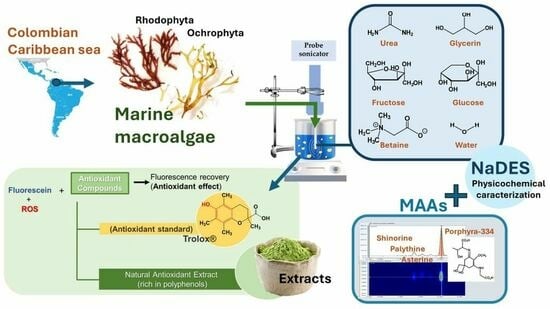
Sustainable Extraction of Prospective Cosmetic Ingredients from Colombian Marine Macroalgae Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Samples
2.2. Preliminary Chemical Screening
2.3. Preparation and Analysis of NADESs
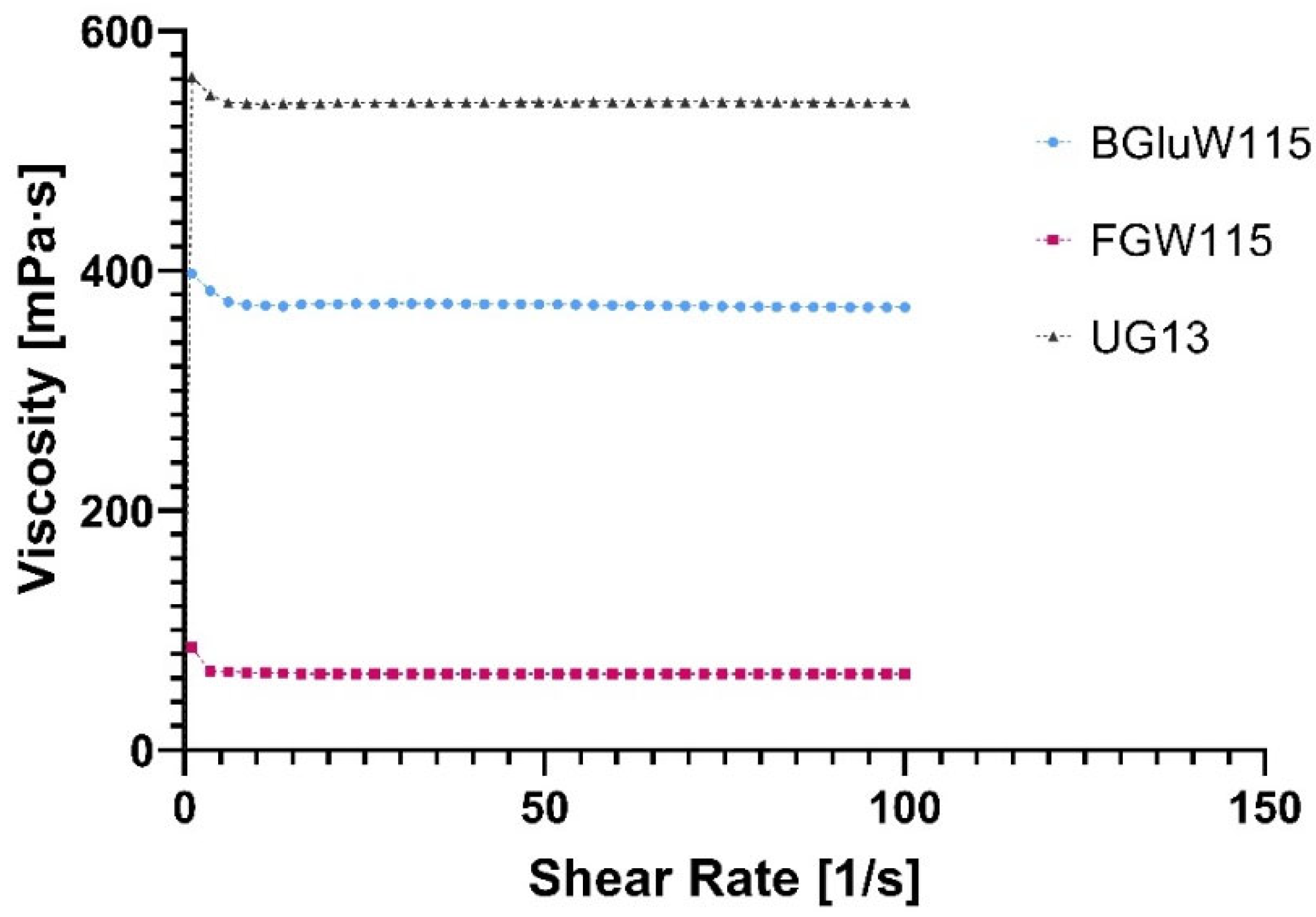
2.3.1. Flow Profile of NADESs
2.3.2. Surface Tension of NADESs
2.3.3. pH of NADESs
2.3.4. Conductivity of NADESs
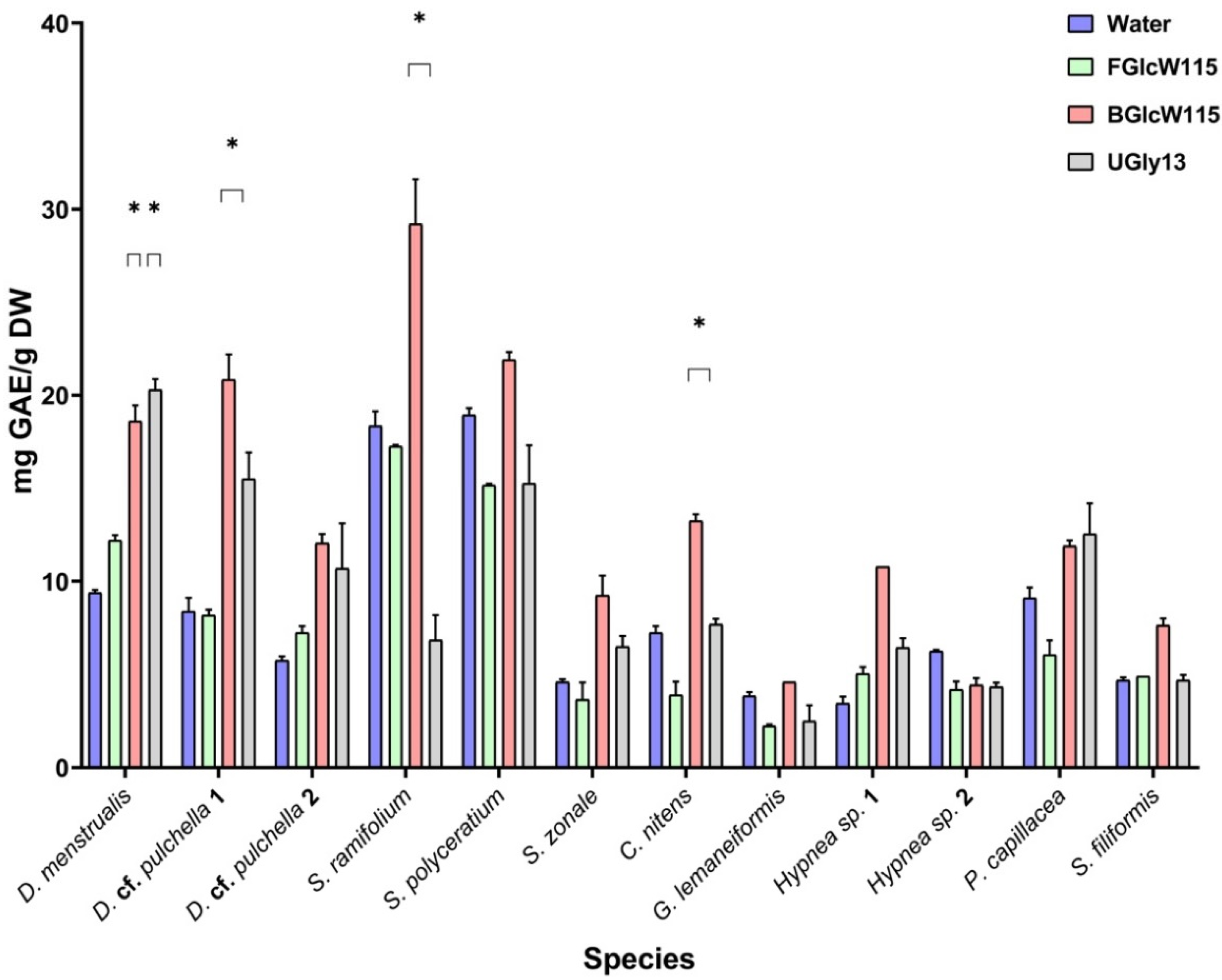
2.4. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds with the NADESs
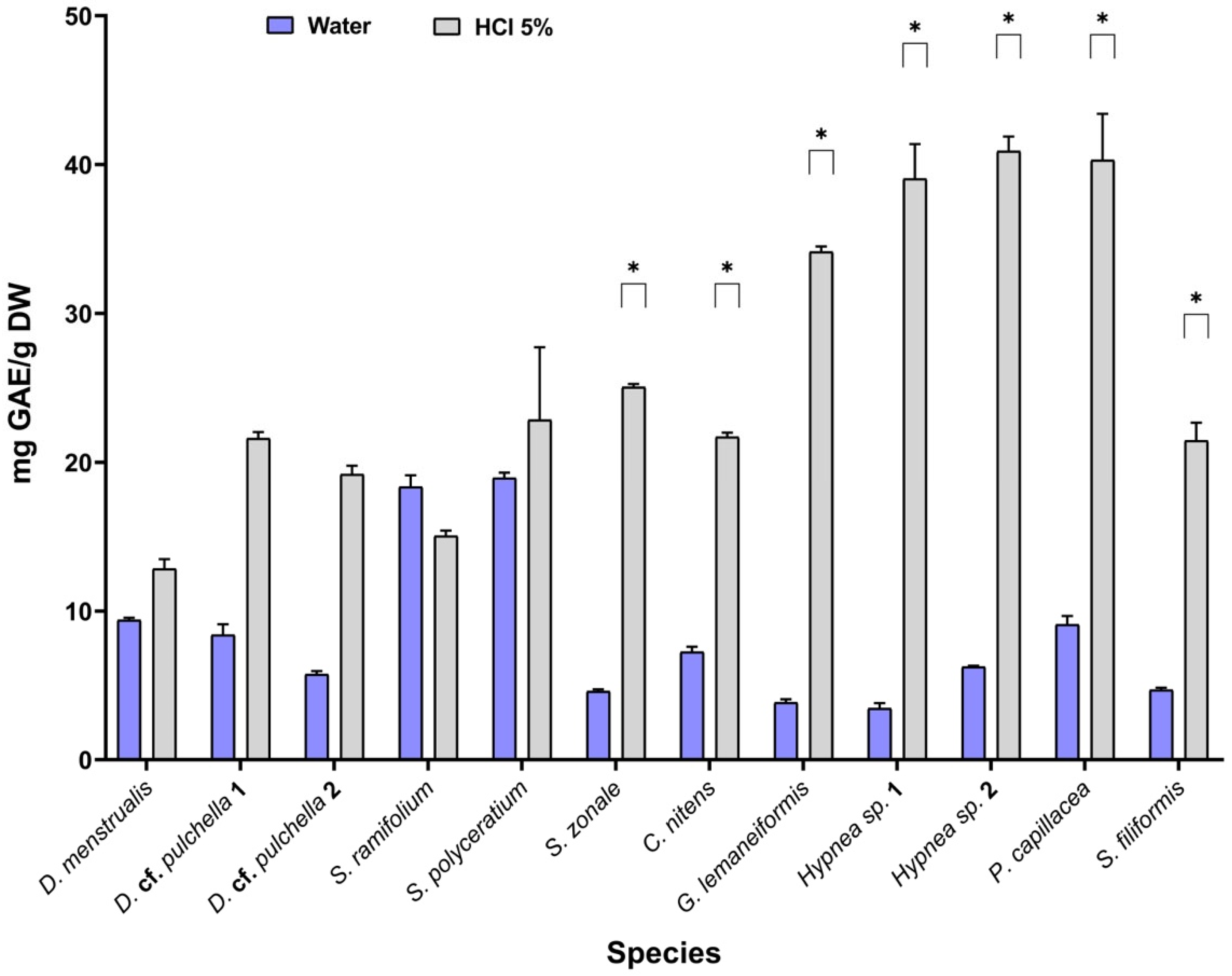
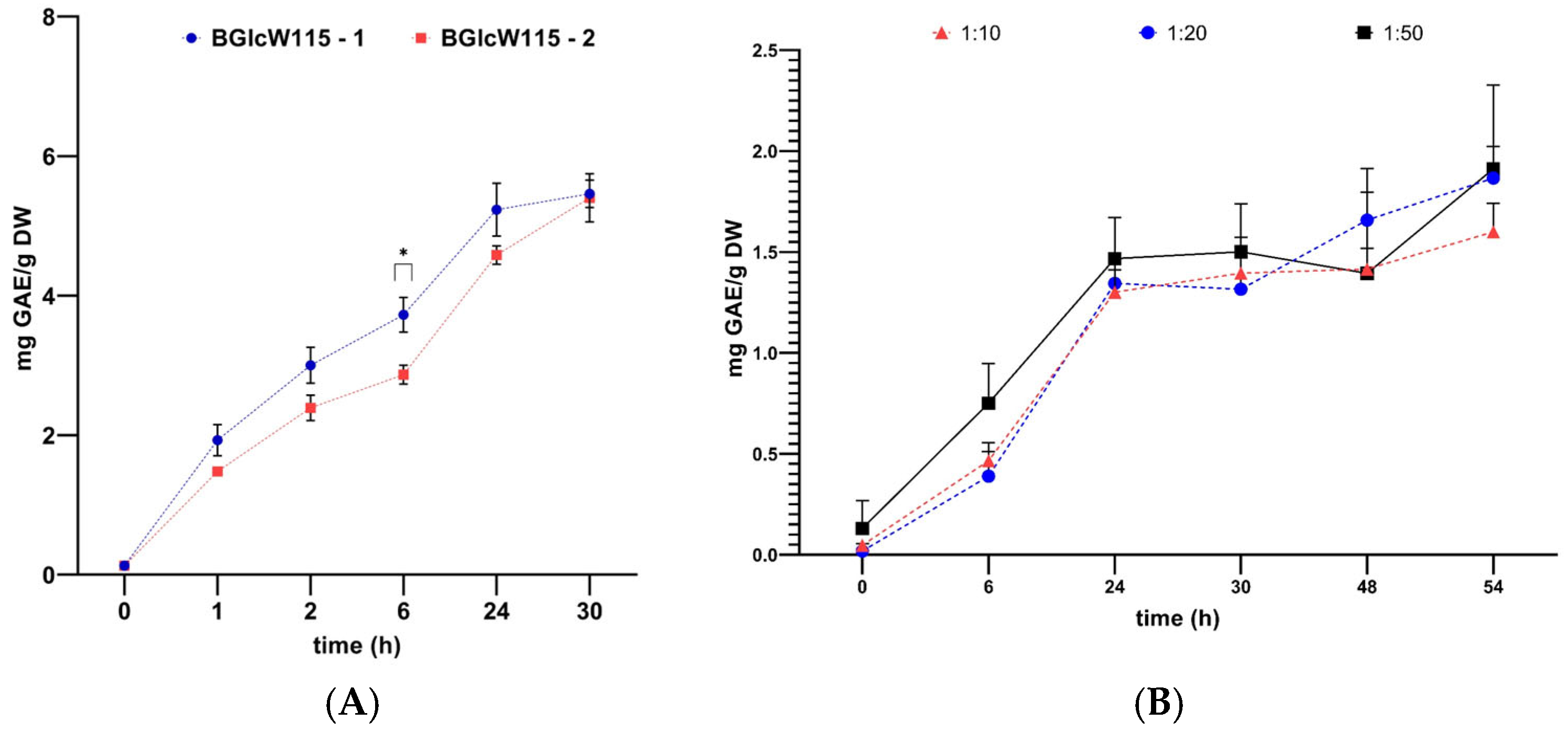
2.5. Pre-Scaling of Phenolic Compound Extraction
2.6. UV Preliminary Scanning of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids (MAAs)
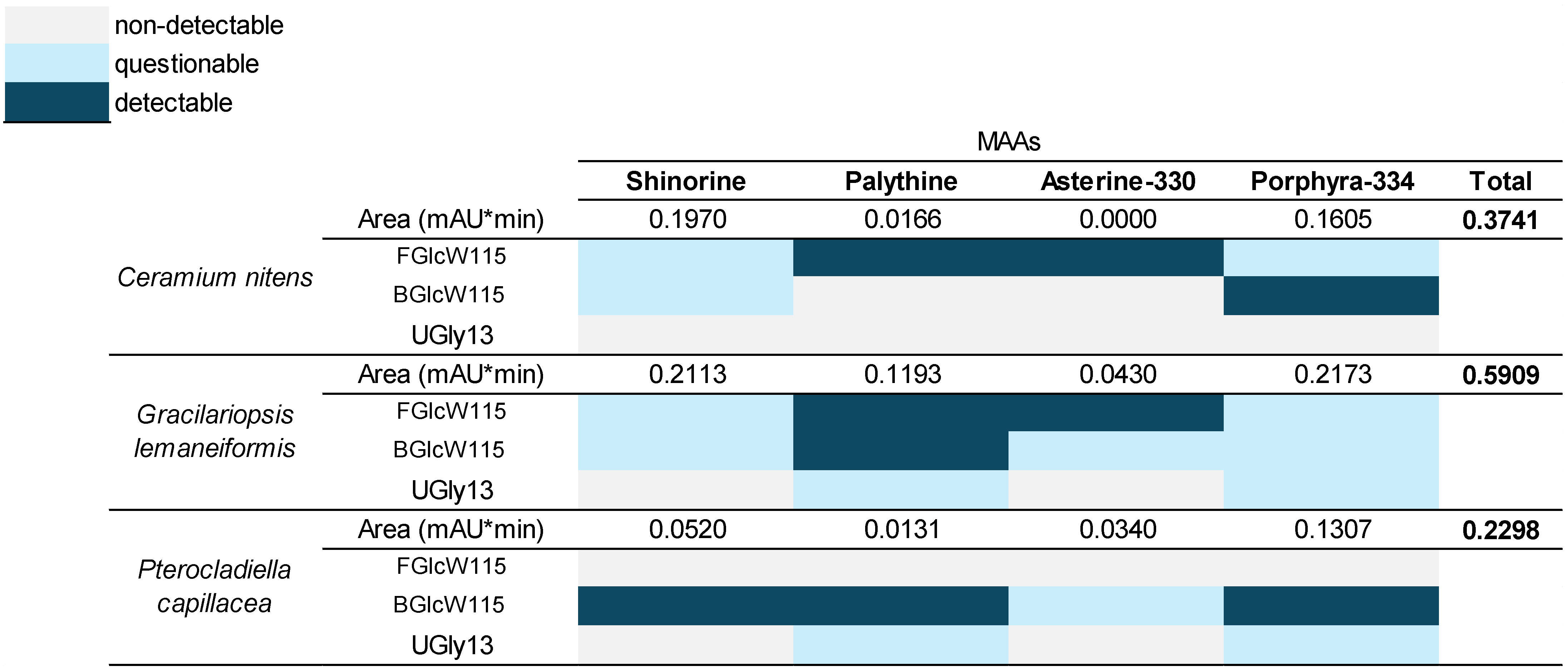
2.7. Identification of MAAs by UHPLC-DAD in Red Macroalgae
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Chemical Screening Tests
3.3. Preparation of the NADESs
3.4. NADES Physicochemical Parameters
3.4.1. Flow Profile Assay
3.4.2. Determination of Surface Tension
3.4.3. Determination of pH
3.4.4. Conductivity Test
3.5. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Macroalgae with NADESs
3.6. Phenolic Content Determination
3.7. Pre-Scaling of NADESs Extraction
3.8. UV Preliminary Scanning
3.9. Identification of MAAs by UHPLC-DAD Analysis
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NADES | Natural deep eutectic solvent |
| FGlcW115 | Fructose/glycerine/water 1:1:5 |
| BGlcW115 | Betaine/glucose/water 1:1:5 |
| UGly13 | Urea/glycerine 1:3 |
| MAAs | Mycosporine-like amino acids |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy |
| UHPLC-DAD | Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode-Array Detection |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
References
