Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Ameliorates the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Neurovascular Dysfunction-Associated Vascular Dementia in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
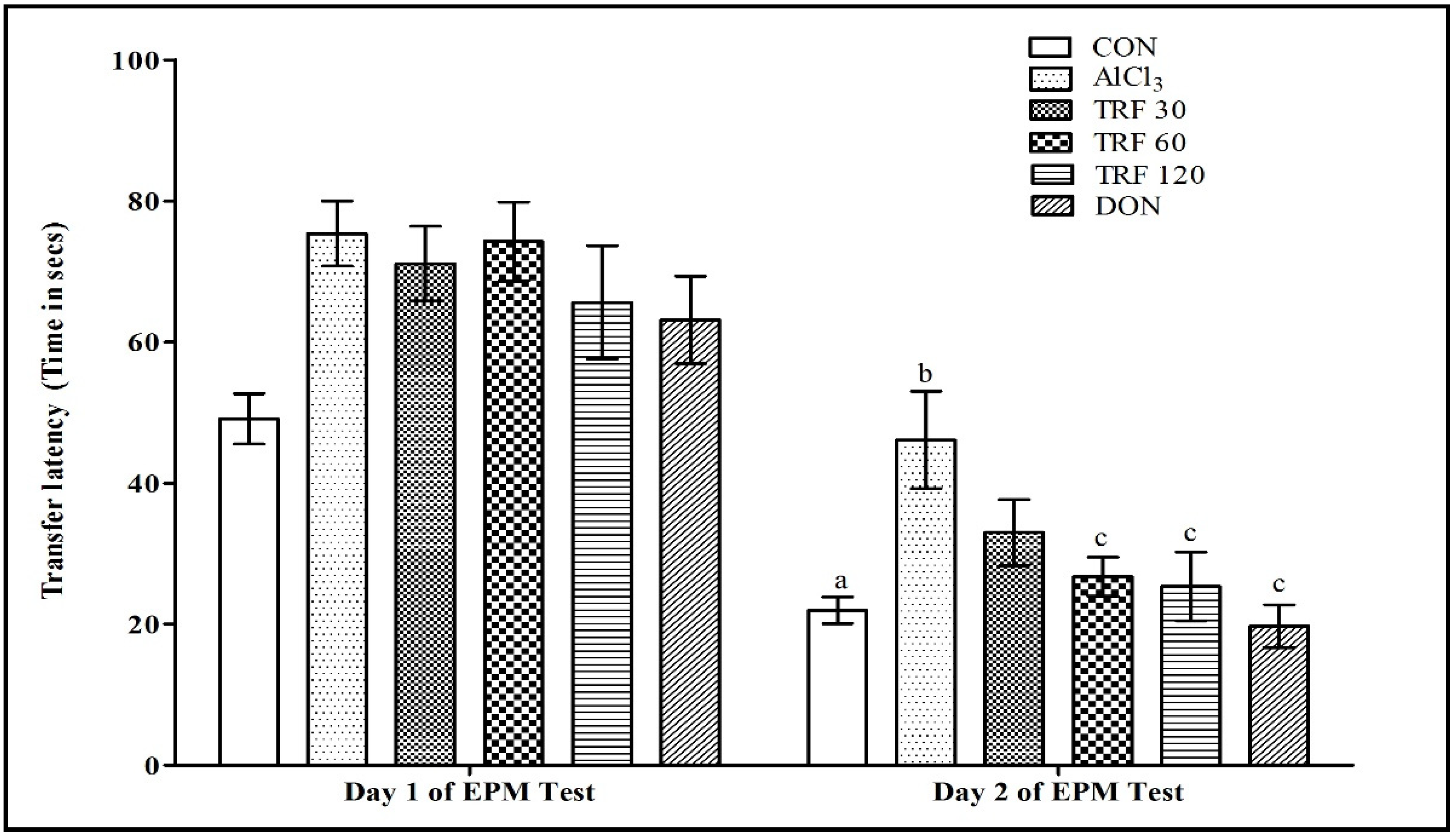
2.1. Effect of TRF on Learning and Memory Function during the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Test
