Feasibility of Developing Radiotracers for MDM2: Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of an 18F-Labeled Analogue of the MDM2 Inhibitor SP-141
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
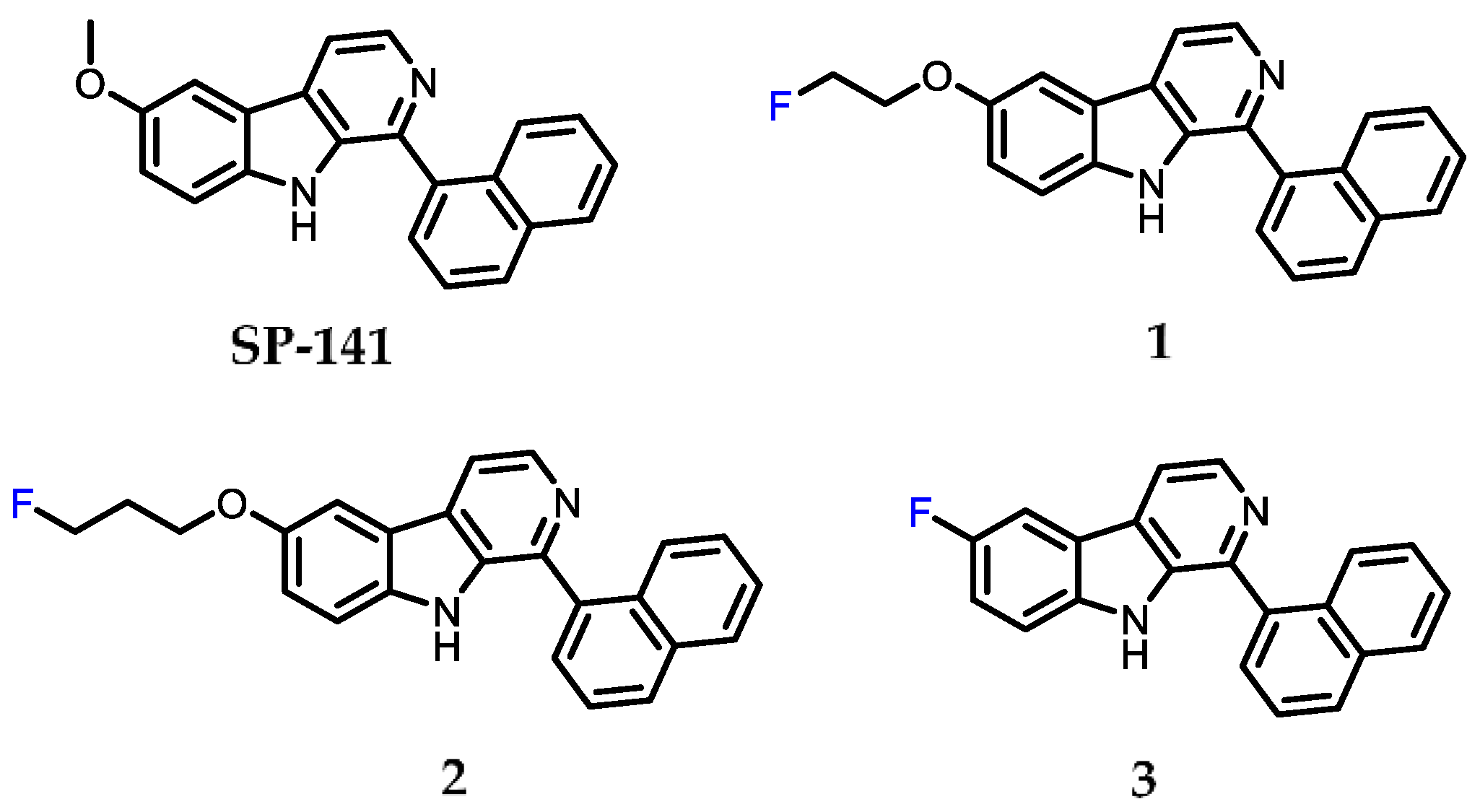
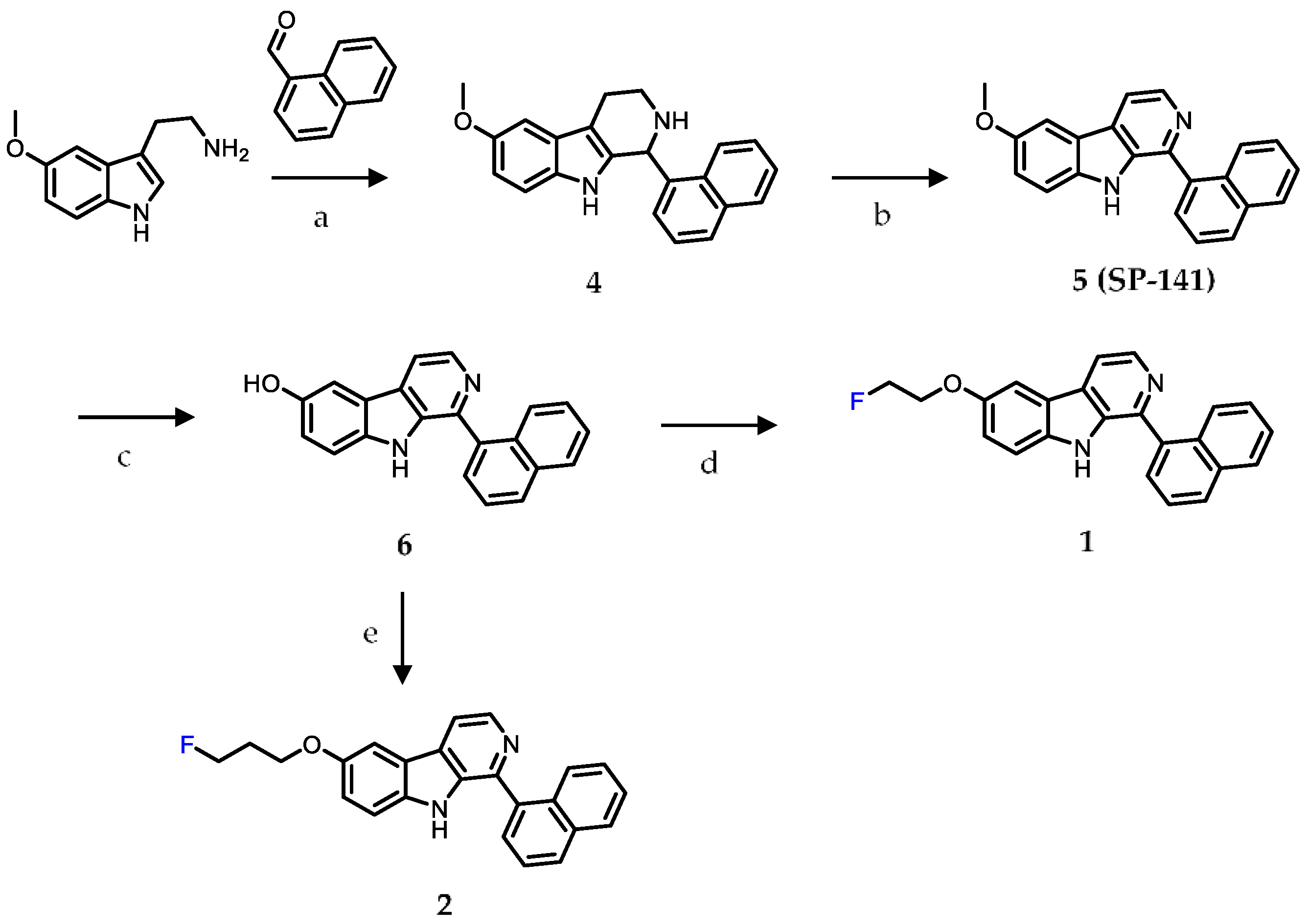
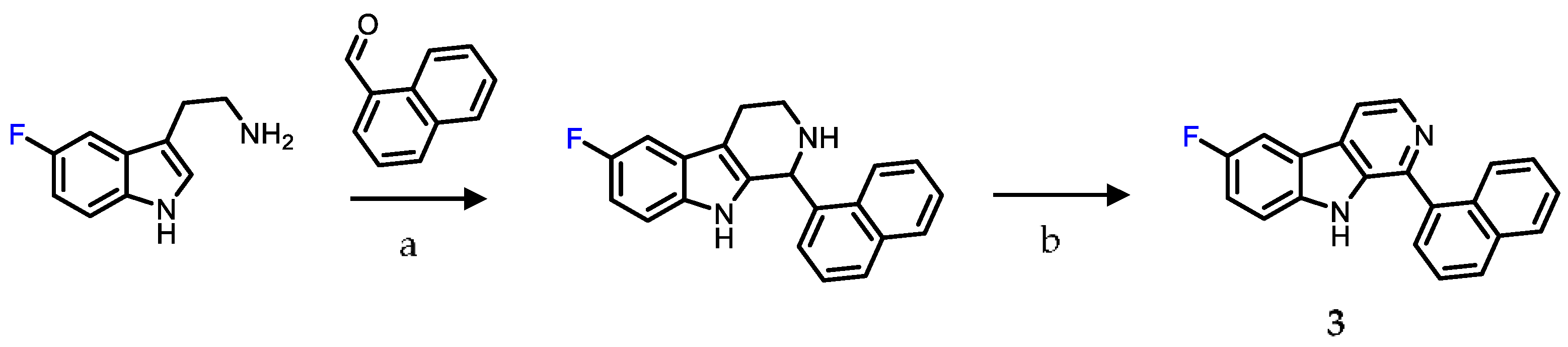
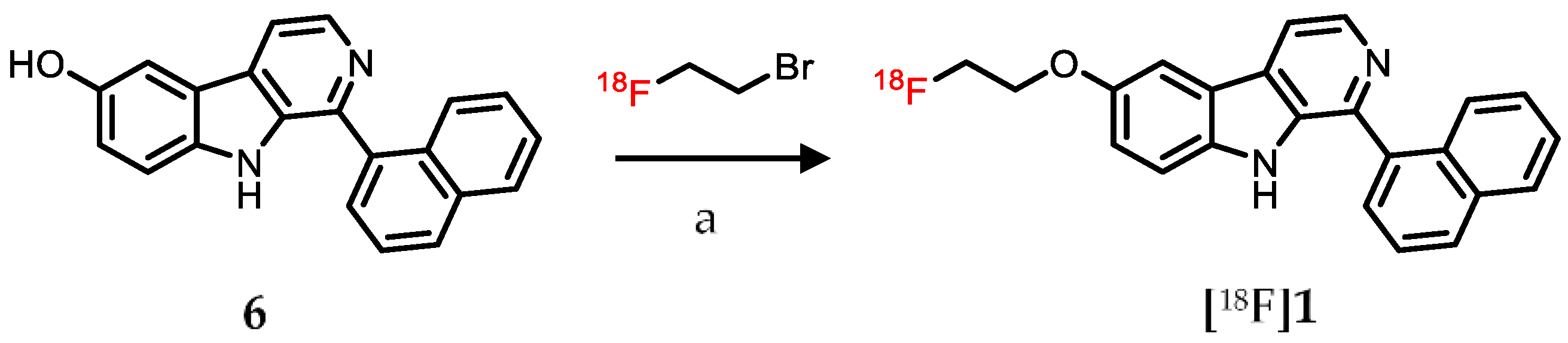
2.1. Chemistry
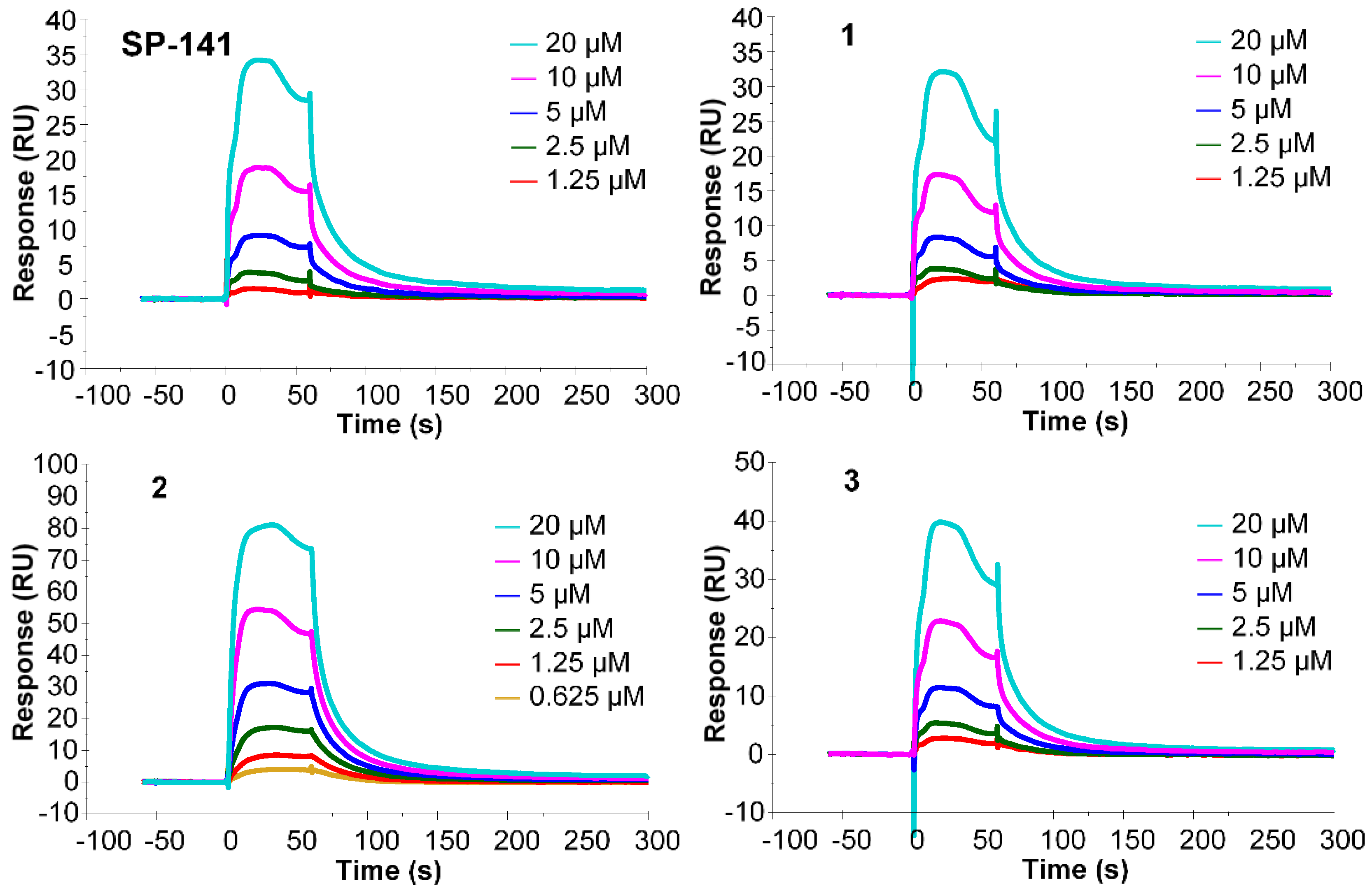
2.2. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis
2.3. Radiolabeling
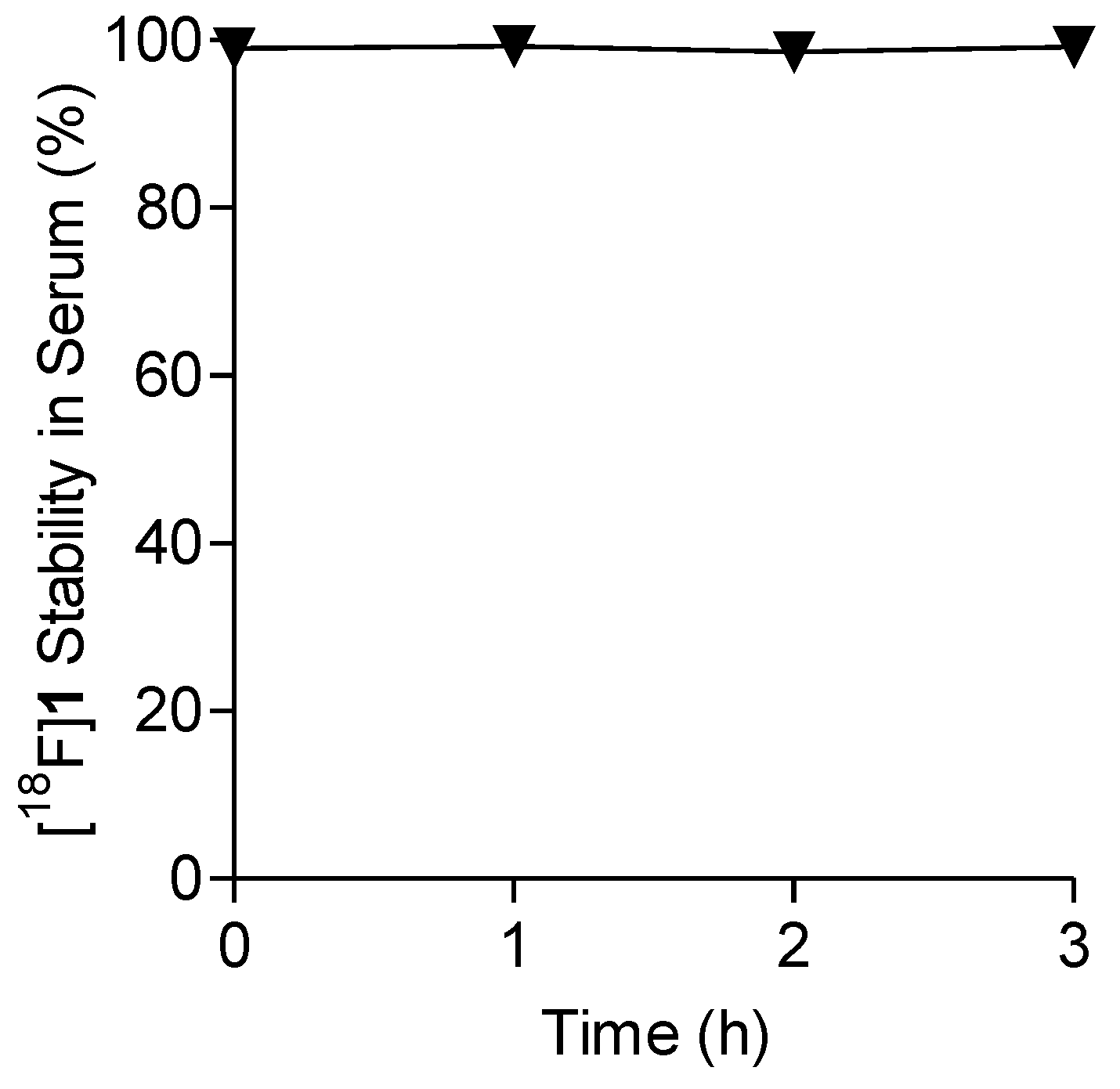
2.4. Lipophilicity and In Vitro Stability of [18F]1 in Human Serum
2.5. Uptake in MDM2 Expressing Tumor Cell Lines
2.6. Saturation Binding Assay
2.7. Measuring Changes in [18F]1 Uptake in Response to MDM2 Inhibition with SP-141
2.8. Tissue Distribution Studies in HepG2 Xenografts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis
4.3. Radiochemistry
4.4. Determination of Lipophilicity of [18F]1
4.5. Cell Uptake Studies with [18F]1
4.6. Saturation Binding Assay with [18F]1
4.7. Measuring Changes in [18F]1 Uptake in Response to MDM2 Inhibition with SP-141 In Vitro
4.8. Serum Stability Analysis
4.9. Tissue Distribution Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, E.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Wang, H. MDM2 and human malignancies: Expression, clinical pathology, prognostic markers, and implications for chemotherapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2005, 5, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringshausen, I.; O’Shea, C.C.; Finch, A.J.; Swigart, L.B.; Evan, G.I. Mdm2 is critically and continuously required to suppress lethal p53 activity in vivo. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, Y.; Maya, R.; Kazaz, A.; Oren, M. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 1997, 387, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, S.Y.; Ikeda, M.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2. Cell 1997, 91, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastan, M.B.; Onyekwere, O.; Sidransky, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Craig, R.W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 6304–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M. Census and evaluation of p53 target genes. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3943–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Manshouri, T.; Haidar, M.A.; Yang, Y.; McCown, P.; Ordonez, N.; Glassman, A.; Sneige, N.; Albitar, M. Abnormal expression of MDM-2 in breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1996, 37, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, P.M.; Wolf, E.R.; Olivos, D.J., 3rd; Batuello, C.N.; McElyea, K.C.; McAtarsney, C.P.; Cournoyer, R.M.; Sandusky, G.E.; Mayo, L.D. Early-Stage Metastasis Requires Mdm2 and Not p53 Gain of Function. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, F.S.; Tokino, T.; Meltzer, P.; Burrell, M.; Oliner, J.D.; Smith, S.; Hill, D.E.; Sidransky, D.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. p53 Mutation and MDM2 amplification in human soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 2231–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger, G.; Liu, L.; Ichimura, K.; Schmidt, E.E.; Collins, V.P. Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2 gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 2736–2739. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.S.; Graves, B.; Guerlavais, V.; Tovar, C.; Packman, K.; To, K.H.; Olson, K.A.; Kesavan, K.; Gangurde, P.; Mukherjee, A.; et al. Stapled alpha-helical peptide drug development: A potent dual inhibitor of MDM2 and MDMX for p53-dependent cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3445–E3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeff, M.; Kelly, K.R.; Yee, K.; Assouline, S.; Strair, R.; Popplewell, L.; Bowen, D.; Martinelli, G.; Drummond, M.W.; Vyas, P.; et al. Results of the Phase I Trial of RG7112, a Small-Molecule MDM2 Antagonist in Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Liao, W.; Zeng, S.X.; Lu, H. Reviving the guardian of the genome: Small molecule activators of p53. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 178, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.; Jukofsky, L.; Chen, G.; Martinelli, G.; Zhong, H.; So, W.V.; Dickinson, M.J.; Drummond, M.; Assouline, S.; Hashemyan, M.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia patients’ clinical response to idasanutlin (RG7388) is associated with pre-treatment MDM2 protein expression in leukemic blasts. Haematologica 2016, 101, e185–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluck, W.L.; Gounder, M.M.; Frank, R.; Eskens, F.; Blay, J.Y.; Cassier, P.A.; Soria, J.C.; Chawla, S.; de Weger, V.; Wagner, A.J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the MDM2 inhibitor AMG 232 in patients with advanced P53 wild-type solid tumors or multiple myeloma. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Dobashi, Y.; Nojima, T.; Nakamura, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Tsuchiya, H.; Ikeda, H.; Sawada-Kitamura, S.; Oyama, T.; Ooi, A. Utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization to detect MDM2 amplification in liposarcomas and their morphological mimics. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Turbin, D.A.