Advanced MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Incidental Glioma Grading and Genetic Status: Where Are We?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of MRI in Glioma Detection and Grading
2.1. Standard MRI Sequences
2.2. Advanced MRI Sequences
2.2.1. Black-Blood Imaging
2.2.2. Perfusion-Weighted Imaging
Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast
Dynamic Contrast Enhancement
Arterial Spin Labelling
2.2.3. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Proton (1H) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
2-Hydroxyglutarate Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
2.2.4. Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging
2.2.5. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Map
2.2.6. Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Tractography
2.2.7. Functional MRI
3. The Role of AI in Glioma Detection, Grading and Prediction of Genetic Profile
3.1. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
3.2. Radiomics and Radiogenomics
3.3. Limitations
3.3.1. Standardisation Challenges in Image Acquisition
3.3.2. Segmentation and Feature Extraction Variability
3.3.3. Data Scarcity and Single-Omics Analysis
3.3.4. Model Reproducibility and Generalizability
3.3.5. Black Box and Interpretability Concerns
3.3.6. Ethical and Privacy Issues
3.4. Future Directions
3.4.1. Enhanced Standardisation and Multi-Institutional Validation
3.4.2. Advancements in Multi-Omics Integration
3.4.3. Explainable AI and Federated Learning
3.4.4. Integration into Clinical Workflow and Decision Support
4. The Role of MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Glioma Genetic Profile
4.1. IDH
4.2. EGFR
4.3. TERT
4.4. MGMT
4.5. 1p/19q Codeletion
4.6. H3-K27M
4.7. Ki-67
4.8. p53
4.9. ATRX
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gogos, A.J.; Young, J.S.; Pereira, M.P.; Morshed, R.A.; Potts, M.B.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Berger, M.S. Surgical Management of Incidentally Discovered Low-Grade Gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 135, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, T.; Cesselli, D.; Isola, M.; Pauletto, G.; Tomasino, B.; D’Auria, S.; Bagatto, D.; Pegolo, E.; Beltrami, A.P.; di Loreto, C.; et al. Incidental Low-Grade Gliomas: Single-Institution Management Based on Clinical, Surgical, and Molecular Data. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Duffau, H.; Taillandier, L. New Concepts in the Management of Diffuse Low-Grade Glioma: Proposal of a Multistage and Individualized Therapeutic Approach. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, T.; Ng, S.; Young, J.S.; Tomasino, B.; Polano, M.; Ben-Israel, D.; Kelly, J.J.P.; Skrap, M.; Duffau, H.; Berger, M.S. The Benefit of Early Surgery on Overall Survival in Incidental Low-Grade Glioma Patients: A Multicenter Study. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robe, P.A.; Rados, M.; Spliet, W.G.; Hoff, R.G.; Gosselaar, P.; Broekman, M.L.D.; van Zandvoort, M.J.; Seute, T.; Snijders, T.J. Early Surgery Prolongs Professional Activity in IDH Mutant Low-Grade Glioma Patients: A Policy Change Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 851803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Herbet, G.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Duffau, H. Return to Work Following Surgery for Incidental Diffuse Low-Grade Glioma: A Prospective Series With 74 Patients. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 720–729. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Central Nervous System Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022; ISBN 9789283245087. [Google Scholar]
- Martucci, M.; Russo, R.; Schimperna, F.; D’Apolito, G.; Panfili, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Perna, A.; Ferranti, A.M.; Varcasia, G.; Giordano, C.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Primary Adult Brain Tumors: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.-L.; Wei, X.-T. Advanced Diagnosis of Glioma by Using Emerging Magnetic Resonance Sequences. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 694498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Mabray, M.C.; Cha, S. Current Clinical Brain Tumor Imaging. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, H.; Nagashima, H.; Tanaka, K.; Uno, T.; Hashiguchi, M.; Maeyama, M.; Somiya, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Hirose, T.; Itoh, T.; et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Adult Brainstem Glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 139, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armocida, D.; Bianconi, A.; Zancana, G.; Jiang, T.; Pesce, A.; Tartara, F.; Garbossa, D.; Salvati, M.; Santoro, A.; Serra, C.; et al. DTI Fiber-Tracking Parameters Adjacent to Gliomas: The Role of Tract Irregularity Value in Operative Planning, Resection, and Outcome. J. Neurooncol. 2025, 171, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, W.L.; Helfand, A.I.; Swanson, S.J.; Conant, L.L.; Humphries, C.J.; Raghavan, M.; Mueller, W.M.; Busch, R.M.; Allen, L.; Anderson, C.T.; et al. Prediction of Naming Outcome With fMRI Language Lateralization in Left Temporal Epilepsy Surgery. Neurology 2022, 98, e2337–e2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnera, A.; Romano, A.; Moltoni, G.; Ius, T.; Palizzi, S.; Romano, A.; Bagatto, D.; Minniti, G.; Bozzao, A. The Role of Advanced MRI Sequences in the Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Adult Brainstem Gliomas: A Neuroradiological Review. Tomography 2023, 9, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.; Rudie, J.D.; Rauschecker, A.M.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Clarke, J.L.; Solomon, D.A.; Cha, S. Combining Radiomics and Deep Convolutional Neural Network Features from Preoperative MRI for Predicting Clinically Relevant Genetic Biomarkers in Glioblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac060. [Google Scholar]
