SPECT Imaging of SST2-Expressing Tumors with 99mTc-Based Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: The Role of Tetraamine, HYNIC, and Spacers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis, Radiolabeling and Partition Coefficients (log D)
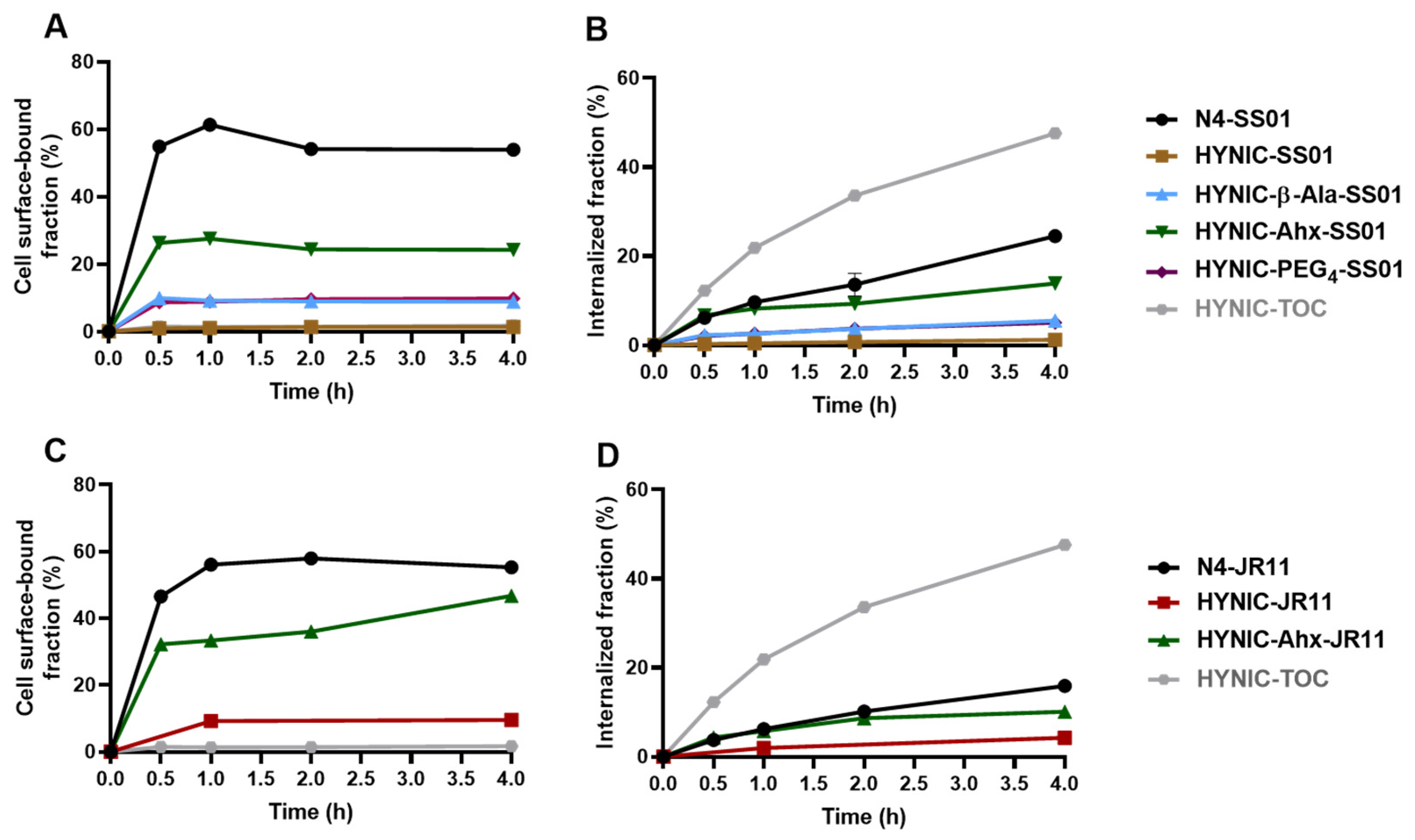
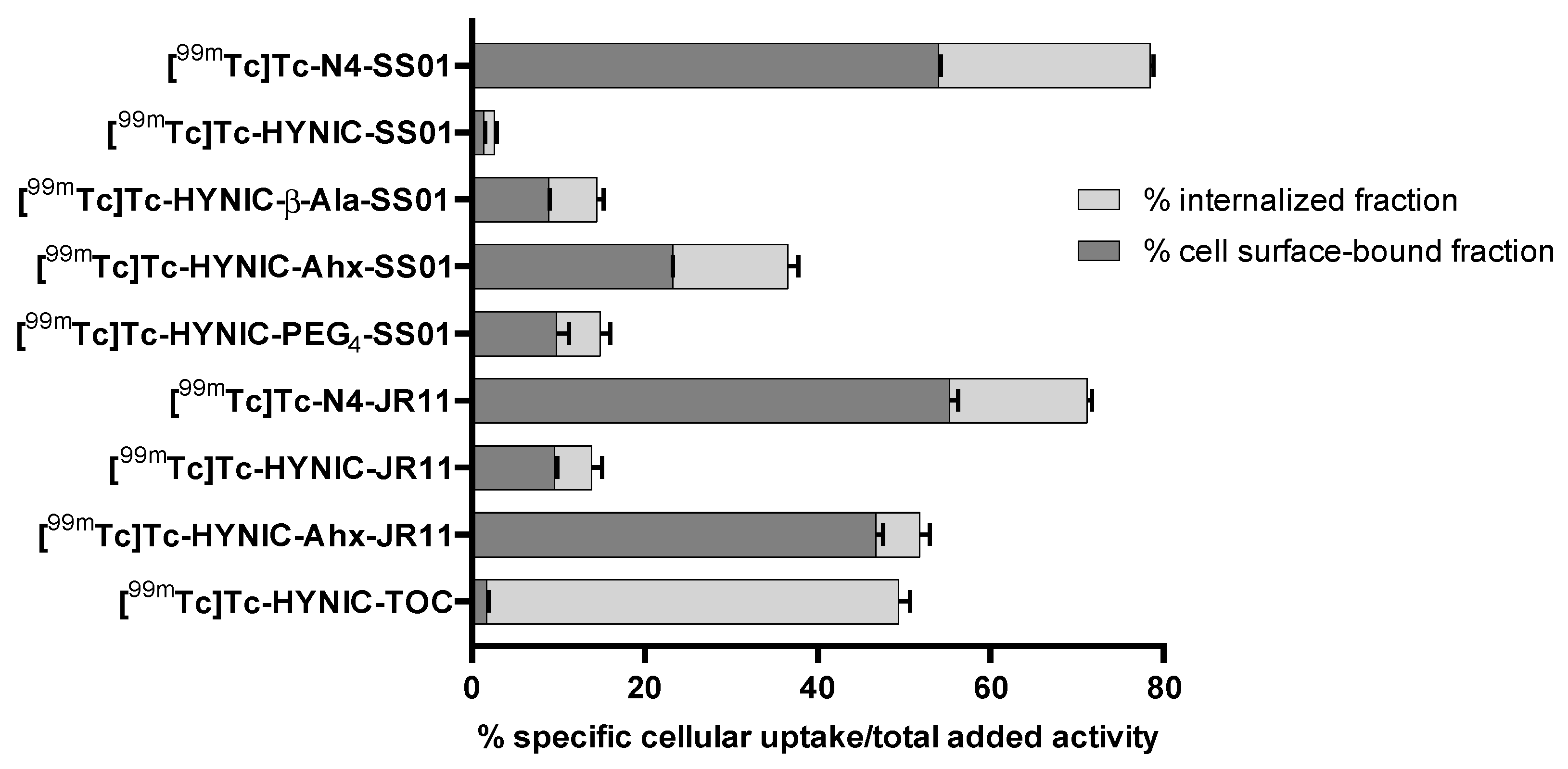
2.2. Cellular Distribution
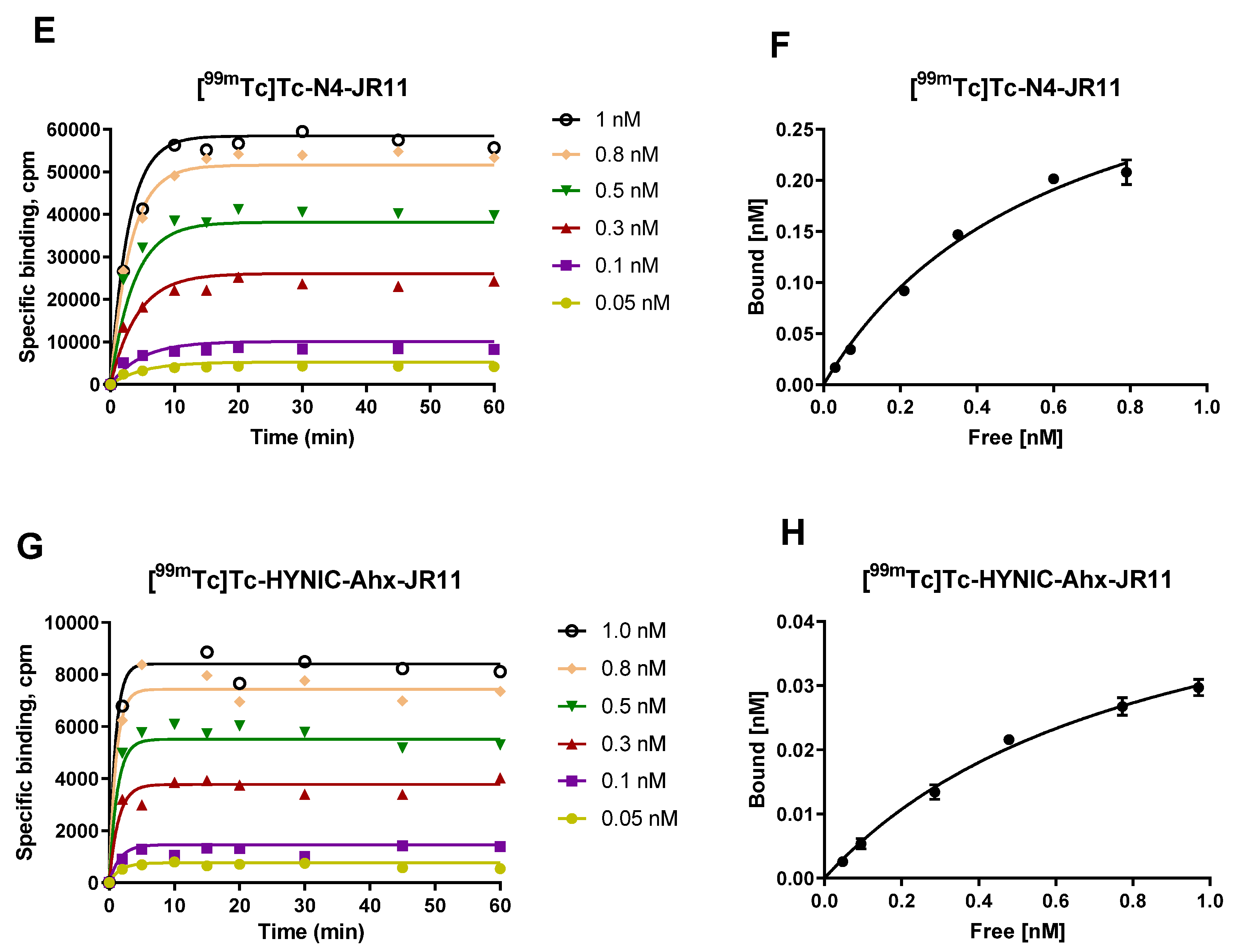
2.3. Kinetics of Association on HEK-SST2 Cell Membranes and Related Saturation Binding
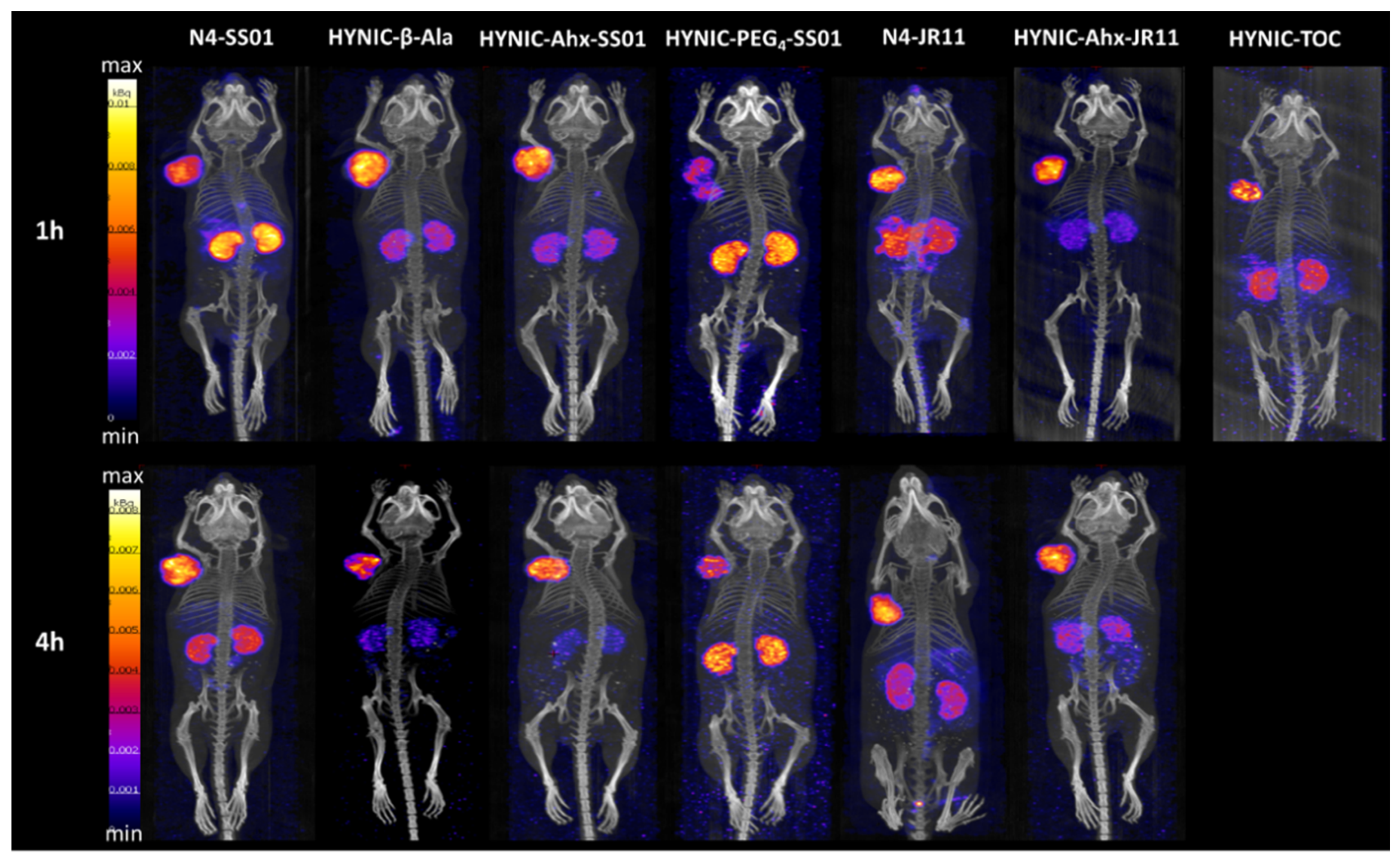
2.4. SPECT/CT Imaging
2.5. Biodistribution Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of the Chelator-Peptide Conjugates
4.2. Synthesis of the Radiolabeled Conjugated and Stability
4.3. Log D Measurements
4.4. In Vitro Characterization
4.4.1. Cell Cultures and Cell Membranes
4.4.2. In Vitro Internalization
4.4.3. Kinetics of the Association on HEK-SST2 Cell Membranes and Related Saturation Binding
4.5. In Vivo Evaluation
4.5.1. Tumor Implantation
4.5.2. SPECT/CT Imaging
4.5.3. Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrio, M.; Czernin, J.; Fanti, S.; Ambrosini, V.; Binse, I.; Du, L.; Eiber, M.; Herrmann, K.; Fendler, W.P. The Impact of Somatostatin Receptor-Directed PET/CT on the Management of Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumor: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Braun, F.; Waser, B.; Beetschen, K.; Cescato, R.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.E.; Weber, W.A.; Maecke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Unexpected sensitivity of sst2 antagonists to N-terminal radiometal modifications. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, G.P.; Mansi, R.; McDougall, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Bouterfa, H.; Wild, D.; Fani, M. Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, and Dosimetry of (177)Lu-, (90)Y-, and (111)In-Labeled Somatostatin Receptor Antagonist OPS201 in Comparison to the Agonist (177)Lu-DOTATATE: The Mass Effect. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, G.P.; Schreiter, N.; Kaul, F.; Uiters, J.; Bouterfa, H.; Kaufmann, J.; Erlanger, T.E.; Cathomas, R.; Christ, E.; Fani, M.; et al. Sensitivity Comparison of (68)Ga-OPS202 and (68)Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Prospective Phase II Imaging Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, D.; Fani, M.; Behe, M.; Brink, I.; Rivier, J.E.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R.; Weber, W.A. First clinical evidence that imaging with somatostatin receptor antagonists is feasible. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decristoforo, C.; Mather, S.J.; Cholewinski, W.; Donnemiller, E.; Riccabona, G.; Moncayo, R. 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-TOC: A new 99mTc-labelled radiopharmaceutical for imaging somatostatin receptor-positive tumours; first clinical results and intra-patient comparison with 111In-labelled octreotide derivatives. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decristoforo, C.; Melendez-Alafort, L.; Sosabowski, J.K.; Mather, S.J. 99mTc-HYNIC-[Tyr3]-octreotide for imaging somatostatin-receptor-positive tumors: Preclinical evaluation and comparison with 111In-octreotide. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Cwikla, J.B.; Mikolajczak, R.; Pawlak, D.; Buscombe, J.R.; Nasierowska-Guttmejer, A.; Bator, A.; Maecke, H.R.; Walecki, J. Initial direct comparison of 99mTc-TOC and 99mTc-TATE in identifying sites of disease in patients with proven GEP NETs. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decristoforo, C.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.; Gabriel, M.; Cordopatis, P.; Moncayo, R. 99mTc-Demotate 1: First data in tumour patients-results of a pilot/phase I study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.; vonGuggenberg, E.; Cordopatis, P.; Moncayo, R. 99mTc-N4-[Tyr3]Octreotate Versus 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-[Tyr3]Octreotide: An intrapatient comparison of two novel Technetium-99m labeled tracers for somatostatin receptor scintigraphy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2004, 19, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, G.; Kuchuk, M.; Gallazzi, F.; Jurisson, S.S.; Smith, C.J.; Hennkens, H.M. Somatostatin receptor targeting with hydrophilic [Tc-99m/Re-186]Tc/Re-tricarbonyl NODAGA and NOTA complexes. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019, 71, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, G.; Radford, L.L.; Kuchuk, M.; Gallazzi, F.; Jurisson, S.S.; Smith, C.J.; Hennkens, H.M. NOTA and NODAGA [Tc-99m]Tc- and [Re-186]Re-Tricarbonyl Complexes: Radiochemistry and First Example of a [Tc-99m]Tc-NODAGA Somatostatin Receptor-Targeting Bioconjugate. Bioconj. Chem. 2018, 29, 4040–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, L.; Gallazzi, F.; Watkinson, L.; Carmack, T.; Berendzen, A.; Lewis, M.R.; Jurisson, S.S.; Papagiannopoulou, D.; Hennkens, H.M. Synthesis and evaluation of a Tc-99m tricarbonyl-labeled somatostatin receptor-targeting antagonist peptide for imaging of neuroendocrine tumors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 47, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, L.L.; Papagiannopoulou, D.; Gallazzi, F.; Berendzen, A.; Watkinson, L.; Carmack, T.; Lewis, M.R.; Jurisson, S.S.; Hennkens, H.M. Synthesis and evaluation of Re/Tc-99m(I) complexes bearing a somatostatin receptor-ntargeting antagonist and labeled via a novel [N, S, O] clickable bifunctional chelating agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiraj, K.; Ursillo, S.; Tamma, M.L.; Rylova, S.N.; Waser, B.; Constable, E.C.; Fani, M.; Nicolas, G.P.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. The tetraamine chelator outperforms HYNIC in a new technetium-99m-labelled somatostatin receptor 2 antagonist. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, M.; Weingaertner, V.; Kolenc Peitl, P.; Mansi, R.; Gaonkar, R.H.; Garnuszek, P.; Mikolajczak, R.; Novak, D.; Simoncic, U.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; et al. Selection of the First (99m)Tc-Labelled Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist for Clinical Translation-Preclinical Assessment of Two Optimized Candidates. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, M.; Nicolas, G.P.; Wild, D. Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists for Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 61S–66S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansi, R.; Fani, M. Design and development of the theranostic pair (177) Lu-OPS201/(68) Ga-OPS202 for targeting somatostatin receptor expressing tumors. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginj, M.; Zhang, H.; Waser, B.; Cescato, R.; Wild, D.; Wang, X.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.; Macke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16436–16441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, R.; Santoianni-Klauer, D.; Del Pozzo, L.; Plas, P.; Fani, M. Differences on the Mechanism of Action between the Radiolabeled Somatostatin Receptor Antagonist 177Lu-OPS201 and the Agonist 177Lu-DOTA-TATE: An in vitro Investigation. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D.; Fani, M.; Fischer, R.; Del Pozzo, L.; Kaul, F.; Krebs, S.; Fischer, R.; Rivier, J.E.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R.; et al. Comparison of somatostatin receptor agonist and antagonist for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: A pilot study. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalm, S.U.; Nonnekens, J.; Doeswijk, G.N.; de Blois, E.; van Gent, D.C.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; de Jong, M. Comparison of the Therapeutic Response to Treatment with a 177Lu-Labeled Somatostatin Receptor Agonist and Antagonist in Preclinical Models. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, P.; Ginj, M.; Walter, M.A.; Chen, J.