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Bajdik, C.D.; Gelmon, K.A.; Yorida, E.; De Luca, A.; Nielsen, T.O.; Huntsman, D.G.; Gilks, C.B. MDM2 protein expression is a negative prognostic marker in breast carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Shen, B.; Zhao, C.; Tian, G. Molecular imaging of MDM2 messenger RNA with 99mTc-labeled antisense oligonucleotides in experimental human breast cancer xenografts. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Sun, L.; Cao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, C. MDM2 molecular imaging for the prediction of chemotherapeutic sensitivity in human breast cancer xenograft. Mol. Imaging 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Bickel, P.J.; Biggin, M.D. System wide analyses have underestimated protein abundances and the importance of transcription in mammals. PeerJ 2014, 2, e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Aguilar, A.; Bernard, D.; Wang, S. Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction (MDM2 Inhibitors) in clinical trials for cancer treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1038–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, J.J.; Voruganti, S.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Nag, S.; Patil, S.; Sharma, H.; Wang, M.H.; Wang, H.; Buolamwini, J.K.; et al. The pyrido[b]indole MDM2 inhibitor SP-141 exerts potent therapeutic effects in breast cancer models. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Qin, J.J.; Cheng, J.W.; Li, X.; Rajaei, M.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.R.; Zhang, R. A novel inhibitor of MDM2 oncogene blocks metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma and overcomes chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 2019, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, J.J.; Voruganti, S.; Wang, M.H.; Sharma, H.; Patil, S.; Zhou, J.W.; Wang, H.