- Haubold, J.; Hosch, R.; Parmar, V.; Glas, M.; Guberina, N.; Catalano, O.A.; Pierscianek, D.; Wrede, K.; Deuschl, C.; Forsting, M.; et al. Fully Automated MR Based Virtual Biopsy of Cerebral Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, E.; Sanelli, P.C.; Aboian, M.; Payabvash, S. Radiomics: A Primer on Processing Workflow and Analysis. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2022, 43, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cè, M.; Irmici, G.; Foschini, C.; Danesini, G.M.; Falsitta, L.V.; Serio, M.L.; Fontana, A.; Martinenghi, C.; Oliva, G.; Cellina, M. Artificial Intelligence in Brain Tumor Imaging: A Step toward Personalized Medicine. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2673–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, W.; Gasalberti, D.P.; Rayi, A. Low-Grade Gliomas. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, N.; Waldman, A.D. Conventional MRI Evaluation of Gliomas. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, S107–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.H.; Poisson, L.M.; Brat, D.J.; Zhou, Y.; Cooper, L.; Snuderl, M.; Thomas, C.; Franceschi, A.M.; Griffith, B.; Flanders, A.E.; et al. T2-FLAIR Mismatch, an Imaging Biomarker for IDH and 1p/19q Status in Lower-Grade Gliomas: A TCGA/TCIA Project. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6078–6085. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, G.; Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Jiang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. The Sinuous, Wave-like Intratumoral-Wall Sign Is a Sensitive and Specific Radiological Biomarker for Oligodendrogliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4440–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F., Jr.; Hess, C.P.; Phillips, J.J.; Von Morze, C.J.; Yu, J.P.; Chang, S.M.; Nelson, S.J.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; Cha, S. Super-Resolution Track Density Imaging of Glioblastoma: Histopathologic Correlation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, T.; Gempt, J.; Zimmer, C.; Kirschke, J.S.; Sollmann, N. MR Imaging by 3D T1-Weighted Black Blood Sequences May Improve Delineation of Therapy-Naive High-Grade Gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammer, N.N.; Coppenrath, E.; Treitl, K.M.; Kooijman, H.; Dietrich, O.; Saam, T. Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced Modified T1-Weighted 3D TSE Black-Blood and 3D MP-RAGE Sequences for the Detection of Cerebral Metastases and Brain Tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, E.; Shin, D.J.; Jo, S.W.; Yoo, R.-E.; Kang, K.M.; Yun, T.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Sohn, C.-H. Application of 3D Fast Spin-Echo T1 Black-Blood Imaging in the Diagnosis and Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulakbaşı, N.; Paksoy, Y. Advanced Imaging in Adult Diffusely Infiltrating Low-Grade Gliomas. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilario, A.; Hernandez-Lain, A.; Sepulveda, J.M.; Lagares, A.; Perez-Nuñez, A.; Ramos, A. Perfusion MRI Grading Diffuse Gliomas: Impact of Permeability Parameters on Molecular Biomarkers and Survival. Neurocirugia 2019, 30, 11–18. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, J.R.; Provenzale, J.M. MR Perfusion Imaging of the Brain: Techniques and Applications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; van den Bent, M.J.; Nabors, B.; Wen, P.Y.; Schiff, D. Surveillance Imaging Frequency in Adult Patients with Lower-Grade (WHO Grade 2 and 3) Gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrigo, J.M.; Fountain, D.M.; Provenzale, J.M.; Law, E.K.; Kwong, J.S.; Hart, M.G.; Tam, W.W.S. Magnetic Resonance Perfusion for Differentiating Low-Grade from High-Grade Gliomas at First Presentation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD011551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnera, A.; Trasimeni, G.; Romano, A.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Serio, M.; Miscusi, M.; Bozzao, A. Dermoid Cysts of the Asterion: An Unusual Location for Unusual Dermoids, Radiological Findings and Neurosurgical Implications. Tomography 2022, 8, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M. Imaging of Oligodendroglioma. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M. MRI Biomarkers in Neuro-Oncology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk Delgado, A.; De Luca, F.; van Westen, D.; Falk Delgado, A. Arterial Spin Labeling MR Imaging for Differentiation between High- and Low-Grade Glioma-a Meta-Analysis. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L. A Meta-Analysis of Arterial Spin Labelling Perfusion Values for the Prediction of Glioma Grade. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.F.; Delgado, A.F. Discrimination between Glioma Grades II and III Using Dynamic Susceptibility Perfusion MRI: A Meta-Analysis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Park, M.; Joo, B.; Ahn, S.J.; Suh, S.H. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI and Its Applications in Various Central Nervous System Diseases. Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 26, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, M.; Shiroishi, M.S.; Nguyen, T.B.; Saake, M.; Provenzale, J.M.; Enterline, D.; Anzalone, N.; Dörfler, A.; Rovira, A.; Wintermark, M.; et al. Perfusion MRI: The Five Most Frequently Asked Technical Questions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendle, C.; Hempel, J.-M.; Schittenhelm, J.; Skardelly, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Bender, B.; Ernemann, U.; Klose, U. Glioma Grading and Determination of IDH Mutation Status and ATRX Loss by DCE and ASL Perfusion. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2018, 28, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Visconti, E.; Longo, D.; Romano, A.; Tomà, P.; Rossi Espagnet, M.C. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent-Related Toxicities. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Günther, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Lu, H.; MacIntosh, B.J.; Parkes, L.M.; Smits, M.; et al. Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the European Consortium for ASL in Dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, A.; Doniselli, F.; Jäger, H.R.; Panovska-Griffiths, J.; Rojas-Garcia, A.; Golay, X.; Bisdas, S. The Value of Arterial Spin Labelling in Adults Glioma Grading: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Talaat, M.; El-Serougy, L.; Gaballa, G.; Abdelsalam, M. Clinical Applications of Arterial Spin Labeling in Brain Tumors. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2019, 43, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuro, A.; DeAngelis, L.M. Glioblastoma and Other Malignant Gliomas: A Clinical Review. JAMA 2013, 310, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.M.; La, P.L.; Walker, R.; Harris, A.D. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Traumatic Brain Injury and Subconcussive Hits: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2022, 39, 1455–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horská, A.; Barker, P.B. Imaging of Brain Tumors: MR Spectroscopy and Metabolic Imaging. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2010, 20, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzillo, T.C.; Hu, J.; Nguyen, L.; Whiting, N.; Lee, J.; Weygand, J.; Dutta, P.; Pudakalakatti, S.; Millward, N.Z.; Gammon, S.T.; et al. Interrogating Metabolism in Brain Cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 687–703. [Google Scholar]
