Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel S-alkyl Phthalimide- and S-benzyl-oxadiazole-quinoline Hybrids as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Inhibitory Activity and SAR
2.3. Kinetic Studies
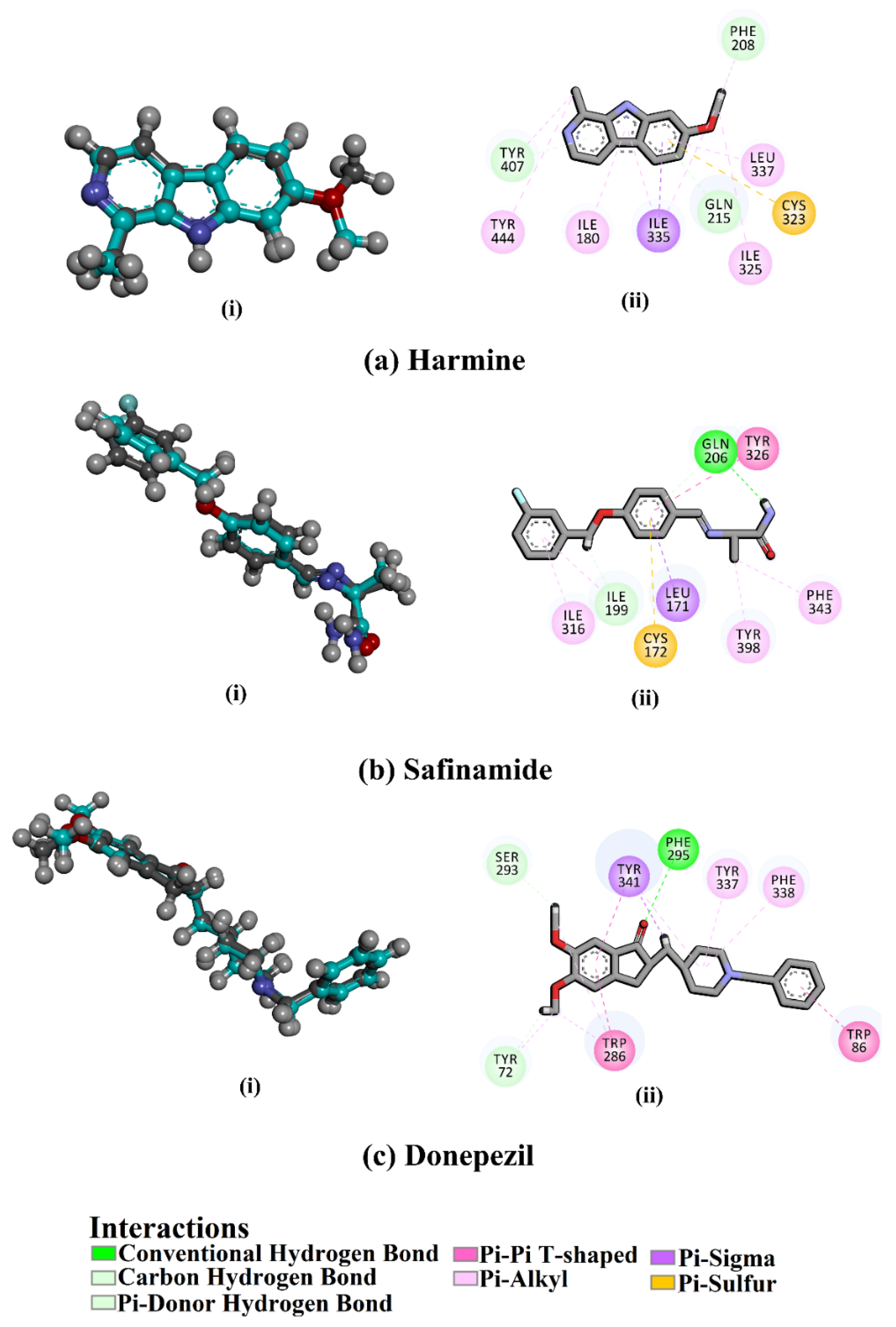
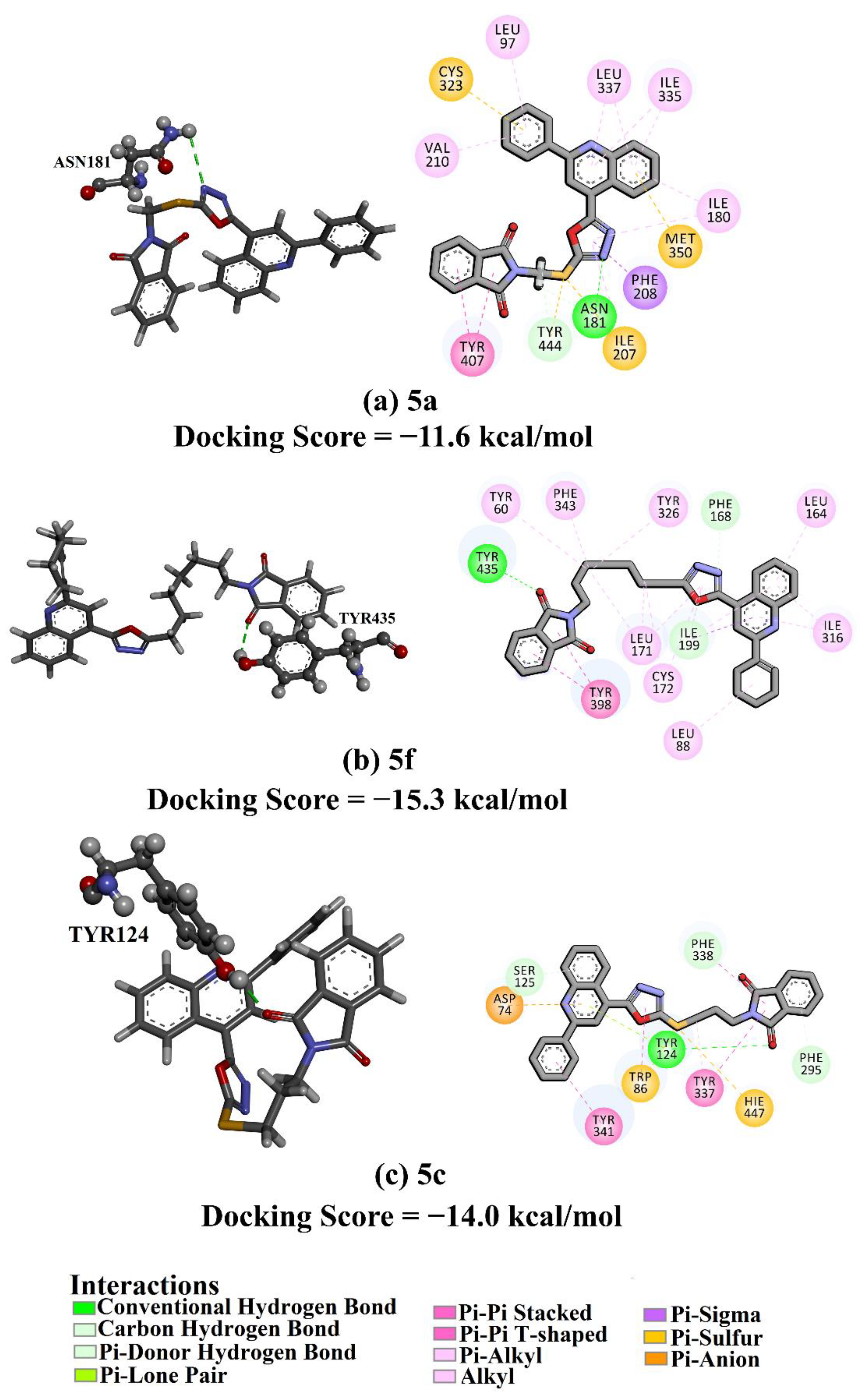
2.4. Docking Studies
2.5. Drug-Like and ADMET Characteristics
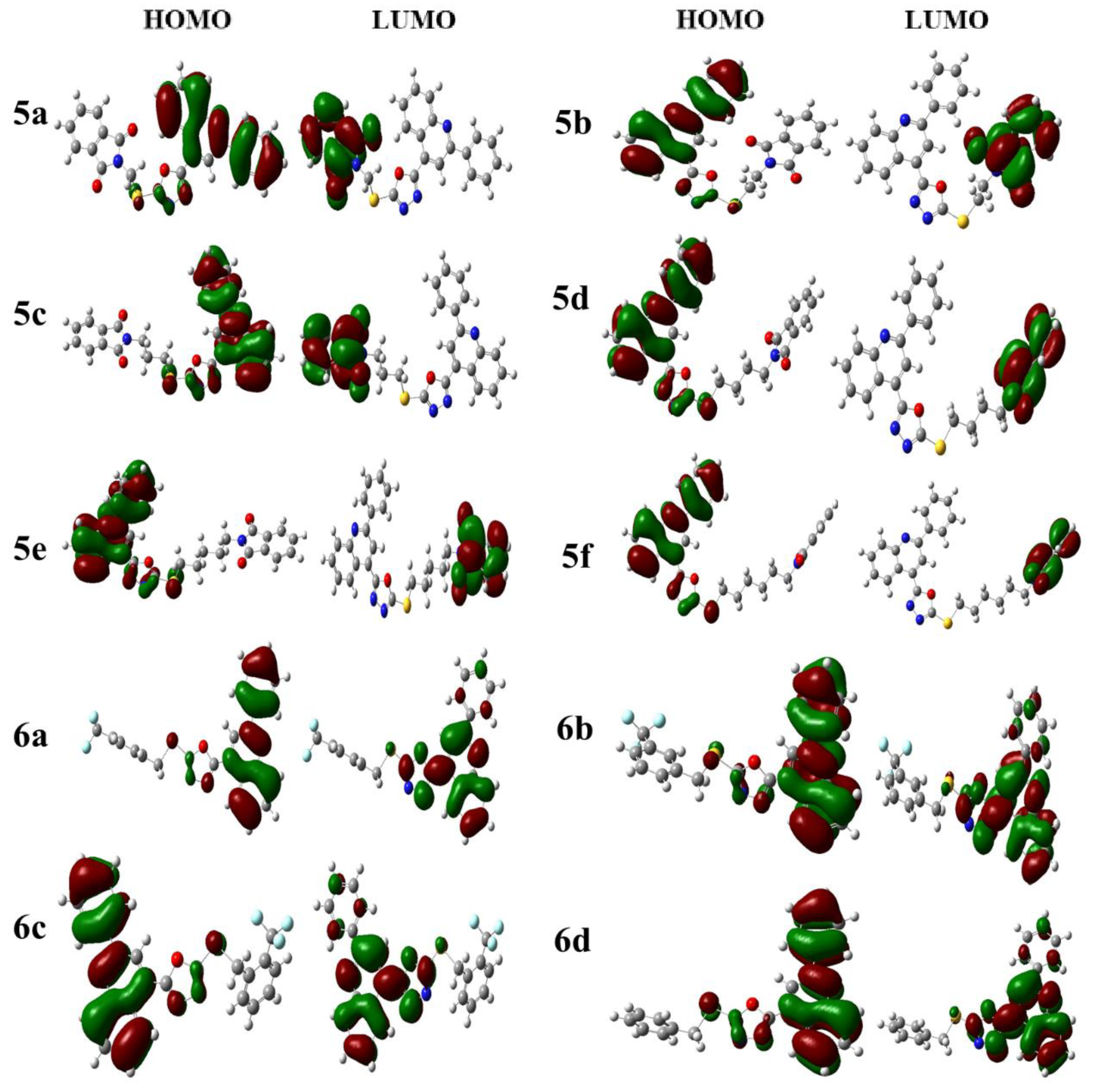
2.6. Density Function Theory (DFT) Calculations
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Apparatus
3.2. General Procedure
3.2.1. 2-((5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)methyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5a)
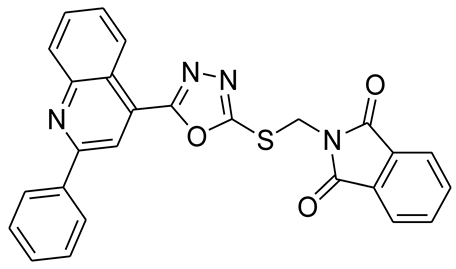
3.2.2. 2-(2-(5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)ethyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5b)
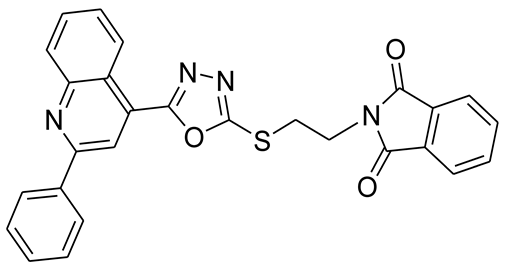
3.2.3. 2-(3-(5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)propyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5c)
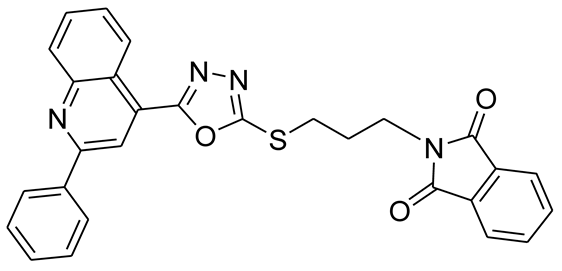
3.2.4. 2-(4-(5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)butyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5d)
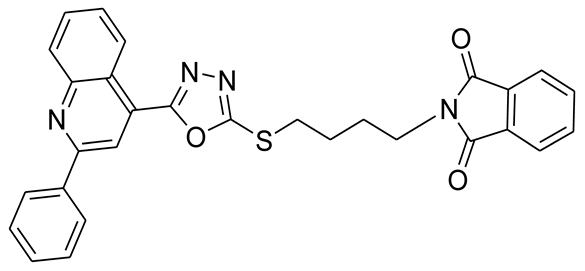
3.2.5. 2-(5-(5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)pentyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5e)
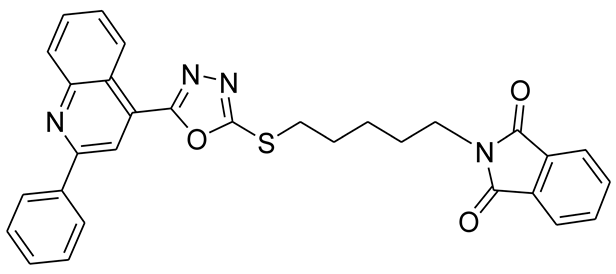
3.2.6. 2-(6-(5-(2-Phenylquinolin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-ylthio)hexyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (5f)
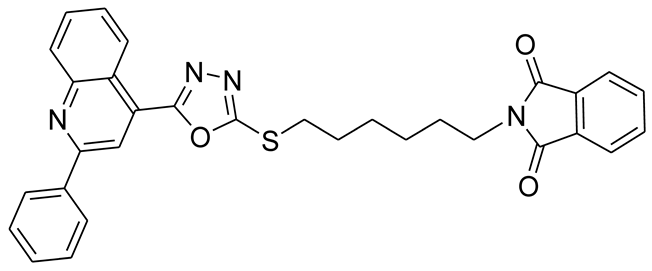
3.2.7. 4-(5-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-2-phenylquinoline (6a)
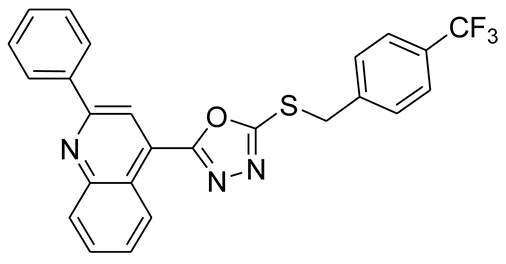
3.2.8. 4-(5-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-2-phenylquinoline (6b)
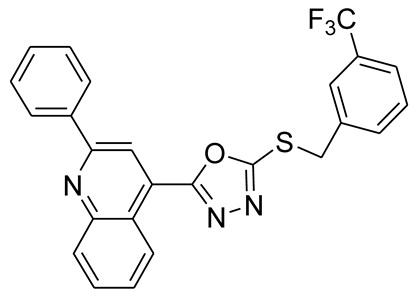
3.2.9. 4-(5-(2-(Trifluoromethyl)benzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-2-phenylquinoline (6c)
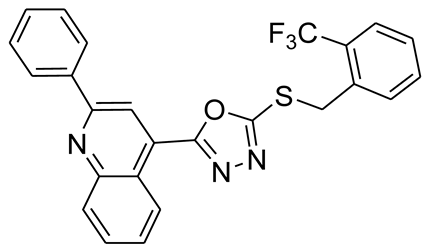
3.2.10. 4-(5-(Benzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-2-phenylquinoline (6d)
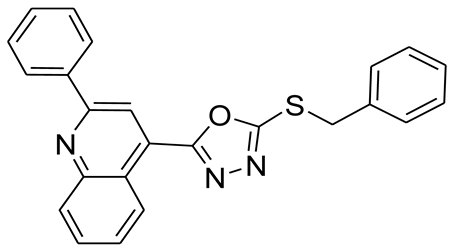
3.3. Inhibition Assay Protocol
3.3.1. Monoamine Oxidase
3.3.2. Acetylcholinesterase
3.4. Molecular Docking and ADMET Characteristics
3.4.1. Enzyme Preparation
3.4.2. Inhibitor Preparation
3.4.3. Docking Calculations
3.4.4. ADMET Properties
3.5. DFT Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saez-Atienzar, S.; Masliah, E. Author Correction: Cellular senescence and Alzheimer disease: The egg and the chicken scenario. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. From Plan to Impact: Progress towards Targets of the Global Action Plan on Dementia; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.K. The Structural Hybrids of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Alzheimer’s Neurodegener. Dis. 2019, 4, 015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez, M.; Vina, D. Dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase for the treatment of Alzheimer disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1692–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Silvestri, R. New Frontiers in Selective Human MAO-B Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6717–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Sheetal, S.; Mantha, A.K.; Kumar, V. Recent developments on the structure-activity relationship studies of MAO inhibitors and their role in different neurological disorders. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42660–42683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Cai, P.; Liu, Q.H.; Yang, X.L.