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. Influence of different spacers on the biological profile of a DOTA-somatostatin analogue. Bioconj. Chem. 2007, 18, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Schar, J.C.; Waser, B.; Wenger, S.; Heppeler, A.; Schmitt, J.S.; Macke, H.R. Affinity profiles for human somatostatin receptor subtypes SST1-SST5 of somatostatin radiotracers selected for scintigraphic and radiotherapeutic use. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Ginj, M.; Zhang, H.; Waser, B.; Baum, R.P.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H. Are radiogallium-labelled DOTA-conjugated somatostatin analogues superior to those labelled with other radiometals? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. New Insights in the Design of Bioactive Peptides and Chelating Agents for Imaging and Therapy in Oncology. Molecules 2017, 22, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, M.; Del Pozzo, L.; Abiraj, K.; Mansi, R.; Tamma, M.L.; Cescato, R.; Waser, B.; Weber, W.A.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. PET of somatostatin receptor-positive tumors using 64Cu- and 68Ga-somatostatin antagonists: The chelate makes the difference. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulou, D. Technetium-99m radiochemistry for pharmaceutical applications. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; Martini, P. A Picture of Modern Tc-99m Radiopharmaceuticals: Production, Chemistry, and Applications in Molecular Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duatti, A. Review on (99m)Tc radiopharmaceuticals with emphasis on new advancements. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Conjugate | m/z Calcd. | m/z Meas. | tR (min) a | Log D (pH = 7.4) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4-SS01 | 1331.01 | 1331.35 | 10.5 | −2.49 ± 0.34 c |
| HYNIC-SS01 | 1279.88 | 1279.46 | 12.2 | −2.21 ± 0.07 |