- Stagg, C.; Rothman, D.L. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Tools for Neuroscience Research and Emerging Clinical Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780124016972. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-Associated IDH1 Mutations Produce 2-Hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, M.E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Patel, J.; Shih, A.; Li, Y.; Bhagwat, N.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Fernandez, H.F.; et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations Result in a Hypermethylation Phenotype, Disrupt TET2 Function, and Impair Hematopoietic Differentiation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.C.; Smith, A.A.; Zheng, S.; Koestler, D.C.; Houseman, E.A.; Marsit, C.J.; Wiemels, J.L.; Nelson, H.H.; Karagas, M.R.; Wrensch, M.R.; et al. DNA Methylation, Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Mutation, and Survival in Glioma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Ganji, S.K.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Rakheja, D.; Kovacs, Z.; Yang, X.-L.; Mashimo, T.; Raisanen, J.M.; Marin-Valencia, I.; et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate Detection by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in IDH-Mutated Patients with Gliomas. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.; Haacke, E.M.; Thurnher, M.M.; Barkhof, F. Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging: Technical Essentials and Clinical Neurologic Applications. Radiology 2021, 299, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Dumrongpisutikul, N.; Intrapiromkul, J.; Yousem, D.M. Detection of Intratumoral Calcification in Oligodendrogliomas by Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.-W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Yao, K.; Fang, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, S.-W. Intratumoral Susceptibility Signals Reflect Biomarker Status in Gliomas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, H.S.; Jahng, G.-H.; Ryu, C.-W.; Park, S.M.; Kim, S.Y. Semiquantitative Assessment of Intratumoral Susceptibility Signals Using Non-Contrast-Enhanced High-Field High-Resolution Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging in Patients with Gliomas: Comparison with MR Perfusion Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabner, G.; Kiesel, B.; Wöhrer, A.; Millesi, M.; Wurzer, A.; Göd, S.; Mallouhi, A.; Knosp, E.; Marosi, C.; Trattnig, S.; et al. Local Image Variance of 7 Tesla SWI Is a New Technique for Preoperative Characterization of Diffusely Infiltrating Gliomas: Correlation with Tumour Grade and IDH1 Mutational Status. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gihr, G.; Horvath-Rizea, D.; Kohlhof-Meinecke, P.; Ganslandt, O.; Henkes, H.; Härtig, W.; Donitza, A.; Skalej, M.; Schob, S. Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Gliomas: A Histogram-Based Approach for Tumor Characterization. Cancers 2022, 14, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.-W.; Xi, Y.-B.; Liu, T.-T.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.-R.; Guo, F. Grading of Glioma: Combined Diagnostic Value of Amide Proton Transfer Weighted, Arterial Spin Labeling and Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauleit, D.; Langen, K.-J.; Floeth, F.; Hautzel, H.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Reifenberger, G.; Shah, N.J.; Müller, H.-W. Can the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Be Used as a Noninvasive Parameter to Distinguish Tumor Tissue from Peritumoral Tissue in Cerebral Gliomas? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, D.; Delmaire, C.; de Champfleur, N.M.; Chiras, J.; Lehéricy, S. Diffusion Tractography: Methods, Validation and Applications in Patients with Neurosurgical Lesions. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 253–268, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollmann, N.; Kelm, A.; Ille, S.; Schröder, A.; Zimmer, C.; Ringel, F.; Meyer, B.; Krieg, S.M. Setup Presentation and Clinical Outcome Analysis of Treating Highly Language-Eloquent Gliomas via Preoperative Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Tractography. Neurosurg. Focus. 2018, 44, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essayed, W.I.; Zhang, F.; Unadkat, P.; Cosgrove, G.R.; Golby, A.J.; O’Donnell, L.J. White Matter Tractography for Neurosurgical Planning: A Topography-Based Review of the Current State of the Art. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 15, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.J.; Gaggl, W.; Gilloon, B.; Swan, B.; Greenstein, M.; Voss, J.; Hussain, N.; Holdsworth, R.L.; Nair, V.A.; Meyerand, M.E.; et al. The Impact of Intracranial Tumor Proximity to White Matter Tracts on Morbidity and Mortality: A Retrospective Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caverzasi, E.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Jordan, K.M.; Lobach, I.V.; Li, J.; Panara, V.; Racine, C.A.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Amirbekian, B.; Papinutto, N.; et al. Identifying Preoperative Language Tracts and Predicting Postoperative Functional Recovery Using HARDI Q-Ball Fiber Tractography in Patients with Gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altabella, L.; Broggi, S.; Mangili, P.; Conte, G.M.; Pieri, V.; Iadanza, A.; Del Vecchio, A.; Anzalone, N.; di Muzio, N.; Calandrino, R.; et al. Integration of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Tractography into Tomotherapy Radiation Treatment Planning for High-Grade Gliomas. Phys. Med. 2018, 55, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ius, T.; Somma, T.; Baiano, C.; Guarracino, I.; Pauletto, G.; Nilo, A.; Maieron, M.; Palese, F.; Skrap, M.; Tomasino, B. Risk Assessment by Pre-Surgical Tractography in Left Hemisphere Low-Grade Gliomas. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 648432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xiao, C.-Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yin, X. Analysis of DTI-Derived Tensor Metrics in Differential Diagnosis between Low-Grade and High-Grade Gliomas. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serougy, L.; Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Ezzat, A.; Eldawoody, H.; El-Morsy, A. Assessment of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Metrics in Differentiating Low-Grade from High-Grade Gliomas. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, T.; Rozovski, U.; Marko, N.F.; Tummala, S.; Ziu, M.; Weinberg, J.S.; Rao, G.; Kumar, V.A.; Sawaya, R.; Prabhu, S.S. Preoperative Imaging to Predict Intraoperative Changes in Tumor-to-Corticospinal Tract Distance: An Analysis of 45 Cases Using High-Field Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-L.; van der Hoorn, A.; Larkin, T.J.; Boonzaier, N.R.; Matys, T.; Price, S.J. Extent of Resection of Peritumoral Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Detected Abnormality as a Predictor of Survival in Adult Glioblastoma Patients. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoli, M.; Talozzi, L.; Martinoni, M.; Manners, D.N.; Badaloni, F.; Testa, C.; Asioli, S.; Mitolo, M.; Bartiromo, F.; Rochat, M.J.; et al. From Neurosurgical Planning to Histopathological Brain Tumor Characterization: Potentialities of Arcuate Fasciculus Along-Tract Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography Measures. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 633209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, M.; Ius, T.; Skrap, M.; Fadiga, L. Alterations in Fiber Pathways Reveal Brain Tumor Typology: A Diffusion Tractography Study. PeerJ 2014, 2, e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassal, F.; Schneider, F.; Nuti, C. Intraoperative Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Based Tractography for Resection of Gliomas Located near the Pyramidal Tract: Comparison with Subcortical Stimulation Mapping and Contribution to Surgical Outcomes. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 27, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Familiari, P.; Di Lauro, A.; Angelini, A.; Sessa, G. Safe Resection of Gliomas of the Dominant Angular Gyrus Availing of Preoperative FMRI and Intraoperative DTI: Preliminary Series and Surgical Technique. World Neurosurg. 2016, 87, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparacia, G.; Parla, G.; Lo Re, V.; Cannella, R.; Mamone, G.; Carollo, V.; Midiri, M.; Grasso, G. Resting-State Functional Connectome in Patients with Brain Tumors Before and After Surgical Resection. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e182–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwali, H.; Samii, A. Seed-Based Connectivity Analysis of Resting-State fMRI in Patients with Brain Tumors: A Feasibility Study. World Neurosurg. 2019, 128, e165–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristo, G.; Rutten, G.-J.; Raemaekers, M.; de Gelder, B.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B.; Ramsey, N.F. Task and Task-Free FMRI Reproducibility Comparison for Motor Network Identification. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, C.J.; Fan, A.P. BOLD Signal Physiology: Models and Applications. Neuroimage 2019, 187, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, T.N.; Andreoli, M.J.; Nair, V.A.; Yin, P.; Young, B.M.; Kundu, B.; Pankratz, J.; Radtke, A.; Holdsworth, R.; Kuo, J.S.; et al. Usage of fMRI for Pre-Surgical Planning in Brain Tumor and Vascular Lesion Patients: Task and Statistical Threshold Effects on Language Lateralization. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 7, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Olson, J.; Ali, S.; Fan, T.; Mao, H. Re-Examine Tumor-Induced Alterations in Hemodynamic Responses of BOLD fMRI: Implications in Presurgical Brain Mapping. Acta Radiol. 2012, 53, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.L.; Bradbury, M.; Peck, K.K.; Petrovich, N.M.; Gutin, P.H.; Holodny, A.I. Effect of Brain Tumor Neovasculature Defined by rCBV on BOLD fMRI Activation Volume in the Primary Motor Cortex. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, P.R.; Reitsma, J.B.; Houweling, B.M.; Ferrier, C.H.; Ramsey, N.F. Can fMRI Safely Replace the Wada Test for Preoperative Assessment of Language Lateralisation? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, C.; Brennan, N.; Peck, K.K.; Holodny, A.I. Preoperative Functional MRI of Motor and Sensory Cortices: How Imaging Can Save Vital Functions. Imaging Med. 2012, 4, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.F.; Clark, A.; Smith, J.S.; Polley, M.-Y.; Chang, S.M.; Barbaro, N.M.; Parsa, A.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S. Functional Mapping-Guided Resection of Low-Grade Gliomas in Eloquent Areas of the Brain: Improvement of Long-Term Survival. Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengenroth, M.; Blatow, M.; Guenther, J.; Akbar, M.; Tronnier, V.M.; Stippich, C. Diagnostic Benefits of Presurgical fMRI in Patients with Brain Tumours in the Primary Sensorimotor Cortex. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakasu, S.; Nakasu, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Fukami, T.; Nitta, N.; Kawano, H.; Notsu, A.; Nozaki, K. Incidental Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Treatment Results with Correction of Lead-Time and Length-Time Biases. Neurooncol. Pract. 2023, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Chandra, P.S.; Sharma, B.S.; Garg, A.; Rath, G.K.; Bithal, P.K.; Tripathi, M. The Role of Neuronavigation-Guided Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Tractography along with Cortical Stimulation in Patients with Eloquent Cortex Lesions. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 28, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiser, R.; Staempfli, P.; Valavanis, A.; Boesiger, P.; Kollias, S. Impact of fMRI-Guided Advanced DTI Fiber Tracking Techniques on Their Clinical Applications in Patients with Brain Tumors. Neuroradiology 2010, 52, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudie, J.D.; Rauschecker, A.M.; Bryan, R.N.; Davatzikos, C.; Mohan, S. Emerging Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neuro-Oncology. Radiology 2019, 290, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidey-Gibbons, J.A.M.; Sidey-Gibbons, C.J. Machine Learning in Medicine: A Practical Introduction. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, K.C.; Das, N.; Ghosh, S. Deep Learning Models for Medical Imaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9780128236505. [Google Scholar]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, P.; Franceschi, E.; Vollmuth, P.; Dhermain, F.; Weller, M.; Preusser, M.; Smits, M.; Galldiks, N. Radiomics in Neuro-Oncological Clinical Trials. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e841–e849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Luo, Y.; Gu, F.; Tian, B.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, G.; Nie, X.; Yu, J.; Tong, J.; Liao, X. Artificial Intelligence-Based MRI Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Glioma. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Fan, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; et al. Radiogenomics of Lower-Grade Gliomas: A Radiomic Signature as a Biological Surrogate for Survival Prediction. Aging 2018, 10, 2884–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.K.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, D.J.; Jo, S.W.; Yoo, R.-E.; Kang, K.M.; Yun, T.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Sohn, C.-H.; Park, S.-H.; et al. Radiogenomics Correlation between MR Imaging Features and Major Genetic Profiles in Glioblastoma. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4350–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarch, C.; Ribas, V.; Vellido, A. AI-Based Glioma Grading for a Trustworthy Diagnosis: An Analytical Pipeline for Improved Reliability. Cancers 2023, 15, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hu, L.; Lu, Q.; Xiao, F.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Lu, L. A Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Brain Tumors Based on Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1120781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Yan, L.