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents–Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Mbous, Y.P.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Hayyan, A.; Salleh, Z.; Mohd-Ali, O. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Cytotoxic Profile. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Caviglia, D.; Robustelli della Cuna, F.S.; Zuccari, G.; Russo, E. NaDES Application in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Fields: An Overview. Gels 2024, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Daurtseva, A.V.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Alternatives for Extracting Phlorotannins from Brown Algae. Pharm. Chem. J. 2019, 53, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Kosman, V.M.; Flissyuk, E.V.; Smekhova, I.E.; Elameen, A.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Phenyletanes and Phenylpropanoids of Rhodiola rosea L. Molecules 2020, 25, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shevyrin, V.A.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Optimization of Extraction of Phlorotannins from the Arctic Fucus Vesiculosus Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their HPLC Profiling with Tandem High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Terninko, I.I.; Generalova, Y.E.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. The Impact of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Extraction Method on the Co-Extraction of Trace Metals from Fucus Vesiculosus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wils, L.; Yagmur, M.; Phelippe, M.; Montigny, B.; Clément-Larosière, B.; Jacquemin, J.; Boudesocque-Delaye, L. Alternative Solvents for the Biorefinery of Spirulina: Impact of Pretreatment on Free Fatty Acids with High Added Value. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Y. Efficient Purification of R-Phycoerythrin from Marine Algae (Porphyra yezoensis) Based on a Deep Eutectic Solvents Aqueous Two-Phase System. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, C.; Adrien, A.; Petitpas, A.; Rubatat, L.; Fernandes, S.C.M. Double Valorization for a Discard-α-Chitin and Calcium Lactate Production from the Crab Polybius Henslowii Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent Approach. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Concise Review of the Brown Macroalga Ascophyllum Nodosum (Linnaeus) Le Jolis Journal of Applied Phycology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10811-020-02246-6 (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Olfat, A.; Mostaghim, T.; Shahriari, S.; Salehifar, M. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds of Hypnea flagelliformis by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Coupled with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Enzyme Inhibitory Activity. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiño, S.; Peteiro, C.; Aymerich, T.; Hortós, M. Brown Macroalgae (Phaeophyceae): A Valuable Reservoir of Antimicrobial Compounds on Northern Coast of Spain. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoux, G.; Hardouin, K.; Burlot, A.-S.; Bourgougnon, N. Bioactive Components from Seaweeds: Cosmetic Applications and Future Development. Adv. Bot. Res. 2014, 71, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.D.O.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.C.; Paiva, A.; Haghbakhsh, R.; Rita, C.; Duarte, A. Is It Possible to Correlate Various Physicochemical Properties of Natural Deep Eutectic Systems in Order to Predict Their Behaviours as Solvents? J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, L.K.; Dias, M.C.G.C.; Carpine, D.; Waszczynskyj, N.; Ribani, R.H.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) Based on Citric Acid and Sucrose as a Potential Green Technology: A Comprehensive Study of Water Inclusion and Its Effect on Thermal, Physical and Rheological Properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extraction Media for Valuable Flavonoids from Natural Sources. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Ho, C.W. Effect of Solid-to-Solvent Ratio on Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacities of “Dukung Anak” (Phyllanthus Niruri). Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Hartanti, D.; Insani, A.A.; Wahono, S.K.; Hamad, A. Extraction Method and Crude Drug-to-Solvent Ratio Effects on the Antioxidant Properties and Physicochemical Profile during Storage of a Polyherbal Formulation Extract. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 135, 06002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Armas, H.; Jaramillo-Jaramillo, C.; D’Armas, M.; Ordaz-González, G.J. Fatty acid profile, total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of seaweeds in Salinas Bay, Ecuador. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2023, 58, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Tsao, R. A Review on Insoluble-Bound Phenolics in Plant-Based Food Matrix and Their Contribution to Human Health with Future Perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, J.; et al. Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Contents, Profiles, and Antioxidant Abilities of Free and Bound Phenolics of Sargassum Polycystum from the South China Sea. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olate-Gallegos, C.; Barriga, A.; Vergara, C.; Fredes, C.; García, P.; Giménez, B.; Robert, P. Identification of Polyphenols from Chilean Brown Seaweeds Extracts by LC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Pico, J.; Sun, B.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Gerbrandt, E.; Castellarin, D.S. Phenolic Profiles and Their Responses to Pre- and Post-Harvest Factors in Small Fruits: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 3574–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Jayakumar, N.S. New Horizons in the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 979, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalić Mekinić, I.; Skroza, D.; Šimat, V.; Hamed, I.; Čagalj, M.; Popović Perković, Z. Phenolic Content of Brown Algae (Pheophyceae) Species: Extraction, Identification, and Quantification. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.A.O.; Félix, R.; Pais, A.C.S.; Rocha, S.M.; Silvestre, A.J.D. The Quest for Phenolic Compounds from Macroalgae: A Review of Extraction and Identification Methodologies. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, D.B.; Connan, S.; Popper, Z.A. Algal Chemodiversity and Bioactivity: Sources of Natural Variability and Implications for Commercial Application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivikko, R.; Loponen, J.; Honkanen, T.; Jormalainen, V. Contents of Soluble, Cell-Wall-Bound and Exuded Phlorotannins in the Brown Alga Fucus Vesiculosus, with Implications on Their Ecological Functions. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.J.; Xie, C.; Ng, K.; Suleria, H.A.R. Study of Phenolic-Polysaccharide Interactions in Brown Seaweed. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Hu, K.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R.; Su, D. Comparative Analysis of the Morphological Property and Chemical Composition of Soluble and Insoluble Dietary Fiber with Bound Phenolic Compounds from Different Algae. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3843–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sanz, M.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Ballester, A.R.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Brodkorb, A.; López-Rubio, A. Production of Unpurified Agar-Based Extracts from Red Seaweed Gelidium sesquipedale by Means of Simplified Extraction Protocols. Algal Res. 2019, 38, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, A.A.; Đorđević, V.B.; Zdunić, G.M.; Pljevljakušić, D.S.; Šavikin, K.P.; Gođevac, D.M.; Bugarski, B.M. Optimization of the Extraction Process of Polyphenols from Thymus serpyllum L. Herb Using Maceration, Heat- and Ultrasound-Assisted Techniques. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikong, W.; Bovornreungroj, N.; Mittraparparthorn, P.; Bovornreungroj, P. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Differential Solvent Extractions from the Green Seaweed Ulva Intestinalis. ScienceAsia 2017, 43, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishlah, T.; Mun’im, A.; Jufri, M. Optimization of Urea-Glycerin Based NADES-UAE for Oxyresveratrol Extraction from Morus Alba Roots for Preparation of Skin Whitening Lotion–Journal of Young Pharmacists. J. Young Pharm. 2019, 11, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrea-Victoria, V.; Costa, G.; Gavio, B.; Ramos, F.; Castellanos, L. Mycosporine-like Amino Acids Profile in Red Algae from High UV-Index Geographical Areas (San Andrés Island and La Guajira) of the Colombian Caribbean Coast. Algal Res. 2025, 86, 103927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Guo, F.; Liu, S.; Fang, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, T. Recent Advances and Future Prospects of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids. Molecules 2023, 28, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, C.; Virginie, C.; Boris, V. Chapter Twelve-The Use of NADES to Support Innovation in the Cosmetic Industry. In Advances in Botanical Research; Verpoorte, R., Witkamp, G.-J., Choi, Y.H., Eds.; Eutectic Solvents and Stress in Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 97, pp. 309–332. [Google Scholar]
| Group | Species | Order | Family | Collection Date | Collection Site | Voucher Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown macroalgae | Dictyota menstrualis | Dictyotales | Dictyoptaceae | 26 September 2021 | Providencia | JIW00004951 |
| Dictyota cf. pulchella * | Dictyotales | Dictyoptaceae | 26 September 2021 | Providencia | JIW00004956 | |
| Dictyota cf. pulchella * | Dictyotales | Dictyoptaceae | 26 September 2021 | Providencia | JIW00004952 | |