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Buolamwini, J.K.; et al. Identification of a New Class of MDM2 Inhibitor That Inhibits Growth of Orthotopic Pancreatic Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punganuru, S.R.; Artula, V.; Zhao, W.; Rajaei, M.; Deokar, H.; Zhang, R.; Buolamwini, J.K.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wang, W. Targeted Brain Tumor Therapy by Inhibiting the MDM2 Oncogene: In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of Action. Cells 2020, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.A.; Addo, J.K.; Deokar, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Suttle, D.P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Buolamwini, J.K. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies of New Pyrido[3,4-b]indole Derivatives as Broad-Spectrum Potent Anticancer Agents. Drug Des. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClurg, U.L.; Cork, D.M.W.; Darby, S.; Ryan-Munden, C.A.; Nakjang, S.; Mendes Cortes, L.; Treumann, A.; Gaughan, L.; Robson, C.N. Identification of a novel K311 ubiquitination site critical for androgen receptor transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Ross, T.M.; Chu, X.J.; Bartkovitz, D.; Podlaski, F.; Janson, C.; et al. Discovery of RG7388, a potent and selective p53-MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5979–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thean, D.; Ebo, J.S.; Luxton, T.; Lee, X.C.; Yuen, T.Y.; Ferrer, F.J.; Johannes, C.W.; Lane, D.P.; Brown, C.J. Enhancing Specific Disruption of Intracellular Protein Complexes by Hydrocarbon Stapled Peptides Using Lipid Based Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitneni, S.K.; Reitman, Z.J.; Gooden, D.M.; Yan, H.; Zalutsky, M.R. Radiolabeled inhibitors as probes for imaging mutant IDH1 expression in gliomas: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of