2.2. Effect of TRF on Brain-Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) Levels
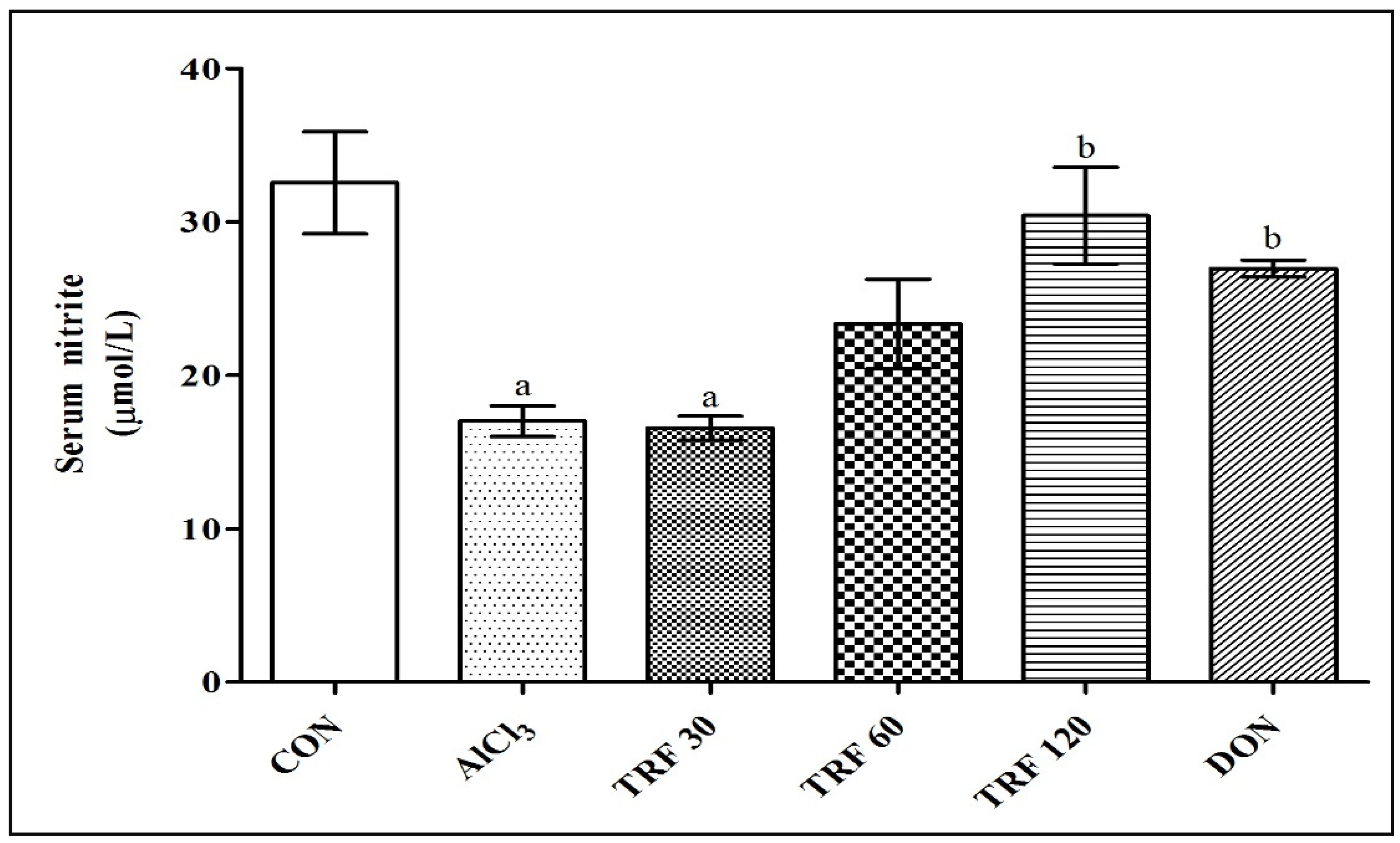
2.3. Effect of TRF on Serum Nitrite Levels
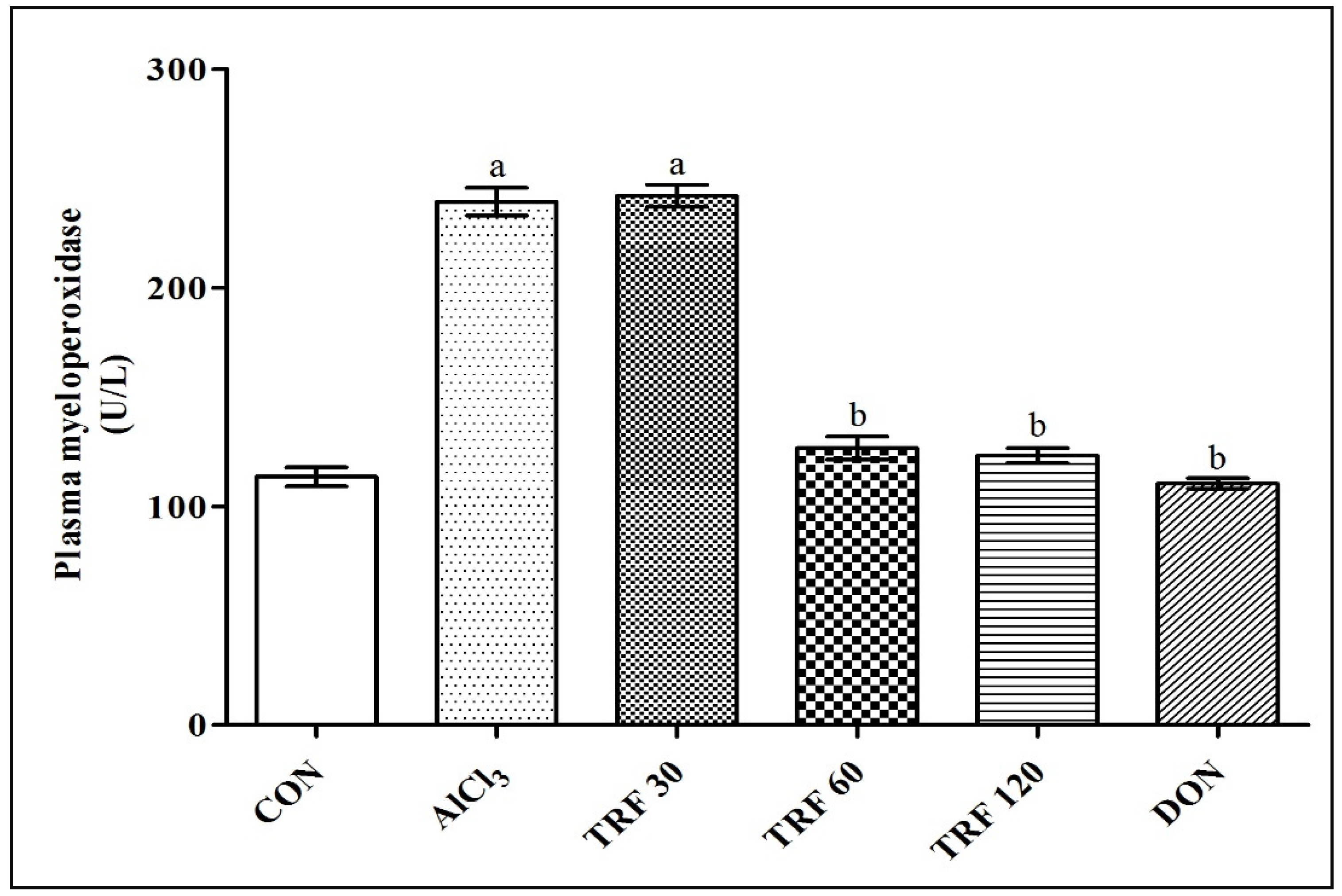
2.4. Effect of TRF on Plasma Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Levels
2.5. Effect of TRF on Hippocampus PDGF-C Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals and Assay Kits
4.3. Experimental Design
- CON: Normal control rats received an equal volume of vehicle.
- AlCl3: AlCl3-induced rats received an equal volume of vehicle.
- TRF 30: AlCl3-induced rats received TRF 30 mg/kg/bw; p.o.
- TRF 60: AlCl3-induced rats received TRF 60 mg/kg/bw; p.o.
- TRF 120: AlCl3-induced rats received TRF 120 mg/kg/bw; p.o.
- DON: AlCl3-induced rats received DON 1 mg/kg/bw; p.o. [63].
