Application of Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation and Toxicity Testing of Natural Products
Abstract
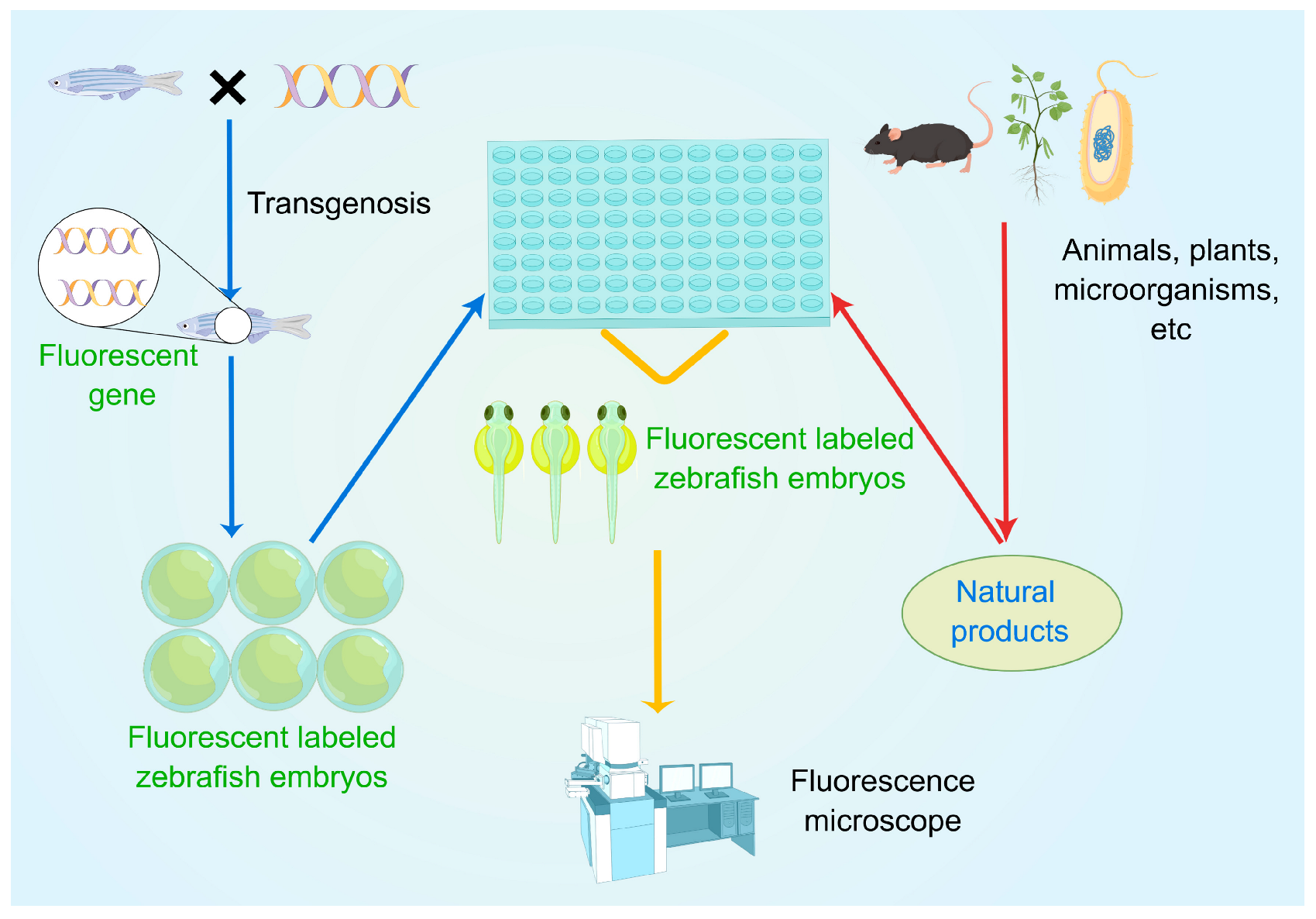
1. Introduction
2. Evaluation of the Anti-Cancer Effect of Natural Products Using Zebrafish Models
2.1. Chemical Carcinogen-Induced Zebrafish Models
2.2. Genetically Engineered Zebrafish Models
2.2.1. Tg (fli1:EGFP) Transgenic Zebrafish Models
| Year | Compound/Extract | Source | Effective Concentration | Blood Vessel | Positive Control | Growing Stage of Zebrafish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 [35] | Leaves extract | Moricandia sinaica (Boiss.) Boiss. | 40 mg/mL | ISVs, DLAVs, SIVs. | - | 48 and 72 hpf |
| 2023 [46] | extract | Lepista nuda (Bull.) Cooke | - | ISVs | - | 24 hpf |
| 2022 [49] | Leaves extract | Synsepalum dulcificum (Schumach. & Thonn.) Daniell (Miracle berry) leaves | - | SIVs | - | 72 hpf |
| 2016 [50] | Proanthocyanidins | Choerospondias axillaris (Roxb.) B.L.Burtt & A.W.Hillpeels | - | SIVs | SU5416 | 72 hpf |
| 2020 [39] | Fucoidan | Fucus vesiculosus | 300 µg/mL | ISVs, DLAVs, DA. | - | 48 hpf |
| 2020 [40] | Fucoidan | Laminaria japonica J.E.Areschoug | - | the trunk, vasculature. | - | 48 hpf |
| 2019 [36] | Ginsenoside Rh2 (1) | red ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) | - | ISVs | SU5416 | 48 hpf |
| 2018 [37] | Murrangatin (2) | Murraya alata Drake | - | SIVs | - | 72 hpf |
| 2011 [38] | Nobiletin (3) | Citrus depressa Hayata | - | ISVs | VEGFR inhibitor II | 32 hpf |
| 2022 [29] | Sinularin (4) | soft coral (Sinularia flexibilis) | - | ISVs | - | 72 hpf |
| 2016 [41] | Capsicodendrin (5) | Cinnamosma macrocarpa H.Perrier | 2 μM | DLAVs, SIVs. | - | 48 hpf |
| 2022 [42] | Penisterine C (6) | Algicolous Penicillium sumatraense SC29 | - | ISVs, DLAVs. | Sorafenib | 96 hpf |
| 2022 [43] | Xipsxanthone H (7) | Garcinia xishuanbannaensis Y.H. Li | - | ISVs | Sunitinib malate | 48 hpf |
| 2021 [44] | Crocetin (8) | saffron (Crocus sativus L.) | - | SIVs | VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor II | 72 hpf |
| 2020 [45] | Fucosterol (9) | brown algae (Sargassum fusiforme (Harv.) Setch.) | - | ISVs, DLAVs, DA. | - | 24 hpf |
| 2022 [47] | Cratoxylumxanthone C (10) | Cratoxylum cochinchinense (Lour.) Blume | - | ISVs | Sunitinib malate | 54 hpf |
| 2020 [48] | Eupatilin (11) | Artemisia asiatica Nakai ex Pamp. | 100 μM | DLAVs, ISVs, DA. | - | 48 hpf |
| 2011 [51] | Dehydro-α-lapachone (12) | Tabebuia avellanedae Lorentz ex Griseb. tree | 5 μM | ISVs | - | 48 hpf |
| 2017 [52] | Amentoflavone (13) | Garcinia xanthochymus Hook.f. ex T.Anderson | - | SIVs | Eriocalyxin B | 72 hpf |
| 2015 [53] | Aromatic turmerone (14) | Curcuma longa L. (Turmeric) | - | SIVs | - | 48 hpf |
| 2015 [54] | R-(-)-β-O-Methylsynephrine (15) | Rutaceae (Juss.) family | - | ISVs | - | 30 hpf |
| 2020 [55] | Deoxysappanone B 7.4′-dimethyl ether (16) | Biancaea sappan (L.) Tod. | 5 μM | ISVs | PTK787 | 48 hpf |
| 2019 [56] | Timosaponin AIII (17) | Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge | - | ISVs, SIVs. | - | 36 hpf |
| 2018 [57] | Mundoserone (18) | Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre | - | ISVs | PTK787 | 24 and 48 hpf |
| 2018 [58] | Protocatechuic acid (19) | Pleurotus tuberregium (Fries) Sing and Agrocybe aegerita (Aa, V. Brig.) Singer | 25 µM | SIVs | SU5416 | 48 and 72 hpf |
2.2.2. Other Transgenic Zebrafish Models
| Year | Compound/Extract | Source | Zebrafish Type | Effective Concentration | Blood Vessel | Positive Control | Growing Stage of Zebrafish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 [59] | water extract | Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. | Tg (flk:mCherry) | - | ISVs | PTK787 | 72 hpf |
| 2017 [60] | kudingcha extract | Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng | Tg (flk1:EGFP) | - | ISVs | - | 52 hpf |
| 2015 [30] | Kaempferol (20) | Dysosma versipellis (Hance) M.Cheng | Tg (kdrl:GRCFP)zn1 | 40 µM | ISVs | - | 48 hpf |
| 2015 [34] | Deoxypodophyllotoxin (21) | Anthriscus sylvestris (L.) Hoffm. | Tg (VEGFR2:GFP) | 50 nM | ISVs | - | 50 hpf |
2.3. Human Cancer Cell Zebrafish Xenograft Models
2.3.1. Ovarian Cancer
2.3.2. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
2.3.3. Breast Cancer
2.3.4. Liver Cancer
2.3.5. Melanoma
2.3.6. Other Malignancies
| Year | Compound/Extract | Source | Cells | Effective Concentration | Type of Cancer | Positive Control | Growing Stage of Zebrafish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 [39] | Fucoidan | F. vesiculosus | ES2 cells and OV90 cells | - | Ovarian Cancer | - | 72 hpf |