| HYNIC-β-Ala-SS01 | 1350.95 | 1350.95 | 11.8 | −1.91 ± 0.19 |
| HYNIC-Ahx-SS01 | 1393.04 | 1394.76 | 12.4 | −1.96 ± 0.06 |
| HYNIC-Aun-SS01 | 1463.18 | 1463.61 | 14.7 | n.d. |
| HYNIC-PEG4-SS01 | 1525.59 | 1526.36 | 12.5 | −2.03 ± 0.13 |
| N4-JR11 | 1489.12 | 1488.58 | 9.6 | −2.80 ± 0.19 |
| HYNIC-JR11 | 1437.99 | 1437.52 | 11.0 | −2.88 ± 0.11 |
| HYNIC-Ahx-JR11 | 1551.15 | 1551.5 | 11.2 | −3.15 ± 0.06 |
| HYNIC-TOC | 1170.36 | 1170.53 | 11.1 | −2.77 ± 0.07 |
| Organ | [99mTc]Tc-N4-SS01 a | [99mTc]Tc-HYNIC-Ahx-SS01 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | |
| Blood | 1.80 ± 0.44 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.12 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.004 |
| Heart | 1.64 ± 0.60 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.004 |
| Lung | 17.00 ± 5.75 | 2.52 ± 0.53 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 2.45 ± 0.56 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Liver | 5.38 ± 1.36 | 3.72 ± 0.92 | 1.07 ± 0.24 | 1.48 ± 0.26 | 0.44 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.06 |
| Pancreas | 16.37 ± 4.53 | 1.96 ± 0.58 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 4.19 ± 1.08 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.03 ± 0.003 |
| Spleen | 1.61 ± 0.46 | 0.55 ± 0.15 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 0.51 ± 0.09 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| Stomach | 14.60 ± 4.89 | 2.17 ± 0.39 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | 2.69 ± 0.39 | 0.59 ± 0.16 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| Intestine | 4.05 ± 1.12 | 0.86 ± 0.40 | 0.31 ± 0.17 | 0.91 ± 0.33 | 0.26 ± 0.13 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Adrenal | 5.14 ± 1.79 | 1.25 ± 0.33 | 0.73 ± 0.20 | 0.74 ± 0.13 | 0.30 ± 0.11 | 0.04 ± 0.03 |
| Kidney | 43.63 ± 11.37 | 25.85 ± 5.23 | 3.42 ± 1.44 | 9.47 ± 1.74 | 5.60 ± 0.47 | 1.15 ± 0.15 |
| Muscle | 0.69 ± 0.22 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.004 |