4.4. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Test
4.5. Blood Sample Collection and Brain Homogenate Preparation
4.6. Estimation of Brain-Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances
4.7. Estimation of Serum Nitrite
4.8. Estimation of Plasma Myeloperoxidase
4.9. Immunohistochemistry Study for Identification of PDGF-C Expression in Hippocampus
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tariq, S.; Barber, P.A. Dementia Risk and Prevention by Targeting Modifiable Vascular Risk Factors. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabir, O.; Berwick, J.; Francis, S.E. Neurovascular Dysfunction in Vascular Dementia, Alzheimer’s and Atherosclerosis. BMC Neurosci. 2018, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, F.J.; Ikram, M.A. Epidemiology of Vascular Dementia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Zhou, Z.-F.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Wan, Z.-K.; Yang, M.-W.; Hong, F.-F.; Yang, S.-L. Pharmacological Treatment of Vascular Dementia: A Molecular Mechanism Perspective. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sashindranath, M.; Nandurkar, H.H. Endothelial Dysfunction in the Brain. Stroke 2021, 52, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Filho, R.K.; Zotin, M.C.; Rodrigues, G.; Pontes-Neto, O. Biomarkers Related to Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 49, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, S.; Moss, J.; Rajani, R.M.; Williams, A. A Vessel for Change: Endothelial Dysfunction in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Neurovascular Unit: A Critical Role in Ischemic Stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwa, J.; Flora, S.J.S. Heavy Metal-Induced Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Possible Reversal Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Yu, S.; Feng, J. Advances in the Role of Endothelial Cells in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 861714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisardi, V.; Solfrizzi, V.; Kehoe, P.G.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Vendemiale, G.; Capurso, A.; Panza, F. Aluminium in the Diet, Cognitive Decline and Dementia. In Handbook of Behavior, Food and Nutrition; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2829–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Madhu, K.D.; Goli, D. Multifaceted Effects of Aluminium in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, A.; Srivastava, S.; Siow, R.C.M.; Modo, M.; Fraser, P.A.; Mann, G.E. Targeting the Nrf2–Keap1 Antioxidant Defence Pathway for Neurovascular Protection in Stroke. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 4125–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, M.J.C.; Nelson, L.; Slade, J.Y.; Oakley, A.E.; Khundakar, A.A.; Kalaria, R.N. Morphometry of the Hippocampal Microvasculature in Post-Stroke and Age-Related Dementias. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Alsalahi, A.; Imam, M.U.; Ooi, D.J.; Khaza’ai, H.; Aljaberi, M.A.; Shamsudin, M.N.; Idrus, Z. Safety and Neuroprotective Efficacy of Palm Oil and Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction from Palm Oil: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, A.; Alrawaiq, N.S.; Abdullah, A. Tocotrienols Activate Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation and Increase the Antioxidant- Related Hepatoprotective Mechanism in Mice Liver. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikan, M.Z.; Nasir, N.A.A.; Iezhitsa, I.; Agarwal, R. Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction against Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Retinopathy in Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Mathai, M.; Zulli, A. Revisiting the Therapeutic Potential of Tocotrienol. BioFactors Oxf. Engl. 2022, 48, 813–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, Z.; Khaza’ai, H.; Kutty Radhakrishnan, A.; Chang, S.K. Therapeutic Potential of Palm Oil Vitamin E-Derived Tocotrienols in Inflammation and Chronic Diseases: Evidence from Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.A.; Varatharajan, R.; Muthuraman, A. Palm Oil Derived Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Attenuates Vascular Dementia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koladiya, R.U.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N.; Sharma, B.K. Beneficial Effects of Donepezil on Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction-Associated Dementia Induced by L-Methionine in Rats. J. Health Sci. 2009, 55, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokel, R.A. Aluminum in Food–The Nature and Contribution of Food Additives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0067-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P. Conjecturable Role of Aluminum in Pathophysiology of Stroke. In Metal Ion in Stroke; Li, Y.V., Zhang, J.H., Eds.; Springer Series in Translational Stroke Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 649–680. ISBN 978-1-4419-9663-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Dang, M.; Zhang, W.; Lei, Y.; Ramesh, T.; Priya Veeraraghavan, V.; Hou, X. Neuroprotective Effects of Syringic Acid against Aluminium Chloride Induced Oxidative Stress Mediated Neuroinflammation in Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 71, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, P.S.; Biradar, P.R.; Tubachi, S.; Patil, V.S. Evaluation of Neuroprotective Effects of Canna Indica L against Aluminium Chloride Induced Memory Impairment in Rats. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2022, 23, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durani, L.W.; Hamezah, H.S.; Ibrahim, N.F.; Yanagisawa, D.; Nasaruddin, M.L.; Mori, M.; Azizan, K.A.; Damanhuri, H.A.; Makpol, S.; Wan Ngah, W.Z. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction of Palm Oil Improves Behavioral Impairments and Regulates Metabolic Pathways in AβPP/PS1 Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagapan, G.; Meng Goh, Y.; Shameha Abdul Razak, I.; Nesaretnam, K.; Ebrahimi, M. The Effects of Prenatal and Early Postnatal Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Supplementation on Cognitive Function Development in Male Offspring Rats. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taridi, N.M.; Yahaya, M.F.; Teoh, S.L.; Latiff, A.A.; Ngah, W.Z.W.; Das, S.; Mazlan, M. Tocotrienol Rich Fraction (TRF) Supplementation Protects against Oxidative DNA Damage and Improves Cognitive Functions in Wistar Rats. Clin. Ter. 2011, 162, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z. Inhibition of Ferroptosis Alleviates Atherosclerosis through Attenuating Lipid Peroxidation and Endothelial Dysfunction in Mouse Aortic Endothelial Cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongxia, Z.; Jian, X.; Suyuan, H.; Aixin, N.; Lihong, Z. Isolation and Characterization of Ergosterol from Monascus Anka for Anti-Lipid Peroxidation Properties. J. Mycol. Med. 2020, 30, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. The Pro-Oxidant Activity of Aluminum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, N.M.; Shehata, M.G.; Alsulami, T.; Badr, A.N.; Elbakatoshy, M.R.; Ali, H.S.; El-Sohaimy, S.A. Characterization of Orange Peel Extract and Its Potential Protective Effect against Aluminum Chloride-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, D.; Acun, A.D.; Danışman, B. Effects of Thymoquinone on Scopolamine-Induced Spatial and Echoic Memory Changes through Regulation of Lipid Peroxidation and Cholinergic Impairment. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 431, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, E.; Elsharkawy, E.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Salama, M. The Protective Effect of Indian Catechu Methanolic Extract against Aluminum Chloride-Induced Neurotoxicity, A Rodent Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xing, X.; Zhang, C.; Meng, H. Neuroprotective Effects of D-(-)-Quinic Acid on Aluminum Chloride-Induced Dementia in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 5602597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological Potential of Tocotrienols: A Review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, J.; Chakraborty, R.; Raychaudhuri, U. The 21st Century Form of Vitamin E--Tocotrienol. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budin, S.B.; Othman, F.; Louis, S.R.; Bakar, M.A.; Das, S.; Mohamed, J. The Effects of Palm Oil Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Supplementation on Biochemical Parameters, Oxidative Stress and the Vascular Wall of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Clin. Sao Paulo Braz. 2009, 64, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Attenuation of Diabetic Nephropathy by Tocotrienol: Involvement of NFkB Signaling Pathway. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matough, F.A.; Budin, S.B.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abdul-Rahman, M.; Al-Wahaibi, N.; Mohammed, J. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction from Palm Oil Prevents Oxidative Damage in Diabetic Rats. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2014, 14, e95–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.Y.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Tocotrienol Research: Past into Present. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J. Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Properties of a Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction from Grape Seeds. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, D.; Kumar, A.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N. Ameliorative Role of Rolipram, PDE-4 Inhibitor, against Sodium Arsenite–Induced Vascular Dementia in Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63250–63262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, L.; Zas, R.; Rodríguez, S.; Fernández-Novoa, L.; Cacabelos, R. Decreased Levels of Serum Nitric Oxide in Different Forms of Dementia. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 420, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.-Y.; Hong, F.-F.; Yang, S.-L. The Roles of Nitric Oxide Synthase/Nitric Oxide Pathway in the Pathology of Vascular Dementia and Related Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norsidah, K.-Z.; Asmadi, A.Y.; Azizi, A.; Faizah, O.; Kamisah, Y. Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Improves Vascular Proatherosclerotic Changes in Hyperhomocysteinemic Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, e976967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosche, B.; Molcanyi, M.; Noll, T.; Rej, S.; Zatschler, B.; Doeppner, T.R.; Hescheler, J.; Müller, D.J.; Macdonald, R.L.; Härtel, F.V. A Differential Impact of Lithium on Endothelium-Dependent but Not on Endothelium-Independent Vessel Relaxation. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 67, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.; Zechmeister, B.; Bosche, B.; Lieschke, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Venkataramani, V.; Jin, F.; Hein, K.; Weber, M.S.; et al. Lithium Enhances Post-Stroke Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity, Activates the MAPK/ERK1/2 Pathway and Alters Immune Cell Migration in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2020, 181, 108357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karel, M.F.A.; Roosen, M.G.C.H.; Tullemans, B.M.E.; Zhang, C.E.; Staals, J.; Cosemans, J.M.E.M.; Koenen, R.R. Characterization of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease by Neutrophil and Platelet Activation Markers Using Artificial Intelligence. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 367, 577863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nor, N.A.; Budin, S.B.; Zainalabidin, S.; Jalil, J.; Sapian, S.; Jubaidi, F.F.; Mohamad Anuar, N.N. The Role of Polyphenol in Modulating Associated Genes in Diabetes-Induced Vascular Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianca, M.; Panichella, G.; Fabiani, I.; Giannoni, A.; Aimo, A.; Franco, A.D.; Vergaro, G.; Grigoratos, C.; Castiglione, V.; Cipolla, C.M. Bidirectional Relationship between Cancer and Heart Failure: Insights on Circulating Biomarkers. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; Liu, J.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y. Cardiac Biomarkers for the Detection and Management of Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiovascular Toxicity. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Ton, S.H.; Tan, J.B.L.; Abdul Kadir, K. The Ameliorative Effects of a Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction on the AGE-RAGE Axis and Hypertension in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Rats with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2017, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, T.Y.; Malik, N.A.; Lim, K.P.; Teo, C.W.L.; Wong, E.S.M.; Kong, S.C.; Fong, C.W.; Petkov, J.; Yap, W.N. Oral Supplementation of Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alleviates Severity of Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, W.; Li, X. Expression and Function of PDGF-C in Development and Stem Cells. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 210268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, J.; Wu, X.; Zavala-Solorio, J.; Ross, J.; Liang, X.H.; Ferrara, N. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor C Promotes Revascularization in Ischemic Limbs of Diabetic Mice. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 59, 1402–1409.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grismaldo, A.; Sobrevia, L.; Morales, L. Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor c on Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grismaldo Rodríguez, A.; Zamudio Rodríguez, J.A.; Mendieta, C.V.; Quijano Gómez, S.; Sanabria Barrera, S.; Morales Álvarez, L. Effect of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor C on Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Induced by High d-Glucose in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, T.M.; King, J.H.; Ho, K.L.; Lau, H.L.N. Wound Healing Potential of Palm Oil Tocotrienols Rich Fraction. Food Res. 2021, 5, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Bentinger, M.; Savu, O.; Moshfegh, A.; Sunkari, V.; Dallner, G.; Swiezewska, E.; Catrina, S.-B.; Brismar, K.; Tekle, M. Mono-Epoxy-Tocotrienol-α Enhances Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice and Stimulates in Vitro Angiogenesis and Cell Migration. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaquat, L.; Sadir, S.; Batool, Z.; Tabassum, S.; Shahzad, S.; Afzal, A.; Haider, S. Acute Aluminum Chloride Toxicity Revisited: Study on DNA Damage and Histopathological, Biochemical and Neurochemical Alterations in Rat Brain. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, Y. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Supplementation Reduces Hyperglycemia-Induced Skeletal Muscle Damage through Regulation of Insulin Signaling and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiroma, S.M.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Amom, Z.; Jagadeesan, S.; Adenan, M.I.; Mohd Moklas, M.A. Protective Effect of Centella Asiatica against D-Galactose and Aluminium Chloride Induced Rats: Behavioral and Ultrastructural Approaches. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, D.; Parle, M.; Kulkarni, S. Memory Enhancing Activity of Glycyrrhiza Glabra in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, V.; Riju, T.; Venkatesh, S.; Babu, G. Memory Enhancing Activity of Lawsonia inermis Linn. Leaves against Scopolamine Induced Memory Impairment in Swiss Albino Mice. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2017, 17, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishitha, N.; Muthuraman, A. Preventative Effects of Alpha-Naphtho Flavone in Vascular Dementia. Front. Biosci. Elite 2020, 12, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Brain TBARS (nM/mg of Protein) |
|---|---|
| CON | 59.40 ± 2.84 |
| AlCl3 | 83.58 ± 4.80 a |
| TRF 30 | 68.71 ± 1.48 |
| TRF 60 | 53.14 ± 5.21 b |
| TRF 120 | 53.84 ± 3.83 b |
| DON | 51.15 ± 1.38 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaikh, S.A.; Muthuraman, A. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Ameliorates the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Neurovascular Dysfunction-Associated Vascular Dementia in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060828
Shaikh SA, Muthuraman A. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Ameliorates the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Neurovascular Dysfunction-Associated Vascular Dementia in Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(6):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060828
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaikh, Sohrab A., and Arunachalam Muthuraman. 2023. "Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Ameliorates the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Neurovascular Dysfunction-Associated Vascular Dementia in Rats" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 6: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060828
APA StyleShaikh, S. A., & Muthuraman, A. (2023). Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Ameliorates the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Neurovascular Dysfunction-Associated Vascular Dementia in Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16060828