| 2020 [68] | Osthole (22) | Angelica archangelica L., Angelica pubescens Maxim., Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson | ES2 cells and OV90 cells | - | Ovarian Cancer | - | 72 hpf |
| 2020 [45] | Fucosterol (9) | brown algae (S. fusiforme) | ES2 cells and OV90 cells | - | Ovarian Cancer | - | 72 hpf |
| 2021 [48] | Eupatilin (11) | A. asiatica | ES2 cells and OV90 cells | - | Ovarian Cancer | - | 48 hpf |
| 2022 [43] | Xipsxanthone H (7) | G. xishuanbannaensis | A549 cells | - | Non-small cell lung cancer | Etoposide | 48 hpf |
| 2022 [47] | Cratoxylumxanthone C (10) | C. cochinchinense | A549 cells | - | Non-small cell lung cancer | Etoposide | 100 hpf |
| 2018 [67] | Cardenolide glucoevatromonoside (23) | Digitalis lanata Ehrh. | A549 cells | - | Non-small cell lung cancer | - | 48 hpf |
| 2020 [40] | Fucoidan | L. japonica | MDA-MB-231 cells | 2 µg/mL | Breast cancer | - | 48 hpf |
| 2022 [69] | Jadomycin B (24) | Streptomyces venezuelae ISP5230 | MDA-MB-231 cells | - | Breast cancer | - | 120 hpf |
| 2018 [70] | Actein (25) | Cimicifuga species | MDA-MB-231 cells | - | Breast cancer | - | 168 hpf |
| 2019 [71] | Betulinic acid (26) | birch (Betula platyphylla Sukaczev) bark | MCF-7 cells | - | Breast cancer | - | 72 and 96 hpf |
| 2017 [72] | Oridonin (27) | Rabdosia rubescens (Henmsl.) H.Hara | HepG2-Luciferase cells | - | Breast cancer | Avastin | 222 hpf |
| 2019 [73] | Furanodiene (28) | Curcuma longa L. | MCF-7 cells | - | Liver cancer | - | 96 hpf |
| 2020 [74] | Saringosterol acetate (29) | sargassum fusiforme (Harv.) Setch. | Hep3B cells | 12.5 μg/mL | Liver cancer | - | 96 hpf |
| 2020 [75] | Theaflavin (TF) (30) | Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze | A375 cells | - | Melanoma | - | 72 hpf |
| 2020 [76] | Shikonin (31) | Arnebia euchroma (Royle ex Benth.) I.M.Johnst. | A375 and A2058 cells | - | Melanoma | Sorafenib | 72 and 96 hpf |
| 2022 [77] | Aiphanol (32) | Smilax glabra Roxb. | HCT116 and HT29 cells | - | Rectal cancer | 5-FU | 96 hpf |
| 2018 [78] | 1-Methoxycarbony-β-carboline (33) | Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Bennet | DU145 cells | 50 µM | Prostatic cancer | - | 72, 144, and 240 hpf |
| 2018 [79] | Theabrownin | Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze | U2OS cells | - | Osteosarcoma | - | 72 hpf |
| 2018 [80] | 2-Methoxy-6-acetyl-7-methyljuglone (34) | Ventilago denticulate Willd., Rumex japonicus Houtt. | U251 cells | - | Glioblastoma | Temozolomide | 144 hpf |
3. Toxicity Testing of Natural Products Using Zebrafish Model
| Year | Compound/Extract | Source | Positive Control | Growing Stage of Zebrafish | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 [86] | leaves, stems, roots, and flowers extract | Rumex vesicarius L. (Humeidh) | - | 24, 48, and 72 hpf | no toxicity below 300 mg/mL |
| 2020 [35] | leaf, stem, root, and shoot extract | M. sinaica | - | 72 hpf | Roots and shoots extracts had less toxicity |
| 2018 [87] | leaf extract | Thuja orientalis L. | - | 96 hpf | LC50 = 0.7029 mg/mL |
| 2022 [49] | leaf extract | S. dulcificum | - | 72 hpf | LC50 = 100 μg/mL |
| 2020 [88] | crude extract | Tephrosia vogelii Hook.f. | rotenone, deguelin, tephrosin. | 48 hpf | LC50 = 4.8 nM |
| 2021 [92] | extract | Jussiaea repens L. | - | 72 hpf | LC50 = 169.2 µg/mL |
| 2021 [98] | ethanol extract | Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze | - | 48, 72, and 96 hpf | no toxicity below 75 mg/L |
| 2015 [99] | aqueous extract | Millettia pachycarpa Benth. | - | 96 hpf | LC50 = 4.28 µg/mL |
| 2020 [39] | fucoidan | F.vesiculosus | - | 48 hpf | no significant effect (100, 200, and 300 μg/mL) |
| 2019 [89] | JBIR-99 | Parengyodontium album MEXU 30054 | cycloheximide | 48 hpf | non-toxic (50 μM) |
| 2021 [100] | exopolysaccharides (EPS) | Lignosus rhinocerotis (Cooke) Ryvarden | - | 96 hpf | LC50 = 0.41 mg/mL |
| 2020 [102] | carlina oxide | Carlina acaulis L. | Acetone, | 96 hpf | LC50 = 10.13 µg/mL |
| 2018 [103] | macrolide | Streptomyces californicus TY004-069 | sodium azide (NaN3). | 24 hpf | lethal (20 μM) |
| 2021 [36] | ginsenoside Rh2 (1) | red ginseng (P. ginseng) | - | 24 hpf | no toxicity below 84.85 μM |
| 2020 [45] | fucosterol (9) | brown algae (S. fusiforme) | - | 24 hpf | no significant effect (40, 60, and 100 μM) |
| 2020 [68] | osthole (22) | A. archangelica, A. pubescens, and C. monnieri | - | 24 hpf | not affecting the survival rate (5,10, and 20 μM) |
| 2019 [71] | betulinic acid (26) | birch (Betula platyphylla Sukaczev) bark | - | 24, 48, 72, and 96 hpf | no obvious embryo toxicity or teratogenicity (10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 μM) |
| 2018 [90] | myxocoumarin B (35) | Stigmatella aurantiaca MYX-030 | - | 114 hpf | no toxicity below 250 μM |