| Sargassum cf. ramifolium | Fucales | Sargassaceae | 1 March 2021 | Guajira | JIW00004940 | |
| Sargassum fluitans | Fucales | Sargassaceae | 1 February 2021 | San Andrés | JIW00004945 | |
| Stypopodium zonale | Dictyotales | Dictyotaceae | 3 March 2021 | Guajira | JIW00003294 | |
| Red macroalgae | Ceramium nitens | Ceramiales | Ceramiaceae | 28 February 2021 | Guajira | JIW005012 |
| Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis | Gracilariales | Gracilariaceae | 1 March 2021 | Guajira | JIW005011 | |
| Hypnea sp. 1 | Gigartinales | Cystocloniaceae | 1 March 2021 | Guajira | ND | |
| Hypnea sp. 2 | Gigartinales | Cystocloniaceae | 28 February 2021 | Guajira | ND | |
| Pterocladiella capillacea | Gelidiales | Pterocladiaceae | 1 March 2021 | Guajira | JIW005015 | |
| Solieria filiformis | Gigartinales | Solieriaceae | 4 March 2021 | Guajira | JIW0005029 |
| Code | Components | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| FGlcW115 | Fructose/glucose/water | 1:1:5 |
| BGlcW115 | Betaine/glucose/water | 1:1:5 |
| UGly13 | Urea/glycerine | 1:3 |
| NADES | η (mPa·s) | γ (mN·m−1) | pH | κ (µS·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGlcW115 | 63.5 | 67.2 | 7.38 | 2.2 |
| BGlcW115 | 370.4 | 77.5 | 8.44 | 0.9 |
| UGly13 | 540.6 | 66.3 | 9.30 | 1.4 |
| Macroalgae Samples | Solvents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGlcW115 | BGlcW115 | UGly13 | H2O | |
| D. menstrualis | 12.2 ± 0.295 | 18.6 ± 0.871 * | 20.3 ± 0.517 * | 9.37 ± 0.168 |
| D. cf. pulchella 1 a | 8.22 ± 0.306 | 20.9 ± 1.39 * | 15.5 ± 1.38 | 8.44 ± 0.686 |
| D. cf. pulchella 2 b | 7.26 ± 0.351 | 12.1 ± 0.484 | 10.7 ± 2.45 | 5.77 ± 0.240 |
| S. cf. ramifolium | 17.3 ± 0.0810 | 29.2 ± 2.36 * | 6.86 ± 1.38 | 18.4 ± 0.777 |
| S. fluitans | 15.1 ± 0.0459 | 21.9 ± 0.433 | 15.3 ± 2.05 | 19.0 ± 0.359 |
| S. zonale | 3.63 ± 0.952 | 9.27 ± 1.03 | 6.50 ± 0.606 | 4.60 ± 0.184 |
| C. nitens | 3.91 ± 0.744 | 13.3 ± 0.368 * | 7.69 ± 0.259 | 7.22 ± 0.355 |