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, X.B.; Kong, L.Y. Design, synthesis and evaluation of coumarin-pargyline hybrids as novel dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidases and amyloid-beta aggregation for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, N.Q.; Nguyen, H.L.; Linh, H.Q.; Li, M.S. Protocol for fast screening of multi-target drug candidates: Application to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2017, 77, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackard, W.G., Jr.; Sood, G.K.; Crowe, D.R.; Fallon, M.B. Tacrine. A cause of fatal hepatotoxicity? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1998, 26, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, D.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S.; Bumbu, A.G. Role of Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Insight into the Therapeutic Potential of Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, V.; Prashar, V.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, A.R.; Bajaj, B.; Mehta, D.; Parkash, J.; Kumar, V. Dipropargyl substituted diphenylpyrimidines as dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina, D.; Matos, M.J.; Yanez, M.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. 3-Substituted coumarins as dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, J.; Herzig, Y.; Goren, T.; Finkelstein, N.; Lerner, D.; Goldenberg, W.; Miskolczi, I.; Molnar, S.; Rantal, F.; Tamas, T.; et al. Novel dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO derived from hydroxy aminoindan and phenethylamine as potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5260–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, M.; Cipolloni, M.; Catto, M.; Colliva, C.; Miniero, D.V.; Latronico, T.; de Candia, M.; Benicchi, T.; Linusson, A.; Giacchè, N.; et al. Probing Fluorinated Motifs onto Dual AChE-MAO B Inhibitors: Rational Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Early-ADME Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3962–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousseau, D.D.; Baker, G.B. Recent developments in the regulation of monoamine oxidase form and function: Is the current model restricting our understanding of the breadth of contribution of monoamine oxidase to brain [dys] function? Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchcliffe, C.; Schumacher, H.C.; Burgut, F.T. Recent advances in Parkinson’s disease therapy: Use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2005, 5, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya Cavusoglu, B.; Saglik, B.N.; Ozkay, Y.; Inci, B.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Design, synthesis, monoamine oxidase inhibition and docking studies of new dithiocarbamate derivatives bearing benzylamine moiety. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.H.; Ding, Y.; Huang, N.W. Synthesis and biological activities of dithiocarbamates containing 1,2,3-triazoles group. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, D.; Sova, M.; Kosak, U.; Gobec, S. Dual inhibitors of cholinesterases and monoamine oxidases for Alzheimer’s disease. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 811–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bao, F.Q.; Gu, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Din, J.L.; Xi, S.S.; Ding, J.S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of quinolinone derivatives containing dithiocarbamate moiety as multifunctional AChE inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, M.