| 2018 [91] | 2-ethoxycarbonyl-2-β-hydroxy-A-nor-cholest-5-ene-4one (ECHC) (36) | Acropora formosa | - | 21 days | nearly non-toxic (1000 µg/L) |
| 2022 [93] | coptisine (37) | Coptis chinensis Franch. | - | 96 hpf | no toxicity below 390.24 μM |
| 2015 [94] | α-mangostin (38) | Thai stingless bee (Tetragonula laeviceps) cerumen | - | 72 hpf | LC50 = 9.4 µM |
| 2010 [95] | celastrol (39) | Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. | - | 24 hpf | LC50 = 1.40 µM |
| 2021 [96] | α-costic acid (40) | Dittrichia viscosa (L.) Greuter | - | 48 hpf | lethal (50 µM) |
| 2022 [97] | kimcoungin (41) | Glycosmis ovoidea Pierre | cycloheximide | 24 hpf | non-toxic (50 µM) |
| 2021 [101] | jegosaponin A and B (42) (43) | Styrax japonicus Siebold & Zucc. | - | 29 hpf | LC50 = 0.5 and 1.3 µM, respectively |
| 2021 [104] | xanthatin (44) | Xanthium spinosum L., Dittrichia graveolens L. | - | 72 hpf | maximum safe concentration = 5 µM |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Cao, M.; Sun, D.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elias, N.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, L.; Saeed, A.; Hegazy, M.F.; Moustafa, M.S.; Abd El-Wahed, A.; Al-Mousawi, S.M.; Musharraf, S.G.; et al. Marine Natural Products: A Source of Novel Anti-cancer Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Jin, J.; Zhao, D.; Rong, Z.; Cao, L.Q.; Li, A.H.; Sun, X.Y.; Jia, L.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Huang, L.; et al. Research Advances on Anti-Cancer Natural Products. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 866154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. Natural products: An upcoming therapeutic approach to cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, R.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Li, A. Plant Natural Products: Promising Resources for Cancer Chemoprevention. Molecules 2021, 26, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jaitak, V. Natural products as multidrug resistance modulators in cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 176, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, J.; Qin, J.; Yang, M. Screening techniques for the identification of bioactive compounds in natural products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 168, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, E.E.; Zon, L.I.; Langenau, D.M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: From preclinical modelling to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.K.; Schiavone, K.; Tazzyman, S.; Heymann, D.; Chico, T.J. Zebrafish xenograft models of cancer and metastasis for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.Y.; Peterson, R.T. Developing zebrafish disease models for in vivo small molecule screens. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 50, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, A.; Otterstrom, J.; Hoade, Y.; Bjedov, I.; Stead, E.; Whelan, M.; Gestri, G.; Paran, Y.; Payne, E. A versatile, automated and high-throughput drug screening platform for zebrafish embryos. Biol. Open 2021, 10, bio058513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.M. Antiangiogenic cancer drug using the zebrafish model. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascallar, M.; Alijas, S.; Pensado-Lopez, A.; Vazquez-Rios, A.J.; Sanchez, L.; Pineiro, R.; de la Fuente, M. What Zebrafish and Nanotechnology Can Offer for Cancer Treatments in the Age of Personalized Medicine. Cancers 2022, 14, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thani, H.F.; Shurbaji, S.; Yalcin, H.C. Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-cancer Nanomedicine Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zon, L.I.; Le, X. Potential of zebrafish for anti-cancer drug screening. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2008, 3, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shive, H.R. Zebrafish Models for Human Cancer. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 50, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberger, S.; Sturtzel, C.; Pascoal, S.; Distel, M. Quo natas, Danio?—Recent Progress in Modeling Cancer in Zebrafish. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Li, H.; Wu, D.T.; Zhuang, Q.G.; Li, H.B.; Geng, F.; Gan, R.Y. Recent development in zebrafish model for bioactivity and safety evaluation of natural products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8646–8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunton, T.E. Experimental chemical carcinogenesis in fish. Toxicol. Pathol. 1996, 24, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Tsai, H.