; Kwon, O.C.; Lee, S.; Park, K.H.; Kim, J.K. An antithrombotic fucoidan, unlike heparin, does not prolong bleeding time in a murine arterial thrombosis model: A comparative study of Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls and Fucus vesiculosus. Phytother. Res. PTR 2012, 26, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ye, X.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Xiong, Q.; Li, S. Sulfated polysaccharide from Undaria pinnatifida stabilizes the atherosclerotic plaque via enhancing the dominance of the stabilizing components. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadja, P.; Tan, C.Y.; Ouyang, J.M.; Yu, K. Repair Effect of Seaweed Polysaccharides with Different Contents of Sulfate Group and Molecular Weights on Damaged HK-2 Cells. Polymers 2016, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.T.; Sun, X.Y.; Yu, K.; Gui, B.S.; Gui, Q.; Ouyang, J.M. Effect of Content of Sulfate Groups in Seaweed Polysaccharides on Antioxidant Activity and Repair Effect of Subcellular Organelles in Injured HK-2 Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2542950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.L.; He, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y.J.; Song, H.L.; An, H.T.; Zhang, H.B.; Qian, Y.J.; et al. Therapeutic effects of fucoidan in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Role of NADPH oxidase-1. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazwi, M.; Smid, S.; Karpiniec, S.; Zhang, W. Comparative study on neuroprotective activities of fucoidans from Fucus vesiculosus and Undaria pinnatifida. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannat, K.; Balakrishnan, R.; Han, J.H.; Yu, Y.J.; Kim, G.W.; Choi, D.K. The Neuropharmacological Evaluation of Seaweed: A Potential Therapeutic Source. Cells 2023, 12, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-Y.; Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Lee, J.M.; Noh, G.; Jo, G.-a.; Lee, J.-H.; Kong, I.-S. Structural features of glycoprotein purified from Saccharina japonica and its effects on the selected probiotic properties of Lactobacillus plantarum in Caco-2 cell. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 27, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Sur, B.; Park, J.; Shin, H.; Kwon, S.; Yeom, M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.; Shim, I.; Yin, C.S.; et al. Fucoidan ameliorates scopolamine-induced neuronal impairment and memory dysfunction in rats via activation of cholinergic system and regulation of cAMP-response element-binding protein and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expressions. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2012, 55, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, X.; et al. Fucoidan protects against dopaminergic neuron death in vivo and in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 617, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Valado, A. The Seaweed Diet in Prevention and Treatment of the Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Mohibbullah, M.; Alam, M.B.; Soo Moon, I.; Kim, J.-M.; Kong, I.-S. Anti-Alzheimers and anti-inflammatory activities of a glycoprotein purified from the edible brown alga Undaria pinnatifida. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Souza, M.C.; Marques, C.T.; Guerra Dore, C.M.; Ferreira da Silva, F.R.; Oliveira Rocha, H.A.; Leite, E.L. Antioxidant activities of sulfated polysaccharides from brown and red seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasa-López, A.; Miliar-García, Á.; Quevedo-Corona, L.; Paniagua-Castro, N.; Escalona-Cardoso, G.; Reyes-Maldonado, E.; Jaramillo-Flores, M.-E. Undaria pinnatifida and fucoxanthin ameliorate lipogenesis and markers of both inflammation and cardiovascular dysfunction in an animal model of diet-induced obesity. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, M.N.; Jeon, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.K.; Shin, S.K.; Shin, Y.C.; Park, Y.B.; Choi, M.S. Fucoxanthin supplementation improves plasma and hepatic lipid metabolism and blood glucose concentration in high-fat fed C57BL/6N mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 186, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Kong, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Fucoxanthin: A Promising Medicinal and Nutritional Ingredient. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2015, 2015, 723515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, R.; Alsous, L.; Sabbah, D.A.; Gul, H.I.; Gul, M.; Bardaweel, S.K. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) as a potential target for anticancer drug design and development. Molecules 2021, 26, 6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, A.; Hamid, N.; Lu, J. Fucoxanthin content and antioxidant properties of Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.J.; MacDougall, D.E.; Ntanios, F.; Vanstone, C.A. Dietary phytosterols as cholesterol-lowering agents in humans. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 75, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinita, M.D.N.; Harwanto, D.; Tirtawijaya, G.; Negara, B.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.S. Fucosterol of Marine Macroalgae: Bioactivity, Safety and Toxicity on Organism. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M.; Jabbari, A. Antioxidant potential and DPPH radical scavenging kinetics of water-insoluble flavonoid naringenin in aqueous solution of micelles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 489, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Goncalves, A.M.M. Marine Macroalgae Polyphenols as Potential Neuroprotective Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasehinde, T.A.; Olaniran, A.O.; Okoh, A.I. Macroalgae as a Valuable Source of Naturally Occurring Bioactive Compounds for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Loy, C.; Siew-Moi, P. Marine Algae as a Potential Source for Anti-Obesity Agents. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. On the softening effect of salty drugs. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 47, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Schepers, M.; Martens, N.; Tiane, A.; Vanbrabant, K.; Liu, H.B.; Lutjohann, D.; Mulder, M.; Vanmierlo, T. Edible seaweed-derived constituents: An undisclosed source of neuroprotective compounds. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Tsukui, T.; Sashima, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Seaweed carotenoid, fucoxanthin, as a multi-functional nutrient. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S1), 196–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frozza, R.; Lourenco, M.; De Felice, F. Challenges for Alzheimer’s disease therapy: Insights from novel mechanisms beyond memory defects. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, L.; Cuervo, A.; Salazar, N.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Gueimonde, M.; Gonzalez, S. The relationship between phenolic compounds from diet and microbiota: Impact on human health. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2424–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.R.L.d. A Importância das Macroalgas Castanhas para o Desenvolvimento de Nutracêuticos. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidade Fernando Pessoa, Porto, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, S.J.; Park, E.J.; Lee, K.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.S.D. Prospeção de Compostos Bioativos nas Macroalgas Himanthalia elongata, Laminaria ochroleuca e Undaria pinnatifida. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.A.; Islam, M.M.; Ahmed, S.T.; Mun, H.S.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, C.J. Seamustard (Undaria pinnatifida) Improves Growth, Immunity, Fatty Acid Profile and Reduces Cholesterol in Hanwoo Steers. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, D.M. Communication networks in the brain: Neurons, receptors, neurotransmitters, and alcohol. Alcohol Res. Health 2008, 31, 196–214. [Google Scholar]
- Niyonambaza, S.D.; Kumar, P.; Xing, P.; Mathault, J.; De Koninck, P.; Boisselier, E.; Boukadoum, M.; Miled, A. A Review of Neurotransmitters Sensing Methods for Neuro-Engineering Research. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, E.M.B.; Mantilla, A.B.P.; Perera, O.H. Neurotransmitters, Their Effects on the Human Organism. Anat. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. 2017, 2, 555–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.G.; Bottiglieri, T.; Snead, O.C., 3rd. GABA, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, and neurological disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54 (Suppl. S6), S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Gray, J.A.; Roth, B.L. The expanded biology of serotonin. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, V.P.d. Estudo computacional das monoaminoxidases A e B com substratos e inibidores. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Petronilho, E.; Figueroa-Villar, J. Agents for defense against chemical warfare: Reactivators of acetylcholinesterase inhibited with neurotoxic organophosphorus compounds. Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. 2015, 84, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevinho, M.F.; Soares-Fortunato, J. Dopamina e receptores. Rev. Port. Psicossomática 2003, 5, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Fujita, N.; Odaka, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Yonemori, S.; Nakamoto, K.; Kuninaga, H. Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of ethanol extracts from medicinal and edible plants cultivated in okinawa and identification of a water-soluble inhibitor from the leaves of Nandina domestica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2316–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Odaka, Y.; Ogawa, N.; Nakamoto, K.; Kuninaga, H. Identification of geranic acid, a tyrosinase inhibitor in lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Yamashita, D.; Takeda, Y.; Yonemori, S. Screening for tyrosinase inhibitors among extracts of seashore plants and identification of potent inhibitors from Garcinia subelliptica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsu, T.; Nakashima, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Neuromelanin in Parkinson’s Disease: Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Tyrosinase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss-Coray, T. Ageing, neurodegeneration and brain rejuvenation. Nature 2016, 539, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Dementia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Kovacs, G.G.; Budka, H. Current concepts of neuropathological diagnostics in practice: Neurodegenerative diseases. Clin. Neuropathol. 2010, 29, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.H.; Ironside, J.W. Molecular pathology in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tycko, R. Amyloid polymorphism: Structural basis and neurobiological relevance. Neuron 2015, 86, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalace, M.C.; Malaguti, M.; Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Marine Algae in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Anaeigoudari, A.; Hashemzehi, M.; Mohebbati, R. Neuroprotective potency of some spice herbs, a literature review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2019, 9, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milatovic, D.; Zaja-Milatovic, S.; Breyer, R.M.; Aschner, M.; Montine, T.J. Neuroinflammation and oxidative injury in developmental neurotoxicity. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 847–854. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, S. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, A.; Lotharius, J. Oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Is there a causal link? Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, F.; Tasset, I.; Aguera, E.; Feijoo, M.; Fernandez-Bolanos, R.; Sanchez, F.M.; Ruiz, M.C.; Cruz, A.H.; Gascon, F.; Tunez, I. Oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers in the blood of patients with Huntington’s disease. Neurol Res. 2012, 34, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; the International Natural Product Sciences; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, R.N.L.; Chaulagain, B.; Trivedi, R.; Gothwal, A.; Layek, B.; Singh, J. A Review of the Common Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Therapeutic Approaches and the Potential Role of Nanotherapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntibeju, O.O. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: Examining the links. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Gutierrez, E.; Munoz-Arenas, G.; Trevino, S.; Espinosa, B.; Chavez, R.; Rojas, K.; Flores, G.; Diaz, A.; Guevara, J. Alzheimer’s disease and metabolic syndrome: A link from oxidative stress and inflammation to neurodegeneration. Synapse 2017, 71, e21990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazwi, M.; Kan, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.; Gai, W.P.; Garson, M.J.; Smid, S. Neuroprotective activities of natural products from marine macroalgae during 1999–2015. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3599–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Nutritional Composition of the Main Edible Algae. In Therapeutic and Nutritional Uses of Algae, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, R.; Gill, K.D.; Mahdi, A.A. Therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease: Past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt A, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.R.M.; Santos, V.d.A.; Gonsalves, A.A. Acetylcholinesterase-AChE: A pharmacological interesting enzyme. Rev. Virtual Química 2016, 8, 1818–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Morstorf, T.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug-development pipeline: Few candidates, frequent failures. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, M.S.; Hemnani, T. Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 11, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, T.; Rao, P.P. Alzheimer’s disease: Emerging trends in small molecule therapies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4299–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Nam, T.J.; Kong, I.S. Antioxidant and DNA protection activities of a glycoprotein isolated from a seaweed, Saccharina japonica. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, L.; Vianello, F. Potential of microalgae as functional foods applied to mitochondria protection and healthy aging promotion. Nutraceuticals 2023, 3, 119–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Q.; Jia, Y.J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wang, X.M. Fucoidan protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced rat neuronal damage and inhibits the production of proinflammatory mediators in primary microglia. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, D.Z.; Jia, Y.J.; Guo, Z.X.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.M. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, J.W.; Forno, L.S.; Tetrud, J.; Reeves, A.G.; Kaplan, J.A.; Karluk, D. Evidence of active nerve cell degeneration in the substantia nigra of humans years after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, M.; Maetzler, W.; Broich, K.; Hampel, H.; Rems, L.; Reum, T.; Riederer, P.; Stöffler, A.; Streffer, J.; Berg, D. Biomarker candidates of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease for the evaluation of disease-modifying therapeutics. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Verma, A.K.; Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, R. Oxidative stress and major depression. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC04–CC07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Nagappa, A.N.; Patil, C.R. Role of oxidative stress in depression. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Depressive Disorder (Depression). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 12 May 2025).

| Bioactive Compounds of U. pinnatifida | Bioactivities | Possible Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fucoidan | Anti-angiogenic |
| [48] |
| Anti-tumour |
| [3,50,51,52,54] | |
| Hypertension prevention |
| [3,61] | |
| Anti-coagulant and anti-thrombosis |
| [3,80,81,82] | |
| Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulation |
| [3,28,62,63,69,70,71,72,74] | |
| Anti-oxidant |
| [26,63,67,73] | |
| Anti-microorganisms |
| [3,25,76,78,79,85] | |
| Neuroprotective |
| [27,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] | |
| Glycoproteins (UPGP) | Neuroprotective |
| [92] |
| Fucoxanthin | Anti-obesity |
| [94,95,96] |
| Neuroprotective |
| [9,96,97,98] | |
| Alginates | Anti-obesity |
| [42,43] |
| Fucosterol | Neuroprotective |
| [11,99,100] |
| Phenolic compounds | Antioxidant |
| [39,101,102,103] |
| Anti-obesity |
| [104] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machado, H.; Machado, J.P.; Alves, C.; Soares, C.; Grosso, C.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Criado, M.B. Exploring the Pharmacological Landscape of Undaria pinnatifida: Insights into Neuroprotective Actions and Bioactive Constituents. Nutraceuticals 2025, 5, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030020
Machado H, Machado JP, Alves C, Soares C, Grosso C, Rodrigues JM, Criado MB. Exploring the Pharmacological Landscape of Undaria pinnatifida: Insights into Neuroprotective Actions and Bioactive Constituents. Nutraceuticals. 2025; 5(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachado, Helena, Jorge Pereira Machado, Christian Alves, Cristina Soares, Clara Grosso, Jorge Magalhães Rodrigues, and Maria Begoña Criado. 2025. "Exploring the Pharmacological Landscape of Undaria pinnatifida: Insights into Neuroprotective Actions and Bioactive Constituents" Nutraceuticals 5, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030020
APA StyleMachado, H., Machado, J. P., Alves, C., Soares, C., Grosso, C., Rodrigues, J. M., & Criado, M. B. (2025). Exploring the Pharmacological Landscape of Undaria pinnatifida: Insights into Neuroprotective Actions and Bioactive Constituents. Nutraceuticals, 5(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030020