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Khodarahmi, G.A.; Rostami, M.; Azimi, F.; Nadri, H.; Moghadam, F.H. Design, synthesis, and bio-evaluation of new isoindoline-1,3-dione derivatives as possible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabeliov, V.R.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.S.; Vassilev, N.G.; Elena, K.; Angelova, V.T. Neuroprotective evaluation of novel substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazole and aroylhydrazone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 59, 128516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, K.; Salahuddin; Sahu, J.K. Significance of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Containing Compounds in New Drug Development. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hkiri, S.; Hafidh, A.; Cavalier, J.F.; Touil, S.; Samarat, A. Design, synthesis, antimicrobial evaluation, and molecular docking studies of novel symmetrical 2,5-difunctionalized 1,3,4-oxadiazoles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 57, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar-Eldeen, H. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Some Bis-1,3,4-Butane-1-3, 4-Oxadiazole Derivatives. Ibn AL-Haitham J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2009, 22, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, G.; Palaska, E.; Ekizoğlu, M.; Özalp, M. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Il Farmaco 2002, 57, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel, R.; Farghaly, A.H. Synthesis, Reactions and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Indolyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazole, Triazole and Pyrazole Derivatives. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2004, 51, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasirad, A.; Vousooghi, N.; Tabatabai, S.A.; Kebriaeezadeh, A.; Shafiee, A. Synthesis, Anticonvulsant and Muscle Relaxant Activities of Substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazole, 1,3,4-thiadiazole and 1,2,4-triazole. Acta Chim. Slov. 2007, 54, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kashaw, S.K.; Gupta, V.; Kashaw, V.; Mishra, P.; Stables, J.P.; Jain, N.K. Anticonvulsant and sedative-hypnotic activity of some novel 3-[5-(4-substituted)phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2yl]-2-styrylquinazoline-4(3H)-ones. Med. Chem. Res. 2010, 19, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Lei, K.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Quan, Z. Synthesis of 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives with anticonvulsant activity and their binding to the GABAA receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Siddiqui, N. Synthesis, anticonvulsant and neurotoxicity of some novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives of phthalimide. Pharma Chem. 2010, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nazar, S.; Siddiqui, N.; Alam, O. Recent progress of 1,3,4-oxadiazoles as anticonvulsants: Future horizons. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, e1900342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glomb, T.; Szymankiewicz, K.; Swiatek, P. Anti-Cancer Activity of Derivatives of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole. Molecules 2018, 23, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudipati, R.; Anreddy, R.N.; Manda, S. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of certain 3-{4-(5-mercapto-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-yl)phenylimino}indolin-2-one derivatives. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, S.; Trisciuoglio, D.; De Luca, T.; Nebbioso, A.; Labella, D.; Lenoci, A.; Bigogno, C.; Dondio, G.; Miceli, M.; Brosch, G.; et al. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-containing histone deacetylase inhibitors: Anticancer activities in cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6259–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.; Pathak, D.; Shah, K. 1,3,4-oxadiazole and its derivatives: A review on recent progress in anticancer activities. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 97, 572–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, R.; Pathak, D.P.; Kapoor, G.; Husain, A.; Iqbal, M.A. Novel hybrids of benzothiazole-1,3,4-oxadiazole-4-thiazolidinone: Synthesis, in silico ADME study, molecular docking and in vivo anti-diabetic assessment. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, R.S.; Kudva, A.K.; Timanagouda, K.; Raghuveer; Mujawar, S.B.H.; Joshi, S.D.; Raghu, S.V. Synthesis of novel 5-(2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thiol derivatives as potential glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, S.S.; Khan, B.A.; Ahmed, M.N.; Hameed, S.; Akhter, K.; Ayub, K.; Mahmood, T. Synthesis, crystal structures, computational studies and α-amylase inhibition of three novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1200, 127085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Zafar, M.; Patel, S.; Shah, S.M.; Bishayee, A. Pharmacophore studies of 1,3,4-oxadiazole nucleus: Lead compounds as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, B. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole-chalcone conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4298–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Xue, W. Antibacterial and Antiviral Activities of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Thioether 4H-Chromen-4-one Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11085–11094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Xue, W.; Song, B. Design, synthesis, antiviral activity and three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship study of novel 1,4-pentadien-3-one derivatives containing the 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.N.; Chen, Q.; Tai, A.Q.; Jiang, G.Q.; Ouyang, G.P. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 2-substituted methylthio-5-(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.Y.; Shao, W.B.; Xue, H.T.; Fang, H.S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Song, B.A.; Yang, S. Synthesis of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives containing diamides as promising antibacterial and antiviral agents. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 6115–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, T.; Hameed, S.; Al-Masoudi, N.A.; Loddo, R.; La Colla, P. In vitro antitumor and antiviral activities of new benzothiazole and 1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2008, 58, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, F.A.; Mahfouz, N.M.; Rahman, M.A. Design, synthesis and antiinflammatory activity of some 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 31, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayashankar, B.; Rai, K.M.L.; Baskaran, N.; Sathish, H.S. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 1,3,4-oxadiazole bearing bis (heterocycle) derivatives as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3898–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.V.; Bothara, K.G.; Raut, M.K.; Patil, A.A.; Sarkate, A.P.; Mokale, V.J. Design, synthesis and evaluation of antiinflammatory, analgesic and ulcerogenicity studies of novel S-substituted phenacyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thiol and Schiff bases of diclofenac acid as nonulcerogenic derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Lohani, M.; Parthsarthy, R. Synthesis, Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Some 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, G.; Naaz, B.; Siddiqui, A.A. Exploring 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Scaffold for Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Activities: A Review of Literature from 2005–2016. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, R.R.; Shirodkar, P.Y. Oxadiazole: A biologically important heterocycle. Chem. Inform. 2009, 1, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, G.; Khan, M.F.; Akhtar, W.; Alam, M.M.; Akhter, M.; Shaquiquzzaman, M. A Review Exploring Therapeutic Worth of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Tailored Compounds. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 477–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryan, L.; Marta, M.; Myroslava, K.; Iryna, D.; Stefan, H.; Taras, C.; Ihor, C.; Vasyl, M. Approaches for synthesis and chemical modification of non-condensed heterocyclic systems based on 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring and their biological activity: A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Makawana, J.A.; Zhu, H.L. 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives as potential biological agents. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1725–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Saraf, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, P. Syntheses, Evaluation and Characterization of Some 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles as Antimicrobial Agents. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.D.; Prajapati, S.M.; Panchal, S.N.; Patel, H.D. Review of Synthesis of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives. Synth. Commun. 2014, 44, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxtall, J.D.; Keam, S.J. Raltegravir: A review of its use in the management of HIV infection in treatment-experienced patients. Drugs 2009, 69, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I. Antibacterial Activity of Furamizole on Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Korean J. Vet. Res. 1973, 13, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Chouhan, A. Various approaches for synthesis of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole derivatives and their pharmacological activity. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 1474–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Fizazi, K.; Higano, C.S.; Nelson, J.B.; Gleave, M.; Miller, K.; Morris, T.; Nathan, F.E.; McIntosh, S.; Pemberton, K.; Moul, J.W. Phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of docetaxel in combination with zibotentan in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bawa, S.; Gupta, H. Biological activities of quinoline derivatives. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, J.J. Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 1999, 63, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Fournet, A.; Barrios, A.A.; Munoz, V.; Hocquemiller, R.; Cave, A.; Bruneton, J. 2-substituted quinoline alkaloids as potential antileishmanial drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Gross, J.L.; Kerr, M.A. Synthesis of novel heterocycles related to the dynemicin a ring skeleton. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1996, 33, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Reichert, Y.; Kane, V.V. The total synthesis of streptonigrin and related antitumor antibiotic natural products. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 3539–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprio, V.; Guyen, B.; Opoku-Boahen, Y.; Mann, J.; Gowan, S.M.; Kelland, L.M.; Read, M.A.; Neidle, S. A novel inhibitor of human telomerase derived from 10H-indolo [3,2-b]quinoline. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 2063–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikata, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Ogura, S.; Okura, I.; Kawasaki, M.; Maeda, M.; Yano, S. Effect of side chain location in (2-aminoethyl)aminomethyl-2-phenylquinolines as antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, D.; Spengler, G.; Molnar, J.; Antal, Z.; Molnar, A.; Kiss, J.T.; Szabo, J.A.; Hilgeroth, A.; Gallo, S.; Mahamoud, A.; et al. The interaction between resistance modifiers such as pyrido[3,2-g]quinoline, aza-oxafluorene and pregnane derivatives with DNA, plasmid DNA and tRNA. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, R.; Wang, D.; Kelly, J.; Afonso, A.; James, L.; Kirschmeier, P.; McPhail, A.T. Synthesis and evaluation of pyrazolo [3,4-b]quinoline ribofuranosides and their derivatives as inhibitors of oncogenic Ras. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Z.; Hunt, J.T.; Ricca, C.; Manne, V. 3-Imidazolylmethylaminophenylsulfonyltetrahydroquinolines, a novel series of farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Miller, K.; Boschelli, D.H.; Ye, F.; Wu, B.; Floyd, M.B.; Powell, D.W.; Wissner, A.; Weber, J.M.; Boschelli, F. Inhibitors of src tyrosine kinase: The preparation and structure-activity relationship of 4-anilino-3-cyanoquinolines and 4-anilinoquinazolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 2477–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Dinakaran, M.; Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D.; China, A.; Nagaraja, V. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activities of novel 6-nitroquinolone-3-carboxylic acids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakaran, M.; Senthilkumar, P.; Yogeeswari, P.; China, A.; Nagaraja, V.; Sriram, D. Novel ofloxacin derivatives: Synthesis, antimycobacterial and toxicological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyar, A.; Monga, V.; Malde, A.; Coutinho, E.; Jain, R. Synthesis, anti-tuberculosis activity, and 3D-QSAR study of 4-(adamantan-1-yl)-2-substituted quinolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.V.; Kanth, S.R.; Maitraie, D.; Narsaiah, B.; Rao, P.S.; Kishore, K.H.; Murthy, U.S.N.; Ravi, B.; Kumar, B.A.; Parthasarathy, T. Design, synthesis, structure-activity relationship and antibacterial activity series of novel imidazo fused quinolone carboxamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J.; Wei, C.X.; Jia, J.H.; Zhao, L.M.; Quan, Z.S. Design and synthesis of 5-alkoxy-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoline derivatives with anticonvulsant activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemence, F.; Le Martret, O.; Delevallee, F.; Benzoni, J.; Jouanen, A.; Jouquey, S.; Mouren, M.; Deraedt, R. 4-Hydroxy-3-quinolinecarboxamides with antiarthritic and analgesic activities. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Awano, K.; Miyashita, M.; Fujimori, S.; Kuriyama, K.; Sakoe, Y.; Kudoh, S.; Saito, K.; Kojima, E. Synthesis and antirheumatic activity of novel tetrahydroquinoline-8-carboxylic acid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1997, 7, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, I.; Haleen, S.J.; Burke, S.E.; Barth, H. Synthesis and biological activity of 4-(diphenylmethyl)-alpha-[(4-quinolinyloxy)methyl]-1-piperazineethanol and related compounds. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 4442–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlin, M.G.; Chiarelotto, G.; Antonucci, F.; Caparrotta, L.; Froldi, G. Mannich bases of 3H-pyrrolo[3,2-f]quinoline having vasorelaxing activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, S.S.; Khan, B.A.; Hameed, S.; Batool, F.; Saleem, H.N.; Mughal, E.U.; Saeed, M. Synthesis and evaluation of novel S-benzyl- and S-alkylphthalimide-oxadiazole-benzenesulfonamide hybrids as inhibitors of dengue virus protease. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.A.; Hamdani, S.S.; Ahmed, M.N.; Hameed, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Shawky, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Sidhom, P.A. Synthesis, X-ray diffraction analysis, quantum chemical studies and alpha-amylase inhibition of probenecid derived S-alkylphthalimide-oxadiazole-benzenesulfonamide hybrids. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1464–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Zafar, S.; Mughal, E.U.; Ahmed, M.N.; Hamdani, S.S.; Akhtar, T.; Haq, I.U.; Sadiq, A.; Khan, K.M. Design and Synthesis of Novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole Derivatives Bearing Azo Moiety as Biologically Significant Scaffolds. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 15, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesiti, F.; Maruca, A.; Silva, V.; Rocca, R.; Fernandes, C.; Remiao, F.; Uriarte, E.; Alcaro, S.; Gaspar, A.; Borges, F. 4-Oxoquinolines and monoamine oxidase: When tautomerism matters. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Munir, R.; Younas, M.T.; Kausar, N.; Ibrar, A.; Aqsa, S.; Shahid, N.; Asif, T.T.; Alsaab, H.O.; Khan, I. Hybrid Quinoline-Thiosemicarbazone Therapeutics as a New Treatment Opportunity for Alzheimer’s DiseaseSynthesis, In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibitory Potential and Computational Modeling Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-A resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti-Renom, M.A.; Stuart, A.C.; Fiser, A.; Sanchez, R.; Melo, F.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2000, 29, 291–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.C.; Myers, J.B.; Folta, T.; Shoja, V.; Heath, L.S.; Onufriev, A. H++: A server for estimating pKas and adding missing hydrogens to macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W368–W371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. MMFF VI. MMFF94s option for energy minimization studies. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenEye Scientific Software, SZYBKI 1.9.0.3; OpenEye Scientific Software: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2016.
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative Partial Equalization of Orbital Electronegativity—A Rapid Access to Atomic Charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA, B.D.S.V. Version 2019; Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019.