-W.; Reddy, A.; Miller, T.; Arbogast, D.; Hendricks, J.D.; Bailey, G. Neoplasia in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Treated with N-methyl-N’nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine by Three Exposure Routes at different Developmental Stages. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Tsai, H.-W.; Reddy, A.; Miller, T.; Arbogast, D.; Hendricks, J.D.; Bailey, G. Neoplasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio) treated with 7, 12-Diniethylbenz [a] anthracene by two exposure routes at different developmental stages. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckwith, L.G.; Moore, J.L.; Tsao-Wu, G.S.; Harshbarger, J.C.; Cheng, K.C. Ethylnitrosourea induces neoplasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizgireuv, I.V.; Majorova, I.G.; Gorodinskaya, V.M.; Khudoley, V.V.; Revskoy, S.Y. Carcinogenic effect of N-nitrosodimethylamine on diploid and triploid zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Shimizu, Y. Carcinogenesis Models Using Small Fish. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimeault, M.; Batra, S.K. Emergence of zebrafish models in oncology for validating novel anti-cancer drug targets and nanomaterials. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Shih, P.C.; Kuo, H.M.; Lin, S.C.; Liu, H.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, W.F.; Chen, N.F. Sinularin Induces Oxidative Stress-Mediated Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Inhibits Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Han, Y.; Gao, H.; Xin, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, N.; Qin, W.; Zhong, H.; Lin, S.; Yao, X.; et al. Kaempferol Identified by Zebrafish Assay and Fine Fractionations Strategy from Dysosma versipellis Inhibits Angiogenesis through VEGF and FGF Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Lin, Q.; Gong, G.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q.; Feng, F.; Qu, W. Anti-angiogenic and anti-cancer effects of baicalein derivatives based on transgenic zebrafish model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4481–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafaella, d.S.B.; Canedo, P.A.; Davi, F.; Lopes, R.T. Transgenic zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an emerging model system in ecotoxicology and toxicology: Historical review, recent advances, and trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157665. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, C.P.; Choi, S.Y.; Kee, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.C.; Ro, H. Transgenic fluorescent zebrafish lines that have revolutionized biomedical research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2021, 37, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Guerram, M.; Sun, L.; Shi, W.; Tian, C.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Deoxypodophyllotoxin suppresses tumor vasculature in HUVECs by promoting cytoskeleton remodeling through LKB1-AMPK dependent Rho A activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Nasr, F.A.; Almoutiri, N.D.; Al-yahya, N.; Wadaan, M.A.; Abutaha, N. The phytochemical screening and antiangiogenic activity of audthan al himar (Moricandia sinaica Boiss.) extracts in zebrafish embryos and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liman, M.A.; Yongxiao, Q.I.; Wenji, W.; Qianyi, Z. Anti-angiogenic Effect of Ginsenoside Rh2 by Downregulation of VEGF in a Zebrafish Model. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 53, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Wang, M.; Luo, X.; Huang, G.; Chen, J. Murrangatin suppresses angiogenesis induced by tumor cell-derived media and inhibits AKT activation in zebrafish and endothelial cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Alex, D.; Lam, I.K.; Tsui, S.K.; Yang, Z.F.; Lee, S.M. Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid from citrus, shows anti-angiogenic activity in a zebrafish in vivo model and HUVEC in vitro model. J. Cell Biochem. 2011, 112, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.J.; Lin, M.H.; Kuo, T.C.; Chou, C.M.; Mi, F.L.; Cheng, C.H.; Lin, C.W. Fucoidan from Laminaria japonica exerts antitumor effects on angiogenesis and micrometastasis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.C.; Shah, N.; Kumar, S.; Wheeler, S.E.; Cinti, J.; Hoyt, D.G.; Beattie, C.E.; An, M.; Mythreye, K.; Rakotondraibe, L.H. Angiostatic actions of capsicodendrin through selective inhibition of VEGFR2-mediated AKT signaling and disregulated autophagy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsi, H.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Cheng, C.H.; Pang, K.L.; Leu, J.