| Bone | 1.67 ± 0.94 | 0.41 ± 0.14 | 0.20 ± 0.19 | 0.48 ± 0.19 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| HEK-SST2 | 19.12 ± 4.47 | 28.41 ± 4.84 | 10.98 ± 4.69 | 14.94 ± 5.15 | 12.82 ± 3.09 | 3.82 ± 0.83 |
| Tumor (T)-to-Non-Tumor Ratios | ||||||
| T/Blood | 11 | 124 | 366 | 18 | 128 | 382 |
| T/Liver | 3.6 | 7.6 | 10 | 10 | 29 | 18 |
| T/Kidney | 0.4 | 1.1 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.3 |
| T/Muscle | 28 | 189 | 183 | 62 | 256 | 382 |
| T/Bone | 11 | 69 | 55 | 31 | 80 | 96 |
| Organ | [99mTc]Tc-N4-JR11 | [99mTc]Tc-HYNIC-Ahx-JR11 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | 1 h | 4 h | 24 h | |
| Blood | 0.84 ± 0.09 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| Heart | 0.57 ± 0.08 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| Lung | 8.99 ± 3.41 | 2.02 ± 0.87 | 0.27 ± 0.05 | 5.66 ± 0.68 | 0.58 ± 0.27 | 0.20 ± 0.08 |
| Liver | 1.79 ± 0.24 | 1.01 ± 0.13 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.15 | 0.70 ± 0.05 | 0.47 ± 0.06 |
| Pancreas | 29.14 ± 4.22 | 8.47 ± 1.92 | 0.60 ± 0.04 | 11.71 ± 2.62 | 1.64 ± 0.77 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| Spleen | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 1.87 ± 0.55 | 1.74 ± 0.39 | 1.52 ± 0.15 |
| Stomach | 29.32 ± 5.04 | 8.70 ± 0.80 | 1.12 ± 0.35 | 8.06 ± 0.84 | 1.51 ± 0.57 | 0.29 ± 0.03 |
| Intestine | 2.69 ± 0.94 | 3.21 ± 1.12 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1.78 ± 1.28 | 0.40 ± 0.23 | 0.16 ± 0.03 |
| Adrenal | 5.49 ± 1.22 | 2.36 ± 0.60 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 1.05 ± 0.24 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.004 |
| Kidney | 12.76 ± 1.98 | 9.70 ± 0.85 | 2.23 ± 0.28 | 7.49 ± 1.21 | 5.26 ± 0.71 | 2.14 ± 0.11 |
| Muscle | 0.27 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Bone | 2.18 ± 0.43 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.22 | 0.20 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| HEK-SST2 | 16.41 ± 2.87 | 19.07 ± 1.83 | 12.29 ± 1.59 | 14.22 ± 1.25 | 13.49 ± 2.07 | 5.83 ± 0.43 |