labeled butyl-phenyl sulfonamide analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 119, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitneni, S.K.; Yan, H.; Zalutsky, M.R. Synthesis and Evaluation of a F-18-Labeled Triazinediamine Analogue for Imaging Mutant IDH1 Expression in Gliomas by PET. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piette, J.; Neel, H.; Marechal, V. Mdm2: Keeping p53 under control. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Yang, X.; Qi, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Hoppmann, S.; Cao, Q.; Chua, M.S.; So, S.K.; Cheng, Z. Molecular imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts with epidermal growth factor receptor targeted affibody probes. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 759057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Qin, J.J.; Voruganti, S.; Wang, M.H.; Sharma, H.; Patil, S.; Buolamwini, J.K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R. Development and validation of a rapid HPLC method for quantitation of SP-141, a novel pyrido[b]indole anticancer agent, and an initial pharmacokinetic study in mice. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Organ | 30 min | 1 h | 1 h Block 2 | 2 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.8 |
| Heart | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.9 |
| Kidneys | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.6 |
| Liver | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 0.5 |
| Spleen | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.4 |
| Stomach | 5.1 ± 2.0 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.7 |
| Small Intestine | 3.9 ± 1.0 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.5 |
| Large Intestine | 6.1 ± 1.7 | 7.7 ± 1.8 | 3.4 ± 1.4 * | 7.1 ± 2.9 |