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Kuo, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, T.H. Chemical Constituents and Anti-Angiogenic Principles from a Marine Algicolous Penicillium sumatraense SC29. Molecules 2022, 27, 8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y. A natural xanthone suppresses lung cancer growth and metastasis by targeting STAT3 and FAK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Kam, H.T.; Chen, Y.; Gong, G.; Hoi, M.P.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Dias, A.C.P.; Lee, S.M. Crocetin and Its Glycoside Crocin, Two Bioactive Constituents from Crocus sativus L. (Saffron), Differentially Inhibit Angiogenesis by Inhibiting Endothelial Cytoskeleton Organization and Cell Migration Through VEGFR2/SRC/FAK and VEGFR2/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 675359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Fucosterol Suppresses the Progression of Human Ovarian Cancer by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, D.; Hsu, Y.F.; Chiu, C.C.; Jadhao, M.; Hsu, S.C.N.; Hu, S.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Liu, W. Antiangiogenic potential of Lepista nuda extract suppressing MAPK/p38 signaling-mediated developmental angiogenesis in zebrafish and HUVECs. Biomed. Pharm. 2023, 159, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Hou, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, P. Cratoxylumxanthone C, a natural xanthone, inhibits lung cancer proliferation and metastasis by regulating STAT3 and FAK signal pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 920422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bae, H.; Yang, C.; Park, S.; Youn, B.S.; Kim, H.S.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Eupatilin Promotes Cell Death by Calcium Influx through ER-Mitochondria Axis with SERPINB11 Inhibition in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tu, X.H.; Du, L.Q. Identification of phenolics from miracle berry (Synsepalum dulcificum) leaf extract and its antiangiogenesis and anti-cancer activities. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 970019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Dai, T.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. Proanthocyanidins, Isolated from Choerospondias axillaris Fruit Peels, Exhibit Potent Antioxidant Activities in Vitro and a Novel Anti-angiogenic Property in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garkavtsev, I.; Chauhan, V.P.; Wong, H.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Glicksman, M.A.; Peterson, R.T.; Jain, R.K. Dehydro-alpha-lapachone, a plant product with antivascular activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11596–11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yue, G.G.; Kwok, H.F.; Long, C.L.; Lau, C.B.; Kennelly, E.J. Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry-Based Chemometrics for the Identification of Anti-angiogenic Biflavonoids from Edible Garcinia Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8348–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.G.-L.; Kwok, H.-F.; Lee, J.K.-M.; Jiang, L.; Chan, K.-M.; Cheng, L.; Wong, E.C.-W.; Leung, P.-C.; Fung, K.-P.; Lau, C.B.-S. Novel anti-angiogenic effects of aromatic-turmerone, essential oil isolated from spice turmeric. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Pham, N.B.; Quinn, R.J.; Shim, J.S.; Cho, H.; Cho, S.M.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Seok, S.H.; Oh, J.W.; et al. The Small Molecule R-(-)-beta-O-Methylsynephrine Binds to Nucleoporin 153 kDa and Inhibits Angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Fan, Y.; Gu, J.; Han, Z.; Zeng, H.; Mao, C.; Wang, C. In vivo Screening of Natural Products Against Angiogenesis and Mechanisms of Anti-Angiogenic Activity of Deoxysappanone B 7,4′-Dimethyl Ether. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 3069–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhao, W.R.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Huang, C.; Shi, W.T.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Chen, X.L.; Tang, J.Y. Antiangiogenesis effect of timosaponin AIII on HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish embryos in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Fan, Y.; Gu, J.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zeng, H. Identification of mundoserone by zebrafish in vivo screening as a natural product with anti-angiogenic activity. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4562–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lin, S.; Huang, J.J.; Cheung, P.C.K. Mechanistic Study of the In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibitory Effects of Protocatechuic Acid and Syringic Acid on VEGF-Induced Angiogenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6742–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, J.; Xia, Q.; Ni, Y.; Li, F.; Lin, R. Anti-angiogenic activity of water extract from Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Piao, L.; Kim, H.J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, G. Chlorogenic Acid-Enriched Extract of Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng Inhibits Angiogenesis in Zebrafish. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xuan, C.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Zebrafish xenotransplantation as a tool for in vivo cancer study. Fam. Cancer 2015, 14, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertman, J.; Veinotte, C.J.; Dellaire, G.; Berman, J.N. The Zebrafish Xenograft Platform: Evolution of a Novel Cancer Model and Preclinical Screening Tool. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 916, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.M.J.; Seftor, E.A.; Bonde, G.; Cornell, R.A.; Hendrix, M.J.C. The fate of human malignant melanoma cells transplanted into zebrafish embryos: Assessment of migration and cell division in the absence of tumor formation. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Glasgow, E.; Agarwal, S. Zebrafish Xenografts for Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konantz, M.; Balci, T.B.; Hartwig, U.F.; Dellaire, G.; Andre, M.C.; Berman, J.N.; Lengerke, C. Zebrafish xenografts as a tool for in vivo studies on human cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1266, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriuso, J.; Nagaraju, R.; Hurlstone, A. Zebrafish: A new companion for translational research in oncology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, N.F.Z.; Cerella, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Mazumder, A.; Kim, K.R.; de Carvalho, A.; Munkert, J.; Padua, R.M.; Kreis, W.; Kim, K.W.; et al. Cardiac Glycoside Glucoevatromonoside Induces Cancer Type-Specific Cell Death. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Osthole interacts with an ER-mitochondria axis and facilitates tumor suppression in ovarian cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, B.T.; Relja, N.J.; Hall, S.R.; Gebremeskel, S.; MacLeod, J.M.; Veinotte, C.J.; Bennett, L.G.; Ohlund, L.B.; Sleno, L.; Jakeman, D.L.; et al. Pilot study of jadomycin B pharmacokinetics and anti-tumoral effects in zebrafish larvae and mouse breast cancer xenograft models. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 100, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Yue, G.G.; Dong, J.R.; Lam, C.W.; Wong, C.K.; Qiu, M.H.; Lau, C.B. Actein Inhibits the Proliferation and Adhesion of Human Breast Cancer Cells and Suppresses Migration in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, D.; Mei, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z. Betulinic acid suppresses breast cancer aerobic glycolysis via caveolin-1/NF-kappaB/c-Myc pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 161, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Xie, K.; Sheng, D.; Wan, X.; Zhu, G. Antiangiogenic effects of oridonin. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Guo, D.W.; Lao, Q.C.; Xu, Y.Q.; Meng, Z.K.; Xia, B.; Yang, H.; Li, C.Q.; Li, P. Sensitization and synergistic anti-cancer effects of Furanodiene identified in zebrafish models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.A.; Lee, J.H.; Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Saringosterol acetate isolated from Hizikia fusiforme, an edible brown alga, suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis in a zebrafish xenograft model. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 335, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, B.; Meng, S.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Du, W.; Shan, L. Theaflavin Induces Apoptosis of A375 Human Melanoma Cells and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Xenograft Zebrafishes Through P53- and JNK-Related Mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yu, L.Z.; Shao, M.; Liu, J.S. Inhibition of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway Contributes to the Anti-Melanoma Activities of Shikonin. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-M.; Feng, J.-N.; Zhao, C.-K.; Yao, L.-C.; Wang, L.-X.; Meng, L.; Cai, S.-Q.; Liu, C.-Y.; Qu, L.-K.; Jia, Y.-X. A multi-targeting natural product, aiphanol, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 4930. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.H.; Qu, W.; Xu, J.; Feng, F.; He, M.F. 1-Methoxycarbony-beta-carboline from Picrasma quassioides exerts anti-angiogenic properties in HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish embryos in vivo. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 599–609. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Zhou, L.; Yan, B.; Yan, L.; Liu, F.; Tong, P.; Yu, W.; Dong, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Theabrownin triggers DNA damage to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells by activating p53 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4423–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhong, B.; Jin, L.; Hou, Y.; Ai, N.; Ge, W.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, X. 2-Methoxy-6-acetyl-7-methyljuglone (MAM) induced programmed necrosis in glioblastoma by targeting NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eimon, P.M.; Rubinstein, A.L. The use of in vivo zebrafish assays in drug toxicity screening. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Gao, J.M.; Huang, C.J.; Li, C.Q. Zebrafish models for assessing developmental and reproductive toxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 42, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, I. Application of zebrafish to safety evaluation in drug discovery. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 33, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Gong, Z.; Tse, W.K.F. Zebrafish as the toxicant screening model: Transgenic and omics approaches. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 234, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, K.; Jin, H.; Liu, K. Progress in using zebrafish as a toxicological model for traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Abutaha, N.; Mahboob, S.; Baabbad, A.; Almoutiri, N.D.; Wadaan, M. Investigating the antiangiogenic potential of Rumex vesicarius (humeidh), anti-cancer activity in cancer cell lines and assessment of developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeta, R.E.; Jesubatham, P.D.; Grace, V.M.B.; Viswanathan, S. Srividya Non-toxic and non teratogenic extract of Thuja orientalis L. inhibited angiogenesis in zebra fish and suppressed the growth of human lung cancer cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Said, A.H.; Solhaug, A.; Sandvik, M.; Msuya, F.E.; Kyewalyanga, M.S.; Mmochi, A.J.; Lyche, J.L.; Hurem, S. Isolation of the Tephrosia vogelii extract and rotenoids and their toxicity in the RTgill-W1 trout cell line and in zebrafish embryos. Toxicon 2020, 183, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya-Eugenio, G.D.; Rebollar-Ramos, D.; Gonzalez, M.D.C.; Raja, H.; Mata, R.; Carcache de Blanco, E.J. Apoptotic activity of xanthoquinodin JBIR-99, from Parengyodontium album MEXU 30054, in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 311, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.I.; Kusserow, K.; Hertrampf, G.; Pavic, A.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Gulder, T.A.M. Synthesis and initial biological evaluation of myxocoumarin B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1966–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, V.; Rajaram, R. 2-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-beta-hydroxy-a-nor-cholest-5-ene-4one: Extraction, structural characterization, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-cancer and acute toxicity studies. Steroids 2018, 140, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajiv, C.; Roy, S.S.; Tamreihao, K.; Kshetri, P.; Singh, T.S.; Sanjita Devi, H.; Sharma, S.K.; Ansari, M.A.; Devi, E.D.; Devi, A.K.; et al. Anticarcinogenic and Antioxidant Action of an Edible Aquatic Flora Jussiaea repens L. Using In Vitro Bioassays and In Vivo Zebrafish Model. Molecules 2021, 26, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakonieczna, S.; Grabarska, A.; Gawel, K.; Wroblewska-Luczka, P.; Czerwonka, A.; Stepulak, A.; Kukula-Koch, W. Isoquinoline Alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Franch: Focus on Coptisine as a Potential Therapeutic Candidate against Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugitrangson, P.; Puthong, S.; Iempridee, T.; Pimtong, W.; Pornpakakul, S.; Chanchao, C. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the anti-cancer activity of Thai stingless bee (Tetragonula laeviceps) cerumen. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Chen, X. Toxic effects of celastrol on embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangermano, F.; Masi, M.; Kumar, A.; Peravali, R.; Tuzi, A.; Cimmino, A.; Vallone, D.; Giamundo, G.; Conte, I.; Evidente, A.