-F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.-C.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.-C.; Nan, H.-Y.; Sun, Q.; Sun, Y.-Z.; et al. Radiomics Strategy for Glioma Grading Using Texture Features from Multiparametric MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogen, K.; Schulz, A.; Dormagen, J.B.; Ganeshan, B.; Helseth, E.; Server, A. Diagnostic Performance of Texture Analysis on MRI in Grading Cerebral Gliomas. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Kang, H.; Xue, W.; Tong, H.; Cao, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Textural Features of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Derived Model-Free and Model-Based Parameter Maps in Glioma Grading. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Alksas, A.; Shehata, M.; AbdelKhalek, A.; Abdel Baky, K.; El-Baz, A.; Helmy, E. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics in Neuro-Oncology Imaging. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shboul, Z.A.; Chen, J.; Iftekharuddin, K.M. Prediction of Molecular Mutations in Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas Using MR Imaging Features. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, K.; Qian, Z.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. MRI Features Can Predict EGFR Expression in Lower Grade Gliomas: A Voxel-Based Radiomic Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Shan, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, R.; Cai, J.; Li, H.; Chan, W.S.; Liu, P.; Yi, L.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Model for Brain Tumor Diagnosis and Classification Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2225608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltyn-Dumitru, M.; Schell, M.; Rastogi, A.; Sahm, F.; Kessler, T.; Wick, W.; Bendszus, M.; Brugnara, G.; Vollmuth, P. Impact of Signal Intensity Normalization of MRI on the Generalizability of Radiomic-Based Prediction of Molecular Glioma Subtypes. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Radiomics in Glioma: Emerging Trends and Challenges. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2025, 12, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Hajianfar, G.; Hall, B.; Servaes, S.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Ghafarian, P.; Zaidi, H.; Ay, M.R. Robust vs. Non-Robust Radiomic Features: The Quest for Optimal Machine Learning Models Using Phantom and Clinical Studies. Cancer Imaging 2025, 25, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lam, S.; Li, W.; Xiao, H.; Li, T.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; et al. Improving Radiomic Model Reliability Using Robust Features from Perturbations for Head-and-Neck Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 974467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, A.B.; Aalam, S.W.; Masoodi, T.A.; Shah, A.; Khan, M.A.; Bhat, A.A.; Assad, A.; Macha, M.A.; Bhat, M.R. Radiogenomics and Machine Learning Predict Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in Glioblastoma. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, K.; Topatana, W.; Li, S.; Wei, C.; Chen, T.; Chen, M.; Ding, Z.; Niu, G. Applications of Artificial Intelligence Based on Medical Imaging in Glioma: Current State and Future Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 892056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. The Clinical Implications and Interpretability of Computational Medical Imaging (radiomics) in Brain Tumors. Insights Imaging 2025, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rončević, A.; Koruga, N.; Soldo Koruga, A.; Rončević, R. Artificial Intelligence in Glioblastoma-Transforming Diagnosis and Treatment. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2025, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herington, J.; McCradden, M.D.; Creel, K.; Boellaard, R.; Jones, E.C.; Jha, A.K.; Rahmim, A.; Scott, P.J.H.; Sunderland, J.J.; Wahl, R.L.; et al. Ethical Considerations for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging: Data Collection, Development, and Evaluation. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrazabal, A.J.; Nieto, N.; Peterson, V.; Milone, D.H.; Ferrante, E. Gender Imbalance in Medical Imaging Datasets Produces Biased Classifiers for Computer-Aided Diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12592–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Kucharczyk, M.J.; Daniel, P.; Sabri, S.; Jean-Claude, B.J.; Niazi, T.; Abdulkarim, B. Radiomics in Glioblastoma: Current Status and Challenges Facing Clinical Implementation. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Holloway, L.; Metcalfe, P.; Koh, E.-S.; Brighi, C. Challenges in Glioblastoma Radiomics and the Path to Clinical Implementation. Cancers 2022, 14, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Q.; Cai, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Modal Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Grading Analysis for Gliomas by Integrating Radiomics and Deep Features. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedhia, M.; Germano, I.M. The Evolving Landscape of Radiomics in Gliomas: Insights into Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Research Trends. Cancers 2025, 17, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, Q.-U.-A.; Latif, S.; Brohi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Alqhatani, A.; Alshehri, M.S.; Al Mazroa, A.; Ullah, R. Explainable AI in Medical Imaging: An Interpretable and Collaborative Federated Learning Model for Brain Tumor Classification. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1535478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Guleria, K.; Dogra, A.; Gupta, D.; Juneja, S.; Kumari, S.; Nauman, A. A Privacy-Preserved Horizontal Federated Learning for Malignant Glioma Tumour Detection Using Distributed Data-Silos. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0316543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awuah, W.A.; Ben-Jaafar, A.; Roy, S.; Nkrumah-Boateng, P.A.; Tan, J.K.; Abdul-Rahman, T.; Atallah, O. Predicting Survival in Malignant Glioma Using Artificial Intelligence. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderich, D.M.; Weisstanner, C.; Van Cauter, S.; Federau, C.; Edjlali, M.; Radbruch, A.; Gerke, S.; Haller, S. Artificial Intelligence Tools in Clinical Neuroradiology: Essential Medico-Legal Aspects. Neuroradiology 2023, 65, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, X.; Li, H. Perfusion Parameters Derived from MRI for Preoperative Prediction of IDH Mutation and MGMT Promoter Methylation Status in Glioblastomas. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 83, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpo, V.; Guida, L.; Bellomo, J.; Van Niftrik, C.H.B.; Sebök, M.; Berhouma, M.; Bink, A.; Weller, M.; Kulcsar, Z.; Regli, L.; et al. Hemodynamic Imaging in Cerebral Diffuse Glioma-Part B: Molecular Correlates, Treatment Effect Monitoring, Prognosis, and Future Directions. Cancers 2022, 14, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Yang, X.; She, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D. Noninvasive Assessment of Mutational Status in World Health Organization Grade II and III Astrocytomas Using DWI and DSC-PWI Combined with Conventional MR Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.K.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, D.J.; Jo, S.W.; Yoo, R.E.; Kang, K.M.; Yun, T.J.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, C.H.; Park, S.H.; et al. Comparison of Genetic Profiles and Prognosis of High-Grade Gliomas Using Quantitative and Qualitative MRI Features: A Focus on G3 Gliomas. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.M.; Altabella, L.; Castellano, A.; Cuccarini, V.; Bizzi, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Costa, A.; Caulo, M.; Falini, A.; Anzalone, N. Comparison of T1 Mapping and Fixed T1 Method for Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Perfusion in Brain Gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-W.; Lyu, G.-W.; He, W.-J.; Lei, Y.; Lin, F.; Wang, M.-Z.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.-H.; Feng, Y.-N.; Yang, J.-H. DSC and DCE Histogram Analyses of Glioma Biomarkers, Including IDH, MGMT, and TERT, on Differentiation and Survival. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, e263–e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.-E.; Yun, T.J.; Hwang, I.; Hong, E.K.; Kang, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.-K.; Won, J.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Sohn, C.-H. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion-Weighted Imaging Aids in Prediction of Molecular Biomarkers and Survival in Glioblastomas. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Cheng, G.; Kang, X.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, C.; Ye, J.; Li, P.; Yin, H. Noninvasively Evaluating the Grading and IDH1 Mutation Status of Diffuse Gliomas by Three-Dimensional Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Hiwatashi, A.; Togao, O.; Kikuchi, K.; Hatae, R.; Yoshimoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; Suzuki, S.O.; Yoshiura, T.; Honda, H. MR Imaging-Based Analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme: Estimation of IDH1 Mutation Status. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paech, D.; Windschuh, J.; Oberhollenzer, J.; Dreher, C.; Sahm, F.; Meissner, J.-E.; Goerke, S.; Schuenke, P.; Zaiss, M.; Regnery, S.; et al. Assessing the Predictability of IDH Mutation and MGMT Methylation Status in Glioma Patients Using Relaxation-Compensated Multipool CEST MRI at 7.0 T. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zijl, P.C.M.; Yadav, N.N. Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST): What Is in a Name and What Isn’t? Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zou, T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Villalobos, M.A.V.; Heo, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Du, Y.; et al. Predicting IDH Mutation Status in Grade II Gliomas Using Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted (APTw) MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thust, S.C.; Hassanein, S.; Bisdas, S.; Rees, J.H.; Hyare, H.; Maynard, J.A.; Brandner, S.; Tur, C.; Jäger, H.R.; Yousry, T.A.; et al. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Molecular Subtyping of Non-Gadolinium-Enhancing WHO Grade II/III Glioma: Volumetric Segmentation versus Two-Dimensional Region of Interest Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Tagliente, E.; Dellepiane, F.; Lucignani, M.; Vidiri, A.; Ranazzi, G.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Moltoni, G.; Nicolai, M.; et al. Deep Learning Can Differentiate IDH-Mutant from IDH-Wild GBM. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Grinband, J.; Weinberg, B.D.; Bardis, M.; Khy, M.; Cadena, G.; Su, M.-Y.; Cha, S.; Filippi, C.G.; Bota, D.; et al. Deep-Learning Convolutional Neural Networks Accurately Classify Genetic Mutations in Gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Ahn, S.S.; Park, C.J.; Han, K.; Kim, E.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.-K. Diffusion and Perfusion MRI May Predict EGFR Amplification and the TERT Promoter Mutation Status of IDH-Wildtype Lower-Grade Gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6475–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Perez, J.; Thomas, A.A.; Kaley, T.; Lyo, J.; Peck, K.K.; Holodny, A.I.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Young, R.J. T1-Weighted Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor vIII Status. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykocinski, E.S.; Grant, R.A.; Kapoor, G.S.; Krejza, J.; Bohman, L.-E.; Gocke, T.A.; Chawla, S.; Halpern, C.H.; Lopinto, J.; Melhem, E.R.; et al. Use of Magnetic Perfusion-Weighted Imaging to Determine Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III Expression in Glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.J.; Ellingson, B.M.; Kim, H.J.; Wang, D.J.J.; Salamon, N.; Linetsky, M.; Sepahdari, A.R.; Jiang, B.; Tian, J.J.; Esswein, S.R.; et al. Arterial Spin-Labeling Perfusion MRI Stratifies Progression-Free Survival and Correlates with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Status in Glioblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J.; Gupta, A.; Shah, A.D.; Graber, J.J.; Schweitzer, A.D.; Prager, A.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huse, J.; Omuro, A.M.P. Potential Role of Preoperative Conventional MRI Including Diffusion Measurements in Assessing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Amplification Status in Patients with Glioblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Vargas, O.; Ho, M.; Hogshead, M.H.; Papenberg, B.W.; Lee, C.-H.; Forsythe, K.; Jones, K.; Luo, W.; Teshome, K.; Blauwendraat, C.; et al. Genetic Regulation of TERT Splicing Affects Cancer Risk by Altering Cellular Longevity and Replicative Potential. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, F.; Perez Bercoff, D. The Play of Promoter Mutations. Cells 2020, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Xu, G. Noninvasive Prediction of TERT Promoter Mutations in High-Grade Glioma by Radiomics Analysis Based on Multiparameter MRI. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3872314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Yu, Y.; Grimmer, M.R.; Wahl, M.; Chang, S.M.; Costello, J.F. Temozolomide-Associated Hypermutation in Gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.; Ravi, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Chang, S.; Oberheim Bush, N.; Taylor, J.; Clarke, J.; Solomon, D.; Scheffler, A.; Witte, J.