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision E01; Gaussian09, Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]





| No | Compound | IC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | AChE | ||
| 1 | 5a | 0.91 ± 0.15 | 1.59 ± 1.66 | 1.40 ± 0.45 |
| 2 | 5b | 1.81 ± 0.38 | 2.61 ± 2.48 | 2.55 ± 0.96 |
| 3 | 5c | 3.31 ± 0.80 | 3.39 ± 0.42 | 1.02 ± 0.65 |
| 4 | 5d | 3.18 ± 1.23 | 3.76 ± 1.04 | 2.38 ± 0.92 |
| 5 | 5e | 4.14 ± 0.35 | 3.84 ± 0.91 | 1.29 ± 0.75 |
| 6 | 5f | 4.88 ± 1.75 | 0.84 ± 0.06 | 3.32 ± 0.45 |
| 7 | 6a | 1.51 ± 0.52 | 3.71 ± 2.88 | 3.23 ± 0.95 |
| 8 | 6b | 1.02 ± 0.92 | 2.71 ± 0.88 | 3.54 ± 1.05 |
| 9 | 6c | 6.81 ± 2.65 | 5.59 ± 3.22 | 4.38 ± 1.45 |
| 10 | 6d | 4.16 ± 1.71 | 2.90 ± 1.85 | 4.98 ± 1.85 |
| 11 | Clorgyline b | 0.0045 ± 0.0003 | 61.35 ± 1.13 | |
| 12 | Deprenyl b | 67.25 ± 1.02 | 0.0196 ± 0.001 | |
| 13 | Donepezil b | 0.032 ± 0.003 a | ||
| Compound | Physicochemical Properties | ADMET Properties | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption and Distribution | Metab-Olism (CYP2C19 Inhibitor) | Excretion (Clearance) |
Toxicity (AMES) | ||||||||
| MW | nHBA | nHBD | Log P | Lipinski Rule | HIA | CaCo-2 | BBB | ||||
| 5a | 464.1 | 7 | 0 | 5.2 | Accepted | 0.007 | −4.55 | 0.058 | 0.889 | 3.10 | 0.043 |
| 5c | 492.1 | 7 | 0 | 5.4 | Accepted | 0.006 | −4.534 | 0.078 | 0.862 | 3.22 | 0.012 |
| 5f | 534.2 | 7 | 0 | 6.7 | Accepted | 0.006 | −4.582 | 0.050 | 0.819 | 3.46 | 0.011 |
| Clorgyline | 271.1 | 2 | 0 | 3.7 | Accepted | −0.001 | −4.251 | 0.992 | 0.679 | 11.24 | 0.017 |
| Deprenyl | 187.1 | 1 | 0 | 2.7 | Accepted | −0.005 | −4.915 | 0.996 | 0.133 | 10.46 | 0.035 |
| Donepezil | 379.2 | 4 | 0 | 4.2 | Accepted | 0.003 | −4.793 | 0.975 | 0.413 | 10.63 | 0.026 |
| Compound | Eopt (au) | EHOMO (eV) | ELUMO (eV) | ∆Egap (eV) | η (eV) | σ (eV−1) | μ (Debye) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | −1842.831 | −0.221 | −0.112 | 0.108 | 0.054 | 9.206 | 8.358 | 347.284 |
| 5b | −1882.144 | −0.221 | −0.109 | 0.112 | 0.056 | 8.917 | 7.599 | 351.377 |
| 5c | −1921.445 | −0.226 | −0.100 | 0.125 | 0.063 | 7.955 | 6.751 | 363.499 |
| 5d | −1960.751 | −0.226 | −0.098 | 0.127 | 0.064 | 7.846 | 7.320 | 370.377 |
| 5e | −2000.055 | −0.225 | −0.096 | 0.129 | 0.065 | 7.721 | 6.769 | 385.049 |
| 5f | −2039.360 | −0.225 | −0.095 | 0.130 | 0.065 | 7.651 | 7.268 | 393.625 |
| 6a | −1899.057 | −0.227 | −0.089 | 0.137 | 0.069 | 7.266 | 1.194 | 331.243 |
| 6b | −1899.057 | −0.227 | −0.088 | 0.138 | 0.069 | 7.237 | 2.973 | 329.504 |
| 6c | −1899.059 | −0.226 | −0.088 | 0.138 | 0.069 | 7.245 | 2.446 | 323.636 |
| 6d | −1562.098 | −0.223 | −0.084 | 0.138 | 0.069 | 7.204 | 3.093 | 318.962 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, B.A.; Hamdani, S.S.; Jalil, S.; Ejaz, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Shawky, A.M.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Gabr, G.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Sidhom, P.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel S-alkyl Phthalimide- and S-benzyl-oxadiazole-quinoline Hybrids as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010011
Khan BA, Hamdani SS, Jalil S, Ejaz SA, Iqbal J, Shawky AM, Alqahtani AM, Gabr GA, Ibrahim MAA, Sidhom PA. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel S-alkyl Phthalimide- and S-benzyl-oxadiazole-quinoline Hybrids as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Bilal Ahmad, Syeda Shamila Hamdani, Saquib Jalil, Syeda Abida Ejaz, Jamshed Iqbal, Ahmed M. Shawky, Alaa M. Alqahtani, Gamal A. Gabr, Mahmoud A. A. Ibrahim, and Peter A. Sidhom. 2023. "Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel S-alkyl Phthalimide- and S-benzyl-oxadiazole-quinoline Hybrids as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010011
APA StyleKhan, B. A., Hamdani, S. S., Jalil, S., Ejaz, S. A., Iqbal, J., Shawky, A. M., Alqahtani, A. M., Gabr, G. A., Ibrahim, M. A. A., & Sidhom, P. A. (2023). Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel S-alkyl Phthalimide- and S-benzyl-oxadiazole-quinoline Hybrids as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase. Pharmaceuticals, 16(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010011