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation of Natural Products with Potential Applications as Biopesticides. Toxins 2021, 13, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco Carcache, P.J.; Anaya Eugenio, G.D.; Ninh, T.N.; Moore, C.E.; Rivera-Chavez, J.; Ren, Y.; Soejarto, D.D.; Kinghorn, A.D. Cytotoxic constituents of Glycosmis ovoidea collected in Vietnam. Fitoterapia 2022, 162, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich-Loan, N.T.; Kien, K.T.; Thanh, N.L.; Kim-Thanh, N.T.; Huy, N.Q.; The-Hai, P.; Muller, M.; Nachtergael, A.; Duez, P.; Thang, N.D. Toxicity and Anti-Proliferative Properties of Anisomeles indica Ethanol Extract on Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Life 2021, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumnamcha, T.; Roy, D.; Devi, M.D.; Nongthomba, U. Evaluation of developmental toxicity and apoptotic induction of the aqueous extract of Millettia pachycarpa using zebrafish as model organism. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuldin, S.R.A.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ilham, Z.; Jamaludin, A.A.; Abdullah, N.R.; Rowan, N. In vivo toxicity of bioreactor-grown biomass and exopolysaccharides from Malaysian tiger milk mushroom mycelium for potential future health applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Fuchino, H.; Takayanagi, K.; Kawakami, H.; Nakayama, H.; Kawahara, N.; Shimada, Y. Toxicity of Jegosaponins A and B from Styrax japonica Siebold et al. Zuccarini in Prostate Cancer Cells and Zebrafish Embryos Resulting from Increased Membrane Permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnorowski, A.; Wnorowska, S.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Grenda, A.; Staniak, M.; Michalak, A.; Wozniak, S.; Matosiuk, D.; Biala, G.; Wojciak, M.; et al. Toxicity of Carlina Oxide-A Natural Polyacetylene from the Carlina acaulis Roots-In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Toxins 2020, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.J.; Lau, B.F.; Krishnasamy, G.; Ng, M.F.; Husin, L.S.; Ruslan, N.; Song, D.S.S.; Velaithan, V.; Okuda, K.S.; Patel, V. Zebrafish embryonic development-interfering macrolides from Streptomyces californicus impact growth and mitochondrial function in human colorectal cancer cells. Process Biochem. 2018, 74, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, S.; Ma, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R. Xanthatin Selectively Targets Retinoblastoma by Inhibiting the PLK1-Mediated Cell Cycle. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, G.; Gaudenzi, G.; Circelli, L.; Manzoni, M.F.; Bassi, A.; Fioritti, N.; Faggiano, A.; Colao, A.; Group, N. Animal models of medullary thyroid cancer: State of the art and view to the future. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R1–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamaly, M.A.; Turner, L.T.; Rivera-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Blackburn, J.S. Zebrafish Cancer Avatars: A Translational Platform for Analyzing Tumor Heterogeneity and Predicting Patient Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, H.J. Zebrafish, an In Vivo Platform to Screen Drugs and Proteins for Biomedical Use. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, J.; Kannan, R.R. Antiangiogenic molecules from marine actinomycetes and the importance of using zebrafish model in cancer research. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K.S.; Lee, H.M.; Velaithan, V.; Ng, M.F.; Patel, V. Utilizing Zebrafish to Identify Anti-(Lymph)Angiogenic Compounds for Cancer Treatment: Promise and Future Challenges. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Sheng, R.; Guo, R. Application of Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation and Toxicity Testing of Natural Products. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060827
Shen Y, Sheng R, Guo R. Application of Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation and Toxicity Testing of Natural Products. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(6):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060827
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yifan, Ruilong Sheng, and Ruihua Guo. 2023. "Application of Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation and Toxicity Testing of Natural Products" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 6: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060827
APA StyleShen, Y., Sheng, R., & Guo, R. (2023). Application of Zebrafish as a Model for Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation and Toxicity Testing of Natural Products. Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060827