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Promoter Methylation in Glioblastoma Suggests Nonlinear Prognostic Effect. Neurooncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, S.; Pearson, D.M.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Malley, D.S.; Smith, C.M.; Weaver, J.M.J.; Jones, D.T.W.; Kocialkowski, S.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Collins, V.P.; et al. MGMT CpG Island Is Invariably Methylated in Adult Astrocytic and Oligodendroglial Tumors with IDH1 or IDH2 Mutations. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, K.; Soylu, E.; Cayci, Z. Correlation between Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion MRI and Genomic Alterations in Glioblastoma. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindil, E.; Sendur, H.N.; Cerit, M.N.; Erdogan, N.; Celebi, F.; Dag, N.; Celtikci, E.; Inan, A.; Oner, Y.; Tali, T. Prediction of IDH Mutation Status in High-Grade Gliomas Using DWI and High T1-Weight DSC-MRI. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29 (Suppl. S3), S52–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Rui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Heo, H.-Y.; Zou, T.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Wen, X.; et al. Discriminating MGMT Promoter Methylation Status in Patients with Glioblastoma Employing Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MRI Metrics. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle-Thiele, D.; Day, B.; Stringer, B.; Fay, M.; Martin, J.; Jeffree, R.L.; Thomas, P.; Bell, C.; Salvado, O.; Gal, Y.; et al. Using the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient to Identifying MGMT Promoter Methylation Status Early in Glioblastoma: Importance of Analytical Method. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2015, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunwoo, L.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, J.W.; Yi, K.S.; Lee, W.J.; Yoon, T.J.; Song, S.W.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Correlation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values Measured by Diffusion MRI and MGMT Promoter Methylation Semiquantitatively Analyzed with MS-MLPA in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Shan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Dong, C.; Zhao, G.; Lu, J. Static F-FET PET and DSC-PWI Based on Hybrid PET/MR for the Prediction of Gliomas Defined by IDH and 1p/19q Status. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latysheva, A.; Emblem, K.E.; Brandal, P.; Vik-Mo, E.O.; Pahnke, J.; Røysland, K.; Hald, J.K.; Server, A. Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Diffusion MR Imaging Identify Oligodendroglioma as Defined by the 2016 WHO Classification for Brain Tumors: Histogram Analysis Approach. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, L.; Choi, S.H.; Yoo, R.-E.; Kang, K.M.; Yun, T.J.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-W.; et al. Paradoxical Perfusion Metrics of High-Grade Gliomas with an Oligodendroglioma Component: Quantitative Analysis of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion MR Imaging. Neuroradiology 2015, 57, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Ahn, K.J.; Lee, S.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, H.S.; Jung, S.L.; Kim, B.S.; Jeun, S.S.; Hong, Y.K. Differential Diagnosis of Oligodendroglial and Astrocytic Tumors Using Imaging Results: The Added Value of Perfusion MR Imaging. Neuroradiology 2017, 59, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ahn, K.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Jang, J.H.; Jung, S.L.; Kim, B.S. Differentiation of Grade II and III Oligodendrogliomas from Grade II and III Astrocytomas: A Histogram Analysis of Perfusion Parameters Derived from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE) and Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) MRI. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, W.; He, H.; Yang, Y.; Wen, G.; Lv, X. Noninvasive Assessment of H3 K27M Mutational Status in Diffuse Midline Gliomas by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Measurements. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Qu, L.; Sun, T.; Duan, Y.; Wu, M.; Weng, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Deep Learning for Noninvasive Assessment of H3 K27M Mutation Status in Diffuse Midline Gliomas Using MR Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.; Nahar, N.; Hau, E.; Varikatt, W.; Gebski, V.; Ng, T.; Jayamohan, J.; Sundaresan, P. Cut-Point for Ki-67 Proliferation Index as a Prognostic Marker for Glioblastoma. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 15, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Tong, D.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yuan, T.-T.; Yan, Y.-Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, R. Correlation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Ki-67 in the Diagnosis of Gliomas. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2012, 34, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Batalov, A.I.; Zakharova, N.E.; Chekhonin, I.V.; Pogosbekyan, E.L.; Sudarikova, A.V.; Goryainov, S.A.; Shulgina, A.A.; Belyaev, A.Y.; Usachev, D.Y.; Pronin, I.N. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion in Determining the IDH1 Status and Ki-67 Index in Brain Gliomas. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, K. Noninvasive Assessment of Ki-67 Labeling Index in Glioma Patients Based on Multi-Parameters Derived from Advanced MR Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1362990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Jiang, B.; Shi, F.; Ling, C.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J. 3D Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin-Labeling MR Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Schneider, F.; Vaupel, P.; Sommer, C.; Schmidberger, H. Differential Expression of HIF-1 in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Anaplastic Astrocytoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.M.; Judy, K.D.; Dunphy, I.; Jenkins, W.T.; Hwang, W.-T.; Nelson, P.T.; Lustig, R.A.; Jenkins, K.; Magarelli, D.P.; Hahn, S.M.; et al. Hypoxia Is Important in the Biology and Aggression of Human Glial Brain Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8177–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Pang, P.; Lou, L.; Feng, Q.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, J. Radiomic Prediction Models for the Level of Ki-67 and p53 in Glioma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520914466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J.; Xu, K.; Shen, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Radiomics Based on Multicontrast MRI Can Precisely Differentiate among Glioma Subtypes and Predict Tumour-Proliferative Behaviour. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surget, S.; Khoury, M.P.; Bourdon, J.