| G. lemaneiformis | 2.24 ± 0.0344 | 2.29 ± 3.25 | 2.48 ± 0.875 | 3.83 ± 0.181 |
| Hypnea sp. 1 | 5.08 ± 0.352 | 10.8 ± 0.010 | 6.45 ± 0.500 | 3.44 ± 0.342 |
| Hypnea sp. 2 | 4.24 ± 0.436 | 4.47 ± 0.378 | 4.35 ± 0.178 | 6.21 ± 0.0609 |
| P. capillacea | 6.09 ± 0.773 | 11.9 ± 0.293 | 12.6 ± 1.60 | 9.08 ± 0.541 |
| S. filiformis | 4.94 ± 0.00740 | 7.66 ± 0.303 | 4.71 ± 0.333 | 4.67 ± 0.128 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamayo-Rincón, V.M.; Colorado-Ríos, J.; Alvarez-Bustamante, D.J.; Urrea-Victoria, V.; Márquez-Fernández, D.M.; Salamanca, C.H.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Castellanos-Hernandez, L.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Sustainable Extraction of Prospective Cosmetic Ingredients from Colombian Marine Macroalgae Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060239
Tamayo-Rincón VM, Colorado-Ríos J, Alvarez-Bustamante DJ, Urrea-Victoria V, Márquez-Fernández DM, Salamanca CH, Dall’Acqua S, Castellanos-Hernandez L, Martínez-Martínez A. Sustainable Extraction of Prospective Cosmetic Ingredients from Colombian Marine Macroalgae Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060239
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamayo-Rincón, Verónica María, Jhonny Colorado-Ríos, Didier Johan Alvarez-Bustamante, Vanessa Urrea-Victoria, Diana Margarita Márquez-Fernández, Constain H. Salamanca, Stefano Dall’Acqua, Leonardo Castellanos-Hernandez, and Alejandro Martínez-Martínez. 2025. "Sustainable Extraction of Prospective Cosmetic Ingredients from Colombian Marine Macroalgae Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060239
APA StyleTamayo-Rincón, V. M., Colorado-Ríos, J., Alvarez-Bustamante, D. J., Urrea-Victoria, V., Márquez-Fernández, D. M., Salamanca, C. H., Dall’Acqua, S., Castellanos-Hernandez, L., & Martínez-Martínez, A. (2025). Sustainable Extraction of Prospective Cosmetic Ingredients from Colombian Marine Macroalgae Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060239