| Skin | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.4 |
| Muscle | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.7 |
| Blood | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 2.7 ± 0.9 * | 3.3 ± 0.8 |
| Bone | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 1.0 | 1.9 ± 0.4 * | 5.4 ± 0.8 |
| Brain | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.7 |
| Tumor | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 3.0 ± 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitneni, S.K.; Zhou, Z.; Watts, B.E.; Zalutsky, M.R. Feasibility of Developing Radiotracers for MDM2: Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of an 18F-Labeled Analogue of the MDM2 Inhibitor SP-141. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040358
Chitneni SK, Zhou Z, Watts BE, Zalutsky MR. Feasibility of Developing Radiotracers for MDM2: Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of an 18F-Labeled Analogue of the MDM2 Inhibitor SP-141. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(4):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040358
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitneni, Satish K., Zhengyuan Zhou, Brian E. Watts, and Michael R. Zalutsky. 2021. "Feasibility of Developing Radiotracers for MDM2: Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of an 18F-Labeled Analogue of the MDM2 Inhibitor SP-141" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 4: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040358
APA StyleChitneni, S. K., Zhou, Z., Watts, B. E., & Zalutsky, M. R. (2021). Feasibility of Developing Radiotracers for MDM2: Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of an 18F-Labeled Analogue of the MDM2 Inhibitor SP-141. Pharmaceuticals, 14(4), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040358