| Tumor (T)-to-Non-Tumor Ratios | ||||||
| T/Blood | 19 | 95 | 614 | 19 | 112 | 292 |
| T/Liver | 9.2 | 19 | 27 | 13 | 19 | 12 |
| T/Kidney | 1.3 | 2 | 5.5 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 2.7 |
| T/Muscle | 6.8 | 212 | 307 | 68 | 225 | 194 |
| T/Bone | 7.5 | 60 | 49 | 25 | 67 | 42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaonkar, R.H.; Wiesmann, F.; Del Pozzo, L.; McDougall, L.; Zanger, S.; Mikołajczak, R.; Mansi, R.; Fani, M. SPECT Imaging of SST2-Expressing Tumors with 99mTc-Based Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: The Role of Tetraamine, HYNIC, and Spacers. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040300
Gaonkar RH, Wiesmann F, Del Pozzo L, McDougall L, Zanger S, Mikołajczak R, Mansi R, Fani M. SPECT Imaging of SST2-Expressing Tumors with 99mTc-Based Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: The Role of Tetraamine, HYNIC, and Spacers. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(4):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040300
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaonkar, Raghuvir Haridas, Fabius Wiesmann, Luigi Del Pozzo, Lisa McDougall, Sandra Zanger, Renata Mikołajczak, Rosalba Mansi, and Melpomeni Fani. 2021. "SPECT Imaging of SST2-Expressing Tumors with 99mTc-Based Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: The Role of Tetraamine, HYNIC, and Spacers" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 4: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040300
APA StyleGaonkar, R. H., Wiesmann, F., Del Pozzo, L., McDougall, L., Zanger, S., Mikołajczak, R., Mansi, R., & Fani, M. (2021). SPECT Imaging of SST2-Expressing Tumors with 99mTc-Based Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists: The Role of Tetraamine, HYNIC, and Spacers. Pharmaceuticals, 14(4), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040300