-C. Uncovering the Role of p53 Splice Variants in Human Malignancy: A Clinical Perspective. Onco Targets Ther. 2013, 7, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Ju, H.; Dou, C. A Study on the Correlation between STAT-1 and Mutant p53 Expression in Glioma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7807–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. MRI Features Predict p53 Status in Lower-Grade Gliomas via a Machine-Learning Approach. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 17, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiestler, B.; Capper, D.; Holland-Letz, T.; Korshunov, A.; von Deimling, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Platten, M.; Weller, M.; Wick, W. ATRX Loss Refines the Classification of Anaplastic Gliomas and Identifies a Subgroup of IDH Mutant Astrocytic Tumors with Better Prognosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Skardelly, M.; Bonzheim, I.; Ott, I.; Mühleisen, H.; Eckert, F.; Tabatabai, G.; Schittenhelm, J. ATRX Immunostaining Predicts IDH and H3F3A Status in Gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeper, H.E.; Caron, A.A.; Decker, P.A.; Jenkins, R.B.; Lachance, D.H.; Giannini, C. IDH Mutation, 1p19q Codeletion and ATRX Loss in WHO Grade II Gliomas. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30295–30305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, Z.; Sun, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Genotype Prediction of ATRX Mutation in Lower-Grade Gliomas Using an MRI Radiomics Signature. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2960–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
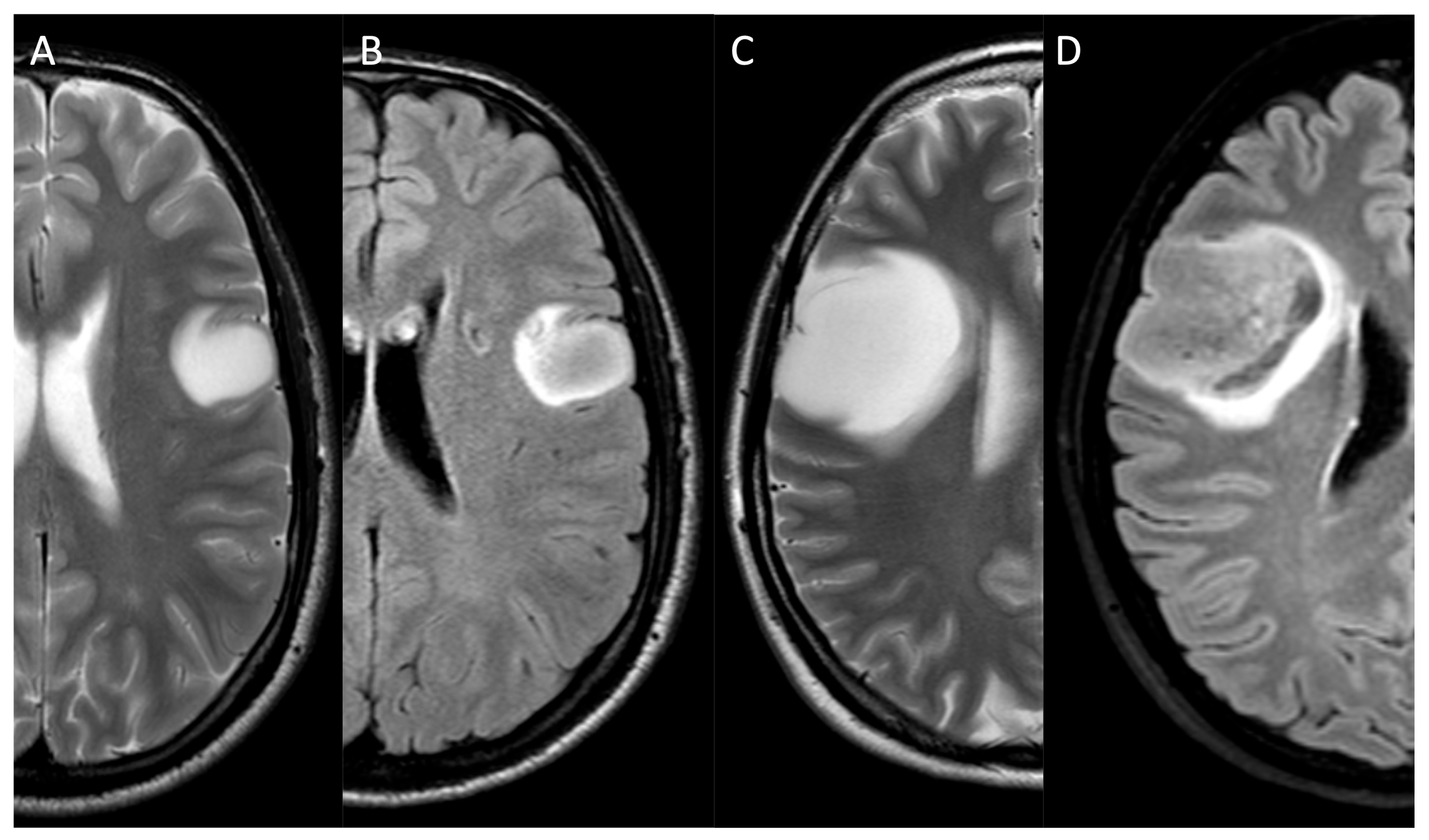
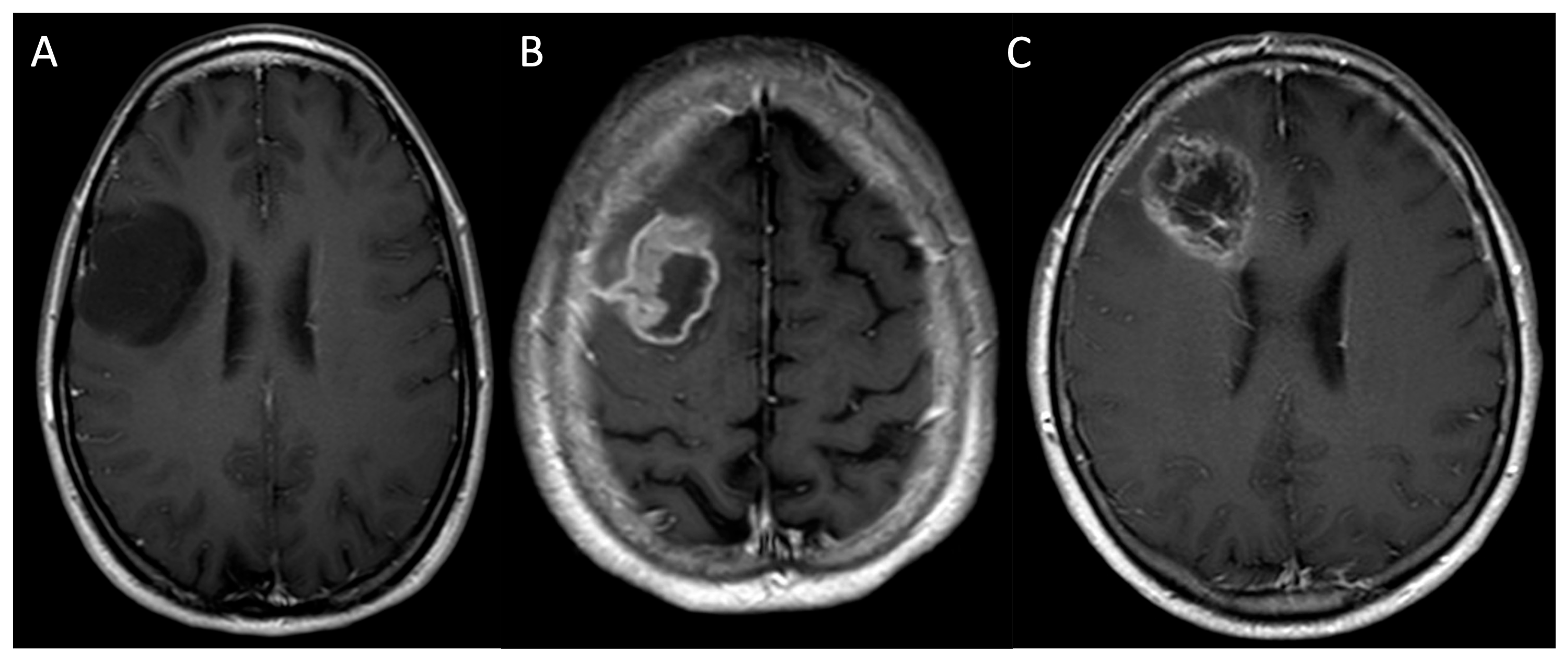
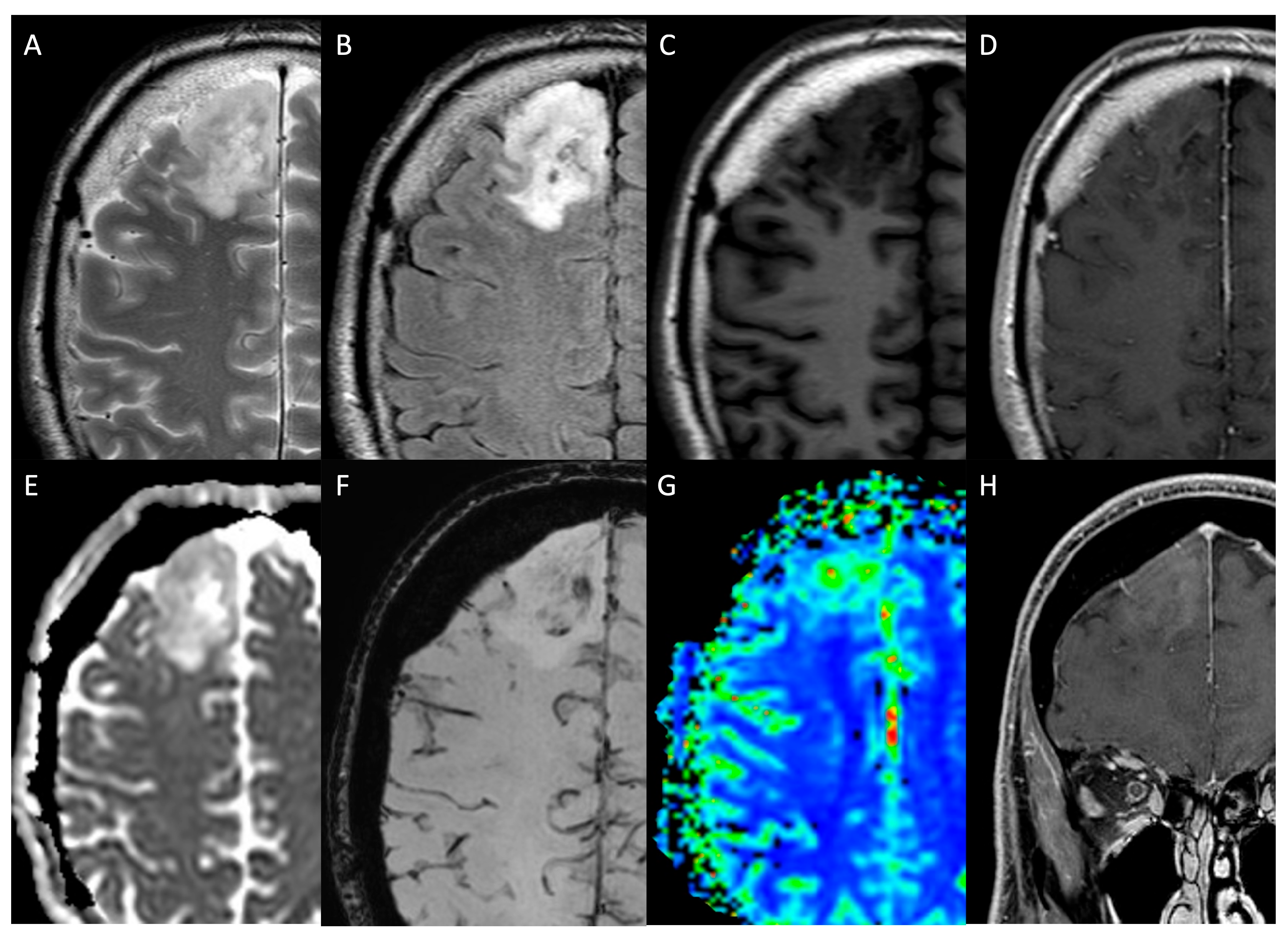

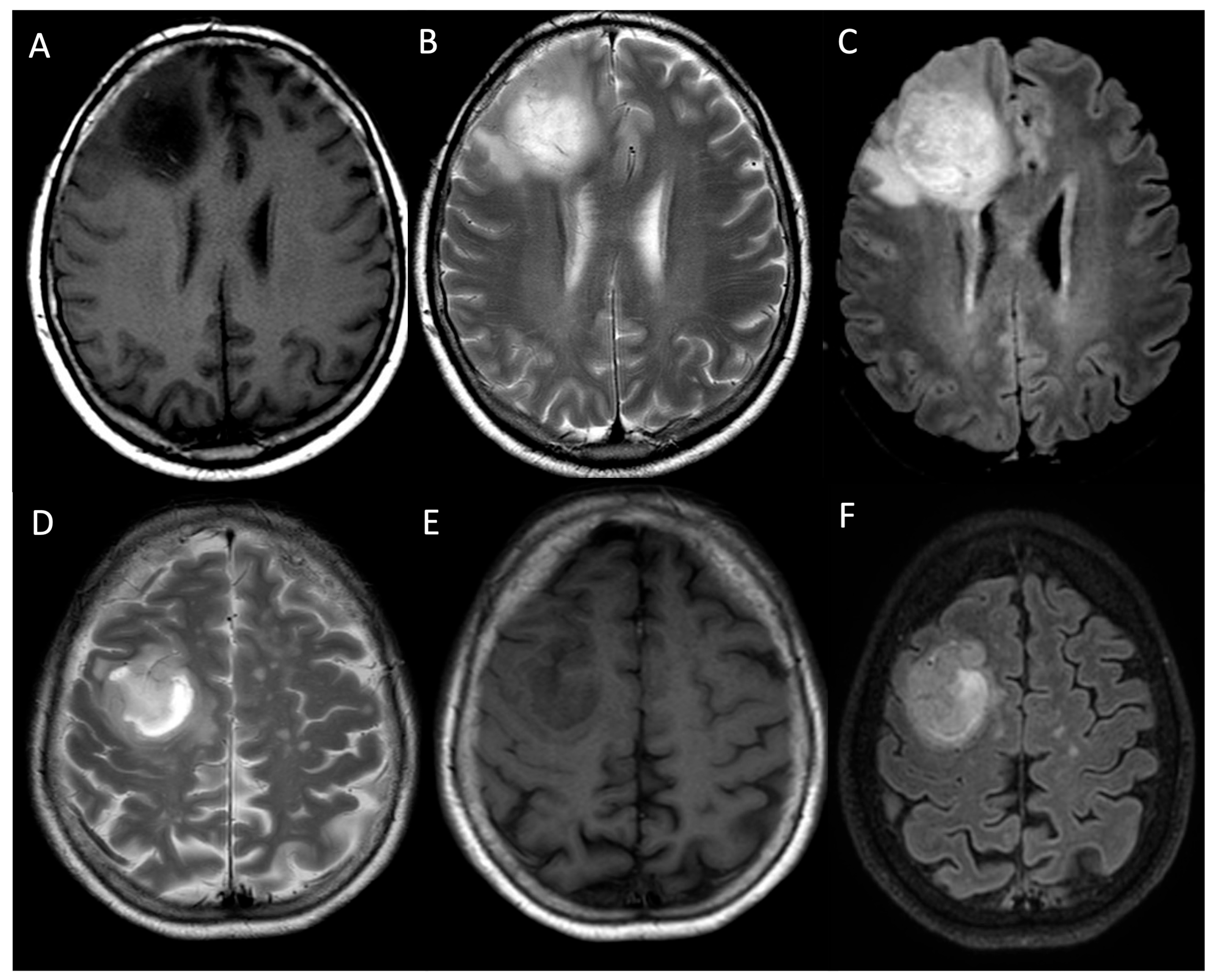
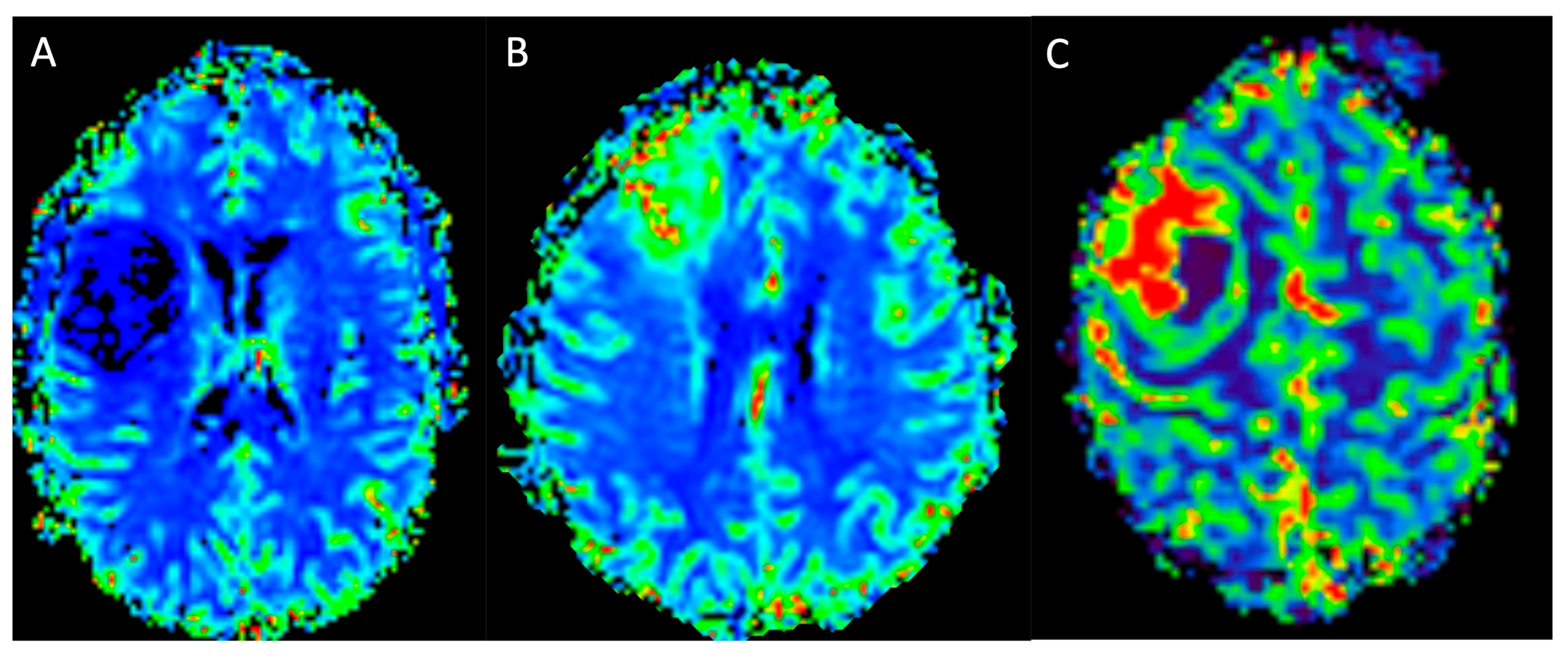
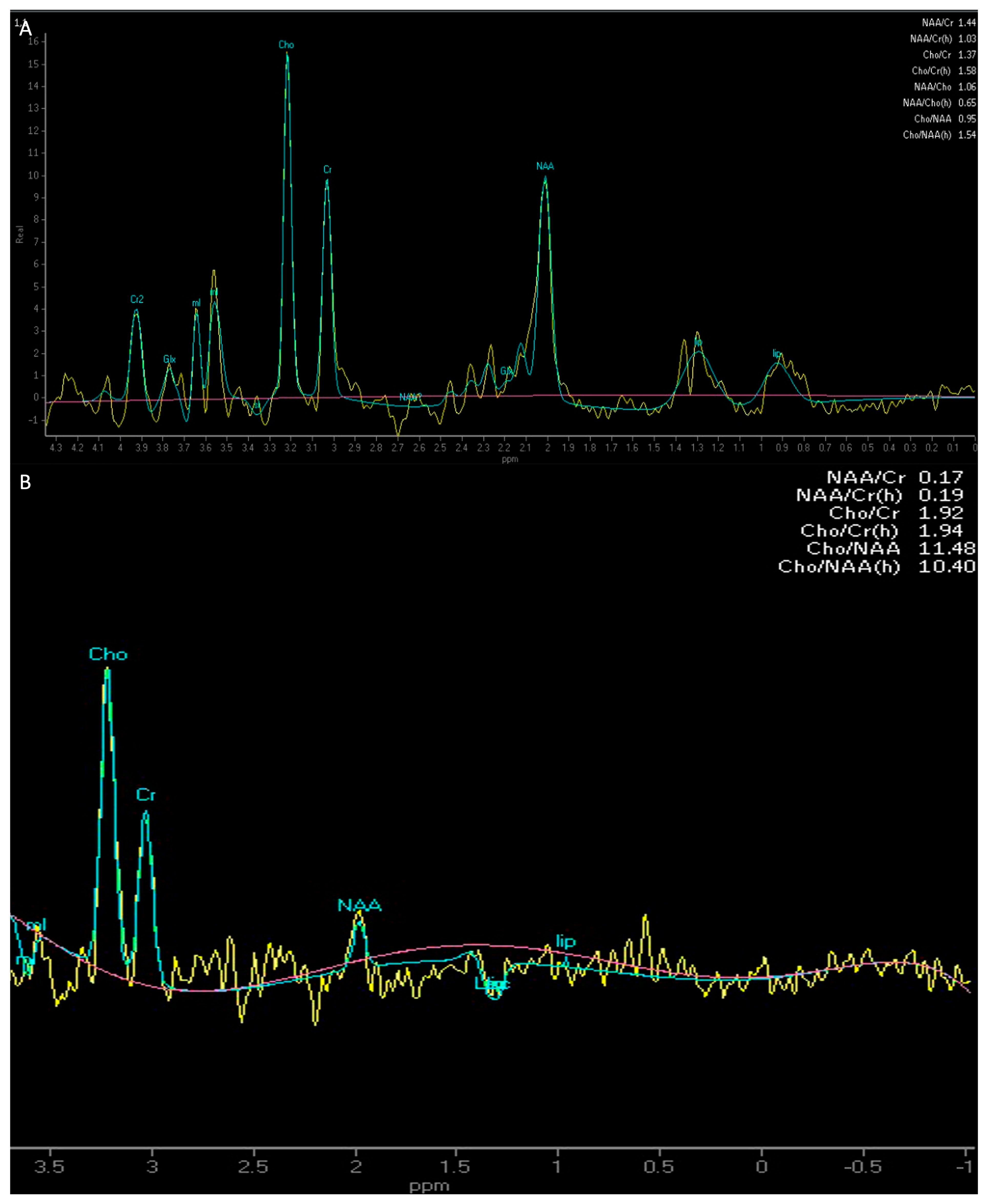
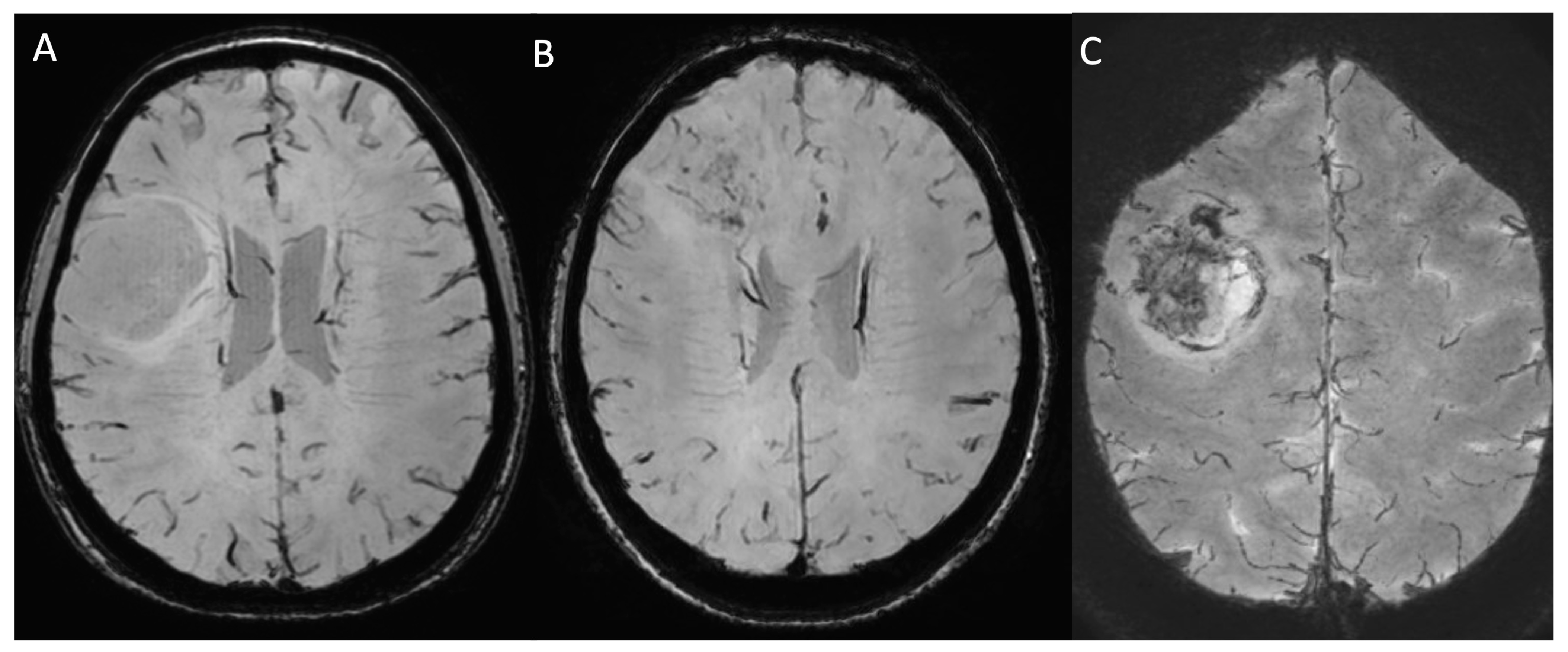



| MRI Protocol | |
|---|---|
| Scanner | 1.5T or 3T |
| Brain Coil | 32- or 64-channel head coil |
| Sequences | |
| Pre-contrast | Parameters |
| Axial TSE T2WI | TR 3000 ms, TE 89 ms, ST 4 mm |
| (Axial or) 3D FLAIR | TR 4600 ms, TE 328 ms, ST 1 mm—isotropic voxel |
| Axial T1WI SE (optional) | TR 8600 ms, TE 10 ms, ST 4 mm |
| SWI | TR 49 ms, TE 40 ms, FA 15°, ST 2 mm |
| Axial DWI | TR 3150 ms, TE 47 ms, FA 75°, ST 4 mm, b0-500–1000 |
| (32- or) 64-direction axial DTI | TR 8869 ms, TE 73 ms, ST 2.10 mm |
| Sagittal 3D T1 IR | TR 8.2 ms, TE 3.8 ms, ST 1 mm—isotropic voxel |
| MRS | SV PRESS (TR 2000 ms, TE 144 ms, voxel 20 × 20 × 20) |
| Post-contrast | Parameters |
| Sagittal 3D T1 IR | TR 8.2 ms, TE 3.8 ms, ST 1 mm—isotropic voxel |
| Axial T1WI SE (optional) | TR 8600 ms, TE 10 ms, ST 4 mm |
| PWI | * DSC (TR 1500 ms, TE 40 ms, FA: 60°, ST 4 mm, FOV 24–26 cm, bandwidth 250 kHz—scan time 90 s) * DCE (TR 4.5 ms, TE 1.6 ms, FA 12°, ST 2.20 mm, FOV 24–26 cm, bandwidth 41.67 kHz—scan time 8 min) * ASL (3D-PseudoContinuous ASL: LD 1800 ms, PLD 2025 ms, SI 8; PPS: 512, ST 4.0 mm, FOV 24–26 cm; IPR 3.64–4.53 mm2, bandwidth 62.5 kHz, TE 10.9 ms, TR 4840 ms—scan time 4–5 min)—no contrast administration |
| Task-Based fMRI | The patient usually performs 4 runs of 1 task each: 2 motor tasks and 2 language tasks organized in a box car paradigm (6 baseline and 6 activation periods; 15 s on, 15 s off). The neuroradiologist indicate the motor tasks to the patient, who performs repetitive clenching movements of the hands (in one run) and feet (in the second run). The language tasks consist of silently name objects (in one run) hand actions (in a second run). Stimuli are taken from the object and action naming of the BADA (Battery for the assessment of aphasic disorders). fMRI analysis is performed on the subject’s data using the FMRIB Software Library. |
| Genetic Biomarker | IDH | EGFR | TERT | MGMT | 1p/19q | H3-K27M | Ki-67 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Role | Regulates angiogenesis | Regulates angiogenesis | Promoter of a component of the enzyme telomerase | Removes the methyl group added to DNA by temozolomide | Typical codeletion of oligodendrogliomas | Biomarker of paediatric diffuse midline gliomas | Reflects human cell proliferation (low values) |
| Mutation | Downregulation of HIF-1α and neoangiogenesis | Amplification favours tumour neoangiogenesis and accelerates proangiogenetic growth factors | Mutation enhances telomerase activity causing alteration of cell longevity and replicative potential | Methylation decreases MGMT promoter activity, improves response to temozolomide and patients’ overall survival | Typical codeletion of oligodendrogliomas | Aggressive growth patterns and resistance to therapy | High values of Ki-67 |
| PWI | DSC: Decreased rCBV DCE: decreased Ktrans, vp, ve ASL: increased TBF, nTBG | DSC: Increased rCBV DCE: increased Ktrans, vp ASL: increased CBF | DSC: Increased rCBV DCE: increased ve | DSC: Decreased rCBV DCE: decreased ve ASL: increased CBF | DSC: Increased rCBV in OG3 vs. IDH-mutant gliomas, and decreased rCBV in OG3 vs. IDH-wt gliomas DCE: decreased Ktrans and ve as vs. HGGs | _ | ASL: increased/decreased TBF |
| MRS | Increased 2HG | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| CEST—APT | Lower APT signal | _ | _ | Lower APT signal | _ | _ | _ |
| SWI | Lower ITSS score, Lower LIV | _ | _ | Lower ITSS | _ | _ | _ |
| ADC | Increased values | Lower values | _ | Higher values | _ | Lower values | Lower values |
| T2/FLAIR | T2-FLAIR mismatch | _ | _ | _ | SWITW sign on T2WI | _ | _ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarnera, A.; Ius, T.; Romano, A.; Bagatto, D.; Denaro, L.; Aiudi, D.; Iacoangeli, M.; Palmieri, M.; Frati, A.; Santoro, A.; et al. Advanced MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Incidental Glioma Grading and Genetic Status: Where Are We? Medicina 2025, 61, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081453
Guarnera A, Ius T, Romano A, Bagatto D, Denaro L, Aiudi D, Iacoangeli M, Palmieri M, Frati A, Santoro A, et al. Advanced MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Incidental Glioma Grading and Genetic Status: Where Are We? Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081453
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarnera, Alessia, Tamara Ius, Andrea Romano, Daniele Bagatto, Luca Denaro, Denis Aiudi, Maurizio Iacoangeli, Mauro Palmieri, Alessandro Frati, Antonio Santoro, and et al. 2025. "Advanced MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Incidental Glioma Grading and Genetic Status: Where Are We?" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081453
APA StyleGuarnera, A., Ius, T., Romano, A., Bagatto, D., Denaro, L., Aiudi, D., Iacoangeli, M., Palmieri, M., Frati, A., Santoro, A., & Bozzao, A. (2025). Advanced MRI, Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Unravelling Incidental Glioma Grading and Genetic Status: Where Are We? Medicina, 61(8), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081453









